Forming parameters optimizations with drawing force and die stress in wire rod drawing using rotating die under Coulomb friction
|
|
|
- Joshua Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Forming parameters optimizations with drawing force and die stress in wire rod drawing using rotating die under Coulomb friction Ing-Kiat Tiong, Un-Chin Chai, and Gow-Yi Tzou * Department of Mechanical and Automation Engineering, Chung Chou University of Science and Technology, Changhua, 510, Taiwan Abstract. An optimization research is performed on the related forming parameters of wire rod drawing through a rotating die under Coulomb friction. The optimization research is conducted through finite element method (FEM) simulation combined with Taguchi method. There are two drawing characteristic optimizations have been carried out. They are the optimizations with drawing force and die stress. The forming parameters considered in this study are half die angle, frictional coefficient, die fillet, and rotating angular velocity of the rotating die. The same procedure is carried out in both optimizations. The geometrical models of the wire rod, top die and rotating die are constructed firstly in SolidWorks and imported into the FEM simulation software named DEFORM 3D. With the aid of Taguchi method, the simulation experiments are carried out. The results such as drawing force, die stress, and the corresponding signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio are obtained and compared. The influence rank of the forming parameters and the optimal combination of parameters are obtained through the response table for both optimizations. The results such as effective stress, effective strain, velocity field, drawing force, and die stress are studied. The results show that the minimizations of drawing force and die stress are successfully achieved. 1 Introduction Metal rod drawing is a well-known manufacturing process which applies a tensile force to stretch a metal rod into a desired cross-section or shape. This process is carried out at room temperature and it is considered as a cold working process. Sas-Boca et al. [1] carried out a FEM simulation on wire drawing process including the analysis of stress distribution and determined the optimum process parameters for the desired wire diameter. Chevalier [2] studied about the influence of geometrical parameters and friction on the quality of final wire through FEM simulation, and the result showed the friction ratio has no effect on the stress distribution, but it affects the global drawing force. Tang et al. [3] investigated the influence of drawing parameters on the forming of the micro copper tube with straight grooves and the results showed the reduction and die angle affect the drawing force while * Corresponding author:gowyitzou@gm.ccut.edu.tw The Authors, published by EDP Sciences. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (
2 the die angle affects the stress in the multi-pass drawing process. Haddi et al. [4] performed a study on the relationship between drawing parameters and they developed a modified model to obtain the minimum drawing force and stress through the optimal combination of parameters obtained. El-Dominaty et al. [5] studied the thermal aspects of the wire-drawing process and the results obtained can be used for selecting the process parameters so that the minimization of temperature rise can be achieved. Kleinermann et al. [6] applied FEM simulation to solve a more complex problem named as inverse problem including parameters identification, initial geometry, and tool shape design. Wang et al. [7] successfully performed die design and modification by using advanced process simulation software and proved that it is better than old empirical method. Beland et al. [8] performed an optimization research on cold drawing process of 6063 aluminium tubes for reducing the drawing steps and drawing stress in the drawn tube. Tiernan et al. [9, 10] developed a machine for carrying out wire drawing without the use of conventional dies and they also presented a mathematical model of die-less drawing to represent the process of wire deformation. Walter et al. [11] performed process simulation on cold forming process and demonstrated die stress analysis on industrial problems. The results showed that the threedimensional simulation is very important for analyzing the die stress accurately. The reference mentioned above is related to the traditional drawing with a fixed die or without the use of a die. Tzou et al. [12] has demonstrated the FEM simulation using DEFORM 3D on rotating drawing with constant shear friction and they successfully explored the effect of forming parameters on the drawing characteristics. They also proved that the use of rotating die is able to reduce the drawing force and increase the material flow. The aim of this study is to study the relationship between drawing characteristics and drawing parameters by performing the optimization research on the related forming parameters of metal rod drawing through a rotating die under Coulomb friction. In this study, the influence rank of forming parameters and the optimal combination of parameters are obtained. 2 Pre-processing of drawing characteristics optimization Fig. 1 shows the schematic diagram of metal rod drawing with a front die and a rotating die. The material of the metal rod is set as SWRCH22AB. The flow rate of the metal rod is σ= ε MPa and this indicates that it is an elastic-plastic material. Coulomb friction is assumed along the interface between dies and work-piece. In this study, the metal rod is pulled by the top die with a fixed velocity, V 0. As shown in Fig. 1, V 0 is 33.5 mm/s and the rotating die rotates with an angular velocity, ω (rad/s) in an anticlockwise direction. The forming parameters related to drawing process are shown in Fig. 2; they are half die angle (αº), frictional efficient (µ), die fillet (R, mm), and angular velocity of the rotating die (ω, rad/s). Rigid-plastic FEM simulations are carried out through DEFORM 3D. With the aid of Taguchi method, the process of drawing characteristic optimizations is performed. The drawing parameters mentioned earlier are considered as the control factors for this study. Each control factor has three different levels. The overall simulation conditions are summarized in Table 1. 2
3 Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of metal rod drawing with rotating die and front die. Fig. 2. Forming parameters of metal rod drawing. Material Object type Table 1. FEM simulation conditions. Metal Rod Conditions SWRCH22AB Plastic Young's Modulus, E [GPa] 210 Poisson's Ratio, υ 0.3 Power law [MPa] σ= ε Number of Elements Diameter of Metal Rod, D 0 [mm] 6.4 Velocity of Metal Rod, V o [mm/s] 33.5 Die Conditions Diameter of Die, D d [mm] 5.6 Half Die Angle, α [º] 10, 14, 18 Frictional Coefficient, µ 0.05, 0.10, 0.15 Die Fillet, R [mm] 3, 5, 7 Rotating Angular Velocity, ω [rad/s] 2.5, 4.5, 6.5 3
4 3 Optimization analysis of drawing force The objective of performing drawing force optimization is to obtain the minimum drawing force in a rotating drawing process. Fig. 3 shows the fishbone diagram for drawing force optimization involving the control factors and levels mentioned in the previous part. Table 2 shows the L 9 (3 4 ) orthogonal table for drawing force optimization. Referring to Table 2, nine sets of simulation experiments with different combinations of drawing parameters are carried out. The values of the parameters are determined by referring to the fishbone diagram in Fig. 3. FEM simulation experiments are performed through DEFORM 3D. The corresponding drawing force and S/N ratio for each experiment are obtained and summarized in Table 2. According to the results from Table 2, experiment 1 has the lowest value of drawing force (4.33 kn) and the highest value of S/N ratio (-12.73), whereas experiment 9 has the largest value of drawing force (6.35 kn) and the smallest value of S/N ratio (-16.06). Since minimum drawing force is required, experiment 1 is determined as the best result for this study and experiment 9 is considered as the worst result. Table 3 is the response table of Taguchi method. Referring to Table 3, the frictional efficient (µ) has the highest influence on the drawing force following by half die angle (α), die fillet (R) and angular velocity of the rotating die (ω). In Table 3, the level of each control factor with the highest value of S/N ratio is selected and combined to form the optimal combination of parameters. The optimal combination of parameters is A 1 B 1 C 3 D 2 (α=10º, µ=0.05, R=7 mm, ω=4.5 rad/s). Fig. 3. Fishbone diagram for optimization of drawing force. Table 2. L 9 (3 4 ) orthogonal table for drawing force optimization and simulation results. Experiment A(α) B(µ) C(R) D(ω) Drawing Force (kn) S/N Ratio
5 Table 3. Response table of S/N ratio for drawing force optimization. S/N Ratio A (α) B (µ) C (R) D (ω) Level Level Level E(1->2) E(2->3) Effect Rank Fig. 4 shows the diagram of effective stress, effective strain, and velocity field for experiment 9 which is the worst result. In Fig. 4, the maximum effective stress of experiment 9 is 734 MPa and its maximum effective strain is mm/mm. The velocity experienced by the metal rod is set to be the same value for all the experiment simulations. However, the range of the velocity field for each experiment simulation occurs to be slightly different. The range of velocity field for experiment 9 is between 23.7 mm/s and 33.5 mm/s. Fig. 4. Diagram of effective stress, effective strain, and velocity field for experiment 9 (worst result). Fig. 5 shows the diagram of effective stress, effective strain, and velocity field for experiment 1 which is the best result. Referring to Fig. 5, the maximum effective stress for experiment 1 is 644 MPa and its maximum effective strain is mm/mm. Both of the maximum effective stress and strain for experiment 9 is higher than experiment 1. The range of velocity field for experiment 1 is ranged from 25.4 mm/s to 33.5 mm/s which are overall higher than experiment 9. 5
6 Fig. 5. Diagram of effective stress, effective strain, and velocity field for experiment 1 (best result). Fig. 6 shows the diagram of effective stress, effective strain and velocity field for the optimal result (A 1 B 1 C 3 D 2 ). According to Fig. 6, the maximum effective stress for the optimal result is 614 MPa and its maximum effective strain is mm/mm. The maximum effective stress and strain are lower than experiment 1 and 9.The range of velocity field for the optimal result is ranged from 25.5 mm/s to 33.5 mm/s which are higher than the best and worst simulation results. The minimization of metal rod drawing force is successfully carried out. 6
7 Fig. 6. Diagram of effective stress, effective strain, and velocity field for the optimal result. 4 Optimization analysis of die stress Fig. 7 shows the fishbone diagram for the optimization of die stress involving the control factors and the corresponding levels. Table 4 shows the L 9 (3 4 ) orthogonal table for die stress optimization. According to Table 4, there are nine simulation experiments with different combinations of parameters carried out for performing the die stress optimization. The combinations of parameters are similar for the optimizations of drawing force and die stress because the same orthogonal table is used for both optimizations. The value of levels for each control factors are chosen by referring to Fig. 7. FEM simulations are carried out by using DEFORM 3D. The die stress for each simulation experiment and its corresponding S/N ratio are obtained and recorded in Table 4. From Table 4, the results show that experiment 3 has the lowest die stress (770.94MPa) and the highest value of S/N ratio (-57.74) while experiment 1 has the largest die stress ( MPa) and the smallest S/N ratio (-62.38). The optimization of die stress aims to minimize the die stress. Since the minimum die stress is required, experiment 9 with the lowest die stress is considered as the best result and experiment 8 is determined as the worst result. Table 5 is the response table for the optimization of die stress. In Table 5, the die fillet (R) has the most significant influence on the die stress following by half die angle (α), frictional efficient (µ), and angular velocity of the rotating die (ω). Referring to Table 5, the level of each control factor with the highest S/N ratio is chosen and combined to form the optimal combination of parameters. The optimal combination of parameters is determined as A 1 B 3 C 3 D 2 (α=10º, µ=0.15, R=7 mm, ω=4.5 rad/s). Fig. 7. Fishbone diagram for optimization of die stress. 7
8 Table 4. L 9 (3 4 ) orthogonal table for die stress optimization and simulation results. Experiment A (α) B (µ) C (R) D (ω) Die Stress (MPa) S/N Ratio Table 5. Response table of S/N ratio for die stress optimization. S/N Ratio A (α) B (µ) C (R) D (ω) Level Level Level E(1->2) E(2->3) Effect Rank Fig. 8 shows the diagram of die stress for experiment 8 which is the worst result of all the experiment simulations. Referring to Table 4, the average die stress of experiment 8 is MPa. Fig. 8. Diagram of die stress for experiment 8 (worst result). 8
9 Fig. 9 shows the diagram of die stress for experiment 3 which is the best result among all the experiment simulations. According to Table 4, the average die stress of experiment 3 is MPa and it is lower than the die stress of experiment 8. Fig. 9. Diagram of die stress for experiment 3 (best result). Fig. 10 shows the diagram of die stress for the optimal result (A 1 B 3 C 3 D 2 ). The average die stress for the optimal result is MPa. The average die stress of the optimal result is lower than both of the best and worst simulation results. The minimization of die stress for metal rod drawing process is successfully performed. Fig. 10. Diagram of die stress for the optimal result. 9
10 5 Conclusions 5.1 Optimization of drawing force The objective of performing the optimization research on the drawing force for the metal rod drawing through FEM simulation and Taguchi method is to obtain the minimum drawing force. The influence rank of the drawing parameters to the drawing force is obtained through the response table of Taguchi method. The frictional coefficient (µ) has the largest influence to drawing force following by half die angle (α), die fillet (R), and angular velocity of the rotating die (ω). The optimal combination of drawing parameters for drawing force optimization is A 1 B 1 C 3 D 2 (α=10º, µ=0.05, R=7 mm, ω=4.5 rad/s). The drawing force, effective stress, effective strain, and velocity field for each experiment simulations are obtained and compared. Table 6 shows the improvement rate of the best and the worst results compared to the optimal result for the drawing force optimization. The drawing force of the optimal result is obtained to be 4.17 kn which is smaller than the best (4.33 kn) and the worst results (6.35 kn). The drawing force is improved by 34.40% and 3.81% compared to the best and the worst results respectively. The improvement rate of the effective stress is in the range between 4.66% and 16.35% while the improvement rate of the effective strain is in the range between 11.55% and 37.22%. Table 6. Improvement rate (%) of the best and worst results compared to the optimal result for the drawing force optimization. Effective Stress (MPa) Effective Strain (mm/mm) Drawing Force (kn) Best Result (BR) Worst Result (WR) Optimal Result (OR) Improvement (OR-BR)/BR Improvement (OR-WR)/WR % % % % % % 5.2 Optimization of die stress The objective of performing the optimization research on the die stress for the metal rod drawing by applying FEM simulation and Taguchi method is to obtain the minimum die stress. The influence rank of the drawing parameters to the die stress is obtained through the response table. Die fillet (R) has the highest influence on the die stress for metal rod drawing following by half die angle (α), frictional coefficient (µ) and angular velocity of the rotating die (ω). The optimal combination of drawing parameters for die stress optimization is A 1 B 3 C 3 D 2 (α=10º, µ=0.15, R=7 mm, ω=4.5 rad/s). The die stress for each experiment simulations is summarized and compared. Table 7 shows the improvement rate of the best and the worst results compared to the optimal result for the die stress optimization. According to Table 7, the die stress is improved by 2.60% and 43.58% compared to the best and the worst results respectively. 10
11 Table 7. Improvement rate (%) of the best and worst results compared to the optimal result for the die stress optimization. Best Result (BR) Worst Result (WR) Optimum Result (OR) Improvement (OR-BR)/BR Improvement (OR-WR)/WR Die Stress (MPa) % 43.58% Thanks for the financial support from Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST E ) to carry out this research successfully. References 1. I.M. Sac-Boca, M. Tintelecan, M. Pop, D.A. Ilutiu-Varvara, A.M. Mihu, Pro. E. 181, (2017) 2. L. Chevalier, J. Mat. P. Tech, 32, (1992) 3. Y. Tang, D.S. Ou, Z.P. Wan, L.S. Lu, B. Lian, T. N. M. S. China, 21, (2011) 4. A. Haddi, A. Imad, G. Vega, Mat. D, 32, (2011) 5. A. El-Domiaty, S.Z. Kassab, J. Mat. P. Tach, 83, (1998) 6. J.P. Kleinermann, J.P. Ponthot, J. Mat. P. Tech, 139, (2003) 7. K.L. Wang, V. Argyropoulos, J. Mat. P. Tech, 166, (2005) 8. J.F. Beland, M. Farard, A. Rahem, G, D Amours, T. Cote, App. Math. M., 35, (2011) 9. P. Tiernan, M.T. Hillery, J. Mat. P. Tech., , (2004) 10. P. Tiernan, M.T. Hillery, J. Mat. P. Tech., 10, (2008) 11. J. Walter, S. Kurtz, W.T. Wu, J. Tang, J. Mat. P. Tech., 71, (1997) 12. G.Y. Tzou, D.C. Chen, S.H. Lin, Key. E. Mat, 716, (2016) 11
CHAPTER 3 THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS
 CHAPTER THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS EXERCISE 1, Page 50 1. A rectangular bar having a cross-sectional area of 80 mm has a tensile force of 0 kn applied to it. Determine the stress in the bar. Stress
CHAPTER THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS EXERCISE 1, Page 50 1. A rectangular bar having a cross-sectional area of 80 mm has a tensile force of 0 kn applied to it. Determine the stress in the bar. Stress
Effects of the semi die/plug angles on cold tube drawing with a fixed plug by FEM for AISI 1010 steel tube
 2016 Published in 4th International Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineering and Science 3-5 November 2016 (ISITES2016 Alanya/Antalya - Turkey) Effects of the semi die/plug angles on cold tube
2016 Published in 4th International Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineering and Science 3-5 November 2016 (ISITES2016 Alanya/Antalya - Turkey) Effects of the semi die/plug angles on cold tube
Stress-Strain Behavior
 Stress-Strain Behavior 6.3 A specimen of aluminum having a rectangular cross section 10 mm 1.7 mm (0.4 in. 0.5 in.) is pulled in tension with 35,500 N (8000 lb f ) force, producing only elastic deformation.
Stress-Strain Behavior 6.3 A specimen of aluminum having a rectangular cross section 10 mm 1.7 mm (0.4 in. 0.5 in.) is pulled in tension with 35,500 N (8000 lb f ) force, producing only elastic deformation.
Solid Mechanics Homework Answers
 Name: Date: Solid Mechanics Homework nswers Please show all of your work, including which equations you are using, and circle your final answer. Be sure to include the units in your answers. 1. The yield
Name: Date: Solid Mechanics Homework nswers Please show all of your work, including which equations you are using, and circle your final answer. Be sure to include the units in your answers. 1. The yield
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading
 MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science Zhe Cheng (2018) 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading Statics
MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading MA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science Zhe Cheng (2018) 2 Stress & Strain - Axial Loading Statics
Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided
 Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Liang Dao Zhou 1,2,* and Zhuo Zhuang 1 1 School of Aerospace,
Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Prediction of Elastic Constants on 3D Four-directional Braided Composites Liang Dao Zhou 1,2,* and Zhuo Zhuang 1 1 School of Aerospace,
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
A study of forming pressure in the tube-hydroforming process
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 192 19 (2007) 404 409 A study of forming pressure in the tube-hydroforming process Fuh-Kuo Chen, Shao-Jun Wang, Ray-Hau Lin Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 192 19 (2007) 404 409 A study of forming pressure in the tube-hydroforming process Fuh-Kuo Chen, Shao-Jun Wang, Ray-Hau Lin Department of Mechanical Engineering,
ME 243. Mechanics of Solids
 ME 243 Mechanics of Solids Lecture 2: Stress and Strain Ahmad Shahedi Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.bd, shakil6791@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.bd/sshakil
ME 243 Mechanics of Solids Lecture 2: Stress and Strain Ahmad Shahedi Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.bd, shakil6791@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.bd/sshakil
N = Shear stress / Shear strain
 UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
STANDARD SAMPLE. Reduced section " Diameter. Diameter. 2" Gauge length. Radius
 MATERIAL PROPERTIES TENSILE MEASUREMENT F l l 0 A 0 F STANDARD SAMPLE Reduced section 2 " 1 4 0.505" Diameter 3 4 " Diameter 2" Gauge length 3 8 " Radius TYPICAL APPARATUS Load cell Extensometer Specimen
MATERIAL PROPERTIES TENSILE MEASUREMENT F l l 0 A 0 F STANDARD SAMPLE Reduced section 2 " 1 4 0.505" Diameter 3 4 " Diameter 2" Gauge length 3 8 " Radius TYPICAL APPARATUS Load cell Extensometer Specimen
6.4 A cylindrical specimen of a titanium alloy having an elastic modulus of 107 GPa ( psi) and
 6.4 A cylindrical specimen of a titanium alloy having an elastic modulus of 107 GPa (15.5 10 6 psi) and an original diameter of 3.8 mm (0.15 in.) will experience only elastic deformation when a tensile
6.4 A cylindrical specimen of a titanium alloy having an elastic modulus of 107 GPa (15.5 10 6 psi) and an original diameter of 3.8 mm (0.15 in.) will experience only elastic deformation when a tensile
Three-Dimensional simulation for the rock fragmentation induced by TBM with GFEM
 Recent Advances in Rock Engineering (RARE 2016) Three-Dimensional simulation for the rock fragmentation induced by TBM with GFEM XY Xu, XH Tang and QS Liu School of Civil Engineering, Wuhan University,
Recent Advances in Rock Engineering (RARE 2016) Three-Dimensional simulation for the rock fragmentation induced by TBM with GFEM XY Xu, XH Tang and QS Liu School of Civil Engineering, Wuhan University,
Fig. 1. Circular fiber and interphase between the fiber and the matrix.
 Finite element unit cell model based on ABAQUS for fiber reinforced composites Tian Tang Composites Manufacturing & Simulation Center, Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47906 1. Problem Statement In
Finite element unit cell model based on ABAQUS for fiber reinforced composites Tian Tang Composites Manufacturing & Simulation Center, Purdue University West Lafayette, IN 47906 1. Problem Statement In
Mechanics of Solids. Mechanics Of Solids. Suraj kr. Ray Department of Civil Engineering
 Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3
 MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3 Samantha Ramirez TENSION AND COMPRESSION TESTS Tension and compression tests are used primarily to determine the relationship between σ avg and ε avg in any material.
MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3 Samantha Ramirez TENSION AND COMPRESSION TESTS Tension and compression tests are used primarily to determine the relationship between σ avg and ε avg in any material.
Stress Analysis of Mandrel Used In Pilger Technology
 Stress Analysis of Mandrel Used In Pilger Technology Ruchil A. Patel 1, Apurvkumar Patel 2, Rajesh Kumar 3, Dr. D. V. Patel 4 1, 2, 3,4 Mechanical Engineering, GTU, Ahmedabad Abstract Cold pilgering is
Stress Analysis of Mandrel Used In Pilger Technology Ruchil A. Patel 1, Apurvkumar Patel 2, Rajesh Kumar 3, Dr. D. V. Patel 4 1, 2, 3,4 Mechanical Engineering, GTU, Ahmedabad Abstract Cold pilgering is
Chapter Two: Mechanical Properties of materials
 Chapter Two: Mechanical Properties of materials Time : 16 Hours An important consideration in the choice of a material is the way it behave when subjected to force. The mechanical properties of a material
Chapter Two: Mechanical Properties of materials Time : 16 Hours An important consideration in the choice of a material is the way it behave when subjected to force. The mechanical properties of a material
SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1. State and prove the relationship between shearing stress and rate of change of bending moment at a section in a loaded beam.
 ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING
 ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR THE MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-I 1. A rod 150 cm long and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kn. If the modulus
ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR THE MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-I 1. A rod 150 cm long and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kn. If the modulus
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 Third E CHAPTER 2 Stress MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University and Strain Axial Loading Contents Stress & Strain:
Third E CHAPTER 2 Stress MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University and Strain Axial Loading Contents Stress & Strain:
(1) Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, consists of 70% by volume of copper and 30% by volume of zinc.
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. (a) Define the density of a material....... (1) (b) Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, consists of 70% by volume of copper and 30% by volume of zinc. density of copper =
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. (a) Define the density of a material....... (1) (b) Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, consists of 70% by volume of copper and 30% by volume of zinc. density of copper =
Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 189 (2007) 459 465 Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method B.Y. Jun a, S.M. Kang b, M.C. Lee c, R.H. Park b, M.S.
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 189 (2007) 459 465 Prediction of geometric dimensions for cold forgings using the finite element method B.Y. Jun a, S.M. Kang b, M.C. Lee c, R.H. Park b, M.S.
Failure analysis and optimization design of a centrifuge rotor
 Engineering Failure Analysis 14 (2007) 101 109 www.elsevier.com/locate/engfailanal Failure analysis and optimization design of a centrifuge rotor Xuan Hai-jun *, Song Jian Institute of Chemical Process
Engineering Failure Analysis 14 (2007) 101 109 www.elsevier.com/locate/engfailanal Failure analysis and optimization design of a centrifuge rotor Xuan Hai-jun *, Song Jian Institute of Chemical Process
ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Chapter III. Mechanical Properties of Materials 1 Tension and Compression Test The strength of a material depends on its ability to sustain a load without undue deformation
ME 2570 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Chapter III. Mechanical Properties of Materials 1 Tension and Compression Test The strength of a material depends on its ability to sustain a load without undue deformation
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 20, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT
Simulation of the effect of DIE Radius on Deep Drawing Process
 Simulation the effect DIE Radius on Deep Drawing Process Kopanathi Gowtham, K.V.N.S. Srikanth & K.L.N. Murty CAD-CAM, Dept. Mechanical Engineering, Godavari Institute Engg. & Tech., Rajahmundry, India
Simulation the effect DIE Radius on Deep Drawing Process Kopanathi Gowtham, K.V.N.S. Srikanth & K.L.N. Murty CAD-CAM, Dept. Mechanical Engineering, Godavari Institute Engg. & Tech., Rajahmundry, India
End forming of thin-walled tubes
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 177 (2006) 183 187 End forming of thin-walled tubes M.L. Alves a, B.P.P. Almeida b, P.A.R. Rosa b, P.A.F. Martins b, a Escola Superior de Tecnologia e Gestão
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 177 (2006) 183 187 End forming of thin-walled tubes M.L. Alves a, B.P.P. Almeida b, P.A.R. Rosa b, P.A.F. Martins b, a Escola Superior de Tecnologia e Gestão
A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging
 A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging Y T Im*, S H Kang, and J S Cheon Department of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and
A novel technique of friction and material property measurement by tip test in cold forging Y T Im*, S H Kang, and J S Cheon Department of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and
PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics
![PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics](/thumbs/92/109382806.jpg) Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Class XI Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics
 Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Chapter 5 Torsion STRUCTURAL MECHANICS: CE203. Notes are based on Mechanics of Materials: by R. C. Hibbeler, 7th Edition, Pearson
 STRUCTURAL MECHANICS: CE203 Chapter 5 Torsion Notes are based on Mechanics of Materials: by R. C. Hibbeler, 7th Edition, Pearson Dr B. Achour & Dr Eng. K. El-kashif Civil Engineering Department, University
STRUCTURAL MECHANICS: CE203 Chapter 5 Torsion Notes are based on Mechanics of Materials: by R. C. Hibbeler, 7th Edition, Pearson Dr B. Achour & Dr Eng. K. El-kashif Civil Engineering Department, University
 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
, causing the length to increase to l 1 R U M. L Q P l 2 l 1
 1 1 Which of the following correctly defines the terms stress, strain and oung modulus? stress strain oung modulus (force) x (area) (extension) x (original length) (stress) / (strain) (force) x (area)
1 1 Which of the following correctly defines the terms stress, strain and oung modulus? stress strain oung modulus (force) x (area) (extension) x (original length) (stress) / (strain) (force) x (area)
Effect of Temperature on Mechanical Properties and Dynamic Characteristics of the Rotor in High Acceleration Mei-Hui JIA a,*, Cheng-Lin WANG b
 2016 International Conference on Mechanics Design, Manufacturing and Automation (MDM 2016) ISBN: 978-1-609-34-0 Effect of Temperature on Mechanical Properties and Dynamic Characteristics of the Rotor in
2016 International Conference on Mechanics Design, Manufacturing and Automation (MDM 2016) ISBN: 978-1-609-34-0 Effect of Temperature on Mechanical Properties and Dynamic Characteristics of the Rotor in
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Sample Problem 4.2
 Sample Problem 4. SOLUTON: Based on the cross section geometry, calculate the location of the section centroid and moment of inertia. ya ( + Y Ad ) A A cast-iron machine part is acted upon by a kn-m couple.
Sample Problem 4. SOLUTON: Based on the cross section geometry, calculate the location of the section centroid and moment of inertia. ya ( + Y Ad ) A A cast-iron machine part is acted upon by a kn-m couple.
STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Class XI Physics. Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids. NCERT Solutions
 Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
22 Which of the following correctly defines the terms stress, strain and Young modulus? stress strain Young modulus
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com Which of the following correctly defines the terms stress, strain and Young modulus? 97/1/M/J/ stress strain Young modulus () x (area) (extension) x (original length) (stress) /
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com Which of the following correctly defines the terms stress, strain and Young modulus? 97/1/M/J/ stress strain Young modulus () x (area) (extension) x (original length) (stress) /
Plane Strain Test for Metal Sheet Characterization
 Plane Strain Test for Metal Sheet Characterization Paulo Flores 1, Felix Bonnet 2 and Anne-Marie Habraken 3 1 DIM, University of Concepción, Edmundo Larenas 270, Concepción, Chile 2 ENS - Cachan, Avenue
Plane Strain Test for Metal Sheet Characterization Paulo Flores 1, Felix Bonnet 2 and Anne-Marie Habraken 3 1 DIM, University of Concepción, Edmundo Larenas 270, Concepción, Chile 2 ENS - Cachan, Avenue
UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS
 Subject with Code : SM-1(15A01303) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES
Subject with Code : SM-1(15A01303) Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns
 Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns Hideo Koguchi Mechanical Engineering, 603- Kamitomioka, Nagaoka Univ. of Tech., Nagaoka, Niigata, Japan Email: koguchi@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Takayoshi
Friction Properties of Surface with Circular Micro-patterns Hideo Koguchi Mechanical Engineering, 603- Kamitomioka, Nagaoka Univ. of Tech., Nagaoka, Niigata, Japan Email: koguchi@mech.nagaokaut.ac.jp Takayoshi
Twinning Engineering Programmes (TEP) & Thammasat English Programme of Engineering (TEPE) Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University
 " Twinning Engineering Programmes (TEP) & Thammasat English Programme of Engineering (TEPE) Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University Undergraduate Examination 2 nd Semester of 2019 (Mid-term) CE221:
" Twinning Engineering Programmes (TEP) & Thammasat English Programme of Engineering (TEPE) Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University Undergraduate Examination 2 nd Semester of 2019 (Mid-term) CE221:
INFLUENCE OF PROCESSING PARAMETERS ON FORMING QUALITY OF NON-CIRCULAR SPINNING
 Proceedings of the 11 th International Conference on Manufacturing Research (ICMR2013), Cranfield University, UK, 19th 20th September 2013, pp 275-280 INFLUENCE OF PROCESSING PARAMETERS ON FORMING QUALITY
Proceedings of the 11 th International Conference on Manufacturing Research (ICMR2013), Cranfield University, UK, 19th 20th September 2013, pp 275-280 INFLUENCE OF PROCESSING PARAMETERS ON FORMING QUALITY
Question Figure shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What are (a) Young s modulus and (b) approximate yield strength for this material?
 Question. A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 x 10-5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m 2 under a given load.
Question. A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 x 10-5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 x 10-5 m 2 under a given load.
Question 9.1: Answer. Length of the steel wire, L 1 = 4.7 m. Area of cross-section of the steel wire, A 1 = m 2
 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
The Nonlinear Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Research for Sheet Steel Stamping Forming Problems Based on Finite Element Method
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 198 The Open Materials Science Journal, 2015, 9, 198-202 Open Access The Nonlinear Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Research for Sheet Steel Stamping
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 198 The Open Materials Science Journal, 2015, 9, 198-202 Open Access The Nonlinear Dynamic Behavior Analysis and Research for Sheet Steel Stamping
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 146 (2004) 28 34 Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process Hariharasudhan Palaniswamy, Gracious Ngaile, Taylan Altan ERC
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 146 (2004) 28 34 Optimization of blank dimensions to reduce springback in the flexforming process Hariharasudhan Palaniswamy, Gracious Ngaile, Taylan Altan ERC
Shock wave speed and stress-strain relation of aluminium honeycombs under dynamic compression
 EPJ Web of Conferences 83, 7 (8) DYMAT 8 https://doi.org/.5/epjconf/8837 Shock wave speed and stress-strain relation of aluminium honeycombs under dynamic compression Peng Wang,*, Jun Zhang, Haiying Huang,
EPJ Web of Conferences 83, 7 (8) DYMAT 8 https://doi.org/.5/epjconf/8837 Shock wave speed and stress-strain relation of aluminium honeycombs under dynamic compression Peng Wang,*, Jun Zhang, Haiying Huang,
Effect of Strain Hardening on Unloading of a Deformable Sphere Loaded against a Rigid Flat A Finite Element Study
 Effect of Strain Hardening on Unloading of a Deformable Sphere Loaded against a Rigid Flat A Finite Element Study Biplab Chatterjee, Prasanta Sahoo 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jadavpur University
Effect of Strain Hardening on Unloading of a Deformable Sphere Loaded against a Rigid Flat A Finite Element Study Biplab Chatterjee, Prasanta Sahoo 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jadavpur University
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2 Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties of Metals Dr. Coates 6.2 Concepts of Stress and Strain tension compression shear torsion Tension Tests The specimen is deformed
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2 Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties of Metals Dr. Coates 6.2 Concepts of Stress and Strain tension compression shear torsion Tension Tests The specimen is deformed
Tensile stress strain curves for different materials. Shows in figure below
 Tensile stress strain curves for different materials. Shows in figure below Furthermore, the modulus of elasticity of several materials effected by increasing temperature, as is shown in Figure Asst. Lecturer
Tensile stress strain curves for different materials. Shows in figure below Furthermore, the modulus of elasticity of several materials effected by increasing temperature, as is shown in Figure Asst. Lecturer
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
INTRODUCTION TO STRAIN
 SIMPLE STRAIN INTRODUCTION TO STRAIN In general terms, Strain is a geometric quantity that measures the deformation of a body. There are two types of strain: normal strain: characterizes dimensional changes,
SIMPLE STRAIN INTRODUCTION TO STRAIN In general terms, Strain is a geometric quantity that measures the deformation of a body. There are two types of strain: normal strain: characterizes dimensional changes,
Effect Of The In-Situ Stress Field On Casing Failure *
 Effect Of The In-Situ Stress Field On Casing Failure * Tang Bo Southwest Petroleum Institute, People's Republic of China Lian Zhanghua Southwest Petroleum Institute, People's Republic of China Abstract
Effect Of The In-Situ Stress Field On Casing Failure * Tang Bo Southwest Petroleum Institute, People's Republic of China Lian Zhanghua Southwest Petroleum Institute, People's Republic of China Abstract
Deformation Processing - Drawing
 eformation Processing - rawing ver. Overview escription Characteristics Mechanical Analysis Thermal Analysis Tube drawing Geometry b α a F b, σ xb F a, σ xa 3 4 Equipment 5 Cold rawing 6 A. urer - Wire
eformation Processing - rawing ver. Overview escription Characteristics Mechanical Analysis Thermal Analysis Tube drawing Geometry b α a F b, σ xb F a, σ xa 3 4 Equipment 5 Cold rawing 6 A. urer - Wire
Lateral Crushing of Square and Rectangular Metallic Tubes under Different Quasi-Static Conditions
 Vol:, No:1, 2 Lateral Crushing of Square and Rectangular Metallic Tubes under Different Quasi-Static Conditions Sajjad Dehghanpour, Ali Yousefi International Science Index, Mechanical and Mechatronics
Vol:, No:1, 2 Lateral Crushing of Square and Rectangular Metallic Tubes under Different Quasi-Static Conditions Sajjad Dehghanpour, Ali Yousefi International Science Index, Mechanical and Mechatronics
Strength of Material. Shear Strain. Dr. Attaullah Shah
 Strength of Material Shear Strain Dr. Attaullah Shah Shear Strain TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION Poisson's Ratio Relationship Between E, G, and ν BIAXIAL DEFORMATION Bulk Modulus of Elasticity or Modulus of Volume
Strength of Material Shear Strain Dr. Attaullah Shah Shear Strain TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION Poisson's Ratio Relationship Between E, G, and ν BIAXIAL DEFORMATION Bulk Modulus of Elasticity or Modulus of Volume
Stress Test Based on Planar Flexible Eddy Current Sensor
 5th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, 13-15th November 2013, Singapore Stress Test Based on Planar Flexible Eddy Current Sensor TANG Ying 1, LI Ji 1, ZHAO Jianqiang 1, HE Yunze 1, TAN Xianglin
5th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace, 13-15th November 2013, Singapore Stress Test Based on Planar Flexible Eddy Current Sensor TANG Ying 1, LI Ji 1, ZHAO Jianqiang 1, HE Yunze 1, TAN Xianglin
X has a higher value of the Young modulus. Y has a lower maximum tensile stress than X
 Bulk Properties of Solids Old Exam Questions Q1. The diagram shows how the stress varies with strain for metal specimens X and Y which are different. Both specimens were stretched until they broke. Which
Bulk Properties of Solids Old Exam Questions Q1. The diagram shows how the stress varies with strain for metal specimens X and Y which are different. Both specimens were stretched until they broke. Which
CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Concepts of Stress and Strain 6.1 Using mechanics of materials principles (i.e., equations of mechanical equilibrium applied to a free-body diagram),
CHAPTER 6 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF METALS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Concepts of Stress and Strain 6.1 Using mechanics of materials principles (i.e., equations of mechanical equilibrium applied to a free-body diagram),
Development and analysis for the large-scale tee-forming process
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 104 (2000) 265±270 Development and analysis for the large-scale tee-forming process Quang-Cherng Hsu a,*, Sio-Hou Lei b a Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 104 (2000) 265±270 Development and analysis for the large-scale tee-forming process Quang-Cherng Hsu a,*, Sio-Hou Lei b a Department of Mechanical Engineering,
PURE BENDING. If a simply supported beam carries two point loads of 10 kn as shown in the following figure, pure bending occurs at segment BC.
 BENDING STRESS The effect of a bending moment applied to a cross-section of a beam is to induce a state of stress across that section. These stresses are known as bending stresses and they act normally
BENDING STRESS The effect of a bending moment applied to a cross-section of a beam is to induce a state of stress across that section. These stresses are known as bending stresses and they act normally
Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus. Case study
 Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Case study 2 In field of Physics, it explains how an object deforms under an applied force Real rigid bodies are elastic we can
Stress Strain Elasticity Modulus Young s Modulus Shear Modulus Bulk Modulus Case study 2 In field of Physics, it explains how an object deforms under an applied force Real rigid bodies are elastic we can
Elastic Properties of Solid Materials. Notes based on those by James Irvine at
 Elastic Properties of Solid Materials Notes based on those by James Irvine at www.antonine-education.co.uk Key Words Density, Elastic, Plastic, Stress, Strain, Young modulus We study how materials behave
Elastic Properties of Solid Materials Notes based on those by James Irvine at www.antonine-education.co.uk Key Words Density, Elastic, Plastic, Stress, Strain, Young modulus We study how materials behave
Mechanical Engineering Ph.D. Preliminary Qualifying Examination Solid Mechanics February 25, 2002
 student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
Structural Metals Lab 1.2. Torsion Testing of Structural Metals. Standards ASTM E143: Shear Modulus at Room Temperature
 Torsion Testing of Structural Metals Standards ASTM E143: Shear Modulus at Room Temperature Purpose To determine the shear modulus of structural metals Equipment Tinius-Olsen Lo-Torq Torsion Machine (figure
Torsion Testing of Structural Metals Standards ASTM E143: Shear Modulus at Room Temperature Purpose To determine the shear modulus of structural metals Equipment Tinius-Olsen Lo-Torq Torsion Machine (figure
Experimental and analytical studies on the pullout strength of round thread casing connections
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Science Vol. 20, December 2013, pp. 497-503 Experimental and analytical studies on the pullout strength of round thread casing connections Lianxin Gao a * & Jiaoqi
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Science Vol. 20, December 2013, pp. 497-503 Experimental and analytical studies on the pullout strength of round thread casing connections Lianxin Gao a * & Jiaoqi
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS)
 BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
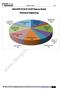 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
MICROMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF FRP COMPOSITES SUBJECTED TO LONGITUDINAL LOADING
 MICROMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF FRP COMPOSITES SUBJECTED TO LONGITUDINAL LOADING N. Krishna Vihari 1, P. Phani Prasanthi 1, V. Bala Krishna Murthy 2* and A. Srihari Prasad 3 1 Mech. Engg. Dept., P. V. P. Siddhartha
MICROMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF FRP COMPOSITES SUBJECTED TO LONGITUDINAL LOADING N. Krishna Vihari 1, P. Phani Prasanthi 1, V. Bala Krishna Murthy 2* and A. Srihari Prasad 3 1 Mech. Engg. Dept., P. V. P. Siddhartha
Theory at a Glance (for IES, GATE, PSU)
 1. Stress and Strain Theory at a Glance (for IES, GATE, PSU) 1.1 Stress () When a material is subjected to an external force, a resisting force is set up within the component. The internal resistance force
1. Stress and Strain Theory at a Glance (for IES, GATE, PSU) 1.1 Stress () When a material is subjected to an external force, a resisting force is set up within the component. The internal resistance force
Chapter 4-b Axially Loaded Members
 CIVL 222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 4-b Axially Loaded Members AXIAL LOADED MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Determine the elastic deformation of axially loaded member b) Apply
CIVL 222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 4-b Axially Loaded Members AXIAL LOADED MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Determine the elastic deformation of axially loaded member b) Apply
Experimental study of mechanical and thermal damage in crystalline hard rock
 Experimental study of mechanical and thermal damage in crystalline hard rock Mohammad Keshavarz Réunion Technique du CFMR - Thèses en Mécanique des Roches December, 3 nd 2009 1 Overview Introduction Characterization
Experimental study of mechanical and thermal damage in crystalline hard rock Mohammad Keshavarz Réunion Technique du CFMR - Thèses en Mécanique des Roches December, 3 nd 2009 1 Overview Introduction Characterization
Finite-Element Analysis of Stress Concentration in ASTM D 638 Tension Specimens
 Monika G. Garrell, 1 Albert J. Shih, 2 Edgar Lara-Curzio, 3 and Ronald O. Scattergood 4 Journal of Testing and Evaluation, Vol. 31, No. 1 Paper ID JTE11402_311 Available online at: www.astm.org Finite-Element
Monika G. Garrell, 1 Albert J. Shih, 2 Edgar Lara-Curzio, 3 and Ronald O. Scattergood 4 Journal of Testing and Evaluation, Vol. 31, No. 1 Paper ID JTE11402_311 Available online at: www.astm.org Finite-Element
International Conference on Mechanics and Civil Engineering (ICMCE 2014)
 International Conference on Mechanics and Civil Engineering (ICMCE 2014) Parametric Design and Experimental Study for Weak Area Structure of Circle Composite Fragile Cover Ran CAO 1,a, Guang-Ming ZHOU
International Conference on Mechanics and Civil Engineering (ICMCE 2014) Parametric Design and Experimental Study for Weak Area Structure of Circle Composite Fragile Cover Ran CAO 1,a, Guang-Ming ZHOU
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
M1. (a) density = (1) 1
 [or ρ b = (0.7 8900) + (0.3 700) () = 8.4 0 3 kg m 3 ()] max 4 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 6 M. (a) density = () (b) (i) volume of copper = 0.8 0 3 (= 0.56 0 3 m 3 ) (volume of zinc = 0.4 0 3 m 3 ) m c (=
[or ρ b = (0.7 8900) + (0.3 700) () = 8.4 0 3 kg m 3 ()] max 4 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 6 M. (a) density = () (b) (i) volume of copper = 0.8 0 3 (= 0.56 0 3 m 3 ) (volume of zinc = 0.4 0 3 m 3 ) m c (=
BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS. Level 3 Unit 5
 BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS Level 3 Unit 5 FORCES AS VECTORS Vectors have a magnitude (amount) and a direction. Forces are vectors FORCES AS VECTORS (2 FORCES) Forces F1 and F2 are in
BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS Level 3 Unit 5 FORCES AS VECTORS Vectors have a magnitude (amount) and a direction. Forces are vectors FORCES AS VECTORS (2 FORCES) Forces F1 and F2 are in
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
Structural Analysis I Chapter 4 - Torsion TORSION
 ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
Analysis of Tube End Formability of AA 2024 Tubes Using FEM
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, Vol.2, No.1 (March 2012) ISSN 2277-4106 Research Article Analysis of Tube End Formability of AA 2024 Tubes Using FEM Bharathi. P a*, Venkateswarlu.
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, Vol.2, No.1 (March 2012) ISSN 2277-4106 Research Article Analysis of Tube End Formability of AA 2024 Tubes Using FEM Bharathi. P a*, Venkateswarlu.
Sean Carey Tafe No Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test
 Sean Carey Tafe No. 366851615 Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test August 2012 The Hounsfield Tester The Hounsfield Tester can do a variety of tests on a small test-piece. It is mostly used for tensile
Sean Carey Tafe No. 366851615 Lab Report: Hounsfield Tension Test August 2012 The Hounsfield Tester The Hounsfield Tester can do a variety of tests on a small test-piece. It is mostly used for tensile
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON WESTERN INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE FZE BENG(HONS) MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2016/2017 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 1
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON WESTERN INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE FZE BENG(HONS) MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2016/2017 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 1 MOULE NO: AME4052 ate: Saturda 14 Januar 2017 Time :
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON WESTERN INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE FZE BENG(HONS) MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER ONE EXAMINATION 2016/2017 ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES 1 MOULE NO: AME4052 ate: Saturda 14 Januar 2017 Time :
THE EFFECT OF GEOMETRY ON FATIGUE LIFE FOR BELLOWS
 Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP2011) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (2012) 343-348 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512003418
Advanced Materials Development and Performance (AMDP2011) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 6 (2012) 343-348 World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S2010194512003418
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
Outline. Tensile-Test Specimen and Machine. Stress-Strain Curve. Review of Mechanical Properties. Mechanical Behaviour
 Tensile-Test Specimen and Machine Review of Mechanical Properties Outline Tensile test True stress - true strain (flow curve) mechanical properties: - Resilience - Ductility - Toughness - Hardness A standard
Tensile-Test Specimen and Machine Review of Mechanical Properties Outline Tensile test True stress - true strain (flow curve) mechanical properties: - Resilience - Ductility - Toughness - Hardness A standard
Solution: The strain in the bar is: ANS: E =6.37 GPa Poison s ration for the material is:
 Problem 10.4 A prismatic bar with length L 6m and a circular cross section with diameter D 0.0 m is subjected to 0-kN compressive forces at its ends. The length and diameter of the deformed bar are measured
Problem 10.4 A prismatic bar with length L 6m and a circular cross section with diameter D 0.0 m is subjected to 0-kN compressive forces at its ends. The length and diameter of the deformed bar are measured
Study on the Energy Absorption and the Local Buckling of the Expansion Tubes
 * Study on the Energy Absorption and the Local Buckling of the Expansion Tubes Kwanghyun Ahn * Jinsung Kim Hoon Huh School of Mechanical, Aerospace & System Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science
* Study on the Energy Absorption and the Local Buckling of the Expansion Tubes Kwanghyun Ahn * Jinsung Kim Hoon Huh School of Mechanical, Aerospace & System Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science
A Transparent Perovskite Light Emitting Touch-
 Supporting Information for A Transparent Perovskite Light Emitting Touch- Responsive Device Shu-Yu Chou, Rujun Ma, Yunfei Li,, Fangchao Zhao, Kwing Tong, Zhibin Yu, and Qibing Pei*, Department of Materials
Supporting Information for A Transparent Perovskite Light Emitting Touch- Responsive Device Shu-Yu Chou, Rujun Ma, Yunfei Li,, Fangchao Zhao, Kwing Tong, Zhibin Yu, and Qibing Pei*, Department of Materials
Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam adapted from
 1 Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam adapted from Choi, J. B. and Lakes, R. S., "Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam", Cellular Polymers, 10, 205-212 (1991).
1 Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam adapted from Choi, J. B. and Lakes, R. S., "Design of a fastener based on negative Poisson's ratio foam", Cellular Polymers, 10, 205-212 (1991).
Sample Question Paper
 Scheme I Sample Question Paper Program Name : Mechanical Engineering Program Group Program Code : AE/ME/PG/PT/FG Semester : Third Course Title : Strength of Materials Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
Scheme I Sample Question Paper Program Name : Mechanical Engineering Program Group Program Code : AE/ME/PG/PT/FG Semester : Third Course Title : Strength of Materials Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
Effects of Core Softness and Bimodularity of Fibreglass Layers on Flexural Stiffness of Polymer Sandwich Structures
 Effects of Core Softness and Bimodularity of Fibreglass Layers on Flexural Stiffness of Polymer Sandwich Structures Oldřich Šuba 1,*, Oldřich Šuba jr. 1, and Soňa Rusnáková 1 1 Tomas Bata University in
Effects of Core Softness and Bimodularity of Fibreglass Layers on Flexural Stiffness of Polymer Sandwich Structures Oldřich Šuba 1,*, Oldřich Šuba jr. 1, and Soňa Rusnáková 1 1 Tomas Bata University in
Solution: T, A1, A2, A3, L1, L2, L3, E1, E2, E3, P are known Five equations in five unknowns, F1, F2, F3, ua and va
 ME 323 Examination # 1 February 18, 2016 Name (Print) (Last) (First) Instructor PROBLEM #1 (20 points) A structure is constructed from members 1, 2 and 3, with these members made up of the same material
ME 323 Examination # 1 February 18, 2016 Name (Print) (Last) (First) Instructor PROBLEM #1 (20 points) A structure is constructed from members 1, 2 and 3, with these members made up of the same material
Solution to Multi-axial Fatigue Life of Heterogenic Parts & Components Based on Ansys. Na Wang 1, Lei Wang 2
 5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 215) Solution to Multi-axial Fatigue Life of Heterogenic Parts & Components Based on Ansys Na Wang 1, Lei Wang
5th International Conference on Information Engineering for Mechanics and Materials (ICIMM 215) Solution to Multi-axial Fatigue Life of Heterogenic Parts & Components Based on Ansys Na Wang 1, Lei Wang
