Machine Foundation Analysis VERIFICATION MANUAL REV D
|
|
|
- Basil Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Machine Foundation Analysis VERIFICATION MANUAL REV D TM
2 Page:2 COPYRIGHT The computer program CLOCKWORK and all associated documentation are proprietary and copyrighted products. Worldwide rights of ownership rest with NEWTONIAN MACHINES. Unlicensed use of the program or reproduction of the documentation in any form, without prior written authorization from NEWTONIAN MACHINES is explicitly prohibited. NEWTONIAN MACHINES ANDRÉS DE FUENZALIDA 147 PROVIDENCIA, SANTIAGO, CHILE Tel: (+56 2) contact@newtonianmachines.com Web:
3 Page:3 CONTENT I. INTRODUCTION TEST CASE TEST CASE TEST CASE TEST CASE TEST CASE
4 Page:4 I. INTRODUCTION Clockwork is a foundation design and analysis software, based on well-known and internationally accepted theories. This document provides example problems from recognized publications in order to verify the achievement of accuracy and acceptable results. However and by the nature of this software, it is difficult to find suitable examples for this verification manual since most publications are conceived to be a guide for engineers by doing hand calculations, aside from the laborious task that it is for example calculate a structure with six degree of freedom, natural frequencies for a coupled system, intricate periodic loads, etc. The analyzed tests in this manual are just a small part of the rigorous tests that our developers run in the testing stage to ensure the quality of Clockwork.
5 Page:5 1. TEST CASE 1 Dynamic load of single-cylinder compressor. a. Overview Reference: [1] Foundation Vibration Analysis Using Simple Physical Models, John P. Wolf, pg. 56., ISBN: Dynamic Load Type: Periodic Excitation Units: tonnef / m b. Problem Description On a rigid block foundation rests a reciprocating machine composed of a compressor and a driving motor, which generates a vertical unbalanced dynamic load with two components. The first component acts at a frequency of 9Hz and the second component at twice this frequency. The resulting dynamic total load it is represented by P(t) (Fig.1.1). c. Input Parameters Compressor and driving motor mass = Dynamic Load Total load acts vertically on the foundation block. Total Load P(t) = Total Load Operation Frequency = 9 Hz Number of terms used in Fourier Series = 20 Fig. 1.1 Dynamic total load from vertical single-cylinder compressor.
6 Page:6 Rigid Foundation Block Size Length = 2.0 m Width = 1.5 m Height = 1.0 m Soil Poisson s Ratio µ = 0.33 Specific Mass Density ρ = d. Analysis Shear Modulus G = For this analysis the Cone method it is used in Clockwork. e. Results Comparison Measured Value Clockwork Displacement Ref[1] Displacement [mm] [mm] Lower Peak ± * Higher Peak ± * * Displacement value from Fig. XX [1] Fig1.2 - Dynamic vertical displacement from Clockwork results.
7 Page:7 2. TEST CASE 2 Dynamic load of weaver s loom. a. Overview Reference: [1] Foundation Vibration Analysis Using Simple Physical Models, John P. Wolf, pg. 56, ISBN: Dynamic Load Type: Periodic Excitation Units: tonnef / m b. Problem Description On a rigid block foundation rests a weaver s loom operating at 9Hz with a mass of 2750kg. In this case the load is expressed as a Fourier series with 20 terms (Fig 2.1). c. Input Parameters Weaver s loom mass = Dynamic Load Load acts vertically on the foundation block. Vertical Load P(t) Fig 2.1 Dynamic vertical load from weaver s loom. Load Operation Frequency = 9 Hz up to 180 Hz Number of terms used in Fourier Series = 20
8 Page:8 Rigid Foundation Block Size Length = 2.0 m Width = 1.5 m Height = 1.0 m Soil Poisson s Ratio µ = 0.33 Mass Density ρ = d. Analysis Shear Modulus G = For this analysis the Cone method it is used in Clockwork e. Results Comparison Measured Value Clockwork Displacement Ref[1] Displacement [mm] [mm] Lower Peak ± * Higher Peak ± * * Displacement value from Fig [1] Fig 2.2 Dynamic vertical displacement from Clockwork results.
9 Page:9 3. TEST CASE 3 Vertical single-cylinder compressor. a. Overview Reference: [2] Vibration of Soils and Foundations, F. E. Richart, Jr., pg ISBN: Dynamic Load Type: Harmonic Excitation Measured Units: lbf / ft b. Problem Description c. Input Parameters Weight * f compressor = Dynamic Load Load acts vertically on the foundation block. Vertical Load = Fig. 3.1 Dynamic vertical load Load Operation Frequency = 7.5 Hz
10 Page:10 Rigid Foundation Block Size Length = 16 ft Width = 7 ft Height = 3 ft Soil Poisson s Ratio µ = 0.33 Mass Density ρ = d. Analysis Shear Modulus G = For this analysis all available methods were used in Clockwork. e. Results Comparison Measured Clockwork Displacement Displacement Ref[2] Value [in] Zero to Peak [ft] [in]
11 Page:11 4. TEST CASE 4 a. OVERVIEW The Foundation from Fig 4.1 was subjected to six load cases in order to compare results using SAP2000 and Clockwork. Dynamic Load Type: Harmonic Excitation Units: SI Damping and Group Effect were not considered. a. PROBLEM DESCRIPTION A square foundation is loaded on one of its edges and on the geometric center of gravity of the soil contact area. b. PARAMETERS FOUNDATION PARAMETERS Number of Piles 4 Pile Diameter Foundation Height Foundation Length Foundation Width 400 mm 1000 mm 3000 mm 3000 mm Specific Weight 2500 kgf/m 3 Soil Stiffness 80 kgf/cm 2 Foundation Weight kgf PILES LOCATION X - mm Y - mm Pile Pile Pile Pile Fig 4. 1 Pile Foundation on SAP2000 CASE Location Load Location Load X Y Z tonf mm mm mm 1 X Y Z X Y Z
12 Page:12 c. RESULTS - SAP2000 v15 Measured Points Displacements Angular Displacements CASE X Y Z u1 u2 u3 θ1 θ2 θ3 mm mm mm m m m rad rad rad ,77E-04 2,29E-04 4,00E ,70E-05-1,52E ,29E-04 4,77E-04-4,00E-05-2,70E ,52E ,00E-05 4,00E-05-8,90E-05-2,40E-05-2,40E ,21E ,60E ,10E ,21E-04-1,60E-05-1,10E ,70E ,21E ,70E-05-1,52E ,21E ,70E ,52E ,60E-05 1,60E-05-1,70E-05-2,40E-05-2,40E ,10E ,10E ,10E ,10E ,70E RESULTS - CLOCKWORK v12 Measured Points Displacements Angular Displacements CASE X Y Z u1 u2 u3 θ1 θ2 θ3 mm mm mm m m m rad rad rad ,76E-04 2,28E-04 4,01E ,67E-05-1,52E ,28E-04 4,76E-04-4,01E-05-2,67E ,52E ,01E-05 4,01E-05-8,85E-05-2,39E-05-2,39E ,21E ,61E ,07E ,21E-04-1,61E-05-1,07E ,65E ,21E ,67E-05-1,52E ,21E ,67E ,52E ,61E-05 1,61E-05-1,65E-05-2,39E-05-2,39E ,10E ,07E ,10E ,07E ,65E Fig 4.2 Pile Foundation on Clockwork 12
13 Page:13 Porcentual Difference of Results between SAP2000 and Clockwork Measured Point Location Displacements Angular Displacements CASE X Y Z u1 u2 u3 θ1 θ2 θ3 mm mm mm m m m rad rad rad ,21% 0,44% 0,25% 0,00% 1,11% 0,00% ,44% 0,21% 0,25% 1,11% 0,00% 0,00% ,25% 0,25% 0,56% 0,42% 0,42% 0,00% ,00% 0,00% 0,62% 0,00% 2,73% 0,00% ,00% 0,00% 0,62% 2,73% 0,00% 0,00% ,00% 0,00% 2,94% 0,00% 0,00% 0,00% ,00% 0,00% 0,00% 0,00% 1,11% 0,00% ,00% 0,00% 0,00% 1,11% 0,00% 0,00% ,62% 0,62% 2,94% 0,42% 0,42% 0,00% ,00% 0,00% 0,00% 0,00% 2,73% 0,00% ,00% 0,00% 0,00% 2,73% 0,00% 0,00% ,00% 0,00% 2,94% 0,00% 0,00% 0,00%
14 Page:14 5. TEST CASE 5 a. OVERVIEW The Foundation from Fig 5.1 was subjected to six load cases in order to compare results using SAP2000 and Clockwork. Dynamic Load Type: Harmonic Excitation Units: SI Damping and Group Effect were not considered b. PROBLEM DESCRIPTION A square foundation is loaded on one of its edges and on the geometric center of gravity of the soil contact area. c. PARAMETERS FOUNDATION PARAMETERS Piles: 6 Pile Diameter: 400 mm Block 1 - Height: 1500 mm Block 1 - Length: 2000 mm Block 1 - Width: 3000 mm Block 2 - Height: 2500 mm Block 2 - Length: 3000 mm Block 2 - Width: 3000 mm Reinf. Concrete Specific Weight 2500 kgf/m 3 Peso fundación : 78,75 kgf Soil Stiffness 80 kgf/cm 2 Fig 5. 1 Pile Foundation on SAP2000 Fig 5. 2 Pile Foundation on Clockwork 12
15 Page:15 PILES LOCATION X mm Y mm CASE Location Load tonf X mm Y mm Pile 1 : Pile 2 : Pile 3 : Pile 4 : Pile 5 : Pile 6 : X Y Z X Y Z RESULTS SAP2000 v15 Measured Points Displacements Angular Displacements Caso X Y Z u1 u2 u3 θ1 θ2 θ3 mm mm mm m m m rad rad rad ,49E-04 1,57E-04 2,20E ,87E-06-6,30E ,57E-04 4,84E-04-6,00E-05-4,00E ,05E ,20E-05 6,00E-05-7,80E-05-2,80E-05-1,00E ,41E ,84E ,73E ,62E-04-1,80E-05-1,20E ,10E ,41E ,87E-06-6,30E ,62E ,00E ,05E ,84E-06 1,80E-05-1,10E-05-2,80E-05-1,00E ,37E ,73E ,44E ,20E ,10E RESULTS - CLOCKWORK v12 Measured Points Displacements Angular Displacements Caso X Y Z u1 u2 u3 θ1 θ2 θ3 mm mm mm m m m rad rad rad ,49E-04 1,57E-04 2,22E ,88E-06-6,29E ,57E-04 4,84E-04-6,01E-05-4,00E ,04E ,22E-05 6,00E-05-7,80E-05-2,76E-05-1,02E ,41E ,87E ,75E ,62E-04-1,86E-05-1,24E ,10E ,41E ,88E-06-6,29E ,62E ,00E ,04E ,87E-06 1,86E-05-1,10E-05-2,76E-05-1,02E ,37E ,75E ,43E ,24E ,10E
16 Page:16
Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking
 Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking What is the maximum relative displacement and the amplitude of the total displacement of a SDOF structure subjected to ground shaking? magnitude of ground
Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking What is the maximum relative displacement and the amplitude of the total displacement of a SDOF structure subjected to ground shaking? magnitude of ground
Chapter 2: Rigid Bar Supported by Two Buckled Struts under Axial, Harmonic, Displacement Excitation..14
 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Chapter a. Spring constant, k : The change in the force per unit length change of the spring. b. Coefficient of subgrade reaction, k:
 Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATORS
 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATORS Clemens A.J. Beijers and André de Boer University of Twente P.O. Box 7, 75 AE Enschede, The Netherlands email: c.a.j.beijers@utwente.nl Abstract An important
NUMERICAL MODELLING OF RUBBER VIBRATION ISOLATORS Clemens A.J. Beijers and André de Boer University of Twente P.O. Box 7, 75 AE Enschede, The Netherlands email: c.a.j.beijers@utwente.nl Abstract An important
ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS
 Transactions, SMiRT-24 ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS 1 Principal Engineer, MTR & Associates, USA INTRODUCTION Mansour Tabatabaie 1 Dynamic response
Transactions, SMiRT-24 ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS 1 Principal Engineer, MTR & Associates, USA INTRODUCTION Mansour Tabatabaie 1 Dynamic response
CIVL 8/7117 Chapter 12 - Structural Dynamics 1/75. To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass
 CIV 8/77 Chapter - /75 Introduction To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass system. To derive the finite element equations for the time-dependent stress analysis of the one-dimensional
CIV 8/77 Chapter - /75 Introduction To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass system. To derive the finite element equations for the time-dependent stress analysis of the one-dimensional
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Active Impact Sound Isolation with Floating Floors. Gonçalo Fernandes Lopes
 Active Impact Sound Isolation with Floating Floors Gonçalo Fernandes Lopes Outubro 009 Active impact sound isolation with floating floors Abstract The users of buildings are, nowadays, highly demanding
Active Impact Sound Isolation with Floating Floors Gonçalo Fernandes Lopes Outubro 009 Active impact sound isolation with floating floors Abstract The users of buildings are, nowadays, highly demanding
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material
 Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material The candidate is expected to have a thorough understanding of engineering vibrations topics. These topics are listed below for clarification. Not all instructors
Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material The candidate is expected to have a thorough understanding of engineering vibrations topics. These topics are listed below for clarification. Not all instructors
Structural System, Machines and Load Cases
 Machine-Induced Vibrations Machine-Induced Vibrations In the following example the dynamic excitation of two rotating machines is analyzed. A time history analysis in the add-on module RF-DYNAM Pro - Forced
Machine-Induced Vibrations Machine-Induced Vibrations In the following example the dynamic excitation of two rotating machines is analyzed. A time history analysis in the add-on module RF-DYNAM Pro - Forced
Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Computational Simulation of Dynamic Response of Vehicle Tatra T815 and the Ground To cite this article: Jozef Vlek and Veronika
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Varuvan Vadivelan. Institute of Technology LAB MANUAL. : 2013 : B.E. MECHANICAL ENGINEERING : III Year / V Semester. Regulation Branch Year & Semester
 Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation Branch Year & Semester : 2013 : B.E. MECHANICAL ENGINEERING : III Year / V Semester ME 6511 - DYNAMICS LABORATORY GENERAL
Varuvan Vadivelan Institute of Technology Dharmapuri 636 703 LAB MANUAL Regulation Branch Year & Semester : 2013 : B.E. MECHANICAL ENGINEERING : III Year / V Semester ME 6511 - DYNAMICS LABORATORY GENERAL
Influence of the Soil Structure Interaction on the Fundamental Period of Large Dynamic Machine Foundation
 Influence of the Soil Structure Interaction on the Fundamental Period of Large Dynamic Machine Foundation Jingbo Liu, Wenhui Wang, Xiaobo Zhang, Dongdong Zhao Department of Civil Engineering, Tsinghua
Influence of the Soil Structure Interaction on the Fundamental Period of Large Dynamic Machine Foundation Jingbo Liu, Wenhui Wang, Xiaobo Zhang, Dongdong Zhao Department of Civil Engineering, Tsinghua
Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction
 Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng. Professor Graduate School of Engineering Hiroshima University Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Chapter 1 : Introduction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng.
Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng. Professor Graduate School of Engineering Hiroshima University Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Chapter 1 : Introduction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng.
Mechatronics. MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1
 Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
APPROXIMATE DYNAMIC MODEL SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR LARGE, COMPLEX SPACE STRUCTURES. Timothy S. West, Senior Engineer
 APPROXIMATE DYNAMIC MODEL SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR LARGE, COMPLEX SPACE STRUCTURES Timothy S. West, Senior Engineer McDonnell Douglas Aerospace Space Station Division, Houston, Texas ABSTRACT During the
APPROXIMATE DYNAMIC MODEL SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS FOR LARGE, COMPLEX SPACE STRUCTURES Timothy S. West, Senior Engineer McDonnell Douglas Aerospace Space Station Division, Houston, Texas ABSTRACT During the
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
COMPLEX MODULUS AND DAMPING MEASUREMENTS USING RESONANT AND NON-RESONANT METHODS
 COMPLEX MODULUS AND DAMPING MEASUREMENTS USING RESONANT AND NON-RESONANT METHODS S. Gade, K. Zaveri, H. Konstantin-Hansen and H. Herlufsen Briiel & Kjaer, Skodsborgvej 307,285O Naerum, Denmark ABSTRACT
COMPLEX MODULUS AND DAMPING MEASUREMENTS USING RESONANT AND NON-RESONANT METHODS S. Gade, K. Zaveri, H. Konstantin-Hansen and H. Herlufsen Briiel & Kjaer, Skodsborgvej 307,285O Naerum, Denmark ABSTRACT
Structural Dynamics. Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma).
 Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Vibrations of Machine Foundations
 Vibrations of Machine Foundations Richard P. Ray, Ph.D., P.E. Civil and Environmental Engineering University of South Carolina Thanks To: Prof. Richard D. Woods, Notre Dame Univ. Prof. F.E. Richart, Jr.
Vibrations of Machine Foundations Richard P. Ray, Ph.D., P.E. Civil and Environmental Engineering University of South Carolina Thanks To: Prof. Richard D. Woods, Notre Dame Univ. Prof. F.E. Richart, Jr.
UNITS AND DEFINITIONS RELATED TO BIOMECHANICAL AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL MEASUREMENTS
 APPENDIX B UNITS AND DEFINITIONS RELATED TO BIOMECHANICAL AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL MEASUREMENTS All units used are SI (Système International d Unités). The system is based on seven well-defined base units
APPENDIX B UNITS AND DEFINITIONS RELATED TO BIOMECHANICAL AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL MEASUREMENTS All units used are SI (Système International d Unités). The system is based on seven well-defined base units
Advanced Vibrations. Elements of Analytical Dynamics. By: H. Ahmadian Lecture One
 Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
k 21 k 22 k 23 k 24 k 31 k 32 k 33 k 34 k 41 k 42 k 43 k 44
 CE 6 ab Beam Analysis by the Direct Stiffness Method Beam Element Stiffness Matrix in ocal Coordinates Consider an inclined bending member of moment of inertia I and modulus of elasticity E subjected shear
CE 6 ab Beam Analysis by the Direct Stiffness Method Beam Element Stiffness Matrix in ocal Coordinates Consider an inclined bending member of moment of inertia I and modulus of elasticity E subjected shear
Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1
 Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS 1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.2 Relation to Equivalent-Linear Methods... 1-2 1.2.1 Characteristics of the Equivalent-Linear Method... 1-2 1.2.2
Dynamic Analysis Contents - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS 1.1 Overview... 1-1 1.2 Relation to Equivalent-Linear Methods... 1-2 1.2.1 Characteristics of the Equivalent-Linear Method... 1-2 1.2.2
Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee
 Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee Module - 02 Lecture - 15 Machine Foundations - 3 Hello viewers, In the last class we
Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee Module - 02 Lecture - 15 Machine Foundations - 3 Hello viewers, In the last class we
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
EXPERIMENTAL DETERMINATION OF DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF STRUCTURES
 EXPERIMENTAL DETERMINATION OF DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF STRUCTURES RADU CRUCIAT, Assistant Professor, Technical University of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Railways, Roads and Bridges, e-mail: rcruciat@utcb.ro
EXPERIMENTAL DETERMINATION OF DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF STRUCTURES RADU CRUCIAT, Assistant Professor, Technical University of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Railways, Roads and Bridges, e-mail: rcruciat@utcb.ro
NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PILE-SOIL SYSTEM UNDER VERTICAL VIBRATION
 IGC 2009, Guntur, INDIA NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PILE-SOIL SYSTEM UNDER VERTICAL VIBRATION B. Manna Lecturer, Civil Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela 769008, India.
IGC 2009, Guntur, INDIA NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PILE-SOIL SYSTEM UNDER VERTICAL VIBRATION B. Manna Lecturer, Civil Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela 769008, India.
A Circular Cavity Embedded in a Full-Plane Under Impulse Pressure
 Benchmark Example No. 50 A Circular Cavity Embedded in a Full-Plane Under Impulse Pressure SOFiSTiK 2018 VERiFiCATiON MANUAL BE50: A Circular Cavity Embedded in a Full-Plane Under Impulse Pressure VERiFiCATiON
Benchmark Example No. 50 A Circular Cavity Embedded in a Full-Plane Under Impulse Pressure SOFiSTiK 2018 VERiFiCATiON MANUAL BE50: A Circular Cavity Embedded in a Full-Plane Under Impulse Pressure VERiFiCATiON
Oscillations. Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Oscillations Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum Ref: 11-1,,3,4. Page 1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object oscillates
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Oscillations Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum Ref: 11-1,,3,4. Page 1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object oscillates
Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 2002
 Abstract Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 00 Paresh V. Patel Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Nirma Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad 38481 In this article codal provisions of IS 1893
Abstract Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 00 Paresh V. Patel Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Nirma Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad 38481 In this article codal provisions of IS 1893
Dynamic Analysis of Pile Foundations: Effects of Material Nonlinearity of Soil
 Dynamic Analysis of Pile Foundations: Effects of Material Nonlinearity of Soil Bal Krishna Maheshwari Asst. Professor, Department of Earthquake Engineering, IIT Roorkee, Roorkee, U.A. 247 667, India (Formerly
Dynamic Analysis of Pile Foundations: Effects of Material Nonlinearity of Soil Bal Krishna Maheshwari Asst. Professor, Department of Earthquake Engineering, IIT Roorkee, Roorkee, U.A. 247 667, India (Formerly
Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 Module 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in URL:
Module 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in URL:
*Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units
 INTRODUCTION *Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units Mechanics may be defined as the physical science which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under
INTRODUCTION *Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units Mechanics may be defined as the physical science which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under
557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer
 557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer M. Sivčák 1, J. Škoda, Technical University in Liberec, Studentská, Liberec, Czech Republic e-mail: 1 michal.sivcak@tul.cz; jan.skoda@pevnosti.cz
557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer M. Sivčák 1, J. Škoda, Technical University in Liberec, Studentská, Liberec, Czech Republic e-mail: 1 michal.sivcak@tul.cz; jan.skoda@pevnosti.cz
Analyses of Soil-Structure Systems
 Analyses of Soil-Structure Systems Julio García Paul C. Rizzo Associates, Inc., 105 Mall Blvd. Suite 270E, Monroeville, PA 15146, USA Phone: +1 (412)856-9700, Fax: +1 (412)856-9749, Email: julio.garcia@rizzoassoc.com
Analyses of Soil-Structure Systems Julio García Paul C. Rizzo Associates, Inc., 105 Mall Blvd. Suite 270E, Monroeville, PA 15146, USA Phone: +1 (412)856-9700, Fax: +1 (412)856-9749, Email: julio.garcia@rizzoassoc.com
Sound radiation and sound insulation
 11.1 Sound radiation and sound insulation We actually do not need this chapter You have learned everything you need to know: When waves propagating from one medium to the next it is the change of impedance
11.1 Sound radiation and sound insulation We actually do not need this chapter You have learned everything you need to know: When waves propagating from one medium to the next it is the change of impedance
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF PILES IN SAND BASED ON SOIL-PILE INTERACTION
 October 1-17,, Beijing, China DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF PILES IN SAND BASED ON SOIL-PILE INTERACTION Mohammad M. Ahmadi 1 and Mahdi Ehsani 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Geotechnical Group,
October 1-17,, Beijing, China DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF PILES IN SAND BASED ON SOIL-PILE INTERACTION Mohammad M. Ahmadi 1 and Mahdi Ehsani 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Geotechnical Group,
NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS
 NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Using FE Methods emphasizes fundamental mechanics principles and outlines a modern approach to understanding structural dynamics.
NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS USING FE METHODS Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Using FE Methods emphasizes fundamental mechanics principles and outlines a modern approach to understanding structural dynamics.
Modal analysis of shear buildings
 Modal analysis of shear buildings A comprehensive modal analysis of an arbitrary multistory shear building having rigid beams and lumped masses at floor levels is obtained. Angular frequencies (rad/sec),
Modal analysis of shear buildings A comprehensive modal analysis of an arbitrary multistory shear building having rigid beams and lumped masses at floor levels is obtained. Angular frequencies (rad/sec),
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic. FEMAP & NX Nastran
 Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
Response Spectrum Analysis Shock and Seismic FEMAP & NX Nastran Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 2. THE ACCELEROGRAM... 4 3. CREATING A RESPONSE SPECTRUM... 5 4. NX NASTRAN METHOD... 8 5. RESPONSE
WORK SHEET FOR MEP311
 EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Vibration analysis of compressor piping system with fluid pulsation
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 6 () () 393~399 www.springerlink.com/content/738-494x DOI.7/s6--89-8 Vibration analysis of compressor piping system with fluid pulsation Seong-Hyeon Lee, Sang-Mo
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 6 () () 393~399 www.springerlink.com/content/738-494x DOI.7/s6--89-8 Vibration analysis of compressor piping system with fluid pulsation Seong-Hyeon Lee, Sang-Mo
Design Procedures For Dynamically Loaded Foundations
 Design Procedures For Dynamically Loaded Foundations 1/11 Choice of parameters for equivalent lumped systems Lumped mass : the mass of the foundation and supported machinery Damping : 1 Geometrical(or
Design Procedures For Dynamically Loaded Foundations 1/11 Choice of parameters for equivalent lumped systems Lumped mass : the mass of the foundation and supported machinery Damping : 1 Geometrical(or
SHOCK RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS VIA THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Revision C
 SHOCK RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS VIA THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com November 19, 2010 Introduction This report gives a method for determining the response of
SHOCK RESPONSE SPECTRUM ANALYSIS VIA THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Revision C By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com November 19, 2010 Introduction This report gives a method for determining the response of
ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010
 ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010 PROBLEM 1: You are given the lumped parameter dynamic differential equations of motion for a two degree-offreedom model of an automobile suspension system for small
ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010 PROBLEM 1: You are given the lumped parameter dynamic differential equations of motion for a two degree-offreedom model of an automobile suspension system for small
Effect of Soil-Foundation Interaction on the Dynamic Response of a Four-Cylinder Compressor Foundation
 Case Study Effect of Soil-Foundation Interaction on the Dynamic Response of a Four-Cylinder Compressor Foundation O. S. Ali, Ph.D., P.E., M.ASCE 1 ; and Mustafa Mahamid, Ph.D., P.E., S.E., F.ASCE 2 Abstract:
Case Study Effect of Soil-Foundation Interaction on the Dynamic Response of a Four-Cylinder Compressor Foundation O. S. Ali, Ph.D., P.E., M.ASCE 1 ; and Mustafa Mahamid, Ph.D., P.E., S.E., F.ASCE 2 Abstract:
Chap. 15: Simple Harmonic Motion
 Chap. 15: Simple Harmonic Motion Announcements: CAPA is due next Tuesday and next Friday. Web page: http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phys1110/phys1110_sp12/ Examples of periodic motion vibrating guitar
Chap. 15: Simple Harmonic Motion Announcements: CAPA is due next Tuesday and next Friday. Web page: http://www.colorado.edu/physics/phys1110/phys1110_sp12/ Examples of periodic motion vibrating guitar
T1 T e c h n i c a l S e c t i o n
 1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
DEVELOPMENT OF ACTIVELY TUNED VIBRATION ABSORBER FOR WASHING MACHINE
 DEVELOPMENT OF ACTIVELY TUNED VIBRATION ABSORBER FOR WASHING MACHINE Mr.G.M.ABHISHEK 1, Mr. K. S. MANOBALA 2 1M.E.product design and commerce, psg college of technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India 2Assistant
DEVELOPMENT OF ACTIVELY TUNED VIBRATION ABSORBER FOR WASHING MACHINE Mr.G.M.ABHISHEK 1, Mr. K. S. MANOBALA 2 1M.E.product design and commerce, psg college of technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India 2Assistant
Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system
 Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system Edition 1 January 2005 Strand7 Release 2.3 2004-2005 Strand7 Pty Limited All rights reserved Contents Preface Chapter
Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system Edition 1 January 2005 Strand7 Release 2.3 2004-2005 Strand7 Pty Limited All rights reserved Contents Preface Chapter
Explosion Protection of Buildings
 Explosion Protection of Buildings Author: Miroslav Mynarz Explosion Protection of Buildings Introduction to the Problems of Determination of Building Structure's Response 3 Classification of actions According
Explosion Protection of Buildings Author: Miroslav Mynarz Explosion Protection of Buildings Introduction to the Problems of Determination of Building Structure's Response 3 Classification of actions According
18.12 FORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS
 8. ORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS Vibrations A mass m is attached to a helical spring and is suspended from a fixed support as before. Damping is also provided in the system ith a dashpot (ig. 8.). Before the
8. ORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS Vibrations A mass m is attached to a helical spring and is suspended from a fixed support as before. Damping is also provided in the system ith a dashpot (ig. 8.). Before the
TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A. By Tom Irvine February 25, 2008
 TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com February 5, 008 Introduction Consider a base plate mass m and an avionics mass m modeled as two-degree-of-freedom.
TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com February 5, 008 Introduction Consider a base plate mass m and an avionics mass m modeled as two-degree-of-freedom.
NON-LINEAR VISCOELASTIC MODEL OF STRUCTURAL POUNDING
 3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 004 Paper No. 308 NON-LINEAR VISCOELASTIC MODEL OF STRUCTURAL POUNDING Robert JANKOWSKI SUMMARY Pounding between structures
3 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 004 Paper No. 308 NON-LINEAR VISCOELASTIC MODEL OF STRUCTURAL POUNDING Robert JANKOWSKI SUMMARY Pounding between structures
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work.
 PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work. In-Class Activities: 2. Apply the principle of work
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work. In-Class Activities: 2. Apply the principle of work
Final Exam December 13, 2016
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-boo, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Do NOT unstaple your exam. Do NOT write
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-boo, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Do NOT unstaple your exam. Do NOT write
SHAKE TABLE STUDY OF SOIL STRUCTURE INTERACTION EFFECTS ON SEISMIC RESPONSE OF SINGLE AND ADJACENT BUILDINGS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1918 SHAKE TABLE STUDY OF SOIL STRUCTURE INTERACTION EFFECTS ON SEISMIC RESPONSE OF SINGLE AND ADJACENT
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1918 SHAKE TABLE STUDY OF SOIL STRUCTURE INTERACTION EFFECTS ON SEISMIC RESPONSE OF SINGLE AND ADJACENT
Strength Study of Spiral Flexure Spring of Stirling Cryocooler
 Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Strength Study of Spiral of Stirling Cryocooler WANG Wen-Rui, NIE Shuai, ZHANG Jia-Ming School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science
Sensors & Transducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Strength Study of Spiral of Stirling Cryocooler WANG Wen-Rui, NIE Shuai, ZHANG Jia-Ming School of Mechanical Engineering, University of Science
Dynamics Manual. Version 7
 Dynamics Manual Version 7 DYNAMICS MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...1-1 1.1 About this manual...1-1 2 Tutorial...2-1 2.1 Dynamic analysis of a generator on an elastic foundation...2-1 2.1.1 Input...2-1
Dynamics Manual Version 7 DYNAMICS MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction...1-1 1.1 About this manual...1-1 2 Tutorial...2-1 2.1 Dynamic analysis of a generator on an elastic foundation...2-1 2.1.1 Input...2-1
MODELLING OF VIBRATION WITH ABSORBER
 Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 10, No.4, 2010 mumerical modelling, Simulink, vibration, machine, absorber Jiří VONDŘICH 1 Evžen THÖNDE 1 Slavomír JIRKŮ 1 MODEING OF VIBRATION WITH ABSORBER Machine
Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 10, No.4, 2010 mumerical modelling, Simulink, vibration, machine, absorber Jiří VONDŘICH 1 Evžen THÖNDE 1 Slavomír JIRKŮ 1 MODEING OF VIBRATION WITH ABSORBER Machine
Structure Design and Modal Analysis for a New Type of Cycloidal Drives
 Structure Design and Modal nalysis for a New Type of Cycloidal Drives Yiqiang Jiang, Li Hou, Yunxia You, Jingyu Zhang School of Manufacturing Science and Engineering Sichuan University Chengdu, Sichuan,China
Structure Design and Modal nalysis for a New Type of Cycloidal Drives Yiqiang Jiang, Li Hou, Yunxia You, Jingyu Zhang School of Manufacturing Science and Engineering Sichuan University Chengdu, Sichuan,China
SEISMIC RESPONSE OF INDUSTRIAL STRUCTURES CONSIDERING SOIL-PILE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3129 SEISMIC RESPONSE OF INDUSTRIAL STRUCTURES CONSIDERING SOIL-PILE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION Yingcai Han
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 3129 SEISMIC RESPONSE OF INDUSTRIAL STRUCTURES CONSIDERING SOIL-PILE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION Yingcai Han
Engineering Science OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
1. Multiple Degree-of-Freedom (MDOF) Systems: Introduction
 1. Multiple Degree-of-Freedom (MDOF) Systems: Introduction Lesson Objectives: 1) List examples of MDOF structural systems and state assumptions of the idealizations. 2) Formulate the equation of motion
1. Multiple Degree-of-Freedom (MDOF) Systems: Introduction Lesson Objectives: 1) List examples of MDOF structural systems and state assumptions of the idealizations. 2) Formulate the equation of motion
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR.
 LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
Determination of dynamic soil characteristics and transfer functions to support the evaluation of the efficiency of vibration mitigation measures
 RIVAS Final Conference "Vibrations Ways out of the annoyance" Royal Flemish Academy of Belgium, Brussels, 21 November 213 Determination of dynamic soil characteristics and transfer functions to support
RIVAS Final Conference "Vibrations Ways out of the annoyance" Royal Flemish Academy of Belgium, Brussels, 21 November 213 Determination of dynamic soil characteristics and transfer functions to support
STIFFNESS AND DAMPING OF SOIL-PILE SYSTEM IN LIQUEFACTION PROCESS
 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 4 Paper No. 8 STIFFNESS AND DAMPING OF SOIL-PILE SYSTEM IN LIQUEFACTION PROCESS Hatsukazu MIZUNO and Tsutomu HIRADE SUMMARY
th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, 4 Paper No. 8 STIFFNESS AND DAMPING OF SOIL-PILE SYSTEM IN LIQUEFACTION PROCESS Hatsukazu MIZUNO and Tsutomu HIRADE SUMMARY
Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams.
 Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F
 MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 19, 2011 Introduction Consider a launch vehicle with a payload. Intuitively, a realistic payload
MASS LOADING EFFECTS FOR HEAVY EQUIPMENT AND PAYLOADS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 19, 2011 Introduction Consider a launch vehicle with a payload. Intuitively, a realistic payload
MODELING AND FEM ANALYSIS OF DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF THERMALLY OPTIMAL COMPOSITE MATERIALS
 11th World Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI) 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V) 6th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD VI) E. Oñate, J. Oliver
11th World Congress on Computational Mechanics (WCCM XI) 5th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM V) 6th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD VI) E. Oñate, J. Oliver
3. Overview of MSC/NASTRAN
 3. Overview of MSC/NASTRAN MSC/NASTRAN is a general purpose finite element analysis program used in the field of static, dynamic, nonlinear, thermal, and optimization and is a FORTRAN program containing
3. Overview of MSC/NASTRAN MSC/NASTRAN is a general purpose finite element analysis program used in the field of static, dynamic, nonlinear, thermal, and optimization and is a FORTRAN program containing
Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES
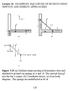 Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES Figure 5.29 (a) Uniform beam moving in frictionless slots and attached to ground via springs at A and B. The vertical force
Lecture 31. EXAMPLES: EQUATIONS OF MOTION USING NEWTON AND ENERGY APPROACHES Figure 5.29 (a) Uniform beam moving in frictionless slots and attached to ground via springs at A and B. The vertical force
Final Exam Solution Dynamics :45 12:15. Problem 1 Bateau
 Final Exam Solution Dynamics 2 191157140 31-01-2013 8:45 12:15 Problem 1 Bateau Bateau is a trapeze act by Cirque du Soleil in which artists perform aerial maneuvers on a boat shaped structure. The boat
Final Exam Solution Dynamics 2 191157140 31-01-2013 8:45 12:15 Problem 1 Bateau Bateau is a trapeze act by Cirque du Soleil in which artists perform aerial maneuvers on a boat shaped structure. The boat
Embedded Foundation with Different Parameters under Dynamic Excitations
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2287 Embedded Foundation with Different Parameters under Dynamic Excitations Jaya K P 1 and Meher Prasad
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2287 Embedded Foundation with Different Parameters under Dynamic Excitations Jaya K P 1 and Meher Prasad
Address for Correspondence
 Research Article EXPERIMENT STUDY OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF SOFT STOREY BUILDING MODEL C. S. Sanghvi 1, H S Patil 2 and B J Shah 3 Address for Correspondence 1 Associate Professor, Applied Mechanics Department,
Research Article EXPERIMENT STUDY OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF SOFT STOREY BUILDING MODEL C. S. Sanghvi 1, H S Patil 2 and B J Shah 3 Address for Correspondence 1 Associate Professor, Applied Mechanics Department,
Modal and Static Structural Analysis of Exhaust Collector Box for Compressor test facility
 Modal and Static Structural Analysis of Exhaust Collector Box for Compressor test facility Shankar Gouda 1, Praveen M P 2 P G student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, EPCET, Bangalore, Karnataka,
Modal and Static Structural Analysis of Exhaust Collector Box for Compressor test facility Shankar Gouda 1, Praveen M P 2 P G student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, EPCET, Bangalore, Karnataka,
COEFFICIENT OF DYNAMIC HORIZONTAL SUBGRADE REACTION OF PILE FOUNDATIONS ON PROBLEMATIC GROUND IN HOKKAIDO Hirofumi Fukushima 1
 COEFFICIENT OF DYNAMIC HORIZONTAL SUBGRADE REACTION OF PILE FOUNDATIONS ON PROBLEMATIC GROUND IN HOKKAIDO Hirofumi Fukushima 1 Abstract In this study, static loading tests and dynamic shaking tests of
COEFFICIENT OF DYNAMIC HORIZONTAL SUBGRADE REACTION OF PILE FOUNDATIONS ON PROBLEMATIC GROUND IN HOKKAIDO Hirofumi Fukushima 1 Abstract In this study, static loading tests and dynamic shaking tests of
ROTATING RING. Volume of small element = Rdθbt if weight density of ring = ρ weight of small element = ρrbtdθ. Figure 1 Rotating ring
 ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
Rigid Part Mating. Goals of this class
 Rigid Part Mating Goals of this class understand the phases of a typical part mate determine the basic scaling laws understand basic physics of part mating for simple geometries relate forces and motions
Rigid Part Mating Goals of this class understand the phases of a typical part mate determine the basic scaling laws understand basic physics of part mating for simple geometries relate forces and motions
3-D FINITE ELEMENT NONLINEAR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS FOR SOIL-PILE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-, 4 Paper No. 157 3-D FINITE ELEMENT NONLINEAR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS FOR SOIL-PILE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION B.K. MAHESHWARI 1,
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-, 4 Paper No. 157 3-D FINITE ELEMENT NONLINEAR DYNAMIC ANALYSIS FOR SOIL-PILE-STRUCTURE INTERACTION B.K. MAHESHWARI 1,
MEC3403. Dynamics II. Introductory book. Faculty of Engineering and Surveying
 MEC3403 Dynamics II Faculty of Engineering and Surveying Introductory book Semester 2 2010 Published by University of Southern Queensland Toowoomba Queensland 4350 Australia http://www.usq.edu.au University
MEC3403 Dynamics II Faculty of Engineering and Surveying Introductory book Semester 2 2010 Published by University of Southern Queensland Toowoomba Queensland 4350 Australia http://www.usq.edu.au University
RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND
 RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND Shahram Taghavi 1 and Eduardo Miranda 2 1 Senior catastrophe risk modeler, Risk Management Solutions, CA, USA 2 Associate Professor,
RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND Shahram Taghavi 1 and Eduardo Miranda 2 1 Senior catastrophe risk modeler, Risk Management Solutions, CA, USA 2 Associate Professor,
Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor
 Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor R Miyauchi 1, B Yue 2, N Matsunaga 1 and S Ishizuka 1 1 Cybernet Systems Co., Ltd. 3 Kanda-neribeicho,Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo,101-0022,Japan
Integration simulation method concerning speed control of ultrasonic motor R Miyauchi 1, B Yue 2, N Matsunaga 1 and S Ishizuka 1 1 Cybernet Systems Co., Ltd. 3 Kanda-neribeicho,Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo,101-0022,Japan
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
 2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
Chapter 5. Vibration Analysis. Workbench - Mechanical Introduction ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Workbench - Mechanical Introduction 12.0 Chapter 5 Vibration Analysis 5-1 Chapter Overview In this chapter, performing free vibration analyses in Simulation will be covered. In Simulation, performing a
Workbench - Mechanical Introduction 12.0 Chapter 5 Vibration Analysis 5-1 Chapter Overview In this chapter, performing free vibration analyses in Simulation will be covered. In Simulation, performing a
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping
 A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
Software Verification
 SAP000 EXAMPLE 6-00 LINK LINEAR LINK WITH RAMP LOADING PROBLEM DESCRIPTION In this example a ramp load is applied to an undamped single degree of freedom structure. The ramp loading has a finite rise time
SAP000 EXAMPLE 6-00 LINK LINEAR LINK WITH RAMP LOADING PROBLEM DESCRIPTION In this example a ramp load is applied to an undamped single degree of freedom structure. The ramp loading has a finite rise time
ABSTRACT. Ossama Salem Ali Ahmed, Ph.D., interaction of the pile with the surrounding soils under vibratory loading will modify
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: VERTICAL DYNAMIC SOIL-PILE INTERACTION FOR MACHINE FOUNDATIONS Ossama Salem Ali Ahmed, Ph.D., 2015 Directed By: Professor, M. Sherif Aggour, Department of Civil and Environmental
ABSTRACT Title of Document: VERTICAL DYNAMIC SOIL-PILE INTERACTION FOR MACHINE FOUNDATIONS Ossama Salem Ali Ahmed, Ph.D., 2015 Directed By: Professor, M. Sherif Aggour, Department of Civil and Environmental
Experimental Study of Seismic Soil-Structure Interaction by using Large Geotechnical Centrifuge System
 October 12-17, 28, Beijing, China Experimental Study of Seismic Soil-Structure Interaction by using Large Geotechnical Centrifuge System T. Kawasato 1, T. Okutani 1, T. Ishikawa 1, T. Fujimori 2, and M.
October 12-17, 28, Beijing, China Experimental Study of Seismic Soil-Structure Interaction by using Large Geotechnical Centrifuge System T. Kawasato 1, T. Okutani 1, T. Ishikawa 1, T. Fujimori 2, and M.
On The Finite Element Modeling Of Turbo Machinery Rotors In Rotor Dynamic Analysis
 Proceedings of The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress 2018 CSME International Congress 2018 May 27-30, 2018, Toronto, On, Canada On The Finite Element Modeling Of Turbo
Proceedings of The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress 2018 CSME International Congress 2018 May 27-30, 2018, Toronto, On, Canada On The Finite Element Modeling Of Turbo
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in URL: http://www.civil.iitb.ac.in/~dc/
Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in URL: http://www.civil.iitb.ac.in/~dc/
Research on Optimization of Bearing Span of Main Reducer Gear System Based on the Transfer Matrix
 MATEC Web of Conferences 3, () DOI:.5/ matecconf/3 MMME Research on Optimization of Bearing Span of Main Reducer Gear System Based on the Transfer Matrix Feng Yun HUANG, Li TIAN a, Ding WEI and Huan Huan
MATEC Web of Conferences 3, () DOI:.5/ matecconf/3 MMME Research on Optimization of Bearing Span of Main Reducer Gear System Based on the Transfer Matrix Feng Yun HUANG, Li TIAN a, Ding WEI and Huan Huan
Graphical User Interface (GUI) for Torsional Vibration Analysis of Rotor Systems Using Holzer and MatLab Techniques
 Basrah Journal for Engineering Sciences, vol. 14, no. 2, 2014 255 Graphical User Interface (GUI) for Torsional Vibration Analysis of Rotor Systems Using Holzer and MatLab Techniques Dr. Ameen Ahmed Nassar
Basrah Journal for Engineering Sciences, vol. 14, no. 2, 2014 255 Graphical User Interface (GUI) for Torsional Vibration Analysis of Rotor Systems Using Holzer and MatLab Techniques Dr. Ameen Ahmed Nassar
EQUIVALENT FRACTURE ENERGY CONCEPT FOR DYNAMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF PROTOTYPE RC GIRDERS
 EQUIVALENT FRACTURE ENERGY CONCEPT FOR DYNAMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF PROTOTYPE RC GIRDERS Abdul Qadir Bhatti 1, Norimitsu Kishi 2 and Khaliq U Rehman Shad 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Structural Engineering,
EQUIVALENT FRACTURE ENERGY CONCEPT FOR DYNAMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF PROTOTYPE RC GIRDERS Abdul Qadir Bhatti 1, Norimitsu Kishi 2 and Khaliq U Rehman Shad 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Structural Engineering,
