Phys 322 Lecture 21. Chapter 8 Polarization
|
|
|
- Dwayne Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phs 3 Lecture 1 Chapter 8 Polarization
2 Plane of polarization Transverse M wave B Plane of polarization - plane defined b vector and k: Plane of polarization z: z t ˆi z, t ˆi coskz t, z Linearl (plane) polarized light: lectric field orientation is constant, though its amplitude can var in time. Can create another wave with polarization along : z t ˆj z, t ˆj coskz t,
3 in-phase: z t + z t = z t Superposition: in-phase & out-of-phase ˆi coskz t, ˆj coskz t, ˆi ˆ coskz t, j =, ±, out-of-phase: = ±, ±3 z t ˆi ˆ cos kz t, j B changing / can create linearl polarized light along an direction in plane.
4 Circular polarization + = z t ˆi coskz t, z t ˆj coskz t, = m ±/, where m=,1,, =-/ z, t ˆcoskz t ˆ sinkz t i j z t ˆj sinkz t, What is the magnitude of the electric field? cos kz t sin kz t Magnitude is constant in time! Is it a wave?
5 Circular polarization z, t ˆcoskz t ˆ sinkz t i j and components oscillate: coskz t sinkz t Angle = kz -t Vector rotates in time with angular frequenc - Vector rotates in space with angular spatial speed k
6 Circular polarization z, t ˆcoskz t ˆ sinkz t i j Right circularl polarized light rotates clockwise as seen b observer Vector makes full turn as wave advances one wavelength Left circularl polarized light rotates counter clockwise z, t ˆcos kz t ˆ i jsin kz t What if we have a superposition of left and right circularl polarized light of equal amplitude? z, t ˆ i cos kz t - linearl polarized light
7 lliptic polarization General case: t kz cos t kz cos changes direction and magnitude What is the trajector of the tip of vector (, ) in plane? sin sin cos cos / t kz t kz sin sin cos t kz 1 sin kz t sin 1 cos sin cos
8 lliptic polarization sin cos quation of ellipse cos tan Can alwas rotate aes to get convenient form (=, or =±/, ): 1 Circular polarization: =
9 lliptic polarization sin cos State of polarization: P - linearl polarized R - right circular polarization L - left circular polarization - elliptical polarization P P P =
10 Superposition of L and R P -state can be represented as superposition of L- and R -states of the same amplitude -state can be represent as superposition of L and R-states:
11 Circular polarization and angular momentum angular momentum What would happen with an electron under circularl polarized light? Angular velocit - angular momentum Light is absorbed, and if it was circularl polarized: L energ of light frequenc of light
12 Photon and angular momentum h L Photon has energ: h Angular momentum of a photon is independent of its energ: L Photon has a spin, - L-state - R-state Whenever a photon is absorbed or emitted b a charged particle, along with the change in its energ the electron will undergo a change in its angular momentum First measured in 1935 b Richard Beth Linearl polarized light: photons eist in either spin state with equal probabilit
13 Polarizer An optical device that transmits (or reflects) onl light polarized in a certain wa. Linear polarizer: passes (reflects) onl light that is linearl polarized in certain direction (plane).
14 Unpolarized light Is sun light polarized? Unpolarized light = randoml polarized Atoms emit wavepackets ~1 ns long
15 Unpolarized light on polarizer Most light comes from electrons accelerating in random directions and is unpolarized. Averaging over all directions I transmitted = ½ I incident
16 Polarized light on polarizer: Malus s law transmitted = incident cos() I~ I transmitted = I incident cos () is the angle between the incoming light s polarization, and the transmission ais TA Incident Transmission ais Transmitted = incident cos()
17 ample: crossed polarizers Unpolarized light I transmitted = I incident cos () I I 1 =I / I = How much light passes through two crossed polarizers?
18 ample: three polarizers Unpolarized light I transmitted = I incident cos () Add one polarizer at 45 in between... I I 1 =I / I =I 1 cos (45 ) I I 4 I I cos 45 3 I I 3 cos 45 4 I I3 8 o o
19 Dichroism = selective absorption of light of certain polarization Linear dichroism - selective absorption of one of the two P-state (linear) orthogonal polarizations Circular dichroism - selective absorption of L-state or R-state circular polarizations Using dichroic materials one can build a polarizer
20 Wire-grid polarizer What is the transmission ais of this wire-grid polarizer Can we use such a polarizer for visible light? 196, George R. Bird and Mafield Parish: 16 wires per mm
21 Wire grid polarizer in the visible Using semiconductor fabrication techniques, a wire-grid polarizer was recentl developed for the visible. The spacing is less than 1 micron.
22 The wires need not be ver long. Hoa has designed a wire-grid polarizer for telecom applications that uses small elongated copper particles. tinction coefficient > 1, Transmission > 99%
23 Dichroic crstals Anisotropic crstal structure: one polarization is absorbed more than the other ample: tourmaline lastic constants for electrons ma be different along two aes
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Polarization of Light Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Types of Polarization Light propagating through different materials: One polarization component can
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Polarization of Light Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Types of Polarization Light propagating through different materials: One polarization component can
Polarized sunglasses. Polarization
 Polarized sunglasses 3 4 : is a propert of the wave of light that can oscillate with certain orientation; the wave ehibits polarization which has onl one possible polarization, namel the direction in which
Polarized sunglasses 3 4 : is a propert of the wave of light that can oscillate with certain orientation; the wave ehibits polarization which has onl one possible polarization, namel the direction in which
POLARISATION. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion.
 POLARISATION Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion. If the E field
POLARISATION Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion. If the E field
Waves, Polarization, and Coherence
 05-0-4 Waves, Polarization, and Coherence Lecture 6 Biophotonics Jae Gwan Kim jaekim@gist.ac.kr, X 0 School of nformation and Communication ngineering Gwangju nstitute of Sciences and Technolog Outline
05-0-4 Waves, Polarization, and Coherence Lecture 6 Biophotonics Jae Gwan Kim jaekim@gist.ac.kr, X 0 School of nformation and Communication ngineering Gwangju nstitute of Sciences and Technolog Outline
14. Matrix treatment of polarization
 14. Matri treatment of polarization This lecture Polarized Light : linear, circular, elliptical Jones Vectors for Polarized Light Jones Matrices for Polarizers, Phase Retarders, Rotators (Linear) Polarization
14. Matri treatment of polarization This lecture Polarized Light : linear, circular, elliptical Jones Vectors for Polarized Light Jones Matrices for Polarizers, Phase Retarders, Rotators (Linear) Polarization
Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light
 1. Objective Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light Understanding the definition of polarized and un-polarized light. Understanding polarizer and analzer definition, Maluse s law. Retarding
1. Objective Experiment 5 Polarization and Modulation of Light Understanding the definition of polarized and un-polarized light. Understanding polarizer and analzer definition, Maluse s law. Retarding
Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction
 Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction Lecture aims to explain: 1. Light as a transverse electro-magnetic wave 2. Importance of polarisation of light 3. Linearly polarised light 4. Natural light
Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction Lecture aims to explain: 1. Light as a transverse electro-magnetic wave 2. Importance of polarisation of light 3. Linearly polarised light 4. Natural light
Phys 2310 Mon. Oct. 30, 2017 Today s Topics. Begin Modern Optics Ch. 2: The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time
 Phys 3 Mon. Oct. 3, 7 Today s Topics Begin Modern Optics Ch. : The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time By Wed.: Reading this Week Begin Ch. of Modern Optics (. 8.) Nature of Polarized Light,
Phys 3 Mon. Oct. 3, 7 Today s Topics Begin Modern Optics Ch. : The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time By Wed.: Reading this Week Begin Ch. of Modern Optics (. 8.) Nature of Polarized Light,
15. Polarization. Linear, circular, and elliptical polarization. Mathematics of polarization. Uniaxial crystals. Birefringence.
 15. Polarization Linear, circular, and elliptical polarization Mathematics of polarization Uniaial crstals Birefringence Polarizers Notation: polarization near an interface Parallel ("p") polarization
15. Polarization Linear, circular, and elliptical polarization Mathematics of polarization Uniaial crstals Birefringence Polarizers Notation: polarization near an interface Parallel ("p") polarization
Lab 9: Polarization Phy208 Spring 2008
 Lab 9: Polarization Ph208 Spring 2008 Name Section This sheet is the lab document our TA will use to score our lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit ou must use complete
Lab 9: Polarization Ph208 Spring 2008 Name Section This sheet is the lab document our TA will use to score our lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit ou must use complete
Lab 10: Polarization Phy248 Spring 2009
 Lab 10: Polarization Ph248 Spring 2009 Name Section This sheet is the lab document our TA will use to score our lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit ou must use complete
Lab 10: Polarization Ph248 Spring 2009 Name Section This sheet is the lab document our TA will use to score our lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit ou must use complete
EM Waves. From previous Lecture. This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization. Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves
 EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Chapter 14 Matrix Treatment of Polarization
 Chapter 4 Matri Treatment of Polarization Lecture Notes for Modern Optics based on Pedrotti & Pedrotti & Pedrotti Instructor: Naer Eradat Spring 29 5//29 Matri Treatment of Polarization Polarization Polarization
Chapter 4 Matri Treatment of Polarization Lecture Notes for Modern Optics based on Pedrotti & Pedrotti & Pedrotti Instructor: Naer Eradat Spring 29 5//29 Matri Treatment of Polarization Polarization Polarization
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 16
 C 6340 Intermediate M Waves Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of C Notes 16 1 Polarization of Waves Consider a plane wave with both and components (,, z) = ( ˆ + ˆ ) e jkz Assume j0 = ae = a = j be
C 6340 Intermediate M Waves Fall 2016 Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of C Notes 16 1 Polarization of Waves Consider a plane wave with both and components (,, z) = ( ˆ + ˆ ) e jkz Assume j0 = ae = a = j be
Chiroptical Spectroscopy
 Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Light Waves and Polarization
 Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Polarization. Polarization. Physics Waves & Oscillations 4/3/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones. Two problems to be considered today:
 4/3/26 Physics 422 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 34 Polarization of Light Spring 26 Semester Matthew Jones Polarization (,)= cos (,)= cos + Unpolarizedlight: Random,, Linear polarization: =,± Circular polarization:
4/3/26 Physics 422 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 34 Polarization of Light Spring 26 Semester Matthew Jones Polarization (,)= cos (,)= cos + Unpolarizedlight: Random,, Linear polarization: =,± Circular polarization:
Electromagnetic wave energy & polarization
 Phys 0 Lecture 6 Electromagnetic wave energy & polarization Today we will... Learn about properties p of electromagnetic waves Energy density & intensity Polarization linear, circular, unpolarized Apply
Phys 0 Lecture 6 Electromagnetic wave energy & polarization Today we will... Learn about properties p of electromagnetic waves Energy density & intensity Polarization linear, circular, unpolarized Apply
Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection
 Lecture 4: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht
Lecture 4: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht
Introduction to Polarization
 Phone: Ext 659, E-mail: hcchui@mail.ncku.edu.tw Fall/007 Introduction to Polarization Text Book: A Yariv and P Yeh, Photonics, Oxford (007) 1.6 Polarization States and Representations (Stokes Parameters
Phone: Ext 659, E-mail: hcchui@mail.ncku.edu.tw Fall/007 Introduction to Polarization Text Book: A Yariv and P Yeh, Photonics, Oxford (007) 1.6 Polarization States and Representations (Stokes Parameters
PH 222-2C Fall Electromagnetic Waves Lectures Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Electromagnetic Waves Lectures 21-22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Electromagnetic Waves Lectures 21-22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
Lecture 5: Polarization. Polarized Light in the Universe. Descriptions of Polarized Light. Polarizers. Retarders. Outline
 Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl ATI 2016,
Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl ATI 2016,
6 Properties of polarized light - polarimetry
 6 Properties of polarized light - polarimetr Supervisors : J.Geandrot, O.Frantz This practical work aims to stud some phenomena caused b the transversalit of light : dichroism, birefingence, rotating power.
6 Properties of polarized light - polarimetr Supervisors : J.Geandrot, O.Frantz This practical work aims to stud some phenomena caused b the transversalit of light : dichroism, birefingence, rotating power.
Chapter 9 - Polarization
 Chapter 9 - Polarization Gabriel Popescu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Beckman Institute Quantitative Light Imaging Laboratory http://light.ece.uiuc.edu Principles of Optical Imaging Electrical
Chapter 9 - Polarization Gabriel Popescu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Beckman Institute Quantitative Light Imaging Laboratory http://light.ece.uiuc.edu Principles of Optical Imaging Electrical
Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236. Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization
 Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236 Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization 1 Electromagnetic Radiation The first requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy source to illuminate the target.
Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236 Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization 1 Electromagnetic Radiation The first requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy source to illuminate the target.
Jones vector & matrices
 Jones vector & matrices Department of Physics 1 Matrix treatment of polarization Consider a light ray with an instantaneous E-vector as shown y E k, t = xe x (k, t) + ye y k, t E y E x x E x = E 0x e i
Jones vector & matrices Department of Physics 1 Matrix treatment of polarization Consider a light ray with an instantaneous E-vector as shown y E k, t = xe x (k, t) + ye y k, t E y E x x E x = E 0x e i
Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection
 Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University,
Lecture 5: Polarization Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Brewster Angle and Total Internal Reflection 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light 4 Polarizers 5 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University,
Polarization of light
 Laboratory#8 Phys4480/5480 Dr. Cristian Bahrim Polarization of light Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave (EM) which travels due to an electric field and a magnetic field oscillating in phase and
Laboratory#8 Phys4480/5480 Dr. Cristian Bahrim Polarization of light Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave (EM) which travels due to an electric field and a magnetic field oscillating in phase and
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Polarimetry in the E-ELT era. Polarized Light in the Universe. Descriptions of Polarized Light. Polarizers. Retarders. Fundamentals of Polarized Light
 Polarimetry in the E-ELT era Fundamentals of Polarized Light 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Polarimetry in the E-ELT era Fundamentals of Polarized Light 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Descriptions of Polarized Light 3 Polarizers 4 Retarders Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves 9.1 Waves in One Dimension 9.1.1 The Wave Equation What is a "wave?" Let's start with the simple case: fixed shape, constant speed: How would you represent such a string
Chapter 9. Electromagnetic Waves 9.1 Waves in One Dimension 9.1.1 The Wave Equation What is a "wave?" Let's start with the simple case: fixed shape, constant speed: How would you represent such a string
POLARIZATION FUNDAMENTAL OPTICS POLARIZATION STATES 1. CARTESIAN REPRESENTATION 2. CIRCULAR REPRESENTATION. Polarization. marketplace.idexop.
 POLARIZATION POLARIZATION STATS Four numbers are required to describe a single plane wave Fourier component traveling in the + z direction. These can be thought of as the amplitude and phase shift of the
POLARIZATION POLARIZATION STATS Four numbers are required to describe a single plane wave Fourier component traveling in the + z direction. These can be thought of as the amplitude and phase shift of the
Electromagnetic Waves
 Physics 102: Lecture 15 Electromagnetic Waves Energy & Polarization Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 1 Checkpoint 1.1, 1.2 y E x loop in xy plane loop in xz plane A B C Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 2 Propagation
Physics 102: Lecture 15 Electromagnetic Waves Energy & Polarization Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 1 Checkpoint 1.1, 1.2 y E x loop in xy plane loop in xz plane A B C Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 2 Propagation
: Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 2002
 151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
Mechanics Departmental Exam Last updated November 2013
 Mechanics Departmental Eam Last updated November 213 1. Two satellites are moving about each other in circular orbits under the influence of their mutual gravitational attractions. The satellites have
Mechanics Departmental Eam Last updated November 213 1. Two satellites are moving about each other in circular orbits under the influence of their mutual gravitational attractions. The satellites have
Polarization and Related Antenna Parameters
 ANTENTOP- 01-007, # 009 Polarization and Related Antenna Parameters Feel Yourself a Student! Dear friends, I would like to give to ou an interesting and reliable antenna theor. Hours searching in the web
ANTENTOP- 01-007, # 009 Polarization and Related Antenna Parameters Feel Yourself a Student! Dear friends, I would like to give to ou an interesting and reliable antenna theor. Hours searching in the web
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials
 Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Chapter 1 - The Nature of Light
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
Lecture 8: Polarimetry 2. Polarizers and Retarders. Polarimeters. Scattering Polarization. Zeeman Effect. Outline
 Lecture 8: Polarimetry 2 Outline 1 Polarizers and Retarders 2 Polarimeters 3 Scattering Polarization 4 Zeeman Effect Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht University, C.U.Keller@uu.nl Observational Astrophysics
Lecture 8: Polarimetry 2 Outline 1 Polarizers and Retarders 2 Polarimeters 3 Scattering Polarization 4 Zeeman Effect Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht University, C.U.Keller@uu.nl Observational Astrophysics
Chapter 34. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves The Goal of the Entire Course Maxwell s Equations: Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell 1831 1879 Scottish theoretical physicist Developed the electromagnetic theory
Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves The Goal of the Entire Course Maxwell s Equations: Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell 1831 1879 Scottish theoretical physicist Developed the electromagnetic theory
Physics I Keystone Institute Technology & Management Unit-II
 Un-polarized light Ordinary light is a collection of wave trains emitted by atoms or group of atoms with coherent time no longer than 10-8 second. Each wave train has different orientation and phase of
Un-polarized light Ordinary light is a collection of wave trains emitted by atoms or group of atoms with coherent time no longer than 10-8 second. Each wave train has different orientation and phase of
Polarized optical wave in optical fiber communication system
 IOSR Journal of Applied Phsics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep. - Oct. 2017), PP 09-14 www.iosrjournals.org Polarized optical wave in optical fiber communication sstem Dinesh
IOSR Journal of Applied Phsics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep. - Oct. 2017), PP 09-14 www.iosrjournals.org Polarized optical wave in optical fiber communication sstem Dinesh
Electromagnetic Waves. Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
Assignment , 7.1, 7.2, 7.5, 7.11, 7.12, 7.15, TIR and FTIR
 LC45-summer, 1 1. 1.1, 7.1, 7., 7.5, 7.11, 7.1, 7.15, 7.1 1.1. TIR and FTIR a) B considering the electric field component in medium B in Figure 1. (b), eplain how ou can adjust the amount of transmitted
LC45-summer, 1 1. 1.1, 7.1, 7., 7.5, 7.11, 7.1, 7.15, 7.1 1.1. TIR and FTIR a) B considering the electric field component in medium B in Figure 1. (b), eplain how ou can adjust the amount of transmitted
Phys 221. Chapter 3. Vectors A. Dzyubenko Brooks/Cole
 Phs 221 Chapter 3 Vectors adzubenko@csub.edu http://www.csub.edu/~adzubenko 2014. Dzubenko 2014 rooks/cole 1 Coordinate Sstems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate sstem consists
Phs 221 Chapter 3 Vectors adzubenko@csub.edu http://www.csub.edu/~adzubenko 2014. Dzubenko 2014 rooks/cole 1 Coordinate Sstems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate sstem consists
Electromagnetic Waves
 May 7, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 7 Maxwell Equations In a region of space where there are no free sources (ρ = 0, J = 0), Maxwell s equations reduce to a simple
May 7, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 7 Maxwell Equations In a region of space where there are no free sources (ρ = 0, J = 0), Maxwell s equations reduce to a simple
NAWAB SHAH ALAM KHAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY UNIT II-a POLARISATION
 NAWAB SHAH ALAM KHAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY UNIT II-a 1 POLARISATION SYLLABUS :Polarization: Introduction, Malus s law, double refraction, Nicol prism, Quarter wave and half wave plates. 1.
NAWAB SHAH ALAM KHAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY UNIT II-a 1 POLARISATION SYLLABUS :Polarization: Introduction, Malus s law, double refraction, Nicol prism, Quarter wave and half wave plates. 1.
Dispersion. f (increasing frequency)
 Dispersion The index of refraction n is usually a property of the medium but equally important, it also varies with the frequency f of light dispersion. n typically increases with increasing f. f (increasing
Dispersion The index of refraction n is usually a property of the medium but equally important, it also varies with the frequency f of light dispersion. n typically increases with increasing f. f (increasing
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
Phys102 Lecture Diffraction of Light
 Phys102 Lecture 31-33 Diffraction of Light Key Points Diffraction by a Single Slit Diffraction in the Double-Slit Experiment Limits of Resolution Diffraction Grating and Spectroscopy Polarization References
Phys102 Lecture 31-33 Diffraction of Light Key Points Diffraction by a Single Slit Diffraction in the Double-Slit Experiment Limits of Resolution Diffraction Grating and Spectroscopy Polarization References
 第 1 頁, 共 8 頁 Chap32&Chap33 1. Test Bank, Question 2 Gauss' law for magnetism tells us: the net charge in any given volume that the line integral of a magnetic around any closed loop must vanish the magnetic
第 1 頁, 共 8 頁 Chap32&Chap33 1. Test Bank, Question 2 Gauss' law for magnetism tells us: the net charge in any given volume that the line integral of a magnetic around any closed loop must vanish the magnetic
Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006
 Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must be placed in
Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must be placed in
16. More About Polarization
 16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods
 Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
Lecture 4: Polarimetry 2. Polarizers and Retarders. Polarimeters. Scattering Polarization. Zeeman Effect. Outline
 Lecture 4: Polarimetry 2 Outline 1 Polarizers and Retarders 2 Polarimeters 3 Scattering Polarization 4 Zeeman Effect Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht University, C.U.Keller@uu.nl Observational Astrophysics
Lecture 4: Polarimetry 2 Outline 1 Polarizers and Retarders 2 Polarimeters 3 Scattering Polarization 4 Zeeman Effect Christoph U. Keller, Utrecht University, C.U.Keller@uu.nl Observational Astrophysics
Polarizers and Retarders
 Phys 531 Lecture 20 11 November 2004 Polarizers and Retarders Last time, discussed basics of polarization Linear, circular, elliptical states Describe by polarization vector ĵ Today: Describe elements
Phys 531 Lecture 20 11 November 2004 Polarizers and Retarders Last time, discussed basics of polarization Linear, circular, elliptical states Describe by polarization vector ĵ Today: Describe elements
polarisation of Light
 Basic concepts to understand polarisation of Light Polarization of Light Nature of light: light waves are transverse in nature i. e. the waves propagates in a direction perpendicular to the direction of
Basic concepts to understand polarisation of Light Polarization of Light Nature of light: light waves are transverse in nature i. e. the waves propagates in a direction perpendicular to the direction of
Effects of birefringence on Fizeau interferometry that uses polarization phase shifting technique
 Effects of birefringence on Fizeau interferometr that uses polarization phase shifting technique Chunu Zhao, Dongel Kang and James H. Burge College of Optical Sciences, the Universit of Arizona 1630 E.
Effects of birefringence on Fizeau interferometr that uses polarization phase shifting technique Chunu Zhao, Dongel Kang and James H. Burge College of Optical Sciences, the Universit of Arizona 1630 E.
C. Incorrect! The velocity of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is the same, 3.14 x 10 8 m/s.
 AP Physics - Problem Drill 21: Physical Optics 1. Which of these statements is incorrect? Question 01 (A) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (B) An electromagnetic wave is a
AP Physics - Problem Drill 21: Physical Optics 1. Which of these statements is incorrect? Question 01 (A) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (B) An electromagnetic wave is a
FIRST YEAR PHYSICS. Unit 4: Light II
 FIRST YEAR PHYSICS Unit 4: Light II Contents PHASORS...3 RESOLUTION OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS...5 Rayleigh s criterion... 7 MORE ON DIFFRACTION...11 Multiple slits:... 11 Diffraction gratings... 14 X-RAY
FIRST YEAR PHYSICS Unit 4: Light II Contents PHASORS...3 RESOLUTION OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS...5 Rayleigh s criterion... 7 MORE ON DIFFRACTION...11 Multiple slits:... 11 Diffraction gratings... 14 X-RAY
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
Your Comments. What does signify?
 Your Comments WHAT? "POYNTING" VECTOR NOT "POINTING" VECTOR? I THOUGHT I COUGHT A SPELLING MISTAKE!!!!!!!! I must now see i
Your Comments WHAT? "POYNTING" VECTOR NOT "POINTING" VECTOR? I THOUGHT I COUGHT A SPELLING MISTAKE!!!!!!!! I must now see i
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 REVIEW Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Teacher Notes and Answers Chapter 4 SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER 1. In order for an electron to be ejected from a metal surface, the electron must be struck
CHAPTER 4 REVIEW Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms Teacher Notes and Answers Chapter 4 SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER 1. In order for an electron to be ejected from a metal surface, the electron must be struck
Electromagnetic Radiation. Physical Principles of Remote Sensing
 Electromagnetic Radiation Physical Principles of Remote Sensing Outline for 4/3/2003 Properties of electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Spectral emissivity Radiant temperature vs. kinematic
Electromagnetic Radiation Physical Principles of Remote Sensing Outline for 4/3/2003 Properties of electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Spectral emissivity Radiant temperature vs. kinematic
Electromagnetic Waves
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 23 Electromagnetic Waves Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Electromagnetic Theory Theoretical understanding of electricity and magnetism
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 23 Electromagnetic Waves Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Electromagnetic Theory Theoretical understanding of electricity and magnetism
High School Curriculum Standards: Physics
 High School Curriculum Standards: Physics Students will understand and apply scientific concepts, principles, and theories pertaining to the physical setting and living environment and recognize the historical
High School Curriculum Standards: Physics Students will understand and apply scientific concepts, principles, and theories pertaining to the physical setting and living environment and recognize the historical
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Course Updates. 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves +
 Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr1/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #11 due Wednesday 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves + 3) In the home stretch [review schedule]
Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr1/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #11 due Wednesday 2) This week: Electromagnetic Waves + 3) In the home stretch [review schedule]
Complete nomenclature for electron orbitals
 Complete nomenclature for electron orbitals Bohr s model worked but it lacked a satisfactory reason why. De Broglie suggested that all particles have a wave nature. u l=h/p Enter de Broglie again It was
Complete nomenclature for electron orbitals Bohr s model worked but it lacked a satisfactory reason why. De Broglie suggested that all particles have a wave nature. u l=h/p Enter de Broglie again It was
Lab 8: L-6, Polarization Lab Worksheet
 Lab 8: L-6, Polarization Lab Worksheet Name This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences
Lab 8: L-6, Polarization Lab Worksheet Name This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Coordinate Systems. Cartesian Coordinate System. Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors.
 PC1221 Fundamentals of Phsics I Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors Dr Ta Seng Chuan 1 Ground ules Switch off our handphone and pager Switch off our laptop computer and keep it No talking while lecture is going on
PC1221 Fundamentals of Phsics I Lectures 5 and 6 Vectors Dr Ta Seng Chuan 1 Ground ules Switch off our handphone and pager Switch off our laptop computer and keep it No talking while lecture is going on
Name: School Name: PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION
 PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION - 2013 Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Please note that i^, j^, and k^ are unit vectors along the x-axis,
PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION - 2013 Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Please note that i^, j^, and k^ are unit vectors along the x-axis,
Physics 214 Course Overview
 Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
Radiative Transfer with Polarization
 The Radiative Transfer Equation with Polarization Han Uitenbroek National Solar Observatory/Sacramento Peak Sunspot, USA Hale COLLAGE, Boulder, Feb 16, 2016 Today s Lecture Equation of transfer with polarization
The Radiative Transfer Equation with Polarization Han Uitenbroek National Solar Observatory/Sacramento Peak Sunspot, USA Hale COLLAGE, Boulder, Feb 16, 2016 Today s Lecture Equation of transfer with polarization
Chapter 16 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Waves. Daniel S. Weile. ELEG 648 Waves. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware. Plane Waves Reflection of Waves
 Waves Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Waves Outline Outline Introduction Let s start by introducing simple solutions to Maxwell s equations
Waves Daniel S. Weile Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Delaware ELEG 648 Waves Outline Outline Introduction Let s start by introducing simple solutions to Maxwell s equations
Physics 101 Lecture 2 Vectors Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN
 Phsics 101 Lecture 2 Vectors Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Department www.aovgun.com Coordinate Sstems qcartesian coordinate sstem qpolar coordinate sstem Januar 21, 2015 qfrom Cartesian to Polar coordinate
Phsics 101 Lecture 2 Vectors Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Department www.aovgun.com Coordinate Sstems qcartesian coordinate sstem qpolar coordinate sstem Januar 21, 2015 qfrom Cartesian to Polar coordinate
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 15. Optical Sources-LASER
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 15 Optical Sources-LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 15 Optical Sources-LASER Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
MOTION IN 2-DIMENSION (Projectile & Circular motion And Vectors)
 MOTION IN -DIMENSION (Projectile & Circular motion nd Vectors) INTRODUCTION The motion of an object is called two dimensional, if two of the three co-ordinates required to specif the position of the object
MOTION IN -DIMENSION (Projectile & Circular motion nd Vectors) INTRODUCTION The motion of an object is called two dimensional, if two of the three co-ordinates required to specif the position of the object
Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2
 Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2 Schroder: Chapters 2, 7, 10 1/68 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June).
Lecture 20 Optical Characterization 2 Schroder: Chapters 2, 7, 10 1/68 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June).
Light as electromagnetic wave and as particle
 Light as electromagnetic wave and as particle Help to understand and learn exam question 5. (How the wave-particle duality can be applied to light?) and to measurements Microscopy II., Light emission and
Light as electromagnetic wave and as particle Help to understand and learn exam question 5. (How the wave-particle duality can be applied to light?) and to measurements Microscopy II., Light emission and
Chapter 4 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS
 Chapter 4 MTIN IN TW AND THREE DIMENSINS Section 4-5, 4-6 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Analzed Important skills from this lecture: 1. Identif the projectile motion and its velocit and acceleration
Chapter 4 MTIN IN TW AND THREE DIMENSINS Section 4-5, 4-6 Projectile Motion Projectile Motion Analzed Important skills from this lecture: 1. Identif the projectile motion and its velocit and acceleration
Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves. Slide 29-1
 Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves Slide 29-1 Equations of electromagnetism: a review We ve now seen the four fundamental equations of electromagnetism, here listed together for the first time.
Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves Slide 29-1 Equations of electromagnetism: a review We ve now seen the four fundamental equations of electromagnetism, here listed together for the first time.
1 Polarization of Light
 J. Rothberg April, 014 Outline: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics 1 Polarization of Light 1.1 Classical Description Light polarized in the x direction has an electric field vector E = E 0 ˆx cos(kz ωt)
J. Rothberg April, 014 Outline: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics 1 Polarization of Light 1.1 Classical Description Light polarized in the x direction has an electric field vector E = E 0 ˆx cos(kz ωt)
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light
 Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
Lecture 9: Introduction to Diffraction of Light Lecture aims to explain: 1. Diffraction of waves in everyday life and applications 2. Interference of two one dimensional electromagnetic waves 3. Typical
First Name Last Name Title Date. Alexandra Stambaugh Slow Light on Chip Dec 8th Ring Resonators and Optofluidics
 Lecture 24 Semiconductor Detectors - Photodetectors Principle of the pn junction photodiode Absorption coefficient and photodiode materials Properties of semiconductor detectors The pin photodiodes Avalanche
Lecture 24 Semiconductor Detectors - Photodetectors Principle of the pn junction photodiode Absorption coefficient and photodiode materials Properties of semiconductor detectors The pin photodiodes Avalanche
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis. SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2
 Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
Lecture 6 Scattering theory Partial Wave Analysis SS2011: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics, Part 2 2 1 The Born approximation for the differential cross section is valid if the interaction
Physics 101. Vectors. Lecture 2. h0r33fy. EMU Physics Department. Assist. Prof. Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN
 Phsics 101 Lecture 2 Vectors ssist. Prof. Dr. li ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Department h0r33f www.aovgun.com Coordinate Sstems qcartesian coordinate sstem qpolar coordinate sstem qfrom Cartesian to Polar coordinate
Phsics 101 Lecture 2 Vectors ssist. Prof. Dr. li ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Department h0r33f www.aovgun.com Coordinate Sstems qcartesian coordinate sstem qpolar coordinate sstem qfrom Cartesian to Polar coordinate
Lab 8 - POLARIZATION
 137 Name Date Partners Lab 8 - POLARIZATION OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate linearly polarized
137 Name Date Partners Lab 8 - POLARIZATION OBJECTIVES To study the general phenomena of electromagnetic wave polarization To investigate linearly polarized microwaves To investigate linearly polarized
Don t Copy This. Michael Faraday 3/1/13. Chapter 25: EM Induction and EM Waves. Key Terms:
 3/1/13 Chapter 25: EM Induction and EM Waves Key Terms: Induced Induced emf current Flux Lenz s Law waves Photons EM Don t Copy This Last chapter we learned that a current can create a magnetic field.
3/1/13 Chapter 25: EM Induction and EM Waves Key Terms: Induced Induced emf current Flux Lenz s Law waves Photons EM Don t Copy This Last chapter we learned that a current can create a magnetic field.
Optics and Optical Design. Chapter 6: Polarization Optics. Lectures 11 13
 Optics and Optical Design Chapter 6: Polarization Optics Lectures 11 13 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Polarization of Light Arbitrary wave vs. paraxial wave One component in x direction y x z Components
Optics and Optical Design Chapter 6: Polarization Optics Lectures 11 13 Cord Arnold / Anne L Huillier Polarization of Light Arbitrary wave vs. paraxial wave One component in x direction y x z Components
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra. Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016
 Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Chapter 4: Polarization of light
 Chapter 4: Polarization of light 1 Preliminaries and definitions B E Plane-wave approximation: E(r,t) ) and B(r,t) are uniform in the plane ^ k We will say that light polarization vector is along E(r,t)
Chapter 4: Polarization of light 1 Preliminaries and definitions B E Plane-wave approximation: E(r,t) ) and B(r,t) are uniform in the plane ^ k We will say that light polarization vector is along E(r,t)
roth t dive = 0 (4.2.3) divh = 0 (4.2.4) Chapter 4 Waves in Unbounded Medium Electromagnetic Sources 4.2 Uniform plane waves in free space
 Chapter 4 Waves in Unbounded Medium 4. lectromagnetic Sources 4. Uniform plane waves in free space Mawell s equation in free space is given b: H rot = (4..) roth = (4..) div = (4..3) divh = (4..4) which
Chapter 4 Waves in Unbounded Medium 4. lectromagnetic Sources 4. Uniform plane waves in free space Mawell s equation in free space is given b: H rot = (4..) roth = (4..) div = (4..3) divh = (4..4) which
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Can be described by means of a classical sinusoidal wave model. Oscillating electric and magnetic field. (Wave model) wavelength,
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Radiation Can be described by means of a classical sinusoidal wave model. Oscillating electric and magnetic field. (Wave model) wavelength,
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back
 Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling
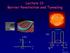 Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling nucleus x U(x) U(x) U 0 E A B C B A 0 L x 0 x Lecture 13, p 1 Today Tunneling of quantum particles Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Nuclear Decay Solar
Lecture 13: Barrier Penetration and Tunneling nucleus x U(x) U(x) U 0 E A B C B A 0 L x 0 x Lecture 13, p 1 Today Tunneling of quantum particles Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Nuclear Decay Solar
