Next: Pushdown automata. Pushdown Automata. Informal Description PDA (1) Informal Description PDA (2) Formal Description PDA
|
|
|
- Suzanna Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CE 2001: Introdution to Theor of Computation ummer 2007 uprakash Datta Net: Pushdown automata dd stak to definition of Finite utomata Can serve as tpe of memor or ounter More powerful than Finite utomata epts Contet-Free Languages (CFLs) Offie: CEB 3043 Phone: et Course page: 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer /25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Pushdown utomata Pushdown automata are for ontet-free languages what finite automata are for regular languages. PDs are reognizing automata that have a single stak (= memor): Last-In First-Out pushing and popping We onsider onl non-deterministi PDs. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Informal Desription PD (1) input w = internal state set Q stak z The PD M reads w and stak element. Depending on - input w i Σ ε, - stak s j Γ ε, and - state q k Q the PD M: - jumps to a new state, - pushes an element Γ ε (nondeterministiall) 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Informal Desription PD (2) input w = internal state set Q stak z fter the PD has read omplete input, M will be in state Q If possible to end in aepting state F Q, then M aepts w 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Formal Desription PD Pushdown utomata M is defined b a si tuple (Q,Σ,Γ,δ,q 0,F), with Q finite set of states Σ finite input alphabet Γ finite stak alphabet q 0 start state Q F set of aepting states Q δ transition funtion δ: Q Σ ε Γ ε P (Q Γ ε ) 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer
2 PD for L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Eample 2.9: The PD first pushes $ 0 n on stak. Then, while reading the 1 n string, the zeros are popped again. If, in the end, $ is left on stak, then aept q 1 q 4 ε, ε $ ε, $ ε 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer q 2 q 3 0, ε 0 Mahine Diagram for 0 n 1 n q 1 q 4 ε, ε $ ε, $ ε 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer q 2 q 3 0, ε 0 On w = (state; stak) evolution: (q 1 ; ε) (q 2 ; $) (q 2 ; 0$) (q 2 ; 00$) (q 2 ; 000$) (q 3 ; 00$) (q 3 ; 0$) (q 3 ; $) (q 4 ; ε) This final q 4 is an aepting state Mahine Diagram for 0 n 1 n q 1 q 4 ε, ε $ ε, $ ε q 2 q 3 0, ε 0 On w = 0101 (state; stak) evolution: (q 1 ; ε) (q 2 ; $) (q 2 ; 0$) (q 3 ; $) (q 4 ; ε) But we still have part of input 01. There is no aepting path. PDs and CFL Theorem 2.12: language L is ontet-free if and onl of there is a pushdown automata M that reognizes L. Two step proof: 1) Given a CFG G, onstrut a PD M G 2) Given a PD M, make a CFG G M 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer /25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Converting a CFL to a PD Basi idea tart with the start smbol Non-deterministiall appl rules top when a string of terminals is left. Compare with input aept if math. Detail: How do ou store the intermediate string on the stak? 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Converting a CFL to a PD - 2 In q start, initialize the stak to ontain $ and make an ε-transition to q loop. In q loop, if top of stak ontains a variable, replae it with a terminal w for some rule w Else, if top of stak ontains a terminal w, ompare with net input smbol. If unequal, rejet. Else if the top of the stak is $ (empt stak), make an ε-transition to q aept. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer
3 Converting a PD to a CFG Basi idea: For eah pair of states p,q use a variable pq whih generates all strings that take the PD from p to q. The start variable is q0 q aept Details: ssume that the PD Has a single aept state Empties stak before aepting Eah transition either pops or pushes. Converting a PD to a CFG - 2 p,q,r,s Q, t Γ, a,b Σ ε, if δ(p,a,ε) ontains (r,t) and if δ(s,b,t) ontains (q, ε) add the rule pq a rs b p,q,r Q, add the rule pq pr rq p Q, add the rule pp ε 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer /25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Converting a PD to a CFG - 3 Corretness - Easier diretion: If pq generates, then brings PD P from p with empt stak to q with empt stak. trong indution on the number of steps in the derivation of. Base ase: (1 step derivation) pp ε Indutive ase: pq a rs bor pq pr rq Converting a PD to a CFG - 4 Corretness - Harder diretion: If brings PD P from p with empt stak to q with empt stak, then pq generates. trong indution on the number of steps in the omputation of P going from p to q (both with empt staks) on input. Base ase: (0 step derivation) = ε [ pp ε] Indutive ase: stak not empt eept before and end [ pq a rs b] OR stak empt some time before the end [ pq pr rq ] 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer /25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Net Non-CF languages CFL pumping lemma Non-CF Languages The language L = { a n b n n n 0 } does not appear to be ontet-free. Informal: The problem is that ever variable an (onl) at b itself (ontet-free). The problem of * v : If * uz * uvz * uvz L, then * uz * uvz * * uv i i z * uv i i z L as well, for all i=0,1,2, 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer /25/2007 CE 2001, ummer
4 Pumping Lemma for CFLs Idea: If we an prove the eistene of derivations for elements of the CFL L that use the step * v, then a new form of v- pumping holds: * v * v 2 2 * v 3 3 * ) Observation: We an prove this eistene if the parse-tree is tall enough. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Remember Parse Trees Parse tree for bbba * bbaba bbaa b b 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer B a a B Pumping a Parse Tree u v z If s = uvz L is long, then its parse-tree is tall. Hene, there is a path on whih a variable repeats itself. We an pump this part. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Tree Tall Enough Let L be a ontet-free language, and let G be its grammar with maimal b smbols on the right side of the rules: X 1 X b parse tree of depth h produes a string with maimum length of b h. Long strings implies tall trees. Let V be the number of variables of G. If h = V +2 or bigger, then there is a variable on a top-down path that ours more than one. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer uvz L uv 2 2 z L u v z B repeating the part we get 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer /25/2007 CE 2001, ummer u v R z v while removing the - gives
5 Pumping down: uz L u z In general uv i i z L for all i=0,1,2, 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Pumping Lemma for CFL For ever ontet-free language L, there is a pumping length p, suh that for ever string s L and s p, we an write s=uvz with 1) uv i i z L for ever i {0,1,2, } 2) v 1 3) v p Note that 1) implies that uz L 2) sas that v annot be the empt string ε Condition 3) is not alwas used 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Different parts of the parse tree u v z 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Formal Proof of Pumping Lemma Let G=(V,Σ,R,) be the grammar of a CFL. Maimum size of rules is b 2: X 1 X b string s requires a minimum tree-depth log b s. If s p=b V +1, then tree-depth V +1 (has V +2 nodes), hene there is a path and variable where repeats itself: * uz * uvz * uvz It follows that uv i i z L for all i=0,1,2, Furthermore: v 1 beause tree is minimal v p beause bottom tree with p leaves has a repeating path 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Pumping a n b n n (E. 2.36) ssume that B = {a n b n n n 0} is CFL Let p be the pumping length, and s = a p b p p B P.L.: s = uvz = a p b p p, with uv i i z B for all i 0 Options for v : 1) The strings v and are uniform (v=a a and =, for eample). Then uv 2 2 z will not ontain the same number of a s, b s and s, hene uv 2 2 z B 2) v and are not uniform. Then uv 2 2 z will not be a ab b Hene uv 2 2 z B 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Pumping a n b n n (ont.) ssume that B = {a n b n n n 0} is CFL Let p be the pumping length, and s = a p b p p B P.L.: s = uvz = a p b p p, with uv i i z B for all i 0 We showed: No options for v suh that uv i i z B for all i. Contradition. B is not a ontet-free language. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer
6 Eample 2.37 (Pumping down) Proof that C = {a i b j k 0 i j k } is not ontet-free. Let p be the pumping length, and s = a p b p p C P.L.: s = uvz, suh that uv i i z C for ever i 0 Two options for 1 v p: 1) v = a*b*, then the string uv 2 2 z has not enough s, hene uv 2 2 z C 2) v = b**, then the string uv 0 0 z = uz has too man a s, hene uv 0 0 z C Contradition: C is not a ontet-free language. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer D = { ww w {0,1}* } (E. 2.38) Carefull take the strings s D. Let p be the pumping length, take s=0 p 1 p 0 p 1 p. Three options for s=uvz with 1 v p: 1) If a part of is to the left of middle ( ) in 0 p 1 p 0 p 1 p, then the seond half of uv 2 2 z starts with 1 2) If a part of v is to the right of middle of 0 p 1 p 0 p 1 p, then the first half of uv 2 2 z ends with 0, hene uv 2 2 z D 3) If is in the middle of 0 p 1 p 0 p 1 p, then uz equals 0 p 1 i 0 j 1 p D (beause i or j p) Contradition: D is not ontet-free. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Pumping Problems Using the CFL pumping lemma is more diffiult than the pumping lemma for regular languages. Net Closure properties of CFL You have to hoose the string s arefull, and divide the options effiientl. dditional CFL properties would be helpful (like we had for regular languages). What about losure under standard operations? 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer /25/2007 CE 2001, ummer Union Closure Properties Lemma: Let 1 and 2 be two CF languages, then the union 1 2 is ontet free as well. Proof: ssume that the two grammars are G 1 =(V 1,Σ,R 1, 1 ) and G 2 =(V 2,Σ,R 2, 2 ). Construt a third grammar G 3 =(V 3,Σ,R 3, 3 ) b: V 3 = V 1 V 2 { 3 } (new start variable) with R 3 = R 1 R 2 { }. It follows that L(G 3 ) = L(G 1 ) L(G 2 ). Intersetion & Complement? Let again 1 and 2 be two CF languages. One an prove that, in general, the intersetion 1 2, and the omplement Ā 1 = Σ* \ 1 are not ontet free languages. One proves this with speifi ounter eamples of languages. 6/25/2007 CE 2001, ummer /25/2007 CE 2001, ummer
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
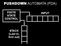 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Lecture 17: Language Recognition
 Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Pushdown Automata. We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata.
 Pushdown Automata We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata. Next we consider a more powerful computation model, called a
Pushdown Automata We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata. Next we consider a more powerful computation model, called a
(pp ) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2)
 (pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
CISC4090: Theory of Computation
 CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
(pp ) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2)
 (pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
CFG and PDA accept the same languages
 Automata and Formal Languages CFG and PDA accept the same languages Sipser pages 115-122 Lecture 14 Tim Sheard 1 Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs The equivalence is expressed by two theorems. Theorem 1. Every
Automata and Formal Languages CFG and PDA accept the same languages Sipser pages 115-122 Lecture 14 Tim Sheard 1 Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs The equivalence is expressed by two theorems. Theorem 1. Every
Computational Models: Class 5
 Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Cliff s notes for equivalence of CFLs and L(PDAs) LisaCFL L = L(M) for some PDA M L=L(M)forsomePDAM L = L(G) for some CFG G
 What s on our plate today? Cliff s notes for equivalence of CFLs and L(PDAs) LisaCFL L = L(M) for some PDA M L=L(M)forsomePDAM L = L(G) for some CFG G Pumping Lemma (one last time) Statement of Pumping
What s on our plate today? Cliff s notes for equivalence of CFLs and L(PDAs) LisaCFL L = L(M) for some PDA M L=L(M)forsomePDAM L = L(G) for some CFG G Pumping Lemma (one last time) Statement of Pumping
Computational Models - Lecture 4
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Introduction to Theory of Computing
 CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
October 6, Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Gramm
 Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA)
 CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture)
 Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3
 SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23)
 Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
CS235 Languages and Automata Fall 2012
 C235 Languages and Automata Fall 2012 MIDERM 2 REVIEW ANWER Revised 12/03/12 to fix solns to Problem 1b(iv); revised 12/13/12 to hange a p/2-1 to a p-1 in Prob. 1b(v) (thanks to Irene Kwok); revised 12/14/12
C235 Languages and Automata Fall 2012 MIDERM 2 REVIEW ANWER Revised 12/03/12 to fix solns to Problem 1b(iv); revised 12/13/12 to hange a p/2-1 to a p-1 in Prob. 1b(v) (thanks to Irene Kwok); revised 12/14/12
Homework. Context Free Languages. Announcements. Before We Start. Languages. Plan for today. Final Exam Dates have been announced.
 Homework Context Free Languages PDAs and CFLs Homework #3 returned Homework #4 due today Homework #5 Pg 169 -- Exercise 4 Pg 183 -- Exercise 4c,e,i (use JFLAP) Pg 184 -- Exercise 10 Pg 184 -- Exercise
Homework Context Free Languages PDAs and CFLs Homework #3 returned Homework #4 due today Homework #5 Pg 169 -- Exercise 4 Pg 183 -- Exercise 4c,e,i (use JFLAP) Pg 184 -- Exercise 10 Pg 184 -- Exercise
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata Salil Vadhan October 4, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.2. Another example of a CFG (with proof) L = {x {a, b} : x has the same # of a s and
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata Salil Vadhan October 4, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.2. Another example of a CFG (with proof) L = {x {a, b} : x has the same # of a s and
Properties of Context-Free Languages
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
COMP-330 Theory of Computation. Fall Prof. Claude Crépeau. Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars
 COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent. We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa.
 CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa. CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted
CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa. CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course
 Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET
 THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
Pushdown Automata. Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation. Chia-Ping Chen
 Pushdown Automata Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung, Taiwan ROC Pushdown Automata p. 1
Pushdown Automata Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung, Taiwan ROC Pushdown Automata p. 1
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL) Objectives Introduce Pumping Lemma for CFL Apply Pumping Lemma to show that some languages are non-cfl Pumping Lemma
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL) Objectives Introduce Pumping Lemma for CFL Apply Pumping Lemma to show that some languages are non-cfl Pumping Lemma
Modal Horn Logics Have Interpolation
 Modal Horn Logis Have Interpolation Marus Kraht Department of Linguistis, UCLA PO Box 951543 405 Hilgard Avenue Los Angeles, CA 90095-1543 USA kraht@humnet.ula.de Abstrat We shall show that the polymodal
Modal Horn Logis Have Interpolation Marus Kraht Department of Linguistis, UCLA PO Box 951543 405 Hilgard Avenue Los Angeles, CA 90095-1543 USA kraht@humnet.ula.de Abstrat We shall show that the polymodal
Pushdown automata. Twan van Laarhoven. Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Radboud University Nijmegen
 Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA
 Syllabus R09 Regulation UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA The context free languages have a type of automaton that defined them. This automaton, called a pushdown automaton, is an extension of the nondeterministic
Syllabus R09 Regulation UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA The context free languages have a type of automaton that defined them. This automaton, called a pushdown automaton, is an extension of the nondeterministic
Context-Free Languages
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Pushdown Automata Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.2. Finite automaton 1 / 13
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Pushdown Automata Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.2. Finite automaton 1 / 13
5 Context-Free Languages
 CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
Before We Start. The Pumping Lemma. Languages. Context Free Languages. Plan for today. Now our picture looks like. Any questions?
 Before We Start The Pumping Lemma Any questions? The Lemma & Decision/ Languages Future Exam Question What is a language? What is a class of languages? Context Free Languages Context Free Languages(CFL)
Before We Start The Pumping Lemma Any questions? The Lemma & Decision/ Languages Future Exam Question What is a language? What is a class of languages? Context Free Languages Context Free Languages(CFL)
CS311 Computational Structures More about PDAs & Context-Free Languages. Lecture 9. Andrew P. Black Andrew Tolmach
 CS311 Computational Structures More about PDAs & Context-Free Languages Lecture 9 Andrew P. Black Andrew Tolmach 1 Three important results 1. Any CFG can be simulated by a PDA 2. Any PDA can be simulated
CS311 Computational Structures More about PDAs & Context-Free Languages Lecture 9 Andrew P. Black Andrew Tolmach 1 Three important results 1. Any CFG can be simulated by a PDA 2. Any PDA can be simulated
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u,
 1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
2.1 Solution. E T F a. E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a
 . Solution E T F a E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a E E + T E + T + T T + T + T F + T + T a + T + T a + F + T a + a + T a + a + F a + a + a E T F ( E) ( T ) ( F) (( E)) (( T )) (( F)) (( a)) . Solution
. Solution E T F a E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a E E + T E + T + T T + T + T F + T + T a + T + T a + F + T a + a + T a + a + F a + a + a E T F ( E) ( T ) ( F) (( E)) (( T )) (( F)) (( a)) . Solution
CPS 220 Theory of Computation
 CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
Pumping Lemma for CFLs
 Pumping Lemma for CFLs v y s Here we go again! Intuition: If L is CF, then some CFG G produces strings in L If some string in L is very long, it will have a very tall parse tree If a parse tree is taller
Pumping Lemma for CFLs v y s Here we go again! Intuition: If L is CF, then some CFG G produces strings in L If some string in L is very long, it will have a very tall parse tree If a parse tree is taller
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages. Foundations of Computer Science Theory
 Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Computational Models Lecture 5
 Computational Models Lecture 5 One More PDAs Example Equivalence of PDAs and CFLs Nondeterminism adds power to PDAs (not in book) Closure Properties of CFLs Algorithmic Aspects of PDAs and CFLs DFAs and
Computational Models Lecture 5 One More PDAs Example Equivalence of PDAs and CFLs Nondeterminism adds power to PDAs (not in book) Closure Properties of CFLs Algorithmic Aspects of PDAs and CFLs DFAs and
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Accept or reject. Stack
 Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Chapter 8 Hypothesis Testing
 Leture 5 for BST 63: Statistial Theory II Kui Zhang, Spring Chapter 8 Hypothesis Testing Setion 8 Introdution Definition 8 A hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter Definition 8 The two
Leture 5 for BST 63: Statistial Theory II Kui Zhang, Spring Chapter 8 Hypothesis Testing Setion 8 Introdution Definition 8 A hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter Definition 8 The two
MTH401A Theory of Computation. Lecture 17
 MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x where
 Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture)
 Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
arxiv: v1 [cs.fl] 5 Dec 2009
![arxiv: v1 [cs.fl] 5 Dec 2009 arxiv: v1 [cs.fl] 5 Dec 2009](/thumbs/83/87668546.jpg) Quotient Complexity of Closed Languages Janusz Brzozowski 1, Galina Jirásková 2, and Chenglong Zou 1 arxiv:0912.1034v1 [s.fl] 5 De 2009 1 David R. Cheriton Shool of Computer Siene, University of Waterloo,
Quotient Complexity of Closed Languages Janusz Brzozowski 1, Galina Jirásková 2, and Chenglong Zou 1 arxiv:0912.1034v1 [s.fl] 5 De 2009 1 David R. Cheriton Shool of Computer Siene, University of Waterloo,
Pushdown Specifications
 Orna Kupferman Hebrew University Pushdown Speifiations Nir Piterman Weizmann Institute of Siene une 9, 2002 Moshe Y Vardi Rie University Abstrat Traditionally, model heking is applied to finite-state systems
Orna Kupferman Hebrew University Pushdown Speifiations Nir Piterman Weizmann Institute of Siene une 9, 2002 Moshe Y Vardi Rie University Abstrat Traditionally, model heking is applied to finite-state systems
Chapter 3 Church-Turing Thesis. CS 341: Foundations of CS II
 CS 341: Foundations of CS II Marvin K. Nakayama Computer Siene Department New Jersey Institute of Tehnology Newark, NJ 07102 CS 341: Chapter 3 3-2 Contents Turing Mahines Turing-reognizable Turing-deidable
CS 341: Foundations of CS II Marvin K. Nakayama Computer Siene Department New Jersey Institute of Tehnology Newark, NJ 07102 CS 341: Chapter 3 3-2 Contents Turing Mahines Turing-reognizable Turing-deidable
Automata and Computability. Solutions to Exercises
 Automata and Computability Solutions to Exercises Fall 28 Alexis Maciel Department of Computer Science Clarkson University Copyright c 28 Alexis Maciel ii Contents Preface vii Introduction 2 Finite Automata
Automata and Computability Solutions to Exercises Fall 28 Alexis Maciel Department of Computer Science Clarkson University Copyright c 28 Alexis Maciel ii Contents Preface vii Introduction 2 Finite Automata
Properties of Context-free Languages. Reading: Chapter 7
 Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Context Free Languages and Grammars
 Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Context Free Languages and Grammars Lecture 7 Tuesday, September 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 36 What stack got to do
Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Context Free Languages and Grammars Lecture 7 Tuesday, September 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 36 What stack got to do
Chapter 2: Solution of First order ODE
 0 Chapter : Solution of irst order ODE Se. Separable Equations The differential equation of the form that is is alled separable if f = h g; In order to solve it perform the following steps: Rewrite the
0 Chapter : Solution of irst order ODE Se. Separable Equations The differential equation of the form that is is alled separable if f = h g; In order to solve it perform the following steps: Rewrite the
Pushdown Automata. Chapter 12
 Pushdown Automata Chapter 12 Recognizing Context-Free Languages We need a device similar to an FSM except that it needs more power. The insight: Precisely what it needs is a stack, which gives it an unlimited
Pushdown Automata Chapter 12 Recognizing Context-Free Languages We need a device similar to an FSM except that it needs more power. The insight: Precisely what it needs is a stack, which gives it an unlimited
Pushdown Automata: Introduction (2)
 Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs
 This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
Intro to Theory of Computation
 Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Lecture III CONTEXT FREE LANGUAGES
 1. Context Free Languages and Grammar Lecture III Page 1 Lecture III CONTEXT FREE LANGUAGES Lecture 3: Honors Theory, Spring 02. We introduce context free languages (CFL), context free grammar (CFG) and
1. Context Free Languages and Grammar Lecture III Page 1 Lecture III CONTEXT FREE LANGUAGES Lecture 3: Honors Theory, Spring 02. We introduce context free languages (CFL), context free grammar (CFG) and
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages
 Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002)
 CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
Automata and Computability. Solutions to Exercises
 Automata and Computability Solutions to Exercises Spring 27 Alexis Maciel Department of Computer Science Clarkson University Copyright c 27 Alexis Maciel ii Contents Preface vii Introduction 2 Finite Automata
Automata and Computability Solutions to Exercises Spring 27 Alexis Maciel Department of Computer Science Clarkson University Copyright c 27 Alexis Maciel ii Contents Preface vii Introduction 2 Finite Automata
Introduction and Motivation. Introduction and Motivation. Introduction to Computability. Introduction and Motivation. Theory. Lecture5: Context Free
 ntroduction to Computability Theory Lecture5: Context Free Languages Prof. Amos sraeli 1 ntroduction and Motivation n our study of RL-s we Covered: 1. Motivation and definition of regular languages. 2.
ntroduction to Computability Theory Lecture5: Context Free Languages Prof. Amos sraeli 1 ntroduction and Motivation n our study of RL-s we Covered: 1. Motivation and definition of regular languages. 2.
Pushdown Automata. Reading: Chapter 6
 Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska
 cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 11 CHAPTER 3 CONTEXT-FREE LANGUAGES 1. Context Free Grammars 2. Pushdown Automata 3. Pushdown automata and context -free
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 11 CHAPTER 3 CONTEXT-FREE LANGUAGES 1. Context Free Grammars 2. Pushdown Automata 3. Pushdown automata and context -free
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
Overview. Regular Expressions and Finite-State. Motivation. Regular expressions. RE syntax Additional functions. Regular languages Properties
 Overview L445/L545/B659 Dept. of Linguistis, Indiana University Spring 2016 languages Finite-state tehnology is: Fast and effiient Useful for a variety of language tasks Three main topis we ll disuss:
Overview L445/L545/B659 Dept. of Linguistis, Indiana University Spring 2016 languages Finite-state tehnology is: Fast and effiient Useful for a variety of language tasks Three main topis we ll disuss:
After the completion of this section the student should recall
 Chapter I MTH FUNDMENTLS I. Sets, Numbers, Coordinates, Funtions ugust 30, 08 3 I. SETS, NUMERS, COORDINTES, FUNCTIONS Objetives: fter the ompletion of this setion the student should reall - the definition
Chapter I MTH FUNDMENTLS I. Sets, Numbers, Coordinates, Funtions ugust 30, 08 3 I. SETS, NUMERS, COORDINTES, FUNCTIONS Objetives: fter the ompletion of this setion the student should reall - the definition
max min z i i=1 x j k s.t. j=1 x j j:i T j
 AM 221: Advaned Optimization Spring 2016 Prof. Yaron Singer Leture 22 April 18th 1 Overview In this leture, we will study the pipage rounding tehnique whih is a deterministi rounding proedure that an be
AM 221: Advaned Optimization Spring 2016 Prof. Yaron Singer Leture 22 April 18th 1 Overview In this leture, we will study the pipage rounding tehnique whih is a deterministi rounding proedure that an be
Outline. CS21 Decidability and Tractability. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA.
 Outline CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 5 January 16, 219 and Languages equivalence of NPDAs and CFGs non context-free languages January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture 5 1 January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture
Outline CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 5 January 16, 219 and Languages equivalence of NPDAs and CFGs non context-free languages January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture 5 1 January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III. 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems. 3.2 Derivation. 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar
 TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
ECS 120: Theory of Computation UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, Midterm Exam
 ECS 120: Theory of Computation Handout MT UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, 2012 Midterm Exam Instructions: The exam has six pages, including this cover page, printed out two-sided (no more wasted
ECS 120: Theory of Computation Handout MT UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, 2012 Midterm Exam Instructions: The exam has six pages, including this cover page, printed out two-sided (no more wasted
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Push-Down Automata CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard Janicki Computability
Computability and Complexity Push-Down Automata CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard Janicki Computability
Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7
 Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about
Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA) Objectives Introduce the Pumping Lemma for CFL Show that some languages are non- CFL Discuss the DPDA, which
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA) Objectives Introduce the Pumping Lemma for CFL Show that some languages are non- CFL Discuss the DPDA, which
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016
 CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review Forced handles Definition A handle h of a valid string v = xhy is a forced handle if h is the unique handle in every valid string xhŷ where
Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review Forced handles Definition A handle h of a valid string v = xhy is a forced handle if h is the unique handle in every valid string xhŷ where
Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions)
 Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions) 1. Finite Automata & Regular Sets 01. Ans: (a) & (c) Sol: (a) The reversal of a regular set is regular as the reversal of a regular expression
Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions) 1. Finite Automata & Regular Sets 01. Ans: (a) & (c) Sol: (a) The reversal of a regular set is regular as the reversal of a regular expression
Automata Theory. CS F-10 Non-Context-Free Langauges Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages. David Galles
 Automata Theory CS411-2015F-10 Non-Context-Free Langauges Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 10-0: Fun with CFGs Create
Automata Theory CS411-2015F-10 Non-Context-Free Langauges Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 10-0: Fun with CFGs Create
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG:
![Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG: Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG:](/thumbs/87/95229917.jpg) Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] S X T#X X#T T#X#T X axa bxb #T# # T at bt #T ε Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG: R XRX S S atb bta T XTX X ε X a b q start ε, ε $ ε, R X ε, ε R ε, ε X ε, R S ε, T X ε, T ε ε, X a
Problem 2.6(d) [4 pts] S X T#X X#T T#X#T X axa bxb #T# # T at bt #T ε Problem 2.12 [3pts] Original CFG: R XRX S S atb bta T XTX X ε X a b q start ε, ε $ ε, R X ε, ε R ε, ε X ε, R S ε, T X ε, T ε ε, X a
The View Over The Horizon
 The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
Plan for 2 nd half. Just when you thought it was safe. Just when you thought it was safe. Theory Hall of Fame. Chomsky Normal Form
 Plan for 2 nd half Pumping Lemma for CFLs The Return of the Pumping Lemma Just when you thought it was safe Return of the Pumping Lemma Recall: With Regular Languages The Pumping Lemma showed that if a
Plan for 2 nd half Pumping Lemma for CFLs The Return of the Pumping Lemma Just when you thought it was safe Return of the Pumping Lemma Recall: With Regular Languages The Pumping Lemma showed that if a
How to Pop a Deep PDA Matters
 How to Pop a Deep PDA Matters Peter Leupold Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science Kyoto Sangyo University Kyoto 603-8555, Japan email:leupold@cc.kyoto-su.ac.jp Abstract Deep PDA are push-down automata
How to Pop a Deep PDA Matters Peter Leupold Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science Kyoto Sangyo University Kyoto 603-8555, Japan email:leupold@cc.kyoto-su.ac.jp Abstract Deep PDA are push-down automata
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules).
 Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Lesson 23: The Defining Equation of a Line
 Student Outomes Students know that two equations in the form of ax + y = and a x + y = graph as the same line when a = = and at least one of a or is nonzero. a Students know that the graph of a linear
Student Outomes Students know that two equations in the form of ax + y = and a x + y = graph as the same line when a = = and at least one of a or is nonzero. a Students know that the graph of a linear
