6.8 The Post Correspondence Problem
|
|
|
- Gertrude Hardy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 6.8. THE POST CORRESPONDENCE PROBLEM The Post Correspondence Problem The Post correspondence problem (due to Emil Post) is another undecidable problem that turns out to be a very helpful tool for proving problems in logic or in formal language theory to be undecidable. Let Σ be an alphabet with at least two letters. An instance of the Post Correspondence problem (for short, PCP) is given by two sequences U = (u 1,..., u m ) and V = (v 1,..., v m ), of strings u i, v i Σ. The problem is to find whether there is a (finite) sequence (i 1,..., i p ), with i j {1,..., m} for j = 1,..., p, so that u i1 u i2 u ip = v i1 v i2 v ip. Equivalently, an instance of the PCP is a sequence of pairs ( ) ( ) u1 um,...,. v 1 v m
2 424 For example, consider the following problem: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( abab aaabbb aab ba,,, ababaaa bb baab baa There is a solution for the string : ), ( ) ab, ba ( ) aa. a abab aaabbb aab ba ab ab aa = ababaaa bb baab baa ba ba a. We are beginning to suspect that this is a hard problem. Indeed, it is undecidable! Theorem (Emil Post, 1946) The Post correspondence problem is undecidable, provided that the alphabet Σ has at least two symbols.
3 6.8. THE POST CORRESPONDENCE PROBLEM 425 There are several ways of proving Theorem 6.8.1, but the strategy is more or less the same: Reduce the halting problem to the PCP, by encoding sequences of ID s as partial solutions of the PCP. For instance, this can be done for RAM programs. The first step is to show that every RAM program can be simulated by a single register RAM program. Then, the halting problem for RAM programs with one register is reduced to the PCP (using the fact that only four kinds of instructions are needed). A proof along these lines was given by Dana Scott.
4 426 As an application, we prove the following result: Theorem It is undecidable whether a context-free grammar is ambiguous. Proof. We reduce the PCP to the ambiguity problem for CFG s. Given any instance U = (u 1,..., u m ) and V = (v 1,..., v m ) of the PCP, let c 1,..., c m be m new symbols, and consider the following languages: L U = {u i1 u ip c ip c i1 1 i j m, 1 j p, p 1}, L V = {v i1 v ip c ip c i1 1 i j m, 1 j p, p 1}, and L U,V = L U L V.
5 6.8. THE POST CORRESPONDENCE PROBLEM 427 We can easily construct a CFG, G U,V, generating L U,V. productions are: The S S S U S U S U S V u i S U c i u i c i S V v i S V c i S V v i c i. It is easily seen that the PCP for (U, V ) has a solution iff L U L V iff G is ambiguous. Remark: As a corollary, we also obtain the following result: It is undecidable for arbitrary context-free grammars G 1 and G 2 whether L(G 1 ) L(G 2 ) = (see also Theorem 6.9.2).
6 Undecidable Properties of Languages, Greibach s Theorem Recall that the computations of a Turing Machine, M, can be described in terms of instantaneous descriptions, upav. We can encode computations ID 0 ID 1 ID n halting in a proper ID, as the language, L M, consisting all of strings w 0 #w R 1 #w 2 #w R 3 # #w 2k #w R 2k+1, or w 0 #w R 1 #w 2 #w R 3 # #w 2k 2 #w R 2k 1#w 2k, where k 0, w 0 is a starting ID, w i w i+1 for all i with 0 i < 2k+1 and w 2k+1 is proper halting ID in the first case, 0 i < 2k and w 2k is proper halting ID in the second case.
7 6.9. UNDECIDABLE PROPERTIES OF LANGUAGES 429 The language L M turns out to be the intersection of two contextfree languages L 0 M and L1 M defined as follows: (1) The strings in L 0 M are of the form or w 0 #w R 1 #w 2 #w R 3 # #w 2k #w R 2k+1 w 0 #w R 1 #w 2 #w R 3 # #w 2k 2 #w R 2k 1#w 2k, where w 2i w 2i+1 for all i 0, and w 2k is a proper halting ID in the second case. (2) The strings in L 1 M are of the form or w 0 #w R 1 #w 2 #w R 3 # #w 2k #w R 2k+1 w 0 #w R 1 #w 2 #w R 3 # #w 2k 2 #w R 2k 1#w 2k, where w 2i+1 w 2i+2 for all i 0, w 0 is a starting ID, and w 2k+1 is a proper halting ID in the first case.
8 430 Theorem Given any Turing machine M, the languages L 0 M and L1 M are context-free, and L M = L 0 M L1 M. Proof. We can construct PDA s accepting L 0 M easily checked that L M = L 0 M L1 M. and L1 M. It is As a corollary, we obtain the following undecidability result: Theorem It is undecidable for arbitrary context-free grammars G 1 and G 2 whether L(G 1 ) L(G 2 ) =. Proof. We can reduce the problem of deciding whether a partial recursive function is undefined everywhere to the above problem. By Rice s theorem, the first problem is undecidable.
9 6.9. UNDECIDABLE PROPERTIES OF LANGUAGES 431 However, this problem is equivalent to deciding whether a Turing machine never halts in a proper ID. By Theorem 6.9.1, the languages L 0 M and L1 M are context-free. Thus, we can construct context-free grammars G 1 and G 2 so that L 0 M = L(G 1) and L 1 M = L(G 2). Then, M never halts in a proper ID iff L M = iff (by Theorem 6.9.1), L M = L(G 1 ) L(G 2 ) =. Given a Turing machine M, the language L M is defined over the alphabet = Γ Q {#}. The following fact is also useful to prove undecidability: Theorem Given any Turing machine M, the language L M is context-free. Proof. One can easily check that the conditions for not belonging to L M can be checked by a PDA.
10 432 As a corollary, we obtain: Theorem Given any context-free grammar, G = (V, Σ, P, S), it is undecidable whether L(G) = Σ. Proof. We can reduce the problem of deciding whether a Turing machine never halts in a proper ID to the above problem. Indeed, given M, by Theorem 6.9.3, the language L M is context-free. Thus, there is a CFG, G, so that L(G) = L M. However, M never halts in a proper ID iff L M = iff L(G) =. As a consequence, we also obtain the following:
11 6.9. UNDECIDABLE PROPERTIES OF LANGUAGES 433 Theorem Given any two context-free grammar, G 1 and G 2, and any regular language, R, the following facts hold: (1) L(G 1 ) = L(G 2 ) is undecidable. (2) L(G 1 ) L(G 2 ) is undecidable. (3) L(G 1 ) = R is undecidable. (4) R L(G 2 ) is undecidable. In contrast to (4), the property L(G 1 ) R is decidable!
12 434 We conclude with a nice theorem of S. Greibach, which is a sort of version of Rice s theorem for families of languages. Let L be a countable family of languages. We assume that there is a coding function c: L N and that this function can be extended to code the regular languages (all alphabets are subsets of some given countably infinite set). We also assume that L is effectively closed under union and concatenation with regular languages. This means that given any two languages L 1 and L 2 in L, we have L 1 L 2 L, and c(l 1 L 2 ) is given by a recursive function of c(l 1 ) and c(l 2 ), and that for every regular language R, we have L 1 R L, RL 1 L, and c(rl 1 ) and c(l 1 R) are recursive functions of c(r) and c(l 1 ).
13 6.9. UNDECIDABLE PROPERTIES OF LANGUAGES 435 Given any language, L Σ, and any string, w Σ, we define L/w by L/w = {u Σ uw L}. Theorem (Greibach) Let L be a countable family of languages that is effectively closed under union and concatenation with the regular languages, and assume that the problem L = Σ is undecidable for L L and any given sufficiently large alphabet Σ. Let P be any nontrivial property of languages that is true for the regular languages and so that if P (L) holds then P (L/a) also holds for any letter a. Then, P is undecidable for L. Proof. Since P is nontrivial for L, there is some L 0 L so that P (L 0 ) is false. Let Σ be large enough, so that L 0 Σ, and the problem L = Σ is undecidable for L L.
14 436 We show that given any L L, with L Σ, we can construct a language L 1 L, so that L = Σ iff P (L 1 ) holds. Thus, the problem L = Σ for L L reduces to property P for L, and since for Σ big enough, the first problem is undecidable, so is the second. For any L L, with L Σ, let L 1 = L 0 #Σ Σ #L. Since L is effectively closed under union and concatenation with the regular languages, we have L 1 L. If L = Σ, then L 1 = Σ #Σ, a regular language, and thus, P (L 1 ) holds, since P holds for the regular languages.
15 6.9. UNDECIDABLE PROPERTIES OF LANGUAGES 437 Conversely, we would like to prove that if L Σ, then P (L 1 ) is false. Since L Σ, there is some w / L. But then, L 1 /#w = L 0. Since P is preserved under quotient by a single letter, by a trivial induction, if P (L 1 ) holds, then P (L 0 ) also holds. However, P (L 0 ) is false, so P (L 1 ) must be false. Thus, we proved that L = Σ iff P (L 1 ) holds, as claimed. Greibach s theorem can be used to show that it is undecidable whether a context-free grammar generates a regular language. It can also be used to show that it is undecidable whether a context-free language is inherently ambiguous.
The Post Correspondence Problem; Applications to Undecidability Results
 Chapter 8 The Post Correspondence Problem; Applications to Undecidability Results 8.1 The Post Correspondence Problem The Post correspondence problem (due to Emil Post) is another undecidable problem that
Chapter 8 The Post Correspondence Problem; Applications to Undecidability Results 8.1 The Post Correspondence Problem The Post correspondence problem (due to Emil Post) is another undecidable problem that
The Turing Machine. Computability. The Church-Turing Thesis (1936) Theory Hall of Fame. Theory Hall of Fame. Undecidability
 The Turing Machine Computability Motivating idea Build a theoretical a human computer Likened to a human with a paper and pencil that can solve problems in an algorithmic way The theoretical provides a
The Turing Machine Computability Motivating idea Build a theoretical a human computer Likened to a human with a paper and pencil that can solve problems in an algorithmic way The theoretical provides a
CS481F01 Solutions 8
 CS481F01 Solutions 8 A. Demers 7 Dec 2001 1. Prob. 111 from p. 344 of the text. One of the following sets is r.e. and the other is not. Which is which? (a) { i L(M i ) contains at least 481 elements }
CS481F01 Solutions 8 A. Demers 7 Dec 2001 1. Prob. 111 from p. 344 of the text. One of the following sets is r.e. and the other is not. Which is which? (a) { i L(M i ) contains at least 481 elements }
Undecidable Problems and Reducibility
 University of Georgia Fall 2014 Reducibility We show a problem decidable/undecidable by reducing it to another problem. One type of reduction: mapping reduction. Definition Let A, B be languages over Σ.
University of Georgia Fall 2014 Reducibility We show a problem decidable/undecidable by reducing it to another problem. One type of reduction: mapping reduction. Definition Let A, B be languages over Σ.
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
} Some languages are Turing-decidable A Turing Machine will halt on all inputs (either accepting or rejecting). No infinite loops.
 and their languages } Some languages are Turing-decidable A Turing Machine will halt on all inputs (either accepting or rejecting). No infinite loops. } Some languages are Turing-recognizable, but not
and their languages } Some languages are Turing-decidable A Turing Machine will halt on all inputs (either accepting or rejecting). No infinite loops. } Some languages are Turing-recognizable, but not
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET
 THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
SYLLABUS. Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 3 : REGULAR EXPRESSIONS AND LANGUAGES
 Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Section 14.1 Computability then else
 Section 14.1 Computability Some problems cannot be solved by any machine/algorithm. To prove such statements we need to effectively describe all possible algorithms. Example (Turing machines). Associate
Section 14.1 Computability Some problems cannot be solved by any machine/algorithm. To prove such statements we need to effectively describe all possible algorithms. Example (Turing machines). Associate
Functions on languages:
 MA/CSSE 474 Final Exam Notation and Formulas page Name (turn this in with your exam) Unless specified otherwise, r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z are strings over alphabet Σ; while a, b, c, d are individual alphabet
MA/CSSE 474 Final Exam Notation and Formulas page Name (turn this in with your exam) Unless specified otherwise, r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z are strings over alphabet Σ; while a, b, c, d are individual alphabet
DM17. Beregnelighed. Jacob Aae Mikkelsen
 DM17 Beregnelighed Jacob Aae Mikkelsen January 12, 2007 CONTENTS Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Operations with languages...................... 2 2 Finite Automata 3 2.1 Regular expressions/languages....................
DM17 Beregnelighed Jacob Aae Mikkelsen January 12, 2007 CONTENTS Contents 1 Introduction 2 1.1 Operations with languages...................... 2 2 Finite Automata 3 2.1 Regular expressions/languages....................
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 15 Ana Bove May 17th 2018 Recap: Context-free Languages Chomsky hierarchy: Regular languages are also context-free; Pumping lemma
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 15 Ana Bove May 17th 2018 Recap: Context-free Languages Chomsky hierarchy: Regular languages are also context-free; Pumping lemma
ECS 120 Lesson 20 The Post Correspondence Problem
 ECS 120 Lesson 20 The Post Correspondence Problem Oliver Kreylos Wednesday, May 16th, 2001 Today we will continue yesterday s discussion of reduction techniques by looking at another common strategy, reduction
ECS 120 Lesson 20 The Post Correspondence Problem Oliver Kreylos Wednesday, May 16th, 2001 Today we will continue yesterday s discussion of reduction techniques by looking at another common strategy, reduction
Comment: The induction is always on some parameter, and the basis case is always an integer or set of integers.
 1. For each of the following statements indicate whether it is true or false. For the false ones (if any), provide a counter example. For the true ones (if any) give a proof outline. (a) Union of two non-regular
1. For each of the following statements indicate whether it is true or false. For the false ones (if any), provide a counter example. For the true ones (if any) give a proof outline. (a) Union of two non-regular
Theory of Computation
 Thomas Zeugmann Hokkaido University Laboratory for Algorithmics http://www-alg.ist.hokudai.ac.jp/ thomas/toc/ Lecture 14: Applications of PCP Goal of this Lecture Our goal is to present some typical undecidability
Thomas Zeugmann Hokkaido University Laboratory for Algorithmics http://www-alg.ist.hokudai.ac.jp/ thomas/toc/ Lecture 14: Applications of PCP Goal of this Lecture Our goal is to present some typical undecidability
Theory of Computation
 Fall 2002 (YEN) Theory of Computation Midterm Exam. Name:... I.D.#:... 1. (30 pts) True or false (mark O for true ; X for false ). (Score=Max{0, Right- 1 2 Wrong}.) (1) X... If L 1 is regular and L 2 L
Fall 2002 (YEN) Theory of Computation Midterm Exam. Name:... I.D.#:... 1. (30 pts) True or false (mark O for true ; X for false ). (Score=Max{0, Right- 1 2 Wrong}.) (1) X... If L 1 is regular and L 2 L
1. (a) Explain the procedure to convert Context Free Grammar to Push Down Automata.
 Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
Reducability. Sipser, pages
 Reducability Sipser, pages 187-214 Reduction Reduction encodes (transforms) one problem as a second problem. A solution to the second, can be transformed into a solution to the first. We expect both transformations
Reducability Sipser, pages 187-214 Reduction Reduction encodes (transforms) one problem as a second problem. A solution to the second, can be transformed into a solution to the first. We expect both transformations
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3
 SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction) Objectives This lecture shows more undecidable languages Our proof is not based on diagonalization Instead, we reduce the problem
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction) Objectives This lecture shows more undecidable languages Our proof is not based on diagonalization Instead, we reduce the problem
Advanced Undecidability Proofs
 17 Advanced Undecidability Proofs In this chapter, we will discuss Rice s Theorem in Section 17.1, and the computational history method in Section 17.3. As discussed in Chapter 16, these are two additional
17 Advanced Undecidability Proofs In this chapter, we will discuss Rice s Theorem in Section 17.1, and the computational history method in Section 17.3. As discussed in Chapter 16, these are two additional
Chap. 4,5 Review. Algorithms created in proofs from prior chapters
 Chap. 4,5 Review Algorithms created in proofs from prior chapters (p. 55) Theorem 1.39: NFA to DFA (p. 67) Lemma 1.55: Regex to NFA (p. 69) Lemma 1.60: DFA to regex (through GNFA) (p. 112) Lemma 2.21:
Chap. 4,5 Review Algorithms created in proofs from prior chapters (p. 55) Theorem 1.39: NFA to DFA (p. 67) Lemma 1.55: Regex to NFA (p. 69) Lemma 1.60: DFA to regex (through GNFA) (p. 112) Lemma 2.21:
CPSC 421: Tutorial #1
 CPSC 421: Tutorial #1 October 14, 2016 Set Theory. 1. Let A be an arbitrary set, and let B = {x A : x / x}. That is, B contains all sets in A that do not contain themselves: For all y, ( ) y B if and only
CPSC 421: Tutorial #1 October 14, 2016 Set Theory. 1. Let A be an arbitrary set, and let B = {x A : x / x}. That is, B contains all sets in A that do not contain themselves: For all y, ( ) y B if and only
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska
 cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 14 SMALL REVIEW FOR FINAL SOME Y/N QUESTIONS Q1 Given Σ =, there is L over Σ Yes: = {e} and L = {e} Σ Q2 There are uncountably
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 14 SMALL REVIEW FOR FINAL SOME Y/N QUESTIONS Q1 Given Σ =, there is L over Σ Yes: = {e} and L = {e} Σ Q2 There are uncountably
Theory of Computation
 Theory of Computation Lecture #10 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 43 Lecture 10: Overview Linear Bounded Automata Acceptance Problem for LBAs
Theory of Computation Lecture #10 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 43 Lecture 10: Overview Linear Bounded Automata Acceptance Problem for LBAs
Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata
 Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata 1. What is a Turing Machine? A Turing Machine is an accepting device which accepts the languages (recursively enumerable set) generated by type
Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata 1. What is a Turing Machine? A Turing Machine is an accepting device which accepts the languages (recursively enumerable set) generated by type
V Honors Theory of Computation
 V22.0453-001 Honors Theory of Computation Problem Set 3 Solutions Problem 1 Solution: The class of languages recognized by these machines is the exactly the class of regular languages, thus this TM variant
V22.0453-001 Honors Theory of Computation Problem Set 3 Solutions Problem 1 Solution: The class of languages recognized by these machines is the exactly the class of regular languages, thus this TM variant
Undecidability COMS Ashley Montanaro 4 April Department of Computer Science, University of Bristol Bristol, UK
 COMS11700 Undecidability Department of Computer Science, University of Bristol Bristol, UK 4 April 2014 COMS11700: Undecidability Slide 1/29 Decidability We are particularly interested in Turing machines
COMS11700 Undecidability Department of Computer Science, University of Bristol Bristol, UK 4 April 2014 COMS11700: Undecidability Slide 1/29 Decidability We are particularly interested in Turing machines
A Universal Turing Machine
 A Universal Turing Machine A limitation of Turing Machines: Turing Machines are hardwired they execute only one program Real Computers are re-programmable Solution: Universal Turing Machine Attributes:
A Universal Turing Machine A limitation of Turing Machines: Turing Machines are hardwired they execute only one program Real Computers are re-programmable Solution: Universal Turing Machine Attributes:
CS20a: Turing Machines (Oct 29, 2002)
 CS20a: Turing Machines (Oct 29, 2002) So far: DFA = regular languages PDA = context-free languages Today: Computability 1 Church s thesis The computable functions are the same as the partial recursive
CS20a: Turing Machines (Oct 29, 2002) So far: DFA = regular languages PDA = context-free languages Today: Computability 1 Church s thesis The computable functions are the same as the partial recursive
Theory of Computation
 Thomas Zeugmann Hokkaido University Laboratory for Algorithmics http://www-alg.ist.hokudai.ac.jp/ thomas/toc/ Lecture 13: Algorithmic Unsolvability The Halting Problem I In the last lecture we have shown
Thomas Zeugmann Hokkaido University Laboratory for Algorithmics http://www-alg.ist.hokudai.ac.jp/ thomas/toc/ Lecture 13: Algorithmic Unsolvability The Halting Problem I In the last lecture we have shown
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
Theory of Computation - Module 4
 Theory of Computation - Module 4 Syllabus Turing Machines Formal definition Language acceptability by TM TM as acceptors, Transducers - designing of TM- Two way infinite TM- Multi tape TM - Universal Turing
Theory of Computation - Module 4 Syllabus Turing Machines Formal definition Language acceptability by TM TM as acceptors, Transducers - designing of TM- Two way infinite TM- Multi tape TM - Universal Turing
where A, B, C N, a Σ, S ϵ is in P iff ϵ L(G), and S does not occur on the right-hand side of any production. 3.6 The Greibach Normal Form
 262 CHAPTER 3. CONTEXT-FREE LANGUAGES AND PDA S 3.6 The Greibach Normal Form Every CFG G can also be converted to an equivalent grammar in Greibach Normal Form (for short, GNF). Acontext-freegrammarG =(V,Σ,P,S)
262 CHAPTER 3. CONTEXT-FREE LANGUAGES AND PDA S 3.6 The Greibach Normal Form Every CFG G can also be converted to an equivalent grammar in Greibach Normal Form (for short, GNF). Acontext-freegrammarG =(V,Σ,P,S)
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages. Foundations of Computer Science Theory
 Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
CS154 Final Examination
 CS154 Final Examination June 7, 2010, 7-10PM Directions: CS154 students: answer all 13 questions on this paper. Those taking CS154N should answer only questions 8-13. The total number of points on this
CS154 Final Examination June 7, 2010, 7-10PM Directions: CS154 students: answer all 13 questions on this paper. Those taking CS154N should answer only questions 8-13. The total number of points on this
NODIA AND COMPANY. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer Science Engineering Theory of Computation. Copyright By NODIA & COMPANY
 No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer
No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Computer
Solution to CS375 Homework Assignment 11 (40 points) Due date: 4/26/2017
 Solution to CS375 Homework Assignment 11 (40 points) Due date: 4/26/2017 1. Find a Greibach normal form for the following given grammar. (10 points) S bab A BAa a B bb Ʌ Solution: (1) Since S does not
Solution to CS375 Homework Assignment 11 (40 points) Due date: 4/26/2017 1. Find a Greibach normal form for the following given grammar. (10 points) S bab A BAa a B bb Ʌ Solution: (1) Since S does not
16.1 Countability. CS125 Lecture 16 Fall 2014
 CS125 Lecture 16 Fall 2014 16.1 Countability Proving the non-existence of algorithms for computational problems can be very difficult. Indeed, we do not know how to prove P NP. So a natural question is
CS125 Lecture 16 Fall 2014 16.1 Countability Proving the non-existence of algorithms for computational problems can be very difficult. Indeed, we do not know how to prove P NP. So a natural question is
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Turing s thesis: (1930) Any computation carried out by mechanical means can be performed by a Turing Machine
 Turing s thesis: (1930) Any computation carried out by mechanical means can be performed by a Turing Machine There is no known model of computation more powerful than Turing Machines Definition of Algorithm:
Turing s thesis: (1930) Any computation carried out by mechanical means can be performed by a Turing Machine There is no known model of computation more powerful than Turing Machines Definition of Algorithm:
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION "Winter" 2018 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi18/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 4.2 Trace high-level descriptions of algorithms for computational problems. Use
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION "Winter" 2018 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/wi18/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 4.2 Trace high-level descriptions of algorithms for computational problems. Use
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Decidability, Undecidability and Reducibility; Codes, Algorithms and Languages CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario,
Computability and Complexity Decidability, Undecidability and Reducibility; Codes, Algorithms and Languages CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario,
Non-emptiness Testing for TMs
 180 5. Reducibility The proof of unsolvability of the halting problem is an example of a reduction: a way of converting problem A to problem B in such a way that a solution to problem B can be used to
180 5. Reducibility The proof of unsolvability of the halting problem is an example of a reduction: a way of converting problem A to problem B in such a way that a solution to problem B can be used to
Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions)
 Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions) 1. Finite Automata & Regular Sets 01. Ans: (a) & (c) Sol: (a) The reversal of a regular set is regular as the reversal of a regular expression
Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions) 1. Finite Automata & Regular Sets 01. Ans: (a) & (c) Sol: (a) The reversal of a regular set is regular as the reversal of a regular expression
What Is a Language? Grammars, Languages, and Machines. Strings: the Building Blocks of Languages
 Do Homework 2. What Is a Language? Grammars, Languages, and Machines L Language Grammar Accepts Machine Strings: the Building Blocks of Languages An alphabet is a finite set of symbols: English alphabet:
Do Homework 2. What Is a Language? Grammars, Languages, and Machines L Language Grammar Accepts Machine Strings: the Building Blocks of Languages An alphabet is a finite set of symbols: English alphabet:
4.2 The Halting Problem
 172 4.2 The Halting Problem The technique of diagonalization was discovered in 1873 by Georg Cantor who was concerned with the problem of measuring the sizes of infinite sets For finite sets we can simply
172 4.2 The Halting Problem The technique of diagonalization was discovered in 1873 by Georg Cantor who was concerned with the problem of measuring the sizes of infinite sets For finite sets we can simply
Limits of Computability
 Limits of Computability Wolfgang Schreiner Wolfgang.Schreiner@risc.jku.at Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC) Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria http://www.risc.jku.at Wolfgang Schreiner
Limits of Computability Wolfgang Schreiner Wolfgang.Schreiner@risc.jku.at Research Institute for Symbolic Computation (RISC) Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria http://www.risc.jku.at Wolfgang Schreiner
Lecture Notes: The Halting Problem; Reductions
 Lecture Notes: The Halting Problem; Reductions COMS W3261 Columbia University 20 Mar 2012 1 Review Key point. Turing machines can be encoded as strings, and other Turing machines can read those strings
Lecture Notes: The Halting Problem; Reductions COMS W3261 Columbia University 20 Mar 2012 1 Review Key point. Turing machines can be encoded as strings, and other Turing machines can read those strings
6.045: Automata, Computability, and Complexity Or, Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Spring, Class 8 Nancy Lynch
 6.045: Automata, Computability, and Complexity Or, Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Spring, 2010 Class 8 Nancy Lynch Today More undecidable problems: About Turing machines: Emptiness, etc. About
6.045: Automata, Computability, and Complexity Or, Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Spring, 2010 Class 8 Nancy Lynch Today More undecidable problems: About Turing machines: Emptiness, etc. About
Decidability (What, stuff is unsolvable?)
 University of Georgia Fall 2014 Outline Decidability Decidable Problems for Regular Languages Decidable Problems for Context Free Languages The Halting Problem Countable and Uncountable Sets Diagonalization
University of Georgia Fall 2014 Outline Decidability Decidable Problems for Regular Languages Decidable Problems for Context Free Languages The Halting Problem Countable and Uncountable Sets Diagonalization
Introduction to Turing Machines. Reading: Chapters 8 & 9
 Introduction to Turing Machines Reading: Chapters 8 & 9 1 Turing Machines (TM) Generalize the class of CFLs: Recursively Enumerable Languages Recursive Languages Context-Free Languages Regular Languages
Introduction to Turing Machines Reading: Chapters 8 & 9 1 Turing Machines (TM) Generalize the class of CFLs: Recursively Enumerable Languages Recursive Languages Context-Free Languages Regular Languages
Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability.
 Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability. A Turing machine is a finite automaton with an infinite memory (tape). Formally, a Turing machine is a 6-tuple M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0,
Final exam study sheet for CS3719 Turing machines and decidability. A Turing machine is a finite automaton with an infinite memory (tape). Formally, a Turing machine is a 6-tuple M = (Q, Σ, Γ, δ, q 0,
CSE 311: Foundations of Computing I Autumn 2014 Practice Final: Section X. Closed book, closed notes, no cell phones, no calculators.
 CSE 311: Foundations of Computing I Autumn 014 Practice Final: Section X YY ZZ Name: UW ID: Instructions: Closed book, closed notes, no cell phones, no calculators. You have 110 minutes to complete the
CSE 311: Foundations of Computing I Autumn 014 Practice Final: Section X YY ZZ Name: UW ID: Instructions: Closed book, closed notes, no cell phones, no calculators. You have 110 minutes to complete the
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course
 Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 3.3, 4.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Give examples of decidable problems.
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 3.3, 4.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Give examples of decidable problems.
CSCE 551: Chin-Tser Huang. University of South Carolina
 CSCE 551: Theory of Computation Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Computation History A computation history of a TM M is a sequence of its configurations C 1, C 2,, C l such
CSCE 551: Theory of Computation Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Computation History A computation history of a TM M is a sequence of its configurations C 1, C 2,, C l such
CS154 Final Examination
 CS154 Final Examination June 7, 2010, 7-10PM Directions: CS154 students: answer all 13 questions on this paper. Those taking CS154N should answer only questions 8-13. The total number of points on this
CS154 Final Examination June 7, 2010, 7-10PM Directions: CS154 students: answer all 13 questions on this paper. Those taking CS154N should answer only questions 8-13. The total number of points on this
Unambiguous Morphic Images of Strings
 Unambiguous Morphic Images of Strings Daniel Reidenbach, University of Kaiserslautern A joint work with: Dominik D. Freydenberger, University of Kaiserslautern Johannes C. Schneider, University of Kaiserslautern
Unambiguous Morphic Images of Strings Daniel Reidenbach, University of Kaiserslautern A joint work with: Dominik D. Freydenberger, University of Kaiserslautern Johannes C. Schneider, University of Kaiserslautern
Context Free Languages. Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6. Languages That Are Not Regular. Non-Regular Languages
 Context Free Languages Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6 Context Free Languages Last Time Decision procedures for FAs Minimum-state DFAs Today The Myhill-Nerode Theorem The Pumping Lemma Context-free
Context Free Languages Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6 Context Free Languages Last Time Decision procedures for FAs Minimum-state DFAs Today The Myhill-Nerode Theorem The Pumping Lemma Context-free
CSCI 2200 Foundations of Computer Science Spring 2018 Quiz 3 (May 2, 2018) SOLUTIONS
 CSCI 2200 Foundations of Computer Science Spring 2018 Quiz 3 (May 2, 2018) SOLUTIONS 1. [6 POINTS] For language L 1 = {0 n 1 m n, m 1, m n}, which string is in L 1? ANSWER: 0001111 is in L 1 (with n =
CSCI 2200 Foundations of Computer Science Spring 2018 Quiz 3 (May 2, 2018) SOLUTIONS 1. [6 POINTS] For language L 1 = {0 n 1 m n, m 1, m n}, which string is in L 1? ANSWER: 0001111 is in L 1 (with n =
CS 373: Theory of Computation. Fall 2010
 CS 373: Theory of Computation Gul Agha Mahesh Viswanathan Fall 2010 1 1 Normal Forms for CFG Normal Forms for Grammars It is typically easier to work with a context free language if given a CFG in a normal
CS 373: Theory of Computation Gul Agha Mahesh Viswanathan Fall 2010 1 1 Normal Forms for CFG Normal Forms for Grammars It is typically easier to work with a context free language if given a CFG in a normal
Theory of Computation
 Theory of Computation Lecture #2 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 1 Lecture 2: Overview Recall some basic definitions from Automata Theory.
Theory of Computation Lecture #2 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 1 Lecture 2: Overview Recall some basic definitions from Automata Theory.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DUNDIGAL 500 043, HYDERABAD COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Course Code : A40509 Class :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DUNDIGAL 500 043, HYDERABAD COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Course Code : A40509 Class :
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Rewriting Systems and Chomsky Grammars CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard
Computability and Complexity Rewriting Systems and Chomsky Grammars CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard
Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7
 Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about
Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about
The View Over The Horizon
 The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
Lecture 12: Mapping Reductions
 Lecture 12: Mapping Reductions October 18, 2016 CS 1010 Theory of Computation Topics Covered 1. The Language EQ T M 2. Mapping Reducibility 3. The Post Correspondence Problem 1 The Language EQ T M The
Lecture 12: Mapping Reductions October 18, 2016 CS 1010 Theory of Computation Topics Covered 1. The Language EQ T M 2. Mapping Reducibility 3. The Post Correspondence Problem 1 The Language EQ T M The
Context-Free Grammars and Languages. Reading: Chapter 5
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
CS 7220 Computational Complexity and Algorithm Analysis
 CS 7220 Computational Complexity and Algorithm Analysis Spring 2016 Section 7: Computability Part IV Undecidability Pascal Hitzler Data Semantics Laboratory Wright State University, Dayton, OH http://www.pascal-hitzler.de
CS 7220 Computational Complexity and Algorithm Analysis Spring 2016 Section 7: Computability Part IV Undecidability Pascal Hitzler Data Semantics Laboratory Wright State University, Dayton, OH http://www.pascal-hitzler.de
ECS 120: Theory of Computation UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, Midterm Exam
 ECS 120: Theory of Computation Handout MT UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, 2012 Midterm Exam Instructions: The exam has six pages, including this cover page, printed out two-sided (no more wasted
ECS 120: Theory of Computation Handout MT UC Davis Phillip Rogaway February 16, 2012 Midterm Exam Instructions: The exam has six pages, including this cover page, printed out two-sided (no more wasted
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Decidability: Church-Turing Thesis
 Decidability: Church-Turing Thesis While there are a countably infinite number of languages that are described by TMs over some alphabet Σ, there are an uncountably infinite number that are not Are there
Decidability: Church-Turing Thesis While there are a countably infinite number of languages that are described by TMs over some alphabet Σ, there are an uncountably infinite number that are not Are there
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages
 Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
NPDA, CFG equivalence
 NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
Fall, 2017 CIS 262. Automata, Computability and Complexity Jean Gallier Solutions of the Practice Final Exam
 Fall, 2017 CIS 262 Automata, Computability and Complexity Jean Gallier Solutions of the Practice Final Exam December 6, 2017 Problem 1 (10 pts). Let Σ be an alphabet. (1) What is an ambiguous context-free
Fall, 2017 CIS 262 Automata, Computability and Complexity Jean Gallier Solutions of the Practice Final Exam December 6, 2017 Problem 1 (10 pts). Let Σ be an alphabet. (1) What is an ambiguous context-free
Pushdown automata. Twan van Laarhoven. Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Radboud University Nijmegen
 Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Undecidable Problems. Z. Sawa (TU Ostrava) Introd. to Theoretical Computer Science May 12, / 65
 Undecidable Problems Z. Sawa (TU Ostrava) Introd. to Theoretical Computer Science May 12, 2018 1/ 65 Algorithmically Solvable Problems Let us assume we have a problem P. If there is an algorithm solving
Undecidable Problems Z. Sawa (TU Ostrava) Introd. to Theoretical Computer Science May 12, 2018 1/ 65 Algorithmically Solvable Problems Let us assume we have a problem P. If there is an algorithm solving
DD2371 Automata Theory
 KTH CSC VT 2008 DD2371 Automata Theory Dilian Gurov Lecture Outline 1. The lecturer 2. Introduction to automata theory 3. Course syllabus 4. Course objectives 5. Course organization 6. First definitions
KTH CSC VT 2008 DD2371 Automata Theory Dilian Gurov Lecture Outline 1. The lecturer 2. Introduction to automata theory 3. Course syllabus 4. Course objectives 5. Course organization 6. First definitions
CS Automata, Computability and Formal Languages
 Automata, Computability and Formal Languages Luc Longpré faculty.utep.edu/longpre 1 - Pg 1 Slides : version 3.1 version 1 A. Tapp version 2 P. McKenzie, L. Longpré version 2.1 D. Gehl version 2.2 M. Csűrös,
Automata, Computability and Formal Languages Luc Longpré faculty.utep.edu/longpre 1 - Pg 1 Slides : version 3.1 version 1 A. Tapp version 2 P. McKenzie, L. Longpré version 2.1 D. Gehl version 2.2 M. Csűrös,
COMP-330 Theory of Computation. Fall Prof. Claude Crépeau. Lecture 1 : Introduction
 COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lecture 1 : Introduction COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite automata
COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lecture 1 : Introduction COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite automata
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
ACS2: Decidability Decidability
 Decidability Bernhard Nebel and Christian Becker-Asano 1 Overview An investigation into the solvable/decidable Decidable languages The halting problem (undecidable) 2 Decidable problems? Acceptance problem
Decidability Bernhard Nebel and Christian Becker-Asano 1 Overview An investigation into the solvable/decidable Decidable languages The halting problem (undecidable) 2 Decidable problems? Acceptance problem
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
CS 125 Section #10 (Un)decidability and Probability November 1, 2016
 CS 125 Section #10 (Un)decidability and Probability November 1, 2016 1 Countability Recall that a set S is countable (either finite or countably infinite) if and only if there exists a surjective mapping
CS 125 Section #10 (Un)decidability and Probability November 1, 2016 1 Countability Recall that a set S is countable (either finite or countably infinite) if and only if there exists a surjective mapping
Part I: Definitions and Properties
 Turing Machines Part I: Definitions and Properties Finite State Automata Deterministic Automata (DFSA) M = {Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F} -- Σ = Symbols -- Q = States -- q 0 = Initial State -- F = Accepting States
Turing Machines Part I: Definitions and Properties Finite State Automata Deterministic Automata (DFSA) M = {Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F} -- Σ = Symbols -- Q = States -- q 0 = Initial State -- F = Accepting States
COMP-330 Theory of Computation. Fall Prof. Claude Crépeau. Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars
 COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
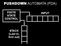 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
Primitive recursive functions: decidability problems
 Primitive recursive functions: decidability problems Armando B. Matos October 24, 2014 Abstract Although every primitive recursive (PR) function is total, many problems related to PR functions are undecidable.
Primitive recursive functions: decidability problems Armando B. Matos October 24, 2014 Abstract Although every primitive recursive (PR) function is total, many problems related to PR functions are undecidable.
Theory of Computer Science
 Theory of Computer Science D1. Turing-Computability Malte Helmert University of Basel April 18, 2016 Overview: Course contents of this course: logic How can knowledge be represented? How can reasoning
Theory of Computer Science D1. Turing-Computability Malte Helmert University of Basel April 18, 2016 Overview: Course contents of this course: logic How can knowledge be represented? How can reasoning
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs
 This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
1 Showing Recognizability
 CSCC63 Worksheet Recognizability and Decidability 1 1 Showing Recognizability 1.1 An Example - take 1 Let Σ be an alphabet. L = { M M is a T M and L(M) }, i.e., that M accepts some string from Σ. Prove
CSCC63 Worksheet Recognizability and Decidability 1 1 Showing Recognizability 1.1 An Example - take 1 Let Σ be an alphabet. L = { M M is a T M and L(M) }, i.e., that M accepts some string from Σ. Prove
Properties of context-free Languages
 Properties of context-free Languages We simplify CFL s. Greibach Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form We prove pumping lemma for CFL s. We study closure properties and decision properties. Some of them remain,
Properties of context-free Languages We simplify CFL s. Greibach Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form We prove pumping lemma for CFL s. We study closure properties and decision properties. Some of them remain,
Undecidability. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]
![Undecidability. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch] Undecidability. Andreas Klappenecker. [based on slides by Prof. Welch]](/thumbs/81/83378912.jpg) Undecidability Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Sources Theory of Computing, A Gentle Introduction, by E. Kinber and C. Smith, Prentice-Hall, 2001 Automata Theory, Languages and
Undecidability Andreas Klappenecker [based on slides by Prof. Welch] 1 Sources Theory of Computing, A Gentle Introduction, by E. Kinber and C. Smith, Prentice-Hall, 2001 Automata Theory, Languages and
CSCI3390-Lecture 6: An Undecidable Problem
 CSCI3390-Lecture 6: An Undecidable Problem September 21, 2018 1 Summary The language L T M recognized by the universal Turing machine is not decidable. Thus there is no algorithm that determines, yes or
CSCI3390-Lecture 6: An Undecidable Problem September 21, 2018 1 Summary The language L T M recognized by the universal Turing machine is not decidable. Thus there is no algorithm that determines, yes or
Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages
 Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
CSCE 551: Chin-Tser Huang. University of South Carolina
 CSCE 551: Theory of Computation Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Church-Turing Thesis The definition of the algorithm came in the 1936 papers of Alonzo Church h and Alan
CSCE 551: Theory of Computation Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Church-Turing Thesis The definition of the algorithm came in the 1936 papers of Alonzo Church h and Alan
