Unit Workbook 4 - Level 4 ENG U8 Mechanical Principles 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
|
|
|
- Samson Ferdinand Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pearson BTEC Level 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 8: Mechanical Principles Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Dynamic Mechanical Systems Page 1 of 17
2 1.3 Work Done and power transmitted by a constant torque Figure 1 shows a pulley wheel of radius r metres attached to a shaft and a force F Newton s applied to the rim at point P. Figure 1 Pulley Wheel Figure 1(b) shows the pulley wheel having turned through an angle θ radians as a result of the force F being applied. The force moves through a distance s, where arc length s = rθ Work done = force distance moved by the force = F rθ = Frθ (N m) = Frθ (J) But, Fr is the torque T, so, Work Done = Tθ joules Average power = work done/time taken = = T θ/time taken for a constant torque T However, (angle θ) / (time taken) = angular velocity, ω rad/s. Hence, Power = Tω watts (Eq 1) Angular velocity, ω = 2πn rad/s where n is the speed in rev/s. Hence, Power P = 2πnT watts (Eq 2) Sometimes power is in units of horsepower (hp), where 1 horsepower = watts Worked Example 1 A motor connected to a shaft develops a torque of 5 kn m. Determine the number of revolutions made by the shaft if the work done is 9 MJ. Work Done = T θ, from which, Angular displacement, θ = Work Done/Torque Hence, Angular displacement, θ = 9 x 10 6 / 5000 = 1800 rad. But 2π rad = 1 rev., hence, No of revs made by the shaft = 1800/2π = revs 1.4 Power transmission and efficiency A common and simple method of transmitting power from one shaft to another is by means of a belt passing over pulley wheels which are keyed to the shafts, as shown in Figure 2. Typical applications include an electric motor driving a lathe or a drill, and an engine driving a pump or generator. Page 5 of 17
3 Figure 2 Pulley Belt Drive For a belt to transmit power between two pulleys there must be a difference in tensions in the belt on either side of the driving and driven pulleys. For the direction of rotation shown in Figure 2, F2 > F1. The torque T available at the driving wheel to do work is given by: T = (F2 F1) rx (N m) and the available power P is given by: P = Tω = (F2 F1) rxωx (Watts) The linear velocity of a point on the driver wheel is vx = rxωx Similarly, the linear velocity of a point on the driven wheel, vy = ryωy. Assuming no slipping, vx = vy and therefore, rxωx = ryωy Hence rx(2πnx) = ry (2πny) from which, rx/ry = ny/nx Percentage efficiency = useful work output / energy output 100 or, efficiency = power output / power input 100% Page 6 of 17
4 2 Linear and angular motion. 2.1 Linear and Angular velocity Linear velocity v is defined as the rate of change of linear displacement s with respect to time t, and for motion in a straight line: Linear velocity = change of displacement / change of time i.e. v = s/t (ms -1 ) (Eq 3) Angular velocity is defined as the rate of change of angular displacement θ, with respect to time t, and for an object rotating about a fixed axis at a constant speed: Angular velocity = angle turned through / time taken i.e. ω = θ/t (rads-1) (Eq 4) An object rotating at a constant speed of n revolutions per second subtends an angle of 2πn radians in one second. Hence, its angular velocity, ω = 2πn rads -1 (Eq 5) From s (arc length) = r (radius) θ (angle) and ω = θ/t s = r ω t or s/t = ωr and v = s/t Hence, v = ωr (Eq 6) This equation gives the relationship between linear velocity, v and angular velocity, ω. 2.2 Linear and Angular acceleration Linear acceleration, a, is defined as the rate of change of linear velocity with respect to time. For an object whose linear velocity is increasing uniformly: linear acceleration = change of linear velocity/time taken i.e. a = (v2 v1)/t (Eq 7) The unit of linear acceleration is metres per second squared (m/s 2 ). Rewriting equation (Eq 7) with v2 as the subject of the formula gives: v2 = v1 + at (Eq 8) where v2 = final velocity and v1 = initial velocity. Angular acceleration, α, is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity with respect to time. For an object whose angular velocity is increasing uniformly: Angular acceleration = change of angular velocity/time taken i.e. α = (ω2 ω1)/t (Eq 9) The unit of angular acceleration is radians per second squared (rad/s 2 ). Rewriting equation (Eq 9) with ω2 as the subject of the formula gives: ω2 = ω1 + αt (Eq 10) where ω2 = final angular velocity and ω1 = initial angular velocity. From equation (Eq 6), v = ωr. For motion in a circle having a constant radius r, v2 = ω2r and v1 = ω1r, hence equation (Eq 9) can be rewritten as: a = (ω2r - ω1r)/t = r (ω2 - ω1)/t But from equation (Eq 9), (ω2 - ω1)/t = α, Hence a = r α (Eq 11) 2.3 Relative Velocity Quantities used in engineering and science can be divided into two groups: Scalar quantities have a size or magnitude only and need no other information to specify them. Thus 20 centimetres, 5 seconds, 3 litres and 4 kilograms are all examples of scalar quantities. Page 7 of 17
5 Vector quantities have both a size (or magnitude), and a direction, called the line of action of the quantity. Thus, a velocity of 30 km/h due west, and an acceleration of 7 m/s2 acting vertically downwards, are both vector quantities. Figure 3 Vector quantity A vector quantity is represented by a straight line lying along the line of action of the quantity, and having a length that is proportional to the size of the quantity. Thus, ab in Figure 3. represents a velocity of 20m/s, whose line of action is due west. The bold letters, ab, indicate a vector quantity and the order of the letters indicate that the line of action is from a to b. Consider two aircraft A and B flying at a constant altitude, A travelling due north at 200 m/s and B travelling 30 east of north, written N 30 E, at 300 m/s, as shown in Figure 4. Relative to a fixed-point o, oa represents the velocity of A and ob the velocity of B. The velocity of B relative to A, that is the velocity at which B seems to be travelling to an observer on A, is given by ab, and by measurement is 160 m/s in a direction E 22 N. The velocity of A relative to B, that is, the velocity at which A seems to be travelling to an observer on B, is given by ba and by measurement is 160 m/s in a direction W 22 S. Figure 4 Relative velocities Page 8 of 17
6 Worked Example 6 Two cars are travelling on horizontal roads in straight lines, car A at 70 km/h at N 10 E and car B at 50 km/h at W 60 N. Determine, by drawing a vector diagram to scale, the velocity of car A relative to car B. Worked Example 7 Figure 5 Vector solution to problem (a) With reference to Figure 5, oa represents the velocity of car A relative to a fixed-point o, and ob represents the velocity of car B relative to a fixed-point o. The velocity of car A relative to car B is given by ba and by measurement is 45 km/h in a direction of E 35 N. Verify the result obtained in the previous worked example by calculation. Figure 6 Vector solution to problem (b) The triangle shown in Figure 6 is similar to the vector diagram shown in Figure 9. Angle BOA is 40. Using the cosine rule: BA 2 = cos 40 from which, BA = Using the sine rule: 50/sin (angle BAO) = 45.14/sin 40 from which, sin (angle BAO) = 50 sin 40 /45.14 = Hence, angle BA0 = thus, angle ABO = 180 ( ) = 94.60, and angle θ = = Thus, ba is km/h in a direction E N by calculation. Page 9 of 17
7 2.4 Gyroscopic motion. A Gyroscope is a spinning disc mounted in gimbals such that it may pivot in the x, y and z axis, as indicated in Figure 7 Figure 7 Gyroscopic motion Now consider a disc spinning about the x-axis with velocity ωx as shown. The angular momentum of the disc is L = I ωx. This is a vector quantity and the vector is drawn with a direction conforming to the corkscrew rule (point the index finger of your right hand in the direction of the vector, as shown in Figure 8. Figure 8 Corkscrew rule Suppose the disc also rotates about the y-axis as shown in Figure 9 through a small angle δθ. The vector for L changes direction but mot magnitude. This produces a change in the angular momentum of δl = δ (I ωx). Figure 9 Vector for change in angular momentum The vector diagram conforms to the vector rule (final vector = first vector + change). The change is the arrow going from the tip of the first to the tip of the second, so the direction is as shown. Page 10 of 17
8 The vector representing the change is almost an arc of radius I ωx and angle δθ. The length of the arc is the product of radius and angle. Taking the radius as I ωx and the angle as δθ, the change is: δ (I ωx) = I ωx δθ = L δθ Newton s second law of motion applied to rotating bodies tells us that the change in momentum can only be brought about by applying a torque. Torque = rate of change of angular momentum. If the rotation occurred in time δt seconds, the rate of change of momentum is L (δθ/ δt). δθ/ δt is the angular velocity ωy so the rate T = L ωy = I ωx ωy This is the torque that must be applied to produce the change in angle and the direction of the vector is the same as the change in momentum. The applied torque may hence be deduced in magnitude and direction. Examining the vector for this torque we can deduce that it applied in the z-axis. Figure 10 Applied torque and precession If the torque is applied about the z-axis, the result will be rotation about the z-axis and this is called precession. Torque-induced precession (gyroscopic precession) is the phenomenon in which the axis of a spinning object (e.g., a gyroscope) describes a cone in space when an external torque is applied to it. The phenomenon is commonly seen in a spinning toy top, but all rotating objects can undergo precession. If the torque is not applied and the rotation is made to happen (applied), a reaction torque will be produced (Newton s 3 rd law) and the disc will respond to the reaction torque. Page 11 of 17
9 Video Figure 11 Reaction torque A gyroscopic torque may occur in any machine with rotating parts if a change in the direction of the x-axis occurs. Examples include any vehicle where a gyroscopic torque is produced by the engines when a course alteration is made. You can watch a video of gyroscopic torque at 2.5 Spinning tops. A top is a spinning body that is symmetrical about its axis of spin. This could be a cylinder or a cone rotating about its axis. If the axis is inclined at angle φ as shown in Figure 12 and the top is spinning at ω rad/s, it will have angular momentum L = Iω in the direction shown. Figure 12 shows the top precessing about the vertical axis that intercepts with the axis of spin at O. Point O is a fixed-point, so the axis of spin forms a surface of a cone as it precesses. Figure 12 Precession in a spinning top Suppose the axis of spin rotates through an angle δθ in time δt. The change in angular momentum is δl = L δθ, but this is the change for the axis of spin. The change in the horizontal plane is δl = L sin φ δθ. Divide through by the time it takes to happen. Therefore δl / δt = L sin φ δθ / δt In the limit when the change is infinitesimally small dl / dt = L sin φ dθ /dt = L sin φ ωp The rate of change of angular momentum must be produced by a torque T and equal to T = L sin φ ωp and the direction may be deduced from the corkscrew rule from the direction of the change. If the axis of spin is vertical φ = 0, T = 0, and ωp = 0. Page 12 of 17
10 At any other angle, there must be applied torque, and this could be due to the weight, for example. Worked Example 8 A top consists of a spinning disc of radius 50 mm and mass 0.8 kg mounted at the end of a light rod as shown in Figure 13. If the disc rests on a pivot with its axis of spin horizontal as shown, and the distance X is 30 mm, calculate the velocity of the precession when it spins at 40 rev/min. Worked Example 9 Figure 13 Diagram for worked example 4 The angle φ is 90 o so T = L sin φ ωp For a plain disc I = MR 2 / 2 = 0.8 x (0.05) 2 / 2 = kg m 2 ω = 2π x 50 = 100π rad/s L = I ω = x 100π = kg m 2 /s T is due to the weight acting at 30 mm from the rest point. T = mgx = 0.8 x 9.81 x 0.03 = Nm. ωp = T/L = / = 0187 rad/s A top consists of a spinning disc of radius 40 mm and mass 0.5 kg mounted at the end of a light rod as shown. The distance from the tip to the centre of gravity is 100 mm. Calculate the velocity of the precession when it spins at 30 rev/min. Figure 14 Diagram for worked example 5 The angle φ is 30 o so T = L sin φ ωp = 0.5 L ωp For a plain disc I = MR 2 / 2 = 0.5 x (0.04) 2 / 2 = kg m 2 ω = 2π x 30 = 60π rad/s L = I ω = x 60π = kg m 2 /s T is due to the weight acting at 100 cos 30 o = 86.6 mm from the rest point. T = mg x = 0.5 x 9.81 x = Nm Page 13 of 17
11 ωp = T / L = / = 5.63 rad/s Worked Example 10 A cycle takes a right-hand bend at a velocity of v m/s and radius R. Show that the cyclist must lean into the bend in order to go around it. Figure 15 Diagram (a) for worked example 6 First, remember that the velocity of the edge of the wheel must be the same as the velocity of the bike. So, ωx = v/r where r is the radius of the wheel. Figure 16 Diagram (b) for worked example 6 Now draw the vector diagrams to determine the change. As the wheel goes around a right hand bend the direction of the vector for ωx changes as shown in Figure 17 (c). The applied torque is a vector in the same direction as the change, so we deduce that the torque must act clockwise viewed from behind the cyclist. This torque may be produced by leaning into the bend and letting gravity do the job. By applying this torque, the wheels must precess in the correct direction to go around the bend. Figure 17 Diagram (c) for worked example 6 If the cyclist steers around the bend by turning the handlebars, then the reaction torque would throw him over outwards (anticlockwise as viewed from the back). Page 14 of 17
OUTCOME 2 KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS
 Unit 60: Dynamics of Machines Unit code: H/601/1411 QCF Level:4 Credit value:15 OUTCOME 2 KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS TUTORIAL 3 GYROSCOPES 2 Be able to determine the kinetic and dynamic parameters of mechanical
Unit 60: Dynamics of Machines Unit code: H/601/1411 QCF Level:4 Credit value:15 OUTCOME 2 KINEMATICS AND DYNAMICS TUTORIAL 3 GYROSCOPES 2 Be able to determine the kinetic and dynamic parameters of mechanical
ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 6 - GYROSCOPES. On completion of this tutorial you should be able to
 ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 6 - GYROSCOPES This tutorial examines linear and angular motion. The work is then linked with earlier studies of materials and mechanisms
ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 6 - GYROSCOPES This tutorial examines linear and angular motion. The work is then linked with earlier studies of materials and mechanisms
Chapter 10. Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis
 Chapter 10 Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line. Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin. A small
Chapter 10 Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line. Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin. A small
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics. UCVTS AIT Physics
 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL MECHANICAL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING C105 TUTORIAL 13 - MOMENT OF INERTIA
 ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL MECHANICAL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING C15 TUTORIAL 1 - MOMENT OF INERTIA This tutorial covers essential material for this exam. On completion of this tutorial you
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL MECHANICAL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING C15 TUTORIAL 1 - MOMENT OF INERTIA This tutorial covers essential material for this exam. On completion of this tutorial you
Gyroscopic Couple and Precessional Motion
 480 l Theory of Machines 14 Fea eatur tures es 1. Introduction.. Precessional Angular Motion. 3. Gyroscopic Couple. 4. Effect of Gyroscopic Couple on an Aeroplane. 5. Terms Used in a Naval Ship. 6. Effect
480 l Theory of Machines 14 Fea eatur tures es 1. Introduction.. Precessional Angular Motion. 3. Gyroscopic Couple. 4. Effect of Gyroscopic Couple on an Aeroplane. 5. Terms Used in a Naval Ship. 6. Effect
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 10 Homework
 Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 0 Homework Chapter 0 Questions: 4, 6, 8 Exercises & Problems 6, 3, 6, 4, 45, 5, 5, 7, 8 Answers to Questions: Q 0-4 (a) positive (b) zero (c) negative (d) negative Q 0-6
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 0 Homework Chapter 0 Questions: 4, 6, 8 Exercises & Problems 6, 3, 6, 4, 45, 5, 5, 7, 8 Answers to Questions: Q 0-4 (a) positive (b) zero (c) negative (d) negative Q 0-6
AP Physics QUIZ Chapters 10
 Name: 1. Torque is the rotational analogue of (A) Kinetic Energy (B) Linear Momentum (C) Acceleration (D) Force (E) Mass A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a rigid rod of negligible
Name: 1. Torque is the rotational analogue of (A) Kinetic Energy (B) Linear Momentum (C) Acceleration (D) Force (E) Mass A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a rigid rod of negligible
Kinematics of. Motion. 8 l Theory of Machines
 8 l Theory of Machines Features 1. 1ntroduction.. Plane Motion. 3. Rectilinear Motion. 4. Curvilinear Motion. 5. Linear Displacement. 6. Linear Velocity. 7. Linear Acceleration. 8. Equations of Linear
8 l Theory of Machines Features 1. 1ntroduction.. Plane Motion. 3. Rectilinear Motion. 4. Curvilinear Motion. 5. Linear Displacement. 6. Linear Velocity. 7. Linear Acceleration. 8. Equations of Linear
Rotational Motion and Torque
 Rotational Motion and Torque Introduction to Angular Quantities Sections 8- to 8-2 Introduction Rotational motion deals with spinning objects, or objects rotating around some point. Rotational motion is
Rotational Motion and Torque Introduction to Angular Quantities Sections 8- to 8-2 Introduction Rotational motion deals with spinning objects, or objects rotating around some point. Rotational motion is
Chapter 8- Rotational Kinematics Angular Variables Kinematic Equations
 Chapter 8- Rotational Kinematics Angular Variables Kinematic Equations Chapter 9- Rotational Dynamics Torque Center of Gravity Newton s 2 nd Law- Angular Rotational Work & Energy Angular Momentum Angular
Chapter 8- Rotational Kinematics Angular Variables Kinematic Equations Chapter 9- Rotational Dynamics Torque Center of Gravity Newton s 2 nd Law- Angular Rotational Work & Energy Angular Momentum Angular
Rotation. Rotational Variables
 Rotation Rigid Bodies Rotation variables Constant angular acceleration Rotational KE Rotational Inertia Rotational Variables Rotation of a rigid body About a fixed rotation axis. Rigid Body an object that
Rotation Rigid Bodies Rotation variables Constant angular acceleration Rotational KE Rotational Inertia Rotational Variables Rotation of a rigid body About a fixed rotation axis. Rigid Body an object that
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Formulas: v = l / t = r θ / t = rω a T = v / t = r ω / t =rα a C = v 2 /r = ω 2 r ω = ω 0 + αt θ = ω 0 t +(1/2)αt 2 θ = (1/2)(ω 0 +ω)t ω 2 = ω 0 2 +2αθ τ
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Formulas: v = l / t = r θ / t = rω a T = v / t = r ω / t =rα a C = v 2 /r = ω 2 r ω = ω 0 + αt θ = ω 0 t +(1/2)αt 2 θ = (1/2)(ω 0 +ω)t ω 2 = ω 0 2 +2αθ τ
Name: Date: Period: AP Physics C Rotational Motion HO19
 1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA ADVANCED MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT 18 NQF LEVEL 3
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA ADVANCED MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT 18 NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 3 BE ABLE TO DETERMINE RELATIVE AND RESULTANT VELOCITY IN ENGINEERING SYSTEMS Resultant
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA ADVANCED MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT 18 NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 3 BE ABLE TO DETERMINE RELATIVE AND RESULTANT VELOCITY IN ENGINEERING SYSTEMS Resultant
ENGINEERING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D225 TUTORIAL 4 MOMENT OF INERTIA. On completion of this tutorial you should be able to
 ENGINEEING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D5 TUTOIAL 4 MOMENT OF INETIA On completion of this tutorial you should be able to evise angular motion. Define and derive the moment of inertia of a body.
ENGINEEING COUNCIL DYNAMICS OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS D5 TUTOIAL 4 MOMENT OF INETIA On completion of this tutorial you should be able to evise angular motion. Define and derive the moment of inertia of a body.
Rotational Kinematics
 Rotational Kinematics Rotational Coordinates Ridged objects require six numbers to describe their position and orientation: 3 coordinates 3 axes of rotation Rotational Coordinates Use an angle θ to describe
Rotational Kinematics Rotational Coordinates Ridged objects require six numbers to describe their position and orientation: 3 coordinates 3 axes of rotation Rotational Coordinates Use an angle θ to describe
A Level. A Level Physics. Circular Motion (Answers) Edexcel. Name: Total Marks: /30
 Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. Edexcel A Level A Level Physics Circular Motion (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. Total for
Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. Edexcel A Level A Level Physics Circular Motion (Answers) Name: Total Marks: /30 Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition Ltd 2017 1. Total for
MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME 3 CENTRIPETAL ACCELERATION AND CENTRIPETAL FORCE TUTORIAL 1 CENTRIFUGAL FORCE
 MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME 3 CENTRIPETAL ACCELERATION AND CENTRIPETAL FORCE TUTORIAL 1 CENTRIFUGAL FORCE Centripetal acceleration and force: derivation of expressions for centripetal acceleration and
MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES OUTCOME 3 CENTRIPETAL ACCELERATION AND CENTRIPETAL FORCE TUTORIAL 1 CENTRIFUGAL FORCE Centripetal acceleration and force: derivation of expressions for centripetal acceleration and
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion. Preparation for unit test
 Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Physics 12. Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1
 Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Physics 12 Unit 5 Circular Motion and Gravitation Part 1 1. Nonlinear motions According to the Newton s first law, an object remains its tendency of motion as long as there is no external force acting
Translational vs Rotational. m x. Connection Δ = = = = = = Δ = = = = = = Δ =Δ = = = = = 2 / 1/2. Work
 Translational vs Rotational / / 1/ Δ m x v dx dt a dv dt F ma p mv KE mv Work Fd / / 1/ θ ω θ α ω τ α ω ω τθ Δ I d dt d dt I L I KE I Work / θ ω α τ Δ Δ c t s r v r a v r a r Fr L pr Connection Translational
Translational vs Rotational / / 1/ Δ m x v dx dt a dv dt F ma p mv KE mv Work Fd / / 1/ θ ω θ α ω τ α ω ω τθ Δ I d dt d dt I L I KE I Work / θ ω α τ Δ Δ c t s r v r a v r a r Fr L pr Connection Translational
Name:. Set:. Don: Physics: Pre-U Revision Toytime Rotational and Circular Motion
 Name:. Set:. Don: Physics: Pre-U Revision Toytime 2015-16 Rotational and Circular Motion 1 19 (ii) Place ticks in the table below to identify the effect on waves of light as they refract from diamond into
Name:. Set:. Don: Physics: Pre-U Revision Toytime 2015-16 Rotational and Circular Motion 1 19 (ii) Place ticks in the table below to identify the effect on waves of light as they refract from diamond into
a +3bt 2 4ct 3) =6bt 12ct 2. dt 2. (a) The second hand of the smoothly running watch turns through 2π radians during 60 s. Thus,
 1. a) Eq. 11-6 leads to ω d at + bt 3 ct 4) a +3bt 4ct 3. dt b) And Eq. 11-8 gives α d a +3bt 4ct 3) 6bt 1ct. dt. a) The second hand of the smoothly running watch turns through π radians during 60 s. Thus,
1. a) Eq. 11-6 leads to ω d at + bt 3 ct 4) a +3bt 4ct 3. dt b) And Eq. 11-8 gives α d a +3bt 4ct 3) 6bt 1ct. dt. a) The second hand of the smoothly running watch turns through π radians during 60 s. Thus,
Two-Dimensional Rotational Kinematics
 Two-Dimensional Rotational Kinematics Rigid Bodies A rigid body is an extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Springs or human bodies are non-rigid
Two-Dimensional Rotational Kinematics Rigid Bodies A rigid body is an extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Springs or human bodies are non-rigid
Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion
 Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion Circular Motion Milky Way Galaxy Orbital Speed of Solar System: 220 km/s Orbital Period: 225 Million Years Mercury: 48 km/s Venus: 35 km/s Earth: 30
Chapter 8: Newton s Laws Applied to Circular Motion Circular Motion Milky Way Galaxy Orbital Speed of Solar System: 220 km/s Orbital Period: 225 Million Years Mercury: 48 km/s Venus: 35 km/s Earth: 30
. d. v A v B. e. none of these.
 General Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, the essential
General Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, the essential
Balancing of Masses. 1. Balancing of a Single Rotating Mass By a Single Mass Rotating in the Same Plane
 lecture - 1 Balancing of Masses Theory of Machine Balancing of Masses A car assembly line. In this chapter we shall discuss the balancing of unbalanced forces caused by rotating masses, in order to minimize
lecture - 1 Balancing of Masses Theory of Machine Balancing of Masses A car assembly line. In this chapter we shall discuss the balancing of unbalanced forces caused by rotating masses, in order to minimize
Rotation. Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy. Torque Rolling. featuring moments of Inertia
 Rotation Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy featuring moments of Inertia Torque Rolling Angular Motion We think about rotation in the same basic way we do about linear motion How far does it go? How
Rotation Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy featuring moments of Inertia Torque Rolling Angular Motion We think about rotation in the same basic way we do about linear motion How far does it go? How
Angular velocity and angular acceleration CHAPTER 9 ROTATION. Angular velocity and angular acceleration. ! equations of rotational motion
 Angular velocity and angular acceleration CHAPTER 9 ROTATION! r i ds i dθ θ i Angular velocity and angular acceleration! equations of rotational motion Torque and Moment of Inertia! Newton s nd Law for
Angular velocity and angular acceleration CHAPTER 9 ROTATION! r i ds i dθ θ i Angular velocity and angular acceleration! equations of rotational motion Torque and Moment of Inertia! Newton s nd Law for
31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS
 31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS 1. Compare and contrast circular motion and rotation? Address the following Which involves an object and which involves a system? Does an object/system in circular motion have
31 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS 1. Compare and contrast circular motion and rotation? Address the following Which involves an object and which involves a system? Does an object/system in circular motion have
Textbook Reference: Wilson, Buffa, Lou: Chapter 8 Glencoe Physics: Chapter 8
 AP Physics Rotational Motion Introduction: Which moves with greater speed on a merry-go-round - a horse near the center or one near the outside? Your answer probably depends on whether you are considering
AP Physics Rotational Motion Introduction: Which moves with greater speed on a merry-go-round - a horse near the center or one near the outside? Your answer probably depends on whether you are considering
Gyroscopes and statics
 Gyroscopes and statics Announcements: Welcome back from Spring Break! CAPA due Friday at 10pm We will finish Chapter 11 in H+R on angular momentum and start Chapter 12 on stability. Friday we will begin
Gyroscopes and statics Announcements: Welcome back from Spring Break! CAPA due Friday at 10pm We will finish Chapter 11 in H+R on angular momentum and start Chapter 12 on stability. Friday we will begin
We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω. What's a radian?
 We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω Units: θ = rad ω = rad/s What's a radian? Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius note: counterclockwise is + clockwise
We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω Units: θ = rad ω = rad/s What's a radian? Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius note: counterclockwise is + clockwise
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion. Torque and angular momentum
 Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion.notebook November 03, 2017
 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion Rotational motion is the motion of objects that spin about an axis. Section 7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion We use the angle θ from the positive
Describing Circular and Rotational Motion Rotational motion is the motion of objects that spin about an axis. Section 7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion We use the angle θ from the positive
Dynamics Plane kinematics of rigid bodies Section 4: TJW Rotation: Example 1
 Section 4: TJW Rotation: Example 1 The pinion A of the hoist motor drives gear B, which is attached to the hoisting drum. The load L is lifted from its rest position and acquires an upward velocity of
Section 4: TJW Rotation: Example 1 The pinion A of the hoist motor drives gear B, which is attached to the hoisting drum. The load L is lifted from its rest position and acquires an upward velocity of
Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Ladybugs on a Rotating Disk. v = ωr, where r is the distance between the object and the axis of rotation. Chapter 9. Part A.
![Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Ladybugs on a Rotating Disk. v = ωr, where r is the distance between the object and the axis of rotation. Chapter 9. Part A. Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Ladybugs on a Rotating Disk. v = ωr, where r is the distance between the object and the axis of rotation. Chapter 9. Part A.](/thumbs/77/75060038.jpg) Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Chapter 9 Overview Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Due: 11:59pm on Sunday, October 30, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this
Chapter 9 [ Edit ] Chapter 9 Overview Summary View Diagnostics View Print View with Answers Due: 11:59pm on Sunday, October 30, 2016 To understand how points are awarded, read the Grading Policy for this
Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion What causes an angular acceleration? The effectiveness of a force at causing a rotation is called torque. QuickCheck 12.5 The four forces shown have the same strength.
Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion What causes an angular acceleration? The effectiveness of a force at causing a rotation is called torque. QuickCheck 12.5 The four forces shown have the same strength.
Exam Question 6/8 (HL/OL): Circular and Simple Harmonic Motion. February 1, Applied Mathematics: Lecture 7. Brendan Williamson.
 in a : Exam Question 6/8 (HL/OL): Circular and February 1, 2017 in a This lecture pertains to material relevant to question 6 of the paper, and question 8 of the Ordinary Level paper, commonly referred
in a : Exam Question 6/8 (HL/OL): Circular and February 1, 2017 in a This lecture pertains to material relevant to question 6 of the paper, and question 8 of the Ordinary Level paper, commonly referred
CHAPTER 8: ROTATIONAL OF RIGID BODY PHYSICS. 1. Define Torque
 7 1. Define Torque 2. State the conditions for equilibrium of rigid body (Hint: 2 conditions) 3. Define angular displacement 4. Define average angular velocity 5. Define instantaneous angular velocity
7 1. Define Torque 2. State the conditions for equilibrium of rigid body (Hint: 2 conditions) 3. Define angular displacement 4. Define average angular velocity 5. Define instantaneous angular velocity
Exercise Torque Magnitude Ranking Task. Part A
 Exercise 10.2 Calculate the net torque about point O for the two forces applied as in the figure. The rod and both forces are in the plane of the page. Take positive torques to be counterclockwise. τ 28.0
Exercise 10.2 Calculate the net torque about point O for the two forces applied as in the figure. The rod and both forces are in the plane of the page. Take positive torques to be counterclockwise. τ 28.0
Rotation. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
1 Problems 1-3 A disc rotates about an axis through its center according to the relation θ (t) = t 4 /4 2t
 Slide 1 / 30 1 Problems 1-3 disc rotates about an axis through its center according to the relation θ (t) = t 4 /4 2t etermine the angular velocity of the disc at t= 2 s 2 rad/s 4 rad/s 6 rad/s 8 rad/s
Slide 1 / 30 1 Problems 1-3 disc rotates about an axis through its center according to the relation θ (t) = t 4 /4 2t etermine the angular velocity of the disc at t= 2 s 2 rad/s 4 rad/s 6 rad/s 8 rad/s
TutorBreeze.com 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION. 3. If the angular velocity of a spinning body points out of the page, then describe how is the body spinning?
 1. rpm is about rad/s. 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION 2. A wheel rotates with constant angular acceleration of π rad/s 2. During the time interval from t 1 to t 2, its angular displacement is π rad. At time t 2
1. rpm is about rad/s. 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION 2. A wheel rotates with constant angular acceleration of π rad/s 2. During the time interval from t 1 to t 2, its angular displacement is π rad. At time t 2
Slide 1 / 30. Slide 2 / 30. Slide 3 / m/s -1 m/s
 1 Problems 1-3 disc rotates about an axis through its center according to the relation θ (t) = t 4 /4 2t Slide 1 / 30 etermine the angular velocity of the disc at t= 2 s 2 rad/s 4 rad/s 6 rad/s 8 rad/s
1 Problems 1-3 disc rotates about an axis through its center according to the relation θ (t) = t 4 /4 2t Slide 1 / 30 etermine the angular velocity of the disc at t= 2 s 2 rad/s 4 rad/s 6 rad/s 8 rad/s
Chapter 10.A. Rotation of Rigid Bodies
 Chapter 10.A Rotation of Rigid Bodies P. Lam 7_23_2018 Learning Goals for Chapter 10.1 Understand the equations govern rotational kinematics, and know how to apply them. Understand the physical meanings
Chapter 10.A Rotation of Rigid Bodies P. Lam 7_23_2018 Learning Goals for Chapter 10.1 Understand the equations govern rotational kinematics, and know how to apply them. Understand the physical meanings
Phys 106 Practice Problems Common Quiz 1 Spring 2003
 Phys 106 Practice Problems Common Quiz 1 Spring 2003 1. For a wheel spinning with constant angular acceleration on an axis through its center, the ratio of the speed of a point on the rim to the speed
Phys 106 Practice Problems Common Quiz 1 Spring 2003 1. For a wheel spinning with constant angular acceleration on an axis through its center, the ratio of the speed of a point on the rim to the speed
Chapter 3.5. Uniform Circular Motion
 Chapter 3.5 Uniform Circular Motion 3.5 Uniform Circular Motion DEFINITION OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Uniform circular motion is the motion of an object traveling at a constant speed on a circular path.
Chapter 3.5 Uniform Circular Motion 3.5 Uniform Circular Motion DEFINITION OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Uniform circular motion is the motion of an object traveling at a constant speed on a circular path.
Chapter 8. Accelerated Circular Motion
 Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion 8.1 Rotational Motion and Angular Displacement A new unit, radians, is really useful for angles. Radian measure θ(radians) = s = rθ s (arc length) r (radius) (s in
Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion 8.1 Rotational Motion and Angular Displacement A new unit, radians, is really useful for angles. Radian measure θ(radians) = s = rθ s (arc length) r (radius) (s in
The acceleration due to gravity g, which varies with latitude and height, will be approximated to 101m1s 2, unless otherwise specified.
 The acceleration due to gravity g, which varies with latitude and height, will be approximated to 101m1s 2, unless otherwise specified. F1 (a) The fulcrum in this case is the horizontal axis, perpendicular
The acceleration due to gravity g, which varies with latitude and height, will be approximated to 101m1s 2, unless otherwise specified. F1 (a) The fulcrum in this case is the horizontal axis, perpendicular
Topic 1: Newtonian Mechanics Energy & Momentum
 Work (W) the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Scalar but can be positive or negative ΔE = W = F! d = Fdcosθ Units N m or Joules (J) Work, Energy & Power Power (P) the
Work (W) the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance. Scalar but can be positive or negative ΔE = W = F! d = Fdcosθ Units N m or Joules (J) Work, Energy & Power Power (P) the
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Eleven Instantaneous Centre and General Motion Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 5/93 from Meriam and Kraige - Dynamics) For the instant
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Eleven Instantaneous Centre and General Motion Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 5/93 from Meriam and Kraige - Dynamics) For the instant
Concept Question: Normal Force
 Concept Question: Normal Force Consider a person standing in an elevator that is accelerating upward. The upward normal force N exerted by the elevator floor on the person is 1. larger than 2. identical
Concept Question: Normal Force Consider a person standing in an elevator that is accelerating upward. The upward normal force N exerted by the elevator floor on the person is 1. larger than 2. identical
Circular motion minutes. 62 marks. theonlinephysicstutor.com. facebook.com/theonlinephysicstutor Page 1 of 22. Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks:
 Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Circular motion 2 Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 62 marks Comments: Page 1 of 22 1 A lead ball of mass 0.25 kg is swung round on the end of a string so that the ball moves in a horizontal circle
Chapter 10: Rotation
 Chapter 10: Rotation Review of translational motion (motion along a straight line) Position x Displacement x Velocity v = dx/dt Acceleration a = dv/dt Mass m Newton s second law F = ma Work W = Fdcosφ
Chapter 10: Rotation Review of translational motion (motion along a straight line) Position x Displacement x Velocity v = dx/dt Acceleration a = dv/dt Mass m Newton s second law F = ma Work W = Fdcosφ
Webreview Torque and Rotation Practice Test
 Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview - 8.2 Torque and Rotation Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 0.30-m-radius automobile
Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview - 8.2 Torque and Rotation Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 0.30-m-radius automobile
Rotational Dynamics continued
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued 9.4 Newton s Second Law for Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis ROTATIONAL ANALOG OF NEWTON S SECOND LAW FOR A RIGID BODY ROTATING ABOUT A FIXED AXIS I = ( mr 2
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued 9.4 Newton s Second Law for Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis ROTATIONAL ANALOG OF NEWTON S SECOND LAW FOR A RIGID BODY ROTATING ABOUT A FIXED AXIS I = ( mr 2
Kinematics. 1. Introduction to Kinematics. 2. Position and displacement
 Kinematics 1. Introduction to Kinematics. Scalars & vectors 2. Position & displacement 3. Velocity 4. Acceleration 5. Uniform linear motion 6. Uniformly accelerated motion 7. Uniform circular motion 1.
Kinematics 1. Introduction to Kinematics. Scalars & vectors 2. Position & displacement 3. Velocity 4. Acceleration 5. Uniform linear motion 6. Uniformly accelerated motion 7. Uniform circular motion 1.
Advanced Higher Physics. Rotational motion
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Cams. 774 l Theory of Machines
 774 l Theory of Machines 0 Fea eatur tures es 1. Introduction.. Classification of Followers. 3. Classification of Cams. 4. Terms used in Radial cams. 5. Motion of the Follower. 6. Displacement, Velocity
774 l Theory of Machines 0 Fea eatur tures es 1. Introduction.. Classification of Followers. 3. Classification of Cams. 4. Terms used in Radial cams. 5. Motion of the Follower. 6. Displacement, Velocity
ROTATORY MOTION. ii) iii) iv) W = v) Power = vi) Torque ( vii) Angular momentum (L) = Iω similar to P = mv 1 Iω. similar to F = ma
 OTATOY MOTION Synopsis : CICULA MOTION :. In translatory motion, every particle travels the same distance along parallel paths, which may be straight or curved. Every particle of the body has the same
OTATOY MOTION Synopsis : CICULA MOTION :. In translatory motion, every particle travels the same distance along parallel paths, which may be straight or curved. Every particle of the body has the same
Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14)
 Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS QUESTION 1. Which of the following defines a scalar quantity? (a) (b) (c) (d) Magnitude only Magnitude and direction Direction None of the above QUESTION 2. Which of the
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS QUESTION 1. Which of the following defines a scalar quantity? (a) (b) (c) (d) Magnitude only Magnitude and direction Direction None of the above QUESTION 2. Which of the
Definition. is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau)
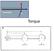 Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Position: Angular position =! = s r. Displacement: Angular displacement =!" = " 2
 Chapter 11 Rotation Perfectly Rigid Objects fixed shape throughout motion Rotation of rigid bodies about a fixed axis of rotation. In pure rotational motion: every point on the body moves in a circle who
Chapter 11 Rotation Perfectly Rigid Objects fixed shape throughout motion Rotation of rigid bodies about a fixed axis of rotation. In pure rotational motion: every point on the body moves in a circle who
PLANAR RIGID BODY MOTION: TRANSLATION &
 PLANAR RIGID BODY MOTION: TRANSLATION & Today s Objectives : ROTATION Students will be able to: 1. Analyze the kinematics of a rigid body undergoing planar translation or rotation about a fixed axis. In-Class
PLANAR RIGID BODY MOTION: TRANSLATION & Today s Objectives : ROTATION Students will be able to: 1. Analyze the kinematics of a rigid body undergoing planar translation or rotation about a fixed axis. In-Class
Torque and Rotation Lecture 7
 Torque and Rotation Lecture 7 ˆ In this lecture we finally move beyond a simple particle in our mechanical analysis of motion. ˆ Now we consider the so-called rigid body. Essentially, a particle with extension
Torque and Rotation Lecture 7 ˆ In this lecture we finally move beyond a simple particle in our mechanical analysis of motion. ˆ Now we consider the so-called rigid body. Essentially, a particle with extension
Motion in Space. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Motion in Space
 Motion in Space MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Suppose the position vector of a moving object is given by r(t) = f (t), g(t), h(t), Background
Motion in Space MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Suppose the position vector of a moving object is given by r(t) = f (t), g(t), h(t), Background
3. Kinetics of Particles
 3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
Chapter 8. Rotational Motion
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Rotational Work and Energy W = Fs = s = rθ Frθ Consider the work done in rotating a wheel with a tangential force, F, by an angle θ. τ = Fr W =τθ Rotational Work and Energy
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion Rotational Work and Energy W = Fs = s = rθ Frθ Consider the work done in rotating a wheel with a tangential force, F, by an angle θ. τ = Fr W =τθ Rotational Work and Energy
Tute M4 : ROTATIONAL MOTION 1
 Tute M4 : ROTATIONAL MOTION 1 The equations dealing with rotational motion are identical to those of linear motion in their mathematical form. To convert equations for linear motion to those for rotational
Tute M4 : ROTATIONAL MOTION 1 The equations dealing with rotational motion are identical to those of linear motion in their mathematical form. To convert equations for linear motion to those for rotational
Advanced Higher Physics. Rotational Motion
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational Motion Solutions AH Physics: Rotational Motion Problems Solutions Page 1 013 TUTORIAL 1.0 Equations of motion 1. (a) v = ds, ds
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational Motion Solutions AH Physics: Rotational Motion Problems Solutions Page 1 013 TUTORIAL 1.0 Equations of motion 1. (a) v = ds, ds
Chapter 8 continued. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.6 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.6 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
6. Find the net torque on the wheel in Figure about the axle through O if a = 10.0 cm and b = 25.0 cm.
 1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
Mechanics Cycle 1 Chapter 12. Chapter 12. Forces Causing Curved Motion
 Chapter 1 Forces Causing Curved Motion A Force Must be Applied to Change Direction Coordinates, Angles, Angular Velocity, and Angular Acceleration Centripetal Acceleration and Tangential Acceleration Along
Chapter 1 Forces Causing Curved Motion A Force Must be Applied to Change Direction Coordinates, Angles, Angular Velocity, and Angular Acceleration Centripetal Acceleration and Tangential Acceleration Along
= o + t = ot + ½ t 2 = o + 2
 Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
It will be most difficult for the ant to adhere to the wheel as it revolves past which of the four points? A) I B) II C) III D) IV
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 16 Homework Newton s First and Second Law of Rotational Motion Outcomes Define rotational inertia, torque, and center of gravity. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion as it
AP Physics 1 Lesson 16 Homework Newton s First and Second Law of Rotational Motion Outcomes Define rotational inertia, torque, and center of gravity. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion as it
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium. 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum Copyright 11.2 Rolling as Translational and Rotation Combined Motion of Translation : i.e.motion along a straight line Motion of Rotation : rotation about a
Chapter 11 Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum Copyright 11.2 Rolling as Translational and Rotation Combined Motion of Translation : i.e.motion along a straight line Motion of Rotation : rotation about a
Central Angles and Arcs
 Advance Algebra & Trigonometry Angles & Circular Functions Central Angles and Arcs Arc Length 1. A central angle an angle whose vertex lies at the center of the circle: A B ABC is a central angle C 2.
Advance Algebra & Trigonometry Angles & Circular Functions Central Angles and Arcs Arc Length 1. A central angle an angle whose vertex lies at the center of the circle: A B ABC is a central angle C 2.
Rotational Kinematics, Physics. Worksheet 1: Practice working with rotation and revolution
 Rotational Kinematics, Physics Worksheet 1: Practice working with rotation and revolution Circular motion can involve rotation and/or revolution. Rotation occurs when the object spins about an internal
Rotational Kinematics, Physics Worksheet 1: Practice working with rotation and revolution Circular motion can involve rotation and/or revolution. Rotation occurs when the object spins about an internal
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
Suggested Problems. Chapter 1
 Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Conservation of Angular Momentum
 Physics 101 Section 3 March 3 rd : Ch. 10 Announcements: Monday s Review Posted (in Plummer s section (4) Today start Ch. 10. Next Quiz will be next week Test# (Ch. 7-9) will be at 6 PM, March 3, Lockett-6
Physics 101 Section 3 March 3 rd : Ch. 10 Announcements: Monday s Review Posted (in Plummer s section (4) Today start Ch. 10. Next Quiz will be next week Test# (Ch. 7-9) will be at 6 PM, March 3, Lockett-6
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions. Newton s second law in terms of momentum:
 linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
Option B Engineering physics
 Option B Engineering physics B1 Rotational dynamics In the mechanics we have studied so far, we have assumed that we were dealing with point masses. A net force applied to a point mass will accelerate
Option B Engineering physics B1 Rotational dynamics In the mechanics we have studied so far, we have assumed that we were dealing with point masses. A net force applied to a point mass will accelerate
Rigid Object. Chapter 10. Angular Position. Angular Position. A rigid object is one that is nondeformable
 Rigid Object Chapter 10 Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis A rigid object is one that is nondeformable The relative locations of all particles making up the object remain constant All real objects
Rigid Object Chapter 10 Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis A rigid object is one that is nondeformable The relative locations of all particles making up the object remain constant All real objects
dt 2 For an object travelling in a circular path: State that angular velocity (ω) is the rate of change of angular displacement (θ).
 For an object travelling in a circular path: State that angular velocity (ω) is the rate of change of angular displacement (θ). ω = dθ dt State that angular acceleration (α) is the rate of change of angular
For an object travelling in a circular path: State that angular velocity (ω) is the rate of change of angular displacement (θ). ω = dθ dt State that angular acceleration (α) is the rate of change of angular
Practice Test 3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20 rad/s. During
Practice Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20 rad/s. During
ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS
 CHAPTER 8 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS. (d) Using Equation 8. (θ = Arc length / Radius) to calculate the angle (in radians) that each object subtends at your eye shows that
CHAPTER 8 ROTATIONAL KINEMATICS ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS. (d) Using Equation 8. (θ = Arc length / Radius) to calculate the angle (in radians) that each object subtends at your eye shows that
Honors Physics Review
 Honors Physics Review Work, Power, & Energy (Chapter 5) o Free Body [Force] Diagrams Energy Work Kinetic energy Gravitational Potential Energy (using g = 9.81 m/s 2 ) Elastic Potential Energy Hooke s Law
Honors Physics Review Work, Power, & Energy (Chapter 5) o Free Body [Force] Diagrams Energy Work Kinetic energy Gravitational Potential Energy (using g = 9.81 m/s 2 ) Elastic Potential Energy Hooke s Law
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3
 Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
Circular Motion Dynamics
 Circular Motion Dynamics 8.01 W04D2 Today s Reading Assignment: MIT 8.01 Course Notes Chapter 9 Circular Motion Dynamics Sections 9.1-9.2 Announcements Problem Set 3 due Week 5 Tuesday at 9 pm in box outside
Circular Motion Dynamics 8.01 W04D2 Today s Reading Assignment: MIT 8.01 Course Notes Chapter 9 Circular Motion Dynamics Sections 9.1-9.2 Announcements Problem Set 3 due Week 5 Tuesday at 9 pm in box outside
Physics 2514 Lecture 22
 Physics 2514 Lecture 22 P. Gutierrez Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Oklahoma Physics 2514 p. 1/15 Information Information needed for the exam Exam will be in the same format as the practice
Physics 2514 Lecture 22 P. Gutierrez Department of Physics & Astronomy University of Oklahoma Physics 2514 p. 1/15 Information Information needed for the exam Exam will be in the same format as the practice
Complete the table by filling in the symbols and equations. Include any notes that will help you remember and understand what these terms mean.
 AP Physics Rotational kinematics Rotational Kinematics Complete the table by filling in the symbols and equations. Include any notes that will help you remember and understand what these terms mean. Translational
AP Physics Rotational kinematics Rotational Kinematics Complete the table by filling in the symbols and equations. Include any notes that will help you remember and understand what these terms mean. Translational
