Standard Small Angle Generator Using Laser Interferometer
|
|
|
- Benedict Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
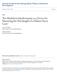
1 40 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40 : (2006) Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40(5) Standard Small Angle Generator Using Laser Interferometer Kittisak Nugkim 1, Kanokpoj Areekul 1 * and Bancha Panacharoensawad 2 ABSTRACT Small angle generator is equipment used for making an adjustable small inclined angle. This equipment is use for calibration of gradual scale of level measurement instrument, such as, bubble level, electronic level, inclinometer, survey scope, collimator, etc. In the research, the possible method to make the low cost high accuracy small angle generator is studied. The materials employed in this project are available in Thailand. The accuracy of the inclined angle measurement relies on the sine principle of triangle. Hypotenuse length (l) of mm is measured by steel ruler which uncertainty about ±0.5 mm. The small displacement of the opposite side ( h) is determined by the Michelson s interferometer. The shift of one fringe is half wavelength of 650 nm laser diode. The constructed system is capable to measure inclined angle of resolution about 325 nm /500 mm or about an order of 1 nm/m. Key words: small angle generator, incline angle, Michelson s Interferometer INTRODUCTION 1. Sine principle According to Naval Plant Representative Office [NPRO] (1977). Considering the basic right angle triangle illustrated in Figure 1. Any angle which is formed between the adjacent and hypotenuse sides of the right angle triangle. There exists one and only one ratio between the lengths of the opposite side against the length of the hypotenuse. Thus, if the certain length of hypotenuse and adjacent side are fixed, and the length of the opposite side is precisely adjustable ( h), the variation of h can generate standard inclined level. The standard inclined level is capable in calibrating several kind of the level measurement equipment. An accuracy of the level measurement depends on how accurate of the Dh measurement. Figure 1 The right angle triangle used to describe sine principle. 1 Metrology and Physics of Instrumentation Research Unit. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Bangkok 10900, Thailand. 2 Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, Bangkok 10900, Thailand.. * Corresponding author, Kanokpoj.A@ku.ac.th
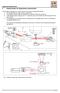
2 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40(5) The incline level standard There are several methods to design reference standard which is used to calibrate the level measurement equipment. The reference standards commonly used to calibrate the level are elaborated as follows. 2.1 Sine Bar, Sine Plate, and Small Angle Generator According to NPRO (1977), a practical small angle calibration with sine bar setting on two stacks of gauge block set is illustrated in Figure 2. In order to obtain accurate measurement, two criteria have to be fulfilled. First, for any sine bar size, the diameters of the two cylinders have to be exactly the same. Second, the distance between centers of both cylinders is precisely known. The triangle illustrated in Figure 2 (a) is an equivalent triangle as defined by the sine bar illustrated in Figure 2 (b). Since the diameters of both cylinders are the same, the angle opposite side is equal to the height difference between the two stacks of gauge blocks. The hypotenuse (l) of the triangle is an accurately known constant. It is the distance between axes os two cylinders. The angle (θ) generated by the sine bar is calculate as follow. sin θ = = difference in gage block stack heights length of sinebar side opposite hypotenuse 2.2 Michelson Interferometer A schematic of the Michelson interferometer is shown in Figure 3 (a). A beam from an extended source S, (1), is split by the beam splitter (BS). A transmitted beam 2 and reflected beam 3 which equal amplitude reflected by mirrors Figure 2 (a) Sine bar for angle level calibration, (b) Sine bar and sine plate Figure 3 (a) Michelson Interferometer, which designed optical path for the system. (b) Hardware design.
3 42 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40(5) M 1 and M 2, respectively. On returning to the beam splitter, beam 2 is now transmitted, and beam 3 is reflected so that they come together to detector. Thus beam 4 includes ray that have traveled difference optical path and will demonstrate interference. At least one of the mirrors is equipped with tilting adjustment screws that allow the surface of M 1 to be made perpendicular to that of M 2. One of the mirrors is also movable along the direction of the beam by means of an accurate track and micrometer screw. The actual interferometer in Figure 3 possesses two optical axes at right angle to one another. The optical path difference between the two beams emerging from the interferometer is p = 2d cos θ, (1) The optical system of Figure 3 (b) is now equivalent to the case of interference due to a plane parallel air film, illuminated by an extended source. Assuming that the two interfering beams are of equal amplitude, the irradiance of the fringe system of circles concentric with the optical axis is given by the equation 2 d I = 4I0 cos (2) 2 δ is the phase difference, defined by equation. δ = k = 2π λ (3) The net optical path difference is = p + r. A relative phase shift π between the two beams occurs because beam 3 experiences one reflections, but beam 2 experiences only one. For dark fringe then, p + r = 2d cos θ + λ 2 = 1 m + 2 λ (4) Or more simply, 2d cosθ = mλ (5) Note: the path differences with m = 1, 2, 3 correspond to dark fringes Equation (5) requires an increase in angular separation of θ of a given small fringe interval m as the mirror spacing d becomes smaller, since λ m θ = (6) 2 d sinθ This means that the fringes are more widely separated when optical path differences are smaller. In fact, if d = λ/2, then from the equation (5), m = cosθ, and the entire field of view encompasses no more than one fringe. For a mirror translation d, and the number m of fringe passing a point at or near the center of the pattern is according to the equation (5). m = 2 d (7) λ As described above, the Michelson interferometer is capable in several kinds of measurement, especially the length measurement. The length measurement for the h of opposite side is designed as follow MATERIAL AND METHODS The experimental design follows the Guidelines for Designing Experiments. This guideline provides steps to carry out the experimental design with Tagushi s method. 1. Choice of factors and levels The temperature factor can be controlled by adjusting air condition, this parameter is divided into 3 levels, i.e. 20 C (TC-1), 23 C (TC-2), and 25 C (TC-3). The ground vibration is an uncontrollable parameter. According to the usual working time, thus the experiment should be performed in separate times defined in 3 levels as 09:00 to 10:00 on the days off (Saturday or Sunday; VC-1), 17:00 to 18:00 on working day (VC-2), and 11:00 to 13:00 on working day (VC- 3). The third parameter is battery life of laser diode, also divide into 3 levels. The first pack is a brand new battery (BC-1), the second is a 2-3 hour used battery (BC-2), and the third is the 5-6 hour used battery (BC-3).
4 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40(5) Choice of experimental design The Tagushi s method (Design of Experiment from the Minitab software) designs the (3 factors 3 levels) experiment as illustrated in table Performing the experiment The precision dial comparator which established at the opposite side of the sine arm is the standard equipment that measuring the displacement of Dh. This dial comparator indicates this displacement in mm. The movable mirror M 1 and the dial comparator are held, they move together. The fringe counter should count the number of fringe(s) proportional to M 1 displacement as recorded in table 3. Table 1 Factors and levels of experimentation. Number Parameter Level-1 Level-2 Level-3 1 Temperature TC-1 TC-2 TC-2 2 Ground vibration VC-1 VC-2 VC-3 3 Battery life BC-1 BC-2 BC-3 Table 2 Design of experimentation. Experiment No. Factor-1 (Temperature) Factor-2 (Vibration) Factor-3 (Battery life) 1 TC-1 VC-1 BC-1 2 TC-1 VC-2 BC-2 3 TC-1 VC-3 BC-3 4 TC-2 VC-1 BC-2 5 TC-2 VC-2 BC-3 6 TC-2 VC-3 BC-1 7 TC-3 VC-1 BC-3 8 TC-3 VC-2 BC-1 9 TC-3 VC-3 BC-2 Table 3 Experimental data with calculated average value, and standard deviation. Exp. Fringe counter indication along 10 mm displacement (Counts) Mean S.D. No. Run1 Run2 Run3 Run4 Run5 Run6 Run7 Run8 Run9 Run
5 44 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40(5) RESULT 1. Data analysis The Minitab software analyzes data from the experimental results, the main effect plot for mean values illustrate in Figure 4, and the main effect plot for standard deviation in Figure 5. The response variable is the fringe counter indication, which this experiment need to know the best factor effect from each variable. The three line graph showed the effect of data cause by varying the controllable factor and level (3 3 levels). 2. Statistical analysis The summary flowchart that used for calculation of uncertainty in measurement is illustrated in Figure The Statistical (Type A) Uncertainty Mathematical model of measurement is defined by f(x i ) = x i ± U (8) where x i = fringe counter measurement (counts). U = uncertainty of measurement (± counts) To calculate the real displacement length ( d) that measured by this system, use equation (7), calculation as follow m = 2 d λ (9) where m = number of fringe(s) those move pass detection point d = mjj or (M 2 ) displacement length (mm) λ = wave length of laser light ( ± 0.01 µm) d = mλ 2 = ( ) / 2 = µm 2.2 Systematic (Type B) Uncertainty. The length measurement which using equipment list above concern with 3 main parts those includes self systematic uncertainty source. Figure 4 Main effect plot for the experimental mean value. Figure 5 Main effect plot for the experimental standard deviation.
6 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40(5) 45 The 3 main parts are: (1) The granite set of small angle generator; (2) The reference standard (precision dial gage); (3) The interferometer set (includes fringe counter). Each of parts perform the same measuring function is (vertical) length measurement, so the sensitivity coefficient c i should equal to 1. Figure 6 Flowchart for the determination of measurement uncertainty. Table 4 Calculated experimental data. Exp. Measurement result report as counts number Mean S.D. Type A No. 10 µm displacement (counts) Run 1-2 Run 3-4 Run 5-6 Run 7-8 Run Note: Type A uncertainty is ± 1 count due to the counter resolution is 1 count. Table 5 Experimental data corrected from fringes number to length (mm). Exp. Result of 10 µm displacement (µm) Mean S.D. Type A No. Run 1-2 Run 3-4 Run 5-6 Run 7-8 Run 9-10 (µm) (µm) (±µm)
7 46 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40(5) Systematic uncertainty budget from the granite set. The small angle generator granite set consists of steel, aluminum, and granite bar, those possible to provide uncertainty to the system. The temperature deviation in photonic laboratory controlled approximately 20 to 23 ± 1 C (for an experiment control at 20 ± 0.5 C) Systematic uncertainty budget from the reference standard. The reference standard used in this thesis is the dial comparator, Mahr, model 1002, which measurements range of ± 25 µm, scale resolution 0.5 µm, and accuracy of 0.6 µm (This standard equipment comply with standard DIN 879-1) Systematic uncertainty budget from the interferometer set. 2.3 Combined uncertainty (U c (l)) The estimate uncertainty list in section 1 (Type A uncertainty) and section 2 (Type B uncertainty) summarize in table 11 in purpose of combined uncertainty calculation as follow M3003 (1997) The uncertainty budgets listed in table 12 should calculate the combined uncertainty for length measurement U c (l) by the Root Sum Square (R.S.S.) calculation as follow n 2 U c (l) = Ui () l = ± µm i= 1 This calculated result is the combined uncertainty which represent variant of ±1σ. 2.4 Expanded Uncertainty (U c (l)) The following step is method to expand the confidence level to 95 % of confidence level. The effective degree of freedom, ν eff 4 u l ν eff = c () = N 4 ui () l i= 1 νi (10) M3003 (1997) In this case, the calculated ν eff is approximate 13295, compare this value in table 10, the coverage factor value k 95 should approximately 2. The expanded uncertainty can calculate as following U 95 = k 95 U c (l) (11) = ± µm Table 6 Uncertainty budget for material thermal expansion. Symbol Source of uncertainty Value ( C) -1 Prob. distribution U i (µm) U tea Thermal expansion for aluminum 23 Rectangular 1.15 U tes Thermal expansion for steel 12 Rectangular 0.3 U teg Thermal expansion for granite base and granite bar 8.5 Rectangular 0.2 Table 7 Uncertainty budget for precision dial gage. Symbol Source of uncertainty Value (mm) Prob. Distribution U i (µm) U rsa Reference standard accuracy Rectangular 0.6 U rsr Reference standard resolution Semi-Rectangular 0.5 Table 8 Uncertainty budget for the interferometer set. Symbol Source of uncertainty Value Prob. Distribution U i U rfc Resolution of fringe counter ±1 count Semi-Rectangular 650 nm U lsr Laser source λ uncertainty ± 10 nm Rectangular 10 nm U teb Thermal expansion for Al base 23 ( C) -1 Rectangular 0.86 µm
8 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 40(5) 47 Table 9 Uncertainty budget table. Symbol Source of uncertainty Value (µm) Prob. dist. Divisor c I U i (µm) v i U a Type A Uncertainty 0.16 Normal U tea T.E. for aluminum part 1.15 Rectangular U tes T.E. for steel part 0.3 Rectangular U teg T.E. for granite bar 0.2 Rectangular U rsa Reference std. accuracy 0.6 Rectangular U rsr Reference std. resolution 0.5 Semi-Rectan U rfc Fringe counter resolution 0.65 Semi-Rectan U lsr Laser λ uncertainty 0.01 Rectangular U teb T.E. for aluminum base 0.86 Rectangular U c (l) Combined uncertainty Normal (k=1) Table 10 Uncertainty budget with combined and expanded uncertainty. Symbol Source of uncertainty Value Prob. Divisor C i U i v i ±[µm] distribution ±[µm] U a Type A Uncertainty 0.13 Normal U tea T.E. for aluminum part 1.15 Rectangular U tes T.E. for steel part 0.3 Rectangular U teg T.E. for granite bar 0.2 Rectangular U rsa Reference std. accuracy 0.6 Rectangular U rsr Reference std. resolution 0.5 Semi-Rectan U rfc Fringe counter resolu n 0.65 Semi-Rectan U teb T.E. for aluminum base 0.86 Rectangular U c (l) Combined uncertainty Normal (k=1) U 95 Expanded uncertainty Normal (k=2) LITERATURE CITED Busch, T Fundamental of Dimensional Metrology. 2nd ed. Delmar Publisher Inc. Albany, New York. Eom, T.B Precision Angle Measurement. Ministry of Science and Technology, Korea Standard Research Institute. Taedok Science Town, Korea. Metrology Engineering Center, Dimensional Measurement. 2nd rev. Naval Plant Representative Office. California. United Kingdom Accreditation Service The Expression of Uncertainty and Confidence in Measurement, M st ed. UKAS Teddington, Middlesex, England. Anonymous MINITAB Statistical Software, Release Minitab Inc. Available Source: June 15, 2005.
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Introduction. Procedure. In this experiment, you'll use the interferometer to EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Lens 18mm FL. Component holder.
 12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
12-7137A Precision Interferometer Experiment 1: Introduction to Interferometry EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Basic Interferometer (OS-9255A) Laser (OS-9171) Laser Alignment Bench (OS-9172) Interferometer Accessories
TA/TI survey. Phy Phy
 TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
Interference- Michelson Interferometer. Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam
 Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Measurments with Michelson interferometers
 Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Measurments with Michelson interferometers Objectives In this experiment you will: Understand the
Please do not remove this manual from from the lab. It is available at www.cm.ph.bham.ac.uk/y2lab Optics Measurments with Michelson interferometers Objectives In this experiment you will: Understand the
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
PH 222-3A Spring 2010
 PH -3A Spring 010 Interference Lecture 6-7 Chapter 35 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding
PH -3A Spring 010 Interference Lecture 6-7 Chapter 35 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding
Interferometers. PART 1: Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the most useful of all optical instru
 Interferometers EP421 Lab Interferometers Introduction: Interferometers are the key to accurate distance measurement using optics. Historically, when mechanical measurements dominated, interferometers
Interferometers EP421 Lab Interferometers Introduction: Interferometers are the key to accurate distance measurement using optics. Historically, when mechanical measurements dominated, interferometers
Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting
 Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting PHYS 3330: Experiments in Optics Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30602 (Dated: Revised
Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting PHYS 3330: Experiments in Optics Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia 30602 (Dated: Revised
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Farooq Hassan Roll no: 2012-10-0101 LUMS School of Science and Engineering November 13, 2010 1 Abstract Michelson Interferometer was first used in the classic experiment in 1887
Michelson Interferometer Farooq Hassan Roll no: 2012-10-0101 LUMS School of Science and Engineering November 13, 2010 1 Abstract Michelson Interferometer was first used in the classic experiment in 1887
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2016 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Michelson Interferometer. crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity.
 Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
Michelson Interferometer The interferometer Michelson experiment Interferometer of Michelson and Morley played 0 a crucial role in Einstein s development of the Special Theory of Relativity. Michelson
25 LIGHT INTERFERENCE
 Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics Physics Laboratory I P Politechnika Warszawska Andrzej Kubiaczyk Wydział Fizyki Laboratorium Fizyki I 5 LIGHT INTERFERENCE NEWTON S ZJAWISKO RINGS, MICHELSON
Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics Physics Laboratory I P Politechnika Warszawska Andrzej Kubiaczyk Wydział Fizyki Laboratorium Fizyki I 5 LIGHT INTERFERENCE NEWTON S ZJAWISKO RINGS, MICHELSON
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER:
 LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
PS210 - Optical Techniques. Section VI
 PS210 - Optical Techniques Section VI Section I Light as Waves, Rays and Photons Section II Geometrical Optics & Optical Instrumentation Section III Periodic and Non-Periodic (Aperiodic) Waves Section
PS210 - Optical Techniques Section VI Section I Light as Waves, Rays and Photons Section II Geometrical Optics & Optical Instrumentation Section III Periodic and Non-Periodic (Aperiodic) Waves Section
Interference. Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website
 Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Chapter 9 Interference Phys 322 Lecture 25 Reminder: Exam 2 and Review quiz, more details on the course website Interferometers Wavefront-splitting interferometers Amplitude-splitting interferometers ed
Lab 2: Mach Zender Interferometer Overview
 Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
Coherence and width of spectral lines with Michelson interferometer
 Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
ABSTRACT. The following values for the wavelength of the sodium doublet lines were calculated:
 Determination of the wavelengths of the Sodium doublet lines and the measurement of the thickness of a thin transparent film using a Michelson interferometer Luke Pomfrey Tutor: Dr. P. Doel March 22, 2007
Determination of the wavelengths of the Sodium doublet lines and the measurement of the thickness of a thin transparent film using a Michelson interferometer Luke Pomfrey Tutor: Dr. P. Doel March 22, 2007
Chapter 8 Optical Interferometry
 Chapter 8 Optical Interferometry Lecture Notes for Modern Optics based on Pedrotti & Pedrotti & Pedrotti Instructor: Nayer Eradat Spring 009 4/0/009 Optical Interferometry 1 Optical interferometry Interferometer
Chapter 8 Optical Interferometry Lecture Notes for Modern Optics based on Pedrotti & Pedrotti & Pedrotti Instructor: Nayer Eradat Spring 009 4/0/009 Optical Interferometry 1 Optical interferometry Interferometer
1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light
 1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light 1. Double-Slit Eperiment reading: Chapter 22 2. Single-Slit Diffraction reading: Chapter 22 3. Diffraction Grating reading: Chapter
1. Waves and Particles 2. Interference of Waves 3. Wave Nature of Light 1. Double-Slit Eperiment reading: Chapter 22 2. Single-Slit Diffraction reading: Chapter 22 3. Diffraction Grating reading: Chapter
Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference
 Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference Waves that combine in phase add up to relatively high irradiance. = Constructive interference (coherent) Waves that combine
Constructive vs. destructive interference; Coherent vs. incoherent interference Waves that combine in phase add up to relatively high irradiance. = Constructive interference (coherent) Waves that combine
Interference. Part-2. Gambar: Museum Victoria Australia
 Interference Part-2 Gambar: Museum Victoria Australia Amplitude Splitting Interferometer S 2. Michelson Interferometer The principle: amplitude splitting d HM D F B M1 Detector C M1 E Interference at F
Interference Part-2 Gambar: Museum Victoria Australia Amplitude Splitting Interferometer S 2. Michelson Interferometer The principle: amplitude splitting d HM D F B M1 Detector C M1 E Interference at F
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
and the radiation from source 2 has the form. The vector r points from the origin to the point P. What will the net electric field be at point P?
 Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Physics 3 Interference and Interferometry Page 1 of 6 Interference Imagine that we have two or more waves that interact at a single point. At that point, we are concerned with the interaction of those
Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this.
 Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this. Superposition of Sinusoidal Waves Assume two waves are traveling in the same direction, with the same frequency,
Double Slit is VERY IMPORTANT because it is evidence of waves. Only waves interfere like this. Superposition of Sinusoidal Waves Assume two waves are traveling in the same direction, with the same frequency,
Chapter 35. Interference
 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding many natural phenomena, ranging from color shifting in butterfly wings to intensity patterns formed by small apertures.
Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding many natural phenomena, ranging from color shifting in butterfly wings to intensity patterns formed by small apertures.
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Annex A Procedure for Determining the Uncertainty of Coordinate Measurement Using Multiple Method
 Annex A Procedure for Determining the Uncertainty of Coordinate Measurement Using Multiple Method A.1 Procedure Rules Equipment 1. Measuring tips needed for the measurement of the feature. Measuring tips
Annex A Procedure for Determining the Uncertainty of Coordinate Measurement Using Multiple Method A.1 Procedure Rules Equipment 1. Measuring tips needed for the measurement of the feature. Measuring tips
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT.
 CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
CLOSED BOOK. Equation Sheet is provided. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED. (Except dimensionless units like
Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer
 Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 19, 2018 Last time diffraction patterns diffraction and interference resolution and Raleigh s criterion
Optics Interference from Films Newton s Rings Michelson Interferometer Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 19, 2018 Last time diffraction patterns diffraction and interference resolution and Raleigh s criterion
Engineering Metrology and Instrumentation
 3 types Mechanical Cleaning Physically disturb contaminants Electrolytic Cleaning Abrasive bubbles aid in contaminant removal Chemical Cleaning Solution Saponification Emulsification Dispersion Aggregation
3 types Mechanical Cleaning Physically disturb contaminants Electrolytic Cleaning Abrasive bubbles aid in contaminant removal Chemical Cleaning Solution Saponification Emulsification Dispersion Aggregation
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers
 Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Upgrade of 5m-Bench System for Traceable Measurements of Tapes and Rules at SASO-NMCC Dimensional Laboratory
 Upgrade of 5m-Bench System for Traceable Measurements of Tapes and Rules at SASO-NMCC Dimensional Laboratory Bülent ÖZGÜR 1,*, Okhan GANİOĞLU 1, Nasser Al-Qahtani 2, Faisal Al-Qahtani 2 1 TÜBİTAK, National
Upgrade of 5m-Bench System for Traceable Measurements of Tapes and Rules at SASO-NMCC Dimensional Laboratory Bülent ÖZGÜR 1,*, Okhan GANİOĞLU 1, Nasser Al-Qahtani 2, Faisal Al-Qahtani 2 1 TÜBİTAK, National
Experiment 6: Interferometers
 Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Fundamentals of Low Intensity Shock Calibration
 Low intensity shock metrology for safety related applications Fundamentals of Low Intensity Shock Calibration Speaker : Yu-Chung Huang Date : 2014.08.20 Center for Measurement Standards/ Industrial Technology
Low intensity shock metrology for safety related applications Fundamentals of Low Intensity Shock Calibration Speaker : Yu-Chung Huang Date : 2014.08.20 Center for Measurement Standards/ Industrial Technology
A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth.
 Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Geometrical Optics. = n r. sinθ i
 Name Section Number Lab Partner s Name Geometrical Optics Introduction In geometrical optics, refraction is described by Snell s Law. Refraction refers to the bending of light as it passes from one medium
Name Section Number Lab Partner s Name Geometrical Optics Introduction In geometrical optics, refraction is described by Snell s Law. Refraction refers to the bending of light as it passes from one medium
PHYSICS LABORATORY III
 T.C. MARMARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY III DEPARTMENT: NAME: SURNAME: NUMBER: 2 T.C.MARMARA UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY III MANUAL
T.C. MARMARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY III DEPARTMENT: NAME: SURNAME: NUMBER: 2 T.C.MARMARA UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY III MANUAL
Speed of Light in Glass
 Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Engineering Metrology
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Engineering Metrology Lecture 04: Angular Measurements Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Engineering Metrology Lecture 04: Angular Measurements Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department
Path Entanglement. Liat Dovrat. Quantum Optics Seminar
 Path Entanglement Liat Dovrat Quantum Optics Seminar March 2008 Lecture Outline Path entangled states. Generation of path entangled states. Characteristics of the entangled state: Super Resolution Beating
Path Entanglement Liat Dovrat Quantum Optics Seminar March 2008 Lecture Outline Path entangled states. Generation of path entangled states. Characteristics of the entangled state: Super Resolution Beating
INTERFEROMETERS. There are 4 principal types of measurements that can be made with this type of interferometer.
 INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides
INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides
Fourier Transform Spectrograph Development Project
 Fourier Transform Spectrograph Development Project NARIT Research Colloquium / Research Project Evaluation 2018 August 2 nd, Flora Creek Hotel, Chiangmai C. Buisset 1, P. Artsang 2, P. Meemon 2, 1 National
Fourier Transform Spectrograph Development Project NARIT Research Colloquium / Research Project Evaluation 2018 August 2 nd, Flora Creek Hotel, Chiangmai C. Buisset 1, P. Artsang 2, P. Meemon 2, 1 National
Optics Polarization. Lana Sheridan. June 20, De Anza College
 Optics Polarization Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 20, 2018 Last time interference from thin films Newton s rings Overview the interferometer and gravitational waves polarization birefringence 7 Michelson
Optics Polarization Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 20, 2018 Last time interference from thin films Newton s rings Overview the interferometer and gravitational waves polarization birefringence 7 Michelson
Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy
 Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy An FT-IR Spectrometer is an instrument which acquires broadband NIR to FIR spectra. Unlike a dispersive instrument, i.e. grating monochromator or spectrograph, an FT-IR
Introduction to FT-IR Spectroscopy An FT-IR Spectrometer is an instrument which acquires broadband NIR to FIR spectra. Unlike a dispersive instrument, i.e. grating monochromator or spectrograph, an FT-IR
Geometry Survey of the Time-of-Flight Neutron-Elastic Scattering (Antonella) Experiment
 Geometry Survey of the Time-of-Flight Neutron-Elastic Scattering (Antonella) Experiment Babatunde O Sheg Oshinowo a and Federico Izraelevitch a, b a Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), Batavia,
Geometry Survey of the Time-of-Flight Neutron-Elastic Scattering (Antonella) Experiment Babatunde O Sheg Oshinowo a and Federico Izraelevitch a, b a Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), Batavia,
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS6012W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 Coherent Light, Coherent Matter Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS6012W1 SEMESTER 1 EXAMINATION 2012/13 Coherent Light, Coherent Matter Duration: 120 MINS Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries
32. Interference and Coherence
 32. Interference and Coherence Interference Only parallel polarizations interfere Interference of a wave with itself The Michelson Interferometer Fringes in delay Measure of temporal coherence Interference
32. Interference and Coherence Interference Only parallel polarizations interfere Interference of a wave with itself The Michelson Interferometer Fringes in delay Measure of temporal coherence Interference
A Comprehensive Overview of the Laser Based Calibration Facility at Measurement Standards Laboratory
 A Comprehensive Overview of the Laser Based Calibration Facility at Measurement Standards Laboratory Fazil Syed, Faheem Mohammad*, and Luai M. Al-Hadhrami King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals,
A Comprehensive Overview of the Laser Based Calibration Facility at Measurement Standards Laboratory Fazil Syed, Faheem Mohammad*, and Luai M. Al-Hadhrami King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals,
Phys 2310 Mon. Dec. 11, 2014 Today s Topics. Begin Chapter 9: Interference Reading for Next Time
 Phys 30 Mon. Dec., 04 Todays Topics Begin Chapter 9: nterference Reading for Next Time Reading this Week By Wed.: Begin Ch. 9 (9. 9.3) General Considerations, Conditions for nterference, Wavefront-splitting
Phys 30 Mon. Dec., 04 Todays Topics Begin Chapter 9: nterference Reading for Next Time Reading this Week By Wed.: Begin Ch. 9 (9. 9.3) General Considerations, Conditions for nterference, Wavefront-splitting
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings. Abstract
 Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
Chapter 1. Optical Interferometry. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Optical Interferometry Experiment objectives: Assemble and align Michelson and Fabry-Perot interferometers, calibrate them using a laser of known wavelength, and then use them characterize the
Chapter 1 Optical Interferometry Experiment objectives: Assemble and align Michelson and Fabry-Perot interferometers, calibrate them using a laser of known wavelength, and then use them characterize the
HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES
 HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES David R. Dana, Robert A. Maffione Hydro-Optics, Biology and Instrumentation Laboratories,
HYDROBETA: A NEW INSTRUMENT FOR MEASURING IN-SITU PROFILES OF THE VOLUME SCATTERING FUNCTION FROM 10 TO 170 DEGREES David R. Dana, Robert A. Maffione Hydro-Optics, Biology and Instrumentation Laboratories,
Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy
 Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy Absorption peaks in an infrared absorption spectrum arise from molecular vibrations Absorbed energy causes molecular motions which create a net change in the dipole moment.
Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy Absorption peaks in an infrared absorption spectrum arise from molecular vibrations Absorbed energy causes molecular motions which create a net change in the dipole moment.
The Anomalous Zeeman Splitting of the Sodium 3P States
 Advanced Optics Laboratory The Anomalous Zeeman Splitting of the Sodium 3P States David Galey Lindsay Stanceu Prasenjit Bose April 5, 010 Objectives Calibrate Fabry-Perot interferometer Determine the Zeeman
Advanced Optics Laboratory The Anomalous Zeeman Splitting of the Sodium 3P States David Galey Lindsay Stanceu Prasenjit Bose April 5, 010 Objectives Calibrate Fabry-Perot interferometer Determine the Zeeman
Machine Positioning Uncertainty with Laser Interferometer Feedback
 Machine Positioning Uncertainty with Laser Interferometer Feedback The purpose of this discussion is to explain the major contributors to machine positioning uncertainty in systems with laser interferometer
Machine Positioning Uncertainty with Laser Interferometer Feedback The purpose of this discussion is to explain the major contributors to machine positioning uncertainty in systems with laser interferometer
Waves Part 3B: Interference
 Waves Part 3B: Interference Last modified: 31/01/2018 Contents Links Interference Path Difference & Interference Light Young s Double Slit Experiment What Sort of Wave is Light? Michelson-Morley Experiment
Waves Part 3B: Interference Last modified: 31/01/2018 Contents Links Interference Path Difference & Interference Light Young s Double Slit Experiment What Sort of Wave is Light? Michelson-Morley Experiment
SPECIMEN. Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes. AS Level Physics A H156/01 Breadth in physics Sample Question Paper PMT
 AS Level Physics A H156/01 Breadth in physics Sample Question Paper Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: the Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet You may use: a scientific
AS Level Physics A H156/01 Breadth in physics Sample Question Paper Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: the Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet You may use: a scientific
The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser
 Journal of Advanced Undergraduate Physics Laboratory Investigation Volume 3 2017-2018 Article 2 2018 The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser Carly E.
Journal of Advanced Undergraduate Physics Laboratory Investigation Volume 3 2017-2018 Article 2 2018 The Michelson Interferometer as a Device for Measuring the Wavelength of a Helium-Neon Laser Carly E.
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Interferometric determination of thermal expansion coefficient of piston/cylinder unit preliminary investigation
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Interferometric determination of thermal expansion coefficient of piston/cylinder unit preliminary investigation To cite this article: L Grgec Bermanec
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Interferometric determination of thermal expansion coefficient of piston/cylinder unit preliminary investigation To cite this article: L Grgec Bermanec
Fabry-Perot Interferometers
 Fabry-Perot Interferometers Astronomy 6525 Literature: C.R. Kitchin, Astrophysical Techniques Born & Wolf, Principles of Optics Theory: 1 Fabry-Perots are best thought of as resonant cavities formed between
Fabry-Perot Interferometers Astronomy 6525 Literature: C.R. Kitchin, Astrophysical Techniques Born & Wolf, Principles of Optics Theory: 1 Fabry-Perots are best thought of as resonant cavities formed between
Renewal of the gage-block interferometer at INRIM
 Renewal of the gage-block interferometer at INRIM R. Bellotti, M. Franco, G. B. Picotto* and M. Pometto Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRIM), Strada delle Cacce 73, 10135 Torino, Italy * Corresponding
Renewal of the gage-block interferometer at INRIM R. Bellotti, M. Franco, G. B. Picotto* and M. Pometto Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRIM), Strada delle Cacce 73, 10135 Torino, Italy * Corresponding
Michelson Interferometry Hassan Mirza
 Michelson Interferometry Hassan Mirza Queen Mary University, Department of Physics Mile End Road, London, England, E1 4NS Introduction Interferometry is a method of experiment in which electromagnetic
Michelson Interferometry Hassan Mirza Queen Mary University, Department of Physics Mile End Road, London, England, E1 4NS Introduction Interferometry is a method of experiment in which electromagnetic
The Diffraction Grating
 The Diffraction Grating If one extends the double slit to large number of slits very closely spaced, one gets what is called a diffraction grating. d sin θ. Maxima are still at d sin θ m = mλ, m = 0, 1,
The Diffraction Grating If one extends the double slit to large number of slits very closely spaced, one gets what is called a diffraction grating. d sin θ. Maxima are still at d sin θ m = mλ, m = 0, 1,
Read the following BEFORE getting started:
 BASIC MEASUREMENTS Read the following BEFORE getting started: Ruler: A ruler, or rule, is an instrument used in geometry, technical drawing and engineering/ building to measure distances and/or to rule
BASIC MEASUREMENTS Read the following BEFORE getting started: Ruler: A ruler, or rule, is an instrument used in geometry, technical drawing and engineering/ building to measure distances and/or to rule
Experimental detection of the ether
 Experimental detection of the ether E.W. Silvertooth Star Route, Box 166, Olga, Washington 98279, USA Received: May 1986 Abstract Michelson-Morley type experiments are shown to be non-sequitors because
Experimental detection of the ether E.W. Silvertooth Star Route, Box 166, Olga, Washington 98279, USA Received: May 1986 Abstract Michelson-Morley type experiments are shown to be non-sequitors because
Optics.
 Optics www.optics.rochester.edu/classes/opt100/opt100page.html Course outline Light is a Ray (Geometrical Optics) 1. Nature of light 2. Production and measurement of light 3. Geometrical optics 4. Matrix
Optics www.optics.rochester.edu/classes/opt100/opt100page.html Course outline Light is a Ray (Geometrical Optics) 1. Nature of light 2. Production and measurement of light 3. Geometrical optics 4. Matrix
Particle-Wave Duality and Which-Way Information
 Particle-Wave Duality and Which-Way Information Graham Jensen and Samantha To University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, U.S. September 25, 2013 Abstract Samantha To This experiment aimed to support
Particle-Wave Duality and Which-Way Information Graham Jensen and Samantha To University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, U.S. September 25, 2013 Abstract Samantha To This experiment aimed to support
Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer Introduction This week s experiment utilizes the Michelson interferometer. You are to measure the wavelength of the green mercury light, the wavelength of the sodium
Experiment 8 Michelson Interferometer Introduction This week s experiment utilizes the Michelson interferometer. You are to measure the wavelength of the green mercury light, the wavelength of the sodium
Development of a cryogenic compact interferometric displacement sensor
 Development of a cryogenic compact interferometric displacement sensor Fabián E. Peña Arellano National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Outline of the presentation Motivation: local position sensor for
Development of a cryogenic compact interferometric displacement sensor Fabián E. Peña Arellano National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Outline of the presentation Motivation: local position sensor for
BANNARI AMMAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SATHYAMANGALAM DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES. UNIT II Applied Optics
 BANNAI AMMAN INSTITTE OF TECHNOLOGY SATHYAMANGALAM DEPATMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES NIT II Applied Optics PAT A A1 The superimposition of one light wave over another is called as a) interference b) Diffraction
BANNAI AMMAN INSTITTE OF TECHNOLOGY SATHYAMANGALAM DEPATMENT OF PHYSICAL SCIENCES NIT II Applied Optics PAT A A1 The superimposition of one light wave over another is called as a) interference b) Diffraction
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E
 THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E INTRODUCTION The Zeeman effect is a demonstration of spatial quantization of angular momentum in atomic physics. Since an electron circling a nucleus is analogous to a current
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E INTRODUCTION The Zeeman effect is a demonstration of spatial quantization of angular momentum in atomic physics. Since an electron circling a nucleus is analogous to a current
Profs. P. Avery, A. Rinzler, S. Hershfield. Final Exam Solution
 PHY2049 Spring 2010 Profs. P. Avery, A. Rinzler, S. Hershfield Final Exam Solution 1. A proton traveling along the x axis (toward increasing x) has a speed of 1.0 10 5 m/s. At time t = 0 it enters a region
PHY2049 Spring 2010 Profs. P. Avery, A. Rinzler, S. Hershfield Final Exam Solution 1. A proton traveling along the x axis (toward increasing x) has a speed of 1.0 10 5 m/s. At time t = 0 it enters a region
C. Incorrect! The velocity of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is the same, 3.14 x 10 8 m/s.
 AP Physics - Problem Drill 21: Physical Optics 1. Which of these statements is incorrect? Question 01 (A) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (B) An electromagnetic wave is a
AP Physics - Problem Drill 21: Physical Optics 1. Which of these statements is incorrect? Question 01 (A) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (B) An electromagnetic wave is a
Bureau International des Poids et Mesures. Rapport BIPM -89/1
 Bureau International des Poids et Mesures Rapport BIPM -89/1 Shape Measurements of Standard Length Scales Using Interferometry with Small Angles of Incidence by Lennart Robertsson Abstract An interferometric
Bureau International des Poids et Mesures Rapport BIPM -89/1 Shape Measurements of Standard Length Scales Using Interferometry with Small Angles of Incidence by Lennart Robertsson Abstract An interferometric
SPEED OF SOUND AND SPEED OF LIGHT IN AIR
 University of Oulu Student laboratory in Physics Laboratory Exercises in Physics 1 SPEED OF SOUND AND SPEED OF LIGHT IN AIR 1. Introduction Sound can be determined as a longitudinal, mechanical wave motion
University of Oulu Student laboratory in Physics Laboratory Exercises in Physics 1 SPEED OF SOUND AND SPEED OF LIGHT IN AIR 1. Introduction Sound can be determined as a longitudinal, mechanical wave motion
INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT
 1 INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT In the year 1678, Christian Huygens proposed the wave theory of light. According to this, a Luminous body is a source of disturbance in hypothetical medium called ether
1 INTERFERENCE 1.1 NATURE OF LIGHT In the year 1678, Christian Huygens proposed the wave theory of light. According to this, a Luminous body is a source of disturbance in hypothetical medium called ether
Waves Part 3: Superposition
 Waves Part 3: Superposition Last modified: 06/06/2017 Superposition Standing Waves Definition Standing Waves Summary Standing Waves on a String Standing Waves in a Pipe Standing Waves in a Pipe with One
Waves Part 3: Superposition Last modified: 06/06/2017 Superposition Standing Waves Definition Standing Waves Summary Standing Waves on a String Standing Waves in a Pipe Standing Waves in a Pipe with One
Interferometric Measuring Systems of Nanopositioning and Nanomeasuring Machines
 Interferometric Measuring Systems of Nanopositioning and Nanomeasuring Machines T. Hausotte, University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Chair Manufacturing Metrology, Erlangen, Germany; B. Percle, N. Vorbringer-Dorozhovets,
Interferometric Measuring Systems of Nanopositioning and Nanomeasuring Machines T. Hausotte, University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Chair Manufacturing Metrology, Erlangen, Germany; B. Percle, N. Vorbringer-Dorozhovets,
A laser metroscope for the calibration of setting rings
 THE 0 th INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM OF MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY AND INTELLIGENT INSTRUMENTS JUNE 29 JULY 2 20 / A laser metroscope for the of setting rings S.Zahwi,*, M.Amer 2, M.A.Abdo 3, A.El-Melegy 4 Professor,
THE 0 th INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM OF MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY AND INTELLIGENT INSTRUMENTS JUNE 29 JULY 2 20 / A laser metroscope for the of setting rings S.Zahwi,*, M.Amer 2, M.A.Abdo 3, A.El-Melegy 4 Professor,
Scalar & Vector tutorial
 Scalar & Vector tutorial scalar vector only magnitude, no direction both magnitude and direction 1-dimensional measurement of quantity not 1-dimensional time, mass, volume, speed temperature and so on
Scalar & Vector tutorial scalar vector only magnitude, no direction both magnitude and direction 1-dimensional measurement of quantity not 1-dimensional time, mass, volume, speed temperature and so on
Interferometer for Squareness measurement
 F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
F Interferometer for Squareness measurement The deviation of squareness of two machine axes can be measured as follows: 1. The straightness of a machine axis is measured. 2. The Angular reflector stops
Innovation and Development of Study Field. nano.tul.cz
 Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
Innovation and Development of Study Field Nanomaterials at the Technical University of Liberec nano.tul.cz These materials have been developed within the ESF project: Innovation and development of study
Phys 132: Supplementary Exercises
 Phys 132 Fall 2017 Phys 132: Supplementary Exercises 1 Charged spheres Various identical metal spheres are separated and charged. The excess charges on each sphere, whose charges have the same magnitude,
Phys 132 Fall 2017 Phys 132: Supplementary Exercises 1 Charged spheres Various identical metal spheres are separated and charged. The excess charges on each sphere, whose charges have the same magnitude,
Geometrical Optics. sin( i. n r
 Name Section Number Lab Partner s Name Geometrical Optics Introduction In geometrical optics, refraction is described by Snell s Law. Refraction refers to the bending of light as it passes from one medium
Name Section Number Lab Partner s Name Geometrical Optics Introduction In geometrical optics, refraction is described by Snell s Law. Refraction refers to the bending of light as it passes from one medium
An Overview of Advanced LIGO Interferometry
 An Overview of Advanced LIGO Interferometry Luca Matone Columbia Experimental Gravity group (GECo) Jul 16-20, 2012 LIGO-G1200743 Day Topic References 1 2 3 4 5 Gravitational Waves, Michelson IFO, Fabry-Perot
An Overview of Advanced LIGO Interferometry Luca Matone Columbia Experimental Gravity group (GECo) Jul 16-20, 2012 LIGO-G1200743 Day Topic References 1 2 3 4 5 Gravitational Waves, Michelson IFO, Fabry-Perot
Holography and Optical Vortices
 WJP, PHY381 (2011) Wabash Journal of Physics v3.3, p.1 Holography and Optical Vortices Z. J. Rohrbach, J. M. Soller, and M. J. Madsen Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated:
WJP, PHY381 (2011) Wabash Journal of Physics v3.3, p.1 Holography and Optical Vortices Z. J. Rohrbach, J. M. Soller, and M. J. Madsen Department of Physics, Wabash College, Crawfordsville, IN 47933 (Dated:
Michelson Interferometer
 Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum O10e Michelson Interferometer Tasks 1. Adjust a Michelson interferometer and determine the wavelength of a He-Ne laser. 2. Measure
Fakultät für Physik und Geowissenschaften Physikalisches Grundpraktikum O10e Michelson Interferometer Tasks 1. Adjust a Michelson interferometer and determine the wavelength of a He-Ne laser. 2. Measure
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics. Final Exam. April 16, 2007.
 Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE318S Fundamentals of Optics Final Exam April 16, 2007 Exam Type: D (Close-book + two double-sided aid sheets + a non-programmable
MOY/SCMI/36 SPECIFICATION OF ACCURACY FOR A PRECISION CLINOMETER
 Centre for Basic, Thermal and Length Metrology National Physical Laboratory MOY/SCMI/36 SPECIFICATION OF ACCURACY FOR A PRECISION CLINOMETER A Watts Precision Clinometer fitted with a circular glass scale
Centre for Basic, Thermal and Length Metrology National Physical Laboratory MOY/SCMI/36 SPECIFICATION OF ACCURACY FOR A PRECISION CLINOMETER A Watts Precision Clinometer fitted with a circular glass scale
CHAPTER 9 PERFORMANCE OF THE INTERFEROMETER
 Performance of the interferometer 235 CHAPTER 9 PERFORMANCE OF THE INTERFEROMETER Deus ex machina. ( A god from the machine. ) Menander 9.1 ASSESSMENT OF THE INTERFEROMETER One major problem in assessing
Performance of the interferometer 235 CHAPTER 9 PERFORMANCE OF THE INTERFEROMETER Deus ex machina. ( A god from the machine. ) Menander 9.1 ASSESSMENT OF THE INTERFEROMETER One major problem in assessing
= nm. = nm. = nm
 Chemistry 60 Analytical Spectroscopy PROBLEM SET 5: Due 03/0/08 1. At a recent birthday party, a young friend (elementary school) noticed that multicolored rings form across the surface of soap bubbles.
Chemistry 60 Analytical Spectroscopy PROBLEM SET 5: Due 03/0/08 1. At a recent birthday party, a young friend (elementary school) noticed that multicolored rings form across the surface of soap bubbles.
PHYS 229: Experiment 1 Expansion Coefficients of Copper and Invar Bars Through Laser Interferometry
 PHYS 229: Experiment 1 Expansion Coefficients of Copper and Invar Bars Through Laser Interferometry Jack Hong 30935134 Partner: Omar Mrani Zentar January 15, 2015 1 Introduction: When objects are heated,
PHYS 229: Experiment 1 Expansion Coefficients of Copper and Invar Bars Through Laser Interferometry Jack Hong 30935134 Partner: Omar Mrani Zentar January 15, 2015 1 Introduction: When objects are heated,
Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
MODERN INTERFEROMETRY
 MODERN INTERFEROMETRY * No actual laser photons were harmed during the filming of this cover. Build Michelson, Sagnac, and Mach-Zehnder Interferometers Generate and Count Interference Fringes Manually
MODERN INTERFEROMETRY * No actual laser photons were harmed during the filming of this cover. Build Michelson, Sagnac, and Mach-Zehnder Interferometers Generate and Count Interference Fringes Manually
Coherence and Fringe Localization
 5 Coherence and Fringe Localization T.D. Milster and N.A. Beaudry A basic functional form for an electromagnetic disturbance from a laser can be described as a simple plane wave traveling in the z direction
5 Coherence and Fringe Localization T.D. Milster and N.A. Beaudry A basic functional form for an electromagnetic disturbance from a laser can be described as a simple plane wave traveling in the z direction
