Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata
|
|
|
- Camilla Ross
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata Salil Vadhan October 4, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.2.
2 Another example of a CFG (with proof) L = {x {a, b} : x has the same # of a s and b s}. 1
3 More examples of CFGs Arithmetic Expressions G 1 : E x y E E E + E (E) G 2 : E T E + T T T F F F (E) x y Q: Which is preferable? Why? 2
4 Parse Trees Derivations in a CFG can be represented by parse trees. Examples: Each parse tree corresponds to many derivations, but has unique leftmost derivation. 3
5 Parsing Parsing: Given x L(G), produce a parse tree for x. (Used to interpret x. Compilers parse, rather than merely recognize, so they can assign semantics to expressions in the source language.) Ambiguity: A grammar is ambiguous if some string has two parse trees. Example: 4
6 Context-free Grammars and Automata What is the fourth term in the analogy: Regular Languages : Finite Automata as Context-free Languages :??? 5
7 Regular Grammars Regular Grammars Hint: Hint: There There areisa aspecial kind kind of CFGs, of CFGs, the the regular regular grammars, grammars, that gene languages. that generate exactly the regular languages. A CFG A CFG is (right-)regular is (right-)regular if any if anyoccurrence of of a anonterminal on onthe R rightmost the RHS symbol. of a rule is as the rightmost symbol. DFA Turning Regular a DFA Grammar into an equivalent Regular Grammar Variables are states. Variables are states. Transition δ(p, σ) = R P σ R becomes becomes P P σr σr If is accepting, add rule ε If P is accepting, add rule P ε Example: {x : x has an even # of a s and an even # of b s} Other Direction: Omitted. 6
8 Regular Grammars (cont.) Example of DFA Regular Grammars: {x : x has an even # of a s and an even # of b s}. Other Direction: Omitted. 7
9 Context-free Grammars and Automata What is the fourth term in the analogy: Regular Languages : Finite Automata as Context-free Languages :??? 8
10 Sheila Greibach, AB Radcliffe 60 summa cum laude Inverses of Phrase Structure Generators Harvard PhD Thesis,
11 Pushdown Automata Pushdown Automata Finite automaton + pushdown store = Finite automaton + pushdown store The pushdown store is a stack of symbols of unlimited size which the machine can read and alter only at the top. The pushdown store is a stack of symbols of unlimited size which the machine can read and alter only at the top. Input a b b a b a reading head (L to R only, one symbol at a time, or stays put) F.C. pushdown store head can push (add symbols) or pop (remove and check symbols) a d c b b Stack Transitions of PDA are of form (q, σ, γ) (q, γ ), which means: If in state q with σ on the input tape and γ on top of the stack, replace γ by γ on the stack and enter state q while advancing Transitions of PDA are of form (q, σ, γ) (q, γ ) If in state q with σ on the input tape and γ on top of the stack, replace γ by γ on the stack and enter the state reading q while head advancing over theσ. reading head over σ. 10
12 (Nondeterministic) PDA for even palindromes {ww R : w {a, b} } (q, a, ε) (q, a) (q, b, ε) (q, b) (q, ε, ε) (r, ε) (r, a, a) (r, ε) (r, b, b) (r, ε) Push a s and b s switch to other state pop a s matching input pop b s matching input So the precondition (q, σ, γ) means that the next σ symbols (0 or 1) of the input are σ and the top γ symbols (0 or 1) on the stack are γ 11
13 (Nondeterministic) PDA for even palindromes {ww R : w {a, b} } (q, a, ε) (q, a) (q, b, ε) (q, b) (q, ε, ε) (r, ε) (r, a, a) (r, ε) (r, b, b) (r, ε) Push a s and b s switch to other state pop a s matching input pop b s matching input Need to test whether stack empty: push $ at beginning and check at end. (q 0, ε, ε) (q, $) (r, ε, $) (q f, ε) 12
14 Language recognition with PDAs A PDA accepts an input string If there is a computation that starts in the start state with reading head at the beginning of string and the stack is empty and ends in a final state with all the input consumed A PDA computation becomes blocked (i.e. dies ) if no transition matches both the input and stack 13
15 Formal Definition of a PDA M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0, F ) Q = states Σ = input alphabet Γ = stack alphabet δ = transition function Q (Σ {ε}) (Γ {ε}) P (Q (Γ {ε})). q 0 = start state F = final states 14
16 Computation by a PDA M accepts w if we can write w = w 1 w m, where each w i Σ {ε}, and there is a sequence of states r 0,..., r m and stack strings s 0,..., s m Γ that satisfy 1. r 0 = q 0 and s 0 = ε. 2. For each i, (r i+1, γ ) δ(r i, w i+1, γ) where s i = γt and s i+1 = γ t for some γ, γ Γ {ε} and t Γ. 3. r m F. L(M) = {w Σ : M accepts w}. 15
17 PDA for {w {a, b} : # a (w) = # b (w)} 16
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture)
 Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars Salil Vadhan October 2, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.1 (except Chomsky Normal Form). Algorithmic questions about regular
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars Salil Vadhan October 2, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.1 (except Chomsky Normal Form). Algorithmic questions about regular
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u,
 1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
Context-Free Languages
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Pushdown Automata Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.2. Finite automaton 1 / 13
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Pushdown Automata Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.2. Finite automaton 1 / 13
Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x where
 Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
CISC4090: Theory of Computation
 CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course
 Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
October 6, Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Gramm
 Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Introduction to Theory of Computing
 CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA)
 CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42
 Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability Pushdown Automata K. Krithivasan and R. Rama Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42 Introduction We have considered
Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability Pushdown Automata K. Krithivasan and R. Rama Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42 Introduction We have considered
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
Intro to Theory of Computation
 Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Pushdown Automata: Introduction (2)
 Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET
 THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Pushdown automata. Twan van Laarhoven. Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Radboud University Nijmegen
 Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Pushdown Automata. We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata.
 Pushdown Automata We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata. Next we consider a more powerful computation model, called a
Pushdown Automata We have seen examples of context-free languages that are not regular, and hence can not be recognized by finite automata. Next we consider a more powerful computation model, called a
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Push-Down Automata CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard Janicki Computability
Computability and Complexity Push-Down Automata CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard Janicki Computability
Accept or reject. Stack
 Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Outline. CS21 Decidability and Tractability. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA.
 Outline CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 5 January 16, 219 and Languages equivalence of NPDAs and CFGs non context-free languages January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture 5 1 January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture
Outline CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 5 January 16, 219 and Languages equivalence of NPDAs and CFGs non context-free languages January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture 5 1 January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture
5 Context-Free Languages
 CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
CPS 220 Theory of Computation
 CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
Computational Models - Lecture 4
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
CS Pushdown Automata
 Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.2 L ww R = {ww R w (0+1) * } Palindromes over {0, 1}. A cfg P 0 1 0P0 1P1. Consider a FA with a stack(= a Pushdown automaton; PDA).
Chap. 6 Pushdown Automata 6.1 Definition of Pushdown Automata Example 6.2 L ww R = {ww R w (0+1) * } Palindromes over {0, 1}. A cfg P 0 1 0P0 1P1. Consider a FA with a stack(= a Pushdown automaton; PDA).
(pp ) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2)
 (pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer.
 Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
Homework Assignment 6 Answers
 Homework Assignment 6 Answers CSCI 2670 Introduction to Theory of Computing, Fall 2016 December 2, 2016 This homework assignment is about Turing machines, decidable languages, Turing recognizable languages,
Homework Assignment 6 Answers CSCI 2670 Introduction to Theory of Computing, Fall 2016 December 2, 2016 This homework assignment is about Turing machines, decidable languages, Turing recognizable languages,
Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23)
 Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent. We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa.
 CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa. CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted
CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa. CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted
Pushdown Automata (PDA) The structure and the content of the lecture is based on
 Pushdown Automata (PDA) The structure and the content of the lecture is based on http://www.eecs.wsu.edu/~ananth/cpts317/lectures/index.htm 1 Excursion: Previous lecture n Context-free grammar G=(V,T,P,S),
Pushdown Automata (PDA) The structure and the content of the lecture is based on http://www.eecs.wsu.edu/~ananth/cpts317/lectures/index.htm 1 Excursion: Previous lecture n Context-free grammar G=(V,T,P,S),
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Design a PDA and a CFG for a given language Give informal description for a PDA,
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Design a PDA and a CFG for a given language Give informal description for a PDA,
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-121 Lecture 14: Turing Machines and the Church Turing Thesis
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-121 Lecture 14: Turing Machines and the Church Turing Thesis Harry Lewis October 22, 2013 Reading: Sipser, 3.2, 3.3. The Basic Turing Machine The Basic Turing Machine a a b a
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-121 Lecture 14: Turing Machines and the Church Turing Thesis Harry Lewis October 22, 2013 Reading: Sipser, 3.2, 3.3. The Basic Turing Machine The Basic Turing Machine a a b a
Automata Theory (2A) Young Won Lim 5/31/18
 Automata Theory (2A) Copyright (c) 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Automata Theory (2A) Copyright (c) 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism
 COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism Kurtuluş Küllü March 2018 The FA we saw until now were deterministic FA (DFA) in the sense that for each state and input symbol there was exactly
COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism Kurtuluş Küllü March 2018 The FA we saw until now were deterministic FA (DFA) in the sense that for each state and input symbol there was exactly
1. (a) Explain the procedure to convert Context Free Grammar to Push Down Automata.
 Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
(pp ) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2)
 (pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
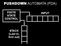 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
Push-down Automata = FA + Stack
 Push-down Automata = FA + Stack PDA Definition A push-down automaton M is a tuple M = (Q,, Γ, δ, q0, F) where Q is a finite set of states is the input alphabet (of terminal symbols, terminals) Γ is the
Push-down Automata = FA + Stack PDA Definition A push-down automaton M is a tuple M = (Q,, Γ, δ, q0, F) where Q is a finite set of states is the input alphabet (of terminal symbols, terminals) Γ is the
Pushdown Automata. Chapter 12
 Pushdown Automata Chapter 12 Recognizing Context-Free Languages We need a device similar to an FSM except that it needs more power. The insight: Precisely what it needs is a stack, which gives it an unlimited
Pushdown Automata Chapter 12 Recognizing Context-Free Languages We need a device similar to an FSM except that it needs more power. The insight: Precisely what it needs is a stack, which gives it an unlimited
SYLLABUS. Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 3 : REGULAR EXPRESSIONS AND LANGUAGES
 Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability.
 Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability. A Turing machine is a finite automaton with an infinite memory (tape). Formally, a Turing machine is a 6-tuple M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0,
Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability. A Turing machine is a finite automaton with an infinite memory (tape). Formally, a Turing machine is a 6-tuple M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0,
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3
 SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages. Pushdown Automata Parsing
 CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Pushdown Automata Parsing Chomsky Hierarchy Categorization of various languages and grammars Each is strictly more restrictive than the previous First described
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Pushdown Automata Parsing Chomsky Hierarchy Categorization of various languages and grammars Each is strictly more restrictive than the previous First described
Please give details of your answer. A direct answer without explanation is not counted.
 Please give details of your answer. A direct answer without explanation is not counted. Your answers must be in English. Please carefully read problem statements. During the exam you are not allowed to
Please give details of your answer. A direct answer without explanation is not counted. Your answers must be in English. Please carefully read problem statements. During the exam you are not allowed to
Homework. Context Free Languages. Announcements. Before We Start. Languages. Plan for today. Final Exam Dates have been announced.
 Homework Context Free Languages PDAs and CFLs Homework #3 returned Homework #4 due today Homework #5 Pg 169 -- Exercise 4 Pg 183 -- Exercise 4c,e,i (use JFLAP) Pg 184 -- Exercise 10 Pg 184 -- Exercise
Homework Context Free Languages PDAs and CFLs Homework #3 returned Homework #4 due today Homework #5 Pg 169 -- Exercise 4 Pg 183 -- Exercise 4c,e,i (use JFLAP) Pg 184 -- Exercise 10 Pg 184 -- Exercise
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
Pushdown Automata. Reading: Chapter 6
 Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
Computational Models: Class 5
 Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata
 Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata 1. What is a Turing Machine? A Turing Machine is an accepting device which accepts the languages (recursively enumerable set) generated by type
Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata 1. What is a Turing Machine? A Turing Machine is an accepting device which accepts the languages (recursively enumerable set) generated by type
Variants of Turing Machine (intro)
 CHAPTER 3 The Church-Turing Thesis Contents Turing Machines definitions, examples, Turing-recognizable and Turing-decidable languages Variants of Turing Machine Multi-tape Turing machines, non-deterministic
CHAPTER 3 The Church-Turing Thesis Contents Turing Machines definitions, examples, Turing-recognizable and Turing-decidable languages Variants of Turing Machine Multi-tape Turing machines, non-deterministic
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Automata and Computability. Solutions to Exercises
 Automata and Computability Solutions to Exercises Spring 27 Alexis Maciel Department of Computer Science Clarkson University Copyright c 27 Alexis Maciel ii Contents Preface vii Introduction 2 Finite Automata
Automata and Computability Solutions to Exercises Spring 27 Alexis Maciel Department of Computer Science Clarkson University Copyright c 27 Alexis Maciel ii Contents Preface vii Introduction 2 Finite Automata
Undecidable Problems and Reducibility
 University of Georgia Fall 2014 Reducibility We show a problem decidable/undecidable by reducing it to another problem. One type of reduction: mapping reduction. Definition Let A, B be languages over Σ.
University of Georgia Fall 2014 Reducibility We show a problem decidable/undecidable by reducing it to another problem. One type of reduction: mapping reduction. Definition Let A, B be languages over Σ.
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
Theory of Computation
 Fall 2002 (YEN) Theory of Computation Midterm Exam. Name:... I.D.#:... 1. (30 pts) True or false (mark O for true ; X for false ). (Score=Max{0, Right- 1 2 Wrong}.) (1) X... If L 1 is regular and L 2 L
Fall 2002 (YEN) Theory of Computation Midterm Exam. Name:... I.D.#:... 1. (30 pts) True or false (mark O for true ; X for false ). (Score=Max{0, Right- 1 2 Wrong}.) (1) X... If L 1 is regular and L 2 L
Pushdown Automata. Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation. Chia-Ping Chen
 Pushdown Automata Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung, Taiwan ROC Pushdown Automata p. 1
Pushdown Automata Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung, Taiwan ROC Pushdown Automata p. 1
Part I: Definitions and Properties
 Turing Machines Part I: Definitions and Properties Finite State Automata Deterministic Automata (DFSA) M = {Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F} -- Σ = Symbols -- Q = States -- q 0 = Initial State -- F = Accepting States
Turing Machines Part I: Definitions and Properties Finite State Automata Deterministic Automata (DFSA) M = {Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F} -- Σ = Symbols -- Q = States -- q 0 = Initial State -- F = Accepting States
Automata and Computability. Solutions to Exercises
 Automata and Computability Solutions to Exercises Fall 28 Alexis Maciel Department of Computer Science Clarkson University Copyright c 28 Alexis Maciel ii Contents Preface vii Introduction 2 Finite Automata
Automata and Computability Solutions to Exercises Fall 28 Alexis Maciel Department of Computer Science Clarkson University Copyright c 28 Alexis Maciel ii Contents Preface vii Introduction 2 Finite Automata
Automata Theory - Quiz II (Solutions)
 Automata Theory - Quiz II (Solutions) K. Subramani LCSEE, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV {ksmani@csee.wvu.edu} 1 Problems 1. Induction: Let L denote the language of balanced strings over Σ =
Automata Theory - Quiz II (Solutions) K. Subramani LCSEE, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV {ksmani@csee.wvu.edu} 1 Problems 1. Induction: Let L denote the language of balanced strings over Σ =
Theory of Computation
 Theory of Computation Lecture #10 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 43 Lecture 10: Overview Linear Bounded Automata Acceptance Problem for LBAs
Theory of Computation Lecture #10 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 43 Lecture 10: Overview Linear Bounded Automata Acceptance Problem for LBAs
Chapter 1. Formal Definition and View. Lecture Formal Pushdown Automata on the 28th April 2009
 Chapter 1 Formal and View Lecture on the 28th April 2009 Formal of PA Faculty of Information Technology Brno University of Technology 1.1 Aim of the Lecture 1 Define pushdown automaton in a formal way
Chapter 1 Formal and View Lecture on the 28th April 2009 Formal of PA Faculty of Information Technology Brno University of Technology 1.1 Aim of the Lecture 1 Define pushdown automaton in a formal way
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing
 CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tale of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set alger relations, functions) (read Chapters
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tale of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set alger relations, functions) (read Chapters
UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA
 Syllabus R09 Regulation UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA The context free languages have a type of automaton that defined them. This automaton, called a pushdown automaton, is an extension of the nondeterministic
Syllabus R09 Regulation UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA The context free languages have a type of automaton that defined them. This automaton, called a pushdown automaton, is an extension of the nondeterministic
Midterm Exam 2 CS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Fall 2018, face-to-face day section Prof. Marvin K. Nakayama
 Midterm Exam 2 CS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Fall 2018, face-to-face day section Prof. Marvin K. Nakayama Print family (or last) name: Print given (or first) name: I have read and understand
Midterm Exam 2 CS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Fall 2018, face-to-face day section Prof. Marvin K. Nakayama Print family (or last) name: Print given (or first) name: I have read and understand
CSE 211. Pushdown Automata. CSE 211 (Theory of Computation) Atif Hasan Rahman
 CSE 211 Pushdown Automata CSE 211 (Theory of Computation) Atif Hasan Rahman Lecturer Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology Adapted from slides
CSE 211 Pushdown Automata CSE 211 (Theory of Computation) Atif Hasan Rahman Lecturer Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology Adapted from slides
Fundamentele Informatica II
 Fundamentele Informatica II Answer to selected exercises 5 John C Martin: Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation M.M. Bonsangue (and J. Kleijn) Fall 2011 5.1.a (q 0, ab, Z 0 ) (q 1, b,
Fundamentele Informatica II Answer to selected exercises 5 John C Martin: Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation M.M. Bonsangue (and J. Kleijn) Fall 2011 5.1.a (q 0, ab, Z 0 ) (q 1, b,
ECS 120 Lesson 15 Turing Machines, Pt. 1
 ECS 120 Lesson 15 Turing Machines, Pt. 1 Oliver Kreylos Wednesday, May 2nd, 2001 Before we can start investigating the really interesting problems in theoretical computer science, we have to introduce
ECS 120 Lesson 15 Turing Machines, Pt. 1 Oliver Kreylos Wednesday, May 2nd, 2001 Before we can start investigating the really interesting problems in theoretical computer science, we have to introduce
Mildly Context-Sensitive Grammar Formalisms: Embedded Push-Down Automata
 Mildly Context-Sensitive Grammar Formalisms: Embedded Push-Down Automata Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Sommersemester 2011 Intuition (1) For a language L, there is a TAG G with
Mildly Context-Sensitive Grammar Formalisms: Embedded Push-Down Automata Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Sommersemester 2011 Intuition (1) For a language L, there is a TAG G with
Lecture 17: Language Recognition
 Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Lecture 3: Nondeterministic Finite Automata
 Lecture 3: Nondeterministic Finite Automata September 5, 206 CS 00 Theory of Computation As a recap of last lecture, recall that a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) consists of (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where
Lecture 3: Nondeterministic Finite Automata September 5, 206 CS 00 Theory of Computation As a recap of last lecture, recall that a deterministic finite automaton (DFA) consists of (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 4: NFAs vs. DFAs, Closure Properties
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 4: NFAs vs. DFAs, Closure Properties Salil Vadhan September 13, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 1.2. How to simulate NFAs? NFA accepts w if there is at least one accepting computational
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 4: NFAs vs. DFAs, Closure Properties Salil Vadhan September 13, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 1.2. How to simulate NFAs? NFA accepts w if there is at least one accepting computational
CS 154, Lecture 2: Finite Automata, Closure Properties Nondeterminism,
 CS 54, Lecture 2: Finite Automata, Closure Properties Nondeterminism, Why so Many Models? Streaming Algorithms 0 42 Deterministic Finite Automata Anatomy of Deterministic Finite Automata transition: for
CS 54, Lecture 2: Finite Automata, Closure Properties Nondeterminism, Why so Many Models? Streaming Algorithms 0 42 Deterministic Finite Automata Anatomy of Deterministic Finite Automata transition: for
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 10: Computability Theory I (Turing Machine)
 CS537 Theory of Computation Lecture : Computability Theory I (Turing Machine) Objectives Introduce the Turing Machine (TM)? Proposed by Alan Turing in 936 finite-state control + infinitely long tape A
CS537 Theory of Computation Lecture : Computability Theory I (Turing Machine) Objectives Introduce the Turing Machine (TM)? Proposed by Alan Turing in 936 finite-state control + infinitely long tape A
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review Forced handles Definition A handle h of a valid string v = xhy is a forced handle if h is the unique handle in every valid string xhŷ where
Theory of Computation (VI) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review Forced handles Definition A handle h of a valid string v = xhy is a forced handle if h is the unique handle in every valid string xhŷ where
CS Lecture 28 P, NP, and NP-Completeness. Fall 2008
 CS 301 - Lecture 28 P, NP, and NP-Completeness Fall 2008 Review Languages and Grammars Alphabets, strings, languages Regular Languages Deterministic Finite and Nondeterministic Automata Equivalence of
CS 301 - Lecture 28 P, NP, and NP-Completeness Fall 2008 Review Languages and Grammars Alphabets, strings, languages Regular Languages Deterministic Finite and Nondeterministic Automata Equivalence of
CS Lecture 29 P, NP, and NP-Completeness. k ) for all k. Fall The class P. The class NP
 CS 301 - Lecture 29 P, NP, and NP-Completeness Fall 2008 Review Languages and Grammars Alphabets, strings, languages Regular Languages Deterministic Finite and Nondeterministic Automata Equivalence of
CS 301 - Lecture 29 P, NP, and NP-Completeness Fall 2008 Review Languages and Grammars Alphabets, strings, languages Regular Languages Deterministic Finite and Nondeterministic Automata Equivalence of
Introduction and Motivation. Introduction and Motivation. Introduction to Computability. Introduction and Motivation. Theory. Lecture5: Context Free
 ntroduction to Computability Theory Lecture5: Context Free Languages Prof. Amos sraeli 1 ntroduction and Motivation n our study of RL-s we Covered: 1. Motivation and definition of regular languages. 2.
ntroduction to Computability Theory Lecture5: Context Free Languages Prof. Amos sraeli 1 ntroduction and Motivation n our study of RL-s we Covered: 1. Motivation and definition of regular languages. 2.
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Lecture 5 Reductions Undecidable problems from language theory Linear bounded automata given by Jiri Srba Lecture 5 Computability and Complexity 1/14 Reduction Informal Definition
Computability and Complexity Lecture 5 Reductions Undecidable problems from language theory Linear bounded automata given by Jiri Srba Lecture 5 Computability and Complexity 1/14 Reduction Informal Definition
CS21 Decidability and Tractability
 CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 8 January 24, 2018 Outline Turing Machines and variants multitape TMs nondeterministic TMs Church-Turing Thesis So far several models of computation finite automata
CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 8 January 24, 2018 Outline Turing Machines and variants multitape TMs nondeterministic TMs Church-Turing Thesis So far several models of computation finite automata
Lecture III CONTEXT FREE LANGUAGES
 1. Context Free Languages and Grammar Lecture III Page 1 Lecture III CONTEXT FREE LANGUAGES Lecture 3: Honors Theory, Spring 02. We introduce context free languages (CFL), context free grammar (CFG) and
1. Context Free Languages and Grammar Lecture III Page 1 Lecture III CONTEXT FREE LANGUAGES Lecture 3: Honors Theory, Spring 02. We introduce context free languages (CFL), context free grammar (CFG) and
(b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3},
![(b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3}, (b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3},](/thumbs/81/83182922.jpg) Code No: 07A50501 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech I Semester Examinations,MAY 2011 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All
Code No: 07A50501 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech I Semester Examinations,MAY 2011 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring Regular Languages. Finite Automata and Regular Expressions. Haniel Barbosa
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Regular Languages Finite Automata and Regular Expressions Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 1 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Sections 1.1 and 1.3.
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Regular Languages Finite Automata and Regular Expressions Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 1 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Sections 1.1 and 1.3.
COMP-330 Theory of Computation. Fall Prof. Claude Crépeau. Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars
 COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 3.3, 4.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Give examples of decidable problems.
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 3.3, 4.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Give examples of decidable problems.
Introduction to Computers & Programming
 16.070 Introduction to Computers & Programming Theory of computation: What is a computer? FSM, Automata Prof. Kristina Lundqvist Dept. of Aero/Astro, MIT Models of Computation What is a computer? If you
16.070 Introduction to Computers & Programming Theory of computation: What is a computer? FSM, Automata Prof. Kristina Lundqvist Dept. of Aero/Astro, MIT Models of Computation What is a computer? If you
Computability Theory
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Languages Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable Languages We
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Languages Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable Languages We
Solution Scoring: SD Reg exp.: a(a
 MA/CSSE 474 Exam 3 Winter 2013-14 Name Solution_with explanations Section: 02(3 rd ) 03(4 th ) 1. (28 points) For each of the following statements, circle T or F to indicate whether it is True or False.
MA/CSSE 474 Exam 3 Winter 2013-14 Name Solution_with explanations Section: 02(3 rd ) 03(4 th ) 1. (28 points) For each of the following statements, circle T or F to indicate whether it is True or False.
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- IV. 4.1 Push Down Automata. 4.2 The Formal Definition of Pushdown Automata. EXAMPLES for PDA. 4.3 The languages of PDA
 TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- IV 4.1 Push Down Automata 4.2 The Formal Definition of Pushdown Automata EXAMPLES for PDA 4.3 The languages of PDA 4.3.1 Acceptance by final state 4.3.2 Acceptance by empty stack
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- IV 4.1 Push Down Automata 4.2 The Formal Definition of Pushdown Automata EXAMPLES for PDA 4.3 The languages of PDA 4.3.1 Acceptance by final state 4.3.2 Acceptance by empty stack
