Scientific Investigation, Engineering, Energy, and Transformation Study Guide
|
|
|
- Anastasia Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scientific Investigation, Engineering, Energy, and Transformation Study Guide Parent Signatures: Inquiry Skills: Parent Signature: 1. Define observation: information gathered with the 5 senses a. Qualitative Observation: information described in words Give 2 examples of qualitative observations. The cat is yellow The leaves are on the ground b. Quantitative Observation: information described in numbers Give 2 examples of quantitative observations. The cat weighs 60 grams. There are 14 leaves on the tree. 2. Define inference: an explanation of data based on prior knowledge or experience The boy is crying because he know he is in trouble. Scientific Method: 3. List the 6 steps of the scientific method in order. Question, research,hypothesis, experiment, analysis, and conclusion 4. How many variables can be tested in a controlled scientific investigation? 1 5. Vocabulary Match: Hypothesis, Independent, Experiment, Control, Dependent, Scientific Method, Conclusion, Analysis i. Control The variable(s) that are constant and don t change. ii. Hypothesis An educated guess about a scientific question. iii. Conclusion Statement that sums up the results of your experiment. iv. Experiment The step where you test your hypothesis. v. Independent The variable being tested, the one that is changed. vi. Analysis This is the step after the experiment where you study your data. vii. Dependent The variable that might change because of the one you changed. viii. Scientific Method Procedures that scientists use to solve problems. 6. Write a hypothesis for the scientific question: Does soda causes kids to have more cavities? If kids drink more soda then they will have more cavities because soda has a lot of sugar which is harmful to teeth. (If then because) Mark as either QL for Qualitative or QN for Quantitative or I for Inference. 7. The clouds changed colors because it is going to rain. I 10. The sand has a mass of 98 grams. _QN 8. The ball is round. QL 11. The shirt is purple and black. QL
2 9. There are 4 lizards in the cage. _QN 12. The lizard is hiding because it is hot outside. I 13. Graphing: What does this helpful tool stand for when making a graph? Ddependent R (SKIP) Y axis M (SKIP) Independent X axis Variables: Read the following investigations and find the variables. 14. A teacher wants to know if listening to music increases students grades on a test. The teacher gets two student volunteers. The volunteers are both 12 year old boys with the same intelligence. One boy listens to music while he studies. The other boy does not. They both take the same test at the same time. The test scores are recorded. Independent: music vs. no music Dependent: grade on tests Controlled: both 12 year old boys, same intelligence, same time, same time 15. A scientist wants to know if different water temperature will affect the amount of time it takes a duck to swim across a wading pool. Two female ducks that are the same age are used in the experiment. Both wading pools are the same size and have the same amount of water in them. In one pool the temperature is 40 F and the other pool is 85 F. The speed of the ducks is measured. Independent: Different temperatures of wading pool 40 degrees and 85 degrees Dependent: speed of duck Controlled: female duck, same age, same amount of water in pool, same size pool Engineering Process: 16. What is the purpose of technology? Make life easier 17: Put the steps of the engineering process in order: Implementation - Solution Design - Evaluation - Problem Identification Problem Identification, Solution Design, Implementation, Evaluation 18. Use the steps above to fill in the blanks below. Problem Identification _ = when you identify, research, understand the cause, understand the limitations and restrictions of a real world problem. Solution Design_ = when you brainstorm, draw, and build a potential solution to a problem. Implementation/Test = when you test your solution to see if it works. Evaluation _ = when you analyze your data from your test, look at the pros and cons, re-design/refine your solution, and communicate your results.
3
4 Types of Energy and Transformations: **Energy is the ability to do work or cause change** Definition Type of Energy Real Life Example/Picture 1. The energy of position/height Potential A book at the edge of a desk A stretched out rubber band A girl at the top of a slide 2. The energy due to the motion of atoms with less/more heat 3. The movement of thermal energy from one object to another Thermal Heat The different movements of atoms in solids (vibrations), liquids (flow), and gases (scatter) as heat is added or taken away Your hand gets warm while holding a cup with hot coffee. You food warms up after being placed in an oven. 4. Energy from the sun Solar Plants use light energy to make sugar through photosynthesis. 5. Energy stored in particles/bonds of matter 6. Energy of moving electric charges and electrons in circuits. Chemical Electrical Energy stored in food before being eaten Energy stored in coal before being burned Energy in a battery before going out to the electrical circuit Electrons moving in wires connecting a battery to a light bulb. Electrons moving from an outlet to a stove 7. Energy of moving objects Kinetic A book falling to the ground A rubber band shooting through the air A girl sliding down a slide 8. Energy from the electromagnetic waves Radiant A light bulb shining light into a hallway. 9. What does the Law of Conservation of Energy state? Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It is only transformed. 10. Green plants use what type of energy during photosynthesis to help them grow? Solar/Radiant 11. Animal use chemical energy from plants/ food to move. This energy is then transformed to kinetic energy when an animal moves. 12. As heat is added to a substance, the particles of matter move faster or slower? faster 13. Explain how a rubber band goes from potential energy to kinetic energy. Potential = pull/stretch a rubber band -> Kinetic = shoot the rubber band forward Example Form of Energy (s) Example Form of Energy(s) Battery not in a circuit Chemical Apple Chemical Battery in a circuit Electrical Light Bulb Radiant Fan Mechanical/kinetic Power lines/ Power Outlet Electrical Girl at the top of a slide Potential Gasoline Chemical Toy Car Mechanical Fire Thermal
5 Label the transformations: Chemical - Thermal Solar/Radiant - Electrical Electrical Radiant/Sound Chemical electrical radiant/ thermal Chemical mechanical/kinetic Fossil Fuel Power Plant Transformation: (1) Coal has stored chemical energy when it enters a power plant. Then it gets burned and changes to thermal energy. Then the fire heats the water into (2) steam which moves up, so it has kinetic energy. The steam then spins the turbine (3) and transfers its kinetic to it. The turbine is connected to a generator (4) which converts energy to electrical which is sent through powerlines (5/6) to our houses for us to use in a variety of different ways.
Heat: the transfer of thermal energy from one substance to another. Electrons: the small particles inside an atom that have negative charge.
 GRADE 5 0 Energy: the ability to cause change OR to do work Kinetic energy: energy of motion Potential energy: energy of position (stored energy) Thermal energy: the energy that moves particles of matter
GRADE 5 0 Energy: the ability to cause change OR to do work Kinetic energy: energy of motion Potential energy: energy of position (stored energy) Thermal energy: the energy that moves particles of matter
Name: Science 3 rd 9 Weeks Test Study Guide
 Scientific Investigation 6.1 Name: Science 3 rd 9 Weeks Test Study Guide 1. Number (1-5) in order the steps of the scientific method. a. design an experiment b. draw a conclusion c. ask a questions/state
Scientific Investigation 6.1 Name: Science 3 rd 9 Weeks Test Study Guide 1. Number (1-5) in order the steps of the scientific method. a. design an experiment b. draw a conclusion c. ask a questions/state
STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA
 1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
produce sugar, which contains stored chemical energy. Most of the energy that we use on Earth originally came from the Sun.
 Conservation of Energy Energy can be in many different forms. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (energy that is
Conservation of Energy Energy can be in many different forms. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (energy that is
is energy in particles of matter. Chemical energy can be released, for example in or, when these particles react to form new substances.
 TYPES OF ENERGY Energy can be in many different. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: is the transfer of energy (energy that is associated with the of the particles
TYPES OF ENERGY Energy can be in many different. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: is the transfer of energy (energy that is associated with the of the particles
What is energy? Ability to do work (change)
 What is energy? Ability to do work (change) Remember the forms of energy! 1. Thermal Energy motion of energy in the particles of matter due to more/less heat. (Heat energy = when thermal energy is transferred)
What is energy? Ability to do work (change) Remember the forms of energy! 1. Thermal Energy motion of energy in the particles of matter due to more/less heat. (Heat energy = when thermal energy is transferred)
Created by Ken Mattingly Combined Curriculum Document Science Seventh Grade
 Combined Curriculum Document Science Seventh Grade Big Idea: Energy Transformations (Unifying Concepts) Grade 7 Energy transformations are inherent in almost every system in the universe from tangible
Combined Curriculum Document Science Seventh Grade Big Idea: Energy Transformations (Unifying Concepts) Grade 7 Energy transformations are inherent in almost every system in the universe from tangible
Energy Transformation
 Background Transformation 1. What is energy? 2. What are the two main forms of energy? Describe them. 3. Match each form of energy to the correct description. a. Chemical a. of the movement of charged
Background Transformation 1. What is energy? 2. What are the two main forms of energy? Describe them. 3. Match each form of energy to the correct description. a. Chemical a. of the movement of charged
Energy & Life PRE READING TASK. State the different types of Energy you know WHICH YOU SEE AROUND YOU, give some EXAMPLES.
 Name: Class: Date: Energy & Life Grade 11A Science Related Reading/Physics Physics Gr11A PRE READING TASK TYPES OF ENERGY State the different types of Energy you know WHICH YOU SEE AROUND YOU, give some
Name: Class: Date: Energy & Life Grade 11A Science Related Reading/Physics Physics Gr11A PRE READING TASK TYPES OF ENERGY State the different types of Energy you know WHICH YOU SEE AROUND YOU, give some
NOTES Foldable must include: - Form of Energy name on OUTSIDE of flap - Definition - At least one example (picture OR word)
 Unit 7: Energy. Bell Ringer: You are on a roller coaster 92 meters above the ground traveling at 14 m/s. You weigh 400 N (or approximately 40.8 kg). What is your mechanical energy? Show your work and include
Unit 7: Energy. Bell Ringer: You are on a roller coaster 92 meters above the ground traveling at 14 m/s. You weigh 400 N (or approximately 40.8 kg). What is your mechanical energy? Show your work and include
Energy and Energy Transformations
 and Transformations Transformations Key Concepts What is the law of conservation of? How does friction affect transformations? How are different types of used? What do you think? Read the three statements
and Transformations Transformations Key Concepts What is the law of conservation of? How does friction affect transformations? How are different types of used? What do you think? Read the three statements
Year 7 Recall Booklet. Name: Class:
 Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Energy It s In The Bag Understanding Potential and Kinetic Energy Time approximately 1 class period
 Energy It s In The Bag Understanding Potential and Kinetic Energy Time approximately 1 class period Adapted from Fossils to Fuel An Elementary Earth Science Curriculum, developed for the Oklahoma Energy
Energy It s In The Bag Understanding Potential and Kinetic Energy Time approximately 1 class period Adapted from Fossils to Fuel An Elementary Earth Science Curriculum, developed for the Oklahoma Energy
Section 1: The Science of Energy¹
 SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
Identify all the forms of energy you see in the picture below.
 Identify all the forms of energy you see in the picture below. Essential Question: How are forms of energy alike and different? Standards: S8P2c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat,
Identify all the forms of energy you see in the picture below. Essential Question: How are forms of energy alike and different? Standards: S8P2c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat,
Energy. Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Energy Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 1 Energy is a substance like quantity that can cause change. Makes objects move. Makes things stop. Is needed to do work.
Energy Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 1 Energy is a substance like quantity that can cause change. Makes objects move. Makes things stop. Is needed to do work.
CURRICULUM MAP Subject: SCIENCE Grade: 4 TH Quarter: 2 ND Teacher(s): 4 th Grade
 CURRICULUM MAP Subject: SCIENCE Grade: 4 TH Quarter: 2 ND Teacher(s): 4 th Grade Month WEEK 1 WEEK 2 WEEK 3 WEEK 4 WEEK 5 Concept GDOE & CCSS Standards GDOE 4.1.1 Observe that results of repeated scientific
CURRICULUM MAP Subject: SCIENCE Grade: 4 TH Quarter: 2 ND Teacher(s): 4 th Grade Month WEEK 1 WEEK 2 WEEK 3 WEEK 4 WEEK 5 Concept GDOE & CCSS Standards GDOE 4.1.1 Observe that results of repeated scientific
Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is energy? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: What is work? Q: Potential Energy
 Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Alief ISD Middle School Science STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Force, Motion, & Energy
 8.6.A demonstrate and calculate how unbalanced forces change the speed or direction of an object s motion Alief ISD Middle School Science STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Force, Motion, & Energy Force
8.6.A demonstrate and calculate how unbalanced forces change the speed or direction of an object s motion Alief ISD Middle School Science STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Force, Motion, & Energy Force
Electric energy Radiant energy Nuclear energy
 CHAPTER 7 LESSON 1: FORMS OF ENERGY Potential Energy Stored Energy Energy Kinetic Potential Work What is Energy? Mechanical Sound Thermal Electric Radiant Nuclear Potential is stored due to the interactions
CHAPTER 7 LESSON 1: FORMS OF ENERGY Potential Energy Stored Energy Energy Kinetic Potential Work What is Energy? Mechanical Sound Thermal Electric Radiant Nuclear Potential is stored due to the interactions
ì<(sk$m)=beabid< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Physical Science by Lillian Duggan Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Captions Charts Diagrams Glossary Forms of Energy Scott Foresman Science 6.17 ì
Physical Science by Lillian Duggan Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Captions Charts Diagrams Glossary Forms of Energy Scott Foresman Science 6.17 ì
Energy, Work, and Simple Machines
 CHAPTER 3 Energy, Work, and Simple Machines Types of Energy What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
CHAPTER 3 Energy, Work, and Simple Machines Types of Energy What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
What is Energy? The ability to do work or cause change.
 What is Energy? The ability to do work or cause change. Two Categories of Energy Kinetic Energy energy of motion. The faster it moves, the more kinetic energy it has. Potential Energy stored energy due
What is Energy? The ability to do work or cause change. Two Categories of Energy Kinetic Energy energy of motion. The faster it moves, the more kinetic energy it has. Potential Energy stored energy due
TYPES OF ENERGY and Energy
 TYPES OF ENERGY and Energy Conversions Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical, Nuclear, and Thermal What is Mechanical Energy? o Energy due to an object s motion (kinetic) or position (potential).
TYPES OF ENERGY and Energy Conversions Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical, Nuclear, and Thermal What is Mechanical Energy? o Energy due to an object s motion (kinetic) or position (potential).
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic
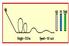 Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
STUDENT NAME. Science Grade 3. Read each question and choose the best answer. Be sure to mark all of your answers.
 FORMTIVE MINI SSESSMENTS First Grading Period 2009-10 October 20-23 STUENT NME TE Science Grade 3 Read each question and choose the best answer. e sure to mark all of your answers. opyright 2004, Texas
FORMTIVE MINI SSESSMENTS First Grading Period 2009-10 October 20-23 STUENT NME TE Science Grade 3 Read each question and choose the best answer. e sure to mark all of your answers. opyright 2004, Texas
Energy and Work ASSIGNMENT EDULABZ
 Energy and Work ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : List : created, constant, destroyed, work, force, mechanical energy, displacement, K.E.,
Energy and Work ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : List : created, constant, destroyed, work, force, mechanical energy, displacement, K.E.,
Name Class Date. Energy Energy
 CHAPTER 13 3 What Is Energy? SECTION Work and Energy KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How are energy and work related? Why is potential energy called energy of position?
CHAPTER 13 3 What Is Energy? SECTION Work and Energy KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How are energy and work related? Why is potential energy called energy of position?
Force, Energy Transfer and Machines Hot Wheels Energy Transfer
 Science Unit: Lesson #1: Force, Energy Transfer and Machines Hot Wheels Energy Transfer Lesson Summary Students conduct an experiment to test two research questions related to energy transfer. Using Hot
Science Unit: Lesson #1: Force, Energy Transfer and Machines Hot Wheels Energy Transfer Lesson Summary Students conduct an experiment to test two research questions related to energy transfer. Using Hot
Energy and Energy Resources
 chapter 32 Energy and Energy Resources section 1 What is energy? PS 4.1d: Different forms of energy include heat, light, electrical, mechanical, sound, nuclear, and chemical. Energy is transformed in many
chapter 32 Energy and Energy Resources section 1 What is energy? PS 4.1d: Different forms of energy include heat, light, electrical, mechanical, sound, nuclear, and chemical. Energy is transformed in many
KS3 Science. Heat and Energy
 KS3 Science Heat and Energy Heat and Energy Key Words Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words States of matter Melt Freeze Evaporate Condense Heat Conduction Convention Radiation
KS3 Science Heat and Energy Heat and Energy Key Words Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words States of matter Melt Freeze Evaporate Condense Heat Conduction Convention Radiation
Energy Unit Test * Required
 Energy Unit Test * Required 1. First and Last Name 2. Class Period 2nd 4th Forms of Energy Standard 6.PS3.1 Analyze the properties and compare sources of kinetic, elastic potential, gravitational potential,
Energy Unit Test * Required 1. First and Last Name 2. Class Period 2nd 4th Forms of Energy Standard 6.PS3.1 Analyze the properties and compare sources of kinetic, elastic potential, gravitational potential,
SPRING Print Student Name. Science GRADE PRACTICE TEST
 Print Student Name SPRING 2018 PRACTICE TEST GRADE 4 DIRECTIONS Read each question carefully. For each multiple-choice question, decide which is the best answer. For each question that asks you to explain
Print Student Name SPRING 2018 PRACTICE TEST GRADE 4 DIRECTIONS Read each question carefully. For each multiple-choice question, decide which is the best answer. For each question that asks you to explain
Unit 1: Energy and Motion
 4 4 Table of Contents Unit 1: Energy and Motion Chapter 4: Energy 4.1: The Nature of Energy 4.2: Conservation of Energy 4.1 The Nature of Energy Change Requires Energy Energy: ability to cause change.
4 4 Table of Contents Unit 1: Energy and Motion Chapter 4: Energy 4.1: The Nature of Energy 4.2: Conservation of Energy 4.1 The Nature of Energy Change Requires Energy Energy: ability to cause change.
Energy: Forms and Changes
 Energy: Forms and Changes Nature of Energy Energy is all around you! You can hear energy as sound. You can see energy as light. And you can feel it as wind. Nature of Energy You use energy when you: hit
Energy: Forms and Changes Nature of Energy Energy is all around you! You can hear energy as sound. You can see energy as light. And you can feel it as wind. Nature of Energy You use energy when you: hit
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Grade Level Expectations for the Sunshine State Standards
 for the Sunshine State Standards FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION http://www.myfloridaeducation.com/ The first grade student: The Nature of Matter knows that objects can be grouped according to their physical
for the Sunshine State Standards FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION http://www.myfloridaeducation.com/ The first grade student: The Nature of Matter knows that objects can be grouped according to their physical
Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound
 Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound Source: Utah State Office of Education A two-year-old has plenty of it, and the sun has a bunch of it. Do you know what it is? If not, let me give you a definition: A source
Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound Source: Utah State Office of Education A two-year-old has plenty of it, and the sun has a bunch of it. Do you know what it is? If not, let me give you a definition: A source
ANSWER KEY. Introduction to Matter
 Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. The object to be massed is placed on one side of the balance. Objects with known masses are placed on the other side of the arm until the balance arm is level. 2. Sample
Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. The object to be massed is placed on one side of the balance. Objects with known masses are placed on the other side of the arm until the balance arm is level. 2. Sample
Name: 1. Which of the following is probably true about 300 ml of sand and 300 ml of water?
 Name: Jaguar Review #2 Physical Sciences Benchmark A: Relate uses, properties and chemical processes to the behavior and/or arrangement of the small particles that compose matter. 1. Which of the following
Name: Jaguar Review #2 Physical Sciences Benchmark A: Relate uses, properties and chemical processes to the behavior and/or arrangement of the small particles that compose matter. 1. Which of the following
You are about to start an exciting series of lessons on physical science. God s Design for the Physical World
 Table of of Contents Unit 1 - Forms of Energy Lesson 1 Forms of Energy 8 Lesson 2 Mechanical Energy 12 Lesson 3 Chemical Energy 16 Lesson 4 Nuclear Energy 18 Lesson 5 Nuclear Weapons 21 Special Feature
Table of of Contents Unit 1 - Forms of Energy Lesson 1 Forms of Energy 8 Lesson 2 Mechanical Energy 12 Lesson 3 Chemical Energy 16 Lesson 4 Nuclear Energy 18 Lesson 5 Nuclear Weapons 21 Special Feature
Forms of Energy. What is energy? Energy is the amount of work that can be done by a force. What is a measure of energy? Joule.
 Forms of Energy What is energy? Energy is the amount of work that can be done by a force. What is a measure of energy? Joule. Major Classes of Energy 1. Kinetic energy (E k ) is the work needed to accelerate
Forms of Energy What is energy? Energy is the amount of work that can be done by a force. What is a measure of energy? Joule. Major Classes of Energy 1. Kinetic energy (E k ) is the work needed to accelerate
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2017 GRADE 6 NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
 GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2017 GRADE 6 NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DISTRICT SCHOOL NAME EMIS NUMBER CLASS (e.g. 6A) SURNAME NAME EKURHULENI NORTH TOM NEWBY SCHOOL
GAUTENG DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2017 GRADE 6 NATURAL SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DISTRICT SCHOOL NAME EMIS NUMBER CLASS (e.g. 6A) SURNAME NAME EKURHULENI NORTH TOM NEWBY SCHOOL
Energy in Animals Classwork. 3) Complete the following chart to show what Energy is used for in animals: Use of Energy Description (slides )
 Energy in Animals Classwork 5 th Grade PSI 1) Define Energy. Give an example. 2) Why do animals need to eat? 3) Complete the following chart to show what Energy is used for in animals: Use of Energy Description
Energy in Animals Classwork 5 th Grade PSI 1) Define Energy. Give an example. 2) Why do animals need to eat? 3) Complete the following chart to show what Energy is used for in animals: Use of Energy Description
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see?
 Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Scientific Reasoning, logic and the nature of science
 Review Packet for Science SOL Scientific Reasoning, logic and the nature of science 1. What is the SI (metric) measurement for: a. Length b. Mass c. Volume d. Density e. Temperature f. Weight g. Force
Review Packet for Science SOL Scientific Reasoning, logic and the nature of science 1. What is the SI (metric) measurement for: a. Length b. Mass c. Volume d. Density e. Temperature f. Weight g. Force
1 Forming New Substances
 CHAPTER 9 1 Forming New Substances SECTION Chemical Reactions BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a What are exothermic reactions? What are
CHAPTER 9 1 Forming New Substances SECTION Chemical Reactions BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a What are exothermic reactions? What are
Georgia Milestones 5TH GRADE PRE-TEST. Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA
 Georgia Milestones 5TH GRADE PRE-TEST Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA 1 1. Students identified the nucleus in an animal cell and a plant cell. Nucleus
Georgia Milestones 5TH GRADE PRE-TEST Rabieh Hafza ATLANTA PUBLIC SCHOOLS ALL QUESTIONS ARE PROPERTY OF THE STATE OF GEORGIA 1 1. Students identified the nucleus in an animal cell and a plant cell. Nucleus
ELEMENTS OF PHYSICS ENERGY: WORK and POWER
 1 Pre-Test Directions: This will help you discover what you know about the subject of energy before you begin this lesson. Answer the following true or false. 1. To a physicist, energy is work or the capacity
1 Pre-Test Directions: This will help you discover what you know about the subject of energy before you begin this lesson. Answer the following true or false. 1. To a physicist, energy is work or the capacity
Energy. Potential Kinetic
 Energy the ability to do work or cause change typically expressed in units of joules (J) can be transferred from one object to another two general types: Potential Kinetic Potential Energy (PE) stored
Energy the ability to do work or cause change typically expressed in units of joules (J) can be transferred from one object to another two general types: Potential Kinetic Potential Energy (PE) stored
Physical Science Across The Grades K-7
 S C I E N C E G R A D E L E V E L CO N T E N T E X P E C TAT I O N S Physical Science Across The Grades K-7 PHYSICAL LIFE The Office of School Improvement has developed the Science Across the Grades companion
S C I E N C E G R A D E L E V E L CO N T E N T E X P E C TAT I O N S Physical Science Across The Grades K-7 PHYSICAL LIFE The Office of School Improvement has developed the Science Across the Grades companion
Thursday Oct 2nd. A Study Session will be held from 4:30 5:30 pm Monday Oct 6th
 Thursday Oct 2nd SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY! TOPIC # 8 Part II LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS & MOTION TEST #2 is NEXT TUESDAY Oct 7th The Top 10 is now posted in D2L under Study Guides and Quick Links A Study
Thursday Oct 2nd SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY! TOPIC # 8 Part II LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS & MOTION TEST #2 is NEXT TUESDAY Oct 7th The Top 10 is now posted in D2L under Study Guides and Quick Links A Study
1 st Six Weeks 25 Days Focal Points Unit Unit 1 Introduction and Safety
 1 st Six Weeks 25 Days 1 Introduction and Safety The Process Standards Must Be Included in Each 10 days (1) Scientific processes. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, conducts laboratory
1 st Six Weeks 25 Days 1 Introduction and Safety The Process Standards Must Be Included in Each 10 days (1) Scientific processes. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, conducts laboratory
3. 4. Go to the following link and watch the Brainpop video: ob6y9rr
 Explore It! Explore It! Radiometer: A radiometer is a small bulb with two vanes inside. It is used to detect radiant energy. Make a prediction about how the distance of the light will affect the radiometer
Explore It! Explore It! Radiometer: A radiometer is a small bulb with two vanes inside. It is used to detect radiant energy. Make a prediction about how the distance of the light will affect the radiometer
Science - 4th grade practice test
 Name: Instructions: Bubble the correct answer. Read each choice before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : Use the picture below to answer question 1. 1. A
Name: Instructions: Bubble the correct answer. Read each choice before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : Use the picture below to answer question 1. 1. A
What is mechanical energy? How do we use it? Energy Energy
 You probably already have some idea what energy is. is easy to recognize. Yet it can be hard to describe. Where do you think you ve seen energy today? How do you think you will use energy tomorrow? Let
You probably already have some idea what energy is. is easy to recognize. Yet it can be hard to describe. Where do you think you ve seen energy today? How do you think you will use energy tomorrow? Let
2 nd Grade Science Cards. 1. Which of these is NOT a basic need for an animal? 2. Why do animals need air to live?
 nd Grade Science Cards 1. Which of these is NOT a basic need for an animal? A. sunlight B. water C. air D. food. Why do animals need air to live? A. to eat B. to breathe C. to run D. to sleep 3. Which
nd Grade Science Cards 1. Which of these is NOT a basic need for an animal? A. sunlight B. water C. air D. food. Why do animals need air to live? A. to eat B. to breathe C. to run D. to sleep 3. Which
Unit b 2 c 3 a. 2 pasture. 3 Students own answers. 4 sheep. 5 2 grass 3 water 4 milk. Lesson d 3 e 4 a 5 c. 3 water light shelter food
 Unit 1 1 hammer 3 screwdriver 4 scissors 5 nails Students own answers 3 a hammer some nails a screwdriver 4 some nails a screwdriver 1 no 3 yes 4 no 5 yes a 3 d 4 b 3 is a scientist 3 are scientists 1
Unit 1 1 hammer 3 screwdriver 4 scissors 5 nails Students own answers 3 a hammer some nails a screwdriver 4 some nails a screwdriver 1 no 3 yes 4 no 5 yes a 3 d 4 b 3 is a scientist 3 are scientists 1
Skills and Knowledge Progression. Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6
 Skills and Progression Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Plants Can identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants:
Skills and Progression Subject: Science KS2 Name: (Child s name) Class: (Child s class) Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Plants Can identify and describe the functions of different parts of flowering plants:
Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7
 Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7 Bill Nye - Energy I. PS.6a - Potential & Kinetic Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. B. Energy is either Potential or Kinetic. a. Potential Energy
Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7 Bill Nye - Energy I. PS.6a - Potential & Kinetic Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. B. Energy is either Potential or Kinetic. a. Potential Energy
New Mexico Public Education Department. Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course (EoC) Exam
 New Mexico Public Education Department PRELIMINARY Assessment Blueprint Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course (EoC) Exam Version 001 Purpose Statement Science: Grade 8 EoC The Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course Exam
New Mexico Public Education Department PRELIMINARY Assessment Blueprint Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course (EoC) Exam Version 001 Purpose Statement Science: Grade 8 EoC The Science: Grade 8 End-of-Course Exam
Energy: Forms and Changes
 Energy: Forms and Changes The Energy Story Nature of Energy Energy is all around you! l You can hear energy as sound. l You can see energy as light. l And you can feel it as wind. Nature of Energy You
Energy: Forms and Changes The Energy Story Nature of Energy Energy is all around you! l You can hear energy as sound. l You can see energy as light. l And you can feel it as wind. Nature of Energy You
SCI Scientific Investigation_KES
 SCI-4 4.1 Scientific Investigation_KES [Exam ID:0AJF30] Scan Number:17120 1 Which statement is a prediction? A The frog stayed on the log for 4 minutes. B The frog has stripes. C The frog will jump off
SCI-4 4.1 Scientific Investigation_KES [Exam ID:0AJF30] Scan Number:17120 1 Which statement is a prediction? A The frog stayed on the log for 4 minutes. B The frog has stripes. C The frog will jump off
Table of Contents. Chapter: Energy. Section 1: The Nature of Energy. Section 2: Conservation of Energy
 Table of Contents Chapter: Energy Section 1: The Nature of Energy Section 2: 1 The Nature of Energy What is energy? Wherever you are sitting as you read this, changes are taking place lightbulbs are heating
Table of Contents Chapter: Energy Section 1: The Nature of Energy Section 2: 1 The Nature of Energy What is energy? Wherever you are sitting as you read this, changes are taking place lightbulbs are heating
Mechanical Energy the energy associated with position and motion of an object
 Unit 3.3 Mechanical Energy the energy associated with position and motion of an object Mechanical Energy is composed of both kinetic and potential energy. Mechanical Energy = Potential Energy + Kinetic
Unit 3.3 Mechanical Energy the energy associated with position and motion of an object Mechanical Energy is composed of both kinetic and potential energy. Mechanical Energy = Potential Energy + Kinetic
Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism
 Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism 2.1 Intro to Energy P.O.D. 11/1/2017 How does the use of electricity and magnetism affect our world? 2.2 Forms of Energy P.O.D. 11/6/2017 Create a web that has ENERGY
Unit 2: Electricity and Magnetism 2.1 Intro to Energy P.O.D. 11/1/2017 How does the use of electricity and magnetism affect our world? 2.2 Forms of Energy P.O.D. 11/6/2017 Create a web that has ENERGY
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
7.1 Stanford Notes Energy Name
 7.1 Stanford Notes Energy Name MAIN POINTS: Write a summary of the main point of each paragraph. Page 164 Questions: Questions you should be able to answer after reading. Energy can cause what? The unit
7.1 Stanford Notes Energy Name MAIN POINTS: Write a summary of the main point of each paragraph. Page 164 Questions: Questions you should be able to answer after reading. Energy can cause what? The unit
Slide 1 Presentation 2: Introduction Duration: 00:00:16 Advance mode: Auto. Slide 2 Reading Assignment Duration: 00:00:24 Advance mode: Auto
 Slide 1 Presentation 2: Introduction Duration: 00:00:16 Advance mode: Auto Welcome to Presentation Two, Physical Science, in the Reviewing Science course. During this presentation, we will explore forces
Slide 1 Presentation 2: Introduction Duration: 00:00:16 Advance mode: Auto Welcome to Presentation Two, Physical Science, in the Reviewing Science course. During this presentation, we will explore forces
PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet May 2016 Science Class 7 (Answering Key)
 The City School PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet May 2016 Science Class 7 (Answering Key) The City School/ PAF Chapter/ Comprehensive Worksheet/ May 2016/ Science/ Class 7 /Ans Key Page 1 of 7 OBJECTIVE
The City School PAF Chapter Comprehensive Worksheet May 2016 Science Class 7 (Answering Key) The City School/ PAF Chapter/ Comprehensive Worksheet/ May 2016/ Science/ Class 7 /Ans Key Page 1 of 7 OBJECTIVE
RELEASED. Spring 2013 North Carolina Measures of Student Learning: NC s Common Exams. Grade 6 Science Form A
 Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Grade 6 Science Form RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction
Released Form Spring 2013 North arolina Measures of Student Learning: N s ommon Exams Grade 6 Science Form RELESE Public Schools of North arolina State oard of Education epartment of Public Instruction
STUDENT PACKET # 9 Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics
 STUDENT PACKET # 9 Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics Name: Date: Reporting Category: Physical Science Benchmark SC.7.P.11.2 Investigate and describe the transformation of energy from one form
STUDENT PACKET # 9 Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics Name: Date: Reporting Category: Physical Science Benchmark SC.7.P.11.2 Investigate and describe the transformation of energy from one form
Kindergarten. Energy. Slide 1 / 33 Slide 2 / 33. Slide 3 / 33. Slide 4 / 33. Slide 6 / 33. Slide 5 / 33. Energy. Teacher Page.
 Slide 1 / 33 Slide 2 / 33 Kindergarten 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 33 Table of Contents Slide 4 / 33 Types of Transfer Click on the topic to go to that section This presentation is designed to be
Slide 1 / 33 Slide 2 / 33 Kindergarten 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 33 Table of Contents Slide 4 / 33 Types of Transfer Click on the topic to go to that section This presentation is designed to be
3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy
 3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy STEMscopedia Forms of Energy Addressed Benchmarks: SC.3.P.10.1: Identify some basic forms of energy, such as light, heat, thermal, sound, electrical, and mechanical. SC.3.P.10.2:
3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy STEMscopedia Forms of Energy Addressed Benchmarks: SC.3.P.10.1: Identify some basic forms of energy, such as light, heat, thermal, sound, electrical, and mechanical. SC.3.P.10.2:
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: 05 5th Grade Science May Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: 05 5th Grade Science May 2010 Student name: Author: Ohio District: Ohio Released Tests Printed: Monday July 02, 2012 1 Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What
Test Booklet Subject: SC, Grade: 05 5th Grade Science May 2010 Student name: Author: Ohio District: Ohio Released Tests Printed: Monday July 02, 2012 1 Scientists found fish fossils in the desert. What
Taste the Rainbow! Using Skittles to explore the chemistry of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Name: Class:
 Taste the Rainbow! Using Skittles to explore the chemistry of photosynthesis and cellular respiration Name: Class: Background Information Plants cells and animal cells use chemical reactions to engage
Taste the Rainbow! Using Skittles to explore the chemistry of photosynthesis and cellular respiration Name: Class: Background Information Plants cells and animal cells use chemical reactions to engage
2 Changes of State KEY IDEAS READING TOOLBOX ADDING AND REMOVING ENERGY. States of Matter. As you read this section, keep these questions in mind:
 CHAPTER 3 States of Matter 2 Changes of State SECTION KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens when a substance changes from one state of matter to another? What happens
CHAPTER 3 States of Matter 2 Changes of State SECTION KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens when a substance changes from one state of matter to another? What happens
Physical Science and Nature of Science Assessment Probes
 Physical Science and Nature of Science Assessment Probes Concept Matrix...6 Pennies...7 2 Is It a Solid?...25 3 Thermometer...33. 4 Floating Balloon... 39 5 Hot and Cold Balloons...45 6 Mirror on the Wall...5
Physical Science and Nature of Science Assessment Probes Concept Matrix...6 Pennies...7 2 Is It a Solid?...25 3 Thermometer...33. 4 Floating Balloon... 39 5 Hot and Cold Balloons...45 6 Mirror on the Wall...5
6 (i)name the hormones that are released in human males and females when they reach puberty.
 PRACTICE PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0 Class X SCIENCE Time Allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 General Instructions :. The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both
PRACTICE PAPER FOR SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0 Class X SCIENCE Time Allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 General Instructions :. The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both
Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, University of California, Santa Barbara
 Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, 2007-08 University of California, Santa Barbara [Remember to get answers from a wide variety of students in the audience.
Performance script for sixth graders By Thomas Kuo and Kimberly Kline LEAPS Fellows, 2007-08 University of California, Santa Barbara [Remember to get answers from a wide variety of students in the audience.
Science Curriculum Map: KS1 & KS
 Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
Subject In KS1 pupils should be taught to use the following practical scientific methods, processes and skills through the teaching of the programme content of study content: Key stage Asking simple questions
8 th Grade Integrated Science Curriculum
 Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the curriculum, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. 8.1 Scientific Thinking and Practice 1. Use scientific methods to develop
Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the curriculum, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. 8.1 Scientific Thinking and Practice 1. Use scientific methods to develop
Energy and Electromagnetism
 4 th Science Notebook Energy and Electromagnetism Investigation 1: Energy and Circuits Name: Big Question: What is evidence that energy is present, and what conditions allow it to flow? 1 Alignment with
4 th Science Notebook Energy and Electromagnetism Investigation 1: Energy and Circuits Name: Big Question: What is evidence that energy is present, and what conditions allow it to flow? 1 Alignment with
Essential Characteristics of Scientists
 SELBY ABBEY CE (VC) PRIMARY SCHOOL SCIENCE CURRICULUM 2018-2019 Essential Characteristics of Scientists The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge
SELBY ABBEY CE (VC) PRIMARY SCHOOL SCIENCE CURRICULUM 2018-2019 Essential Characteristics of Scientists The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge
My Journal By: Copyright 2015 A Dab of Glue Will Do
 My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: Science Notebook Contract This is my Science Notebook for the 20 school year: I promise to take care of my notebook. use one page at a time.
My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: My Journal By: Science Notebook Contract This is my Science Notebook for the 20 school year: I promise to take care of my notebook. use one page at a time.
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry
 Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry I. Observations vs. Inferences Observation: information you gather using your five senses ***You will NEVER use taste in class! o Describes facts Examples You see the
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry I. Observations vs. Inferences Observation: information you gather using your five senses ***You will NEVER use taste in class! o Describes facts Examples You see the
Rashid School for Boys. Year 7 Science. Particles. Name: Form:
 Rashid School for Boys Year Science Particles Name: Form: 1 By the end of this topic.. Unit Particles Level 3 I know that ice melts when it gets too warm and that liquid water turns into solid water (ice)
Rashid School for Boys Year Science Particles Name: Form: 1 By the end of this topic.. Unit Particles Level 3 I know that ice melts when it gets too warm and that liquid water turns into solid water (ice)
3. According to the Law of Conservation of Energy, the total amount of energy in the universe
 Directions: Please choose the best answer choice for each of the following questions. 1. Heating an object excites the surface molecules, causing them to give off infrared rays. is the transmission of
Directions: Please choose the best answer choice for each of the following questions. 1. Heating an object excites the surface molecules, causing them to give off infrared rays. is the transmission of
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes Seasonal changes Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies observe changes across
K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities
 K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities The physical science strand encourages the basic observations of what our physical reality is made of and how it interacts matter, energy, forces, atoms and
K-5 Physical Science Overview with Activities The physical science strand encourages the basic observations of what our physical reality is made of and how it interacts matter, energy, forces, atoms and
UNIT II. Energy Transfer of Energy. Chapter 2: Energy Transfers
 UNIT II Energy Transfer of Energy Chapter 2: Energy Transfers The ability of matter to do work or make things happen is known as Energy. There are various forms of energy. Kinetic energy is the energy
UNIT II Energy Transfer of Energy Chapter 2: Energy Transfers The ability of matter to do work or make things happen is known as Energy. There are various forms of energy. Kinetic energy is the energy
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 1 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How do
CHAPTER 1 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How do
Work and Energy. Work
 Work and Energy Objectives: Students will define work. Students will define and give examples of different forms of energy. Students will describe and give examples of kinetic energy and potential energy.
Work and Energy Objectives: Students will define work. Students will define and give examples of different forms of energy. Students will describe and give examples of kinetic energy and potential energy.
Directed Reading B. Section: What Is Energy? ENERGY AND WORK: WORKING TOGETHER
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: What Is Energy? ENERGY AND WORK: WORKING TOGETHER 1. What do you call the ability to do work? a. movement b. energy c. power d. force KINETIC ENERGY 2. What
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: What Is Energy? ENERGY AND WORK: WORKING TOGETHER 1. What do you call the ability to do work? a. movement b. energy c. power d. force KINETIC ENERGY 2. What
Science Curriculum Map Autumn 1 Autumn 2 Spring 1 Spring 2 Summer 1 Summer 2
 The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
The objectvies in this curriculum map have been outlined by the National Curriculum and include additonal skill and knowledge based learning objectives grouped by units of work, taken from Hamilton Trust,
Unit 3: Physical Science Classifying Matter in our Daily Lives
 Science 7 Unit 3: Physical Science Classifying Matter in our Daily Lives Name Period Purpose: I understand the relationship between atoms, molecules, elements, compounds, and mixtures and can also provide
Science 7 Unit 3: Physical Science Classifying Matter in our Daily Lives Name Period Purpose: I understand the relationship between atoms, molecules, elements, compounds, and mixtures and can also provide
ob6y9rr Go to the following link and watch the Brainpop video:
 Explore It! Explore It! 1. Radiometer: A radiometer is a small bulb with two vanes inside. It is used to detect radiant energy. Make a prediction about how the distance of the light will affect the radiometer
Explore It! Explore It! 1. Radiometer: A radiometer is a small bulb with two vanes inside. It is used to detect radiant energy. Make a prediction about how the distance of the light will affect the radiometer
Science Curriculum Overview
 YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
YEAR 1 Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe and describe weather associated with the seasons and how day length varies Seasonal changes observe changes across the 4 seasons observe
Conducting Energy and Heat. Energy Likes to Move. Radiating Energy
 Energy Likes to Move If there is a temperature difference in a system, heat will naturally move from high to low temperatures. The place you find the higher temperature is the heat source. The area where
Energy Likes to Move If there is a temperature difference in a system, heat will naturally move from high to low temperatures. The place you find the higher temperature is the heat source. The area where
