(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
|
|
|
- Vivien Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the direction of the velocity of the particle marked P? IB Questionbank Physics 1
2 2. Light travels from air into glass as shown below. What is the refractive index of glass? A. B. C. D. sin P sin S sin Q sin R sin P sin R sin Q sin S IB Questionbank Physics 2
3 3. Which of the following electromagnetic waves has a frequency greater than that of visible light? A. Ultraviolet B. Radio C. Microwaves D. Infrared 4. A particle oscillates with simple harmonic motion with period T. At time t = 0, the particle has its maximum displacement. Which graph shows the variation with time t of the kinetic energy E k of the particle? IB Questionbank Physics 3
4 5. The graph shows measurements of the height h of sea level at different times t in the Bay of Fundy. Which of the following gives the approximate amplitude and period of the tides? Amplitude Period A. 6.5 m 6 hours B. 13 m 12 hours C. 6.5 m 12 hours D. 13 m 6 hours IB Questionbank Physics 4
5 6. Two waves meet at a point. The waves have a path difference of 4. The phase difference between the waves is A. B. C. π 8 π 4 π 2 rad. rad. rad. D. π rad. 7. A string vibrates with fundamental frequency f. The wavelength of the sound produced in air is λ. Which of the following correctly gives the frequency of vibration of the fourth harmonic of the string and the wavelength of the sound in air? A. Frequency f 2 Wavelength 4 B. 4 f 4λ C. f 2 4λ D. 4 f 4 IB Questionbank Physics 5
6 8. Which of the following is a value of wavelength that is found in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum? A m B m C m D m 9. Two waves meet at a point in space. Which of the following properties always add together? A. Displacement B. Amplitude C. Speed D. Frequency IB Questionbank Physics 6
7 10. The diagram below is a snapshot of wave fronts of circular waves emitted by a point source S at the surface of water. The source vibrates at a frequency f = 10.0 Hz. The speed of the wave front is A cm s 1. B. 1.5 cm s 1. C. 15 cm s 1. D. 30 cm s 1. IB Questionbank Physics 7
8 11. An object at the end of a spring oscillates vertically with simple harmonic motion. The graph shows the variation with time t of the displacement x. The amplitude is x 0 and the period of oscillation is T. Which of the following is the correct expression for the maximum acceleration of the object? A. 2 x 0 T B. 2 2 x 0 T 2 4 C. x 2 0 T 2 4 D. x0 T IB Questionbank Physics 8
9 12. One end of a horizontal string is fixed to a wall. A transverse pulse moves along the string as shown. Which of the following statements are correct for the reflected pulse compared to the forward pulse? I. It moves more slowly. II. III. It has less energy. It is inverted. A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III 13. Monochromatic light travels from air into water. Which of the following describes the changes in wavelength and speed? Wavelength Speed A. increases decreases B. increases increases C. decreases increases D. decreases decreases IB Questionbank Physics 9
10 14. Which of the following graphs shows the variation with displacement x of the speed v of a particle performing simple harmonic motion. 15. A particle performs simple harmonic oscillations. Which of the following quantities will be unaffected by a reduction in the amplitude of oscillations? A. The total energy B. The maximum speed C. The maximum acceleration D. The period IB Questionbank Physics 10
11 16. A mass on the end of a horizontal spring is displaced from its equilibrium position by a distance A and released. Its subsequent oscillations have total energy E and time period T. An identical mass is attached to an identical spring. The maximum displacement is 2A. Assuming this spring obeys Hooke s law, which of the following gives the correct time period and total energy? New time period New energy A. T 4E B. T 2E C. 2 T 4E D. 2 T 2E 17. What is the best estimate for the refractive index of a medium in which light travels at a speed of m s 1? A. 0.9 B. 1.0 C. 1.1 D. 2.7 IB Questionbank Physics 11
12 18. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that are equidistant from point O. The cart is in equilibrium at A. all points between X and Y. B. point O only. C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. 19. During one complete oscillation, the amplitude of a damped harmonic motion changes from 1.5 cm to 0.30 cm. The total energy at the end of the oscillation is E 2 and the total energy at the E 2 beginning of the oscillation is E 1. The ratio is E 1 A B C. 5. D. 25. IB Questionbank Physics 12
13 20. Plane wavefronts are incident on a boundary between two media labelled 1 and 2 in the diagram. The diagram of the wavefronts is drawn to scale. The ratio of the refractive index of medium 2 to that of medium 1 is A B C D IB Questionbank Physics 13
14 21. A wave pulse is travelling to the right along a string. Which of the following best represents the direction of the velocity of the point P? A. B. C. D. IB Questionbank Physics 14
15 22. Diagram 1 represents equally spaced beads on a spring. The beads are 1 cm apart. Diagram 1 A longitudinal wave propagates along the spring. Diagram 2 shows the position of the beads at a particular instant. Diagram 2 Which of the following is the best estimate of the wavelength? A. 2 cm B. 4 cm C. 8 cm D. 16 cm IB Questionbank Physics 15
16 23. Diagram 1 represents equally spaced beads on a spring. The beads are 1 cm apart. Diagram 1 A longitudinal wave propagates along the spring. Diagram 2 shows the position of the beads at a particular instant. Diagram 2 Which of the following is the best estimate of the amplitude? A. 0.4 cm B. 0.8 cm C. 1.6 cm D. 3.2 cm 24. The fundamental (first harmonic) frequency for a particular organ pipe is 330 Hz. The pipe is closed at one end but open at the other. What is the frequency of its second harmonic? A. 110 Hz B. 165 Hz C. 660 Hz D. 990 Hz IB Questionbank Physics 16
17 25. Plane-polarized light is incident normally on a polarizer which is able to rotate in the plane perpendicular to the light as shown below. In diagram 1, the intensity of the incident light is 8 W m 2 and the transmitted intensity of light is 2 W m 2. Diagram 2 shows the polarizer rotated 90 from the orientation in diagram 1. What is the new transmitted intensity? A. 0 W m 2 B. 2 W m 2 C. 6 W m 2 D. 8 W m 3 IB Questionbank Physics 17
18 26. The fundamental (first harmonic) frequency of the note emitted by an organ pipe closed at one end is f. What is the fundamental frequency of the note emitted by an organ pipe of the same length that is open at both ends? A. B. f 4 f 2 C. 2f D. 4f 27. Unpolarized light is shone through two identical polarizers whose axes are parallel. The ratio I I 0 is A. 100 %. B. 50 %. C. 25 %. D. 0 %. IB Questionbank Physics 18
19 28. Which of the following statements is true for a standing wave on a string? A. No energy is transferred along the string. B. The maximum kinetic energy of each segment of the string is proportional to the amplitude of the segment. C. Each segment of the string oscillates with different phase and frequency. D. The amplitude along the string varies with time. 29. The diagram represents a beam of unpolarized light incident on a diamond. The refractive index of the diamond is n. At an angle θ p, the beam reflected from the diamond is plane polarized normal to the page. The angle θ p is A. tan 1 n. B. tan 1 1. n C. sin 1 1. n D. cos 1 1. n IB Questionbank Physics 19
20 30. Two polarizing sheets have planes of polarization that are initially parallel. The incoming light on sheet 1 is unpolarized. The intensity of the light transmitted is I. To reduce the intensity to 2 I, which sheet must be rotated and through what angle? Sheet to be rotated Rotation angle A. 1 only θ = cos B. 2 only θ = cos C. 1 or 2 θ = cos D. 1 or 2 θ = cos Which of the following is a correct comparison between standing waves and travelling waves? Standing waves A. wave amplitude is constant at all points along the wave Travelling waves wave amplitude depends upon the position along the wave B. energy is always transferred energy is not transferred C. the wavelength is twice the distance between consecutive nodes D. phase varies continuously along the wave the wavelength is the distance between consecutive crests phase is constant between consecutive crests IB Questionbank Physics 20
21 32. A tube is filled with water and a vibrating tuning fork is held above its open end. The tap at the base of the tube is opened. As the water runs out, the sound is loudest when the water level is a distance x below the top of the tube. A second loud sound is heard when the water level is a distance y below the top. Which of the following is a correct expression for the wavelength of the sound produced by the tuning fork? A. = y B. = 2x C. = y x D. = 2(y x) IB Questionbank Physics 21
22 33. Unpolarized light of intensity I 0 is incident on a polarizer. The transmitted light is then incident on a second polarizer. The axis of the second polarizer makes an angle of 60 to the axis of the first polarizer. 1 The cosine of 60 is. The intensity of the light transmitted through the second polarizer is 2 A. I 0. I B I C I D IB Questionbank Physics 22
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right.
 1. This question is about simple harmonic oscillations. A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right. Graph 1 shows the variation with time t of the displacement x of a particle P in
1. This question is about simple harmonic oscillations. A longitudinal wave travels through a medium from left to right. Graph 1 shows the variation with time t of the displacement x of a particle P in
Standing waves [49 marks]
![Standing waves [49 marks] Standing waves [49 marks]](/thumbs/92/110837906.jpg) Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
Standing waves [49 marks] 1. The graph shows the variation with time t of the velocity v of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion (SHM). At which velocity does the displacement from the mean position
A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion
 1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
1. Simple harmonic motion and the greenhouse effect (a) A body is displaced from equilibrium. State the two conditions necessary for the body to execute simple harmonic motion. 1. 2. (b) In a simple model
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Homework Book. Wave Properties. Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2. Name: Homeroom: Physics Class:
 Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
EXAM 1. WAVES, OPTICS AND MODERN PHYSICS 15% of the final mark
 EXAM 1 WAVES, OPTICS AND MODERN PHYSICS 15% of the final mark Autumn 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 3 marks. 1. A light beam is deflected by two mirrors, as shown. The incident beam
EXAM 1 WAVES, OPTICS AND MODERN PHYSICS 15% of the final mark Autumn 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 3 marks. 1. A light beam is deflected by two mirrors, as shown. The incident beam
1 f. result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by
 result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
result from periodic disturbance same period (frequency) as source Longitudinal or Transverse Waves Characterized by amplitude (how far do the bits move from their equilibrium positions? Amplitude of MEDIUM)
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. The student is expected to:
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives
1. Data analysis question.
 1. Data analysis question. The photograph below shows a magnified image of a dark central disc surrounded by concentric dark rings. These rings were produced as a result of interference of monochromatic
1. Data analysis question. The photograph below shows a magnified image of a dark central disc surrounded by concentric dark rings. These rings were produced as a result of interference of monochromatic
Physics Common Assessment Unit 5-8 3rd Nine Weeks
 1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam
 G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice exam G r a d e 1 1 P h y s i c s ( 3 0 s ) Final Practice Exam Instructions The final exam will be weighted as follows: Modules 1 6 15 20% Modules
A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth.
 Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
Waves_P2 [152 marks] A beam of coherent monochromatic light from a distant galaxy is used in an optics experiment on Earth. The beam is incident normally on a double slit. The distance between the slits
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion. Chapter 11. Preview. Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Preview Objectives Hooke s Law Sample Problem Simple Harmonic Motion The Simple Pendulum Section 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Objectives Identify the conditions of simple harmonic
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE Physics Department Tutorial: Wave Motion
 JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE Physics Department Tutorial: Wave Motion 1 The same progressive wave is represented by the following graphs. displacement y against time y p y displacement y against position x q
JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE Physics Department Tutorial: Wave Motion 1 The same progressive wave is represented by the following graphs. displacement y against time y p y displacement y against position x q
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
0.4 s 0.8 s 1.5 s. 2.5 s. 2. A beam of light from a ray box spreads out as shown in the diagram and strikes a plane mirror.
 1. ship is fitted with echo-sounding equipment. pulse of sound is sent downwards from the ship at a speed of 1500 m/s. The seabed is 600m below the ship. How long will it take the pulse of sound to return
1. ship is fitted with echo-sounding equipment. pulse of sound is sent downwards from the ship at a speed of 1500 m/s. The seabed is 600m below the ship. How long will it take the pulse of sound to return
Chapter 13. F =!kx. Vibrations and Waves. ! = 2" f = 2" T. Hooke s Law Reviewed. Sinusoidal Oscillation Graphing x vs. t. Phases.
 Chapter 13 Vibrations and Waves Hooke s Law Reviewed F =!k When is positive, F is negative ; When at equilibrium (=0, F = 0 ; When is negative, F is positive ; 1 2 Sinusoidal Oscillation Graphing vs. t
Chapter 13 Vibrations and Waves Hooke s Law Reviewed F =!k When is positive, F is negative ; When at equilibrium (=0, F = 0 ; When is negative, F is positive ; 1 2 Sinusoidal Oscillation Graphing vs. t
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
PHYSICS. Chapter 16 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion
 Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Oscillatory Motion and Wave Motion Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Wave Motion Waves Motion of an Object Attached to a Spring The Pendulum Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Sinusoidal Wave Function
Superposition and Standing Waves
 Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves 1 Types of Mechanical Waves This chapter and the next are about mechanical waves waves that travel within some material called a medium. Waves play an important role in how
17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet.
 17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet. The diagram below shows a magnet M suspended vertically from a spring. When the magnet is in equilibrium its mid-point P coincides with
17 M00/430/H(2) B3. This question is about an oscillating magnet. The diagram below shows a magnet M suspended vertically from a spring. When the magnet is in equilibrium its mid-point P coincides with
glass Calculate the magnitude of the Young modulus for glass. State your answer to (a) in terms of SI fundamental units.
 Q1.The term ultrasound refers to vibrations in a material that occur at frequencies too high to be detected by a human ear. When ultrasound waves move through a solid, both longitudinal and transverse
Q1.The term ultrasound refers to vibrations in a material that occur at frequencies too high to be detected by a human ear. When ultrasound waves move through a solid, both longitudinal and transverse
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves. The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position.
 Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
Chap 11. Vibration and Waves Sec. 11.1 - Simple Harmonic Motion The impressed force on an object is proportional to its displacement from it equilibrium position. F x This restoring force opposes the change
f 1/ T T 1/ f Formulas Fs kx m T s 2 k l T p 2 g v f
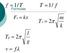 f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
f 1/T Formulas T 1/ f Fs kx Ts 2 m k Tp 2 l g v f What do the following all have in common? Swing, pendulum, vibrating string They all exhibit forms of periodic motion. Periodic Motion: When a vibration
Schedule for the remainder of class
 Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Downloaded from
 Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Chapter 15 (Waves) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. Water waves produced by a motorboat sailing in water are (a) neither longitudinal nor transverse (b) both longitudinal and transverse
Chapter 11. Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves Driven Harmonic Motion and Resonance RESONANCE Resonance is the condition in which a time-dependent force can transmit large amounts of energy to an oscillating object,
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves Driven Harmonic Motion and Resonance RESONANCE Resonance is the condition in which a time-dependent force can transmit large amounts of energy to an oscillating object,
KEY SOLUTION. 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME M 1 M 1. Fig. 1a Fig. 1b Fig. 1c
 KEY SOLUTION 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME Use g = 10 m/s 2 in your calculations. Wherever appropriate answers must include units. 1. Fig. 1a shows a spring, 20 cm long. The spring gets compressed
KEY SOLUTION 05/07/01 PHYSICS 223 Exam #1 NAME Use g = 10 m/s 2 in your calculations. Wherever appropriate answers must include units. 1. Fig. 1a shows a spring, 20 cm long. The spring gets compressed
A 0.2 m s -1. B 10 m s -1. C 20 m s -1. D 40 m s -1
 Q1. Two points on a progressive wave are one-eighth of a wavelength apart. The distance between them is 0.5 m, and the frequency of the oscillation is 10 Hz. What is the minimum speed of the wave? 0.2
Q1. Two points on a progressive wave are one-eighth of a wavelength apart. The distance between them is 0.5 m, and the frequency of the oscillation is 10 Hz. What is the minimum speed of the wave? 0.2
Waves Review Checklist Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one
 5.1.1 Oscillating Systems Waves Review Checklist 5.1.2 Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one Four pendulums are built as shown
5.1.1 Oscillating Systems Waves Review Checklist 5.1.2 Pulses 5.1.1A Explain the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the factors involved in building one Four pendulums are built as shown
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Larbert High School. Quanta and Waves. Homework Exercises ADVANCED HIGHER PHYSICS
 Larbert High School ADVANCED HIGHER PHYSICS Quanta and Waves Homework Exercises 3.1 3.6 3.1 Intro to Quantum Theory HW 1. (a) Explain what is meant by term black body. (1) (b) State two observations that
Larbert High School ADVANCED HIGHER PHYSICS Quanta and Waves Homework Exercises 3.1 3.6 3.1 Intro to Quantum Theory HW 1. (a) Explain what is meant by term black body. (1) (b) State two observations that
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
AP Physics 1 Waves and Simple Harmonic Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) An object is attached to a vertical
CHAPTERS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS
 CET -IPUC: PHYSICS Unit VI : WAVES and SOUND CHAPTERS OSCILLATIONS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS Particle acceleration: a = Aω 2 sinωt= ω 2 y Maximum acceleration: a max = A ω 2 The
CET -IPUC: PHYSICS Unit VI : WAVES and SOUND CHAPTERS OSCILLATIONS WAVES SOUND STATIONARY WAVES ACOUSTICSOF BUILDINGS Particle acceleration: a = Aω 2 sinωt= ω 2 y Maximum acceleration: a max = A ω 2 The
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Reading Quiz 16.05 f = c Slide 16-2 Reading Quiz 16.06 Slide 16-3 Reading Quiz 16.07 Heavier portion looks like a fixed end, pulse is inverted on reflection.
CHAPTER 11 TEST REVIEW
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM CHAPTER TEST
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
 Wave Motion Wave and Wave motion Wave is a carrier of energy Wave is a form of disturbance which travels through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about
Wave Motion Wave and Wave motion Wave is a carrier of energy Wave is a form of disturbance which travels through a material medium due to the repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium about
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar
 Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Lorik educatinal academy vidya nagar ========================================================== PHYSICS-Wave Motion & Sound Assignment. A parachutist jumps from the top of a very high tower with a siren
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
Outline. Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves
 Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Outline Hook s law. Mass spring system Simple harmonic motion Travelling waves Waves in string Sound waves Hooke s Law Force is directly proportional to the displacement of the object from the equilibrium
Waves Encountering Barriers
 Waves Encountering Barriers Reflection and Refraction: When a wave is incident on a boundary that separates two regions of different wave speed, part of the wave is reflected and part is transmitted. Figure
Waves Encountering Barriers Reflection and Refraction: When a wave is incident on a boundary that separates two regions of different wave speed, part of the wave is reflected and part is transmitted. Figure
16 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES
 Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
42 TRAVELING WAVES (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G)
 42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
Physics General Physics. Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Oscillating Motion We have studied linear motion objects moving in straight lines at either constant
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Oscillating Motion We have studied linear motion objects moving in straight lines at either constant
Baccalieu Collegiate. Physics Course Outline
 Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
Baccalieu Collegiate Physics 2204 Course Outline Course Content: Unit 1: Kinematics Motion is a common theme in our everyday lives: birds fly, babies crawl, and we, ourselves, seem to be in a constant
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 117.3 Physics for the Life Sciences FINAL EXAMINATION April 12, 2016 Time: 3 hours NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 117.3 Physics for the Life Sciences FINAL EXAMINATION April 12, 2016 Time: 3 hours NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print
Lecture 17. Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves.
 Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille. Chapter Thirteen. Vibrations and Waves
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
AP Physics Problems Simple Harmonic Motion, Mechanical Waves and Sound 1. 1977-5 (Mechanical Waves/Sound) Two loudspeakers, S 1 and S 2 a distance d apart as shown in the diagram below left, vibrate in
Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension
 Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
Lecture Outline Chapter 16 Waves in One Dimension Slide 16-1 Chapter 16: Waves in One Dimension Chapter Goal: To study the kinematic and dynamics of wave motion, i.e., the transport of energy through a
AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions - Chapter 9
 1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
1 If an object of mass m attached to a light spring is replaced by one of mass 9m, the frequency of the vibrating system changes by what multiplicative factor? a 1/9 b 1/3 c 3 d 9 e 6 2 A mass of 0.40
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Physics General Physics. Lecture 25 Waves. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is:
 1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
Chapter 15. Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
Chapter 15 Mechanical Waves A wave is any disturbance from an equilibrium condition, which travels or propagates with time from one region of space to another. A harmonic wave is a periodic wave in which
[2] [2] Fig. 4.1
![[2] [2] Fig. 4.1 [2] [2] Fig. 4.1](/thumbs/79/80000819.jpg) 1 (a) (i) Explain what is meant by a progressive wave.... [2] (ii) State two differences between a progressive and a stationary wave. 1... 2... [2] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows, at time t = 0, the shape of a section
1 (a) (i) Explain what is meant by a progressive wave.... [2] (ii) State two differences between a progressive and a stationary wave. 1... 2... [2] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows, at time t = 0, the shape of a section
1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero?
 1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero? I. Any motion in a straight line II. Simple harmonic motion III. Any motion in a circle I only II only III that
1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero? I. Any motion in a straight line II. Simple harmonic motion III. Any motion in a circle I only II only III that
is a What you Hear The Pressure Wave sets the Ear Drum into Vibration.
 is a What you Hear The ear converts sound energy to mechanical energy to a nerve impulse which is transmitted to the brain. The Pressure Wave sets the Ear Drum into Vibration. electroencephalogram v S
is a What you Hear The ear converts sound energy to mechanical energy to a nerve impulse which is transmitted to the brain. The Pressure Wave sets the Ear Drum into Vibration. electroencephalogram v S
Physics 1C. Lecture 12C
 Physics 1C Lecture 12C Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of simple harmonic motion. Making a quick force diagram of the situation, we find:! The tension in the string cancels out with
Physics 1C Lecture 12C Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of simple harmonic motion. Making a quick force diagram of the situation, we find:! The tension in the string cancels out with
Chapter 16 Waves. Types of waves Mechanical waves. Electromagnetic waves. Matter waves
 Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 16 Waves Types of waves Mechanical waves exist only within a material medium. e.g. water waves, sound waves, etc. Electromagnetic waves require no material medium to exist. e.g. light, radio, microwaves,
Chapter 16: Oscillations
 Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Chapter 16: Oscillations Brent Royuk Phys-111 Concordia University Periodic Motion Periodic Motion is any motion that repeats itself. The Period (T) is the time it takes for one complete cycle of motion.
Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz. FINAL EXAM December 10, :00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS
 Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
Seat # Physics P201 D. Baxter/R. Heinz FINAL EXAM December 10, 2001 8:00 10:00 AM INSTRUCTIONS 1. Sit in SEAT # given above. 2. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. 3. Print your name (last
Chapter 16: Oscillatory Motion and Waves. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
 Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
Chapter 6: Oscillatory Motion and Waves Hooke s Law (revisited) F = - k x Tthe elastic potential energy of a stretched or compressed spring is PE elastic = kx / Spring-block Note: To consider the potential
UNIT 1 MODULE 2: OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES GENERAL OBJECTIVES EXPLANATORY NOTES SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES. On completion of this Module, students should:
 MODULE 2: OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand the different types of oscillatory motion; 2. appreciate the properties common to all 3.
MODULE 2: OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. understand the different types of oscillatory motion; 2. appreciate the properties common to all 3.
Waves Final Review. Name: Date: 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented?
 Name: Date: Waves Final Review 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented? A. Displacement λ a Distance along wave B. Displacement λ
Name: Date: Waves Final Review 1. On which one of the following graphs is the wavelength λ and the amplitude a of a wave correctly represented? A. Displacement λ a Distance along wave B. Displacement λ
Indicate whether each statement is true or false by circling your answer. No explanation for your choice is required. Each answer is worth 3 points.
 Physics 5B FINAL EXAM Winter 2009 PART I (15 points): True/False Indicate whether each statement is true or false by circling your answer. No explanation for your choice is required. Each answer is worth
Physics 5B FINAL EXAM Winter 2009 PART I (15 points): True/False Indicate whether each statement is true or false by circling your answer. No explanation for your choice is required. Each answer is worth
Chapter 13, Vibrations and Waves. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only m. What is the spring constant of the spring?
 CHAPTER 13 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only 0.010 m. What is the spring constant of the spring? a. 125 000 N/m b. 15 000 N/m c. 15 N/m d. 1.5 N/m 2. A 0.20-kg object is attached
CHAPTER 13 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to compress it only 0.010 m. What is the spring constant of the spring? a. 125 000 N/m b. 15 000 N/m c. 15 N/m d. 1.5 N/m 2. A 0.20-kg object is attached
Exam 3 Review. Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations A stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations.
 Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
PW W A V E S PW CONCEPTS C C Equation of a Travelling Wave The equation of a wave traveling along the positive x-ax given by y = f(x vt) If the wave travelling along the negative x-ax, the wave funcion
1. a) A flag waving in the breeze flaps once each s. What is the period and frequency of the flapping flag?
 PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
AS PHYSICS (7407/2) Paper 2. Specimen 2014 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes SPECIMEN MATERIAL
 SPEIMEN MTERIL S PHYSIS (7407/2) Paper 2 Specimen 2014 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a ruler a calculator a data and formulae booklet. Instructions
SPEIMEN MTERIL S PHYSIS (7407/2) Paper 2 Specimen 2014 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a ruler a calculator a data and formulae booklet. Instructions
1. Types of Waves. There are three main types of waves:
 Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
Chapter 16 WAVES I 1. Types of Waves There are three main types of waves: https://youtu.be/kvc7obkzq9u?t=3m49s 1. Mechanical waves: These are the most familiar waves. Examples include water waves, sound
NARAYANA JUNIOR COLLEGE
 SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
SR IIT ALL STREAMS ADV MODEL DPT-6 Date: 18/04/2016 One (or) More Than One Answer Type: PHYSICS 31. A particle is executing SHM between points -X m and X m, as shown in figure-i. The velocity V(t) of the
α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) κ I ω = g L L g T = 2π mgh rot com I rot
 α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) ω = κ I ω = g L T = 2π L g ω = mgh rot com I rot T = 2π I rot mgh rot com Chapter 16: Waves Mechanical Waves Waves and particles Vibration = waves - Sound - medium vibrates - Surface ocean
α(t) = ω 2 θ (t) ω = κ I ω = g L T = 2π L g ω = mgh rot com I rot T = 2π I rot mgh rot com Chapter 16: Waves Mechanical Waves Waves and particles Vibration = waves - Sound - medium vibrates - Surface ocean
Chapter 34. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves Waves If we wish to talk about electromagnetism or light we must first understand wave motion. If you drop a rock into the water small ripples are seen on the surface of
Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves Waves If we wish to talk about electromagnetism or light we must first understand wave motion. If you drop a rock into the water small ripples are seen on the surface of
1. C [1] 2. D [1] 3. D [1] 4. A [1] 5. (a) (i) the amplitude is constant; 1
![1. C [1] 2. D [1] 3. D [1] 4. A [1] 5. (a) (i) the amplitude is constant; 1 1. C [1] 2. D [1] 3. D [1] 4. A [1] 5. (a) (i) the amplitude is constant; 1](/thumbs/94/118245664.jpg) 1. C. D 3. D 4. A 5. (a) (i) the amplitude is constant 1 period is 0.0s a max = π = = 19.7 0 m s x0 31.4.0 10 T Award [] for correct bald answer and ignore any negative signs in answer. (iii) displacement
1. C. D 3. D 4. A 5. (a) (i) the amplitude is constant 1 period is 0.0s a max = π = = 19.7 0 m s x0 31.4.0 10 T Award [] for correct bald answer and ignore any negative signs in answer. (iii) displacement
Chapter 16 Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
Chapter 6 Mechanical Waves A wave is a disturbance that travels, or propagates, without the transport of matter. Examples: sound/ultrasonic wave, EM waves, and earthquake wave. Mechanical waves, such as
What is a Wave. Why are Waves Important? Power PHYSICS 220. Lecture 19. Waves
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 19 Waves What is a Wave A wave is a disturbance that travels away from its source and carries energy. A wave can transmit energy from one point to another without transporting any matter
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 19 Waves What is a Wave A wave is a disturbance that travels away from its source and carries energy. A wave can transmit energy from one point to another without transporting any matter
Physics Assessment Unit AS 2
 Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY General Certificate of Education January 2011 Physics Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Module 2: Waves, Photons and Medical Physics AY121 [AY121] MONDAY
Centre Number 71 Candidate Number ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY General Certificate of Education January 2011 Physics Assessment Unit AS 2 assessing Module 2: Waves, Photons and Medical Physics AY121 [AY121] MONDAY
AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
Name: Class: _ Date: _ AP physics B - Webreview ch 13 Waves Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A large spring requires a force of 150 N to
