Brief Review of Exam Topics
|
|
|
- Gavin Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math 32A Discussion Session Week 3 Notes October 17 and 19, 2017 We ll use this week s discussion session to prepare for the first midterm. We ll start with a quick rundown of the relevant topics, and then proceed to work examples and answer questions as requested. It s important to note that I m not writing the exam, so nothing presented here or in section should be taken as an indication of what you ll see on exam day. Brief Review of Exam Topics Vectors We first thought of vectors as a basepoint-terminal point pair, and denoted the vector from P to Q by P Q. We say that the vectors P 0 Q 0 and P 1 Q 1 are equivalent if they translate to one another. More simply, they have the same components. The algebraic operations of addition and scalar multiplication are defined on vectors. Graphically we have: In terms of components, these operations are all done component-wise. The magnitude of a vector is defined to be the distance from its basepoint to its terminal point. In components we have a, b, c = a 2 + b 2 + c 2. A linear combination of the vectors v and w is a vector av + bw, where a and b are scalars. If we restrict the scalars to the range 0 a, b 1, the set of linear combinations is called the parallelogram spanned by v and w. Parametrized Lines We describe the line that passes through the point (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) in the direction of v = a, b, c by r(t) = x 0, y 0, z 0 + t a, b, c, 1
2 called a vector parametrization of our line, and also by x(t) = x 0 + at, y(t) = y 0 + bt, z(t) = z 0 + ct, called a set of parametric equations for our line. There are various parametrizations and sets of parametric equations for the same line. Given a parametrization, we often call the point associated to it the initial point and its vector the velocity vector. The speed of the parametrization is the magnitude of the velocity vector. The Dot Product Whenever two vectors have a common number of components, their dot product is defined and is a scalar. Specifically, if u = u 1,..., u n and v = v 1,..., v n, then u v = u 1 v u n v n. The dot product also has a very important geometric interpretation. If θ is the angle between u and v (we always assume that θ [0, π]), then Some important observations: u u = u u cos 0 = u 2 ; u v = 0 if and only if u v; u v = u v cos θ. u v > 0 if and only if θ is acute, and u v < 0 if and only if θ is obtuse. We can rewrite the above equation as a formula which allows us to compute θ: ( ) u v θ = arccos. u v We can also use the dot product to compute the projection of a vector u onto a line L that passes through the basepoint of u. If v is any nonzero vector on L, then the projection of u onto L is given by proj L u = u v v v v. We sometimes write proj L u as proj v u. The Cross Product The cross product is defined only for pairs of three-dimensional vectors. Also unlike the dot product, its output is another three-dimensional vector.the cross product of vectors v = v 1, v 2, v 3 and w = w 1, w 2, w 3 is the vector v w = v 1 v 2 v 3 w 1 w 2 w 3 = v 2 v 3 w 2 w 3 i v 1 v 3 w 1 w 3 j + v 1 v 2 w 1 w 2 k. 2
3 Like the dot product, we start with an algebraic definition, but we really prefer the geometric description. The cross product v w is the unique vector for which v w is orthogonal to both v and w; v w has length v w sin θ; {v, w, v w} forms a right-handed system. Some important observations: w v = v w; v w = 0 if and only if w = λv for some λ R or v = 0; the cross product distributes across sums. The cross product can be used to compute areas. If P is the parallelogram spanned by the vectors v and w, then Area(P) = v w. The cross product can be used alongside the dot product to compute volumes. If P is the parallelepiped spanned by the vectors u, v, and w, then Examples Vol(P) = u (v w). Example 1. ( 13.1, Exercise 69 of the textbook) Use vectors to prove that the diagonals AC and BD of a parallelogram bisect each other. (See figure.) (Solution) Let v = AB and let w = AD. Then C is at the terminal point of v + w, so 1(v + w) is the midpoint of AC. The vector DB is given by v w, so the midpoint of BD is w + 1 (v w), 2 obtained by starting at D and moving half the distance towards B. But w (v w) = 1 2 (v + w), so the midpoint of BD is the same as the midpoint of AC, meaning that the diagonals bisect each other. 2 Example 2. ( 13.2, Exercise 64) Find a vector parametrization for the line x 5 9 = y = z 10. 3
4 (Solution) We ll find two parametrizations: one that works, and one that s much nicer. The first approach is to just let x = t. This leads us to the equations y = t 5 9 y = 7 9 t and z 10 = t 5 z = t , which gives us a perfectly acceptable parametrization of the line: r(t) = 0, 62 9, t 1, 7 9, 1 9 We can find a more pleasant solution, though. Instead of letting x = t, let s choose x so that the expression (x 5)/9 simplifies to t. Setting (x 5)/9 = t yields x = 9t + 5. We then have (y + 3)/7 = t and z 10 = t, giving us This leads to the much nicer parametrization y = 7t 3 z = t r(t) = 5, 3, 10 + t 9, 7, 1. Assuming the common value to be t is generally a good strategy for turning symmetric parametric equations into a nice parametrization for a line. Example 3. ( 13.3, Exercise 92) Use the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality v w v w to prove the triangle inequality: v + w v + w. (Solution) We can write the square of v + w as. v + w 2 = (v + w) (v + w) = (v + w) (v + w). According to the triangle inequality for numbers we have (v + w) (v + w) = v v + 2v w + ww v v w + w 2. Applying the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality to the middle term on the right hand side, we see that v + w 2 = (v + w) (v + w) v v w + w 2 = ( v + w ) 2. So v + w 2 ( v + w ) 2. Since both v + w and v + w are non-negative, we may take the square root on both sides of this inequality to conclude that v + w v + w. Example 4. The vectors l, 0, 0, 0, w, 0, and 0, 0, h span a rectangular prism with length l, width w, an height h. Use the triple scalar product to verify that this rectangular prism has volume lwh. 4
5 (Solution) Write the vectors as l = l, 0, 0, w = 0, w, 0, h = 0, 0, h. Then the volume of the prism spanned by these vectors is V = l (w h). We first compute w h: Then as we suspected. w h = 0 w h = wh, 0, 0. V = l, 0, 0 wh, 0, 0 = lwh, Example 5. ( 13.4, Exercise 39) Compute the volume of the parallelepiped spanned by u = 1, 0, 0, v = 0, 2, 0, w = 1, 1, 2. (Solution) We have V = u (v w). Note that the order of our vectors in the triple scalar product doesn t affect the result, but it can affect how much work we do. Let s be super lazy. Since we see that the vectors u and v have two zeros each, let s make sure they show up in the cross product we have to compute. That is, we ll compute the volume using V = w (u v). We have so u v = = 0, 0, 2, V = 1, 1, 2 0, 0, 2 = 4. Example 6. ( 13.4, Exercise 45) Use cross products to find the area of the triangle in the xy-plane defined by (1, 2), (3, 4), and ( 2, 2). (Solution) Let s outline our approach: we ll fix one of the vertices of the triangle as a basepoint and consider the vectors v and w taking us to the other vertices. Treating these as vectors in three dimensions, we can use the cross product to compute the area of the parallelogram spanned by these vectors. The area of the triangle will be one half of this area. Treat (1, 2) as the basepoint, so that the vectors v = 2, 2 and w = 3, 0 span our triangle. Because the cross product is only defined in three dimensions, we ll actually write v = 2, 2, 0 and w = 3, 0, 0, since the z-component of these vectors is zero. Then Area(P) = v w, 5
6 so we compute v w = = 0, 0, 6, so v w = 6. We conclude that the triangle has area 3. Example 7. ( 13.4, Exercise 75) Show that if a, b are nonzero vectors such that a b, then there exists a vector X such that a X = b. (Solution) Let v = a b, and let w = a v. Then w is perpendicular to both a and v. But b is also perpendicular to both a (by assumption) and v (because v = a b). So w = λb for some scalar λ. Because v is perpendicular to a, the cross product w is nonzero, so λ 0. So we may let X = 1 λ v. Then a X = 1 λ a v = 1 λ w = b, just as we hoped. 6
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017
 Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017 Since we didn t get a chance to discuss parametrized lines last week, we may spend some time discussing those before moving on to the dot
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 2 Notes October 10 and 12, 2017 Since we didn t get a chance to discuss parametrized lines last week, we may spend some time discussing those before moving on to the dot
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012
 Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Math 241, Exam 1 Information.
 Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
3 = arccos. A a and b are parallel, B a and b are perpendicular, C a and b are normalized, or D this is always true.
 Math 210-101 Test #1 Sept. 16 th, 2016 Name: Answer Key Be sure to show your work! 1. (20 points) Vector Basics: Let v = 1, 2,, w = 1, 2, 2, and u = 2, 1, 1. (a) Find the area of a parallelogram spanned
Math 210-101 Test #1 Sept. 16 th, 2016 Name: Answer Key Be sure to show your work! 1. (20 points) Vector Basics: Let v = 1, 2,, w = 1, 2, 2, and u = 2, 1, 1. (a) Find the area of a parallelogram spanned
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Detailed objectives are given in each of the sections listed below. 1. Cartesian Space Coordinates. 2. Displacements, Forces, Velocities and Vectors
 Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
Unit 1 Vectors In this unit, we introduce vectors, vector operations, and equations of lines and planes. Note: Unit 1 is based on Chapter 12 of the textbook, Salas and Hille s Calculus: Several Variables,
Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10
 Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10 Frank Luna, September 6, 009 Solutions to Part I Chapter 1 1. Let u = 1, and v = 3, 4. Perform the following computations and
Exercise Solutions for Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 10 Frank Luna, September 6, 009 Solutions to Part I Chapter 1 1. Let u = 1, and v = 3, 4. Perform the following computations and
1 Vector Geometry in Two and Three Dimensions
 1 Vector Geometry in Two and Three Dimensions 1.1 Vectors in Two Dimensions You ve probably heard of vectors as objects with both magnitude and direction, or something along these lines. Another way to
1 Vector Geometry in Two and Three Dimensions 1.1 Vectors in Two Dimensions You ve probably heard of vectors as objects with both magnitude and direction, or something along these lines. Another way to
12.1. Cartesian Space
 12.1. Cartesian Space In most of your previous math classes, we worked with functions on the xy-plane only meaning we were working only in 2D. Now we will be working in space, or rather 3D. Now we will
12.1. Cartesian Space In most of your previous math classes, we worked with functions on the xy-plane only meaning we were working only in 2D. Now we will be working in space, or rather 3D. Now we will
1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus Rectangular Coordinate Systems... 4
 MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
Review of Coordinate Systems
 Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
MAC Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II
 MAC 2103 Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the cross product of a vector in R 3. 2. Determine a scalar triple
MAC 2103 Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the cross product of a vector in R 3. 2. Determine a scalar triple
Section 13.4 The Cross Product
 Section 13.4 The Cross Product Multiplying Vectors 2 In this section we consider the more technical multiplication which can be defined on vectors in 3-space (but not vectors in 2-space). 1. Basic Definitions
Section 13.4 The Cross Product Multiplying Vectors 2 In this section we consider the more technical multiplication which can be defined on vectors in 3-space (but not vectors in 2-space). 1. Basic Definitions
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University. Shari Ultman
 Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
Course Notes Math 275 Boise State University Shari Ultman Fall 2017 Contents 1 Vectors 1 1.1 Introduction to 3-Space & Vectors.............. 3 1.2 Working With Vectors.................... 7 1.3 Introduction
The Cross Product of Two Vectors
 The Cross roduct of Two Vectors In proving some statements involving surface integrals, there will be a need to approximate areas of segments of the surface by areas of parallelograms. Therefore it is
The Cross roduct of Two Vectors In proving some statements involving surface integrals, there will be a need to approximate areas of segments of the surface by areas of parallelograms. Therefore it is
Calculus 1 for AE (WI1421LR) Lecture 1: 12.3 The dot product 12.4 The cross product
 Calculus 1 for AE (WI1421LR) : 12.3 The dot product 12.4 The cross product About this course Textbook James Stewart, Calculus, Early Transcendentals, 7th edition Course Coordinator Dr. Roelof Koekoek,
Calculus 1 for AE (WI1421LR) : 12.3 The dot product 12.4 The cross product About this course Textbook James Stewart, Calculus, Early Transcendentals, 7th edition Course Coordinator Dr. Roelof Koekoek,
MAT 1339-S14 Class 8
 MAT 1339-S14 Class 8 July 28, 2014 Contents 7.2 Review Dot Product........................... 2 7.3 Applications of the Dot Product..................... 4 7.4 Vectors in Three-Space.........................
MAT 1339-S14 Class 8 July 28, 2014 Contents 7.2 Review Dot Product........................... 2 7.3 Applications of the Dot Product..................... 4 7.4 Vectors in Three-Space.........................
Name: ID: Math 233 Exam 1. Page 1
 Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
Lecture 2: Vector-Vector Operations
 Lecture 2: Vector-Vector Operations Vector-Vector Operations Addition of two vectors Geometric representation of addition and subtraction of vectors Vectors and points Dot product of two vectors Geometric
Lecture 2: Vector-Vector Operations Vector-Vector Operations Addition of two vectors Geometric representation of addition and subtraction of vectors Vectors and points Dot product of two vectors Geometric
Distance Formula in 3-D Given any two points P 1 (x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and P 2 (x 2, y 2, z 2 ) the distance between them is ( ) ( ) ( )
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
Vectors and the Geometry of Space Vector Space The 3-D coordinate system (rectangular coordinates ) is the intersection of three perpendicular (orthogonal) lines called coordinate axis: x, y, and z. Their
10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products
 Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today The Dot Product Equations of Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/29 Direction angles and Direction cosines Projections Definitions: 1. a : a 1, a 2, a 3, b : b 1, b 2, b 3, a
What you will learn today The Dot Product Equations of Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/29 Direction angles and Direction cosines Projections Definitions: 1. a : a 1, a 2, a 3, b : b 1, b 2, b 3, a
The Cross Product. Philippe B. Laval. Spring 2012 KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) The Cross Product Spring /
 The Cross Product Philippe B Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) The Cross Product Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction The cross product is the second multiplication operation between vectors we will
The Cross Product Philippe B Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B Laval (KSU) The Cross Product Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction The cross product is the second multiplication operation between vectors we will
Dot Products. K. Behrend. April 3, Abstract A short review of some basic facts on the dot product. Projections. The spectral theorem.
 Dot Products K. Behrend April 3, 008 Abstract A short review of some basic facts on the dot product. Projections. The spectral theorem. Contents The dot product 3. Length of a vector........................
Dot Products K. Behrend April 3, 008 Abstract A short review of some basic facts on the dot product. Projections. The spectral theorem. Contents The dot product 3. Length of a vector........................
Multiple Choice. 1.(6 pts) Find symmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (2, 5, 1) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3y z = 9.
 Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
Multiple Choice.(6 pts) Find smmetric equations of the line L passing through the point (, 5, ) and perpendicular to the plane x + 3 z = 9. (a) x = + 5 3 = z (c) (x ) + 3( 3) (z ) = 9 (d) (e) x = 3 5 =
Midterm 1 Review. Distance = (x 1 x 0 ) 2 + (y 1 y 0 ) 2.
 Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
Midterm 1 Review Comments about the midterm The midterm will consist of five questions and will test on material from the first seven lectures the material given below. No calculus either single variable
n=0 ( 1)n /(n + 1) converges, but not
 Math 07H Topics for the third exam (and beyond) (Technically, everything covered on the first two exams plus...) Absolute convergence and alternating series A series a n converges absolutely if a n converges.
Math 07H Topics for the third exam (and beyond) (Technically, everything covered on the first two exams plus...) Absolute convergence and alternating series A series a n converges absolutely if a n converges.
which has a check digit of 9. This is consistent with the first nine digits of the ISBN, since
 vector Then the check digit c is computed using the following procedure: 1. Form the dot product. 2. Divide by 11, thereby producing a remainder c that is an integer between 0 and 10, inclusive. The check
vector Then the check digit c is computed using the following procedure: 1. Form the dot product. 2. Divide by 11, thereby producing a remainder c that is an integer between 0 and 10, inclusive. The check
MTH 2310, FALL Introduction
 MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
Vector Geometry. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at
Chapter 5 Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at
Math 290, Midterm II-key
 Math 290, Midterm II-key Name (Print): (first) Signature: (last) The following rules apply: There are a total of 20 points on this 50 minutes exam. This contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and
Math 290, Midterm II-key Name (Print): (first) Signature: (last) The following rules apply: There are a total of 20 points on this 50 minutes exam. This contains 7 pages (including this cover page) and
4.1 Distance and Length
 Chapter Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at vectors
Chapter Vector Geometry In this chapter we will look more closely at certain geometric aspects of vectors in R n. We will first develop an intuitive understanding of some basic concepts by looking at vectors
MATH 12 CLASS 4 NOTES, SEP
 MATH 12 CLASS 4 NOTES, SEP 28 2011 Contents 1. Lines in R 3 1 2. Intersections of lines in R 3 2 3. The equation of a plane 4 4. Various problems with planes 5 4.1. Intersection of planes with planes or
MATH 12 CLASS 4 NOTES, SEP 28 2011 Contents 1. Lines in R 3 1 2. Intersections of lines in R 3 2 3. The equation of a plane 4 4. Various problems with planes 5 4.1. Intersection of planes with planes or
F F. proj cos( ) v. v proj v
 Geometric Definition of Dot Product 1.2 The Dot Product Suppose you are pulling up on a rope attached to a box, as shown above. How would you find the force moving the box towards you? As stated above,
Geometric Definition of Dot Product 1.2 The Dot Product Suppose you are pulling up on a rope attached to a box, as shown above. How would you find the force moving the box towards you? As stated above,
Math Vector Calculus II
 Math 255 - Vector Calculus II Review Notes Vectors We assume the reader is familiar with all the basic concepts regarding vectors and vector arithmetic, such as addition/subtraction of vectors in R n,
Math 255 - Vector Calculus II Review Notes Vectors We assume the reader is familiar with all the basic concepts regarding vectors and vector arithmetic, such as addition/subtraction of vectors in R n,
Chapter 2: Vector Geometry
 Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Daniel Chan UNSW Semester 1 2018 Daniel Chan (UNSW) Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Semester 1 2018 1 / 32 Goals of this chapter In this chapter, we will answer the following geometric
Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Daniel Chan UNSW Semester 1 2018 Daniel Chan (UNSW) Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Semester 1 2018 1 / 32 Goals of this chapter In this chapter, we will answer the following geometric
Vectors, dot product, and cross product
 MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
Main topics for the First Midterm Exam
 Main topics for the First Midterm Exam The final will cover Sections.-.0, 2.-2.5, and 4.. This is roughly the material from first three homeworks and three quizzes, in addition to the lecture on Monday,
Main topics for the First Midterm Exam The final will cover Sections.-.0, 2.-2.5, and 4.. This is roughly the material from first three homeworks and three quizzes, in addition to the lecture on Monday,
(arrows denote positive direction)
 12 Chapter 12 12.1 3-dimensional Coordinate System The 3-dimensional coordinate system we use are coordinates on R 3. The coordinate is presented as a triple of numbers: (a,b,c). In the Cartesian coordinate
12 Chapter 12 12.1 3-dimensional Coordinate System The 3-dimensional coordinate system we use are coordinates on R 3. The coordinate is presented as a triple of numbers: (a,b,c). In the Cartesian coordinate
Math 3c Solutions: Exam 1 Fall Graph by eliiminating the parameter; be sure to write the equation you get when you eliminate the parameter.
 Math c Solutions: Exam 1 Fall 16 1. Graph by eliiminating the parameter; be sure to write the equation you get when you eliminate the parameter. x tan t x tan t y sec t y sec t t π 4 To eliminate the parameter,
Math c Solutions: Exam 1 Fall 16 1. Graph by eliiminating the parameter; be sure to write the equation you get when you eliminate the parameter. x tan t x tan t y sec t y sec t t π 4 To eliminate the parameter,
Extra Problems for Math 2050 Linear Algebra I
 Extra Problems for Math 5 Linear Algebra I Find the vector AB and illustrate with a picture if A = (,) and B = (,4) Find B, given A = (,4) and [ AB = A = (,4) and [ AB = 8 If possible, express x = 7 as
Extra Problems for Math 5 Linear Algebra I Find the vector AB and illustrate with a picture if A = (,) and B = (,4) Find B, given A = (,4) and [ AB = A = (,4) and [ AB = 8 If possible, express x = 7 as
Math 416, Spring 2010 More on Algebraic and Geometric Properties January 21, 2010 MORE ON ALGEBRAIC AND GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES
 Math 46, Spring 2 More on Algebraic and Geometric Properties January 2, 2 MORE ON ALGEBRAIC AND GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES Algebraic properties Algebraic properties of matrix/vector multiplication Last time
Math 46, Spring 2 More on Algebraic and Geometric Properties January 2, 2 MORE ON ALGEBRAIC AND GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES Algebraic properties Algebraic properties of matrix/vector multiplication Last time
The Cross Product. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan The Cross Product
 The Cross Product MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Introduction Recall: the dot product of two vectors is a scalar. There is another binary operation on vectors
The Cross Product MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Introduction Recall: the dot product of two vectors is a scalar. There is another binary operation on vectors
Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors.
 Vectors summary Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors. AB is the position vector of B relative to A and is the vector
Vectors summary Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors. AB is the position vector of B relative to A and is the vector
Analytic Geometry MAT 1035
 Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
Solution to Homework 1
 Solution to Homework 1 Olena Bormashenko September, 0 Section 1.1:, 5b)d), 7b)f), 8a)b), ; Section 1.:, 5, 7, 9, 10, b)c), 1, 15b), 3 Section 1.1. In each of the following cases, find a point that is two-thirds
Solution to Homework 1 Olena Bormashenko September, 0 Section 1.1:, 5b)d), 7b)f), 8a)b), ; Section 1.:, 5, 7, 9, 10, b)c), 1, 15b), 3 Section 1.1. In each of the following cases, find a point that is two-thirds
45. The Parallelogram Law states that. product of a and b is the vector a b a 2 b 3 a 3 b 2, a 3 b 1 a 1 b 3, a 1 b 2 a 2 b 1. a c. a 1. b 1.
 SECTION 10.4 THE CROSS PRODUCT 537 42. Suppose that all sides of a quadrilateral are equal in length and opposite sides are parallel. Use vector methods to show that the diagonals are perpendicular. 43.
SECTION 10.4 THE CROSS PRODUCT 537 42. Suppose that all sides of a quadrilateral are equal in length and opposite sides are parallel. Use vector methods to show that the diagonals are perpendicular. 43.
Math 107. Rumbos Fall Solutions to Review Problems for Exam 1
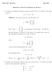 Math 07. Rumbos Fall 0 Solutions to Review Problems for Exam. Compute the (shortest) distance from the point P (4, 0, 7) in R 3 to the plane given by 4x y 3z =. Solution: The point P o (3, 0, 0) is in
Math 07. Rumbos Fall 0 Solutions to Review Problems for Exam. Compute the (shortest) distance from the point P (4, 0, 7) in R 3 to the plane given by 4x y 3z =. Solution: The point P o (3, 0, 0) is in
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS. MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 018 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up 1. Version A. Find the center
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 018 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up 1. Version A. Find the center
Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS
 1. True or False (and give a short reason): Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS (a) If the parametric curve x = f(t), y = g(t) satisfies g (1) = 0, then it has a horizontal tangent line when t = 1. FALSE: To make
1. True or False (and give a short reason): Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS (a) If the parametric curve x = f(t), y = g(t) satisfies g (1) = 0, then it has a horizontal tangent line when t = 1. FALSE: To make
Math 2433 Notes Week The Dot Product. The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b
 Math 2433 Notes Week 2 11.3 The Dot Product The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b a b 3) Given, a = 4i + 4j, b = i - 2j + 3k, c = 2i + 2k Find the angle between a and c Projection
Math 2433 Notes Week 2 11.3 The Dot Product The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b a b 3) Given, a = 4i + 4j, b = i - 2j + 3k, c = 2i + 2k Find the angle between a and c Projection
Overview of vector calculus. Coordinate systems in space. Distance formula. (Sec. 12.1)
 Math 20C Multivariable Calculus Lecture 1 1 Coordinates in space Slide 1 Overview of vector calculus. Coordinate systems in space. Distance formula. (Sec. 12.1) Vector calculus studies derivatives and
Math 20C Multivariable Calculus Lecture 1 1 Coordinates in space Slide 1 Overview of vector calculus. Coordinate systems in space. Distance formula. (Sec. 12.1) Vector calculus studies derivatives and
Math 302 Test 1 Review
 Math Test Review. Given two points in R, x, y, z and x, y, z, show the point x + x, y + y, z + z is on the line between these two points and is the same distance from each of them. The line is rt x, y,
Math Test Review. Given two points in R, x, y, z and x, y, z, show the point x + x, y + y, z + z is on the line between these two points and is the same distance from each of them. The line is rt x, y,
Analytic Geometry MAT 1035
 Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
The Cross Product. In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications.
 The Cross Product In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications. THE CROSS PRODUCT The cross product a x b of two vectors a and b, unlike the dot product, is a
The Cross Product In this section, we will learn about: Cross products of vectors and their applications. THE CROSS PRODUCT The cross product a x b of two vectors a and b, unlike the dot product, is a
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP Contents. 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2
 MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS
 MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS 1. HW 1: Due September 4 1.1.21. Suppose v, w R n and c is a scalar. Prove that Span(v + cw, w) = Span(v, w). We must prove two things: that every element
MATH 221: SOLUTIONS TO SELECTED HOMEWORK PROBLEMS 1. HW 1: Due September 4 1.1.21. Suppose v, w R n and c is a scalar. Prove that Span(v + cw, w) = Span(v, w). We must prove two things: that every element
Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space Many quantities in geometry and physics, such as area, volume, temperature, mass, and time, can be characterized by a single real number scaled to appropriate units of
Vectors and the Geometry of Space Many quantities in geometry and physics, such as area, volume, temperature, mass, and time, can be characterized by a single real number scaled to appropriate units of
v = ( 2)
 Chapter : Introduction to Vectors.. Vectors and linear combinations Let s begin by saying what vectors are: They are lists of numbers. If there are numbers in the list, there is a natural correspondence
Chapter : Introduction to Vectors.. Vectors and linear combinations Let s begin by saying what vectors are: They are lists of numbers. If there are numbers in the list, there is a natural correspondence
58. The Triangle Inequality for vectors is. dot product.] 59. The Parallelogram Law states that
![58. The Triangle Inequality for vectors is. dot product.] 59. The Parallelogram Law states that 58. The Triangle Inequality for vectors is. dot product.] 59. The Parallelogram Law states that](/thumbs/86/94310732.jpg) 786 CAPTER 12 VECTORS AND TE GEOETRY OF SPACE 0, 0, 1, and 1, 1, 1 as shown in the figure. Then the centroid is. ( 1 2, 1 2, 1 2 ) ] x z C 54. If c a a, where a,, and c are all nonzero vectors, show that
786 CAPTER 12 VECTORS AND TE GEOETRY OF SPACE 0, 0, 1, and 1, 1, 1 as shown in the figure. Then the centroid is. ( 1 2, 1 2, 1 2 ) ] x z C 54. If c a a, where a,, and c are all nonzero vectors, show that
web: HOMEWORK 1
 MAT 207 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2009207 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics Instructor: Engin Mermut web: http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK VECTORS IN THE n-dimensional
MAT 207 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2009207 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics Instructor: Engin Mermut web: http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK VECTORS IN THE n-dimensional
MATH 19520/51 Class 2
 MATH 19520/51 Class 2 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-09-27 1 Review dot product. 2 Angles between vectors and orthogonality. 3 Projection of one vector onto another. 4 Cross product and its
MATH 19520/51 Class 2 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-09-27 1 Review dot product. 2 Angles between vectors and orthogonality. 3 Projection of one vector onto another. 4 Cross product and its
Math 8 Winter 2010 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions - 1. xcos 6xdx = 4. = x2 4
 Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions - 1 1 Evaluate xcos 2 3x Solution: First rewrite cos 2 3x using the half-angle formula: ( ) 1 + cos 6x xcos 2 3x = x = 1 x + 1 xcos 6x. 2 2 2 Now use
Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions - 1 1 Evaluate xcos 2 3x Solution: First rewrite cos 2 3x using the half-angle formula: ( ) 1 + cos 6x xcos 2 3x = x = 1 x + 1 xcos 6x. 2 2 2 Now use
1.2 LECTURE 2. Scalar Product
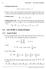 6 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Pythagean theem. cos 2 α 1 + cos 2 α 2 + cos 2 α 3 = 1 There is a one-to-one crespondence between the components of the vect on the one side and its magnitude and the direction
6 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Pythagean theem. cos 2 α 1 + cos 2 α 2 + cos 2 α 3 = 1 There is a one-to-one crespondence between the components of the vect on the one side and its magnitude and the direction
MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 2018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART
 Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and
Math 141 Name: MIDTERM 4 PART 1 (CHAPTERS 5 AND 6: ANALYTIC & MISC. TRIGONOMETRY) MATH 141 FALL 018 KUNIYUKI 150 POINTS TOTAL: 47 FOR PART 1, AND 103 FOR PART Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide
 Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Linear Algebra Homework and Study Guide Phil R. Smith, Ph.D. February 28, 20 Homework Problem Sets Organized by Learning Outcomes Test I: Systems of Linear Equations; Matrices Lesson. Give examples of
Practical Linear Algebra: A Geometry Toolbox
 Practical Linear Algebra: A Geometry Toolbox Third edition Chapter 2: Here and There: Points and Vectors in 2D Gerald Farin & Dianne Hansford CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, An A K Peters Book www.farinhansford.com/books/pla
Practical Linear Algebra: A Geometry Toolbox Third edition Chapter 2: Here and There: Points and Vectors in 2D Gerald Farin & Dianne Hansford CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, An A K Peters Book www.farinhansford.com/books/pla
Introduction to Vectors
 Introduction to Vectors K. Behrend January 31, 008 Abstract An introduction to vectors in R and R 3. Lines and planes in R 3. Linear dependence. 1 Contents Introduction 3 1 Vectors 4 1.1 Plane vectors...............................
Introduction to Vectors K. Behrend January 31, 008 Abstract An introduction to vectors in R and R 3. Lines and planes in R 3. Linear dependence. 1 Contents Introduction 3 1 Vectors 4 1.1 Plane vectors...............................
SUMMARY OF MATH 1600
 SUMMARY OF MATH 1600 Note: The following list is intended as a study guide for the final exam. It is a continuation of the study guide for the midterm. It does not claim to be a comprehensive list. You
SUMMARY OF MATH 1600 Note: The following list is intended as a study guide for the final exam. It is a continuation of the study guide for the midterm. It does not claim to be a comprehensive list. You
Vector Supplement Part 1: Vectors
 Vector Supplement Part 1: Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are drawn as directed line segments and are denoted by boldface letters a or by a. The magnitude
Vector Supplement Part 1: Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are drawn as directed line segments and are denoted by boldface letters a or by a. The magnitude
Quiz 2 Practice Problems
 Quiz Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not essential.
Quiz Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not essential.
Definitions for Quizzes
 Definitions for Quizzes Italicized text (or something close to it) will be given to you. Plain text is (an example of) what you should write as a definition. [Bracketed text will not be given, nor does
Definitions for Quizzes Italicized text (or something close to it) will be given to you. Plain text is (an example of) what you should write as a definition. [Bracketed text will not be given, nor does
MATH Calculus III Fall 2009 Homework 1 - Solutions
 MATH 2300 - Calculus III Fall 2009 Homework 1 - Solutions 1. Find the equations of the two spheres that are tangent with equal radii whose centers are ( 3, 1, 2) and (5, 3, 6). SOLUTION: In order for the
MATH 2300 - Calculus III Fall 2009 Homework 1 - Solutions 1. Find the equations of the two spheres that are tangent with equal radii whose centers are ( 3, 1, 2) and (5, 3, 6). SOLUTION: In order for the
Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008
 Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008 Exam 2 will be held on Tuesday, April 8, 7-8pm in 117 MacMillan What will be covered The exam will cover material from the lectures
Math 520 Exam 2 Topic Outline Sections 1 3 (Xiao/Dumas/Liaw) Spring 2008 Exam 2 will be held on Tuesday, April 8, 7-8pm in 117 MacMillan What will be covered The exam will cover material from the lectures
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Vectors Year 12 Term 1
 Vectors Year 12 Term 1 1 Vectors - A Vector has Two properties Magnitude and Direction - A vector is usually denoted in bold, like vector a, or a, or many others. In 2D - a = xı + yȷ - a = x, y - where,
Vectors Year 12 Term 1 1 Vectors - A Vector has Two properties Magnitude and Direction - A vector is usually denoted in bold, like vector a, or a, or many others. In 2D - a = xı + yȷ - a = x, y - where,
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Midterm 1 Review Solutions
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 11 Midterm 1 Review Solutions 11.1: #19 Particle starts at point ( 1,, traces out a semicircle in the counterclockwise direction, ending at the point (1,. 11.1:
SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math 21a, Spring 2003
 SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math a, Spring 3 Problem ) ( points) Circle for each of the questions the correct letter. No justifications are needed. Your score will be C W where C is the number of
SOLUTIONS TO SECOND PRACTICE EXAM Math a, Spring 3 Problem ) ( points) Circle for each of the questions the correct letter. No justifications are needed. Your score will be C W where C is the number of
Linear Algebra I for Science (NYC)
 Element No. 1: To express concrete problems as linear equations. To solve systems of linear equations using matrices. Topic: MATRICES 1.1 Give the definition of a matrix, identify the elements and the
Element No. 1: To express concrete problems as linear equations. To solve systems of linear equations using matrices. Topic: MATRICES 1.1 Give the definition of a matrix, identify the elements and the
Vectors and Plane Geometry
 Vectors and Plane Geometry Karl Heinz Dovermann Professor of Mathematics University of Hawaii January 7, 0 Preface During the first week of the semester it is difficult to get started with the course
Vectors and Plane Geometry Karl Heinz Dovermann Professor of Mathematics University of Hawaii January 7, 0 Preface During the first week of the semester it is difficult to get started with the course
1. Vectors in the Plane
 CHAPTER 10 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1. Vectors in the Plane We denote the directed line segment from the point P (initial point) to the!! point Q (terminal point) as P Q. The length of P Q is
CHAPTER 10 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1. Vectors in the Plane We denote the directed line segment from the point P (initial point) to the!! point Q (terminal point) as P Q. The length of P Q is
LB 220 Homework 2 (due Tuesday, 01/22/13)
 LB 220 Homework 2 (due Tuesday, 01/22/13) Directions. Please solve the problems below. Your solutions must begin with a clear statement (or re-statement in your own words) of the problem. You solutions
LB 220 Homework 2 (due Tuesday, 01/22/13) Directions. Please solve the problems below. Your solutions must begin with a clear statement (or re-statement in your own words) of the problem. You solutions
Announcements September 19
 Announcements September 19 Please complete the mid-semester CIOS survey this week The first midterm will take place during recitation a week from Friday, September 3 It covers Chapter 1, sections 1 5 and
Announcements September 19 Please complete the mid-semester CIOS survey this week The first midterm will take place during recitation a week from Friday, September 3 It covers Chapter 1, sections 1 5 and
Intro Vectors 2D implicit curves 2D parametric curves. Graphics 2011/2012, 4th quarter. Lecture 2: vectors, curves, and surfaces
 Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: Tutorial 1 will be online later today TA sessions for questions start next week Practicals: Exams: Make sure to find a team partner very
Lecture 2, curves, and surfaces Organizational remarks Tutorials: Tutorial 1 will be online later today TA sessions for questions start next week Practicals: Exams: Make sure to find a team partner very
Mathematics 2203, Test 1 - Solutions
 Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
NOTES ON VECTORS, PLANES, AND LINES
 NOTES ON VECTORS, PLANES, AND LINES DAVID BEN MCREYNOLDS 1. Vectors I assume that the reader is familiar with the basic notion of a vector. The important feature of the vector is that it has a magnitude
NOTES ON VECTORS, PLANES, AND LINES DAVID BEN MCREYNOLDS 1. Vectors I assume that the reader is familiar with the basic notion of a vector. The important feature of the vector is that it has a magnitude
This pre-publication material is for review purposes only. Any typographical or technical errors will be corrected prior to publication.
 This pre-publication material is for review purposes only. Any typographical or technical errors will be corrected prior to publication. Copyright Pearson Canada Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright Pearson
This pre-publication material is for review purposes only. Any typographical or technical errors will be corrected prior to publication. Copyright Pearson Canada Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright Pearson
1 Vectors. c Kun Wang. Math 151, Fall Vector Supplement
 Vector Supplement 1 Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are drawn as directed line segments and are denoted by boldface letters a or by a. The magnitude of a vector
Vector Supplement 1 Vectors A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Vectors are drawn as directed line segments and are denoted by boldface letters a or by a. The magnitude of a vector
EGR2013 Tutorial 8. Linear Algebra. Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial
 EGR1 Tutorial 8 Linear Algebra Outline Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial Vector Algebra Vector Spaces Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial If A is a square matrix, then we define the nonnegative
EGR1 Tutorial 8 Linear Algebra Outline Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial Vector Algebra Vector Spaces Powers of a Matrix and Matrix Polynomial If A is a square matrix, then we define the nonnegative
Solutions to Math 51 First Exam October 13, 2015
 Solutions to Math First Exam October 3, 2. (8 points) (a) Find an equation for the plane in R 3 that contains both the x-axis and the point (,, 2). The equation should be of the form ax + by + cz = d.
Solutions to Math First Exam October 3, 2. (8 points) (a) Find an equation for the plane in R 3 that contains both the x-axis and the point (,, 2). The equation should be of the form ax + by + cz = d.
Inner products. Theorem (basic properties): Given vectors u, v, w in an inner product space V, and a scalar k, the following properties hold:
 Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
SOME PROBLEMS YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO DO
 OME PROBLEM YOU HOULD BE ABLE TO DO I ve attempted to make a list of the main calculations you should be ready for on the exam, and included a handful of the more important formulas. There are no examples
OME PROBLEM YOU HOULD BE ABLE TO DO I ve attempted to make a list of the main calculations you should be ready for on the exam, and included a handful of the more important formulas. There are no examples
Linear Algebra. Alvin Lin. August December 2017
 Linear Algebra Alvin Lin August 207 - December 207 Linear Algebra The study of linear algebra is about two basic things. We study vector spaces and structure preserving maps between vector spaces. A vector
Linear Algebra Alvin Lin August 207 - December 207 Linear Algebra The study of linear algebra is about two basic things. We study vector spaces and structure preserving maps between vector spaces. A vector
Linear Algebra: Homework 3
 Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August 206 - December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k
Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August 206 - December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k
Dot product. The dot product is an inner product on a coordinate vector space (Definition 1, Theorem
 Dot product The dot product is an inner product on a coordinate vector space (Definition 1, Theorem 1). Definition 1 Given vectors v and u in n-dimensional space, the dot product is defined as, n v u v
Dot product The dot product is an inner product on a coordinate vector space (Definition 1, Theorem 1). Definition 1 Given vectors v and u in n-dimensional space, the dot product is defined as, n v u v
VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE
 VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE A line in the xy-plane is determined when a point on the line and the direction of the line (its slope or angle of inclination) are given.
VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE A line in the xy-plane is determined when a point on the line and the direction of the line (its slope or angle of inclination) are given.
Final Exam - Take Home Portion Math 211, Summer 2017
 Final Exam - Take Home Portion Math 2, Summer 207 Name: Directions: Complete a total of 5 problems. Problem must be completed. The remaining problems are categorized in four groups. Select one problem
Final Exam - Take Home Portion Math 2, Summer 207 Name: Directions: Complete a total of 5 problems. Problem must be completed. The remaining problems are categorized in four groups. Select one problem
Math 234. What you should know on day one. August 28, You should be able to use general principles like. x = cos t, y = sin t, 0 t π.
 Math 234 What you should know on day one August 28, 2001 1 You should be able to use general principles like Length = ds, Area = da, Volume = dv For example the length of the semi circle x = cos t, y =
Math 234 What you should know on day one August 28, 2001 1 You should be able to use general principles like Length = ds, Area = da, Volume = dv For example the length of the semi circle x = cos t, y =
Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations.
 1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
