Machine Learning CPSC 340. Tutorial 12
|
|
|
- Janis Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Machine Learning CPSC 340 Tutorial 12
2 Random Walk on Graph Page Rank Algorithm
3 Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A)
4 Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) V: set of nodes
5 Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) V: set of nodes A: adjacency matrix
6 Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) V: set of nodes A: adjacency matrix Two type of nodes: labeled and unlabeled
7 Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) V: set of nodes A: adjacency matrix Two type of nodes: labeled and unlabeled Label is either +1 or -1
8 Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) V: set of nodes A: adjacency matrix Two type of nodes: labeled and unlabeled Label is either +1 or -1 Gaol: assign a label to unlabeled nodes.
9 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk on Graph: we jump from one node to another one with some probability
10 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk on Graph: we jump from one node to another one with some probability Label propagation algorithm
11 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk on Graph: we jump from one node to another one with some probability Label propagation algorithm start from an unlabeled node v
12 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk on Graph: we jump from one node to another one with some probability Label propagation algorithm start from an unlabeled node v do k times random walk starting from v and store the output labels
13 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk on Graph: we jump from one node to another one with some probability Label propagation algorithm start from an unlabeled node v do k times random walk starting from v and store the output labels do majority vote among the stored labels
14 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk Algorithm repeat until you find a label
15 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk Algorithm repeat until you find a label let v be the node you are in and has d v neighbours
16 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk Algorithm repeat until you find a label let v be the node you are in and has d v neighbours if v is unlabeled, with uniform probability 1 d v pick one of its neighbours and jump to that node
17 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk Algorithm repeat until you find a label let v be the node you are in and has d v neighbours if v is unlabeled, with uniform probability 1 d v pick one of its neighbours and jump to that node if v is labeled
18 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk Algorithm repeat until you find a label let v be the node you are in and has d v neighbours if v is unlabeled, with uniform probability 1 d v pick one of its neighbours and jump to that node if v is labeled with probability 1 d v +1 output its label
19 Random Walk for Label Propagation Random Walk Algorithm repeat until you find a label let v be the node you are in and has d v neighbours if v is unlabeled, with uniform probability 1 d v pick one of its neighbours and jump to that node if v is labeled with probability 1 d v +1 output its label with uniform probability 1 d v +1 pick one of its neighbours jump to that node
20 Exercise Assume we are given adjacency matrix, a labellist, a matrix where the first column contains node numbers and the second column contains class labels and starting node, write code for random walk algorithm.
21 RW code
22 Ranking Problem The ranking problem: Input: a large set of objects (and possibly a query object). Output option 1: score of each object (and possibly for query). Output option 2: ordered list of most relevant objects (possibly for query).
23 Ranking Problem The ranking problem: Input: a large set of objects (and possibly a query object). Output option 1: score of each object (and possibly for query). Output option 2: ordered list of most relevant objects (possibly for query). Examples: Country comparisons (Global Hunger Index) Academic journals (Impact factor). Sports/gaming (Elo and TrueSkill) Internet search engines
24 PageRank Goal: ranking webpages based on some score or weight
25 PageRank Goal: ranking webpages based on some score or weight Assuming that we have n webpages and let the score of webpage i be p i, and P = (p i ) be a vector of size n
26 PageRank Goal: ranking webpages based on some score or weight Assuming that we have n webpages and let the score of webpage i be p i, and P = (p i ) be a vector of size n Make the directed webpage graph G node i has an edge into node j if there is a link from page i to j i.e. i j. Assume this graph is strongly connected and aperiodic and does not have absorbing node
27 PageRank Goal: ranking webpages based on some score or weight Assuming that we have n webpages and let the score of webpage i be p i, and P = (p i ) be a vector of size n Make the directed webpage graph G node i has an edge into node j if there is a link from page i to j i.e. i j. Assume this graph is strongly connected and aperiodic and does not have absorbing node Let m j be the number of outgoing edges from node j and m = (m j ) be a vector of size n
28 PageRank Goal: ranking webpages based on some score or weight Assuming that we have n webpages and let the score of webpage i be p i, and P = (p i ) be a vector of size n Make the directed webpage graph G node i has an edge into node j if there is a link from page i to j i.e. i j. Assume this graph is strongly connected and aperiodic and does not have absorbing node Let m j be the number of outgoing edges from node j and m = (m j ) be a vector of size n Let A be the adjacency matrix for G i.e. A ij = 1 if i j o.w. A ij = 0
29 PageRank Goal: ranking webpages based on some score or weight Assuming that we have n webpages and let the score of webpage i be p i, and P = (p i ) be a vector of size n Make the directed webpage graph G node i has an edge into node j if there is a link from page i to j i.e. i j. Assume this graph is strongly connected and aperiodic and does not have absorbing node Let m j be the number of outgoing edges from node j and m = (m j ) be a vector of size n Let A be the adjacency matrix for G i.e. A ij = 1 if i j o.w. A ij = 0 Let Z = A T (diag(m)) 1
30 PageRank Goal: ranking webpages based on some score or weight Assuming that we have n webpages and let the score of webpage i be p i, and P = (p i ) be a vector of size n Make the directed webpage graph G node i has an edge into node j if there is a link from page i to j i.e. i j. Assume this graph is strongly connected and aperiodic and does not have absorbing node Let m j be the number of outgoing edges from node j and m = (m j ) be a vector of size n Let A be the adjacency matrix for G i.e. A ij = 1 if i j o.w. A ij = 0 Let Z = A T (diag(m)) 1 (Z) ij : probability of jumping from page j to page i via a link
31 PageRank Goal: ranking webpages based on some score or weight Assuming that we have n webpages and let the score of webpage i be p i, and P = (p i ) be a vector of size n Make the directed webpage graph G node i has an edge into node j if there is a link from page i to j i.e. i j. Assume this graph is strongly connected and aperiodic and does not have absorbing node Let m j be the number of outgoing edges from node j and m = (m j ) be a vector of size n Let A be the adjacency matrix for G i.e. A ij = 1 if i j o.w. A ij = 0 Let Z = A T (diag(m)) 1 (Z) ij : probability of jumping from page j to page i via a link But we can go directly from page j to i by entering the address of page i in the address-bar of browser add some small amount to all (Z)ij and normalize!
32 PageRank For some d (0, 1) let E = ones(n, n) and T = 1 d n E + dz
33 PageRank For some d (0, 1) let E = ones(n, n) and T = 1 d n E + dz Now with transition matrix T for a webpage graph G, we have P = TP
34 PageRank For some d (0, 1) let E = ones(n, n) and T = 1 d n E + dz Now with transition matrix T for a webpage graph G, we have P = TP Each p i is a probability, so n i=1 p i = 1
35 PageRank For some d (0, 1) let E = ones(n, n) and T = 1 d n E + dz Now with transition matrix T for a webpage graph G, we have P = TP Each p i is a probability, so n i=1 p i = 1 With two above equations, we can find all p i s by solving corresponding linear system
36 PageRank: Exercise Let d = 3 4. For the following webpage graph, find A, m, Z and T. Then make the linear system and solve it and find P.
37 PageRank: Solution m = 2 2 A = Z = T = Z = P = TP (T I )P = 0 (I is Identity matrix) 4 p i = 1 i=
38 PageRank: Solution Combining two equations, we get P = p 1 p 2 p 3 p 4 0 =
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2019 Last Time: Monte Carlo Methods If we want to approximate expectations of random functions, E[g(x)] = g(x)p(x) or E[g(x)]
CPSC 540: Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2019 Last Time: Monte Carlo Methods If we want to approximate expectations of random functions, E[g(x)] = g(x)p(x) or E[g(x)]
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
Link Mining PageRank. From Stanford C246
 Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
Slides based on those in:
 Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
A Note on Google s PageRank
 A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING
 CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING Graph and Network Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu May 31, 2017 Methods Learnt Classification Clustering Vector Data Text Data Recommender System Decision Tree; Naïve
CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING Graph and Network Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu May 31, 2017 Methods Learnt Classification Clustering Vector Data Text Data Recommender System Decision Tree; Naïve
Link Analysis. Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016
 Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y
 Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
Data and Algorithms of the Web
 Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm
 Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
1998: enter Link Analysis
 1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
DATA MINING LECTURE 13. Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
 DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Lecture 15: MCMC Sanjeev Arora Elad Hazan. COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall 2016
 Lecture 15: MCMC Sanjeev Arora Elad Hazan COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall 2016 Course progress Learning from examples Definition + fundamental theorem of statistical learning,
Lecture 15: MCMC Sanjeev Arora Elad Hazan COS 402 Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence Fall 2016 Course progress Learning from examples Definition + fundamental theorem of statistical learning,
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University.
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
Math 304 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks.
 Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012
 Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Graph Mining II
 Welcome to DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Graph Mining II Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 6:00pm 8:50pm Mon. and Wed. Location: SL105 Spring 2016 Reading assignments We will increase the bar a little bit Please
Welcome to DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Graph Mining II Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 6:00pm 8:50pm Mon. and Wed. Location: SL105 Spring 2016 Reading assignments We will increase the bar a little bit Please
Link Analysis. Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze
 Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Graph Mining II
 Welcome to DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Graph Mining II Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 6-8:50PM Thursday Location: AK233 Spring 2018 v Course Project I has been graded. Grading was based on v 1. Project report
Welcome to DS504/CS586: Big Data Analytics Graph Mining II Prof. Yanhua Li Time: 6-8:50PM Thursday Location: AK233 Spring 2018 v Course Project I has been graded. Grading was based on v 1. Project report
Algebraic Representation of Networks
 Algebraic Representation of Networks 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu Describing networks with matrices (1) Adjacency matrix A matrix with rows and columns labeled by
Algebraic Representation of Networks 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu Describing networks with matrices (1) Adjacency matrix A matrix with rows and columns labeled by
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral clustering Course Webpage : http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4786/2016sp/ ANNOUNCEMENT 1 Assignment P1 the Diagnostic assignment 1 will
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 11 Spectral clustering Course Webpage : http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4786/2016sp/ ANNOUNCEMENT 1 Assignment P1 the Diagnostic assignment 1 will
LINK ANALYSIS. Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS
 LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2018 Last Time: Monte Carlo Methods If we want to approximate expectations of random functions, E[g(x)] = g(x)p(x) or E[g(x)]
CPSC 540: Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2018 Last Time: Monte Carlo Methods If we want to approximate expectations of random functions, E[g(x)] = g(x)p(x) or E[g(x)]
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks
 ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3
 Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
IR: Information Retrieval
 / 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
/ 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval
 Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
CS 277: Data Mining. Mining Web Link Structure. CS 277: Data Mining Lectures Analyzing Web Link Structure Padhraic Smyth, UC Irvine
 CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
Lecture Notes: Markov chains Tuesday, September 16 Dannie Durand
 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Lecture Notes: Markov chains Tuesday, September 6 Dannie Durand In the last lecture, we introduced Markov chains, a mathematical formalism for modeling how
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Lecture Notes: Markov chains Tuesday, September 6 Dannie Durand In the last lecture, we introduced Markov chains, a mathematical formalism for modeling how
Link Analysis and Web Search
 Link Analysis and Web Search Episode 11 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Link Analysis and Web Search (Chapter 13, 14) Information networks and
Link Analysis and Web Search Episode 11 Baochun Li Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto Link Analysis and Web Search (Chapter 13, 14) Information networks and
As it is not necessarily possible to satisfy this equation, we just ask for a solution to the more general equation
 Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Lesson Plan. AM 121: Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods. Lecture 17: Markov Chains. Yiling Chen SEAS. Stochastic process Markov Chains
 AM : Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 7: Markov Chains Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Stochastic process Markov Chains n-step probabilities Communicating states, irreducibility Recurrent
AM : Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 7: Markov Chains Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Stochastic process Markov Chains n-step probabilities Communicating states, irreducibility Recurrent
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University.
 Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence
 Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Markov Chains and MCMC
 Markov Chains and MCMC Markov chains Let S = {1, 2,..., N} be a finite set consisting of N states. A Markov chain Y 0, Y 1, Y 2,... is a sequence of random variables, with Y t S for all points in time
Markov Chains and MCMC Markov chains Let S = {1, 2,..., N} be a finite set consisting of N states. A Markov chain Y 0, Y 1, Y 2,... is a sequence of random variables, with Y t S for all points in time
Wiki Definition. Reputation Systems I. Outline. Introduction to Reputations. Yury Lifshits. HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte
 Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
PageRank algorithm Hubs and Authorities. Data mining. Web Data Mining PageRank, Hubs and Authorities. University of Szeged.
 Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Inf 2B: Ranking Queries on the WWW
 Inf B: Ranking Queries on the WWW Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Queries Suppose we have an Inverted Index for a set of webpages. Disclaimer Not really the scenario of
Inf B: Ranking Queries on the WWW Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Queries Suppose we have an Inverted Index for a set of webpages. Disclaimer Not really the scenario of
Improving Diversity in Ranking using Absorbing Random Walks
 Improving Diversity in Ranking using Absorbing Random Walks Andrew B. Goldberg with Xiaojin Zhu, Jurgen Van Gael, and David Andrzejewski Department of Computer Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison
Improving Diversity in Ranking using Absorbing Random Walks Andrew B. Goldberg with Xiaojin Zhu, Jurgen Van Gael, and David Andrzejewski Department of Computer Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison
How does Google rank webpages?
 Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Statistical Problem. . We may have an underlying evolving system. (new state) = f(old state, noise) Input data: series of observations X 1, X 2 X t
 Markov Chains. Statistical Problem. We may have an underlying evolving system (new state) = f(old state, noise) Input data: series of observations X 1, X 2 X t Consecutive speech feature vectors are related
Markov Chains. Statistical Problem. We may have an underlying evolving system (new state) = f(old state, noise) Input data: series of observations X 1, X 2 X t Consecutive speech feature vectors are related
PageRank. Ryan Tibshirani /36-662: Data Mining. January Optional reading: ESL 14.10
 PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
Information Retrieval and Search. Web Linkage Mining. Miłosz Kadziński
 Web Linkage Analysis D24 D4 : Web Linkage Mining Miłosz Kadziński Institute of Computing Science Poznan University of Technology, Poland www.cs.put.poznan.pl/mkadzinski/wpi Web mining: Web Mining Discovery
Web Linkage Analysis D24 D4 : Web Linkage Mining Miłosz Kadziński Institute of Computing Science Poznan University of Technology, Poland www.cs.put.poznan.pl/mkadzinski/wpi Web mining: Web Mining Discovery
Name: Matriculation Number: Tutorial Group: A B C D E
 Name: Matriculation Number: Tutorial Group: A B C D E Question: 1 (5 Points) 2 (6 Points) 3 (5 Points) 4 (5 Points) Total (21 points) Score: General instructions: The written test contains 4 questions
Name: Matriculation Number: Tutorial Group: A B C D E Question: 1 (5 Points) 2 (6 Points) 3 (5 Points) 4 (5 Points) Total (21 points) Score: General instructions: The written test contains 4 questions
An Introduction to Machine Learning
 An Introduction to Machine Learning L6: Structured Estimation Alexander J. Smola Statistical Machine Learning Program Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia Alex.Smola@nicta.com.au Tata Institute, Pune, January
An Introduction to Machine Learning L6: Structured Estimation Alexander J. Smola Statistical Machine Learning Program Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia Alex.Smola@nicta.com.au Tata Institute, Pune, January
Learning from Labeled and Unlabeled Data: Semi-supervised Learning and Ranking p. 1/31
 Learning from Labeled and Unlabeled Data: Semi-supervised Learning and Ranking Dengyong Zhou zhou@tuebingen.mpg.de Dept. Schölkopf, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Germany Learning from
Learning from Labeled and Unlabeled Data: Semi-supervised Learning and Ranking Dengyong Zhou zhou@tuebingen.mpg.de Dept. Schölkopf, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Germany Learning from
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis. Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa
 Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Spectral Graph Theory and You: Matrix Tree Theorem and Centrality Metrics
 Spectral Graph Theory and You: and Centrality Metrics Jonathan Gootenberg March 11, 2013 1 / 19 Outline of Topics 1 Motivation Basics of Spectral Graph Theory Understanding the characteristic polynomial
Spectral Graph Theory and You: and Centrality Metrics Jonathan Gootenberg March 11, 2013 1 / 19 Outline of Topics 1 Motivation Basics of Spectral Graph Theory Understanding the characteristic polynomial
IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval. PageRank Con+nued. with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma
 IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval PageRank Con+nued with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma Exercise: Assump0ons underlying PageRank Assump0on 1: A link on the web is a quality signal the
IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval PageRank Con+nued with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma Exercise: Assump0ons underlying PageRank Assump0on 1: A link on the web is a quality signal the
Data Mining Techniques
 Data Mining Techniques CS 622 - Section 2 - Spring 27 Pre-final Review Jan-Willem van de Meent Feedback Feedback https://goo.gl/er7eo8 (also posted on Piazza) Also, please fill out your TRACE evaluations!
Data Mining Techniques CS 622 - Section 2 - Spring 27 Pre-final Review Jan-Willem van de Meent Feedback Feedback https://goo.gl/er7eo8 (also posted on Piazza) Also, please fill out your TRACE evaluations!
Data Mining and Matrices
 Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
1 Searching the World Wide Web
 Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Graphic sequences, adjacency matrix
 Chapter 2 Graphic sequences, adjacency matrix Definition 2.1. A sequence of integers (d 1,..., d n ) is called graphic if it is the degree sequence of a graph. Example 2.2. 1. (1, 2, 2, 3) is graphic:
Chapter 2 Graphic sequences, adjacency matrix Definition 2.1. A sequence of integers (d 1,..., d n ) is called graphic if it is the degree sequence of a graph. Example 2.2. 1. (1, 2, 2, 3) is graphic:
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Unsupervised Image Segmentation Using Comparative Reasoning and Random Walks
 Unsupervised Image Segmentation Using Comparative Reasoning and Random Walks Anuva Kulkarni Carnegie Mellon University Filipe Condessa Carnegie Mellon, IST-University of Lisbon Jelena Kovacevic Carnegie
Unsupervised Image Segmentation Using Comparative Reasoning and Random Walks Anuva Kulkarni Carnegie Mellon University Filipe Condessa Carnegie Mellon, IST-University of Lisbon Jelena Kovacevic Carnegie
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
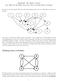 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
Attentive Betweenness Centrality (ABC): Considering Options and Bandwidth when Measuring Criticality
 Attentive Betweenness Centrality (ABC): Considering Options and Bandwidth when Measuring Criticality Sibel Adalı, Xiaohui Lu, M. Magdon-Ismail September 5, 0 Who is the Most Critical? Would you use the
Attentive Betweenness Centrality (ABC): Considering Options and Bandwidth when Measuring Criticality Sibel Adalı, Xiaohui Lu, M. Magdon-Ismail September 5, 0 Who is the Most Critical? Would you use the
Comparing whole genomes
 BioNumerics Tutorial: Comparing whole genomes 1 Aim The Chromosome Comparison window in BioNumerics has been designed for large-scale comparison of sequences of unlimited length. In this tutorial you will
BioNumerics Tutorial: Comparing whole genomes 1 Aim The Chromosome Comparison window in BioNumerics has been designed for large-scale comparison of sequences of unlimited length. In this tutorial you will
Lecture 2: The Simplex method
 Lecture 2 1 Linear and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture 2: The Simplex method Basic solution. The Simplex method (standardform, b>0). 1. Repetition of basic solution. 2. One step in the Simplex algorithm.
Lecture 2 1 Linear and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture 2: The Simplex method Basic solution. The Simplex method (standardform, b>0). 1. Repetition of basic solution. 2. One step in the Simplex algorithm.
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 110
 Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Google PageRank. Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano
 Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
Chapter 10. Finite-State Markov Chains. Introductory Example: Googling Markov Chains
 Chapter 0 Finite-State Markov Chains Introductory Example: Googling Markov Chains Google means many things: it is an Internet search engine, the company that produces the search engine, and a verb meaning
Chapter 0 Finite-State Markov Chains Introductory Example: Googling Markov Chains Google means many things: it is an Internet search engine, the company that produces the search engine, and a verb meaning
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS
 LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS Markov Process and Markov Chains Hidden Markov Models Kalman Filters Types of dynamic systems Problem of future state prediction Predictability Observability Easily
LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS Markov Process and Markov Chains Hidden Markov Models Kalman Filters Types of dynamic systems Problem of future state prediction Predictability Observability Easily
Lecture VI Introduction to complex networks. Santo Fortunato
 Lecture VI Introduction to complex networks Santo Fortunato Plan of the course I. Networks: definitions, characteristics, basic concepts in graph theory II. III. IV. Real world networks: basic properties
Lecture VI Introduction to complex networks Santo Fortunato Plan of the course I. Networks: definitions, characteristics, basic concepts in graph theory II. III. IV. Real world networks: basic properties
Three right directions and three wrong directions for tensor research
 Three right directions and three wrong directions for tensor research Michael W. Mahoney Stanford University ( For more info, see: http:// cs.stanford.edu/people/mmahoney/ or Google on Michael Mahoney
Three right directions and three wrong directions for tensor research Michael W. Mahoney Stanford University ( For more info, see: http:// cs.stanford.edu/people/mmahoney/ or Google on Michael Mahoney
Semi Supervised Distance Metric Learning
 Semi Supervised Distance Metric Learning wliu@ee.columbia.edu Outline Background Related Work Learning Framework Collaborative Image Retrieval Future Research Background Euclidean distance d( x, x ) =
Semi Supervised Distance Metric Learning wliu@ee.columbia.edu Outline Background Related Work Learning Framework Collaborative Image Retrieval Future Research Background Euclidean distance d( x, x ) =
Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page
![Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page](/thumbs/95/125556981.jpg) IV.3 HITS Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) hubs as good link sources (~high outdegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page a
IV.3 HITS Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) hubs as good link sources (~high outdegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page a
Intelligent Data Analysis. PageRank. School of Computer Science University of Birmingham
 Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
Register machines L2 18
 Register machines L2 18 Algorithms, informally L2 19 No precise definition of algorithm at the time Hilbert posed the Entscheidungsproblem, just examples. Common features of the examples: finite description
Register machines L2 18 Algorithms, informally L2 19 No precise definition of algorithm at the time Hilbert posed the Entscheidungsproblem, just examples. Common features of the examples: finite description
Outline for today. Information Retrieval. Cosine similarity between query and document. tf-idf weighting
 Outline for today Information Retrieval Efficient Scoring and Ranking Recap on ranked retrieval Jörg Tiedemann jorg.tiedemann@lingfil.uu.se Department of Linguistics and Philology Uppsala University Efficient
Outline for today Information Retrieval Efficient Scoring and Ranking Recap on ranked retrieval Jörg Tiedemann jorg.tiedemann@lingfil.uu.se Department of Linguistics and Philology Uppsala University Efficient
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity. Due July 18, 2014
 Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK. Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech. Lecture for CS 6505
 INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications
 Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications CDSE Days University at Buffalo, State University of New York Monday April 9, 2018 Dane Taylor Assistant Professor of Mathematics
Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications CDSE Days University at Buffalo, State University of New York Monday April 9, 2018 Dane Taylor Assistant Professor of Mathematics
The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a
 Journal of Web Engineering, Vol. 0, No. 0 (2003) 000 000 c Rinton Press The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a Vassilis Plachouras University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ UK vassilis@dcs.gla.ac.uk Iadh
Journal of Web Engineering, Vol. 0, No. 0 (2003) 000 000 c Rinton Press The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a Vassilis Plachouras University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ UK vassilis@dcs.gla.ac.uk Iadh
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 20, 4/11/2017
 COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 20, 4/11/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University SEQUENTIAL DATA So far, when thinking
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 20, 4/11/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University SEQUENTIAL DATA So far, when thinking
Tutorial 12 Excess Pore Pressure (B-bar method) Undrained loading (B-bar method) Initial pore pressure Excess pore pressure
 Tutorial 12 Excess Pore Pressure (B-bar method) Undrained loading (B-bar method) Initial pore pressure Excess pore pressure Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate the Excess Pore Pressure (Undrained
Tutorial 12 Excess Pore Pressure (B-bar method) Undrained loading (B-bar method) Initial pore pressure Excess pore pressure Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate the Excess Pore Pressure (Undrained
CLUe Training An Introduction to Machine Learning in R with an example from handwritten digit recognition
 CLUe Training An Introduction to Machine Learning in R with an example from handwritten digit recognition Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Department of Information and Computing Sciences Algorithmic Data
CLUe Training An Introduction to Machine Learning in R with an example from handwritten digit recognition Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Department of Information and Computing Sciences Algorithmic Data
Node similarity and classification
 Node similarity and classification Davide Mottin, Anton Tsitsulin HassoPlattner Institute Graph Mining course Winter Semester 2017 Acknowledgements Some part of this lecture is taken from: http://web.eecs.umich.edu/~dkoutra/tut/icdm14.html
Node similarity and classification Davide Mottin, Anton Tsitsulin HassoPlattner Institute Graph Mining course Winter Semester 2017 Acknowledgements Some part of this lecture is taken from: http://web.eecs.umich.edu/~dkoutra/tut/icdm14.html
The Theory behind PageRank
 The Theory behind PageRank Mauro Sozio Telecom ParisTech May 21, 2014 Mauro Sozio (LTCI TPT) The Theory behind PageRank May 21, 2014 1 / 19 A Crash Course on Discrete Probability Events and Probability
The Theory behind PageRank Mauro Sozio Telecom ParisTech May 21, 2014 Mauro Sozio (LTCI TPT) The Theory behind PageRank May 21, 2014 1 / 19 A Crash Course on Discrete Probability Events and Probability
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems. Tutorial Note 9
 ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 9 Outline 1. Exercise(1) Sequential Circuit Analysis 2. Exercise (2) Sequential Circuit Analysis 3. Exercise (3) Sequential Circuit Analysis 4. Ref. Construction
Vector Space Model. Yufei Tao KAIST. March 5, Y. Tao, March 5, 2013 Vector Space Model
 Vector Space Model Yufei Tao KAIST March 5, 2013 In this lecture, we will study a problem that is (very) fundamental in information retrieval, and must be tackled by all search engines. Let S be a set
Vector Space Model Yufei Tao KAIST March 5, 2013 In this lecture, we will study a problem that is (very) fundamental in information retrieval, and must be tackled by all search engines. Let S be a set
MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds
 MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, 2008 Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds Search for information Assume some resource of interest is stored at the vertices of a network: Web pages Files in a file-sharing
MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, 2008 Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds Search for information Assume some resource of interest is stored at the vertices of a network: Web pages Files in a file-sharing
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors
 MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee
 Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee Overview Markov Property Markov Chains Definition Stationary Property Paths in Markov Chains Classification of States Steady States in MCs. 2 Markov Property A discrete
Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee Overview Markov Property Markov Chains Definition Stationary Property Paths in Markov Chains Classification of States Steady States in MCs. 2 Markov Property A discrete
CS54701 Information Retrieval. Link Analysis. Luo Si. Department of Computer Science Purdue University. Borrowed Slides from Prof.
 CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU) Citation Analysis Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site
CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU) Citation Analysis Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site
