CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent. We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa.
|
|
|
- Sibyl Richardson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We provide algorithms to convert a CFG to a PDA and vice versa.
2 CFGs and PDAs are Equivalent We now prove that a language is generated by some CFG if and only if it is accepted by some PDA The proof consists of two conversions. Goddard 8b: 2
3 Conversion from CFG to PDA For the conversion from CFG to PDA, the idea is that the PDA guesses the leftmost derivation and checks that it is correct. (proof by simulation) Each step of the derivation is a string. The machine guesses the next step. The problem is to do this with only a stack. Terminals to the left of leftmost variable are not stored, but are matched with input string. Only current string from leftmost variable onwards is stored on stack, with leftmost symbol on top. Goddard 8b: 3
4 Operating the PDA The PDA starts with start variable on the stack. At each step: If stack-top is a variable, then PDA guesses a production and replaces variable by RH of that production. If stack-top is a terminal, then PDA pops it and reads one symbol from input and checks that the two match. Accept if and only if reach empty stack at end of string. (Note that PDA not guaranteed to halt.) Goddard 8b: 4
5 Example ε The sequence of stacks for the accepting branch of the PDA for starts: stack to read Goddard 8b: 5
6 An Alternative Representation of PDA We show next how to convert from PDA to CFG. This procedure is slightly easier if PDA is in another form: where only the reading states are retained and stack operations are part of the transitions. Goddard 8b: 6
7 Example Here is earlier PDA for 0 n 1 n redrawn: 0 push x 1 pop x 1 pop x pop F G H Goddard 8b: 7
8 Formal Definition In this light, a formal definition of a PDA is a 7-tuple (Q, Σ, Γ, q 0, h a,, δ) where: Q is finite set of states; Σ is finite input alphabet; Γ is finite stack alphabet; q 0 is start state; h a is accept state; is empty-stack and end-of-string symbol; and δ is transition function. The transition function needs more explanation... Goddard 8b: 8
9 The Transition Function The transition function is a function from Q (Γ { }) (Σ {ε, }) to finite subsets of Q (Γ { }). That is, it looks at current state, current stacktop symbol, and (possibly) input symbol; then it updates the state and replaces the current stack-top symbol by a string of symbols: pop = replace stack-top symbol by nothing; push = replace stack-top symbol by itself and a new symbol. Goddard 8b: 9
10 Example For example, δ(q, A, a) = {(p, AB)} means that in state q with A on stack-top, on reading a the PDA pushes symbol B and changes to state p. Goddard 8b: 10
11 Conversion from PDA to CFG The idea for the conversion from PDA to CFG is to make each step in a derivation correspond to a move by the PDA. This is far from trivial! We use the earlier alternative representation. Further, we assume that: (a) stack of the PDA M is empty if and only M is in the accept state; (b) every move is either a push of a single symbol or a pop of a single symbol (Exercise). Goddard 8b: 11
12 The Variables are Triples The variables of the CFG will be all the ordered triples q A p where q, p are states of the PDA, and A is a symbol from the stack alphabet. Goddard 8b: 12
13 Invariant for Triples We construct the CFG such that for all strings w: q A p = w M can go from state q to p while reading w with the net effect of popping symbol A. [q 0,, h a ] will be start variable for the CFG: it will generate string w if and only if one can go from q 0 to h a while reading w and popping the emptystack symbol; that is, w is accepted. Goddard 8b: 13
14 The Productions: Pops The two types of moves of the PDA become productions. Consider a pop move; say (p, ε) δ(q, A, a). That is, in state q the PDA can pop symbol A while reading a and changing to state p (a can be ε). Then we add one production: q A p a Goddard 8b: 14
15 The Productions: Pushes Consider a push move; say (p, AB) δ(q, A, a). That is, in state q with A on stack-top, one can push symbol B while reading a and changing to state p. Then we add the collection of productions: q A r a p B s s A r for every state r and s. Essentially, there are two ways that effectively erase the stack-top symbol: (a) pop it, or (b) push something, and then later erase both symbols. Goddard 8b: 15
16 Proof Details Omitted The rest of the proof is to show that every derivation in this grammar corresponds to a legitimate computation of the PDA. Goddard 8b: 16
17 Example Conversion We use the PDA for {0 n 1 n } from before. 0 push x 1 pop x F 1 pop x G pop H Here goes... Goddard 8b: 17
18 Example CFG tart symbol: F H Popping occurs in three places: F x G 1 G x G 1 G H ε Pushing yields 18 productions of the form F A r 0 F x s s A r for each A {x, } and r, s {F, G, H}. We could stop, but one can simplify: Goddard 8b: 18
19 implification Omit productions that produce triples that are never LH; this leaves 1) F x F 0 F x F F x F 2) F x G 0 F x F F x G 3) F x H 0 F x F F x H 4) F F 0 F x F F F 5) F G 0 F x F F G 6) F H 0 F x F F H 7) F x G 0 F x G G x G 8) F H 0 F x G G H F x F is also unusable (why?); omit its rules. Goddard 8b: 19
20 Final CFG This leaves us with the CFG with start variable F H : F x G 1 G x G 1 G H ε F x G 0 F x G G x G F H 0 F x G G H Whew! Goddard 8b: 20
21 ummary There is an algorithm to convert a CFG to an equivalent PDA: the PDA guesses the leftmost derivation. The algorithm to convert from PDA to CFG is more complex. Goddard 8b: 21
(pp ) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2)
 (pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp ) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2)
 (pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
(pp. 117-124) PDAs and CFGs (Sec. 2.2) A language is context free iff all strings in L can be generated by some context free grammar Theorem 2.20: L is Context Free iff a PDA accepts it I.e. if L is context
October 6, Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Gramm
 Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
Equivalence of Pushdown Automata with Context-Free Grammar October 6, 2013 Motivation Motivation CFG and PDA are equivalent in power: a CFG generates a context-free language and a PDA recognizes a context-free
MTH401A Theory of Computation. Lecture 17
 MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42
 Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability Pushdown Automata K. Krithivasan and R. Rama Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42 Introduction We have considered
Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability Pushdown Automata K. Krithivasan and R. Rama Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42 Introduction We have considered
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture)
 Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA
 Syllabus R09 Regulation UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA The context free languages have a type of automaton that defined them. This automaton, called a pushdown automaton, is an extension of the nondeterministic
Syllabus R09 Regulation UNIT-VI PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA The context free languages have a type of automaton that defined them. This automaton, called a pushdown automaton, is an extension of the nondeterministic
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Define push down automata Trace the computation of a push down automaton Design
Pushdown Automata. Reading: Chapter 6
 Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Accept or reject. Stack
 Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Pushdown Automata CS351 Just as a DFA was equivalent to a regular expression, we have a similar analogy for the context-free grammar. A pushdown automata (PDA) is equivalent in power to contextfree grammars.
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course
 Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Outline. CS21 Decidability and Tractability. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA. Machine view of FA.
 Outline CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 5 January 16, 219 and Languages equivalence of NPDAs and CFGs non context-free languages January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture 5 1 January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture
Outline CS21 Decidability and Tractability Lecture 5 January 16, 219 and Languages equivalence of NPDAs and CFGs non context-free languages January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture 5 1 January 16, 219 CS21 Lecture
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata Salil Vadhan October 4, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.2. Another example of a CFG (with proof) L = {x {a, b} : x has the same # of a s and
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: Ambiguity, Pushdown Automata Salil Vadhan October 4, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.2. Another example of a CFG (with proof) L = {x {a, b} : x has the same # of a s and
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u,
 1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Miscellaneous. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Miscellaneous Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms and inverse homomorphisms.
Miscellaneous Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms and inverse homomorphisms.
Automata Theory (2A) Young Won Lim 5/31/18
 Automata Theory (2A) Copyright (c) 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Automata Theory (2A) Copyright (c) 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x where
 Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
CPSC 421: Tutorial #1
 CPSC 421: Tutorial #1 October 14, 2016 Set Theory. 1. Let A be an arbitrary set, and let B = {x A : x / x}. That is, B contains all sets in A that do not contain themselves: For all y, ( ) y B if and only
CPSC 421: Tutorial #1 October 14, 2016 Set Theory. 1. Let A be an arbitrary set, and let B = {x A : x / x}. That is, B contains all sets in A that do not contain themselves: For all y, ( ) y B if and only
Pushdown Automata: Introduction (2)
 Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
Pushdown Automata: Introduction Pushdown automaton (PDA) M = (K, Σ, Γ,, s, A) where K is a set of states Σ is an input alphabet Γ is a set of stack symbols s K is the start state A K is a set of accepting
CISC4090: Theory of Computation
 CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
Introduction to Theory of Computing
 CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
Please give details of your answer. A direct answer without explanation is not counted.
 Please give details of your answer. A direct answer without explanation is not counted. Your answers must be in English. Please carefully read problem statements. During the exam you are not allowed to
Please give details of your answer. A direct answer without explanation is not counted. Your answers must be in English. Please carefully read problem statements. During the exam you are not allowed to
Push-down Automata = FA + Stack
 Push-down Automata = FA + Stack PDA Definition A push-down automaton M is a tuple M = (Q,, Γ, δ, q0, F) where Q is a finite set of states is the input alphabet (of terminal symbols, terminals) Γ is the
Push-down Automata = FA + Stack PDA Definition A push-down automaton M is a tuple M = (Q,, Γ, δ, q0, F) where Q is a finite set of states is the input alphabet (of terminal symbols, terminals) Γ is the
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2017 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp17/cse105-ab/ Review of CFG, CFL, ambiguity What is the language generated by the CFG below: G 1 = ({S,T 1,T 2 }, {0,1,2}, { S
Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23)
 Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
Chapter 6 Pushdown Automata (2015/11/23) Sagrada Familia, Barcelona, Spain Outline 6.0 Introduction 6.1 Definition of PDA 6.2 The Language of a PDA 6.3 Euivalence of PDA s and CFG s 6.4 Deterministic PDA
Turing Machines. Our most powerful model of a computer is the Turing Machine. This is an FA with an infinite tape for storage.
 Turing Machines Our most powerful model of a computer is the Turing Machine. This is an FA with an infinite tape for storage. A Turing Machine A Turing Machine (TM) has three components: An infinite tape
Turing Machines Our most powerful model of a computer is the Turing Machine. This is an FA with an infinite tape for storage. A Turing Machine A Turing Machine (TM) has three components: An infinite tape
Homework. Context Free Languages. Announcements. Before We Start. Languages. Plan for today. Final Exam Dates have been announced.
 Homework Context Free Languages PDAs and CFLs Homework #3 returned Homework #4 due today Homework #5 Pg 169 -- Exercise 4 Pg 183 -- Exercise 4c,e,i (use JFLAP) Pg 184 -- Exercise 10 Pg 184 -- Exercise
Homework Context Free Languages PDAs and CFLs Homework #3 returned Homework #4 due today Homework #5 Pg 169 -- Exercise 4 Pg 183 -- Exercise 4c,e,i (use JFLAP) Pg 184 -- Exercise 10 Pg 184 -- Exercise
Equivalence of CFG s and PDA s
 Equivalence of CFG s and PDA s Mridul Aanjaneya Stanford University July 24, 2012 Mridul Aanjaneya Automata Theory 1/ 53 Recap: Pushdown Automata A PDA is an automaton equivalent to the CFG in language-defining
Equivalence of CFG s and PDA s Mridul Aanjaneya Stanford University July 24, 2012 Mridul Aanjaneya Automata Theory 1/ 53 Recap: Pushdown Automata A PDA is an automaton equivalent to the CFG in language-defining
CSCC63 Worksheet Turing Machines
 1 An Example CSCC63 Worksheet Turing Machines Goal. Design a turing machine, M that accepts only strings of the form {w#w w {0, 1} }. Idea. Describe in words how the machine would work. Read first symbol
1 An Example CSCC63 Worksheet Turing Machines Goal. Design a turing machine, M that accepts only strings of the form {w#w w {0, 1} }. Idea. Describe in words how the machine would work. Read first symbol
Undecidable Problems and Reducibility
 University of Georgia Fall 2014 Reducibility We show a problem decidable/undecidable by reducing it to another problem. One type of reduction: mapping reduction. Definition Let A, B be languages over Σ.
University of Georgia Fall 2014 Reducibility We show a problem decidable/undecidable by reducing it to another problem. One type of reduction: mapping reduction. Definition Let A, B be languages over Σ.
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3
 SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
SCHEME FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Max Marks: 40 Subject& Code: Automata Theory & Computability (15CS54) Sem: V ISE (A & B) Note: Answer any FIVE full questions, choosing one full question from each
Pushdown automata. Twan van Laarhoven. Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Radboud University Nijmegen
 Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Outline 1 PCP. 2 Decision problems about CFGs. M.Mitra (ISI) Post s Correspondence Problem 1 / 10
 Outline 1 PCP 2 Decision problems about CFGs M.Mitra (ISI) Post s Correspondence Problem 1 / 10 PCP reduction Given: M, w in encoded form To construct: an instance (A, B) of MPCP such that M accepts w
Outline 1 PCP 2 Decision problems about CFGs M.Mitra (ISI) Post s Correspondence Problem 1 / 10 PCP reduction Given: M, w in encoded form To construct: an instance (A, B) of MPCP such that M accepts w
Part I: Definitions and Properties
 Turing Machines Part I: Definitions and Properties Finite State Automata Deterministic Automata (DFSA) M = {Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F} -- Σ = Symbols -- Q = States -- q 0 = Initial State -- F = Accepting States
Turing Machines Part I: Definitions and Properties Finite State Automata Deterministic Automata (DFSA) M = {Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F} -- Σ = Symbols -- Q = States -- q 0 = Initial State -- F = Accepting States
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
CS 301. Lecture 18 Decidable languages. Stephen Checkoway. April 2, 2018
 CS 301 Lecture 18 Decidable languages Stephen Checkoway April 2, 2018 1 / 26 Decidable language Recall, a language A is decidable if there is some TM M that 1 recognizes A (i.e., L(M) = A), and 2 halts
CS 301 Lecture 18 Decidable languages Stephen Checkoway April 2, 2018 1 / 26 Decidable language Recall, a language A is decidable if there is some TM M that 1 recognizes A (i.e., L(M) = A), and 2 halts
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA)
 CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
CSE 211. Pushdown Automata. CSE 211 (Theory of Computation) Atif Hasan Rahman
 CSE 211 Pushdown Automata CSE 211 (Theory of Computation) Atif Hasan Rahman Lecturer Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology Adapted from slides
CSE 211 Pushdown Automata CSE 211 (Theory of Computation) Atif Hasan Rahman Lecturer Department of Computer Science and Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology Adapted from slides
Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL
 Theorem 14.1 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL Statement: Given a CFL L and string w, there is a decision procedure that determines whether w L. Proof: By construction. 1. Proof using a grammar
Theorem 14.1 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL Statement: Given a CFL L and string w, there is a decision procedure that determines whether w L. Proof: By construction. 1. Proof using a grammar
Context-Free Languages
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Pushdown Automata Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.2. Finite automaton 1 / 13
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Pushdown Automata Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.2. Finite automaton 1 / 13
Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. Pushdown Automata. The stack
 A pushdown automata (PDA) is essentially: An NFA with a stack A move of a PDA will depend upon Current state of the machine Current symbol being read in Current symbol popped off the top of the stack With
A pushdown automata (PDA) is essentially: An NFA with a stack A move of a PDA will depend upon Current state of the machine Current symbol being read in Current symbol popped off the top of the stack With
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- IV. 4.1 Push Down Automata. 4.2 The Formal Definition of Pushdown Automata. EXAMPLES for PDA. 4.3 The languages of PDA
 TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- IV 4.1 Push Down Automata 4.2 The Formal Definition of Pushdown Automata EXAMPLES for PDA 4.3 The languages of PDA 4.3.1 Acceptance by final state 4.3.2 Acceptance by empty stack
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- IV 4.1 Push Down Automata 4.2 The Formal Definition of Pushdown Automata EXAMPLES for PDA 4.3 The languages of PDA 4.3.1 Acceptance by final state 4.3.2 Acceptance by empty stack
Busch Complexity Lectures: Turing s Thesis. Costas Busch - LSU 1
 Busch Complexity Lectures: Turing s Thesis Costas Busch - LSU 1 Turing s thesis (1930): Any computation carried out by mechanical means can be performed by a Turing Machine Costas Busch - LSU 2 Algorithm:
Busch Complexity Lectures: Turing s Thesis Costas Busch - LSU 1 Turing s thesis (1930): Any computation carried out by mechanical means can be performed by a Turing Machine Costas Busch - LSU 2 Algorithm:
Intro to Theory of Computation
 Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Intro to Theory of Computation LECTURE 7 Last time: Proving a language is not regular Pushdown automata (PDAs) Today: Context-free grammars (CFG) Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs Sofya Raskhodnikova 1/31/2016
Lecture 13: Turing Machine
 Lecture 13: Turing Machine Instructor: Ketan Mulmuley Scriber: Yuan Li February 19, 2015 Turing machine is an abstract machine which in principle can simulate any computation in nature. Church-Turing Thesis:
Lecture 13: Turing Machine Instructor: Ketan Mulmuley Scriber: Yuan Li February 19, 2015 Turing machine is an abstract machine which in principle can simulate any computation in nature. Church-Turing Thesis:
Pushdown Automata (PDA) The structure and the content of the lecture is based on
 Pushdown Automata (PDA) The structure and the content of the lecture is based on http://www.eecs.wsu.edu/~ananth/cpts317/lectures/index.htm 1 Excursion: Previous lecture n Context-free grammar G=(V,T,P,S),
Pushdown Automata (PDA) The structure and the content of the lecture is based on http://www.eecs.wsu.edu/~ananth/cpts317/lectures/index.htm 1 Excursion: Previous lecture n Context-free grammar G=(V,T,P,S),
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Design a PDA and a CFG for a given language Give informal description for a PDA,
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 2 Design a PDA and a CFG for a given language Give informal description for a PDA,
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION
 CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 3.3, 4.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Give examples of decidable problems.
CSE 105 THEORY OF COMPUTATION Spring 2016 http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse105-ab/ Today's learning goals Sipser Ch 3.3, 4.1 State and use the Church-Turing thesis. Give examples of decidable problems.
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 10/22, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Theory of Computation
 Theory of Computation Lecture #10 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 43 Lecture 10: Overview Linear Bounded Automata Acceptance Problem for LBAs
Theory of Computation Lecture #10 Sarmad Abbasi Virtual University Sarmad Abbasi (Virtual University) Theory of Computation 1 / 43 Lecture 10: Overview Linear Bounded Automata Acceptance Problem for LBAs
Pushdown Automata. Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation. Chia-Ping Chen
 Pushdown Automata Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung, Taiwan ROC Pushdown Automata p. 1
Pushdown Automata Notes on Automata and Theory of Computation Chia-Ping Chen Department of Computer Science and Engineering National Sun Yat-Sen University Kaohsiung, Taiwan ROC Pushdown Automata p. 1
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
C6.2 Push-Down Automata
 Theory of Computer Science April 5, 2017 C6. Context-free Languages: Push-down Automata Theory of Computer Science C6. Context-free Languages: Push-down Automata Malte Helmert University of Basel April
Theory of Computer Science April 5, 2017 C6. Context-free Languages: Push-down Automata Theory of Computer Science C6. Context-free Languages: Push-down Automata Malte Helmert University of Basel April
Formal Definition of a Finite Automaton. August 26, 2013
 August 26, 2013 Why a formal definition? A formal definition is precise: - It resolves any uncertainties about what is allowed in a finite automaton such as the number of accept states and number of transitions
August 26, 2013 Why a formal definition? A formal definition is precise: - It resolves any uncertainties about what is allowed in a finite automaton such as the number of accept states and number of transitions
Context-free Languages and Pushdown Automata
 Context-free Languages and Pushdown Automata Finite Automata vs CFLs E.g., {a n b n } CFLs Regular From earlier results: Languages every regular language is a CFL but there are CFLs that are not regular
Context-free Languages and Pushdown Automata Finite Automata vs CFLs E.g., {a n b n } CFLs Regular From earlier results: Languages every regular language is a CFL but there are CFLs that are not regular
Computational Models: Class 5
 Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
CFG and PDA accept the same languages
 Automata and Formal Languages CFG and PDA accept the same languages Sipser pages 115-122 Lecture 14 Tim Sheard 1 Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs The equivalence is expressed by two theorems. Theorem 1. Every
Automata and Formal Languages CFG and PDA accept the same languages Sipser pages 115-122 Lecture 14 Tim Sheard 1 Equivalence of CFGs and PDAs The equivalence is expressed by two theorems. Theorem 1. Every
Theory of Computation (IX) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IX) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review The Definition of Algorithm Polynomials and their roots A polynomial is a sum of terms, where each term is a product of certain variables and
Theory of Computation (IX) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review The Definition of Algorithm Polynomials and their roots A polynomial is a sum of terms, where each term is a product of certain variables and
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET
 THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
CS154 Final Examination
 CS154 Final Examination June 7, 2010, 7-10PM Directions: CS154 students: answer all 13 questions on this paper. Those taking CS154N should answer only questions 8-13. The total number of points on this
CS154 Final Examination June 7, 2010, 7-10PM Directions: CS154 students: answer all 13 questions on this paper. Those taking CS154N should answer only questions 8-13. The total number of points on this
Languages, regular languages, finite automata
 Notes on Computer Theory Last updated: January, 2018 Languages, regular languages, finite automata Content largely taken from Richards [1] and Sipser [2] 1 Languages An alphabet is a finite set of characters,
Notes on Computer Theory Last updated: January, 2018 Languages, regular languages, finite automata Content largely taken from Richards [1] and Sipser [2] 1 Languages An alphabet is a finite set of characters,
Introduction to Languages and Computation
 Introduction to Languages and Computation George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 400 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Languages and Computation July 2014
Introduction to Languages and Computation George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 400 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Languages and Computation July 2014
Decidability (What, stuff is unsolvable?)
 University of Georgia Fall 2014 Outline Decidability Decidable Problems for Regular Languages Decidable Problems for Context Free Languages The Halting Problem Countable and Uncountable Sets Diagonalization
University of Georgia Fall 2014 Outline Decidability Decidable Problems for Regular Languages Decidable Problems for Context Free Languages The Halting Problem Countable and Uncountable Sets Diagonalization
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata
 Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata 1. What is a Turing Machine? A Turing Machine is an accepting device which accepts the languages (recursively enumerable set) generated by type
Theory of Computation Turing Machine and Pushdown Automata 1. What is a Turing Machine? A Turing Machine is an accepting device which accepts the languages (recursively enumerable set) generated by type
Homework Assignment 6 Answers
 Homework Assignment 6 Answers CSCI 2670 Introduction to Theory of Computing, Fall 2016 December 2, 2016 This homework assignment is about Turing machines, decidable languages, Turing recognizable languages,
Homework Assignment 6 Answers CSCI 2670 Introduction to Theory of Computing, Fall 2016 December 2, 2016 This homework assignment is about Turing machines, decidable languages, Turing recognizable languages,
Lecture 17: Language Recognition
 Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Solution Scoring: SD Reg exp.: a(a
 MA/CSSE 474 Exam 3 Winter 2013-14 Name Solution_with explanations Section: 02(3 rd ) 03(4 th ) 1. (28 points) For each of the following statements, circle T or F to indicate whether it is True or False.
MA/CSSE 474 Exam 3 Winter 2013-14 Name Solution_with explanations Section: 02(3 rd ) 03(4 th ) 1. (28 points) For each of the following statements, circle T or F to indicate whether it is True or False.
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing
 CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tale of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set alger relations, functions) (read Chapters
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Tale of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set alger relations, functions) (read Chapters
COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism
 COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism Kurtuluş Küllü March 2018 The FA we saw until now were deterministic FA (DFA) in the sense that for each state and input symbol there was exactly
COM364 Automata Theory Lecture Note 2 - Nondeterminism Kurtuluş Küllü March 2018 The FA we saw until now were deterministic FA (DFA) in the sense that for each state and input symbol there was exactly
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016
 CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
CSCI 2200 Foundations of Computer Science Spring 2018 Quiz 3 (May 2, 2018) SOLUTIONS
 CSCI 2200 Foundations of Computer Science Spring 2018 Quiz 3 (May 2, 2018) SOLUTIONS 1. [6 POINTS] For language L 1 = {0 n 1 m n, m 1, m n}, which string is in L 1? ANSWER: 0001111 is in L 1 (with n =
CSCI 2200 Foundations of Computer Science Spring 2018 Quiz 3 (May 2, 2018) SOLUTIONS 1. [6 POINTS] For language L 1 = {0 n 1 m n, m 1, m n}, which string is in L 1? ANSWER: 0001111 is in L 1 (with n =
ECS 120 Lesson 15 Turing Machines, Pt. 1
 ECS 120 Lesson 15 Turing Machines, Pt. 1 Oliver Kreylos Wednesday, May 2nd, 2001 Before we can start investigating the really interesting problems in theoretical computer science, we have to introduce
ECS 120 Lesson 15 Turing Machines, Pt. 1 Oliver Kreylos Wednesday, May 2nd, 2001 Before we can start investigating the really interesting problems in theoretical computer science, we have to introduce
How to Pop a Deep PDA Matters
 How to Pop a Deep PDA Matters Peter Leupold Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science Kyoto Sangyo University Kyoto 603-8555, Japan email:leupold@cc.kyoto-su.ac.jp Abstract Deep PDA are push-down automata
How to Pop a Deep PDA Matters Peter Leupold Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science Kyoto Sangyo University Kyoto 603-8555, Japan email:leupold@cc.kyoto-su.ac.jp Abstract Deep PDA are push-down automata
Turing Machines (TM) Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM) Nondeterministic Turing Machine (NDTM)
 Turing Machines (TM) Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM) Nondeterministic Turing Machine (NDTM) 1 Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM).. B B 0 1 1 0 0 B B.. Finite Control Two-way, infinite tape, broken into
Turing Machines (TM) Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM) Nondeterministic Turing Machine (NDTM) 1 Deterministic Turing Machine (DTM).. B B 0 1 1 0 0 B B.. Finite Control Two-way, infinite tape, broken into
Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions
 Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions Annotated version with some (sometimes rather sketchy) answers and notes. This is a collection of sample theory bridge exam questions. This is just to get some idea
Theory Bridge Exam Example Questions Annotated version with some (sometimes rather sketchy) answers and notes. This is a collection of sample theory bridge exam questions. This is just to get some idea
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction) Objectives This lecture shows more undecidable languages Our proof is not based on diagonalization Instead, we reduce the problem
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 14: Computability V (Prove by Reduction) Objectives This lecture shows more undecidable languages Our proof is not based on diagonalization Instead, we reduce the problem
Languages. Non deterministic finite automata with ε transitions. First there was the DFA. Finite Automata. Non-Deterministic Finite Automata (NFA)
 Languages Non deterministic finite automata with ε transitions Recall What is a language? What is a class of languages? Finite Automata Consists of A set of states (Q) A start state (q o ) A set of accepting
Languages Non deterministic finite automata with ε transitions Recall What is a language? What is a class of languages? Finite Automata Consists of A set of states (Q) A start state (q o ) A set of accepting
The Idea of a Pushdown Automaton
 Pushdown Automata 5DV037 Fundamentals of Computer Science Umeå University Department of Computing Science Stephen J. Hegner hegner@cs.umu.se http://www.cs.umu.se/~hegner The Idea of a Pushdown Automaton
Pushdown Automata 5DV037 Fundamentals of Computer Science Umeå University Department of Computing Science Stephen J. Hegner hegner@cs.umu.se http://www.cs.umu.se/~hegner The Idea of a Pushdown Automaton
Turing Machines. Nicholas Geis. February 5, 2015
 Turing Machines Nicholas Geis February 5, 2015 Disclaimer: This portion of the notes does not talk about Cellular Automata or Dynamical Systems, it talks about turing machines, however this will lay the
Turing Machines Nicholas Geis February 5, 2015 Disclaimer: This portion of the notes does not talk about Cellular Automata or Dynamical Systems, it talks about turing machines, however this will lay the
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska
 cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 14 SMALL REVIEW FOR FINAL SOME Y/N QUESTIONS Q1 Given Σ =, there is L over Σ Yes: = {e} and L = {e} Σ Q2 There are uncountably
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 14 SMALL REVIEW FOR FINAL SOME Y/N QUESTIONS Q1 Given Σ =, there is L over Σ Yes: = {e} and L = {e} Σ Q2 There are uncountably
Theory of Computation - Module 3
 Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Theory of Computation
 Thomas Zeugmann Hokkaido University Laboratory for Algorithmics http://www-alg.ist.hokudai.ac.jp/ thomas/toc/ Lecture 3: Finite State Automata Motivation In the previous lecture we learned how to formalize
Thomas Zeugmann Hokkaido University Laboratory for Algorithmics http://www-alg.ist.hokudai.ac.jp/ thomas/toc/ Lecture 3: Finite State Automata Motivation In the previous lecture we learned how to formalize
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules).
 Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Solutions to Old Final Exams (For Fall 2007)
 Solutions to Old Final Exams (For Fall 2007) CS 381 (Fall 2002, Fall 2004, Fall 2005, Fall 2006) Yogi Sharma Disclaimer: I, Yogi Sharma, do not claim these solution to be complete, or even to be absolutely
Solutions to Old Final Exams (For Fall 2007) CS 381 (Fall 2002, Fall 2004, Fall 2005, Fall 2006) Yogi Sharma Disclaimer: I, Yogi Sharma, do not claim these solution to be complete, or even to be absolutely
5 Context-Free Languages
 CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
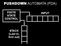 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
What languages are Turing-decidable? What languages are not Turing-decidable? Is there a language that isn t even Turingrecognizable?
 } We ll now take a look at Turing Machines at a high level and consider what types of problems can be solved algorithmically and what types can t: What languages are Turing-decidable? What languages are
} We ll now take a look at Turing Machines at a high level and consider what types of problems can be solved algorithmically and what types can t: What languages are Turing-decidable? What languages are
Pushdown Automata. Chapter 12
 Pushdown Automata Chapter 12 Recognizing Context-Free Languages We need a device similar to an FSM except that it needs more power. The insight: Precisely what it needs is a stack, which gives it an unlimited
Pushdown Automata Chapter 12 Recognizing Context-Free Languages We need a device similar to an FSM except that it needs more power. The insight: Precisely what it needs is a stack, which gives it an unlimited
CpSc 421 Final Exam December 15, 2006
 CpSc 421 Final Exam December 15, 2006 Do problem zero and six of problems 1 through 9. If you write down solutions for more that six problems, clearly indicate those that you want graded. Note that problems
CpSc 421 Final Exam December 15, 2006 Do problem zero and six of problems 1 through 9. If you write down solutions for more that six problems, clearly indicate those that you want graded. Note that problems
Fundamentele Informatica II
 Fundamentele Informatica II Answer to selected exercises 5 John C Martin: Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation M.M. Bonsangue (and J. Kleijn) Fall 2011 5.1.a (q 0, ab, Z 0 ) (q 1, b,
Fundamentele Informatica II Answer to selected exercises 5 John C Martin: Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation M.M. Bonsangue (and J. Kleijn) Fall 2011 5.1.a (q 0, ab, Z 0 ) (q 1, b,
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Push-Down Automata CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard Janicki Computability
Computability and Complexity Push-Down Automata CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard Janicki Computability
Turing Machines. The Language Hierarchy. Context-Free Languages. Regular Languages. Courtesy Costas Busch - RPI 1
 Turing Machines a n b n c The anguage Hierarchy n? ww? Context-Free anguages a n b n egular anguages a * a *b* ww Courtesy Costas Busch - PI a n b n c n Turing Machines anguages accepted by Turing Machines
Turing Machines a n b n c The anguage Hierarchy n? ww? Context-Free anguages a n b n egular anguages a * a *b* ww Courtesy Costas Busch - PI a n b n c n Turing Machines anguages accepted by Turing Machines
