Electromagnetic wave energy & polarization
|
|
|
- Georgiana Davis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phys 0 Lecture 6 Electromagnetic wave energy & polarization
2 Today we will... Learn about properties p of electromagnetic waves Energy density & intensity Polarization linear, circular, unpolarized Apply those concepts Linear polarizers Optical activity Circular dichroism Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide
3 E & B field energy density There is energy stored in an E & B field B d E A Parallel l plate capacitor Recall Lect. 6 Solenoid U ε A Ed ε E Ad d 0 = CV ( ) = = 0 ( ) C 0 Volume containing E field It is convenient to define energy density = energy per volume [J/m 3 ] ue = ε0e ub = B These expressions are correct μ0 for any E & B field in a vacuum Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 3
4 EM wave energy There is energy stored in an EM wave in oscillating E & B fields E 0 B(t) B 0 E(t) Since E and B oscillate, we measure the average energy density ue = ε0 E ub = ε0e rms Erms = = 0 B = B rms Brms = B0 μ0 μ0 u = ε E + B = ε0 E rms = tot 0 + rms μ rms 0 B rms μ 0 E E & B field amplitudes Recall that Et () = cbt () c = ε μ 0 0 Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 4
5 Calculation: EM power A light bulb emits an average 60 W of power. Calculate E rms & B rms at a distance r = m from bulb. (Assume all electric power goes into EM wave) r = m By energy conservation, power emitted = power through spherical surface at r = m What is rate of EM energy flow through surface? Δ U u 4 tot πr cδt P = = Δ t Δt cδt u tot 0 rms = ε E so Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 5
6 ACT: EM wave E field E P is the rms E field at a distance r = m from the 60W light bulb. r = m E P r = 4 m? What is the rms E field at a distance r = 4m? A. 4E P B. E P C. E P / D. E P /4 Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 6
7 EM wave intensity The same power from point source of light flows through surfaces at larger distances, but spread over a larger surface area A. g, p g It is useful to define intensity (I or S): I P = S Units: W/m A Since P = u Ac tot I = S = utot c Intensity corresponds to brightness of light (light is dimmer the further from a point source) I decreases as /r^ Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 7
8 CheckPoint..7 Longitudinal waves: oscillations are to direction or propagation Transverse waves: oscillations are to direction of propagation λ DEMO λ Ex: Sound Ex: Light Radio waves X rays Microwaves Water waves The wave Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 8
9 Polarization EM waves are transverse and have polarization by convention, the direction of the E field oscillation z Linear x z Circular E B E z y x Ex: Vertical polarization z y x x B Ex: Left circular polarization Unpolarized direction is random For convenience we will stop showing the B field Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 9
10 Linear polarizers Linear polarizers consist of metal lines that absorb E field. Transmission axis () is defined in direction that E field passes E E : no light passes E E : light passes What happens for other angles between polarization and? Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 0
11 E inc Law of Malus Given angle θ between and polarization of incident EM wave: θ E inc E trans θ Component of E field to axis is absorbed: E inc E abs Etrans = Einc cosθ Since I = u c E tot I trans I inc θ E trans I = I cos θ trans inc θ Light emerges with polarization to axis Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide
12 ACT: polarizer A vertically polarized EM wave passes through a linear polarizer with at 45 E inc What is the direction of the B field after the polarizer? A. B. C. D. What is the magnitude? Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide
13 Calculation: unpolarized light Unpolarized light is incident on a linear polarizer. What is the transmitted intensity? E inc E trans Unpolarized light has an equal mixture of all possible θ s I trans I inc trans inc cos g I I θ I inc / Itrans = θ Light emerges with polarization to axis = average over all θ: I inc Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 3
14 ACT: CheckPoint. Unpolarized light passes through a linear polarizer with a vertical. I 0 What is the intensity of light when it emerges? A. zero B. / what it was before C. /4 what it was before D. /3 what it was before Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 4
15 ACT: CheckPoint. Now the light that emerged from the previous polarizer passes through a second linear polarizer with a horizontal. I 0 What isthe intensity of light when it emerges? A. zero B. / what it was before C. /4 what it was before D. /3 what it was before Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 5
16 ACT: 3 polarizers Now suppose we add a third polarizer between the two outer polarizers. The polarizer is tilted from vertical. 3 I 0 What is the intensity of the light that emerges? A. zero, same as before B. more than what htit was before bf DEMO C. need more information Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 6
17 Calculation: 3 polarizers 3 I 0 Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 7
18 Chirality & optical activity Many organic molecules are chiral they have handedness L alanine D alanine (unnatural enantiometer) Chiral molecules rotate linearly polarized light optical activity DEMO Dextrorotary CW rotation Levorotary CCW rotation Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 8
19 Circular dichroism Chiral molecules also absorb left vs. right circularly polarized light differently Circular dichroism (CD) measures difference in absorption Tool to distinguish chiral features in biomolecules CD spectra α helix (right handed helix) Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 9
20 ACT: Law of Malus A B I 0 I 0 Compare the light emerging from the two polarizers in A and B: A. I A B A B A B > I B. I = I C. I < I Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide 0
21 Summary of today s lecture Electromagnetic waves Carry energy in E and B fields energy density & intensity Are transverse & polarized linear, circular, unpolarized Applications Linear polarizers Law of Malus Optical activity Circular dichroism Phys. 0, Lecture 6, Slide
Electromagnetic Waves
 Physics 102: Lecture 15 Electromagnetic Waves Energy & Polarization Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 1 Checkpoint 1.1, 1.2 y E x loop in xy plane loop in xz plane A B C Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 2 Propagation
Physics 102: Lecture 15 Electromagnetic Waves Energy & Polarization Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 1 Checkpoint 1.1, 1.2 y E x loop in xy plane loop in xz plane A B C Physics 102: Lecture 15, Slide 2 Propagation
Electromagnetic Waves. Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
PH 222-3A Spring 2007 Electromagnetic Waves Lecture 22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
EM Waves. From previous Lecture. This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization. Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves
 EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
EM Waves This Lecture More on EM waves EM spectrum Polarization From previous Lecture Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves 1 Reminders on waves Traveling waves on a string along x obey the
Phys 102 Lecture 12 Currents & magnetic fields
 Phys 102 Lecture 12 Currents & magnetic fields 1 Today we will... Learn how magnetic fields are created by currents Use specific examples Long straight wire Current loop Solenoid Apply these concepts Electromagnets
Phys 102 Lecture 12 Currents & magnetic fields 1 Today we will... Learn how magnetic fields are created by currents Use specific examples Long straight wire Current loop Solenoid Apply these concepts Electromagnets
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost entirely on the physics of electromagnetic waves. The connection between electric and magnetic fields to produce light is own of
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
LECTURE 11 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES & POLARIZATION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 11 2 25.5 Electromagnetic waves Induced fields Properties of electromagnetic waves Polarization Energy of electromagnetic
Chapter 34. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves The Goal of the Entire Course Maxwell s Equations: Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell 1831 1879 Scottish theoretical physicist Developed the electromagnetic theory
Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves The Goal of the Entire Course Maxwell s Equations: Maxwell s Equations James Clerk Maxwell 1831 1879 Scottish theoretical physicist Developed the electromagnetic theory
E The oscillating E-field defines the polarization of the wave. B
 This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences and explain your reasoning. A. Describing
This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences and explain your reasoning. A. Describing
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods
 Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
Phys 102 Lecture 3 The Electric field
 Phys 102 Lecture 3 The Electric field 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric field Apply the superposition principle Ex: Dipole, line of charges, plane of charges Represent the E field using electric
Phys 102 Lecture 3 The Electric field 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric field Apply the superposition principle Ex: Dipole, line of charges, plane of charges Represent the E field using electric
PH 222-2C Fall Electromagnetic Waves Lectures Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Electromagnetic Waves Lectures 21-22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
PH 222-2C Fall 2012 Electromagnetic Waves Lectures 21-22 Chapter 33 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 33 Electromagnetic Waves Today s information age is based almost
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back
 Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Lab #13: Polarization
 Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Lab #13: Polarization Introduction In this experiment we will investigate various properties associated with polarized light. We will study both its generation and application. Real world applications
Phys 102 Lecture 3 The Electric field
 Phys 102 Lecture 3 The Electric field 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric field Apply the superposition principle Ex: Dipole, line of charges, plane of charges Represent the E field using electric
Phys 102 Lecture 3 The Electric field 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric field Apply the superposition principle Ex: Dipole, line of charges, plane of charges Represent the E field using electric
Revision checklist. Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it! Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it!
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency,
C. Incorrect! The velocity of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum is the same, 3.14 x 10 8 m/s.
 AP Physics - Problem Drill 21: Physical Optics 1. Which of these statements is incorrect? Question 01 (A) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (B) An electromagnetic wave is a
AP Physics - Problem Drill 21: Physical Optics 1. Which of these statements is incorrect? Question 01 (A) Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (B) An electromagnetic wave is a
4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy
 4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy The optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) and the circular dichroism (CD) are special variations of absorption spectroscopy in the UV and VIS region of the spectrum. The
4. Circular Dichroism - Spectroscopy The optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) and the circular dichroism (CD) are special variations of absorption spectroscopy in the UV and VIS region of the spectrum. The
Physics 214 Course Overview
 Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Physics 214 Course Overview Lecturer: Mike Kagan Course topics Electromagnetic waves Optics Thin lenses Interference Diffraction Relativity Photons Matter waves Black Holes EM waves Intensity Polarization
Lecture 34: MON 13 APR Ch ,5
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Lecture 34: MON 13 APR Ch.33.1 3,5 3,5 7: E&M Waves MT03 Avg: 65/100 Q1/P3 K. Schafer Office hours: MW 1:30-2:30 pm 222B Nicholson P1/Q2 J.
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) Lecture 34: MON 13 APR Ch.33.1 3,5 3,5 7: E&M Waves MT03 Avg: 65/100 Q1/P3 K. Schafer Office hours: MW 1:30-2:30 pm 222B Nicholson P1/Q2 J.
Chapter 34. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves Waves If we wish to talk about electromagnetism or light we must first understand wave motion. If you drop a rock into the water small ripples are seen on the surface of
Chapter 34 Electromagnetic Waves Waves If we wish to talk about electromagnetism or light we must first understand wave motion. If you drop a rock into the water small ripples are seen on the surface of
Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction
 Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction Lecture aims to explain: 1. Light as a transverse electro-magnetic wave 2. Importance of polarisation of light 3. Linearly polarised light 4. Natural light
Lecture 4: Polarisation of light, introduction Lecture aims to explain: 1. Light as a transverse electro-magnetic wave 2. Importance of polarisation of light 3. Linearly polarised light 4. Natural light
Revision checklist SP4 5. SP4 Waves. SP4a Describing waves. SP4b Wave speeds. SP4c Refraction
 SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
SP4 Waves SP4a Describing waves Recall that waves transfer energy and information but do not transfer matter. Describe waves using the terms frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period and velocity. Describe
Physics 201. Professor P. Q. Hung. 311B, Physics Building. Physics 201 p. 1/3
 Physics 201 p. 1/3 Physics 201 Professor P. Q. Hung 311B, Physics Building Physics 201 p. 2/3 What are electromagnetic waves? Electromagnetic waves consist of electric fields and magnetic fields which
Physics 201 p. 1/3 Physics 201 Professor P. Q. Hung 311B, Physics Building Physics 201 p. 2/3 What are electromagnetic waves? Electromagnetic waves consist of electric fields and magnetic fields which
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5. What is light? What is a wave? Radiation carries information
 Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Chapter 1 - The Nature of Light
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing only in wavelength, frequency or energy. Electromagnetic radiation comes in many forms, differing
AC Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
 AC Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves Physics 102 Lecture 5 7 March 2002 MIDTERM Wednesday, March 13, 7:30-9:00 pm, this room Material: through next week AC circuits Next week: no lecture, no labs, no
AC Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves Physics 102 Lecture 5 7 March 2002 MIDTERM Wednesday, March 13, 7:30-9:00 pm, this room Material: through next week AC circuits Next week: no lecture, no labs, no
Lab 8: L-6, Polarization Lab Worksheet
 Lab 8: L-6, Polarization Lab Worksheet Name This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences
Lab 8: L-6, Polarization Lab Worksheet Name This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences
UNIT 102-6: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND POLARIZATION Approximate Time Three 100-minute Sessions
 Name St.No. - Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 102-6: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND POLARIZATION Approximate Time Three 100-minute Sessions Hey diddle diddle, what kind of riddle Is this nature of light? Sometimes
Name St.No. - Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 102-6: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND POLARIZATION Approximate Time Three 100-minute Sessions Hey diddle diddle, what kind of riddle Is this nature of light? Sometimes
Topic 4: Waves 4.3 Wave characteristics
 Guidance: Students will be expected to calculate the resultant of two waves or pulses both graphically and algebraically Methods of polarization will be restricted to the use of polarizing filters and
Guidance: Students will be expected to calculate the resultant of two waves or pulses both graphically and algebraically Methods of polarization will be restricted to the use of polarizing filters and
Polarization. Polarization. Physics Waves & Oscillations 4/3/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones. Two problems to be considered today:
 4/3/26 Physics 422 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 34 Polarization of Light Spring 26 Semester Matthew Jones Polarization (,)= cos (,)= cos + Unpolarizedlight: Random,, Linear polarization: =,± Circular polarization:
4/3/26 Physics 422 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 34 Polarization of Light Spring 26 Semester Matthew Jones Polarization (,)= cos (,)= cos + Unpolarizedlight: Random,, Linear polarization: =,± Circular polarization:
PHYS 270 SUPPL. #9 DENNIS PAPADOPOULOS FEBRUARY 24, 2011
 PHYS 270 SUPPL. #9 DENNIS PAPADOPOULOS FEBRUARY 24, 2011 R If it is completely absorbed P R =I/c 1 5 solve 5.1 F = ma P R = I /c F R = P R A = IA /c = ma (I /c)a = ma A = mac /I = (3x108 m /s)x(10 8
PHYS 270 SUPPL. #9 DENNIS PAPADOPOULOS FEBRUARY 24, 2011 R If it is completely absorbed P R =I/c 1 5 solve 5.1 F = ma P R = I /c F R = P R A = IA /c = ma (I /c)a = ma A = mac /I = (3x108 m /s)x(10 8
Electromagnetic Waves
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 23 Electromagnetic Waves Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Electromagnetic Theory Theoretical understanding of electricity and magnetism
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 23 Electromagnetic Waves Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Electromagnetic Theory Theoretical understanding of electricity and magnetism
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 25 Propagation of Light Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Midterm Exam: Date: Wednesday, March 6 th Time: 8:00 10:00 pm Room: PHYS 203 Material: French, chapters
Circular Dichroism & Optical Rotatory Dispersion. Proteins (KCsa) Polysaccharides (agarose) DNA CHEM 305. Many biomolecules are α-helical!
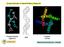 Circular Dichroism & Optical Rotatory Dispersion Polysaccharides (agarose) DNA Proteins (KCsa) Many biomolecules are α-helical! How can we measure the amount and changes in amount of helical structure
Circular Dichroism & Optical Rotatory Dispersion Polysaccharides (agarose) DNA Proteins (KCsa) Many biomolecules are α-helical! How can we measure the amount and changes in amount of helical structure
LECTURE 23: LIGHT. Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle
 LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
Experiment 8. Fresnel Coefficients. 8.1 Introduction. References
 Experiment 8 Fresnel Coefficients References Optics by Eugene Hecht, Chapter 4 Introduction to Modern Optics by Grant Fowles, Chapter 2 Principles of Optics by Max Born and Emil Wolf, Chapter 1 Optical
Experiment 8 Fresnel Coefficients References Optics by Eugene Hecht, Chapter 4 Introduction to Modern Optics by Grant Fowles, Chapter 2 Principles of Optics by Max Born and Emil Wolf, Chapter 1 Optical
Light Waves and Polarization
 Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Light Waves and Polarization Xavier Fernando Ryerson Communications Lab http://www.ee.ryerson.ca/~fernando The Nature of Light There are three theories explain the nature of light: Quantum Theory Light
Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006
 Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must be placed in
Name: Student ID: Section #: Physics 208 Exam 3 Nov. 28, 2006 Print your name and section clearly above. If you do not know your section number, write your TA s name. Your final answer must be placed in
Circular Motion & Oscillations
 A Physics Revision Page 1 of 8 Circular Motion & Oscillations Angular speed, ω = Δθ = πf (assuming angle is a complete revolution, in radians) Δt mv Centripetal Force, F = r Simple Harmonic Motion is a
A Physics Revision Page 1 of 8 Circular Motion & Oscillations Angular speed, ω = Δθ = πf (assuming angle is a complete revolution, in radians) Δt mv Centripetal Force, F = r Simple Harmonic Motion is a
Polarizers and Retarders
 Phys 531 Lecture 20 11 November 2004 Polarizers and Retarders Last time, discussed basics of polarization Linear, circular, elliptical states Describe by polarization vector ĵ Today: Describe elements
Phys 531 Lecture 20 11 November 2004 Polarizers and Retarders Last time, discussed basics of polarization Linear, circular, elliptical states Describe by polarization vector ĵ Today: Describe elements
Exam 3 Solutions. The induced EMF (magnitude) is given by Faraday s Law d dt dt The current is given by
 PHY049 Spring 008 Prof. Darin Acosta Prof. Selman Hershfield April 9, 008. A metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity of 60 cm/s [or 90 cm/s] along two parallel metal rails, which are connected
PHY049 Spring 008 Prof. Darin Acosta Prof. Selman Hershfield April 9, 008. A metal rod is forced to move with constant velocity of 60 cm/s [or 90 cm/s] along two parallel metal rails, which are connected
16. More About Polarization
 16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
16. More About Polarization Polarization control Wave plates Circular polarizers Reflection & polarization Scattering & polarization Birefringent materials have more than one refractive index A special
Physics 102: Lecture 20 Interference. Physics 102: Lecture 20, Slide 1
 Physics 102: Lecture 20 Interference Physics 102: Lecture 20, Slide 1 Phys 102 recent lectures Light as a wave Lecture 14 EM waves Lecture 15 Polarization Lecture 20 & 21 Interference & diffraction Light
Physics 102: Lecture 20 Interference Physics 102: Lecture 20, Slide 1 Phys 102 recent lectures Light as a wave Lecture 14 EM waves Lecture 15 Polarization Lecture 20 & 21 Interference & diffraction Light
LECTURE 23: LIGHT. Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle
 LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
LECTURE 23: LIGHT Propagation of Light Reflection & Refraction Internal Reflection Propagation of Light Huygen s Principle Each point on a primary wavefront serves as the source of spherical secondary
Motional EMF & Lenz law
 Phys 102 Lecture 13 Motional EMF & Lenz law 1 Physics 102 recently Basic principles of magnetism Lecture 10 magnetic fields & forces Lecture 11 magnetic dipoles & current loops Lecture 12 currents & magneticfields
Phys 102 Lecture 13 Motional EMF & Lenz law 1 Physics 102 recently Basic principles of magnetism Lecture 10 magnetic fields & forces Lecture 11 magnetic dipoles & current loops Lecture 12 currents & magneticfields
What is a Wave. Why are Waves Important? Power PHYSICS 220. Lecture 19. Waves
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 19 Waves What is a Wave A wave is a disturbance that travels away from its source and carries energy. A wave can transmit energy from one point to another without transporting any matter
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 19 Waves What is a Wave A wave is a disturbance that travels away from its source and carries energy. A wave can transmit energy from one point to another without transporting any matter
Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization
 Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 10/31/2017 1 Agenda Poynting Theory o Poynting Vector o Time average
Poynting Theory & Wave Polarization Prepared By Dr. Eng. Sherif Hekal Assistant Professor Electronics and Communications Engineering 10/31/2017 1 Agenda Poynting Theory o Poynting Vector o Time average
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation
 The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
LC circuit: Energy stored. This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters
 Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 559
 Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Chapter 33: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES 1 Select the correct statement: A ultraviolet light has a longer wavelength than infrared B blue light has a higher frequency than x rays C radio waves have higher frequency
Polarization of light
 Laboratory#8 Phys4480/5480 Dr. Cristian Bahrim Polarization of light Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave (EM) which travels due to an electric field and a magnetic field oscillating in phase and
Laboratory#8 Phys4480/5480 Dr. Cristian Bahrim Polarization of light Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave (EM) which travels due to an electric field and a magnetic field oscillating in phase and
Dispersion. f (increasing frequency)
 Dispersion The index of refraction n is usually a property of the medium but equally important, it also varies with the frequency f of light dispersion. n typically increases with increasing f. f (increasing
Dispersion The index of refraction n is usually a property of the medium but equally important, it also varies with the frequency f of light dispersion. n typically increases with increasing f. f (increasing
POLARISATION. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion.
 POLARISATION Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion. If the E field
POLARISATION Light is a transverse electromagnetic wave. We have not really discussed the direction of the Electric field other that that it is perpendicular to the direction of motion. If the E field
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017
 Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
Electricity & Magnetism Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Department Exam December 4, 2017 1. a. Find the capacitance of a spherical capacitor with inner radius l i and outer radius l 0 filled with dielectric
APPLIED OPTICS POLARIZATION
 A. La Rosa Lecture Notes APPLIED OPTICS POLARIZATION Linearly-polarized light Description of linearly polarized light (using Real variables) Alternative description of linearly polarized light using phasors
A. La Rosa Lecture Notes APPLIED OPTICS POLARIZATION Linearly-polarized light Description of linearly polarized light (using Real variables) Alternative description of linearly polarized light using phasors
Phys 2310 Mon. Oct. 30, 2017 Today s Topics. Begin Modern Optics Ch. 2: The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time
 Phys 3 Mon. Oct. 3, 7 Today s Topics Begin Modern Optics Ch. : The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time By Wed.: Reading this Week Begin Ch. of Modern Optics (. 8.) Nature of Polarized Light,
Phys 3 Mon. Oct. 3, 7 Today s Topics Begin Modern Optics Ch. : The Nature of Polarized Light Reading for Next Time By Wed.: Reading this Week Begin Ch. of Modern Optics (. 8.) Nature of Polarized Light,
APPLIED OPTICS POLARIZATION
 A. La Rosa Lecture Notes APPLIED OPTICS POLARIZATION Linearly-polarized light Description of linearly polarized light (using Real variables) Alternative description of linearly polarized light using phasors
A. La Rosa Lecture Notes APPLIED OPTICS POLARIZATION Linearly-polarized light Description of linearly polarized light (using Real variables) Alternative description of linearly polarized light using phasors
Chiroptical Spectroscopy
 Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Chiroptical Spectroscopy Theory and Applications in Organic Chemistry Lecture 2: Polarized light Masters Level Class (181 041) Mondays, 8.15-9.45 am, NC 02/99 Wednesdays, 10.15-11.45 am, NC 02/99 28 Electromagnetic
Light as a Transverse Wave.
 Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Waves and Superposition (Keating Chapter 21) The ray model for light (i.e. light travels in straight lines) can be used to explain a lot of phenomena (like basic object and image formation and even aberrations)
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c
 Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 lectromagnetic Waves (H&L Sections 9.5 7) What We Did Last Time! Studied spherical waves! Wave equation of isotropic waves! Solution e! Intensity decreases with! Doppler
Wave Phenomena Physics 15c Lecture 15 lectromagnetic Waves (H&L Sections 9.5 7) What We Did Last Time! Studied spherical waves! Wave equation of isotropic waves! Solution e! Intensity decreases with! Doppler
Maxwell s equations and EM waves. From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law
 Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
Maxwell s equations and EM waves This Lecture More on Motional EMF and Faraday s law Displacement currents Maxwell s equations EM Waves From previous Lecture Time dependent fields and Faraday s Law 1 Radar
Phys 322 Lecture 21. Chapter 8 Polarization
 Phs 3 Lecture 1 Chapter 8 Polarization Plane of polarization Transverse M wave B Plane of polarization - plane defined b vector and k: Plane of polarization z: z t ˆi z, t ˆi coskz t, z Linearl (plane)
Phs 3 Lecture 1 Chapter 8 Polarization Plane of polarization Transverse M wave B Plane of polarization - plane defined b vector and k: Plane of polarization z: z t ˆi z, t ˆi coskz t, z Linearl (plane)
Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance
 Lesson 7 Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance Oscillations in an LC Circuit The RLC Circuit Alternating Current Electromagnetic
Lesson 7 Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance Oscillations in an LC Circuit The RLC Circuit Alternating Current Electromagnetic
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials
 Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
Polarization of Light and Birefringence of Materials Ajit Balagopal (Team Members Karunanand Ogirala, Hui Shen) ECE 614- PHOTONIC INFORMATION PROCESSING LABORATORY Abstract-- In this project, we study
 Electromagnetic Waves Properties. The electric and the magnetic field, associated with an electromagnetic wave, propagating along the z=axis. Can be represented by E = E kˆ, = iˆ E = E ˆj, = ˆj b) E =
Electromagnetic Waves Properties. The electric and the magnetic field, associated with an electromagnetic wave, propagating along the z=axis. Can be represented by E = E kˆ, = iˆ E = E ˆj, = ˆj b) E =
Chapter 9. Reflection, Refraction and Polarization
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization Introduction When you solved Problem 5.2 using the standing-wave approach, you found a rather curious behavior as the wave propagates and meets the boundary. A new
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization Introduction When you solved Problem 5.2 using the standing-wave approach, you found a rather curious behavior as the wave propagates and meets the boundary. A new
Phys 102 Lecture 2 Coulomb s Law & Electric Dipoles
 Phys 102 Lecture 2 Coulomb s Law & Electric Dipoles 1 Today we will... Get practice using Coulomb s law & vector addition Learn about electric dipoles Apply these concepts! Molecular interactions Polar
Phys 102 Lecture 2 Coulomb s Law & Electric Dipoles 1 Today we will... Get practice using Coulomb s law & vector addition Learn about electric dipoles Apply these concepts! Molecular interactions Polar
REVIEW SESSION. Midterm 2
 REVIEW SESSION Midterm 2 Summary of Chapter 20 Magnets have north and south poles Like poles repel, unlike attract Unit of magnetic field: tesla Electric currents produce magnetic fields A magnetic field
REVIEW SESSION Midterm 2 Summary of Chapter 20 Magnets have north and south poles Like poles repel, unlike attract Unit of magnetic field: tesla Electric currents produce magnetic fields A magnetic field
polarisation of Light
 Basic concepts to understand polarisation of Light Polarization of Light Nature of light: light waves are transverse in nature i. e. the waves propagates in a direction perpendicular to the direction of
Basic concepts to understand polarisation of Light Polarization of Light Nature of light: light waves are transverse in nature i. e. the waves propagates in a direction perpendicular to the direction of
Electricity & Magnetism Lecture 23. Electricity & Magne/sm Lecture 23, Slide 1
 Electricity & Magnetism Lecture 23 Electricity & Magne/sm Lecture 23, Slide 1 Today you will play around with the polariza2on filters. Con2nue on Friday. Friday s lecture will be on circular polariza2on
Electricity & Magnetism Lecture 23 Electricity & Magne/sm Lecture 23, Slide 1 Today you will play around with the polariza2on filters. Con2nue on Friday. Friday s lecture will be on circular polariza2on
CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 74 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 4 TEST REVIEW 1. In which of the following regions of the electromagnetic spectrum is radiation
Polarized Light. Nikki Truss. Abstract:
 Polarized Light Nikki Truss 9369481 Abstract: In this experiment, the properties of linearly polarised light were examined. Malus Law was verified using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1. Reflectance of s-polarised
Polarized Light Nikki Truss 9369481 Abstract: In this experiment, the properties of linearly polarised light were examined. Malus Law was verified using the apparatus shown in Fig. 1. Reflectance of s-polarised
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Polarization of Light Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Types of Polarization Light propagating through different materials: One polarization component can
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Polarization of Light Spring 2015 Semester Matthew Jones Types of Polarization Light propagating through different materials: One polarization component can
Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string)
 1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves. Slide 29-1
 Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves Slide 29-1 Equations of electromagnetism: a review We ve now seen the four fundamental equations of electromagnetism, here listed together for the first time.
Chapter 29: Maxwell s Equation and EM Waves Slide 29-1 Equations of electromagnetism: a review We ve now seen the four fundamental equations of electromagnetism, here listed together for the first time.
Lecture 17. Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves.
 Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Phys 102 Lecture 9 RC circuits
 Phys 102 Lecture 9 RC circuits 1 Recall from last time... We solved various circuits with resistors and batteries (also capacitors and batteries) ε R 1 R 2 R 3 R 1 ε 1 ε 2 R 3 What about circuits that
Phys 102 Lecture 9 RC circuits 1 Recall from last time... We solved various circuits with resistors and batteries (also capacitors and batteries) ε R 1 R 2 R 3 R 1 ε 1 ε 2 R 3 What about circuits that
: Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 2002
 151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
151-232: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory 6: The Polarization of Light April 16 & 18, 22 Abstract. In this lab, we will investigate linear and circular polarization of light. Linearly polarized
High School Curriculum Standards: Physics
 High School Curriculum Standards: Physics Students will understand and apply scientific concepts, principles, and theories pertaining to the physical setting and living environment and recognize the historical
High School Curriculum Standards: Physics Students will understand and apply scientific concepts, principles, and theories pertaining to the physical setting and living environment and recognize the historical
Quarter wave plates and Jones calculus for optical system
 2/11/16 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6 1 Quarter wave plates and Jones calculus for optical system T. Johnson 2/11/16 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6
2/11/16 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6 1 Quarter wave plates and Jones calculus for optical system T. Johnson 2/11/16 Electromagnetic Processes In Dispersive Media, Lecture 6
Along with C1 the magnetic field is also observed at location C 2 though no current is threading through this loop.
 Displacement current British physicist James C. Maxwell gave final shape to all phenomenon connecting electricity and magnetism. He noticed an inconsistency in Ampere s Law connecting Electric current
Displacement current British physicist James C. Maxwell gave final shape to all phenomenon connecting electricity and magnetism. He noticed an inconsistency in Ampere s Law connecting Electric current
Electromagnetic Radiation. Physical Principles of Remote Sensing
 Electromagnetic Radiation Physical Principles of Remote Sensing Outline for 4/3/2003 Properties of electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Spectral emissivity Radiant temperature vs. kinematic
Electromagnetic Radiation Physical Principles of Remote Sensing Outline for 4/3/2003 Properties of electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Spectral emissivity Radiant temperature vs. kinematic
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer
 Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Introduction to Electromagnetic Radiation and Radiative Transfer Temperature Dice Results Visible light, infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, γ-rays, microwaves, and radio are all forms of electromagnetic
Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236. Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization
 Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236 Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization 1 Electromagnetic Radiation The first requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy source to illuminate the target.
Satellite Remote Sensing SIO 135/SIO 236 Electromagnetic Radiation and Polarization 1 Electromagnetic Radiation The first requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy source to illuminate the target.
Electromagnetic fields and waves
 Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Electromagnetic fields and waves Maxwell s rainbow Outline Maxwell s equations Plane waves Pulses and group velocity Polarization of light Transmission and reflection at an interface Macroscopic Maxwell
Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES. Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision
 Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision Close the Gap Contemporary record of the Topics / Learning outcomes that I
Name: COMBINED SCIENCE Topics 4, 5 & 6 LEARNING OUTCOMES Maintain a record of your progress Use the booklet to guide revision Close the Gap Contemporary record of the Topics / Learning outcomes that I
PHYS 1444 Section 003 Lecture #23
 PHYS 1444 Section 3 Lecture #3 Monday, Nov. 8, 5 EM Waves from Maxwell s Equations Speed of EM Waves Light as EM Wave Electromagnetic Spectrum Energy in EM Waves Energy Transport The epilogue Today s homework
PHYS 1444 Section 3 Lecture #3 Monday, Nov. 8, 5 EM Waves from Maxwell s Equations Speed of EM Waves Light as EM Wave Electromagnetic Spectrum Energy in EM Waves Energy Transport The epilogue Today s homework
Chapter 18. Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry. Properties of Light
 Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
PHYSICS. Chapter 16 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
Jones vector & matrices
 Jones vector & matrices Department of Physics 1 Matrix treatment of polarization Consider a light ray with an instantaneous E-vector as shown y E k, t = xe x (k, t) + ye y k, t E y E x x E x = E 0x e i
Jones vector & matrices Department of Physics 1 Matrix treatment of polarization Consider a light ray with an instantaneous E-vector as shown y E k, t = xe x (k, t) + ye y k, t E y E x x E x = E 0x e i
Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation.
 Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges would yield
Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges would yield
Physics 294H. lectures will be posted frequently, mostly! every day if I can remember to do so
 Physics 294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 hand-written problem per week) Help-room hours: 12:40-2:40
Physics 294H l Professor: Joey Huston l email:huston@msu.edu l office: BPS3230 l Homework will be with Mastering Physics (and an average of 1 hand-written problem per week) Help-room hours: 12:40-2:40
Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work
 Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric potential energy Relate it to work Ex: charge in uniform electric field, point charges Apply these concepts
Phys 102 Lecture 4 Electric potential energy & work 1 Today we will... Learn about the electric potential energy Relate it to work Ex: charge in uniform electric field, point charges Apply these concepts
iclicker A metal ball of radius R has a charge q. Charge is changed q -> - 2q. How does it s capacitance changed?
 1 iclicker A metal ball of radius R has a charge q. Charge is changed q -> - 2q. How does it s capacitance changed? q A: C->2 C0 B: C-> C0 C: C-> C0/2 D: C->- C0 E: C->-2 C0 2 iclicker A metal ball of
1 iclicker A metal ball of radius R has a charge q. Charge is changed q -> - 2q. How does it s capacitance changed? q A: C->2 C0 B: C-> C0 C: C-> C0/2 D: C->- C0 E: C->-2 C0 2 iclicker A metal ball of
Chapter 25. Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 25 Electromagnetic Waves EXAM # 3 Nov. 20-21 Chapter 23 Chapter 25 Powerpoint Nov. 4 Problems from previous exams Physics in Perspective (pg. 836 837) Units of Chapter 25 The Production of Electromagnetic
Chapter 25 Electromagnetic Waves EXAM # 3 Nov. 20-21 Chapter 23 Chapter 25 Powerpoint Nov. 4 Problems from previous exams Physics in Perspective (pg. 836 837) Units of Chapter 25 The Production of Electromagnetic
Physics I Keystone Institute Technology & Management Unit-II
 Un-polarized light Ordinary light is a collection of wave trains emitted by atoms or group of atoms with coherent time no longer than 10-8 second. Each wave train has different orientation and phase of
Un-polarized light Ordinary light is a collection of wave trains emitted by atoms or group of atoms with coherent time no longer than 10-8 second. Each wave train has different orientation and phase of
