Multivariate density estimation and its applications
|
|
|
- Kelly Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Multivariate density estimation and its applications Wing Hung Wong Stanford University June 2014, Madison, Wisconsin. Conference in honor of the 80 th birthday of Professor Grace Wahba
2 Lessons I learned in graduate school: Estimate the function Put prior on function space Use RKHS, splines, approximation theory.
3 A 3 dimensional density function from flow cytometry
4 Mass cytometry: replace fluorescent labels with elemental labels Holmium amu Mass-spectra
5 The Bayesian nonparametric problem x 1, x 2, x n are independent r.v. on a space Ω Their distribution Q is unknown but assumed to be drawn from a prior distribution π. Our tasks: Prior construction, posterior computation π(q) Q(X) Pr( Q, X) Pr (Q X ) Pr (g(q)) Want this to work well when Ω is of moderately high dimension, e.g. 5 50
6 Ferguson s criteria (1973) Support of the prior should be large The posterior should be tractable Dirichlet process prior satisfies Ferguson s conditions. However, under this prior the random distribution Q does not possess a density
7 Density is useful in many applications Anomaly detection Classification Compression Probabilistic networks Image analysis and more
8 We want to define a prior on the space of simple density functions: f(x) = c i I Ai (x) To reduce complexity of this space, assume that Ω=A 1 U A 2. U A m is a recursive partition
9 Recursive partitions: A A 1 1 A 1 2 A 2 1 A 2 2 Level 1 A Level 2 A In general, A j k = k th part of the j th way to partition A
10 Recursive definition of random simple density function: Suppose Q(A) is known, define how Q( ) is distributed within A Q(A) S ~ Ber(ρ) Q is uniform within A J ~ Multinomial(d, λ) Q(A)θ 1 1 Q(A)θ 1 2 Q(A)θ 2 1 Q(A)θ 2 1 θ j ~ Dirichlet (α j )
11 Density on partitions of finite depth Suppose we have drawn Q (k) supported on a partition composing of regions up to level k For each region not yet stopped, repeat the partitioning process This gives a random distribution Q (k+1) with a density q (k+1) that is piecewise constant on a partition with regions up to level k+1
12 Optional Polya Tree (OPT) (Wong & Li, 2010) Theorem: If the stopping probabilities are uniformly positive, then Q (k) converges almost surely in variational distance to an absolutely continuous distribution Q. P ( q (k) q dx 0 for some density q ) = 1 Q is said to have an OPT distribution with parameters ρ (stopping rule) λ (selection probabilities) α (probability assignment weights)
13 OPT prior satisfies Ferguson s criteria 1) Any L 1 ball has positive prior probability 2) π( Q x 1,..x n ) is also OPT with parameters ρ (x 1,..x n ), λ (x 1,..x n ), α (x 1,..x n ), computable in finite time
14 Q(A) depends on n and ϕ below Q(A)θ 1 1 Q(A)θ 1 2 Q(A)θ 2 1 Q(A)θ 2 1 n 1 =(n 1 1, n 1 2) n 2 =(n 2 1, n 2 2) φ 1 =(φ 1 1, φ 1 2) φ 2 =(φ 2 1, φ 2 2)
15 Computation of Φ(A) by recursion where Recursion ends when A has either 0 or 1 data points.
16 Example
17 Example (continued)
18 2 nd approach: build up partition sequentially t=2 t=3 t=4 v Given t, want to define a posterior score for the partition directly
19 Assume Dirichlet (α) allocation of probabilities given the partition, then Bayesian score of a partition X of size t:
20 Asymptotically, the score tracks distance from true density x t *= best scoring partition of size t log(π(x t *)) Kullback Leibler t
21 Sequential importance sampling Partition Sample Cut 1 Cut 2 Cut 3 Partition 1 Partition 2 w 1 w 1 v v M w 2 w 2 Partition 3 v v v w 3 w 3 Partition 4 v v w 4 w 4 Generate cuts randomly
22 t k n k t t t k A D n n D e y ,,,, ˆ) ( How to choose the proposal density? ) ( )... ( ) ( ) ( ,..., 1 t t t t t t t y y y y y y y y ) ( )... ( ) ( ) ( ,..., 1 t t t t t y y y y y y y y q feasible infeasible
23 Data structure for region counts
24 Counting can be accelerated by hardware Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU 2.67GHz GeForce GTX CUDA cores 1.08GHz 512KB L2 2G RAM Memory clock rate: 3GHz Memory bus width: 256 bit Bandwidth: 150GB/s
25 Experiment result (CountEngine) Partition = 300, Cut = 1000 Dim_# of data CPU GPU Speedup 32_10^ _10^ _10^ _10^ _10^ _10^6 NA NA
26 Resampling:
27 Comparison with Kernel Density Estimate Sample n points from a D-dim distribution: Results:
28 Estimate of conditional density in 7 dimension
29 Case 1: Case 2: Case 3: Case 4:
30 Density estimation is a building block for other statistical methods.
31 Classification: 1) Estimate class density f i (x) for classes 1, k 2) Use Bayes classifier: p(i x) ~ α i f i (x) MAGIC data: 10 dimension, 12,000 cases, 7,000 controls Letter data: 16 dimension, 26 classes, n=16,000 within class
32 Data Compression: the estimated density can guide the design of optimal compression scheme A sequencer yield 1 billion reads in about 1 day. Quality scores associated with the base calls take up too much disk space Test: n=1,940,271 quality score vectors (100 dimensional, divided into 20 sub-vectors) Result: Our method uses 206 bits per read for lossless compression In comparison, 7-zip uses 213 bits per read
33 Visualization of information Contour plot of the energy function of a 2D density with seven modes Sub-level tree of energy (log-density)
34 Sublevel tree of bone marrow data (n=2,000,000) density CD11b B220 TCR-b CD4 CD8
35 Image segmentation
36 Image enhancement
37 Convergence rates (sieve MLE case) 1. Class of simple functions on BPs of size I : Θ I ={ f( ): f( )= β i I Ai ( ), β i 0, β i μ(a i )=1, and A i, i=1, I form a binary partition } 2. Log-likelihood of f : L n (f)= {j=1, n} logf(y j ) = {i=1, I} n i log(β i ) 3. MLE based on Θ I : 4. Sieve MLE based on { Θ I, I=1, 2, }:
38 Classical result (Stone 1980): rate ~ n -α, α= p/(2p+d) p= # of bounded derivatives of f 0 d= dimension of Ω The key is to remove dependency of α on d.
39 A relevant result was given in Wong & Shen (1995): Let H I be the bracketing Hellinger entropy of Θ I, and δ I be the approximation rate of Θ I to f 0, Then (with ρ denoting the Hellinger distance), However δ I was required to be much stronger than ρ
40 Result (Linxi Liu & WW) With r>1/2 and I(n) chosen to be our sieve MLE has a rate upper bounded by This result can be used to establish spatial adaptation and variable selection
41 Acknowledgments BSP: Luo Lu OPT: Li Ma Clustering & image: TY Wu, CY Tseng Flow-cytometry: Michael Yang Compression: Luo Lu, John Mu Convergence rate: Linxi Liu
Probabilistic Machine Learning. Industrial AI Lab.
 Probabilistic Machine Learning Industrial AI Lab. Probabilistic Linear Regression Outline Probabilistic Classification Probabilistic Clustering Probabilistic Dimension Reduction 2 Probabilistic Linear
Probabilistic Machine Learning Industrial AI Lab. Probabilistic Linear Regression Outline Probabilistic Classification Probabilistic Clustering Probabilistic Dimension Reduction 2 Probabilistic Linear
Parametric Models. Dr. Shuang LIANG. School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012
 Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Parameter Estimation. Industrial AI Lab.
 Parameter Estimation Industrial AI Lab. Generative Model X Y w y = ω T x + ε ε~n(0, σ 2 ) σ 2 2 Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) Estimate parameters θ ω, σ 2 given a generative model Given observed
Parameter Estimation Industrial AI Lab. Generative Model X Y w y = ω T x + ε ε~n(0, σ 2 ) σ 2 2 Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) Estimate parameters θ ω, σ 2 given a generative model Given observed
Bayes Decision Theory
 Bayes Decision Theory Minimum-Error-Rate Classification Classifiers, Discriminant Functions and Decision Surfaces The Normal Density 0 Minimum-Error-Rate Classification Actions are decisions on classes
Bayes Decision Theory Minimum-Error-Rate Classification Classifiers, Discriminant Functions and Decision Surfaces The Normal Density 0 Minimum-Error-Rate Classification Actions are decisions on classes
Bayesian Regularization
 Bayesian Regularization Aad van der Vaart Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam International Congress of Mathematicians Hyderabad, August 2010 Contents Introduction Abstract result Gaussian process priors Co-authors
Bayesian Regularization Aad van der Vaart Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam International Congress of Mathematicians Hyderabad, August 2010 Contents Introduction Abstract result Gaussian process priors Co-authors
Learning Bayesian Networks for Biomedical Data
 Learning Bayesian Networks for Biomedical Data Faming Liang (Texas A&M University ) Liang, F. and Zhang, J. (2009) Learning Bayesian Networks for Discrete Data. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis,
Learning Bayesian Networks for Biomedical Data Faming Liang (Texas A&M University ) Liang, F. and Zhang, J. (2009) Learning Bayesian Networks for Discrete Data. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis,
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
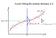 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
 Christopher M. Bishop Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning ÖSpri inger Contents Preface Mathematical notation Contents vii xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Example: Polynomial Curve Fitting 4 1.2 Probability
Christopher M. Bishop Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning ÖSpri inger Contents Preface Mathematical notation Contents vii xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Example: Polynomial Curve Fitting 4 1.2 Probability
NONPARAMETRIC BAYESIAN INFERENCE ON PLANAR SHAPES
 NONPARAMETRIC BAYESIAN INFERENCE ON PLANAR SHAPES Author: Abhishek Bhattacharya Coauthor: David Dunson Department of Statistical Science, Duke University 7 th Workshop on Bayesian Nonparametrics Collegio
NONPARAMETRIC BAYESIAN INFERENCE ON PLANAR SHAPES Author: Abhishek Bhattacharya Coauthor: David Dunson Department of Statistical Science, Duke University 7 th Workshop on Bayesian Nonparametrics Collegio
Data Mining. CS57300 Purdue University. Bruno Ribeiro. February 8, 2018
 Data Mining CS57300 Purdue University Bruno Ribeiro February 8, 2018 Decision trees Why Trees? interpretable/intuitive, popular in medical applications because they mimic the way a doctor thinks model
Data Mining CS57300 Purdue University Bruno Ribeiro February 8, 2018 Decision trees Why Trees? interpretable/intuitive, popular in medical applications because they mimic the way a doctor thinks model
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Outline Introduction to Machine Learning Bayesian Classification Varun Chandola March 8, 017 1. {circular,large,light,smooth,thick}, malignant. {circular,large,light,irregular,thick}, malignant 3. {oval,large,dark,smooth,thin},
Outline Introduction to Machine Learning Bayesian Classification Varun Chandola March 8, 017 1. {circular,large,light,smooth,thick}, malignant. {circular,large,light,irregular,thick}, malignant 3. {oval,large,dark,smooth,thin},
co-bpm: a Bayesian Model for Estimating Divergence and Distance of Distributions
 co-bpm: a Bayesian Model for Estimating Divergence arxiv:1410.0726v1 [stat.co] 2 Oct 2014 and Distance of Distributions Kun Yang 1, Hao Su 2, and Wing Hung Wong 3 1 Institute of Computational and Mathematical
co-bpm: a Bayesian Model for Estimating Divergence arxiv:1410.0726v1 [stat.co] 2 Oct 2014 and Distance of Distributions Kun Yang 1, Hao Su 2, and Wing Hung Wong 3 1 Institute of Computational and Mathematical
MCMC: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 I529: Machine Learning in Bioinformatics (Spring 2013) MCMC: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University, Bloomington Spring 2013 Contents Review of Markov
I529: Machine Learning in Bioinformatics (Spring 2013) MCMC: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University, Bloomington Spring 2013 Contents Review of Markov
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods
 Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
Decision Trees. CS57300 Data Mining Fall Instructor: Bruno Ribeiro
 Decision Trees CS57300 Data Mining Fall 2016 Instructor: Bruno Ribeiro Goal } Classification without Models Well, partially without a model } Today: Decision Trees 2015 Bruno Ribeiro 2 3 Why Trees? } interpretable/intuitive,
Decision Trees CS57300 Data Mining Fall 2016 Instructor: Bruno Ribeiro Goal } Classification without Models Well, partially without a model } Today: Decision Trees 2015 Bruno Ribeiro 2 3 Why Trees? } interpretable/intuitive,
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING Chapter 1. Introduction Shuai Huang April 21, 2014 Outline 1 What is Machine Learning? 2 Curve Fitting 3 Probability Theory 4 Model Selection 5 The curse of dimensionality
Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods
 1 / 27 Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods Part II: Models on the Simplex Peter Orbanz http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/porbanz/npb-tutorial.html 2 / 27 Tutorial Overview Part I: Basics Part II: Models
1 / 27 Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods Part II: Models on the Simplex Peter Orbanz http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/porbanz/npb-tutorial.html 2 / 27 Tutorial Overview Part I: Basics Part II: Models
Convexification and Multimodality of Random Probability Measures
 Convexification and Multimodality of Random Probability Measures George Kokolakis & George Kouvaras Department of Applied Mathematics National Technical University of Athens, Greece Isaac Newton Institute,
Convexification and Multimodality of Random Probability Measures George Kokolakis & George Kouvaras Department of Applied Mathematics National Technical University of Athens, Greece Isaac Newton Institute,
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Bayesian Classification Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
Introduction to Machine Learning Bayesian Classification Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2012 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Peter Schulam and William Wang 1 Introduction
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2012 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Peter Schulam and William Wang 1 Introduction
The Bayes classifier
 The Bayes classifier Consider where is a random vector in is a random variable (depending on ) Let be a classifier with probability of error/risk given by The Bayes classifier (denoted ) is the optimal
The Bayes classifier Consider where is a random vector in is a random variable (depending on ) Let be a classifier with probability of error/risk given by The Bayes classifier (denoted ) is the optimal
9/12/17. Types of learning. Modeling data. Supervised learning: Classification. Supervised learning: Regression. Unsupervised learning: Clustering
 Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Machine Learning. Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics. Feng Li. https://funglee.github.io
 Machine Learning Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 207 Overfitting Problem
Machine Learning Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 207 Overfitting Problem
Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes)
 [70240413 Statistical Machine Learning, Spring, 2015] Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes) Jun Zhu dcszj@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn http://bigml.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/~jun State Key Lab of Intelligent
[70240413 Statistical Machine Learning, Spring, 2015] Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes) Jun Zhu dcszj@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn http://bigml.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/~jun State Key Lab of Intelligent
COS 424: Interacting with Data. Lecturer: Dave Blei Lecture #11 Scribe: Andrew Ferguson March 13, 2007
 COS 424: Interacting with ata Lecturer: ave Blei Lecture #11 Scribe: Andrew Ferguson March 13, 2007 1 Graphical Models Wrap-up We began the lecture with some final words on graphical models. Choosing a
COS 424: Interacting with ata Lecturer: ave Blei Lecture #11 Scribe: Andrew Ferguson March 13, 2007 1 Graphical Models Wrap-up We began the lecture with some final words on graphical models. Choosing a
Online Estimation of Discrete Densities using Classifier Chains
 Online Estimation of Discrete Densities using Classifier Chains Michael Geilke 1 and Eibe Frank 2 and Stefan Kramer 1 1 Johannes Gutenberg-Universtität Mainz, Germany {geilke,kramer}@informatik.uni-mainz.de
Online Estimation of Discrete Densities using Classifier Chains Michael Geilke 1 and Eibe Frank 2 and Stefan Kramer 1 1 Johannes Gutenberg-Universtität Mainz, Germany {geilke,kramer}@informatik.uni-mainz.de
Statistical and Inductive Inference by Minimum Message Length
 C.S. Wallace Statistical and Inductive Inference by Minimum Message Length With 22 Figures Springer Contents Preface 1. Inductive Inference 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Inductive Inference 5 1.3 The Demise
C.S. Wallace Statistical and Inductive Inference by Minimum Message Length With 22 Figures Springer Contents Preface 1. Inductive Inference 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Inductive Inference 5 1.3 The Demise
OPTIONAL PÓLYA TREE AND BAYESIAN INFERENCE. BY WING H. WONG 1 AND LI MA 2 Stanford University
 The Annals of Statistics 2010, Vol. 38, No. 3, 1433 1459 DOI: 10.1214/09-AOS755 Institute of Mathematical Statistics, 2010 OPTIONAL PÓLYA TREE AND BAYESIAN INFERENCE BY WING H. WONG 1 AND LI MA 2 Stanford
The Annals of Statistics 2010, Vol. 38, No. 3, 1433 1459 DOI: 10.1214/09-AOS755 Institute of Mathematical Statistics, 2010 OPTIONAL PÓLYA TREE AND BAYESIAN INFERENCE BY WING H. WONG 1 AND LI MA 2 Stanford
In: Advances in Intelligent Data Analysis (AIDA), International Computer Science Conventions. Rochester New York, 1999
 In: Advances in Intelligent Data Analysis (AIDA), Computational Intelligence Methods and Applications (CIMA), International Computer Science Conventions Rochester New York, 999 Feature Selection Based
In: Advances in Intelligent Data Analysis (AIDA), Computational Intelligence Methods and Applications (CIMA), International Computer Science Conventions Rochester New York, 999 Feature Selection Based
Variational algorithms for marginal MAP
 Variational algorithms for marginal MAP Alexander Ihler UC Irvine CIOG Workshop November 2011 Variational algorithms for marginal MAP Alexander Ihler UC Irvine CIOG Workshop November 2011 Work with Qiang
Variational algorithms for marginal MAP Alexander Ihler UC Irvine CIOG Workshop November 2011 Variational algorithms for marginal MAP Alexander Ihler UC Irvine CIOG Workshop November 2011 Work with Qiang
Parameter Estimation for the Dirichlet-Multinomial Distribution
 Parameter Estimation for the Dirichlet-Multinomial Distribution Amanda Peterson Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County May 20, 2011 Abstract. In the 1998 paper
Parameter Estimation for the Dirichlet-Multinomial Distribution Amanda Peterson Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County May 20, 2011 Abstract. In the 1998 paper
Machine Learning 3. week
 Machine Learning 3. week Entropy Decision Trees ID3 C4.5 Classification and Regression Trees (CART) 1 What is Decision Tree As a short description, decision tree is a data classification procedure which
Machine Learning 3. week Entropy Decision Trees ID3 C4.5 Classification and Regression Trees (CART) 1 What is Decision Tree As a short description, decision tree is a data classification procedure which
Hybrid CPU/GPU Acceleration of Detection of 2-SNP Epistatic Interactions in GWAS
 Hybrid CPU/GPU Acceleration of Detection of 2-SNP Epistatic Interactions in GWAS Jorge González-Domínguez*, Bertil Schmidt*, Jan C. Kässens**, Lars Wienbrandt** *Parallel and Distributed Architectures
Hybrid CPU/GPU Acceleration of Detection of 2-SNP Epistatic Interactions in GWAS Jorge González-Domínguez*, Bertil Schmidt*, Jan C. Kässens**, Lars Wienbrandt** *Parallel and Distributed Architectures
Bayes Classifiers. CAP5610 Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun QI
 Bayes Classifiers CAP5610 Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun QI Recap: Joint distributions Joint distribution over Input vector X = (X 1, X 2 ) X 1 =B or B (drinking beer or not) X 2 = H or H (headache
Bayes Classifiers CAP5610 Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun QI Recap: Joint distributions Joint distribution over Input vector X = (X 1, X 2 ) X 1 =B or B (drinking beer or not) X 2 = H or H (headache
David B. Dahl. Department of Statistics, and Department of Biostatistics & Medical Informatics University of Wisconsin Madison
 AN IMPROVED MERGE-SPLIT SAMPLER FOR CONJUGATE DIRICHLET PROCESS MIXTURE MODELS David B. Dahl dbdahl@stat.wisc.edu Department of Statistics, and Department of Biostatistics & Medical Informatics University
AN IMPROVED MERGE-SPLIT SAMPLER FOR CONJUGATE DIRICHLET PROCESS MIXTURE MODELS David B. Dahl dbdahl@stat.wisc.edu Department of Statistics, and Department of Biostatistics & Medical Informatics University
Bayesian Methods: Naïve Bayes
 Bayesian Methods: aïve Bayes icholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate Last Time Parameter learning Learning the parameter of a simple coin flipping model Prior
Bayesian Methods: aïve Bayes icholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate Last Time Parameter learning Learning the parameter of a simple coin flipping model Prior
12 - Nonparametric Density Estimation
 ST 697 Fall 2017 1/49 12 - Nonparametric Density Estimation ST 697 Fall 2017 University of Alabama Density Review ST 697 Fall 2017 2/49 Continuous Random Variables ST 697 Fall 2017 3/49 1.0 0.8 F(x) 0.6
ST 697 Fall 2017 1/49 12 - Nonparametric Density Estimation ST 697 Fall 2017 University of Alabama Density Review ST 697 Fall 2017 2/49 Continuous Random Variables ST 697 Fall 2017 3/49 1.0 0.8 F(x) 0.6
Gaussian Models
 Gaussian Models ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-04-28 Agenda Introduction Gaussian Discriminant Analysis Inference Linear Gaussian Systems The Wishart Distribution Inferring Parameters Introduction Gaussian Density
Gaussian Models ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-04-28 Agenda Introduction Gaussian Discriminant Analysis Inference Linear Gaussian Systems The Wishart Distribution Inferring Parameters Introduction Gaussian Density
Introduction to Bayesian Learning. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Introduction to Bayesian Learning Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 What we have seen so far What does it mean to learn? Mistake-driven learning Learning by counting (and bounding) number of mistakes PAC learnability
Introduction to Bayesian Learning Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 What we have seen so far What does it mean to learn? Mistake-driven learning Learning by counting (and bounding) number of mistakes PAC learnability
Self Adaptive Particle Filter
 Self Adaptive Particle Filter Alvaro Soto Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile Department of Computer Science Vicuna Mackenna 4860 (143), Santiago 22, Chile asoto@ing.puc.cl Abstract The particle filter
Self Adaptive Particle Filter Alvaro Soto Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile Department of Computer Science Vicuna Mackenna 4860 (143), Santiago 22, Chile asoto@ing.puc.cl Abstract The particle filter
Machine Learning 2017
 Machine Learning 2017 Volker Roth Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Basel 21st March 2017 Volker Roth (University of Basel) Machine Learning 2017 21st March 2017 1 / 41 Section
Machine Learning 2017 Volker Roth Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Basel 21st March 2017 Volker Roth (University of Basel) Machine Learning 2017 21st March 2017 1 / 41 Section
EEL 851: Biometrics. An Overview of Statistical Pattern Recognition EEL 851 1
 EEL 851: Biometrics An Overview of Statistical Pattern Recognition EEL 851 1 Outline Introduction Pattern Feature Noise Example Problem Analysis Segmentation Feature Extraction Classification Design Cycle
EEL 851: Biometrics An Overview of Statistical Pattern Recognition EEL 851 1 Outline Introduction Pattern Feature Noise Example Problem Analysis Segmentation Feature Extraction Classification Design Cycle
Probability Models for Bayesian Recognition
 Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition James L. Crowley ENSIAG / osig Second Semester 06/07 Lesson 9 0 arch 07 Probability odels for Bayesian Recognition Notation... Supervised Learning for Bayesian
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition James L. Crowley ENSIAG / osig Second Semester 06/07 Lesson 9 0 arch 07 Probability odels for Bayesian Recognition Notation... Supervised Learning for Bayesian
Bayesian Decision and Bayesian Learning
 Bayesian Decision and Bayesian Learning Ying Wu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208 http://www.eecs.northwestern.edu/~yingwu 1 / 30 Bayes Rule p(x ω i
Bayesian Decision and Bayesian Learning Ying Wu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208 http://www.eecs.northwestern.edu/~yingwu 1 / 30 Bayes Rule p(x ω i
Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm, Tues April 8
 Introduction to Machine Learning 10-701 Midterm, Tues April 8 [1 point] Name: Andrew ID: Instructions: You are allowed a (two-sided) sheet of notes. Exam ends at 2:45pm Take a deep breath and don t spend
Introduction to Machine Learning 10-701 Midterm, Tues April 8 [1 point] Name: Andrew ID: Instructions: You are allowed a (two-sided) sheet of notes. Exam ends at 2:45pm Take a deep breath and don t spend
Introduction to Machine Learning. Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Inference. Lecturers: Eran Halperin, Yishay Mansour, Lior Wolf
 1 Introduction to Machine Learning Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Inference Lecturers: Eran Halperin, Yishay Mansour, Lior Wolf 2013-14 We know that X ~ B(n,p), but we do not know p. We get a random sample
1 Introduction to Machine Learning Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Inference Lecturers: Eran Halperin, Yishay Mansour, Lior Wolf 2013-14 We know that X ~ B(n,p), but we do not know p. We get a random sample
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
Expect Values and Probability Density Functions
 Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition James L. Crowley ESIAG / osig Second Semester 00/0 Lesson 5 8 april 0 Expect Values and Probability Density Functions otation... Bayesian Classification (Reminder...3
Intelligent Systems: Reasoning and Recognition James L. Crowley ESIAG / osig Second Semester 00/0 Lesson 5 8 april 0 Expect Values and Probability Density Functions otation... Bayesian Classification (Reminder...3
Expectation Propagation Algorithm
 Expectation Propagation Algorithm 1 Shuang Wang School of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Oklahoma, Tulsa, OK, 74135 Email: {shuangwang}@ou.edu This note contains three parts. First,
Expectation Propagation Algorithm 1 Shuang Wang School of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Oklahoma, Tulsa, OK, 74135 Email: {shuangwang}@ou.edu This note contains three parts. First,
Online Bayesian Passive-Agressive Learning
 Online Bayesian Passive-Agressive Learning International Conference on Machine Learning, 2014 Tianlin Shi Jun Zhu Tsinghua University, China 21 August 2015 Presented by: Kyle Ulrich Introduction Online
Online Bayesian Passive-Agressive Learning International Conference on Machine Learning, 2014 Tianlin Shi Jun Zhu Tsinghua University, China 21 August 2015 Presented by: Kyle Ulrich Introduction Online
DEEP LEARNING AND NEURAL NETWORKS: BACKGROUND AND HISTORY
 DEEP LEARNING AND NEURAL NETWORKS: BACKGROUND AND HISTORY 1 On-line Resources http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html Online book by Michael Nielsen http://matlabtricks.com/post-5/3x3-convolution-kernelswith-online-demo
DEEP LEARNING AND NEURAL NETWORKS: BACKGROUND AND HISTORY 1 On-line Resources http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html Online book by Michael Nielsen http://matlabtricks.com/post-5/3x3-convolution-kernelswith-online-demo
Click Prediction and Preference Ranking of RSS Feeds
 Click Prediction and Preference Ranking of RSS Feeds 1 Introduction December 11, 2009 Steven Wu RSS (Really Simple Syndication) is a family of data formats used to publish frequently updated works. RSS
Click Prediction and Preference Ranking of RSS Feeds 1 Introduction December 11, 2009 Steven Wu RSS (Really Simple Syndication) is a family of data formats used to publish frequently updated works. RSS
Topic Models. Brandon Malone. February 20, Latent Dirichlet Allocation Success Stories Wrap-up
 Much of this material is adapted from Blei 2003. Many of the images were taken from the Internet February 20, 2014 Suppose we have a large number of books. Each is about several unknown topics. How can
Much of this material is adapted from Blei 2003. Many of the images were taken from the Internet February 20, 2014 Suppose we have a large number of books. Each is about several unknown topics. How can
Lecture 16-17: Bayesian Nonparametrics I. STAT 6474 Instructor: Hongxiao Zhu
 Lecture 16-17: Bayesian Nonparametrics I STAT 6474 Instructor: Hongxiao Zhu Plan for today Why Bayesian Nonparametrics? Dirichlet Distribution and Dirichlet Processes. 2 Parameter and Patterns Reference:
Lecture 16-17: Bayesian Nonparametrics I STAT 6474 Instructor: Hongxiao Zhu Plan for today Why Bayesian Nonparametrics? Dirichlet Distribution and Dirichlet Processes. 2 Parameter and Patterns Reference:
Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues
 Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2007 c 2007, Selim Aksoy Introduction We have seen many learning
Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2007 c 2007, Selim Aksoy Introduction We have seen many learning
2D Image Processing (Extended) Kalman and particle filter
 2D Image Processing (Extended) Kalman and particle filter Prof. Didier Stricker Dr. Gabriele Bleser Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz
2D Image Processing (Extended) Kalman and particle filter Prof. Didier Stricker Dr. Gabriele Bleser Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz
Notes on Markov Networks
 Notes on Markov Networks Lili Mou moull12@sei.pku.edu.cn December, 2014 This note covers basic topics in Markov networks. We mainly talk about the formal definition, Gibbs sampling for inference, and maximum
Notes on Markov Networks Lili Mou moull12@sei.pku.edu.cn December, 2014 This note covers basic topics in Markov networks. We mainly talk about the formal definition, Gibbs sampling for inference, and maximum
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 11 CRFs, Exponential Family CS/CNS/EE 155 Andreas Krause Announcements Homework 2 due today Project milestones due next Monday (Nov 9) About half the work should
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 11 CRFs, Exponential Family CS/CNS/EE 155 Andreas Krause Announcements Homework 2 due today Project milestones due next Monday (Nov 9) About half the work should
Conditional Random Field
 Introduction Linear-Chain General Specific Implementations Conclusions Corso di Elaborazione del Linguaggio Naturale Pisa, May, 2011 Introduction Linear-Chain General Specific Implementations Conclusions
Introduction Linear-Chain General Specific Implementations Conclusions Corso di Elaborazione del Linguaggio Naturale Pisa, May, 2011 Introduction Linear-Chain General Specific Implementations Conclusions
Machine Learning. Theory of Classification and Nonparametric Classifier. Lecture 2, January 16, What is theoretically the best classifier
 Machine Learning 10-701/15 701/15-781, 781, Spring 2008 Theory of Classification and Nonparametric Classifier Eric Xing Lecture 2, January 16, 2006 Reading: Chap. 2,5 CB and handouts Outline What is theoretically
Machine Learning 10-701/15 701/15-781, 781, Spring 2008 Theory of Classification and Nonparametric Classifier Eric Xing Lecture 2, January 16, 2006 Reading: Chap. 2,5 CB and handouts Outline What is theoretically
The Minimum Message Length Principle for Inductive Inference
 The Principle for Inductive Inference Centre for Molecular, Environmental, Genetic & Analytic (MEGA) Epidemiology School of Population Health University of Melbourne University of Helsinki, August 25,
The Principle for Inductive Inference Centre for Molecular, Environmental, Genetic & Analytic (MEGA) Epidemiology School of Population Health University of Melbourne University of Helsinki, August 25,
Introduction. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Introduction In this book we will be concerned with supervised learning, which is the problem of learning input-output mappings from empirical data (the training dataset). Depending on the characteristics
Chapter 1 Introduction In this book we will be concerned with supervised learning, which is the problem of learning input-output mappings from empirical data (the training dataset). Depending on the characteristics
Privacy-Preserving Data Mining
 CS 380S Privacy-Preserving Data Mining Vitaly Shmatikov slide 1 Reading Assignment Evfimievski, Gehrke, Srikant. Limiting Privacy Breaches in Privacy-Preserving Data Mining (PODS 2003). Blum, Dwork, McSherry,
CS 380S Privacy-Preserving Data Mining Vitaly Shmatikov slide 1 Reading Assignment Evfimievski, Gehrke, Srikant. Limiting Privacy Breaches in Privacy-Preserving Data Mining (PODS 2003). Blum, Dwork, McSherry,
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
S0214 : GPU Based Stacking Sequence Generation For Composite Skins Using GA
 S0214 : GPU Based Stacking Sequence Generation For Composite Skins Using GA Date: 16th May 2012 Wed, 3pm to 3.25pm(Adv. Session) Sathyanarayana K., Manish Banga, and Ravi Kumar G. V. V. Engineering Services,
S0214 : GPU Based Stacking Sequence Generation For Composite Skins Using GA Date: 16th May 2012 Wed, 3pm to 3.25pm(Adv. Session) Sathyanarayana K., Manish Banga, and Ravi Kumar G. V. V. Engineering Services,
Parametric Techniques Lecture 3
 Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 Jason Corso SUNY at Buffalo 22 January 2009 J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 22 January 2009 1 / 39 Introduction In Lecture 2, we learned how to
Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 Jason Corso SUNY at Buffalo 22 January 2009 J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 22 January 2009 1 / 39 Introduction In Lecture 2, we learned how to
Gibbs Sampling Methods for Multiple Sequence Alignment
 Gibbs Sampling Methods for Multiple Sequence Alignment Scott C. Schmidler 1 Jun S. Liu 2 1 Section on Medical Informatics and 2 Department of Statistics Stanford University 11/17/99 1 Outline Statistical
Gibbs Sampling Methods for Multiple Sequence Alignment Scott C. Schmidler 1 Jun S. Liu 2 1 Section on Medical Informatics and 2 Department of Statistics Stanford University 11/17/99 1 Outline Statistical
Scalable and Power-Efficient Data Mining Kernels
 Scalable and Power-Efficient Data Mining Kernels Alok Choudhary, John G. Searle Professor Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and Professor, Kellogg School of Management Director of the
Scalable and Power-Efficient Data Mining Kernels Alok Choudhary, John G. Searle Professor Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and Professor, Kellogg School of Management Director of the
CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning Radford M. Neal, University of Toronto, 2011 Lecture 4 Problem: Density Estimation We have observed data, y 1,..., y n, drawn independently from some unknown
CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning Radford M. Neal, University of Toronto, 2011 Lecture 4 Problem: Density Estimation We have observed data, y 1,..., y n, drawn independently from some unknown
Short Questions (Do two out of three) 15 points each
 Econometrics Short Questions Do two out of three) 5 points each ) Let y = Xβ + u and Z be a set of instruments for X When we estimate β with OLS we project y onto the space spanned by X along a path orthogonal
Econometrics Short Questions Do two out of three) 5 points each ) Let y = Xβ + u and Z be a set of instruments for X When we estimate β with OLS we project y onto the space spanned by X along a path orthogonal
The Particle Filter. PD Dr. Rudolph Triebel Computer Vision Group. Machine Learning for Computer Vision
 The Particle Filter Non-parametric implementation of Bayes filter Represents the belief (posterior) random state samples. by a set of This representation is approximate. Can represent distributions that
The Particle Filter Non-parametric implementation of Bayes filter Represents the belief (posterior) random state samples. by a set of This representation is approximate. Can represent distributions that
Bayesian Classifiers and Probability Estimation. Vassilis Athitsos CSE 4308/5360: Artificial Intelligence I University of Texas at Arlington
 Bayesian Classifiers and Probability Estimation Vassilis Athitsos CSE 4308/5360: Artificial Intelligence I University of Texas at Arlington 1 Data Space Suppose that we have a classification problem The
Bayesian Classifiers and Probability Estimation Vassilis Athitsos CSE 4308/5360: Artificial Intelligence I University of Texas at Arlington 1 Data Space Suppose that we have a classification problem The
Stein Variational Gradient Descent: A General Purpose Bayesian Inference Algorithm
 Stein Variational Gradient Descent: A General Purpose Bayesian Inference Algorithm Qiang Liu and Dilin Wang NIPS 2016 Discussion by Yunchen Pu March 17, 2017 March 17, 2017 1 / 8 Introduction Let x R d
Stein Variational Gradient Descent: A General Purpose Bayesian Inference Algorithm Qiang Liu and Dilin Wang NIPS 2016 Discussion by Yunchen Pu March 17, 2017 March 17, 2017 1 / 8 Introduction Let x R d
Intro. ANN & Fuzzy Systems. Lecture 15. Pattern Classification (I): Statistical Formulation
 Lecture 15. Pattern Classification (I): Statistical Formulation Outline Statistical Pattern Recognition Maximum Posterior Probability (MAP) Classifier Maximum Likelihood (ML) Classifier K-Nearest Neighbor
Lecture 15. Pattern Classification (I): Statistical Formulation Outline Statistical Pattern Recognition Maximum Posterior Probability (MAP) Classifier Maximum Likelihood (ML) Classifier K-Nearest Neighbor
CS446: Machine Learning Fall Final Exam. December 6 th, 2016
 CS446: Machine Learning Fall 2016 Final Exam December 6 th, 2016 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains
CS446: Machine Learning Fall 2016 Final Exam December 6 th, 2016 This is a closed book exam. Everything you need in order to solve the problems is supplied in the body of this exam. This exam booklet contains
Bayesian Support Vector Machines for Feature Ranking and Selection
 Bayesian Support Vector Machines for Feature Ranking and Selection written by Chu, Keerthi, Ong, Ghahramani Patrick Pletscher pat@student.ethz.ch ETH Zurich, Switzerland 12th January 2006 Overview 1 Introduction
Bayesian Support Vector Machines for Feature Ranking and Selection written by Chu, Keerthi, Ong, Ghahramani Patrick Pletscher pat@student.ethz.ch ETH Zurich, Switzerland 12th January 2006 Overview 1 Introduction
27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain. 1 Recap of MCMC and Naive Parallel Gibbs Sampling
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Pengtao Xie, Khoa Luu In this scribe, we are going to review the Parallel
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Pengtao Xie, Khoa Luu In this scribe, we are going to review the Parallel
Probabilistic Time Series Classification
 Probabilistic Time Series Classification Y. Cem Sübakan Boğaziçi University 25.06.2013 Y. Cem Sübakan (Boğaziçi University) M.Sc. Thesis Defense 25.06.2013 1 / 54 Problem Statement The goal is to assign
Probabilistic Time Series Classification Y. Cem Sübakan Boğaziçi University 25.06.2013 Y. Cem Sübakan (Boğaziçi University) M.Sc. Thesis Defense 25.06.2013 1 / 54 Problem Statement The goal is to assign
Expectation Maximization
 Expectation Maximization Bishop PRML Ch. 9 Alireza Ghane c Ghane/Mori 4 6 8 4 6 8 4 6 8 4 6 8 5 5 5 5 5 5 4 6 8 4 4 6 8 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 µ, Σ) α f Learningscale is slightly Parameters is slightly larger larger
Expectation Maximization Bishop PRML Ch. 9 Alireza Ghane c Ghane/Mori 4 6 8 4 6 8 4 6 8 4 6 8 5 5 5 5 5 5 4 6 8 4 4 6 8 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 µ, Σ) α f Learningscale is slightly Parameters is slightly larger larger
Notes on Noise Contrastive Estimation (NCE)
 Notes on Noise Contrastive Estimation NCE) David Meyer dmm@{-4-5.net,uoregon.edu,...} March 0, 207 Introduction In this note we follow the notation used in [2]. Suppose X x, x 2,, x Td ) is a sample of
Notes on Noise Contrastive Estimation NCE) David Meyer dmm@{-4-5.net,uoregon.edu,...} March 0, 207 Introduction In this note we follow the notation used in [2]. Suppose X x, x 2,, x Td ) is a sample of
Parametric Techniques
 Parametric Techniques Jason J. Corso SUNY at Buffalo J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques 1 / 39 Introduction When covering Bayesian Decision Theory, we assumed the full probabilistic structure
Parametric Techniques Jason J. Corso SUNY at Buffalo J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques 1 / 39 Introduction When covering Bayesian Decision Theory, we assumed the full probabilistic structure
Introduction to Statistical Learning Theory
 Introduction to Statistical Learning Theory In the last unit we looked at regularization - adding a w 2 penalty. We add a bias - we prefer classifiers with low norm. How to incorporate more complicated
Introduction to Statistical Learning Theory In the last unit we looked at regularization - adding a w 2 penalty. We add a bias - we prefer classifiers with low norm. How to incorporate more complicated
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Autumn Semester MACHINE LEARNING AND ADAPTIVE INTELLIGENCE
 Data Provided: None DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Autumn Semester 203 204 MACHINE LEARNING AND ADAPTIVE INTELLIGENCE 2 hours Answer THREE of the four questions. All questions carry equal weight. Figures
Data Provided: None DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Autumn Semester 203 204 MACHINE LEARNING AND ADAPTIVE INTELLIGENCE 2 hours Answer THREE of the four questions. All questions carry equal weight. Figures
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 3: Probability, Bayes Theorem, and Bayes Classification Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University Probability Should you play this game? Game: A fair
Fast Non-Parametric Bayesian Inference on Infinite Trees
 Marcus Hutter - 1 - Fast Bayesian Inference on Trees Fast Non-Parametric Bayesian Inference on Infinite Trees Marcus Hutter Istituto Dalle Molle di Studi sull Intelligenza Artificiale IDSIA, Galleria 2,
Marcus Hutter - 1 - Fast Bayesian Inference on Trees Fast Non-Parametric Bayesian Inference on Infinite Trees Marcus Hutter Istituto Dalle Molle di Studi sull Intelligenza Artificiale IDSIA, Galleria 2,
Naïve Bayes classification
 Naïve Bayes classification 1 Probability theory Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. Examples: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss
Naïve Bayes classification 1 Probability theory Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. Examples: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss
Probabilistic Graphical Models: MRFs and CRFs. CSE628: Natural Language Processing Guest Lecturer: Veselin Stoyanov
 Probabilistic Graphical Models: MRFs and CRFs CSE628: Natural Language Processing Guest Lecturer: Veselin Stoyanov Why PGMs? PGMs can model joint probabilities of many events. many techniques commonly
Probabilistic Graphical Models: MRFs and CRFs CSE628: Natural Language Processing Guest Lecturer: Veselin Stoyanov Why PGMs? PGMs can model joint probabilities of many events. many techniques commonly
MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION: STRING CLASSIFICATION
 MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION: STRING CLASSIFICATION THOMAS MAILUND Machine learning means different things to different people, and there is no general agreed upon core set of algorithms that must be
MACHINE LEARNING INTRODUCTION: STRING CLASSIFICATION THOMAS MAILUND Machine learning means different things to different people, and there is no general agreed upon core set of algorithms that must be
Lecture 3a: Dirichlet processes
 Lecture 3a: Dirichlet processes Cédric Archambeau Centre for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning Department of Computer Science University College London c.archambeau@cs.ucl.ac.uk Advanced Topics
Lecture 3a: Dirichlet processes Cédric Archambeau Centre for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning Department of Computer Science University College London c.archambeau@cs.ucl.ac.uk Advanced Topics
Model Averaging With Holdout Estimation of the Posterior Distribution
 Model Averaging With Holdout stimation of the Posterior Distribution Alexandre Lacoste alexandre.lacoste.1@ulaval.ca François Laviolette francois.laviolette@ift.ulaval.ca Mario Marchand mario.marchand@ift.ulaval.ca
Model Averaging With Holdout stimation of the Posterior Distribution Alexandre Lacoste alexandre.lacoste.1@ulaval.ca François Laviolette francois.laviolette@ift.ulaval.ca Mario Marchand mario.marchand@ift.ulaval.ca
Quantization. Robert M. Haralick. Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York
 Quantization Robert M. Haralick Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York Outline Quantizing 1 Quantizing 2 3 4 5 6 Quantizing Data is real-valued Data is integer valued with large
Quantization Robert M. Haralick Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York Outline Quantizing 1 Quantizing 2 3 4 5 6 Quantizing Data is real-valued Data is integer valued with large
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
Lecture 3: More on regularization. Bayesian vs maximum likelihood learning
 Lecture 3: More on regularization. Bayesian vs maximum likelihood learning L2 and L1 regularization for linear estimators A Bayesian interpretation of regularization Bayesian vs maximum likelihood fitting
Lecture 3: More on regularization. Bayesian vs maximum likelihood learning L2 and L1 regularization for linear estimators A Bayesian interpretation of regularization Bayesian vs maximum likelihood fitting
Pattern Recognition Approaches to Solving Combinatorial Problems in Free Groups
 Contemporary Mathematics Pattern Recognition Approaches to Solving Combinatorial Problems in Free Groups Robert M. Haralick, Alex D. Miasnikov, and Alexei G. Myasnikov Abstract. We review some basic methodologies
Contemporary Mathematics Pattern Recognition Approaches to Solving Combinatorial Problems in Free Groups Robert M. Haralick, Alex D. Miasnikov, and Alexei G. Myasnikov Abstract. We review some basic methodologies
Machine Learning. CUNY Graduate Center, Spring Lectures 11-12: Unsupervised Learning 1. Professor Liang Huang.
 Machine Learning CUNY Graduate Center, Spring 2013 Lectures 11-12: Unsupervised Learning 1 (Clustering: k-means, EM, mixture models) Professor Liang Huang huang@cs.qc.cuny.edu http://acl.cs.qc.edu/~lhuang/teaching/machine-learning
Machine Learning CUNY Graduate Center, Spring 2013 Lectures 11-12: Unsupervised Learning 1 (Clustering: k-means, EM, mixture models) Professor Liang Huang huang@cs.qc.cuny.edu http://acl.cs.qc.edu/~lhuang/teaching/machine-learning
Inferring Markov Chains: Bayesian Estimation, Model Comparison, Entropy Rate, and Out-of-class Modeling
 Santa Fe Institute Working Paper 7-4-5 arxiv.org/math.st/7375 Inferring Markov Chains: Bayesian Estimation, Model Comparison, Entropy Rate, and Out-of-class Modeling Christopher C. Strelioff,,2, James
Santa Fe Institute Working Paper 7-4-5 arxiv.org/math.st/7375 Inferring Markov Chains: Bayesian Estimation, Model Comparison, Entropy Rate, and Out-of-class Modeling Christopher C. Strelioff,,2, James
Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm Exam Solutions
 10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm Exam Solutions Instructors: Eric Xing, Ziv Bar-Joseph 17 November, 2015 There are 11 questions, for a total of 100 points. This exam is open book, open notes,
10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm Exam Solutions Instructors: Eric Xing, Ziv Bar-Joseph 17 November, 2015 There are 11 questions, for a total of 100 points. This exam is open book, open notes,
σ(a) = a N (x; 0, 1 2 ) dx. σ(a) = Φ(a) =
 Until now we have always worked with likelihoods and prior distributions that were conjugate to each other, allowing the computation of the posterior distribution to be done in closed form. Unfortunately,
Until now we have always worked with likelihoods and prior distributions that were conjugate to each other, allowing the computation of the posterior distribution to be done in closed form. Unfortunately,
Be able to define the following terms and answer basic questions about them:
 CS440/ECE448 Section Q Fall 2017 Final Review Be able to define the following terms and answer basic questions about them: Probability o Random variables, axioms of probability o Joint, marginal, conditional
CS440/ECE448 Section Q Fall 2017 Final Review Be able to define the following terms and answer basic questions about them: Probability o Random variables, axioms of probability o Joint, marginal, conditional
Context tree models for source coding
 Context tree models for source coding Toward Non-parametric Information Theory Licence de droits d usage Outline Lossless Source Coding = density estimation with log-loss Source Coding and Universal Coding
Context tree models for source coding Toward Non-parametric Information Theory Licence de droits d usage Outline Lossless Source Coding = density estimation with log-loss Source Coding and Universal Coding
