Announcements. Topics: Homework: - section 12.4 (cross/vector product) - section 12.5 (equations of lines and planes)
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topics: Announcements - section 12.4 (cross/vector product) - section 12.5 (equations of lines and planes) Homework: ü review lecture notes thoroughl ü work on eercises from the tetbook in sections 12.4 and 12.5 ü work on Assignment 12 (all questions ecept #11)
2 Equations of Lines in 2D Recall: To write an equation of a line in the -plane, we need to know a point ( 1, 1 ) on the line and the slope, m, of the line. oint-slope equation: 1 = m( 1 ) oint--intercept equation: = m + b Eample: =
3 Vector Equation of a Line in 2D If 0 ( 0, 0 ) is a known point on the line and (,) is an arbitrar point on the line, then b the triangle law for vector addition, we can write that O O O = O O
4 r 0 Vector Equation of a Line in 2D Let vector v=<a,b> be an vector parallel to the line (often called a direction vector for the line). 0 tv If we let r be the the position vector O and r 0 be the position vector O 0, then the vector equation of the line can be written as O r v = a,b r = r 0 + tv where t is called a parameter and can be an real number.
5 arametric Equations of a Line in 2D If we epress the vectors algebraicall, we have that, = 0, 0 + t a,b 0 t a,b 0, 0, Separating the and components, we obtain the parametric equations of the line: O v = a,b = 0 + at = 0 + bt
6 Smmetric Equation of a Line in 2D If we then solve these equations for t (provided that the direction numbers, a and b, are not zero) and equate the components, we obtain the smmetric equation for the line: O 0, 0 0 t a,b, v = a,b 0 a = 0 b
7 Equations of Lines in 2D Eample 1: Find vector and parametric equations of the line =
8 Equations of Lines in 2D Eample 2: Find vector and parametric equations of the line through points (-4,3) and Q(2,-1).
9 Equations of Lines in 2D Eample 3: (a) Find a vector equation of the line through the point (1,5) and perpendicular to the line r = 1,2 + t 4,3. (b) Write the smmetric equation for this line.
10 Vector Equation of a Line in 3D If 0 ( 0, 0, z 0 ) is a known point on the line and (,,z) is an arbitrar point on the line, then b the triangle law for vector addition, we can write that 0 O 0 z 0 O O O = O 0 + 0
11 Vector Equation of a Line in 3D Let vector v=<a,b,c> be an vector parallel to the line (often called a direction vector for the line). 0 z tv If we let r be the the position vector O and r 0 be the position vector O 0, then the vector equation of the line can be written as r 0 O r v = a,b,c r = r 0 + tv where t is called a parameter and can be an real number.
12 arametric Equations of a Line in 3D If we epress the vectors algebraicall, we have that,, z = 0, 0, z 0 + t a, b, c 0 z t a,b,c,,z Separating the,, and z components, we obtain the parametric equations of the line: 0, 0,z 0 O v = a,b,c = 0 + at = 0 + bt z = z 0 + ct
13 Smmetric Equations of a Line in 3D If we then solve these equations for t (provided that the direction numbers, a, b, and c are not zero) and equate the components, we obtain the smmetric equations for the line: 0 0, 0,z 0 z t a,b,c O,,z v = a,b,c 0 a = 0 b = z z 0 c
14 Equations of Lines in 3D Eample 1: Find vector, parametric, and smmetric equations of the line through (1,0,3) and parallel to the line r = 1, 6,0 + t 5,7, 1.
15 Equations of Lines in 3D Eample 2: Find vector, parametric, and smmetric equations of the line through points (1,2,0) and Q(-3,2,1).
16 Equation of a lane A plane is determined b a point 0 ( 0, 0, z 0 ) in the plane and a vector n, called a normal vector, that is perpendicular to the plane.
17 Equation of a lane Let n=<a,b,c> be a normal vector for the plane. This normal vector, or simpl normal, is perpendicular to ever vector in the plane. If 0 ( 0, 0, z 0 ) is a known point in the plane and (,,z) is an arbitrar point in the plane, then n is perpendicular to 0 and so we have that n 0 = 0
18 Equation of a lane Using the definition of the dot product for algebraic vectors, we obtain the scalar equation of the plane through 0 ( 0, 0, z 0 ) with normal vector n=<a,b,c>: a( 0 ) + b( 0 ) + c( 0 ) = 0 This equation is often epanded and simplified to a + b + cz + d = 0 where d = (a 0 + b 0 + cz 0 ).
19 Eample #26. Find an equation of the plane through the point (2,0,1) and perpendicular to the line =3t, =2-t, z=3+4t. Equations of lanes
20 Eample #32. Find an equation of the plane through the origin and the points (3,-2,1) and (1,1,1). Equations of lanes
21 Equations of lanes Eample #36. Find an equation of the plane that passes through the point (6,-1,3) and contains the line /3=+4=z/2.
Lecture 5. Equations of Lines and Planes. Dan Nichols MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts.
 Lecture 5 Equations of Lines and Planes Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 Universit of Massachusetts Februar 6, 2018 (2) Upcoming midterm eam First midterm: Wednesda Feb. 21, 7:00-9:00
Lecture 5 Equations of Lines and Planes Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 Universit of Massachusetts Februar 6, 2018 (2) Upcoming midterm eam First midterm: Wednesda Feb. 21, 7:00-9:00
Vector equations of lines in the plane and 3-space (uses vector addition & scalar multiplication).
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Lines and Planes 1. x(t) = at + b y(t) = ct + d
 1 Lines in the Plane Lines and Planes 1 Ever line of points L in R 2 can be epressed as the solution set for an equation of the form A + B = C. Will we call this the ABC form. Recall that the slope-intercept
1 Lines in the Plane Lines and Planes 1 Ever line of points L in R 2 can be epressed as the solution set for an equation of the form A + B = C. Will we call this the ABC form. Recall that the slope-intercept
MAC Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II
 MAC 2103 Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the cross product of a vector in R 3. 2. Determine a scalar triple
MAC 2103 Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the cross product of a vector in R 3. 2. Determine a scalar triple
MTH MTH Lecture 6. Yevgeniy Kovchegov Oregon State University
 MTH 306 0 MTH 306 - Lecture 6 Yevgeniy Kovchegov Oregon State University MTH 306 1 Topics Lines and planes. Systems of linear equations. Systematic elimination of unknowns. Coe cient matrix. Augmented
MTH 306 0 MTH 306 - Lecture 6 Yevgeniy Kovchegov Oregon State University MTH 306 1 Topics Lines and planes. Systems of linear equations. Systematic elimination of unknowns. Coe cient matrix. Augmented
12.3 Properties of Logarithms
 12.3 Properties of Logarithms The Product Rule Let b, and N be positive real numbers with b 1. N = + N The logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors. Eample 1: Use the product
12.3 Properties of Logarithms The Product Rule Let b, and N be positive real numbers with b 1. N = + N The logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors. Eample 1: Use the product
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4]
![8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4] 8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4]](/thumbs/95/122742655.jpg) Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8-1.. Linear Relations 1. Make a table of values and graph each linear function a) y = 2x b) y = x + 5 c) 2x + 6y = 12 d) x + 7y = 21 2. Find the x- and y-intercepts of
Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8-1.. Linear Relations 1. Make a table of values and graph each linear function a) y = 2x b) y = x + 5 c) 2x + 6y = 12 d) x + 7y = 21 2. Find the x- and y-intercepts of
Math 241, Exam 1 Information.
 Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE
 VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE A line in the xy-plane is determined when a point on the line and the direction of the line (its slope or angle of inclination) are given.
VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE A line in the xy-plane is determined when a point on the line and the direction of the line (its slope or angle of inclination) are given.
Chapter 5: Systems of Equations and Inequalities. Section 5.4. Check Point Exercises
 Chapter : Systems of Equations and Inequalities Section. Check Point Eercises. = y y = Solve the first equation for y. y = + Substitute the epression + for y in the second equation and solve for. ( + )
Chapter : Systems of Equations and Inequalities Section. Check Point Eercises. = y y = Solve the first equation for y. y = + Substitute the epression + for y in the second equation and solve for. ( + )
Kevin James. MTHSC 206 Section 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 MTHSC 206 Section 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Definition A line in R 3 can be described by a point and a direction vector. Given the point r 0 and the direction vector v. Any point r on the line
MTHSC 206 Section 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Definition A line in R 3 can be described by a point and a direction vector. Given the point r 0 and the direction vector v. Any point r on the line
MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11
 MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11 August 7 & 11, 2014 Contents 8 Lines and Planes 1 8.1 Equations of Lines in Two-Space and Three-Space............ 1 8.2 Equations of Planes........................... 5 8.3 Properties
MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11 August 7 & 11, 2014 Contents 8 Lines and Planes 1 8.1 Equations of Lines in Two-Space and Three-Space............ 1 8.2 Equations of Planes........................... 5 8.3 Properties
Vertex form of a quadratic equation
 Verte form of a quadratic equation Nikos Apostolakis Spring 017 Recall 1. Last time we looked at the graphs of quadratic equations in two variables. The upshot was that the graph of the equation: k = a(
Verte form of a quadratic equation Nikos Apostolakis Spring 017 Recall 1. Last time we looked at the graphs of quadratic equations in two variables. The upshot was that the graph of the equation: k = a(
Math 115: Review for Chapter 2
 Math 5: Review for Chapter Can ou determine algebraicall whether an equation is smmetric with respect to the - ais, the -ais, or the origin?. Algebraicall determine whether each equation below is smmetric
Math 5: Review for Chapter Can ou determine algebraicall whether an equation is smmetric with respect to the - ais, the -ais, or the origin?. Algebraicall determine whether each equation below is smmetric
4.6 Model Direct Variation
 4.6 Model Direct Variation Goal p Write and graph direct variation equations. Your Notes VOCABULARY Direct variation Constant of variation Eample Identif direct variation equations Tell whether the equation
4.6 Model Direct Variation Goal p Write and graph direct variation equations. Your Notes VOCABULARY Direct variation Constant of variation Eample Identif direct variation equations Tell whether the equation
Review of Prerequisite Skills, p. 350 C( 2, 0, 1) B( 3, 2, 0) y A(0, 1, 0) D(0, 2, 3) j! k! 2k! Section 7.1, pp
 . 5. a. a a b a a b. Case If and are collinear, then b is also collinear with both and. But is perpendicular to and c c c b 9 b c, so a a b b is perpendicular to. Case If b and c b c are not collinear,
. 5. a. a a b a a b. Case If and are collinear, then b is also collinear with both and. But is perpendicular to and c c c b 9 b c, so a a b b is perpendicular to. Case If b and c b c are not collinear,
Linear Algebra: Homework 3
 Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August 206 - December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k
Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August 206 - December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k
Model Inverse Variation. p Write and graph inverse variation equations. VOCABULARY. Inverse variation. Constant of variation. Branches of a hyperbola
 12.1 Model Inverse Variation Goal p Write and graph inverse variation equations. Your Notes VOCABULARY Inverse variation Constant of variation Hperbola Branches of a hperbola Asmptotes of a hperbola Eample
12.1 Model Inverse Variation Goal p Write and graph inverse variation equations. Your Notes VOCABULARY Inverse variation Constant of variation Hperbola Branches of a hperbola Asmptotes of a hperbola Eample
2.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System
 . The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem In this section ou will learn to: plot points in a rectangular coordinate sstem understand basic functions of the graphing calculator graph equations b generating a table
Name These exercises cover topics from Algebra I and Algebra II. Complete each question the best you can.
 Name These eercises cover topics from Algebra I and Algebra II. Complete each question the best you can. Multiple Choice: Place through the letter of the correct answer. You may only use your calculator
Name These eercises cover topics from Algebra I and Algebra II. Complete each question the best you can. Multiple Choice: Place through the letter of the correct answer. You may only use your calculator
5.4 Solve Special Types of Linear Systems
 Warm up Solve the system of equations. x + y = 3 5x + 3y = 1 5.4 Solve Special Types of Linear Systems I can... 1.) determine whether a system has no solution, infinitely many solutions, or exactly one
Warm up Solve the system of equations. x + y = 3 5x + 3y = 1 5.4 Solve Special Types of Linear Systems I can... 1.) determine whether a system has no solution, infinitely many solutions, or exactly one
Mon Apr dot product, length, orthogonality, projection onto the span of a single vector. Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Math 2270-004 Week 2 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a gien day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent an
Math 2270-004 Week 2 notes We will not necessarily finish the material from a gien day's notes on that day. We may also add or subtract some material as the week progresses, but these notes represent an
Linear Equation Theory - 2
 Algebra Module A46 Linear Equation Theor - Copright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED June., 009 Linear Equation Theor - Statement of Prerequisite
Algebra Module A46 Linear Equation Theor - Copright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED June., 009 Linear Equation Theor - Statement of Prerequisite
Analytic Geometry in Three Dimensions
 Analtic Geometr in Three Dimensions. The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Sstem. Vectors in Space. The Cross Product of Two Vectors. Lines and Planes in Space The three-dimensional coordinate sstem is used
Analtic Geometr in Three Dimensions. The Three-Dimensional Coordinate Sstem. Vectors in Space. The Cross Product of Two Vectors. Lines and Planes in Space The three-dimensional coordinate sstem is used
MATH 152 COLLEGE ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETRY UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS
 0//0 MATH COLLEGE ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETRY UNIT HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions Be sure to write out all our work, because method is as important as getting the correct answer. The answers to
0//0 MATH COLLEGE ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETRY UNIT HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions Be sure to write out all our work, because method is as important as getting the correct answer. The answers to
12. Lines in R 3. through P 0 and is parallel to v is written parametrically as a function of t: Using vector notation, the same line is written
 12. Lines in R 3 Given a point P 0 = (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) and a direction vector v 1 = a, b, c in R 3, a line L that passes through P 0 and is parallel to v is written parametrically as a function of t: x(t)
12. Lines in R 3 Given a point P 0 = (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) and a direction vector v 1 = a, b, c in R 3, a line L that passes through P 0 and is parallel to v is written parametrically as a function of t: x(t)
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
Unit 2: Lines and Planes in 3 Space. Linear Combinations of Vectors
 Lesson10.notebook November 28, 2012 Unit 2: Lines and Planes in 3 Space Linear Combinations of Vectors Today's goal: I can write vectors as linear combinations of each other using the appropriate method
Lesson10.notebook November 28, 2012 Unit 2: Lines and Planes in 3 Space Linear Combinations of Vectors Today's goal: I can write vectors as linear combinations of each other using the appropriate method
Applications. 12 The Shapes of Algebra. 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates x and y for points on the circle.
 Applications 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates and for points on the circle. 1 8 (, ) 1 8 O 8 1 8 1 (13, 0) b. Find the missing coordinates for each of these points on the circle. If
Applications 1. a. Write an equation that relates the coordinates and for points on the circle. 1 8 (, ) 1 8 O 8 1 8 1 (13, 0) b. Find the missing coordinates for each of these points on the circle. If
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Algebraic Expressions and Identities
 9 Algebraic Epressions and Identities introduction In previous classes, you have studied the fundamental concepts of algebra, algebraic epressions and their addition and subtraction. In this chapter, we
9 Algebraic Epressions and Identities introduction In previous classes, you have studied the fundamental concepts of algebra, algebraic epressions and their addition and subtraction. In this chapter, we
10.2 INTRODUCTION TO CONICS: PARABOLAS
 Section 0.2 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 733 0.2 INTRODUCTION TO CONICS: PARABOLAS What ou should learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane a double-napped cone. Write equations of parabolas
Section 0.2 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 733 0.2 INTRODUCTION TO CONICS: PARABOLAS What ou should learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane a double-napped cone. Write equations of parabolas
Math Theory of Number Homework 1
 Math 4050 Theory of Number Homework 1 Due Wednesday, 015-09-09, in class Do 5 of the following 7 problems. Please only attempt 5 because I will only grade 5. 1. Find all rational numbers and y satisfying
Math 4050 Theory of Number Homework 1 Due Wednesday, 015-09-09, in class Do 5 of the following 7 problems. Please only attempt 5 because I will only grade 5. 1. Find all rational numbers and y satisfying
Calculus w/applications Prerequisite Packet Paint Branch High School Math Department
 Updated 6/014 The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous math courses that are important to your success in Calculus with Applications. It is important that you take
Updated 6/014 The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous math courses that are important to your success in Calculus with Applications. It is important that you take
ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Revision of Grade 10 Analytical Geometry
 ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Revision of Grade 10 Analtical Geometr Let s quickl have a look at the analtical geometr ou learnt in Grade 10. 8 LESSON Midpoint formula (_ + 1 ;_ + 1 The midpoint formula is used
ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY Revision of Grade 10 Analtical Geometr Let s quickl have a look at the analtical geometr ou learnt in Grade 10. 8 LESSON Midpoint formula (_ + 1 ;_ + 1 The midpoint formula is used
MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS
 CHAPTER 5. MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS Matri Transformations Definition Let A and B be sets. A function f : A B
CHAPTER 5. MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS INSTITIÚID TEICNEOLAÍOCHTA CHEATHARLACH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CARLOW MATRIX TRANSFORMATIONS Matri Transformations Definition Let A and B be sets. A function f : A B
Coordinates for Projective Planes
 Chapter 8 Coordinates for Projective Planes Math 4520, Fall 2017 8.1 The Affine plane We now have several eamples of fields, the reals, the comple numbers, the quaternions, and the finite fields. Given
Chapter 8 Coordinates for Projective Planes Math 4520, Fall 2017 8.1 The Affine plane We now have several eamples of fields, the reals, the comple numbers, the quaternions, and the finite fields. Given
2. Which of the following expressions represents the product of four less than three times x and two more than x?
 Algebra Topics COMPASS Review You will be allowed to use a calculator on the COMPASS test. Acceptable calculators are: basic calculators, scientific calculators, and graphing calculators up through the
Algebra Topics COMPASS Review You will be allowed to use a calculator on the COMPASS test. Acceptable calculators are: basic calculators, scientific calculators, and graphing calculators up through the
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 The Quadratic Function (Vertex Form): Translations. and axis of symmetry is at x a.
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 Verte form of Quadratic Relations The epression a p q defines a quadratic relation called the verte form with a horizontal translation of p units and vertical translation of
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 Verte form of Quadratic Relations The epression a p q defines a quadratic relation called the verte form with a horizontal translation of p units and vertical translation of
UNCORRECTED. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: y = x 1 y 2 = x
 5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
Precalculus Honors - AP Calculus A Information and Summer Assignment
 Precalculus Honors - AP Calculus A Information and Summer Assignment General Information: Competenc in Algebra and Trigonometr is absolutel essential. The calculator will not alwas be available for ou
Precalculus Honors - AP Calculus A Information and Summer Assignment General Information: Competenc in Algebra and Trigonometr is absolutel essential. The calculator will not alwas be available for ou
Multiple Choice. 1.(6 pts) Find symmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (2, 5, 1) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y z = 9.
 Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
7.3 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 7.3 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Add and subtract rational epressions with common denominators. 2. Add and subtract rational epressions with unlike denominators. 3. Add
7.3 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Add and subtract rational epressions with common denominators. 2. Add and subtract rational epressions with unlike denominators. 3. Add
Beautiful homework # 4 ENGR 323 CESSNA Page 1/5
 Beautiful homework # 4 ENGR 33 CESSNA Page 1/5 Problem 3-14 An operator records the time to complete a mechanical assembly to the nearest second with the following results. seconds 30 31 3 33 34 35 36
Beautiful homework # 4 ENGR 33 CESSNA Page 1/5 Problem 3-14 An operator records the time to complete a mechanical assembly to the nearest second with the following results. seconds 30 31 3 33 34 35 36
Distance Formula in 3-D Given any two points P 1 (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and P 2 (x 2, y 2, z 2 ) the distance between them is ( ) ( ) ( )
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
1.2 LECTURE 2. Scalar Product
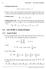 6 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Pythagean theem. cos 2 α 1 + cos 2 α 2 + cos 2 α 3 = 1 There is a one-to-one crespondence between the components of the vect on the one side and its magnitude and the direction
6 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Pythagean theem. cos 2 α 1 + cos 2 α 2 + cos 2 α 3 = 1 There is a one-to-one crespondence between the components of the vect on the one side and its magnitude and the direction
Summer Packet Honors PreCalculus
 Summer Packet Honors PreCalculus Honors Pre-Calculus is a demanding course that relies heavily upon a student s algebra, geometry, and trigonometry skills. You are epected to know these topics before entering
Summer Packet Honors PreCalculus Honors Pre-Calculus is a demanding course that relies heavily upon a student s algebra, geometry, and trigonometry skills. You are epected to know these topics before entering
Mathematics of Cryptography Part I
 CHAPTER 2 Mathematics of Crptograph Part I (Solution to Practice Set) Review Questions 1. The set of integers is Z. It contains all integral numbers from negative infinit to positive infinit. The set of
CHAPTER 2 Mathematics of Crptograph Part I (Solution to Practice Set) Review Questions 1. The set of integers is Z. It contains all integral numbers from negative infinit to positive infinit. The set of
and Rational Functions
 chapter This detail from The School of Athens (painted by Raphael around 1510) depicts Euclid eplaining geometry. Linear, Quadratic, Polynomial, and Rational Functions In this chapter we focus on four
chapter This detail from The School of Athens (painted by Raphael around 1510) depicts Euclid eplaining geometry. Linear, Quadratic, Polynomial, and Rational Functions In this chapter we focus on four
LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions
 LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions Section 11.4, # 40: This problem was solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 42: This problem was also solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 43: Also solved in class
LB 220 Homework 4 Solutions Section 11.4, # 40: This problem was solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 42: This problem was also solved in class on Feb. 03. Section 11.4, # 43: Also solved in class
Math RE - Calculus I Functions Page 1 of 10. Topics of Functions used in Calculus
 Math 0-03-RE - Calculus I Functions Page of 0 Definition of a function f() : Topics of Functions used in Calculus A function = f() is a relation between variables and such that for ever value onl one value.
Math 0-03-RE - Calculus I Functions Page of 0 Definition of a function f() : Topics of Functions used in Calculus A function = f() is a relation between variables and such that for ever value onl one value.
Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment
 Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment To be successful in Math Analysis or Honors Math Analysis, a full understanding of the topics listed below is required prior to the school year. To
Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment To be successful in Math Analysis or Honors Math Analysis, a full understanding of the topics listed below is required prior to the school year. To
Distances in R 3. Last time we figured out the (parametric) equation of a line and the (scalar) equation of a plane:
 Distances in R 3 Last time we figured out the (parametric) equation of a line and the (scalar) equation of a plane: Definition: The equation of a line through point P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) with directional vector
Distances in R 3 Last time we figured out the (parametric) equation of a line and the (scalar) equation of a plane: Definition: The equation of a line through point P(x 0, y 0, z 0 ) with directional vector
4. (6 points) Express the domain of the following function in interval notation:
 Eam 1-A L. Ballou Name Math 131 Calculus I September 1, 016 NO Calculator Allowed BOX YOUR ANSWER! Show all work for full credit! 1. (4 points) Write an equation of a line with y-intercept 4 and -intercept
Eam 1-A L. Ballou Name Math 131 Calculus I September 1, 016 NO Calculator Allowed BOX YOUR ANSWER! Show all work for full credit! 1. (4 points) Write an equation of a line with y-intercept 4 and -intercept
Overview. Distances in R 3. Distance from a point to a plane. Question
 Overview Yesterda we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrar points r in terms of a specific point and the direction vector v.
Overview Yesterda we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrar points r in terms of a specific point and the direction vector v.
Algebra 2 Summer Work Packet
 Algebra Summer Work Packet Covering Prerequisite Concepts for Incoming Algebra 1 Students This workbook contains problems designed to ensure the student's readiness for Algebra. The nine topics covered
Algebra Summer Work Packet Covering Prerequisite Concepts for Incoming Algebra 1 Students This workbook contains problems designed to ensure the student's readiness for Algebra. The nine topics covered
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Name Date Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Section.1 Quadratic Functions Objective: In this lesson ou learned how to sketch and analze graphs of quadratic functions. Important Vocabular Define
Name Date Chapter Polnomial and Rational Functions Section.1 Quadratic Functions Objective: In this lesson ou learned how to sketch and analze graphs of quadratic functions. Important Vocabular Define
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
Lecture 5: Finding limits analytically Simple indeterminate forms
 Lecture 5: Finding its analytically Simple indeterminate forms Objectives: (5.) Use algebraic techniques to resolve 0/0 indeterminate forms. (5.) Use the squeeze theorem to evaluate its. (5.3) Use trigonometric
Lecture 5: Finding its analytically Simple indeterminate forms Objectives: (5.) Use algebraic techniques to resolve 0/0 indeterminate forms. (5.) Use the squeeze theorem to evaluate its. (5.3) Use trigonometric
Rigid Body Transforms-3D. J.C. Dill transforms3d 27Jan99
 ESC 489 3D ransforms 1 igid Bod ransforms-3d J.C. Dill transforms3d 27Jan99 hese notes on (2D and) 3D rigid bod transform are currentl in hand-done notes which are being converted to this file from that
ESC 489 3D ransforms 1 igid Bod ransforms-3d J.C. Dill transforms3d 27Jan99 hese notes on (2D and) 3D rigid bod transform are currentl in hand-done notes which are being converted to this file from that
Math 234. What you should know on day one. August 28, You should be able to use general principles like. x = cos t, y = sin t, 0 t π.
 Math 234 What you should know on day one August 28, 2001 1 You should be able to use general principles like Length = ds, Area = da, Volume = dv For example the length of the semi circle x = cos t, y =
Math 234 What you should know on day one August 28, 2001 1 You should be able to use general principles like Length = ds, Area = da, Volume = dv For example the length of the semi circle x = cos t, y =
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8)
 Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
A11.1 Areas under curves
 Applications 11.1 Areas under curves A11.1 Areas under curves Before ou start You should be able to: calculate the value of given the value of in algebraic equations of curves calculate the area of a trapezium.
Applications 11.1 Areas under curves A11.1 Areas under curves Before ou start You should be able to: calculate the value of given the value of in algebraic equations of curves calculate the area of a trapezium.
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) TNM046: Datorgrafik. Transformations. Linear Algebra. Linear Algebra. Sasan Gooran VT Transposition. Scalar (dot) product:
 TNM046: Datorgrafik Transformations Sasan Gooran VT 04 Linear Algebra ( ) ( ) =,, 3 =,, 3 Transposition t = 3 t = 3 Scalar (dot) product: Length (Norm): = t = + + 3 3 = = + + 3 Normaliation: ˆ = Linear
TNM046: Datorgrafik Transformations Sasan Gooran VT 04 Linear Algebra ( ) ( ) =,, 3 =,, 3 Transposition t = 3 t = 3 Scalar (dot) product: Length (Norm): = t = + + 3 3 = = + + 3 Normaliation: ˆ = Linear
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function 2
 Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
Chapter 18 Quadratic Function Completed Square Form 1 Consider this special set of numbers - the square numbers or the set of perfect squares. 4 = = 9 = 3 = 16 = 4 = 5 = 5 = Numbers like 5, 11, 15 are
GUIDED NOTES 2.2 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE
 GUIDED NOTES 2.2 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Solve equations in one variable algebraically. Solve a rational equation. Find a linear equation. Given
GUIDED NOTES 2.2 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Solve equations in one variable algebraically. Solve a rational equation. Find a linear equation. Given
mathematical objects can be described via equations, functions, graphs, parameterization in R, R, and R.
 Multivariable Calculus Lecture # Notes This lecture completes the discussion of the cross product in R and addresses the variety of different ways that n mathematical objects can be described via equations,
Multivariable Calculus Lecture # Notes This lecture completes the discussion of the cross product in R and addresses the variety of different ways that n mathematical objects can be described via equations,
SAMPLE. A Gallery of Graphs. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: y = x 1,
 Objectives C H A P T E R 5 A Galler of Graphs To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: =, =, = / and + =. To be able to sketch the graphs and simple transformations of these
Objectives C H A P T E R 5 A Galler of Graphs To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relationships: =, =, = / and + =. To be able to sketch the graphs and simple transformations of these
PART A: Answer in the space provided. Each correct answer is worth one mark each.
 PART A: Answer in the space provided. Each correct answer is worth one mark each. 1. Find the slope of the tangent to the curve at the point (,6). =. If the tangent line to the curve k( ) = is horizontal,
PART A: Answer in the space provided. Each correct answer is worth one mark each. 1. Find the slope of the tangent to the curve at the point (,6). =. If the tangent line to the curve k( ) = is horizontal,
Midterm 1 Review. Distance = (x 1 x 0 ) 2 + (y 1 y 0 ) 2.
 Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
r some or all of m, x, yz. Similarly for I yy and I zz.
 Homework 10. Chapters 1, 1. Moments and products of inertia. 10.1 Concepts: What objects have a moment of inertia? (Section 1.1). Consider the moment of inertia S/ bu bu of an object S about a point for
Homework 10. Chapters 1, 1. Moments and products of inertia. 10.1 Concepts: What objects have a moment of inertia? (Section 1.1). Consider the moment of inertia S/ bu bu of an object S about a point for
Fundamentals of Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry. (Self-Study Course)
 Fundamentals of Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry (Self-Study Course) This training is offered eclusively through the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, Business Leadership Office, Technical
Fundamentals of Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry (Self-Study Course) This training is offered eclusively through the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, Business Leadership Office, Technical
ACCUPLACER MATH 0310
 The University of Teas at El Paso Tutoring and Learning Center ACCUPLACER MATH 00 http://www.academics.utep.edu/tlc MATH 00 Page Linear Equations Linear Equations Eercises 5 Linear Equations Answer to
The University of Teas at El Paso Tutoring and Learning Center ACCUPLACER MATH 00 http://www.academics.utep.edu/tlc MATH 00 Page Linear Equations Linear Equations Eercises 5 Linear Equations Answer to
University of Regina Department of Mathematics and Statistics
 u z v 1. Consider the map Universit of Regina Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH431/831 Differential Geometr Winter 2014 Homework Assignment No. 3 - Solutions ϕ(u, v) = (cosusinv, sin u sin
u z v 1. Consider the map Universit of Regina Department of Mathematics and Statistics MATH431/831 Differential Geometr Winter 2014 Homework Assignment No. 3 - Solutions ϕ(u, v) = (cosusinv, sin u sin
Math 2433 Notes Week The Dot Product. The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b
 Math 2433 Notes Week 2 11.3 The Dot Product The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b a b 3) Given, a = 4i + 4j, b = i - 2j + 3k, c = 2i + 2k Find the angle between a and c Projection
Math 2433 Notes Week 2 11.3 The Dot Product The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b a b 3) Given, a = 4i + 4j, b = i - 2j + 3k, c = 2i + 2k Find the angle between a and c Projection
Precalculus with Trigonometry Honors Summer Packet
 Precalculus with Trigonometry Honors Summer Packet Welcome to Precalculus with Trigonometry Honors! We look forward to guiding you through an informative and eciting year en route to Calculus! In order
Precalculus with Trigonometry Honors Summer Packet Welcome to Precalculus with Trigonometry Honors! We look forward to guiding you through an informative and eciting year en route to Calculus! In order
Number Sets 1,0,1,2,3,... } 3. Rational Numbers ( Q) 1. Natural Numbers ( N) A number is a rational number if. it can be written as where a and
 Number Sets 1. Natural Numbers ( N) N { 0,1,,,... } This set is often referred to as the counting numbers that include zero.. Integers ( Z) Z {...,,, 1,0,1,,,... }. Rational Numbers ( Q) A number is a
Number Sets 1. Natural Numbers ( N) N { 0,1,,,... } This set is often referred to as the counting numbers that include zero.. Integers ( Z) Z {...,,, 1,0,1,,,... }. Rational Numbers ( Q) A number is a
Matrices. A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. Cells in a matrix can be referenced in the form.
 Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Math 20C. Lecture Examples.
 Math 20C. Lecture Eamples. (8/1/08) Section 12.2. Vectors in three dimensions To use rectangular z-coordinates in three-dimensional space, e introduce mutuall perpendicular -, -, and z-aes intersecting
Math 20C. Lecture Eamples. (8/1/08) Section 12.2. Vectors in three dimensions To use rectangular z-coordinates in three-dimensional space, e introduce mutuall perpendicular -, -, and z-aes intersecting
6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation
 6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation FOCUS Relate the graph of a line to its equation in general form. We can write an equation in different forms. y 0 6 5 y 10 = 0 An equation for this
6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation FOCUS Relate the graph of a line to its equation in general form. We can write an equation in different forms. y 0 6 5 y 10 = 0 An equation for this
Culminating Review for Vectors
 Culminating Review for Vectors 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 An Introduction to Vectors Applications of Vectors Equations of Lines and Planes 4 12 Relationships between Points, Lines and Planes An
Culminating Review for Vectors 0011 0010 1010 1101 0001 0100 1011 An Introduction to Vectors Applications of Vectors Equations of Lines and Planes 4 12 Relationships between Points, Lines and Planes An
MATH Final Review
 MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
2.1 Evaluate and Graph Polynomial
 2. Evaluate and Graph Polnomial Functions Georgia Performance Standard(s) MM3Ab, MM3Ac, MM3Ad Your Notes Goal p Evaluate and graph polnomial functions. VOCABULARY Polnomial Polnomial function Degree of
2. Evaluate and Graph Polnomial Functions Georgia Performance Standard(s) MM3Ab, MM3Ac, MM3Ad Your Notes Goal p Evaluate and graph polnomial functions. VOCABULARY Polnomial Polnomial function Degree of
Brief Review of Exam Topics
 Math 32A Discussion Session Week 3 Notes October 17 and 19, 2017 We ll use this week s discussion session to prepare for the first midterm. We ll start with a quick rundown of the relevant topics, and
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 3 Notes October 17 and 19, 2017 We ll use this week s discussion session to prepare for the first midterm. We ll start with a quick rundown of the relevant topics, and
LESSON #12 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
Section 5.1: Functions
 Objective: Identif functions and use correct notation to evaluate functions at numerical and variable values. A relationship is a matching of elements between two sets with the first set called the domain
Objective: Identif functions and use correct notation to evaluate functions at numerical and variable values. A relationship is a matching of elements between two sets with the first set called the domain
Quadratics NOTES.notebook November 02, 2017
 1) Find y where y = 2-1 and a) = 2 b) = -1 c) = 0 2) Epand the brackets and simplify: (m + 4)(2m - 3) To find the equation of quadratic graphs using substitution of a point. 3) Fully factorise 4y 2-5y
1) Find y where y = 2-1 and a) = 2 b) = -1 c) = 0 2) Epand the brackets and simplify: (m + 4)(2m - 3) To find the equation of quadratic graphs using substitution of a point. 3) Fully factorise 4y 2-5y
A BRIEF REVIEW OF ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETRY
 A BRIEF REVIEW OF ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETR Some Key Concepts:. The slope and the equation of a straight line. Functions and functional notation. The average rate of change of a function and the DIFFERENCE-
A BRIEF REVIEW OF ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETR Some Key Concepts:. The slope and the equation of a straight line. Functions and functional notation. The average rate of change of a function and the DIFFERENCE-
c) Words: The cost of a taxicab is $2.00 for the first 1/4 of a mile and $1.00 for each additional 1/8 of a mile.
 Functions Definition: A function f, defined from a set A to a set B, is a rule that associates with each element of the set A one, and onl one, element of the set B. Eamples: a) Graphs: b) Tables: 0 50
Functions Definition: A function f, defined from a set A to a set B, is a rule that associates with each element of the set A one, and onl one, element of the set B. Eamples: a) Graphs: b) Tables: 0 50
How can you write an equation of a line when you are given the slope and a point on the line? ACTIVITY: Writing Equations of Lines
 .7 Writing Equations in Point-Slope Form How can ou write an equation of a line when ou are given the slope and a point on the line? ACTIVITY: Writing Equations of Lines Work with a partner. Sketch the
.7 Writing Equations in Point-Slope Form How can ou write an equation of a line when ou are given the slope and a point on the line? ACTIVITY: Writing Equations of Lines Work with a partner. Sketch the
Euclidean Spaces. Euclidean Spaces. Chapter 10 -S&B
 Chapter 10 -S&B The Real Line: every real number is represented by exactly one point on the line. The plane (i.e., consumption bundles): Pairs of numbers have a geometric representation Cartesian plane
Chapter 10 -S&B The Real Line: every real number is represented by exactly one point on the line. The plane (i.e., consumption bundles): Pairs of numbers have a geometric representation Cartesian plane
Roots, Radicals, and Square Root Equations: Multiplication of Square Root Expressions *
 OpenSta-CNX module: m2197 1 Roots, Radicals, and Square Root Equations: Multiplication of Square Root Epressions * Wade Ellis Denn Burznski This work is produced b OpenSta-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenSta-CNX module: m2197 1 Roots, Radicals, and Square Root Equations: Multiplication of Square Root Epressions * Wade Ellis Denn Burznski This work is produced b OpenSta-CNX and licensed under the Creative
4Divergenceandcurl. D ds = ρdv. S
 4Divergenceandcurl Epressing the total charge Q V contained in a volume V as a 3D volume integral of charge density ρ(r), wecanwritegauss s law eamined during the last few lectures in the general form
4Divergenceandcurl Epressing the total charge Q V contained in a volume V as a 3D volume integral of charge density ρ(r), wecanwritegauss s law eamined during the last few lectures in the general form
Quiz #2. A = 1 2 bh 1 2 (6.1)(5.3)
 Math 50C Multivariable Calculus September 11, 2015 Quiz #2 Name: Answer Ke David Arnold Instructions. (20 points) This quiz is open notes, open book. This includes an supplementar tets or online documents.
Math 50C Multivariable Calculus September 11, 2015 Quiz #2 Name: Answer Ke David Arnold Instructions. (20 points) This quiz is open notes, open book. This includes an supplementar tets or online documents.
MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15)
 MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15) Date: Chapter Goals: Identif solutions to an equation. Solve an equation for one variable in terms of another. What is a function? Understand
MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15) Date: Chapter Goals: Identif solutions to an equation. Solve an equation for one variable in terms of another. What is a function? Understand
Algebra Concepts Equation Solving Flow Chart Page 1 of 6. How Do I Solve This Equation?
 Algebra Concepts Equation Solving Flow Chart Page of 6 How Do I Solve This Equation? First, simplify both sides of the equation as much as possible by: combining like terms, removing parentheses using
Algebra Concepts Equation Solving Flow Chart Page of 6 How Do I Solve This Equation? First, simplify both sides of the equation as much as possible by: combining like terms, removing parentheses using
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example degree of a monomial. degree of a polynomial. end behavior. leading coefficient.
 CHAPTER 6 Vocabular The table contains important vocabular terms from Chapter 6. As ou work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifing eample. Term Page Definition Clarifing
CHAPTER 6 Vocabular The table contains important vocabular terms from Chapter 6. As ou work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifing eample. Term Page Definition Clarifing
