Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7
|
|
|
- Poppy Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1
2 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about CFGs. 2
3 Compiler Frontend Rules encoded as regular expressions Rules cannot be encoded as regular expressions for (i=0; i<n; i++) { a++; } Lexical Analyzer Parser stmt for ( id = number ; id < id ; id ++! ) { id ++ ; } for-stmt for ( expr ; expr ; expr ) stmt lval = rval id < id id ++ { stmt } id number expr id ++ ; 3
4 Biological Models 4 en.wikipedia.org/wiki/l-system
5 Biological Models Rule: 5
6 Biological Models Rule: or 6 Grammar: Rewriting rules for generating a set of strings (i.e., a language) from a seed
7 Context-Free Grammar Example: a (simplistic) syntax for arithmetic expressions 7 expr expr + expr expr expr expr expr a b c e.g. expr * a + b c expr expr + expr derives b c (This grammar is ambiguous since there is another parse tree for the same string) a expr expr
8 Context-Free Grammar Example: a (simplistic) syntax for arithmetic expressions expr expr + expr expr expr expr expr a b c e.g. expr * a + b c derives Σ = {a,b,c,+, } V = {expr, } G = (Σ, V, P, S)# (terminals)# (non-terminals)# P = {(A,α) A α} (prod. rules) S = expr expr expr + expr expr expr a b c short-hand (start symbol) 8
9 Context-Free Grammar : Arrows Production Rule: A π, A V, π (Σ V)*! Immediately Derives: α1 α2 if α1, α2 (Σ V)* s.t., α1 = βaγ, α2 = βπ γ and A π % More clearly, if grammar is G, we write α G* α# Derives: α * α# if α1,, αt+1 (Σ V)* s.t. expr expr + expr expr expr a b c expr expr + expr expr + expr expr + expr expr 9 α1=α, αt+1=α#, and for all i [1, t], αi αi+1 t-step derivation α t α# expr * expr + expr expr * + * a + b c! expr * a + b c
10 Context-Free Languages The language generated by a grammar G with start symbol S and alphabet Σ, L(G) = { w Σ* S G* w }# Languages generated by a context free grammars are called Context Free Languages (CFL) 10
11 Examples Over Σ = { 0,1 }, give a grammar for the following languages: L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 }! S ε 0S1 L = { w w = w R }# S ε 0 1 0S0 1S1 L = { 0 m 1 n m n }! S A B Z ε 0Z1 // 0 n 1 n A 0Z 0A // 0 m 1 n with m > n B Z1 B1 // 0 m 1 n with m < n L = { 0 m 1 n m < n }# Z ε 0Z1 // 0 n 1 n S Z1 S1 // 0 m 1 n with m < n 11
12 Parse Tree Parse Tree captures the structure of derivations for a given string (but not the exact order) expr * a + b c expr 12 The exact order of derivations is not important But structure is important! Ambiguous grammar: If some string has two different parse trees expr + expr a expr expr expr * expr + expr expr * + * a + b c! expr * a + expr * a + expr c * a + b c b c
13 Ambiguity expr expr + expr expr expr a b c expr * a + b c expr expr expr expr expr + expr expr + expr expr expr c a a b b c 13
14 An Unambiguous Grammar expr term + expr term! term term a b c In practice, unambiguous grammars are important (e.g., in compilers) expr * a + b c expr term + expr Operator precedence enforced by requiring all carried out (to get a term ) before any + a term term 14 There are CFLs which do not have any unambiguous grammar: inherently ambiguous languages b c
15 Examples L = L(0*)# S ε 0 SS : Ambiguous! S ε 0S : Unambiguous L = set of all strings with balanced parentheses S ε (S) SS : Ambiguous! T ( ) (S) S ε TS : Unambiguous 15
16 Examples L = set of all valid regular expressions over {0, 1} An ambiguous grammar (start symbol S, Σ = {Ø,e,0,1,+,*,(,)} ): S Ø e 0 1 (S) S* SS S+S An unambiguous grammar for a subset of regular expressions: S Ø e 0 1 (S) (S*) (SS) (S+S) Exercise: An unambiguous grammar for all valid regular expressions 16
17 Proving Correctness of Grammars Claim: Let L = { w # 0 (w) = # 1 (w) }. Then, L(G) = L where the productions of G are: S 0S1 1S0 SS ε! Challenge: Give an unambiguous grammar Proof: Need to prove both L(G) L and L(G) L. Prove L(G) L by induction on the length of derivations (or height of parse trees)! Prove L(G) L by induction on the length of strings.! 17
18 Proving Correctness of Grammars Claim: Let L = { w # 0 (w) = # 1 (w) }. Then, L(G) = L where the productions of G are: S 0S1 1S0 SS ε! Proof: Proving L(G) L by induction on the length of derivations.! Let w L(G). S t w for some t 1. Induction on t to show that w L. Base case: t=1. Only string derived is ε. 18 Induction step: Consider t > 1. Suppose all u s.t. S k u, k < t, in L. Let w be such that S t w. i.e., S α 1 t-1 w. Case α 1 =0S1: w = 0u1 and S t-1 u. By IH, # 0 (u)=# 1 (u). Hence # 0 (w) = # 0 (u)+1 = # 1 (v)+1 = # 1 (w). (Case α 1 =1S0 is symmetric.) Case α 1 =SS: w = uv and S m u, S n v, 1 m,n < t (m+n = t-1). By IH, # 0 (u)=# 1 (u) & # 0 (v)=# 1 (v). Hence # 0 (w) = # 0 (u)+# 0 (v) = # 1 (u)+# 1 (v) = # 1 (w)
19 Proving Correctness of Grammars Claim: Let L = { w # 0 (w) = # 1 (w) }. Then, L(G) = L where the productions of G are: S 0S1 1S0 SS ε! Proof: Proving L(G) L by induction on the length of strings.! Suppose w L. To show by induction on w that w L(G). Base cases: w =0. ε L(G). No string with w =1 in L(G). 19 Induction step: Let n 2. Suppose u L(G) for all u L with u < n. Let w L be such that w =n; i.e., # 0 (w)=# 1 (w). Case w=0u1: Then u L and u < n. By IH, u L(G). i.e., S *u. Hence, S 0S1 * 0u1 = w. (Case w=1u0 is symmetric.) Case w=0u0: Let d i = # 0 (i-long prefix of w) # 1 (i-long prefix of w). Then d 1 = 1, d n = 0, d n-1 = -1. So 1 < m n-1 s.t., d m = 0. i.e., w=xy, where x, y < w, and x,y L. By IH, x,y L(G). Hence S SS * xy = w. (Case w=1u1 is symmetric.)
20 Proving Correctness of Grammars Often will need to strengthen the claim to include strings generated by every iable in the grammar! Claim: Let L = { w # 0 (w) = # 1 (w) }. Then, L(G) = L where productions of G are: S AB BA ε A 0 AS SA B 1 BS SB! Stronger Claim: A derives all strings w s.t. # 0 (w) = # 1 (w)+1. B derives all strings w s.t. # 1 (w) = # 0 (w)+1. S derives all strings w s.t. # 0 (w) = # 1 (w). 20
21 Closure Properties for CFL Union: If L1 and L2 are CFLs, so is L1 L2. Let G1 = (Σ, V1, P1, S1), G2 = (Σ, V2, P2, S2) with V1 V2 = Ø. Let G = (Σ, V, P, S) with V = V1 V2 {S}, and P = P1 P2 { S S1 S2 }. Then L(G) = L(G1) L(G2).# Concatenation: If L1 and L2 are CFLs, so is L1 L2. Let G1 = (Σ, V1, P1, S1), G2 = (Σ, V2, P2, S2) with V1 V2 = Ø. Let G = (Σ, V, P, S) with V = V1 V2 {S}, and P = P1 P2 { S S1 S2 }. Then L(G) = L(G1) L(G2).# 21 Kleene Star: If L1 is a CFL, so is L1*. Let G1 = (Σ, V1, P1, S1). Let G = (Σ, V, P, S) with V = V1 {S}, and P = P1 { S ε S S1 }. Then L(G) = L(G1)*.
22 Closure Properties for CFL CFLs are not closed under intersection or complement Intersection: L1 = { 0 i 1 j 0 k i=j } & L1 = { 0 i 1 j 0 k j=k } are CFLs. But it turns out that L1 L2 = { 0 i 1 j 0 k i=j=k } is not a CFL! Complement: If CFLs were to be closed under complementation, since they are already closed under union, they would have been closed under intersection! 22
23 Grammars Rewriting rules for generating strings from a seed In an unrestricted grammar, the rules are of the form α β where α, β (Σ V)* Context-Free Grammar: Rewriting rules apply to individual iables (with no context ) All languages Languages with algorithms/ unrestricted grammars Context Free Languages Regular Languages 23
CFLs and Regular Languages. CFLs and Regular Languages. CFLs and Regular Languages. Will show that all Regular Languages are CFLs. Union.
 We can show that every RL is also a CFL Since a regular grammar is certainly context free. We can also show by only using Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars That is what we will do in this half.
We can show that every RL is also a CFL Since a regular grammar is certainly context free. We can also show by only using Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars That is what we will do in this half.
COMP-330 Theory of Computation. Fall Prof. Claude Crépeau. Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars
 COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III. 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems. 3.2 Derivation. 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar
 TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages
 Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 5 Context-Free Languages n { a b : n n { ww } 0} R Regular Languages a *b* ( a + b) * Example 1 G = ({S}, {a, b}, S, P) Derivations:
Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 5 Context-Free Languages n { a b : n n { ww } 0} R Regular Languages a *b* ( a + b) * Example 1 G = ({S}, {a, b}, S, P) Derivations:
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET
 THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
Properties of Context-Free Languages
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Context Free Languages and Grammars
 Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Context Free Languages and Grammars Lecture 7 Tuesday, September 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 36 What stack got to do
Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Context Free Languages and Grammars Lecture 7 Tuesday, September 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 36 What stack got to do
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages. Foundations of Computer Science Theory
 Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Context Free Grammars
 Automata and Formal Languages Context Free Grammars Sipser pages 101-111 Lecture 11 Tim Sheard 1 Formal Languages 1. Context free languages provide a convenient notation for recursive description of languages.
Automata and Formal Languages Context Free Grammars Sipser pages 101-111 Lecture 11 Tim Sheard 1 Formal Languages 1. Context free languages provide a convenient notation for recursive description of languages.
CPS 220 Theory of Computation
 CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
UNIT II REGULAR LANGUAGES
 1 UNIT II REGULAR LANGUAGES Introduction: A regular expression is a way of describing a regular language. The various operations are closure, union and concatenation. We can also find the equivalent regular
1 UNIT II REGULAR LANGUAGES Introduction: A regular expression is a way of describing a regular language. The various operations are closure, union and concatenation. We can also find the equivalent regular
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Properties of Context-free Languages. Reading: Chapter 7
 Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages
 Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
Context-free Grammars and Languages
 Context-free Grammars and Languages COMP 455 002, Spring 2019 Jim Anderson (modified by Nathan Otterness) 1 Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars provide another way to specify languages. Example:
Context-free Grammars and Languages COMP 455 002, Spring 2019 Jim Anderson (modified by Nathan Otterness) 1 Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars provide another way to specify languages. Example:
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs
 This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
Computational Models - Lecture 4
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Computational Models - Lecture 4 Regular languages: The Myhill-Nerode Theorem Context-free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for context free languages Non context-free languages: Examples Push
Comment: The induction is always on some parameter, and the basis case is always an integer or set of integers.
 1. For each of the following statements indicate whether it is true or false. For the false ones (if any), provide a counter example. For the true ones (if any) give a proof outline. (a) Union of two non-regular
1. For each of the following statements indicate whether it is true or false. For the false ones (if any), provide a counter example. For the true ones (if any) give a proof outline. (a) Union of two non-regular
2.1 Solution. E T F a. E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a
 . Solution E T F a E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a E E + T E + T + T T + T + T F + T + T a + T + T a + F + T a + a + T a + a + F a + a + a E T F ( E) ( T ) ( F) (( E)) (( T )) (( F)) (( a)) . Solution
. Solution E T F a E E + T T + T F + T a + T a + F a + a E E + T E + T + T T + T + T F + T + T a + T + T a + F + T a + a + T a + a + F a + a + a E T F ( E) ( T ) ( F) (( E)) (( T )) (( F)) (( a)) . Solution
FLAC Context-Free Grammars
 FLAC Context-Free Grammars Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality Fall 2017 1 Generating Languages Properties of CFLs Generation vs. Recognition 3 Turing machines can be used to check membership in
FLAC Context-Free Grammars Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality Fall 2017 1 Generating Languages Properties of CFLs Generation vs. Recognition 3 Turing machines can be used to check membership in
Parsing. Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 26
 Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Computational Models - Lecture 3
 Slides modified by Benny Chor, based on original slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University. p. 1 Computational Models - Lecture 3 Equivalence of regular expressions and regular languages (lukewarm leftover
Slides modified by Benny Chor, based on original slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University. p. 1 Computational Models - Lecture 3 Equivalence of regular expressions and regular languages (lukewarm leftover
Before We Start. The Pumping Lemma. Languages. Context Free Languages. Plan for today. Now our picture looks like. Any questions?
 Before We Start The Pumping Lemma Any questions? The Lemma & Decision/ Languages Future Exam Question What is a language? What is a class of languages? Context Free Languages Context Free Languages(CFL)
Before We Start The Pumping Lemma Any questions? The Lemma & Decision/ Languages Future Exam Question What is a language? What is a class of languages? Context Free Languages Context Free Languages(CFL)
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL) Objectives Introduce Pumping Lemma for CFL Apply Pumping Lemma to show that some languages are non-cfl Pumping Lemma
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL) Objectives Introduce Pumping Lemma for CFL Apply Pumping Lemma to show that some languages are non-cfl Pumping Lemma
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002)
 CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course
 Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Non-context-Free Languages. CS215, Lecture 5 c
 Non-context-Free Languages CS215, Lecture 5 c 2007 1 The Pumping Lemma Theorem. (Pumping Lemma) Let be context-free. There exists a positive integer divided into five pieces, Proof for for each, and..
Non-context-Free Languages CS215, Lecture 5 c 2007 1 The Pumping Lemma Theorem. (Pumping Lemma) Let be context-free. There exists a positive integer divided into five pieces, Proof for for each, and..
Functions on languages:
 MA/CSSE 474 Final Exam Notation and Formulas page Name (turn this in with your exam) Unless specified otherwise, r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z are strings over alphabet Σ; while a, b, c, d are individual alphabet
MA/CSSE 474 Final Exam Notation and Formulas page Name (turn this in with your exam) Unless specified otherwise, r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z are strings over alphabet Σ; while a, b, c, d are individual alphabet
} Some languages are Turing-decidable A Turing Machine will halt on all inputs (either accepting or rejecting). No infinite loops.
 and their languages } Some languages are Turing-decidable A Turing Machine will halt on all inputs (either accepting or rejecting). No infinite loops. } Some languages are Turing-recognizable, but not
and their languages } Some languages are Turing-decidable A Turing Machine will halt on all inputs (either accepting or rejecting). No infinite loops. } Some languages are Turing-recognizable, but not
Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y.
 CSE2001, Fall 2006 1 Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y. S 00S1 A - xay, where x = 2 y.
CSE2001, Fall 2006 1 Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y. S 00S1 A - xay, where x = 2 y.
Automata Theory CS F-08 Context-Free Grammars
 Automata Theory CS411-2015F-08 Context-Free Grammars David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 08-0: Context-Free Grammars Set of Terminals (Σ) Set of Non-Terminals Set of
Automata Theory CS411-2015F-08 Context-Free Grammars David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 08-0: Context-Free Grammars Set of Terminals (Σ) Set of Non-Terminals Set of
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
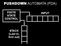 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
Miscellaneous. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Miscellaneous Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms and inverse homomorphisms.
Miscellaneous Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms and inverse homomorphisms.
10. The GNFA method is used to show that
 CSE 355 Midterm Examination 27 February 27 Last Name Sample ASU ID First Name(s) Ima Exam # Sample Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been recorded correctly, return the entire
CSE 355 Midterm Examination 27 February 27 Last Name Sample ASU ID First Name(s) Ima Exam # Sample Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been recorded correctly, return the entire
6.8 The Post Correspondence Problem
 6.8. THE POST CORRESPONDENCE PROBLEM 423 6.8 The Post Correspondence Problem The Post correspondence problem (due to Emil Post) is another undecidable problem that turns out to be a very helpful tool for
6.8. THE POST CORRESPONDENCE PROBLEM 423 6.8 The Post Correspondence Problem The Post correspondence problem (due to Emil Post) is another undecidable problem that turns out to be a very helpful tool for
Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Laurent Vanbever. ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October,
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 5 2017 Part 3 out of 5 Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 5 2017 Part 3 out of 5 Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular
Part 3 out of 5. Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular languages
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 3 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 5 2017 Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 3 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 5 2017 Last week, we learned about closure and equivalence of regular
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Design a PDA and a CFG for a given language Give informal description for a PDA,
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Design a PDA and a CFG for a given language Give informal description for a PDA,
[4203] Compiler Theory Sheet # 3-Answers
![[4203] Compiler Theory Sheet # 3-Answers [4203] Compiler Theory Sheet # 3-Answers](/thumbs/85/91525265.jpg) El-Shourouk cademy cad. Year : 2012 / 2013 Higher Institute for Computer & Term : Second Information Technology Year : Fourth Department of Computer Science [4203] Compiler Theory Sheet # 3-nswers 1- Write
El-Shourouk cademy cad. Year : 2012 / 2013 Higher Institute for Computer & Term : Second Information Technology Year : Fourth Department of Computer Science [4203] Compiler Theory Sheet # 3-nswers 1- Write
Syntax Analysis Part I
 1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2013 2 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model Source Program Lexical Analyzer
1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2013 2 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model Source Program Lexical Analyzer
CS 154, Lecture 3: DFA NFA, Regular Expressions
 CS 154, Lecture 3: DFA NFA, Regular Expressions Homework 1 is coming out Deterministic Finite Automata Computation with finite memory Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Computation with finite memory and
CS 154, Lecture 3: DFA NFA, Regular Expressions Homework 1 is coming out Deterministic Finite Automata Computation with finite memory Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Computation with finite memory and
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages
 Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016
 CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
Theory Of Computation UNIT-II
 Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars: Regular expression formalism- equivalence with finite automata-regular sets and closure properties- pumping lemma for regular languages- decision algorithms
Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars: Regular expression formalism- equivalence with finite automata-regular sets and closure properties- pumping lemma for regular languages- decision algorithms
Fundamentele Informatica 3 Antwoorden op geselecteerde opgaven uit Hoofdstuk 7 en Hoofdstuk 8
 Fundamentele Informatica 3 Antwoorden op geselecteerde opgaven uit Hoofdstuk 7 en Hoofdstuk 8 John Martin: Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation Jetty Kleijn Najaar 2008 7.1 (q 0,bbcbb,Z
Fundamentele Informatica 3 Antwoorden op geselecteerde opgaven uit Hoofdstuk 7 en Hoofdstuk 8 John Martin: Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation Jetty Kleijn Najaar 2008 7.1 (q 0,bbcbb,Z
Syntax Analysis Part I. Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model. The Parser. Chapter 4
 1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van ngelen, Flora State University, 2007 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model 2 Source Program Lexical Analyzer Lexical
1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van ngelen, Flora State University, 2007 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model 2 Source Program Lexical Analyzer Lexical
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture)
 Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Theory of computation: initial remarks (Chapter 11)
 Theory of computation: initial remarks (Chapter 11) For many purposes, computation is elegantly modeled with simple mathematical objects: Turing machines, finite automata, pushdown automata, and such.
Theory of computation: initial remarks (Chapter 11) For many purposes, computation is elegantly modeled with simple mathematical objects: Turing machines, finite automata, pushdown automata, and such.
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05
 Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars
 The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) is a simple and useful form of a CFG Every rule of a CNF grammar is in the form A BC A a Where a is any terminal
The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) is a simple and useful form of a CFG Every rule of a CNF grammar is in the form A BC A a Where a is any terminal
Theory of Computation - Module 3
 Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules).
 Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review. Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed
 HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed For the most part, all about strings! String induction (to some extent) Regular languages Regular expressions (regexps) Deterministic finite
HKN CS/ECE 374 Midterm 1 Review Nathan Bleier and Mahir Morshed For the most part, all about strings! String induction (to some extent) Regular languages Regular expressions (regexps) Deterministic finite
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer.
 Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs
 CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
Theory of computation: initial remarks (Chapter 11)
 Theory of computation: initial remarks (Chapter 11) For many purposes, computation is elegantly modeled with simple mathematical objects: Turing machines, finite automata, pushdown automata, and such.
Theory of computation: initial remarks (Chapter 11) For many purposes, computation is elegantly modeled with simple mathematical objects: Turing machines, finite automata, pushdown automata, and such.
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
Closure Properties of Regular Languages
 Closure Properties of Regular Languages Lecture 13 Section 4.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 21, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Closure Properties of Regular Languages
Closure Properties of Regular Languages Lecture 13 Section 4.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 21, 2016 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) Closure Properties of Regular Languages
Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10
 Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10 Today we look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning the two categories of language we have seen so far: Regular languages (RL). Context-free
Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10 Today we look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning the two categories of language we have seen so far: Regular languages (RL). Context-free
Regular Expressions. Definitions Equivalence to Finite Automata
 Regular Expressions Definitions Equivalence to Finite Automata 1 RE s: Introduction Regular expressions are an algebraic way to describe languages. They describe exactly the regular languages. If E is
Regular Expressions Definitions Equivalence to Finite Automata 1 RE s: Introduction Regular expressions are an algebraic way to describe languages. They describe exactly the regular languages. If E is
SYLLABUS. Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 3 : REGULAR EXPRESSIONS AND LANGUAGES
 Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Syntax Analysis Part I
 1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2013 2 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model Source Program Lexical Analyzer
1 Syntax Analysis Part I Chapter 4 COP5621 Compiler Construction Copyright Robert van Engelen, Florida State University, 2007-2013 2 Position of a Parser in the Compiler Model Source Program Lexical Analyzer
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs
 Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
NPDA, CFG equivalence
 NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
Context-Free Grammars and Languages. Reading: Chapter 5
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars Salil Vadhan October 2, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.1 (except Chomsky Normal Form). Algorithmic questions about regular
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars Salil Vadhan October 2, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.1 (except Chomsky Normal Form). Algorithmic questions about regular
What Is a Language? Grammars, Languages, and Machines. Strings: the Building Blocks of Languages
 Do Homework 2. What Is a Language? Grammars, Languages, and Machines L Language Grammar Accepts Machine Strings: the Building Blocks of Languages An alphabet is a finite set of symbols: English alphabet:
Do Homework 2. What Is a Language? Grammars, Languages, and Machines L Language Grammar Accepts Machine Strings: the Building Blocks of Languages An alphabet is a finite set of symbols: English alphabet:
Theory of Computation 1 Sets and Regular Expressions
 Theory of Computation 1 Sets and Regular Expressions Frank Stephan Department of Computer Science Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore fstephan@comp.nus.edu.sg Theory of Computation
Theory of Computation 1 Sets and Regular Expressions Frank Stephan Department of Computer Science Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore fstephan@comp.nus.edu.sg Theory of Computation
CS 341 Homework 16 Languages that Are and Are Not Context-Free
 CS 341 Homework 16 Languages that Are and Are Not Context-Free 1. Show that the following languages are context-free. You can do this by writing a context free grammar or a PDA, or you can use the closure
CS 341 Homework 16 Languages that Are and Are Not Context-Free 1. Show that the following languages are context-free. You can do this by writing a context free grammar or a PDA, or you can use the closure
Pushdown automata. Twan van Laarhoven. Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Radboud University Nijmegen
 Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Context-Free Grammar
 Context-Free Grammar CFGs are more powerful than regular expressions. They are more powerful in the sense that whatever can be expressed using regular expressions can be expressed using context-free grammars,
Context-Free Grammar CFGs are more powerful than regular expressions. They are more powerful in the sense that whatever can be expressed using regular expressions can be expressed using context-free grammars,
(NB. Pages are intended for those who need repeated study in formal languages) Length of a string. Formal languages. Substrings: Prefix, suffix.
 (NB. Pages 22-40 are intended for those who need repeated study in formal languages) Length of a string Number of symbols in the string. Formal languages Basic concepts for symbols, strings and languages:
(NB. Pages 22-40 are intended for those who need repeated study in formal languages) Length of a string Number of symbols in the string. Formal languages Basic concepts for symbols, strings and languages:
Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms
 Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 6 Normal Forms for CFGs 1. Chomsky Normal Form CNF Productions of form A BC A, B, C V A a a T
Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 6 Normal Forms for CFGs 1. Chomsky Normal Form CNF Productions of form A BC A, B, C V A a a T
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
This Lecture will Cover...
 Last Lecture Covered... DFAs, NFAs, -NFAs and the equivalence of the language classes they accept Last Lecture Covered... This Lecture will Cover... Introduction to regular expressions and regular languages
Last Lecture Covered... DFAs, NFAs, -NFAs and the equivalence of the language classes they accept Last Lecture Covered... This Lecture will Cover... Introduction to regular expressions and regular languages
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Lecture 17: Language Recognition
 Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Lecture Notes on Inductive Definitions
 Lecture Notes on Inductive Definitions 15-312: Foundations of Programming Languages Frank Pfenning Lecture 2 August 28, 2003 These supplementary notes review the notion of an inductive definition and give
Lecture Notes on Inductive Definitions 15-312: Foundations of Programming Languages Frank Pfenning Lecture 2 August 28, 2003 These supplementary notes review the notion of an inductive definition and give
CSCI Compiler Construction
 CSCI 742 - Compiler Construction Lecture 12 Cocke-Younger-Kasami (CYK) Algorithm Instructor: Hossein Hojjat February 20, 2017 Recap: Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) A CFG is in Chomsky Normal Form if each rule
CSCI 742 - Compiler Construction Lecture 12 Cocke-Younger-Kasami (CYK) Algorithm Instructor: Hossein Hojjat February 20, 2017 Recap: Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) A CFG is in Chomsky Normal Form if each rule
Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science. Lecture 4: Deterministic Finite Automaton (DFA), Part 2
 5-25 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Lecture 4: Deterministic Finite Automaton (DFA), Part 2 January 26th, 27 Formal definition: DFA A deterministic finite automaton (DFA) M =(Q,,,q,F) M is
5-25 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Lecture 4: Deterministic Finite Automaton (DFA), Part 2 January 26th, 27 Formal definition: DFA A deterministic finite automaton (DFA) M =(Q,,,q,F) M is
Syntax Analysis Part III
 Syntax Analysis Part III Chapter 4: Top-Down Parsing Slides adapted from : Robert van Engelen, Florida State University Eliminating Ambiguity stmt if expr then stmt if expr then stmt else stmt other The
Syntax Analysis Part III Chapter 4: Top-Down Parsing Slides adapted from : Robert van Engelen, Florida State University Eliminating Ambiguity stmt if expr then stmt if expr then stmt else stmt other The
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
Context-free grammars and languages
 Context-free grammars and languages The next class of languages we will study in the course is the class of context-free languages. They are defined by the notion of a context-free grammar, or a CFG for
Context-free grammars and languages The next class of languages we will study in the course is the class of context-free languages. They are defined by the notion of a context-free grammar, or a CFG for
Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5
 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5 Helle Hvid Hansen helle@cs.ru.nl http://www.cs.ru.nl/~helle/ Foundations Group Intelligent Systems Section Institute for Computing and Information Sciences
Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5 Helle Hvid Hansen helle@cs.ru.nl http://www.cs.ru.nl/~helle/ Foundations Group Intelligent Systems Section Institute for Computing and Information Sciences
Computability Theory
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
The View Over The Horizon
 The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation. Lecture #29: Proving Regular Language Identities David Mix Barrington 6 April 2012
 CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation Lecture #29: Proving Regular Language Identities David Mix Barrington 6 April 2012 Proving Regular Language Identities Regular Language Identities The Semiring Axioms
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation Lecture #29: Proving Regular Language Identities David Mix Barrington 6 April 2012 Proving Regular Language Identities Regular Language Identities The Semiring Axioms
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
ECS 120: Theory of Computation UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, Midterm Exam
 ECS 120: Theory of Computation Handout MT UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, 2012 Midterm Exam Instructions: The exam has six pages, including this cover page, printed out two-sided (no more wasted
ECS 120: Theory of Computation Handout MT UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, 2012 Midterm Exam Instructions: The exam has six pages, including this cover page, printed out two-sided (no more wasted
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
Context-Free Grammars and Languages
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Context-Free Grammars and Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
NODIA AND COMPANY. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer Science Engineering Theory of Computation. Copyright By NODIA & COMPANY
 No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer
No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer
