Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault
|
|
|
- Franklin Sutton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Measurements in the Creeping Section of the Central San Andreas Fault Introduction Duncan Agnew, Andy Michael We propose the PBO instrument, with GPS and borehole strainmeters, the creeping section of the San Andreas fault in central California, to enhance our understanding of the mechanics of how a major transform fault can slip aseismically. This area was studied in the 1970 s, but has been neglected more recently, since the seismic hazard is thought to be low and the risk even lower though at Parkfield, south of the area we discuss here, there is a high density of measurements. We believe that studies of the creeping section can help resolve key issues currently unclear about how transform faults, of which the San Andreas is one of the most accessible, in fact work. Figure 1. On the left, red triangles are CGPS, and blue squares borehole strain: in both cases, solid for existing or planned, open for proposed here. Seismotectonics of the Central San Andreas Figure 1shows the region of central California around the San Andreas fault (SAF). The seismicity associated with the SAF occurs in a very narrow band, but there are significant amounts off the fault, most notably the Coalinga/Kettleman-Hills earthquake sequence. To show off-fault seismicity uncontaminated by this event, we have defined the box shown in the right panel; Figure 2 shows earthquakes in this box in crosssection. The SAF bounds different seismic regions: the Diablo Range to the NE shows
2 -2- diffuse seismicity down to considerable depths, while the Salinas Block is nearly aseismic, with the seismicity increasing again in the region of the Hosgri fault. Figure 2 In Figure 3we show the the different kinds of behavior along the San Andreas. The fault geometry (top) is as simple here as anywhere. The seismicity plots show that the central part of the fault has, for the last 55 years, been free of any earthquakes larger than magnitude 4. Of course, this is also true of parts of the SAF that have broken in great earthquakes; what is remarkable about this section is what is shown in the bottom panel, namely that the fault here creeps continuously at the surface, with slip extending to the surface in a very narrow zone ( 100 m wide). The rate measured over this zone is nearly equal to the full rate of slip for the San Andreas of 34 mm/yr (Burford and Harsh, BSSA, 1980; Lisowski and Prescott, BSSA, 1981) which suggests that there is no depth at which the fault is locked; the motion seems to just be two blocks sliding past each other, with no deformation in either one, and no earthquake cycle. Except for one zone of complexity near Monarch Peak, even the rate of small earthquakes is low. Except perhaps for one part of the North Anatolian fault, in Turkey, such behavior is known nowhere else. What are the mechanics at work to produce these effects? It was thought that the fold belts near the San Andreas were produced as byproducts of the shearing stresses that drove the fault motion in a classic example of transpression. However, stress measurements near this portion of the fault showed that the principal axis of compression was nearly normal to the SAF, which was interpreted as showing that the SAF was weak, in the sense that little shear stress was needed to cause it to slip (a conclusion in consonance with the long-known lack of a heat-flow anomaly along the fault). The stress state would thus be dominated by a large compressional stress nearly normal to the fault: the small part not normal to the fault would provide the shear stress needed to make the fault slip The transpression is then effectively two independent processes (of compression and shear) which are largely decoupled. This decoupling might be accommodated mechanically by a mid-crustal detachment. Such a detachment might change form at the San Andreas; this could provide an explanation of the otherwise puzzling question of why folding (and seismicity) occurs only east of the fault.
3 -3- Figure 3 Given deformation measurements around this part of the fault, we can test between two possibilities: (A) On geodetic time scales, the Diablo Range is deforming while the Salinas side is not. There are then two possible models: (1) the stress field is different on the two sides (because of some structural complexity) or (2) the stress is the same, but different deformation rates result because of differences in the flow laws for the ductile material underneath the elastic lithosphere.
4 -4- (B) The current deformation is the same on both sides of the fault. Then the difference in long-term deformation would imply that one side responds to the tectonic stress by deforming, while the other side never leaves the elastic regime. This requires two conditions: (1) a difference in strength (failure point) between the materials of the lithosphere (on the two sides of the San Andreas), and (2) tectonic stress which at times reaches a level above the failure stress of one side but always remains below that of the other. There is some data available on this already, from Thatcher (1979) using a triangulation network SW of the San Andreas, and by Sauber et al (1989) using a triangulation network to the NE. On neither side of the fault do the rates differ significantly from zero; given the uncertainties in these determinations (dominated by the low precision of even first-order triangulation), it is difficult to conclude much except that the strain rates are not high. We note that there is some reason to question this simple picture of a purely creeping fault. Over the last decade, a number of authors (e.g. Michael and Eberhart-Phillips, Science, 1991; Michelini and McEvilly, BSSA, 1991; Eberhart-Phillips and Michael, JGR, 1993; Zhao and Kanamori, GRL, 1995; Hauksson and Haase, JGR, 1997; Eberhart- Phillips and Michael, JGR, 1998) have found a correlation between seismic images of subsurface geologic structure and the seismogenic behavior of faults. Locked fault segments tend to have higher seismic velocity material in contact with the fault and it is often difficult to identify the fault as a velocity contrast. Creeping segments have lower velocity material on one side with a sharp across-fault velocity contrast. Approximately 20 to 35 km north of Parkfield (on Figure 3, from north of Slack Canyon to south of Monarch Peak) there is a 15-km length of fault that has the seismic velocity structure and low background seismicity of a locked fault segment (Eberhart-Phillips and Michael, JGR, 1993). As noted above, common wisdom is that this whole segment is creeping; but there is no direct evidence that this segment is actually creeping throughout the entire depth of the seismogenic crust, as opposed to being locked over part of its depth. Proposed Measurements We propose the installation of continuous GPS and borehole strainmeters as shown by the open symbols in Figure 1 and Figure 3. There would be three profiles of GPS, and one of borehole strain, extending on either side of the fault, and with gradually incresing spacing going away from it. The closest stations would be 1 km from the fault to capture most of the motion; we further propose that the Bitterwater profile include a GPS creepmeter, with two systems 100 m apart, spanning the creeping zone at a place where it is especially narrow. The profile of borehole strainmeters would be supplemented by four additional instruments, about 4 km from the fault and 20 km from the central profile; these would provide a measure of the lateral extent of any signals seen. The increasing spacing along both profiles is designed to give maximum resolution of the motions of the upper few kmofthe fault, while not putting out more sites than needed: far from the fault, the signals will have a longer wavelength, so there is no point in closer spacing. The total number of GPS installations would be 30 in this plan, with 15 borehole
5 -5- strainmeters. The questions that could be addressed by these measurements would be: 1. How block-like is the deformation off the SAF? This relates to issues (described above) of the local tectonics, and whether locked faults can be detected by their velocity structure. More generally, measurements of off-fault strain accumulation relate to the question of whether the deformation in this region is truly aseismic. This will help to address the question of how much such behavior might occur elsewhere especially, how much moment could be hidden by aseismic slip on other transform faults, notably oceanic ones. 2. From temperature profiling of the boreholes, is there any heat-flow anomaly present? We note that no heat-flow measurements have been made along this part of the SAF, the one place where there would not be lowering of the effective stress during earthquakes (since there are no earthquakes). 3. How steady is the slip on the SAF? Again, this is the one part of the SAF for which we do not think any significant deformation occurs as earthquakes. But, are there stick-slip events with longer time scales especially events at what would usually be seismogenic depths? If there slip is either seismic or perfectly steady, this would be a strong constraint on possible models of fault friction: so would any departure from steadiness. Again, we recognize that this is a unique part of the plate boundary, and one with little seismic hazard but we believe that just because of that uniqueness, it should be a target area for the PBO.
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA
 Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group for the Central and Northern San Andreas Fault System PBO-WG-CNSA Introduction Our proposal focuses on the San Andreas fault system in central and northern California.
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise
 GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
GPS Strain & Earthquakes Unit 5: 2014 South Napa earthquake GPS strain analysis student exercise Strain Analysis Introduction Name: The earthquake cycle can be viewed as a process of slow strain accumulation
Regional deformation and kinematics from GPS data
 Regional deformation and kinematics from GPS data Jessica Murray, Jerry Svarc, Elizabeth Hearn, and Wayne Thatcher U. S. Geological Survey Acknowledgements: Rob McCaffrey, Portland State University UCERF3
Regional deformation and kinematics from GPS data Jessica Murray, Jerry Svarc, Elizabeth Hearn, and Wayne Thatcher U. S. Geological Survey Acknowledgements: Rob McCaffrey, Portland State University UCERF3
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points)
 Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities
 BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
BOLLETTINO DI GEOFISICA TEORICA ED APPLICATA VOL. 40, N. 2, pp. 95-110; JUNE 2000 Ground displacement in a fault zone in the presence of asperities S. SANTINI (1),A.PIOMBO (2) and M. DRAGONI (2) (1) Istituto
Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements
 Title Page Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements Brendan Meade and Bradford Hager Three basic questions Large historical earthquakes One basic question How
Title Page Kinematics of the Southern California Fault System Constrained by GPS Measurements Brendan Meade and Bradford Hager Three basic questions Large historical earthquakes One basic question How
The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting
 The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University 2nd edition CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting Christopher H. Scholz Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Columbia University 2nd edition CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
Focused Observation of the San Andreas/Calaveras Fault intersection in the region of San Juan Bautista, California
 Focused Observation of the San Andreas/Calaveras Fault intersection in the region of San Juan Bautista, California Clifford Thurber, Dept. of Geology and Geophysics, Univ. Wisconsin-Madison Mick Gladwin,
Focused Observation of the San Andreas/Calaveras Fault intersection in the region of San Juan Bautista, California Clifford Thurber, Dept. of Geology and Geophysics, Univ. Wisconsin-Madison Mick Gladwin,
The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a
 The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a A German seismogram of the 1906 SF EQ Image courtesy of San Francisco Public Library Stages of the Earthquake Cycle The Earthquake cycle is split into several distinct
The Earthquake Cycle Chapter :: n/a A German seismogram of the 1906 SF EQ Image courtesy of San Francisco Public Library Stages of the Earthquake Cycle The Earthquake cycle is split into several distinct
Aseismic slip and fault-normal strain along the central creeping section of the San Andreas fault
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L14305, doi:10.1029/2008gl034437, 2008 Aseismic slip and fault-normal strain along the central creeping section of the San Andreas fault
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L14305, doi:10.1029/2008gl034437, 2008 Aseismic slip and fault-normal strain along the central creeping section of the San Andreas fault
Rheology III. Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep
 Rheology III Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
Rheology III Ideal materials Laboratory tests Power-law creep The strength of the lithosphere The role of micromechanical defects in power-law creep Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
Jack Loveless Department of Geosciences Smith College
 Geodetic constraints on fault interactions and stressing rates in southern California Jack Loveless Department of Geosciences Smith College jloveless@smith.edu Brendan Meade Department of Earth & Planetary
Geodetic constraints on fault interactions and stressing rates in southern California Jack Loveless Department of Geosciences Smith College jloveless@smith.edu Brendan Meade Department of Earth & Planetary
to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San
 Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Creepmeter mini-proposal John Langbein, Evelyn Roeloffs, Mick Gladwin, Ross Gwyther
 Creepmeter mini-proposal John Langbein, Evelyn Roeloffs, Mick Gladwin, Ross Gwyther The Proposal We propose to install creepmeters in the creeping section of the San Andreas Fault system adjacent to borehole
Creepmeter mini-proposal John Langbein, Evelyn Roeloffs, Mick Gladwin, Ross Gwyther The Proposal We propose to install creepmeters in the creeping section of the San Andreas Fault system adjacent to borehole
TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project
 TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project Introduction The EarthScope Project is an undertaking funded by the National Science Foundation in partnership with the United States Geological Survey and
TEGAM s Connection to the EarthScope Project Introduction The EarthScope Project is an undertaking funded by the National Science Foundation in partnership with the United States Geological Survey and
Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System
 SRL complex earthquakes 5/22/09 1 Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System Niels Bohr once observed How wonderful that we have met with a paradox. Now we have some hope of making progress. This situation
SRL complex earthquakes 5/22/09 1 Mid-Continent Earthquakes As A Complex System Niels Bohr once observed How wonderful that we have met with a paradox. Now we have some hope of making progress. This situation
Regional Geodesy. Shimon Wdowinski. MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region. University of Miami
 MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
MARGINS-RCL Workshop Lithospheric Rupture in the Gulf of California Salton Trough Region Regional Geodesy Shimon Wdowinski University of Miami Rowena Lohman, Kim Outerbridge, Tom Rockwell, and Gina Schmalze
Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system
 Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system Slow slip in Upper Crust Aseismic creep, afterslip and spontaneous slow slip events on some faults in upper 15 km Mostly aseismic but accompanied by
Slow Slip and Tremor Along San Andreas fault system Slow slip in Upper Crust Aseismic creep, afterslip and spontaneous slow slip events on some faults in upper 15 km Mostly aseismic but accompanied by
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5
 Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip
 Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Seismic and aseismic processes in elastodynamic simulations of spontaneous fault slip Most earthquake simulations study either one large seismic event with full inertial effects or long-term slip history
Earthquakes. Pt Reyes Station 1906
 Earthquakes Pt Reyes Station 1906 Earthquakes Ground shaking caused by the sudden release of accumulated strain by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture in the earth. You Live in Earthquake Country
Earthquakes Pt Reyes Station 1906 Earthquakes Ground shaking caused by the sudden release of accumulated strain by an abrupt shift of rock along a fracture in the earth. You Live in Earthquake Country
Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group Plan for the San Andreas Fault System
 Introduction Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group Plan for the San Andreas Fault System This document puts forward a draft implementation plan for the San Andreas Fault component of the Plate Boundary
Introduction Plate Boundary Observatory Working Group Plan for the San Andreas Fault System This document puts forward a draft implementation plan for the San Andreas Fault component of the Plate Boundary
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Chapter 6: Earthquakes
 Section 1 (Forces in Earth s Crust) Chapter 6: Earthquakes 8 th Grade Stress a that acts on rock to change its shape or volume Under limited stress, rock layers can bend and stretch, but return to their
Section 1 (Forces in Earth s Crust) Chapter 6: Earthquakes 8 th Grade Stress a that acts on rock to change its shape or volume Under limited stress, rock layers can bend and stretch, but return to their
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/ngeo739 Supplementary Information to variability and distributed deformation in the Marmara Sea fault system Tobias Hergert 1 and Oliver Heidbach 1,* 1 Geophysical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 10.1038/ngeo739 Supplementary Information to variability and distributed deformation in the Marmara Sea fault system Tobias Hergert 1 and Oliver Heidbach 1,* 1 Geophysical
Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere. Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University
 3D Viscoelastic Earthquake Cycle Models Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University In collaboration with:
3D Viscoelastic Earthquake Cycle Models Estimating fault slip rates, locking distribution, elastic/viscous properites of lithosphere/asthenosphere Kaj M. Johnson Indiana University In collaboration with:
EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE MECHANISMS SHOW MOTION
 6-1 6: EARTHQUAKE FOCAL MECHANISMS AND PLATE MOTIONS Hebgen Lake, Montana 1959 Ms 7.5 1 Stein & Wysession, 2003 Owens Valley, California 1872 Mw ~7.5 EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE
6-1 6: EARTHQUAKE FOCAL MECHANISMS AND PLATE MOTIONS Hebgen Lake, Montana 1959 Ms 7.5 1 Stein & Wysession, 2003 Owens Valley, California 1872 Mw ~7.5 EARTHQUAKE LOCATIONS INDICATE PLATE BOUNDARIES EARTHQUAKE
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Abstract
 Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Verification of the asperity model using seismogenic fault materials Takehiro Hirose*, Wataru Tanikawa and Weiren Lin Kochi Institute for Core Sample Research/JAMSTEC, JAPAN * Corresponding author: hiroset@jamstec.go.jp
Crustal Deformation. Earth Systems 3209
 Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions. Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions
 Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions Cooling of oceanic lithosphere also increases rock strength and seismic velocity. Thus
Seismotectonics of intraplate oceanic regions Thermal model Strength envelopes Plate forces Seismicity distributions Cooling of oceanic lithosphere also increases rock strength and seismic velocity. Thus
} based on composition
 Learning goals: Predict types of earthquakes that will happen at different plate boundaries based on relative plate motion vector vs. strike (vector subtraction) Understand interseismic and coseismic deformation,
Learning goals: Predict types of earthquakes that will happen at different plate boundaries based on relative plate motion vector vs. strike (vector subtraction) Understand interseismic and coseismic deformation,
Fault Processes on the Anza section of the San Jacinto Fault
 Fault Processes on the nza section of the San Jacinto Fault J. Steidl (USB), M. Gladwin, R. Gwyther (SIRO ust.), F. Vernon (USD) SUMMRY We propose to instrument the nza slip gap and transition areas of
Fault Processes on the nza section of the San Jacinto Fault J. Steidl (USB), M. Gladwin, R. Gwyther (SIRO ust.), F. Vernon (USD) SUMMRY We propose to instrument the nza slip gap and transition areas of
1 How and Where Earthquakes Happen
 CHAPTER 12 1 How and Where Earthquakes Happen SECTION Earthquakes KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is elastic rebound? What are the similarities and differences between
CHAPTER 12 1 How and Where Earthquakes Happen SECTION Earthquakes KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What is elastic rebound? What are the similarities and differences between
Elastic Rebound Theory
 Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Earthquakes Elastic Rebound Theory Earthquakes occur when strain exceeds the strength of the rock and the rock fractures. The arrival of earthquakes waves is recorded by a seismograph. The amplitude of
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Earthquakes. Forces Within Eartth. Faults form when the forces acting on rock exceed the rock s strength.
 Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults OH MY! How do geologic events change and shape Earth s surface?
 Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults OH MY! How do geologic events change and shape Earth s surface? Remember The Lithosphere is made of The CRUST + The Upper Rigid Mantle Plates may be called by different
Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults OH MY! How do geologic events change and shape Earth s surface? Remember The Lithosphere is made of The CRUST + The Upper Rigid Mantle Plates may be called by different
Earthquakes. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left.
 Earthquakes Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Stress that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called a. shearing. b. tension.
Earthquakes Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Stress that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called a. shearing. b. tension.
Journal of Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for
 Journal of Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for InSAR observations of strain accumulation and fault creep along the Chaman Fault system, Pakistan and Afghanistan H. Fattahi 1, F. Amelung
Journal of Geophysical Research Letters Supporting Information for InSAR observations of strain accumulation and fault creep along the Chaman Fault system, Pakistan and Afghanistan H. Fattahi 1, F. Amelung
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics
 Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
Effect of an outer-rise earthquake on seismic cycle of large interplate earthquakes estimated from an instability model based on friction mechanics Naoyuki Kato (1) and Tomowo Hirasawa (2) (1) Geological
A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L15S13, doi:10.1029/2004gl019521, 2004 A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements Jean Chéry Laboratoire Dynamique de la
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L15S13, doi:10.1029/2004gl019521, 2004 A mechanical model of the San Andreas fault and SAFOD Pilot Hole stress measurements Jean Chéry Laboratoire Dynamique de la
Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake. EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole
 Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole Content Earthquakes and faults Examples of SAR interferograms of earthquakes
Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole Content Earthquakes and faults Examples of SAR interferograms of earthquakes
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms
 Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
Earth Movement and Resultant Landforms Structure of the Earth Lithosphere : earth s crust Asthenosphere : upper mantle zone where material is near its melting point & acts almost like liquid (appprox.
GPS Monitoring of the San Andreas Fault and Modeling of Slip Rate on the Mojave Section of the San Andreas Fault
 GPS Monitoring 1 GPS Monitoring of the San Andreas Fault and Modeling of Slip Rate on the Mojave Section of the San Andreas Fault By Nayeli Jimenez and Mischel Bartie PRISM Research Program Coordinator:
GPS Monitoring 1 GPS Monitoring of the San Andreas Fault and Modeling of Slip Rate on the Mojave Section of the San Andreas Fault By Nayeli Jimenez and Mischel Bartie PRISM Research Program Coordinator:
Source parameters II. Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop
 Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Source parameters II Stress drop determination Energy balance Seismic energy and seismic efficiency The heat flow paradox Apparent stress drop Source parameters II: use of empirical Green function for
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle. Read KK&V chapter 2.10
 Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Lecture 2: Deformation in the crust and the mantle Read KK&V chapter 2.10 Tectonic plates What are the structure and composi1on of tectonic plates? Crust, mantle, and lithosphere Crust relatively light
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ).
 Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Friction can increase with hold time. This happens through growth and increasing shear strength of contacts ( asperities ). If sliding speeds up, the average lifespan of asperities decreases This means
Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter Pearson Education, Inc.
 Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter 10 Structural Geology Structural geologists study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. A working knowledge of rock structures
Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter 10 Structural Geology Structural geologists study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. A working knowledge of rock structures
DCPP Seismic FAQ s Geosciences Department 08/04/2011 GM1) What magnitude earthquake is DCPP designed for?
 GM1) What magnitude earthquake is DCPP designed for? The new design ground motions for DCPP were developed after the discovery of the Hosgri fault. In 1977, the largest magnitude of the Hosgri fault was
GM1) What magnitude earthquake is DCPP designed for? The new design ground motions for DCPP were developed after the discovery of the Hosgri fault. In 1977, the largest magnitude of the Hosgri fault was
Introduction Faults blind attitude strike dip
 Chapter 5 Faults by G.H. Girty, Department of Geological Sciences, San Diego State University Page 1 Introduction Faults are surfaces across which Earth material has lost cohesion and across which there
Chapter 5 Faults by G.H. Girty, Department of Geological Sciences, San Diego State University Page 1 Introduction Faults are surfaces across which Earth material has lost cohesion and across which there
Comparison of Strain Rate Maps
 Comparison of Strain Rate Maps David T. Sandwell UNAVCO March 8, 2010 why strain rate matters comparison of 10 strain rate models new data required interseismic model velocity v(x) = V π tan 1 x D strain
Comparison of Strain Rate Maps David T. Sandwell UNAVCO March 8, 2010 why strain rate matters comparison of 10 strain rate models new data required interseismic model velocity v(x) = V π tan 1 x D strain
Introduction to Strain and Borehole Strainmeter Data
 Introduction to Strain and Borehole Strainmeter Data Evelyn Roeloffs U. S. Geological Survey Earthquake Science Center March 28, 2016 Evelyn Roeloffs, USGS ESC Strainmeters: Introduction March 28, 2016
Introduction to Strain and Borehole Strainmeter Data Evelyn Roeloffs U. S. Geological Survey Earthquake Science Center March 28, 2016 Evelyn Roeloffs, USGS ESC Strainmeters: Introduction March 28, 2016
21. Earthquakes I (p ; 306)
 21. Earthquakes I (p. 296-303; 306) How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the last 4,000 years? How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the past century? What two recent earthquakes
21. Earthquakes I (p. 296-303; 306) How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the last 4,000 years? How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the past century? What two recent earthquakes
Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan
 Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan Angelier, J., Chang, T.Y., Hu, J.C., Chang, C.P., Siame, L., Lee, J.C., Deffontaines, B., Chu, H.T, Lu, C.Y., Does extrusion occur
Lateral extrusion and tectonic escape in Ilan Plain of northeastern Taiwan Angelier, J., Chang, T.Y., Hu, J.C., Chang, C.P., Siame, L., Lee, J.C., Deffontaines, B., Chu, H.T, Lu, C.Y., Does extrusion occur
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f
 Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
Material is perfectly elastic until it undergoes brittle fracture when applied stress reaches σ f Material undergoes plastic deformation when stress exceeds yield stress σ 0 Permanent strain results from
The Basics The lithosphere is made up of numerous plates (14 major, 38 minor)
 The Basics The lithosphere is made up of numerous plates (14 major, 38 minor) These plates float atop the asthenosphere, where they can move (albeit very slowly) Plate tectonics describes the formation,
The Basics The lithosphere is made up of numerous plates (14 major, 38 minor) These plates float atop the asthenosphere, where they can move (albeit very slowly) Plate tectonics describes the formation,
Rheology. What is rheology? From the root work rheo- Current: flow. Greek: rhein, to flow (river) Like rheostat flow of current
 Rheology What is rheology? From the root work rheo- Current: flow Greek: rhein, to flow (river) Like rheostat flow of current Rheology What physical properties control deformation? - Rock type - Temperature
Rheology What is rheology? From the root work rheo- Current: flow Greek: rhein, to flow (river) Like rheostat flow of current Rheology What physical properties control deformation? - Rock type - Temperature
Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:! 1. List the three types of tectonic plate boundaries! 2. Describe the processes occurring
Learning Objectives (LO)! Lecture 11: Plate Tectonics II! No Homework!! ** Chapter 3 **! What we ll learn today:! 1. List the three types of tectonic plate boundaries! 2. Describe the processes occurring
MAR110 Lecture #5 Plate Tectonics-Earthquakes
 1 MAR110 Lecture #5 Plate Tectonics-Earthquakes Figure 5.0 Plate Formation & Subduction Destruction The formation of the ocean crust from magma that is upwelled into a pair of spreading centers. Pairs
1 MAR110 Lecture #5 Plate Tectonics-Earthquakes Figure 5.0 Plate Formation & Subduction Destruction The formation of the ocean crust from magma that is upwelled into a pair of spreading centers. Pairs
State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault
 ELEVEN State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault Hirao Kanamori and Harold Magistrale NTRODUCTON Data from the Southern California Seismic Network have been extensively used to map spatial
ELEVEN State of Stress in Seismic Gaps Along the SanJacinto Fault Hirao Kanamori and Harold Magistrale NTRODUCTON Data from the Southern California Seismic Network have been extensively used to map spatial
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller
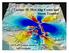 Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
Lecture 20: Slow Slip Events and Stress Transfer GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy Jeff Freymueller Slow Slip Events From Kristine Larson What is a Slow Slip Event? Slip on a fault, like in an earthquake, BUT
The Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Objectives Describe how plates move. Explain the features of plate tectonics. Describe the types of plate boundaries and the features that can form and events that can occur at each. The
Plate Tectonics Objectives Describe how plates move. Explain the features of plate tectonics. Describe the types of plate boundaries and the features that can form and events that can occur at each. The
Read & Learn Earthquakes & Faults
 Read Earthquakes & Faults Read the provided article. Use the information in the reading to answer the questions on the task cards on your answer sheet. Make sure your answers are in the correct spot on
Read Earthquakes & Faults Read the provided article. Use the information in the reading to answer the questions on the task cards on your answer sheet. Make sure your answers are in the correct spot on
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.002 Physics and Chemistry of the Earth and Terrestrial Planets Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Staple this part to part one of lab 6 and turn in. Lab 6, part two: Structural geology (analysis)
 Geology 101 Staple this part to part one of lab 6 and turn in Lab 6, part two: Structural geology (analysis) Recall that the objective of this lab is to describe the geologic structures of Cougar Mountain
Geology 101 Staple this part to part one of lab 6 and turn in Lab 6, part two: Structural geology (analysis) Recall that the objective of this lab is to describe the geologic structures of Cougar Mountain
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES
 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
Predicted reversal and recovery of surface creep on the Hayward fault following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L19305, doi:10.1029/2008gl035270, 2008 Predicted reversal and recovery of surface creep on the Hayward fault following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake D. A. Schmidt
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L19305, doi:10.1029/2008gl035270, 2008 Predicted reversal and recovery of surface creep on the Hayward fault following the 1906 San Francisco earthquake D. A. Schmidt
Objectives. Vocabulary
 Forces Within Earth Objectives Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish among the three types of faults. Contrast three types of seismic waves. Vocabulary stress strain fault primary
Forces Within Earth Objectives Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish among the three types of faults. Contrast three types of seismic waves. Vocabulary stress strain fault primary
Earthquakes Chapter 19
 Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies?
 Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies? F. Riguzzi 1, R. Devoti 1, G. Pietrantonio 1, M. Crespi 2, C. Doglioni 2, A.R. Pisani 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia 2 Università
Can geodetic strain rate be useful in seismic hazard studies? F. Riguzzi 1, R. Devoti 1, G. Pietrantonio 1, M. Crespi 2, C. Doglioni 2, A.R. Pisani 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia 2 Università
Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003239, 2004 Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California Jeanne L. Hardebeck and Andrew J. Michael U.S.
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2004jb003239, 2004 Stress orientations at intermediate angles to the San Andreas Fault, California Jeanne L. Hardebeck and Andrew J. Michael U.S.
Chapter 4 Section 3, 4. Deforming the Earth s Crust
 Chapter 4 Section 3, 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust Deformation The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress Stress The amount of force per unit area on a given material Compression
Chapter 4 Section 3, 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust Deformation The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress Stress The amount of force per unit area on a given material Compression
Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur
 Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur PPT Modified from Troy HS Is there such thing as earthquake weather? Absolutely NOT!!! Geologists believe that there is no connection between weather and earthquakes.
Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur PPT Modified from Troy HS Is there such thing as earthquake weather? Absolutely NOT!!! Geologists believe that there is no connection between weather and earthquakes.
Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation.
 Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation. In the process zone, stress amplitudes are poorly determined and much
Materials and Methods The deformation within the process zone of a propagating fault can be modeled using an elastic approximation. In the process zone, stress amplitudes are poorly determined and much
Overview of Seismic Source Characterization for the Diablo Canyon Power Plant
 Overview of Seismic Source Characterization for the Diablo Canyon Power Plant Steve Thompson (LCI and SSC TI Team), for SWUS GMC Workshop 1, March 19, 2013 Questions from TI Team Summarize tectonic setting.
Overview of Seismic Source Characterization for the Diablo Canyon Power Plant Steve Thompson (LCI and SSC TI Team), for SWUS GMC Workshop 1, March 19, 2013 Questions from TI Team Summarize tectonic setting.
ES Ch 19 Earthquakes 1
 Chapter 19 - Earthquakes Objectives 1. Define stress vs. strain as they apply to rocks. 2. Define faults. 3. Contrast types of seismic waves-3 types according to their type of movement, speed, location
Chapter 19 - Earthquakes Objectives 1. Define stress vs. strain as they apply to rocks. 2. Define faults. 3. Contrast types of seismic waves-3 types according to their type of movement, speed, location
UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS
 UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS CONTINENTAL DRIFT Alfred Wegner proposed the theory that the crustal plates are moving over the mantle. He argued that today s continents once formed a single landmass, called Pangaea
UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS CONTINENTAL DRIFT Alfred Wegner proposed the theory that the crustal plates are moving over the mantle. He argued that today s continents once formed a single landmass, called Pangaea
PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW GAME!!!!
 PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW GAME!!!! Name the four layers of the earth - crust - mantle - outer core - inner core Which part of Earth s structure contains tectonic plates? LITHOSPHERE Name one reason why the
PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW GAME!!!! Name the four layers of the earth - crust - mantle - outer core - inner core Which part of Earth s structure contains tectonic plates? LITHOSPHERE Name one reason why the
What Causes Rock to Deform?
 Crustal Deformation Earth, Chapter 10 Chapter 10 Crustal Deformation What Causes Rock to Deform? Deformation is a general term that refers to all changes in the shape or position of a rock body in response
Crustal Deformation Earth, Chapter 10 Chapter 10 Crustal Deformation What Causes Rock to Deform? Deformation is a general term that refers to all changes in the shape or position of a rock body in response
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress?
 When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
When you are standing on a flat surface, what is the normal stress you exert on the ground? What is the shear stress? How could you exert a non-zero shear stress on the ground? Hydrostatic Pressure (fluids)
Y. Kaneko, 1 Y. Fialko, 1 D. T. Sandwell, 1 X. Tong, 1 and M. Furuya Introduction
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 118, 316 331, doi:1.19/1jb9661, 13 Interseismic deformation and creep along the central section of the North Anatolian Fault (Turkey): InSAR observations
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SOLID EARTH, VOL. 118, 316 331, doi:1.19/1jb9661, 13 Interseismic deformation and creep along the central section of the North Anatolian Fault (Turkey): InSAR observations
What is an Earthquake?
 Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? Earthquake - sometimes violent shaking of ground caused by movement of Earth s tectonic plates; creates seismic waves Often followed by smaller earthquakes (aftershocks);
Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? Earthquake - sometimes violent shaking of ground caused by movement of Earth s tectonic plates; creates seismic waves Often followed by smaller earthquakes (aftershocks);
NEW ZEALAND EARTHQUAKES AND PLATE
 87 NEW ZEALAND EARTHQUAKES AND PLATE TECTONIC THEORY R.I. Walcott * ABSTRACT The rates and direction of shear strain from geodetic data and the direction of slip from earthquake mechanism studies in New
87 NEW ZEALAND EARTHQUAKES AND PLATE TECTONIC THEORY R.I. Walcott * ABSTRACT The rates and direction of shear strain from geodetic data and the direction of slip from earthquake mechanism studies in New
Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other?
 Tectonics Investigation 5: Teacher Guide Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other? Plates move sideways past each other at transform boundaries. At these boundaries, the
Tectonics Investigation 5: Teacher Guide Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other? Plates move sideways past each other at transform boundaries. At these boundaries, the
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law
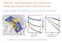 Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Afterslip, slow earthquakes and aftershocks: Modeling using the rate & state friction law Agnès Helmstetter (LGIT Grenoble) and Bruce Shaw (LDE0 Columbia Univ) Days after Nias earthquake Cumulative number
Passive margin earthquakes as indicators of intraplate deformation
 Passive margin earthquakes as indicators of intraplate deformation Emily Wolin and Seth Stein Northwestern University April 23, 2010 Seismicity of the North 1920-2009 American Passive Margin 1933 Baffin
Passive margin earthquakes as indicators of intraplate deformation Emily Wolin and Seth Stein Northwestern University April 23, 2010 Seismicity of the North 1920-2009 American Passive Margin 1933 Baffin
Yellowstone Hotspot Component of the Plate Boundary Observatory
 Yellowstone Hotspot Component of the Plate Boundary Observatory (Investigators: Smith, Thatcher, Meertens, Humphreys, Dzurisin, Oldow Co-Investigators: Christiansen, Doss, Schwartz, Machette, Wong, Olig,
Yellowstone Hotspot Component of the Plate Boundary Observatory (Investigators: Smith, Thatcher, Meertens, Humphreys, Dzurisin, Oldow Co-Investigators: Christiansen, Doss, Schwartz, Machette, Wong, Olig,
The Theory of Plate Tectonics - Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults
 The Theory of Plate Tectonics - Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults 1. What is the theory of plate tectonics? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? What are Plates? The Earth s crust and upper
The Theory of Plate Tectonics - Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults 1. What is the theory of plate tectonics? 2. What are the three types of plate boundaries? What are Plates? The Earth s crust and upper
they help tell Earth s story! Regents Earth Science With Ms. Connery
 they help tell Earth s story! Regents Earth Science With Ms. Connery EARTHQUAKE VOCABULARY earthquake fault convergent divergent transform (or transverse) seismic energy epicenter focus Richter scale magnitude
they help tell Earth s story! Regents Earth Science With Ms. Connery EARTHQUAKE VOCABULARY earthquake fault convergent divergent transform (or transverse) seismic energy epicenter focus Richter scale magnitude
Stress modulation on the San Andreas fault by interseismic fault system interactions Jack Loveless and Brendan Meade, Geology, 2011
 Stress modulation on the San Andreas fault by interseismic fault system interactions Jack Loveless and Brendan Meade, Geology, 2011 A three step process: 1 - Assimilate plate boundary wide GPS data into
Stress modulation on the San Andreas fault by interseismic fault system interactions Jack Loveless and Brendan Meade, Geology, 2011 A three step process: 1 - Assimilate plate boundary wide GPS data into
CRUSTAL DEFORMATION. Chapter 10
 CRUSTAL DEFORMATION and dgeologic Structures t Chapter 10 Deformation Df Deformation involves: Stress the amount of force applied to a given area. Types of Stress: Confining Stress stress applied equally
CRUSTAL DEFORMATION and dgeologic Structures t Chapter 10 Deformation Df Deformation involves: Stress the amount of force applied to a given area. Types of Stress: Confining Stress stress applied equally
Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS. asthenosphere uplift continental drift. known as. tectonic plates move. object. UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use the following terms in the same sentence: crust, mantle, and core. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS 1. Use the following terms in the same sentence: crust, mantle, and core. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the
22.5 Earthquakes. The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia.
 The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia. An earthquake is a movement of Earth s lithosphere that occurs when rocks in the lithosphere
The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia. An earthquake is a movement of Earth s lithosphere that occurs when rocks in the lithosphere
Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL.???, NO., PAGES 1 16, Does Aftershock Duration Scale With Mainshock Size? A. Ziv A. Ziv, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105, Israel. (e-mail: zival@bgu.ac.il)
Geologic Structures. Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress
 Geologic Structures Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress Figure 15.19 Can be as big as a breadbox Or much bigger than a breadbox Three basic types Fractures >>>
Geologic Structures Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress Figure 15.19 Can be as big as a breadbox Or much bigger than a breadbox Three basic types Fractures >>>
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Variations in Tremor Activity and Implications for Lower Crustal Deformation Along the Central San Andreas Fault
 Variations in Tremor Activity and Implications for Lower Crustal Deformation Along the Central San Andreas Fault David R. Shelly USGS, Menlo Park Shelly and Hardebeck, GRL, 2010 Collaborators: Jeanne Hardebeck
Variations in Tremor Activity and Implications for Lower Crustal Deformation Along the Central San Andreas Fault David R. Shelly USGS, Menlo Park Shelly and Hardebeck, GRL, 2010 Collaborators: Jeanne Hardebeck
1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust.
 1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust. 2. What type of stress is shown? 3. Where two plates slide past one another is called a boundary. 4. What type of stress is shown? 5.
1. occurs when the oceanic crust slides under the continental crust. 2. What type of stress is shown? 3. Where two plates slide past one another is called a boundary. 4. What type of stress is shown? 5.
