(a) Use washer cross sections: a washer has
|
|
|
- Franklin Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 8 V / (sec tan ) / / / / [ tan sec tan ] / / (sec sec tan + tan ) + tan sec / + A( ) s w (sec tan ), and / V (sec tan ), which b / same method as in part (a) equals A cross section has width w and area w r The volume is 8 A cross section has width w and area s w ( ) This volume is 8 ( ) Since the diameter of the circular base of the solid etends from to, for a diameter of and a radius of, the solid has the same cross sections as the right circular cone The volumes are equal b Cavalieri s Theorem (a) The volume is the same as if the square had moved without twisting: V Ah s h Still s h : the lateral distribution of the square cross sections doesn t affect the volume That s Cavalieri s Volume Theorem The functions intersect at (, 8) (a) Use washer cross sections: a washer has inner radius r, outer radius R, and area A( ) ( R r ) ( ) The volume is 7 ( ) 7 Use clindrical shells: a shell has a radius / 8 and height The volumeis 8 8 / ( ) 8 / / / 7 / The functions intersect at (, ) and (, ) (a) Use clindrical shells: A shell has radius and height The volume is ( )( ) Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
2 7 Use clindrical shells: a shell has radius and height The volume is ( )( ) ( + ) + The intersection points are,,,, and(, ) (a) A washer has inner radius radius R, and area r, outer ( R r ) The volume is 8 A shell has radius and height The volume is ( ) / / 8 Section 8 7 Use clindrical shells: a shell has radius and height The volume is, which from part (a) is sin [ cos ] 9 (a) A cross section has radius r and area A( ) r ( ) The volume is ( ) cm cm 8 g cm ( / ) 9 g (a) A cross section has radius r and area r The volume is [ ] (a) dv Vh ( ) Ahdh ( ), so Ah ( ) dh dv dv dh dh Ah ( ), dt dh dt dt dh dv so dt A( h) dt For h, the area is () 8, dh units units so dt 8 sec 8 sec (sin ) 8 (a) For <, f( ) sin For, f() sin sin, so f() sin for The remaining solid is that swept out b the shaded region in revolution Use clindrical shells: a shell has radius and Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
3 8 Section 8 height r The volume is r ( ) r r r ( r ) r ( 8) The answer is independent of r Partition the appropriate interval in the ais of revolution and measure the radius r ( ) of the shadow region at these points Then use an approimation such as the trapezoidal rule to b estimate the integral r ( ) a Solve a : This is true at a For revolution about the -ais, a cross section has radius r a and area A ( ) r ( a ) ( a a + ) The volume is a ( a a + ) a a a + a For revolution about the -ais, a clindrical shell has radius and height a The volume is a a ( )( a ) a a Setting the two volumes equal, a a ields a, so a The slant height s of a tin horizontal slice can be written as s + + ( g ( )) So the surface area is approimated b the Riemann 7 8 n sum g( k ) + ( g ( )) The limit of k that is the integral g ( ), and + + g ( ), and + ( ) ( + ) ( ) 8 9 g ( ), and ( + ) / / / + / / + Using NINT, this evaluates to g ( ), and 8 / + 8 / / 8 / 997 Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
4 Section f ( ), and + ( ) + evaluates, using NINT, to f ( ), and ( ) + ( ) evaluates, using NINT, to 877 f ( ), and [ ] 8 + f ( ), and / + / / 9 9 True; b definition False; the volume is given b e A; V (ln( )) B; V ( ) 8 D 9 A cross section has radius r c sin and area A ( ) r ( c sin ) ( c csin+ sin ) The volume is ( c csin + sin ) c ccos + sin c c+ c c c+ (a) Solve d c c+ dc c c c This value of c gives a minimum for V av because > dc Then the volume is + Since the derivative with respect to c is not zero anwhere else besides c, the maimum must occur at c or c The volume for c is 9, and ( 8) for c it is 8 c maimizes the volume E; V / ( ( 8 ) ) 9 Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
5 7 Section 8 (c) The volume gets large without limit This makes sense, since the curve is sweeping out space in an everincreasing radius C d C 7 (a) Using d, and A ields the following areas (in square inches, rounded to the nearest tenth):,,,,, 8, 7, 9, 7, 7, 9,, If C () is the circumference as a function of, then the area of a cross section is C( ) ( C ( )) A ( ), and the volume is ( C( )) A C [ + ( ) + ] 7 in (c) ( ) ( ( )) 7 Hemisphere cross sectional area: R h A Right circular clinder with cone removed cross sectional area: R h A Since A A, the two volumes are equal b Cavalieri s theorem Thus volume of hemisphere volume of clinder volume of cone R R R 7 Use washer cross sections: a washer has inner radius area ( R r ) b a b a + ( ) The volume is a a b a b a a a a b ab r b a, outer radius R b+ a +, and Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
6 Section (a) Put the bottom of the bowl at (, a) The area of a horizontal cross section is a ( a ) The volume for height h is h a a ( a ) a h ( a h) h a a For h, and the area of a cross section is ( ) The rate of rise is dh dv ( ) m/sec dt A dt 7 (a) A cross section has radius r a and area A ( ) r a ( a ) The volume is a ( a ) a a a a a a a + a a A cross section has radius r h and area A ( ) r h r + h h The volume is h r + h h h r + h h r h Quick Quiz Sections 8 8 C; A D (sin ( )) 7 (a) The two graphs intersect where e, which a calculator shows to be 7 Store this value as A The area of R is A( e ) Volume A ( e ) ( ) + + A e (c) Volume Section 8 Lengths of Curves (pp ) Quick Review ( + ), which, since, equals + or + +, equals or which, since, + (tan ) (sec ), which since <, equals sec ( + ) + which, since >, equals Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
7 7 Section 8 + cos cos, which since, equals cos (a) cos, so Length + cos f( ) has a corner at 7 d / ( ) is undefined at f( ) has a cusp there [, ] b [, ] (c) Length 8 d 8 ( ) + ( + ) / is undefined for f() has a vertical tangent there (a) / ( ), so / Length + / 9 + has a corner at d ( sin ) cos + is undefined for / (sin ) k, where k is an integer f() has vertical tangents at these values of Section 8 Eercises (a), so Length + ( ) + [, ] b [, ] (c) Length (a) (c) Length 7 + +, so + + ( + ) +, and + Then +, but NINT ma fail using over the entire interval because is undefined at ( + ) So, use Then + and Length + ( + ) (a) sec, so Length / + sec [, 7] b [, ] (c) Length 99 (a) cos + sin cos sin, so Length + sin (c) Length 7 Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
8 Section 8 7 (c) Length 98 7 (a) tan, so / Length + tan tan ln (sec ) (a), b [, ] (c) Length 9 t t dt t, p b [, ] (c) Length 9 (c) Length 8 (a) sec, so / Length sec / sec tan, ln (cos ), so ln (cos ), < / ( + ) ( ) +, so the length is ( + ) + (c) Length 98 9 (a) sec tan, so / Length + sec tan /, so thelength is / Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
9 7 Section 8, so the length is + +, so the length is + + 8, so the length is (a) + + ( + ) ( + ) ( + ) so the length is + ( + ) ( ) + ( + ) + ( ) + ( + ) ( ) + sec, so the length is / / + (sec ) sec / / / [tan ] /, so the length is + ( ) 7 corresponds to as here, so take Then + C, and, since (, ) lies on the curve, C So Two; we know the value of the function at one value of, and we know the square of the derivative We can also let, which gives the solution Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
10 (a) corresponds to here, so take as Then + C and, since (, ) lies on the curve, C So Section 8 7 The area is times the length of the arch sin, so the length is + sin, which evaluates, using NINT, to 7 8 Multipl that b, then b $7 to obtain the cost (rounded to the nearest dollar): $8, Two; we know the value of the function at one value of, and we know the square of the derivative We can also let, which gives the solution + cos, so the length is / / + cos cos / [sin ] / / / ( ), so the length is / / 8 +( ) / / 8 / / 8 / / 8 / 8 Find the length of the curve sin for cos, so the length is + cos, which evaluates, using NINT, to 7 inches / / f ( ) +, but NINT fails on + ( f ( )) because of the undefined slope at So, instead solve for in terms of using the quadratic formula / / ( ) +, and / ± + Using the positive + Then, 8 values, ( ) ( ) +, and 8 + / / + + ( ) ( + ) ( 8 8) f ( ) ( + ) 8, ( + ) 8 so the length is + / ( ) + which evaluates, using NINT, to 89 7 There is a corner at : Break the function into two smooth segments:, and +, <, < +, < The length is Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
11 7 Section ( ) + ( ) + + ( + ), which evaluates, using NINT for each part, to ( ), True, b definition D; sin( ) / + ( sin( )) 8 C; + ( ) + 9 9, but NINT ma fail using over the entire interval because is undefined at So, split the curve into two equal segments b solving + with : The total length is +, / which evaluates, using NINT, to, but NINT ma fail using over the entire interval, because is undefined at So, use, : and the length is + ( ), which evaluates, using NINT, to 7 Horizontal line segments will not work because the limit of the sum k, as the norm of the partition goes to zero, will alwas be the length (b a) of the interval (a, b) No; the curve can be indefinitel long Consider, for eample, the curve sin + for < < False; the function must be differentiable B; A; For track : at ± ± 7, and NINT fails to evaluate + ( ) because of the undefined slope at the limits, so use the track s smmetr, and back awa from the upper limit a little, and find + ( ) 8 Then, approimating the last little stretch at each end b a straight vertical line, add ( ) to get the total length of track as 7 Using a similar strateg, find the length of the right half of track to be 7 Store the unrounded value as A Now enter Y 7and Y t A+ NINT +, t,, t and graph in a [, ] b [, ] window to see the effect of the -coordinate of the lane- starting position on the length of lane (Be patient!) Solve graphicall to find the intersection at 9 99, which leads to starting point coordinates ( 999, 8) Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
12 Section (a) The fin is the hpotenuse of a right triangle with leg lengths k and df ( ) k k f k k n lim ( k) + ( f ( k ) k) n k n lim k + ( f ( k )) n k b + ( f ( )) a Yes; an curve of the form ± + c, where c is a constant, has constant slope ±, so that a a + ( ) a Section 8 Applications from Science and Statistics (pp ) Quick Review 8 (a) (a) (a) (a) (a) e [ e ] e e [ e ] e 78 sin [ cos ] 77 ( + ) + n ( + ) + [ n 9 n ] 9 n ( + )sin 7 ( )( ) 7 cos 7 ( ) 7 sin Section 8 Eercises / / e [ e ( + )] J / e sin sin cos 87 J ( ) 9 J sin sin ( e cos + ) [ e + ] sin e J When the bucket is m off the ground, the water weighs F( ) N Then W ( 9 ) [ 9 ] 9 J Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
13 78 Section 8 When the bucket is m off the ground, the water weighs F ( ) N Then W ( 9 9 ) [ ] 88 J 7 When the bag is ft off the ground, the sand weighs 8 F ( ) 8 lb 8 Then W ( ) 8 [ ] 9 ft-lb 8 (a) F ks, so 8 k( ) and k lb/in F(), and [ ] in-lb (c) F s, so s 8in 9 (a) F ks, so,7 k(8 ) and k 78 lb/in F() 78 W 78 [ 9 ] 9 7 9in-lb, and W 78 [ 9 ] 7 7 in-lb (a) F ks, so k and k lb/in Then for s 8, F lb [ ] 8 7 in-lb When the end of the rope is m from its starting point, the ( ) m of rope still to go weigh F() ()( ) N The total work is ( )( ) (a) Work 78 J ( p, V ) ( p, V ) F( ) ( p, V ) (, ) (, ) p V p V ( p, V) pa pdv pv ( )( ) 9,, so 9, p and V ( p, V)9, Work dv ( p, V) V 9, [ ] V V V 7,987 in-lb (a) From the equation +, it follows that a thin horizontal rectangle has area 9, where is distance from the top, and pressure The total force is approimatel n ( k) ( 9 k ) k n 8k 9 k k 8 9 [ ( 9 ) ] lb Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
14 Section 8 79 (a) From the equation +, it follows 8 that a thin horizontal rectangle has area, where is distance from the top, and pressure The total force is approimatel n k ( ) k k n k 7 k k lb (a) From the equation 8, it follows that a thin horizontal rectangle has area, where is the distance from the top of the triangle, the pressure is ( ) The total force is approimatel n ( k ) k k n ( 8 k k) k 8 8 ( 8 ) [ 7 ] 9 ( ) 7lb (a) From the equation, it follows that a thin horizontal rectangle has area where is distance from the bottom, and pressure ( ) The total force is approimatel n ( k) ( k ) k n 8 ( k k ) k 8 ( ) (a) Work to raise a thin slice ( )( ) Total work ( ), 97, ft-lb (,97, ft-lb) ( ft-lb/sec) 99 sec min (c) Work to empt half the tank ( ) 7, ft-lb, and 7, 97 sec min (d) The weight per ft of water is a simple multiplicative factor in the answers So divide b and multipl b the appropriate weight-densit For :, 97,, 9, ft-lb and sec min For :, 97,,, ft-lb and 99 sec min Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
15 8 Section 8 8 The work needed to raise a thin disk is ( ) ( )( ), where is height up from the bottom The total work is ( )( ) 7, 8, 9 ft-lb 9 Work to pump through the valve is ( ) ( )( + ) for a thin disk and ( )( + ) 9 + 8, 87 ft-lb for the whole tank Work to pump over the rim is ( ) ( )( + ) for a thin disk and ( )( ) ( )( )( ) 98, 8 8 ft-lb for the whole tank Less work is required to fill the tank from the bottom The work is the same as if the straw were initiall an inch long and just touched the surface, and lengthened as the liquid level dropped For a thin disk, the volume is + 7 and the work to raise it is + 7 ( 8 ) The total work is ( 8 ), which using 9 NINT evaluates to 9 in-oz The work is that alrea calculated (to pump the oil to the rim) plus the work needed to raise the entire amount ft higher The latter comes to r h( 7)( ) 7( ) ( 8), 9ft-lb, and the total is,9 +,,8 ft-lb The weight densit is a simple multiplicative factor: Divide b 7 and multipl b,, 8 8 ft-lb 7 The work to raise a thin disk is r ( ) h ( ) ( )( + ) ( )( ) The total work is ( )( ), which evaluates using NINT to 97, ft-b This will come to (97,)($) $88, so es, there s enough mone to hire the firm Pipe radius ft; Work to fill pipe ( ), ft -b 8 Work to fill tank ( ) ( ) 8,, ft-lb Total work 8,, ft-lb, which will take 8,, +,8 sec hr (a) The pressure at depth is, and the area of a thin horizontal strip is The depth of water is ft, so the total force on an end is ( )( ) 9 7 lb On the sides, which are twice as long as the ends, the initial total force is doubled to 97 lb When the tank is upended, the depth is doubled to ft, and the force on a side becomes ( )( ) 88 9 lb, which means that the fluid force doubles 7 in ft, and 77in ft 8 Force on a side pda 8 ( ) lb Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
16 Section 8 8 t 7 f () t otherwise t dt t 8 f () t otherwise t dt 9 Since σ, then 8% of the calls are answered in minutes Use f( ) e ( 98) /( ) (a) f( ) ( % ) Take as a convenientl high upper limit: f 7 7 ( ), which means about 7 () people (a) (%), since half of a normal distribution lies below the mean Use NINT to find f( ), where ( ) /( ) f( ) e The result is (%) (c) ft 7 in Pick 8 in as a convenientl high upper limit and with NINT, find 8 7 f( ) The result is (%) (d) if we assume a continuous distribution Integration is a good approimation to the area (which represents the probabilit), since the area is a kind of Riemann sum The proportion of lightbulbs that last between and 8 hours False; three times as much work is required E; ( ) 7 7 J 7 D; W ( ) [ ] J 8 B; F k k W [ ] J 9 E; ( 8 )( ) 9, ft-lb, 78, MG dr 7,, r MG r which for, 78,, 7,, M 97, G 7 evaluates to J (a) The distance goes from m to m The work b an eternal force equals the work done b repulsion in moving the electrons from a -m distance to a -m distance: Work r 9 dr 9 r 8 J Again, find the work done b the fied electrons in pushing the third one wa The total work is the sum of the work b each fied electron The changes in distance are m to m and m to m, respectivel Work 9 9 dr + r r 9 + r r 9 77 J dr True; the force against each vertical side is 8 lbs Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
17 8 Section 8 dv dv F m mv, so dt W F( ) dv mv v mv dv v mv mv Since initial velocit, Work Change in kinetic energ mv oz lb 8 m slug, so ft/ sec ft/ sec Work ( ) ft-lb lb lb 97 slug, ft/ sec and 8 ft hr 9 mph 9 mi sec ft/sec, so Work change in kinetic energ 97 ( )( ) 8 ft-lb lb ( ) oz oz oz slug, ( ft/ sec ) so Work 8 ( )( ) ft-lb lb ( ) oz oz oz slug, and ( ft/ sec ) 8 ft hr mph mph mi sec 8 87ft /sec, so Work 8 87 ( ) ft-lb lb ( ) oz oz oz 8slug, ( ft/sec ) so Work ( )( ) ft-lb lb ( ) oz oz oz 7 slug, so ( ft/sec ) Work 7 ( )( ) ft-lb oz lb slug Compression energ 8 of spring ks ( 8) ft-lb, and final height is given b mgh ft-lb, so h ft Quick Quiz Sections 8 and 8 A; D; ( ) + + t t dt t t dt (( ) + ( ) ) C; ( )( ) t t dt t + 9t dt ( ) 8 in (a) n i h h Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
18 Chapter 8 Review 8 h dh h bs 7 (c) h h dh bs Chapter 8 Review Eercises (pp ) vt () dt ( t t ) dt t t 7ft 7 c() t dt 7 ( + t ) dt 7 [ t + t ] gal B ( e ) [ e ] ( ) The curves intersect at and There area is [ ( + )] ( ) implies + ( ) p( ) ( ) [ ] g () t E t dt cos dt t t sin, 9 The area is ( + ) + implies The curves intersect at The area is The curves intersect at 8 The area is 8 8 8, or 8 Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
19 8 Chapter 8 Review implies, and + implies + The curves intersect at (, ) and (, ) The area is The curves intersect at ±8 The area 8 is ( cos ) 8 8 sin The curves intersect at ± 8 The area 8 is ( sec ) 8 8 ( sec ) 8 tan The area is / / ( sin ) cos + + Solve + cos cos for the -values at the two ends of the region: ±, ie, 7 or Use the smmetr of the area: 7 [( + cos ) ( cos )] 7 ( cos ) [ ] 7 sin 7 The area is ( sin sin ) cos + cos [( cos ) ( + cos )] ( cos ) [ sin ] + 7 Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
20 Chapter 8 Review 8 7 Solve to find the intersection + points at and ± / Then use the area s smmetr: the area is / ( ) + In( + ) + ( ) ln / 8 Use the intersect function on a graphing calculator to determine that the curves intersect at The area is, 89 which using NINT evaluates to 7 9 Use the - and -ais smmetries of the area: sin [sin cos ] A cross section has radius r and area 8 ( ) A r 9 8 [ 9 ] v 9 The graphs intersect at (, ) and (, ) (a) Use clindrical shells A shell has radius and height The total volume is ( ) Use clindrical shells A shell has radius and height The total volume is ( ) ( ) / ( ) / 8 (c) Use clindrical shells A shell has radius and height The total volume is ( ) ( ) / ( ) / / (d) Use clindrical shells A shell has radius and height The total volume is ( ) + + (a) Use disks The volume is ( ) k k k dv dk (c) Since V k, k dt dt When k, dk dv ( ), so the dt k dt Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
21 8 Chapter 8 Review depth is increasing at the rate of unit per second The football is a solid of revolution about the -ais A cross section has radius and area r The volume is, given the smmetr, / / / 88 7in The width of a cross section is sin, and the area is r sin The volume is sin sin The volume of the piece cut out is ( ) ( ) ( 8) 8 9 ft 7 The curve crosses the -ais at ±, so the length is + ( ), + which using NINT evaluates to The curves intersect at and ± Use the graphs - and -ais smmetr: d ( ), and the total perimeter is + ( ), which using NINT evaluates to Use washer cross sections A washer has inner radius r, outer radius R e, and area ( R r ) ( e ) The volume is ln ln ( e ) e ( ln ) ( ln ) Use clindrical shells Taking the hole to be vertical, a shell has radius and height equals zero when or The maimum is at, the minimum at The distance between them along the curve is + ( ), which using NINT evaluates to 9 The time taken is about 9 9sec If were true, then the curve k sin would have to get vanishingl short as k approaches zero Since in fact the curve s length approaches instead, is false and (a) is true Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
22 F ( ), so + ( F ( )) 9 Chapter 8 Review 87 the rim is ( )( ) The total 8 work is ( ) 8 ( ) 8 97 in-lb (a) ( N)( m) J When the end has traveled a distance, the weight of the remaining portion is ( )(8) 8 The total work to lift the rope is ( 8 ) [ ] J (c) + J The weight of the water at elevation (starting from ) is 7 8 ( 8)( 8) The total work is , 8, ft-lb F 8 8 F ks, so k N/m Then s 8 8 Work J To stretch the additional meter, 8 8 Work J The same amount of work is done, but gravit supplies the downhill force, so less work is done b the person The radius of a horizontal cross section is 8, where is distance below the rim The area is ( ), the weight is ( ), and the work to lift it over 7 The width of a thin horizontal strip is ( ), and the force against it is 8( ) The total force is ( ) ( + ) lb 7 8 7in ft, in ft, and 8 in ft For the base, 7 Force 7 8lb 8 For the front and back, Force lb For the sides, Force lb 8, and its 9 A square s height is ( ) area is ( ) The volume is ( ) ( / / + + ) / / Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
23 88 Chapter 8 Review Choose cm as a convenientl large upper limit ( 7 ) /( ) e evaluates, using NINT, to (%) Answers will var Find µ, then use the fact that 8% of the class is within σ of µ to find σ, and then choose a convenientl large number b ( µ ) /( σ ) b and calculate e σ Use (a) / f( ) e f( ) evaluates, using NINT, to 87(87%) f( ) 9 ( 9 %) f( ) 997 ( 997 %) Because f() and f( ) The total area gives the probabilit that the variable takes on one of its possible values Since the variable must take on some value, the probabilit must be 7 A shell has radius and height The total volume is ( ) [ ] ϖ A shell has radius and height sin The total volume is ( )(sin ) [ sin cos ] A shell has radius and height The total volume is ( ) [ ] The curves intersect at and A shell has radius and height ( ) + The total volume is ( )( + ) ( + ) + Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
24 Chapter 8 Review 89 8 Use the intersect function on a graphing calculator to determine that the curves intersect at ± 89 A shell has radius and height The volume, which is calculated using the right half of the area, is 89 ( ), which using NINT evaluates to (a) ( + )( ) Revolve about the line, using clindrical shells A shell has radius and height total volume is ( ) + + in The dl Since f + ( ) must equal ( f + ( )), + ( f ( )) + f ( ) + f ( ), and f ( ) Then f( ) ln + C, and the requirement to pass through (, ) means that C The function is ln+ f( ) ln + sec, so the area is (tan ) + (sec ), which using NINT evaluates to 8 and, so the area is, + which using NINT evaluates to (a) The two curves intersect at 78 Store this value as A Area A ( + sin sec ) A Volume (( + sin ) (sec ) ) (c) A Volume ( + sin sec ) 9 (a) Average temp t 8 cos dt 87 F Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
25 9 Chapter 8 Review t Ft () 8 cos 78 for 89 t 8 79 Store these two values as A and B B t (c) Cost 8 cos 78 dt A The cost was about $ (a) 7 people 9 ( t t+ ) dt 7 dt + 8 dollars 9 dt, 7 ( t t+ ) ( t t+ ) (c) H ( 7) E( 7) L( 7) 8 people H(7) is the number of people in the park at :, and H ( 7) is the rate at which the number of people in the park is changing at : (d) When H () t E() t L() t ; that is, at t 79 Copright Pearson Education, Inc Publishing as Prentice Hall
Chapter 8. Applications of Definite Integrals. π π. 1 and 2. The graph is. x 2x + 3 = 0 has no real solutions, since
 Chapter 8 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 8 Accumulation and Net Change (pp 8 96) Eploration Revisiting Eample t 8 st () 8 + + t + 8 s () 8+ + 8 s () 8+ + 6 and The graph is + + Section 8 7
Chapter 8 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 8 Accumulation and Net Change (pp 8 96) Eploration Revisiting Eample t 8 st () 8 + + t + 8 s () 8+ + 8 s () 8+ + 6 and The graph is + + Section 8 7
CHAPTER 6 Applications of Integration
 PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves.......... Section. Volume: The Disk Method................. 7 Section. Volume: The Shell Method................
PART II CHAPTER Applications of Integration Section. Area of a Region Between Two Curves.......... Section. Volume: The Disk Method................. 7 Section. Volume: The Shell Method................
MATH 150/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 0/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the graph that represents the given function without using
MATH 0/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the graph that represents the given function without using
Copyright 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
 Chapter 5 Review 95 (c) f( ) f ( 7) ( 7) 7 6 + ( 6 7) 7 6. 96 Chapter 5 Review Eercises (pp. 60 6). y y ( ) + ( )( ) + ( ) The first derivative has a zero at. 6 Critical point value: y 9 Endpoint values:
Chapter 5 Review 95 (c) f( ) f ( 7) ( 7) 7 6 + ( 6 7) 7 6. 96 Chapter 5 Review Eercises (pp. 60 6). y y ( ) + ( )( ) + ( ) The first derivative has a zero at. 6 Critical point value: y 9 Endpoint values:
Math 122 Fall Solutions to Homework #5. ( ) 2 " ln x. y = x 2
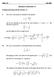 Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
Math 1 Fall 8 Solutions to Homework #5 Problems from Pages 383-38 (Section 7.) 6. The curve in this problem is defined b the equation: = ( ) " ln and we are interested in the part of the curve between
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 07 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
MAC 2311 Chapter 5 Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function
 MAC Chapter Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
MAC Chapter Review Materials Topics Include Areas Between Curves, Volumes (disks, washers, and shells), Work, and Average Value of a Function MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
Chapter 6 Notes, Stewart 8e
 Contents 6. Area between curves........................................ 6.. Area between the curve and the -ais.......................... 6.. Overview of Area of a Region Between Two Curves...................
Contents 6. Area between curves........................................ 6.. Area between the curve and the -ais.......................... 6.. Overview of Area of a Region Between Two Curves...................
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Eam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a function is given. Choose the answer that represents the graph of its derivative.
Eam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a function is given. Choose the answer that represents the graph of its derivative.
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
Review Test 2. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. D) ds dt = 4t3 sec 2 t -
 Review Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the derivative. ) = 7 + 0 sec ) A) = - 7 + 0 tan B) = - 7-0 csc C) = 7-0 sec tan
Review Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the derivative. ) = 7 + 0 sec ) A) = - 7 + 0 tan B) = - 7-0 csc C) = 7-0 sec tan
Review: A Cross Section of the Midterm. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Review: A Cross Section of the Midterm Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the limit, if it eists. 4 + ) lim - - ) A) - B) -
Review: A Cross Section of the Midterm Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the limit, if it eists. 4 + ) lim - - ) A) - B) -
8.2 APPLICATIONS TO GEOMETRY
 8.2 APPLICATIONS TO GEOMETRY In Section 8.1, we calculated volumes using slicing and definite integrals. In this section, we use the same method to calculate the volumes of more complicated regions as
8.2 APPLICATIONS TO GEOMETRY In Section 8.1, we calculated volumes using slicing and definite integrals. In this section, we use the same method to calculate the volumes of more complicated regions as
ANOTHER FIVE QUESTIONS:
 No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
No peaking!!!!! See if you can do the following: f 5 tan 6 sin 7 cos 8 sin 9 cos 5 e e ln ln @ @ Epress sin Power Series Epansion: d as a Power Series: Estimate sin Estimate MACLAURIN SERIES ANOTHER FIVE
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 78 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 8 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. 78 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 8 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
 Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
MATH 150/GRACEY EXAM 2 PRACTICE/CHAPTER 2. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 0/GRACEY EXAM PRACTICE/CHAPTER Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the indicated derivative. ) Find if = 8 sin. A) = 8
MATH 0/GRACEY EXAM PRACTICE/CHAPTER Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the indicated derivative. ) Find if = 8 sin. A) = 8
Practice Exam 1 Solutions
 Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
Answer Key 1973 BC 1969 BC 24. A 14. A 24. C 25. A 26. C 27. C 28. D 29. C 30. D 31. C 13. C 12. D 12. E 3. A 32. B 27. E 34. C 14. D 25. B 26.
 Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval................... 0 Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem...... 0 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and
For Thought. 3.1 Exercises 142 CHAPTER 3 POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS. 1. False, the range of y = x 2 is [0, ).
 CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS For Thought. False, the range of = is [0, ).. False, the verte is the point (, ). -5 -. True. True 5. True, since b a = 6 =. 6. True, the -intercept of = ( + )
CHAPTER POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS For Thought. False, the range of = is [0, ).. False, the verte is the point (, ). -5 -. True. True 5. True, since b a = 6 =. 6. True, the -intercept of = ( + )
1 x 3 3x. x 1 2x 1. 2x 1 2x 1. 2x 1 2x 1. x 2 +4x 1 j. lim. x3 +2x x 5. x2 9
 MATHEMATICS 57 Final Eamination Review Problems. Let f 5. Find each of the following. a. fa+b b. f f. Find the domain of each function. a. f b. g +. The graph of f + is the same as the graph of g ecept
MATHEMATICS 57 Final Eamination Review Problems. Let f 5. Find each of the following. a. fa+b b. f f. Find the domain of each function. a. f b. g +. The graph of f + is the same as the graph of g ecept
Chapter 4 Applications of Derivatives. Section 4.1 Extreme Values of Functions (pp ) Section Quick Review 4.1
 Section. 6 8. Continued (e) vt () t > 0 t > 6 t > 8. (a) d d e u e u du where u d (b) d d d d e + e e e e e e + e e + e (c) y(). (d) m e e y (). 7 y. 7( ) +. y 7. + 0. 68 0. 8 m. 7 y0. 8( ) +. y 0. 8+.
Section. 6 8. Continued (e) vt () t > 0 t > 6 t > 8. (a) d d e u e u du where u d (b) d d d d e + e e e e e e + e e + e (c) y(). (d) m e e y (). 7 y. 7( ) +. y 7. + 0. 68 0. 8 m. 7 y0. 8( ) +. y 0. 8+.
1985 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
Applications of Definite Integrals
 58_Ch7_pp378-433.qd /3/6 :3 PM Page 378 Chapter 7 Applications of Definite Integrals T he art of potter developed independentl in man ancient civilizations and still eists in modern times. The desired
58_Ch7_pp378-433.qd /3/6 :3 PM Page 378 Chapter 7 Applications of Definite Integrals T he art of potter developed independentl in man ancient civilizations and still eists in modern times. The desired
Chapter 2 Polynomial, Power, and Rational Functions
 Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling 6 Chapter Polnomial, Power, and Rational Functions Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling Eploration. $000 per ear.. The equation will
Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling 6 Chapter Polnomial, Power, and Rational Functions Section. Linear and Quadratic Functions and Modeling Eploration. $000 per ear.. The equation will
For the intersections: cos x = 0 or sin x = 1 2
 Chapter 6 Set-up examples The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the work that will be required if you are asked to set-up integrals on an exam and/or quiz.. Areas () Set up, do not evaluate, any
Chapter 6 Set-up examples The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the work that will be required if you are asked to set-up integrals on an exam and/or quiz.. Areas () Set up, do not evaluate, any
1993 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 90 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
99 AP Calculus AB: Section I 90 Minutes Scientific Calculator Notes: () The eact numerical value of the correct answer does not always appear among the choices given. When this happens, select from among
Final Exam Review / AP Calculus AB
 Chapter : Final Eam Review / AP Calculus AB Use the graph to find each limit. 1) lim f(), lim f(), and lim π - π + π f 5 4 1 y - - -1 - - -4-5 ) lim f(), - lim f(), and + lim f 8 6 4 y -4 - - -1-1 4 5-4
Chapter : Final Eam Review / AP Calculus AB Use the graph to find each limit. 1) lim f(), lim f(), and lim π - π + π f 5 4 1 y - - -1 - - -4-5 ) lim f(), - lim f(), and + lim f 8 6 4 y -4 - - -1-1 4 5-4
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 --review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the area of the shaded region. ) f() = + - ) 0 0 (, 8) 0 (0, 0) - - - - - - -0
--review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the area of the shaded region. ) f() = + - ) 0 0 (, 8) 0 (0, 0) - - - - - - -0
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus AB Free-Response Scoring Guidelines
 Question pt The rate at which raw sewage enters a treatment tank is given by Et 85 75cos 9 gallons per hour for t 4 hours. Treated sewage is removed from the tank at the constant rate of 645 gallons per
Question pt The rate at which raw sewage enters a treatment tank is given by Et 85 75cos 9 gallons per hour for t 4 hours. Treated sewage is removed from the tank at the constant rate of 645 gallons per
Math 75B Practice Midterm III Solutions Chapter 6 (Stewart) Multiple Choice. Circle the letter of the best answer.
 Math 75B Practice Midterm III Solutions Chapter 6 Stewart) English system formulas: Metric system formulas: ft. = in. F = m a 58 ft. = mi. g = 9.8 m/s 6 oz. = lb. cm = m Weight of water: ω = 6.5 lb./ft.
Math 75B Practice Midterm III Solutions Chapter 6 Stewart) English system formulas: Metric system formulas: ft. = in. F = m a 58 ft. = mi. g = 9.8 m/s 6 oz. = lb. cm = m Weight of water: ω = 6.5 lb./ft.
Integrals. D. DeTurck. January 1, University of Pennsylvania. D. DeTurck Math A: Integrals 1 / 61
 Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Department of Mathematical x 1 x 2 1
 Contents Limits. Basic Factoring Eample....................................... One-Sided Limit........................................... 3.3 Squeeze Theorem.......................................... 4.4
Contents Limits. Basic Factoring Eample....................................... One-Sided Limit........................................... 3.3 Squeeze Theorem.......................................... 4.4
Calculus - Chapter 2 Solutions
 Calculus - Chapter Solutions. a. See graph at right. b. The velocity is decreasing over the entire interval. It is changing fastest at the beginning and slowest at the end. c. A = (95 + 85)(5) = 450 feet
Calculus - Chapter Solutions. a. See graph at right. b. The velocity is decreasing over the entire interval. It is changing fastest at the beginning and slowest at the end. c. A = (95 + 85)(5) = 450 feet
The region enclosed by the curve of f and the x-axis is rotated 360 about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
 Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Review Exercises for Chapter 3. Review Exercises for Chapter r v 0 2. v ft sec. x 1 2 x dx f x x 99.4.
 Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
= dx. 16. Let the can have radius r cm and height h cm. and. 17. Note that
 Section 5. 5. (a Note that 5 y 5, so y. Then c 5( + y + 0y 5 + 0y 5 5 + 0 5 +, 750 dc 0( 75 0, 750 d The critical point occurs at 5. Since dc dc < 0 for 0 < < 5 and 0 d d > for > 5, the critical point
Section 5. 5. (a Note that 5 y 5, so y. Then c 5( + y + 0y 5 + 0y 5 5 + 0 5 +, 750 dc 0( 75 0, 750 d The critical point occurs at 5. Since dc dc < 0 for 0 < < 5 and 0 d d > for > 5, the critical point
CHAPTER 2 Differentiation
 CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
AP Calculus. (Mr. Surowski) Homework from Chapter 7 (and some of Chapter 8)
 AP Calculus (Mr. Surowski) Homework from Chapter 7 (and some of Chapter 8) Lesson 30 Integral as accumulation (7.):, 3, 5, 8 0, 7, 20 22, 25 (to do quadratic regression on our (TI-84 calculators, refer
AP Calculus (Mr. Surowski) Homework from Chapter 7 (and some of Chapter 8) Lesson 30 Integral as accumulation (7.):, 3, 5, 8 0, 7, 20 22, 25 (to do quadratic regression on our (TI-84 calculators, refer
NOT FOR SALE 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION. 6.1 Areas Between Curves. Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. ( ) = 4 ln 1 = 45.
 6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 6. Areas Between Curves... 4. 8 ( ) 8 8 4 4 ln ( ln 8) 4 ln 45 4 ln 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) + + + + + ( ) ( 4) ( +6) + ( 8 + 7) 9 5. ( ) + ( +) ( + ) + 4 6. ( sin ) +cos 8 8 + 7. The
6 APPLICATIONS OF INTEGRATION 6. Areas Between Curves... 4. 8 ( ) 8 8 4 4 ln ( ln 8) 4 ln 45 4 ln 8 ( ) ( ) ( ) + + + + + ( ) ( 4) ( +6) + ( 8 + 7) 9 5. ( ) + ( +) ( + ) + 4 6. ( sin ) +cos 8 8 + 7. The
Math 2413 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/2016
 Math 243 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/206 Find the average velocity of the function over the given interval.. y = 6x 3-5x 2-8, [-8, ] Find the slope of the curve for the given value of
Math 243 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/206 Find the average velocity of the function over the given interval.. y = 6x 3-5x 2-8, [-8, ] Find the slope of the curve for the given value of
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS
 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS PROBLEM SET #1 Related Rates ***Calculators Allowed*** 1. An oil tanker spills oil that spreads in a circular pattern whose radius increases at the rate of
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS PROBLEM SET #1 Related Rates ***Calculators Allowed*** 1. An oil tanker spills oil that spreads in a circular pattern whose radius increases at the rate of
I. Degrees and Radians minutes equal 1 degree seconds equal 1 minute. 3. Also, 3600 seconds equal 1 degree. 3.
 0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
Quiz 6 Practice Problems
 Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
Quiz 6 Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
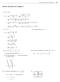 Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. B) = 2t + 1; D) = 2 - t;
 Eam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Calculate the derivative of the function. Then find the value of the derivative as specified.
Eam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Calculate the derivative of the function. Then find the value of the derivative as specified.
AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1. Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 2015
 AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1 Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 015 This is an AP Calc Review packet. As we get closer to the eam, it is time to start reviewing old concepts. Use
AP Calculus Review Assignment Answer Sheet 1 Name: Date: Per. Harton Spring Break Packet 015 This is an AP Calc Review packet. As we get closer to the eam, it is time to start reviewing old concepts. Use
AP Calculus AB/BC ilearnmath.net
 CALCULUS AB AP CHAPTER 1 TEST Don t write on the test materials. Put all answers on a separate sheet of paper. Numbers 1-8: Calculator, 5 minutes. Choose the letter that best completes the statement or
CALCULUS AB AP CHAPTER 1 TEST Don t write on the test materials. Put all answers on a separate sheet of paper. Numbers 1-8: Calculator, 5 minutes. Choose the letter that best completes the statement or
Chapter 7 Applications of Integration
 Chapter 7 Applications of Integration 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method 7.3 Volume: The Shell Method 7.5 Work 7.6 Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids 7.7 Fluid Pressure
Chapter 7 Applications of Integration 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves 7.2 Volume: The Disk Method 7.3 Volume: The Shell Method 7.5 Work 7.6 Moments, Centers of Mass, and Centroids 7.7 Fluid Pressure
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral
 Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral Section 6.1 More on Area a. Representative Rectangle b. Vertical Separation c. Example d. Integration with Respect to y e. Example Section 6.2 Volume by Parallel
Chapter 6 Some Applications of the Integral Section 6.1 More on Area a. Representative Rectangle b. Vertical Separation c. Example d. Integration with Respect to y e. Example Section 6.2 Volume by Parallel
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
CHAPTER EIGHT. Area of region. (2x)dx = x 2. Area = Area of region ( x 2 +6x) x. ( x 2 +6x)dx = x3 3 +3x2. Area of region. dy = 3y y2.
 CHAPTER EIGHT 8. SOLUTIONS 7 Solutions for Section 8. Eercises. (a) The strip stretches between = and =, so (b) We have Area of region Area = (). ()d = = 9.. (a) The strip stretches between = and = +6,
CHAPTER EIGHT 8. SOLUTIONS 7 Solutions for Section 8. Eercises. (a) The strip stretches between = and =, so (b) We have Area of region Area = (). ()d = = 9.. (a) The strip stretches between = and = +6,
C H A P T E R 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
Quick Review 4.1 (For help, go to Sections 1.2, 2.1, 3.5, and 3.6.)
 Section 4. Etreme Values of Functions 93 EXPLORATION Finding Etreme Values Let f,.. Determine graphicall the etreme values of f and where the occur. Find f at these values of.. Graph f and f or NDER f,,
Section 4. Etreme Values of Functions 93 EXPLORATION Finding Etreme Values Let f,.. Determine graphicall the etreme values of f and where the occur. Find f at these values of.. Graph f and f or NDER f,,
Find the volume of the solid generated by revolving the shaded region about the given axis. Use the disc/washer method 1) About the x-axis
 Final eam practice for Math 6 Disclaimer: The actual eam is different Find the volume of the solid generated b revolving the shaded region about the given ais. Use the disc/washer method ) About the -ais
Final eam practice for Math 6 Disclaimer: The actual eam is different Find the volume of the solid generated b revolving the shaded region about the given ais. Use the disc/washer method ) About the -ais
( ) as a fraction. If both numerator and denominator are
 A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes What you are finding: You can be asked to find lim f x x a (H.A.) problem is asking you find lim f x x ( ) and lim f x x ( ). ( ) or lim f x x ± ( ). Typically, a horizontal
A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes What you are finding: You can be asked to find lim f x x a (H.A.) problem is asking you find lim f x x ( ) and lim f x x ( ). ( ) or lim f x x ± ( ). Typically, a horizontal
2 MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE
 MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE Download full Solution manual for Universit phsics with modern phsics 14t http://testbankcollection.com/download/solution-manual-for-universit-phsics-withmodern-phsics-14th.1.
MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE Download full Solution manual for Universit phsics with modern phsics 14t http://testbankcollection.com/download/solution-manual-for-universit-phsics-withmodern-phsics-14th.1.
1. Find A and B so that f x Axe Bx. has a local minimum of 6 when. x 2.
 . Find A and B so that f Ae B has a local minimum of 6 when.. The graph below is the graph of f, the derivative of f; The domain of the derivative is 5 6. Note there is a cusp when =, a horizontal tangent
. Find A and B so that f Ae B has a local minimum of 6 when.. The graph below is the graph of f, the derivative of f; The domain of the derivative is 5 6. Note there is a cusp when =, a horizontal tangent
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. C) 2
 Cal II- Final Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Epress the following logarithm as specified. ) ln 4. in terms of ln and
Cal II- Final Review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Epress the following logarithm as specified. ) ln 4. in terms of ln and
Calculus II. Philippe Rukimbira. Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAC / 1
 Calculus II Philippe Rukimbira Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAC 2312 1 / 1 5.4. Sigma notation; The definition of area as limit Assignment: page 350, #11-15, 27,
Calculus II Philippe Rukimbira Department of Mathematics Florida International University PR (FIU) MAC 2312 1 / 1 5.4. Sigma notation; The definition of area as limit Assignment: page 350, #11-15, 27,
Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses. You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses.
 TEKS 9.4 a.5, A.5.B, A.5.C Before Now Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses. Wh? So ou can model
TEKS 9.4 a.5, A.5.B, A.5.C Before Now Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses. Wh? So ou can model
Problems to practice for FINAL. 1. Below is the graph of a function ( ) At which of the marked values ( and ) is: (a) ( ) greatest = (b) ( ) least
 Problems to practice for FINAL. Below is the graph of a function () At which of the marked values ( and ) is: (a) () greatest = (b) () least = (c) () the greatest = (d) () the least = (e) () = = (f) ()
Problems to practice for FINAL. Below is the graph of a function () At which of the marked values ( and ) is: (a) () greatest = (b) () least = (c) () the greatest = (d) () the least = (e) () = = (f) ()
CALCULUS AB SECTION II, Part A
 CALCULUS AB SECTION II, Part A Time 45 minutes Number of problems 3 A graphing calculator is required for some problems or parts of problems. pt 1. The rate at which raw sewage enters a treatment tank
CALCULUS AB SECTION II, Part A Time 45 minutes Number of problems 3 A graphing calculator is required for some problems or parts of problems. pt 1. The rate at which raw sewage enters a treatment tank
One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maximum or minimum values.
 8 LESSON 5- MAX/MIN APPLICATIONS (OPTIMIZATION) One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maimum or minimum values. Procedure:. Choose variables and/or draw a labeled figure..
8 LESSON 5- MAX/MIN APPLICATIONS (OPTIMIZATION) One of the most common applications of Calculus involves determining maimum or minimum values. Procedure:. Choose variables and/or draw a labeled figure..
(a) At what rate is the circumference of the circle changing when the radius is 10 inches? =2inches per minute and we want to find. c =2 r.
 3.11 Related Rates Problem 1 The radius of a circle is increasing at a rate of 2 inches per minute. (a) At what rate is the circumference of the circle changing when the radius is 10 inches? We know: dr
3.11 Related Rates Problem 1 The radius of a circle is increasing at a rate of 2 inches per minute. (a) At what rate is the circumference of the circle changing when the radius is 10 inches? We know: dr
lim x c) lim 7. Using the guidelines discussed in class (domain, intercepts, symmetry, asymptotes, and sign analysis to
 Math 7 REVIEW Part I: Problems Using the precise definition of the it, show that [Find the that works for any arbitrarily chosen positive and show that it works] Determine the that will most likely work
Math 7 REVIEW Part I: Problems Using the precise definition of the it, show that [Find the that works for any arbitrarily chosen positive and show that it works] Determine the that will most likely work
MATH141: Calculus II Exam #1 review 6/8/2017 Page 1
 MATH: Calculus II Eam # review /8/7 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an eam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well as show you
MATH: Calculus II Eam # review /8/7 Page No review sheet can cover everything that is potentially fair game for an eam, but I tried to hit on all of the topics with these questions, as well as show you
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
MATHEMATICS LEVEL 2 TEST FORM B Continued
 Mathematics Level Test Form B For each of the following problems, decide which is the BEST of the choices given. If the eact numerical value is not one of the choices, select the choice that best approimates
Mathematics Level Test Form B For each of the following problems, decide which is the BEST of the choices given. If the eact numerical value is not one of the choices, select the choice that best approimates
Algebra I. Administered May 2013 RELEASED
 STAAR State of Teas Assessments of Academic Readiness Algebra I Administered Ma 0 RELEASED Copright 0, Teas Education Agenc. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited
STAAR State of Teas Assessments of Academic Readiness Algebra I Administered Ma 0 RELEASED Copright 0, Teas Education Agenc. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited
It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits 1. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4]
![It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits 1. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4] It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits 1. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4]](/thumbs/79/79759146.jpg) It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4] f ( ) =.. It has a vertical asymptote at =, a) What are the critical numbers of f? b)
It s Your Turn Problems I. Functions, Graphs, and Limits. Here s the graph of the function f on the interval [ 4,4] f ( ) =.. It has a vertical asymptote at =, a) What are the critical numbers of f? b)
K. Function Analysis. ). This is commonly called the first derivative test. f ( x) is concave down for values of k such that f " ( k) < 0.
 K. Function Analysis What you are finding: You have a function f ( ). You want to find intervals where f ( ) is increasing and decreasing, concave up and concave down. You also want to find values of where
K. Function Analysis What you are finding: You have a function f ( ). You want to find intervals where f ( ) is increasing and decreasing, concave up and concave down. You also want to find values of where
MATHEMATICS LEVEL 2. MATHEMATICS LEVEL 2 Continued GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE USE THIS SPACE FOR SCRATCHWORK. 1. If xy 0 and 3x = 0.
 MATHEMATICS LEVEL For each of the following problems, decide which is the BEST of the choices given. If the eact numerical value is not one of the choices, select the choice that best approimates this
MATHEMATICS LEVEL For each of the following problems, decide which is the BEST of the choices given. If the eact numerical value is not one of the choices, select the choice that best approimates this
1. Find the area enclosed by the curve y = arctan x, the x-axis and the line x = 3. (Total 6 marks)
 1. Find the area enclosed by the curve y = arctan, the -ais and the line = 3. (Total 6 marks). Show that the points (0, 0) and ( π, π) on the curve e ( + y) = cos (y) have a common tangent. 3. Consider
1. Find the area enclosed by the curve y = arctan, the -ais and the line = 3. (Total 6 marks). Show that the points (0, 0) and ( π, π) on the curve e ( + y) = cos (y) have a common tangent. 3. Consider
CHAPTER 2: Partial Derivatives. 2.2 Increments and Differential
 CHAPTER : Partial Derivatives.1 Definition of a Partial Derivative. Increments and Differential.3 Chain Rules.4 Local Etrema.5 Absolute Etrema 1 Chapter : Partial Derivatives.1 Definition of a Partial
CHAPTER : Partial Derivatives.1 Definition of a Partial Derivative. Increments and Differential.3 Chain Rules.4 Local Etrema.5 Absolute Etrema 1 Chapter : Partial Derivatives.1 Definition of a Partial
Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers x for which f (x) is a real number.
 997 AP Calculus BC: Section I, Part A 5 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number..
997 AP Calculus BC: Section I, Part A 5 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number..
CHAPTER SIXTEEN. = 4 x y + 6 x y + 3 x y + 4 x y = 17 x y = 31(0.1)(0.2) = f(x i, y i) x y = 7 x y + 10 x y + 6 x y + 8 x y = 31 x y. x = 0.
 CHAPTE SIXTEEN 6. SOLUTIONS 5 Solutions for Section 6. Eercises. Mark the values of the function on the plane, as shown in Figure 6., so that ou can guess respectivel at the smallest and largest values
CHAPTE SIXTEEN 6. SOLUTIONS 5 Solutions for Section 6. Eercises. Mark the values of the function on the plane, as shown in Figure 6., so that ou can guess respectivel at the smallest and largest values
Answers Investigation 2
 Applications 1. a. Square Side Area 4 16 2 6 36 7 49 64 9 1 10 100 11 121 Rectangle Length Width Area 0 0 9 1 9 10 2 20 11 3 33 12 4 4 13 6 14 6 4 1 7 10 b. (See Figure 1.) c. The graph and the table both
Applications 1. a. Square Side Area 4 16 2 6 36 7 49 64 9 1 10 100 11 121 Rectangle Length Width Area 0 0 9 1 9 10 2 20 11 3 33 12 4 4 13 6 14 6 4 1 7 10 b. (See Figure 1.) c. The graph and the table both
x f(x)
 CALCULATOR SECTION. For y + y = 8 find d point (, ) on the curve. A. B. C. D. dy at the 7 E. 6. Suppose silver is being etracted from a.t mine at a rate given by A'( t) = e, A(t) is measured in tons of
CALCULATOR SECTION. For y + y = 8 find d point (, ) on the curve. A. B. C. D. dy at the 7 E. 6. Suppose silver is being etracted from a.t mine at a rate given by A'( t) = e, A(t) is measured in tons of
MCB4UW Handout 7.6. Comparison of the Disk/Washer and Shell Methods. V f x g x. V f y g y
 MCBUW Handout 7.6 Comparison of the Disk/Washer and Shell Methods Method Ais of Formula Notes aout the Revolution Representative Rectangle a Disk Method -ais V f d -ais a V g d Washer Method -ais a V f
MCBUW Handout 7.6 Comparison of the Disk/Washer and Shell Methods Method Ais of Formula Notes aout the Revolution Representative Rectangle a Disk Method -ais V f d -ais a V g d Washer Method -ais a V f
Section 2 Practice Tests
 Section Practice Tests This section gives 18 sample problems that mix and match concepts similar to problems on the free-response section of the AP exam. While any of these examples would be a good review
Section Practice Tests This section gives 18 sample problems that mix and match concepts similar to problems on the free-response section of the AP exam. While any of these examples would be a good review
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Eam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine from the graph whether the function has an absolute etreme values on the interval
Eam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine from the graph whether the function has an absolute etreme values on the interval
13.1. For further details concerning the physics involved and animations of the trajectories of the particles, see the following websites:
 8 CHAPTER VECTOR FUNCTIONS N Some computer algebra sstems provide us with a clearer picture of a space curve b enclosing it in a tube. Such a plot enables us to see whether one part of a curve passes in
8 CHAPTER VECTOR FUNCTIONS N Some computer algebra sstems provide us with a clearer picture of a space curve b enclosing it in a tube. Such a plot enables us to see whether one part of a curve passes in
Fall 2009 Instructor: Dr. Firoz Updated on October 4, 2009 MAT 265
 Fall 9 Instructor: Dr. Firoz Updated on October 4, 9 MAT 65 Basic Algebra and Trigonometr Review Algebra Factoring quadratic epressions Eamples Case : Leading coefficient. Factor 5 6 ( )( ), as -, - are
Fall 9 Instructor: Dr. Firoz Updated on October 4, 9 MAT 65 Basic Algebra and Trigonometr Review Algebra Factoring quadratic epressions Eamples Case : Leading coefficient. Factor 5 6 ( )( ), as -, - are
5. Find the intercepts of the following equations. Also determine whether the equations are symmetric with respect to the y-axis or the origin.
 MATHEMATICS 1571 Final Examination Review Problems 1. For the function f defined by f(x) = 2x 2 5x find the following: a) f(a + b) b) f(2x) 2f(x) 2. Find the domain of g if a) g(x) = x 2 3x 4 b) g(x) =
MATHEMATICS 1571 Final Examination Review Problems 1. For the function f defined by f(x) = 2x 2 5x find the following: a) f(a + b) b) f(2x) 2f(x) 2. Find the domain of g if a) g(x) = x 2 3x 4 b) g(x) =
Chapter 8: Radical Functions
 Chapter 8: Radical Functions Chapter 8 Overview: Types and Traits of Radical Functions Vocabulary:. Radical (Irrational) Function an epression whose general equation contains a root of a variable and possibly
Chapter 8: Radical Functions Chapter 8 Overview: Types and Traits of Radical Functions Vocabulary:. Radical (Irrational) Function an epression whose general equation contains a root of a variable and possibly
Section 3.2 Applications of Radian Measure
 Section. Applications of Radian Measure 07 (continued) 88. 80 radians = = 0 5 5 80 radians = = 00 7 5 = 5 radian s 0 = 0 radian s = radian 80 89. (a) In hours, the hour hand will rotate twice around the
Section. Applications of Radian Measure 07 (continued) 88. 80 radians = = 0 5 5 80 radians = = 00 7 5 = 5 radian s 0 = 0 radian s = radian 80 89. (a) In hours, the hour hand will rotate twice around the
x f(x)
 CALCULATOR SECTION. For y y 8 find d point (, ) on the curve. A. D. dy at the 7 E. 6. Suppose silver is being etracted from a.t mine at a rate given by A'( t) e, A(t) is measured in tons of silver and
CALCULATOR SECTION. For y y 8 find d point (, ) on the curve. A. D. dy at the 7 E. 6. Suppose silver is being etracted from a.t mine at a rate given by A'( t) e, A(t) is measured in tons of silver and
Chapter 6: Applications of Integration
 Chapter 6: Applications of Integration Section 6.3 Volumes by Cylindrical Shells Sec. 6.3: Volumes: Cylindrical Shell Method Cylindrical Shell Method dv = 2πrh thickness V = න a b 2πrh thickness Thickness
Chapter 6: Applications of Integration Section 6.3 Volumes by Cylindrical Shells Sec. 6.3: Volumes: Cylindrical Shell Method Cylindrical Shell Method dv = 2πrh thickness V = න a b 2πrh thickness Thickness
CHAPTER 11 Vector-Valued Functions
 CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
Student s Printed Name:
 MATH 1060 Test Answer Ke Spring 016 Calculus of One Variable I Version A Sections..9 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: CUID: Section: Instructions: You are not permitted to use a calculator on an portion
MATH 1060 Test Answer Ke Spring 016 Calculus of One Variable I Version A Sections..9 Student s Printed Name: Instructor: CUID: Section: Instructions: You are not permitted to use a calculator on an portion
Math 76 Practice Problems for Midterm II Solutions
 Math 76 Practice Problems for Midterm II Solutions 6.4-8. DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam. You may expect to
Math 76 Practice Problems for Midterm II Solutions 6.4-8. DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam. You may expect to
3 Applications of Derivatives Instantaneous Rates of Change Optimization Related Rates... 13
 Contents Limits Derivatives 3. Difference Quotients......................................... 3. Average Rate of Change...................................... 4.3 Derivative Rules...........................................
Contents Limits Derivatives 3. Difference Quotients......................................... 3. Average Rate of Change...................................... 4.3 Derivative Rules...........................................
A11.1 Areas under curves
 Applications 11.1 Areas under curves A11.1 Areas under curves Before ou start You should be able to: calculate the value of given the value of in algebraic equations of curves calculate the area of a trapezium.
Applications 11.1 Areas under curves A11.1 Areas under curves Before ou start You should be able to: calculate the value of given the value of in algebraic equations of curves calculate the area of a trapezium.
Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. is continuous.
 Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. + +. Evaluate lim + (a (b (c (d 0 (e None of the above.. Evaluate lim (a (b (c (d 0 (e + + None of the above.. Find
Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. + +. Evaluate lim + (a (b (c (d 0 (e None of the above.. Evaluate lim (a (b (c (d 0 (e + + None of the above.. Find
Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables.
 Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables. Partial derivatives and directional derivatives. Directional derivative of functions of
Directional derivatives and gradient vectors (Sect. 14.5). Directional derivative of functions of two variables. Partial derivatives and directional derivatives. Directional derivative of functions of
Review of elements of Calculus (functions in one variable)
 Review of elements of Calculus (functions in one variable) Mainly adapted from the lectures of prof Greg Kelly Hanford High School, Richland Washington http://online.math.uh.edu/houstonact/ https://sites.google.com/site/gkellymath/home/calculuspowerpoints
Review of elements of Calculus (functions in one variable) Mainly adapted from the lectures of prof Greg Kelly Hanford High School, Richland Washington http://online.math.uh.edu/houstonact/ https://sites.google.com/site/gkellymath/home/calculuspowerpoints
f x and the x axis on an interval from x a and
 Unit 6: Chapter 8 Areas and Volumes & Density Functions Part 1: Areas To find the area bounded by a function bwe use the integral: f d b a b 0 f d f d. a b a f and the ais on an interval from a and. This
Unit 6: Chapter 8 Areas and Volumes & Density Functions Part 1: Areas To find the area bounded by a function bwe use the integral: f d b a b 0 f d f d. a b a f and the ais on an interval from a and. This
