Lecture Notes: Markov chains Tuesday, September 16 Dannie Durand
|
|
|
- Kerrie Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Lecture Notes: Markov chains Tuesday, September 6 Dannie Durand In the last lecture, we introduced Markov chains, a mathematical formalism for modeling how a random variable progresses over time. We introduced the following notation for describing the properties of a Markov chain: A Markov chain has states E, E,... E s corresponding to the range of the associated random variable. ϕ j (t) is the probability that the chain is in state E j at time t. The vector ϕ(t) = (ϕ (t),... ϕ s (t)) is the state probability distribution at time t. π = ϕ() is the initial state probability distribution. P is the transition probability matrix. P jk gives the probability of making a transition to state E k at time t +, given that the chain was in state E j at time t. The rows of this matrix sum to one ( k P jk = ). The state probability distribution at time t+ is given by ϕ(t+) = ϕ(t) P. The probability of being in state E j at t + is ϕ j (t + ) = j ϕ j (t)p jk () The Markov property states that Markov chains are memoryless. The probability that the chain is in state E k at time t +, depends only on ϕ(t) and is independent of ϕ(t ), ϕ(t ), ϕ(t 3)... In this course, we will focus on discrete, finite, time-homogeneous Markov chains. These are models with a finite number of states, in which time (or space) is split into discrete steps. A Markov chain is time-homogeneous if the transition matrix does not change over time. Absorbing states Last Thursday, we considered a Markov chain to model the position of a drunk moving back and forth on a railroad track on top of a mesa. When the drunk reaches either end of the railway (either the th or the th tie), he falls off the mesa. In the Markov model, states E and E are absorbing states: Once the system enters one of these states, it remains in that state forever, because P = P =. Our model of the drunk is an example of a random walk with absorbing boundaries.
2 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, The transition matrix of a Markov chain can be represented as a graph, where the nodes represent states and the edges represent transitions with non-zero probability. For example, the random walk with absorbing boundaries can be modeled like this: Periodic Markov chains In order to save the drunk from an early death, we introduced a random walk with reflecting boundaries. At each step, the drunk moves to the left or to the right with equal probability. When the drunk reaches one of the boundary states (E or E ), he returns to the adjacent state (E or E 3 ) at the next step, with probability one. This yields the following transition probability matrix: 3 3 and can be represented graphically like this:
3 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, 3 The initial state probability distribution and the state distribution for the first two time steps are the same in both random walk models, namely ϕ() = (,,,, ) ϕ() = (,,,, ) ϕ() = (,,,, ). We calculate the state probability distribution at t = 3 by multiplying the vector ϕ() times the matrix P : ϕ(3) = ϕ() P = (,,,, ) P = (,,,, ). This demonstrates that ϕ(3) = ϕ(). Similarly, ϕ() = ϕ() as can be seen from the following calculation: ϕ() = ϕ(3) P = (,,,, ) P = (,,,, ). From this we can see that the probability state distribution will be (,,,, ) at all odd time steps and (,,,, ) at all even time steps. Thus, the random walk with reflecting boundaries is a periodic Markov chain. A Markov chain is periodic if there is some state that can only be visited in multiples of m time steps, where m >. We do not require periodic Markov chains for modeling sequence evolution and will only consider aperiodic Markov chains going forward. Stationary distributions A state probability distribution, ϕ, that satisfies the equation ϕ = ϕ P () is called a stationary distribution. A key question for a given Markov chain is whether such a stationary distribution exists. Equation is equivalent to a system of s equations in s unknowns.
4 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, One way to determine the steady state distribution is to solve that system of equations. The stationary distribution can also be obtained using matrix algebra, but that approach is beyond the scope of this course. The random walk with reflecting boundaries clearly does not have a stationary distribution, since every state with non-zero probability at time t has zero probability at time t +. The random walk with absorbing boundaries does have a stationary distribution, but it is not unique. For example, both (,,,, ) and (,,,, ) are stationary distributions of the random walk with absorbing boundaries. For the rest of this course, we will concern ourselves only with aperiodic Markov chains that do not have absorbing states. In fact, we will make an even stronger assumption and restrict our consideration to Markov chains in which every state is connected to every other state via a series of zero or more states. If a finite Markov chain is aperiodic and connected in this way, it has a unique stationary distribution. We will not attempt to prove this or even to state the theorem in a rigorous way. That is beyond the scope of this class. For those who are interested, a very nice treatment can be found in Chapter 5 of Probability Theory and its Applications ( Volume I ) by William Feller (John Wiley & Sons). As an example of a Markov chain with a unique stationary distribution, we introduced a random walk that has neither absorbing, nor reflecting boundaries. In this third random walk model, if the drunk is in one of the boundary states (E or E ) at time t, then at time t + he either remains in the boundary state or returns to the adjacent state (E or E 3 ). In the model we considered in class, we assigned a probability of.5 to each of these events, resulting in the following state transition matrix, P : 3 3 We can determine the stationary state distribution for this random walk model by substitution this
5 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, 5 transition matrix into Equation. The probability of being in state E is ϕ = ϕ j P j j= = ϕ P + ϕ P + ϕ P + ϕ 3 P 3 + ϕ P = ϕ + ϕ, since P, P 3 and P are all equal to zero. The other steady state probabilities are derived similarly, yielding ϕ = ϕ + ϕ (3) ϕ = ϕ + ϕ () ϕ = ϕ + ϕ 3 (5) ϕ 3 = ϕ + ϕ (6) ϕ = ϕ 3 + ϕ. (7) In addition, the probability that the system is in some state is unity, imposing an additional constraint: ϕ + ϕ + ϕ + ϕ 3 + ϕ =. (8) The model has a stationary distribution if the above equations have a solution. In class, we showed that Equations 3-7 reduce to ϕ = ϕ = ϕ = ϕ 3 = ϕ. Applying the constraint in Equation 8, we see that the solution to the above equations must be ϕ = (.,.,.,.,.). If we know the stationary state distribution, or have an educated guess, we can verify that it indeed satisfies Equation. For example, it is easy to verify that (.,.,.,.,.) P = (.,.,.,.,.).
Lecture Notes: Markov chains
 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 5 Lecture Notes: Markov chains Dannie Durand At the beginning of the semester, we introduced two simple scoring functions for pairwise alignments: a similarity
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 5 Lecture Notes: Markov chains Dannie Durand At the beginning of the semester, we introduced two simple scoring functions for pairwise alignments: a similarity
No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1.
 Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions
 CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions Instructor: Erik Sudderth Brown University Computer Science April 14, 215 Review: Discrete Markov Chains Some
CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions Instructor: Erik Sudderth Brown University Computer Science April 14, 215 Review: Discrete Markov Chains Some
Outlines. Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC)
 Markov Chains (2) Outlines Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC) 2 pj ( n) denotes the pmf of the random variable p ( n) P( X j) j We will only be concerned with homogenous
Markov Chains (2) Outlines Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC) 2 pj ( n) denotes the pmf of the random variable p ( n) P( X j) j We will only be concerned with homogenous
ISM206 Lecture, May 12, 2005 Markov Chain
 ISM206 Lecture, May 12, 2005 Markov Chain Instructor: Kevin Ross Scribe: Pritam Roy May 26, 2005 1 Outline of topics for the 10 AM lecture The topics are: Discrete Time Markov Chain Examples Chapman-Kolmogorov
ISM206 Lecture, May 12, 2005 Markov Chain Instructor: Kevin Ross Scribe: Pritam Roy May 26, 2005 1 Outline of topics for the 10 AM lecture The topics are: Discrete Time Markov Chain Examples Chapman-Kolmogorov
Markov Model. Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states
 Markov Model Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states (applicable to repairable, as well as non-repairable systems) System behavior
Markov Model Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states (applicable to repairable, as well as non-repairable systems) System behavior
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 110
 Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Discrete Markov Chain. Theory and use
 Discrete Markov Chain. Theory and use Andres Vallone PhD Student andres.vallone@predoc.uam.es 2016 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Concept and definition Examples Transitions Matrix Chains Classification 3 Empirical
Discrete Markov Chain. Theory and use Andres Vallone PhD Student andres.vallone@predoc.uam.es 2016 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Concept and definition Examples Transitions Matrix Chains Classification 3 Empirical
At the boundary states, we take the same rules except we forbid leaving the state space, so,.
 Birth-death chains Monday, October 19, 2015 2:22 PM Example: Birth-Death Chain State space From any state we allow the following transitions: with probability (birth) with probability (death) with probability
Birth-death chains Monday, October 19, 2015 2:22 PM Example: Birth-Death Chain State space From any state we allow the following transitions: with probability (birth) with probability (death) with probability
1 Ways to Describe a Stochastic Process
 purdue university cs 59000-nmc networks & matrix computations LECTURE NOTES David F. Gleich September 22, 2011 Scribe Notes: Debbie Perouli 1 Ways to Describe a Stochastic Process We will use the biased
purdue university cs 59000-nmc networks & matrix computations LECTURE NOTES David F. Gleich September 22, 2011 Scribe Notes: Debbie Perouli 1 Ways to Describe a Stochastic Process We will use the biased
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty
 CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 24 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu April 24, 2012 Reminders Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/ Eighth
CMPSCI 240: Reasoning Under Uncertainty Lecture 24 Prof. Hanna Wallach wallach@cs.umass.edu April 24, 2012 Reminders Check the course website: http://www.cs.umass.edu/ ~wallach/courses/s12/cmpsci240/ Eighth
1 Random Walks and Electrical Networks
 CME 305: Discrete Mathematics and Algorithms Random Walks and Electrical Networks Random walks are widely used tools in algorithm design and probabilistic analysis and they have numerous applications.
CME 305: Discrete Mathematics and Algorithms Random Walks and Electrical Networks Random walks are widely used tools in algorithm design and probabilistic analysis and they have numerous applications.
IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt. Introduction to Markov Chains
 IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt Introduction to Markov Chains 1. Markov Mouse: The Closed Maze We start by considering how to model a mouse moving around in a maze. The maze is a closed space containing nine
IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt Introduction to Markov Chains 1. Markov Mouse: The Closed Maze We start by considering how to model a mouse moving around in a maze. The maze is a closed space containing nine
Definition A finite Markov chain is a memoryless homogeneous discrete stochastic process with a finite number of states.
 Chapter 8 Finite Markov Chains A discrete system is characterized by a set V of states and transitions between the states. V is referred to as the state space. We think of the transitions as occurring
Chapter 8 Finite Markov Chains A discrete system is characterized by a set V of states and transitions between the states. V is referred to as the state space. We think of the transitions as occurring
Readings: Finish Section 5.2
 LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
So in terms of conditional probability densities, we have by differentiating this relationship:
 Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Discrete time Markov chains. Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting. Limiting Distribution and Classification. Regular Transition Probability Matrices
 Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting Distribution and Classification DTU Informatics 02407 Stochastic Processes 3, September 9 207 Today: Discrete time Markov chains - invariant
Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting Distribution and Classification DTU Informatics 02407 Stochastic Processes 3, September 9 207 Today: Discrete time Markov chains - invariant
6.842 Randomness and Computation February 24, Lecture 6
 6.8 Randomness and Computation February, Lecture 6 Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribe: Mutaamba Maasha Outline Random Walks Markov Chains Stationary Distributions Hitting, Cover, Commute times Markov Chains
6.8 Randomness and Computation February, Lecture 6 Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribe: Mutaamba Maasha Outline Random Walks Markov Chains Stationary Distributions Hitting, Cover, Commute times Markov Chains
Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, :12 PM
 stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
Random Walk on a Graph
 IOR 67: Stochastic Models I Second Midterm xam, hapters 3 & 4, November 2, 200 SOLUTIONS Justify your answers; show your work.. Random Walk on a raph (25 points) Random Walk on a raph 2 5 F B 3 3 2 Figure
IOR 67: Stochastic Models I Second Midterm xam, hapters 3 & 4, November 2, 200 SOLUTIONS Justify your answers; show your work.. Random Walk on a raph (25 points) Random Walk on a raph 2 5 F B 3 3 2 Figure
Lecture 20 : Markov Chains
 CSCI 3560 Probability and Computing Instructor: Bogdan Chlebus Lecture 0 : Markov Chains We consider stochastic processes. A process represents a system that evolves through incremental changes called
CSCI 3560 Probability and Computing Instructor: Bogdan Chlebus Lecture 0 : Markov Chains We consider stochastic processes. A process represents a system that evolves through incremental changes called
( ) is symmetric about the y - axis.
 (Section 1.5: Analyzing Graphs of Functions) 1.51 PART F: FUNCTIONS THAT ARE EVEN / ODD / NEITHER; SYMMETRY A function f is even f ( x) = f ( x) x Dom( f ) The graph of y = f x for every x in the domain
(Section 1.5: Analyzing Graphs of Functions) 1.51 PART F: FUNCTIONS THAT ARE EVEN / ODD / NEITHER; SYMMETRY A function f is even f ( x) = f ( x) x Dom( f ) The graph of y = f x for every x in the domain
8. Statistical Equilibrium and Classification of States: Discrete Time Markov Chains
 8. Statistical Equilibrium and Classification of States: Discrete Time Markov Chains 8.1 Review 8.2 Statistical Equilibrium 8.3 Two-State Markov Chain 8.4 Existence of P ( ) 8.5 Classification of States
8. Statistical Equilibrium and Classification of States: Discrete Time Markov Chains 8.1 Review 8.2 Statistical Equilibrium 8.3 Two-State Markov Chain 8.4 Existence of P ( ) 8.5 Classification of States
2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains
 2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains Angela Peace Biomathematics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology. CRC Press,
2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains Angela Peace Biomathematics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology. CRC Press,
MAS275 Probability Modelling Exercises
 MAS75 Probability Modelling Exercises Note: these questions are intended to be of variable difficulty. In particular: Questions or part questions labelled (*) are intended to be a bit more challenging.
MAS75 Probability Modelling Exercises Note: these questions are intended to be of variable difficulty. In particular: Questions or part questions labelled (*) are intended to be a bit more challenging.
Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee
 Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee Overview Markov Property Markov Chains Definition Stationary Property Paths in Markov Chains Classification of States Steady States in MCs. 2 Markov Property A discrete
Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee Overview Markov Property Markov Chains Definition Stationary Property Paths in Markov Chains Classification of States Steady States in MCs. 2 Markov Property A discrete
Markov Chains, Stochastic Processes, and Matrix Decompositions
 Markov Chains, Stochastic Processes, and Matrix Decompositions 5 May 2014 Outline 1 Markov Chains Outline 1 Markov Chains 2 Introduction Perron-Frobenius Matrix Decompositions and Markov Chains Spectral
Markov Chains, Stochastic Processes, and Matrix Decompositions 5 May 2014 Outline 1 Markov Chains Outline 1 Markov Chains 2 Introduction Perron-Frobenius Matrix Decompositions and Markov Chains Spectral
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/15.085J Fall 2008 Recitation 13 10/31/2008. Markov Chains
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/5.085J Fall 008 Recitation 3 0/3/008 Marko Chains Problem 9 from Poisson process exercises in [BT] Fact: If there is a single recurrent class, the frequency
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 6.436J/5.085J Fall 008 Recitation 3 0/3/008 Marko Chains Problem 9 from Poisson process exercises in [BT] Fact: If there is a single recurrent class, the frequency
Prime numbers and Gaussian random walks
 Prime numbers and Gaussian random walks K. Bruce Erickson Department of Mathematics University of Washington Seattle, WA 9895-4350 March 24, 205 Introduction Consider a symmetric aperiodic random walk
Prime numbers and Gaussian random walks K. Bruce Erickson Department of Mathematics University of Washington Seattle, WA 9895-4350 March 24, 205 Introduction Consider a symmetric aperiodic random walk
Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain
 Spectral Graph Theory and Applications WS 20/202 Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Sun Introduction to Markov Chains Definition 5.. A sequence of random variables
Spectral Graph Theory and Applications WS 20/202 Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Sun Introduction to Markov Chains Definition 5.. A sequence of random variables
Markov Chains. X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2 <... < t k < t k+1. If X(t) is discrete-valued. If X(t) is continuous-valued
 Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
ECE-517: Reinforcement Learning in Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 4: Discrete-Time Markov Chains
 ECE-517: Reinforcement Learning in Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4: Discrete-Time Markov Chains September 1, 215 Dr. Itamar Arel College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer
ECE-517: Reinforcement Learning in Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4: Discrete-Time Markov Chains September 1, 215 Dr. Itamar Arel College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer
9.5 HONORS Determine Odd and Even Functions Graphically and Algebraically
 9.5 HONORS Determine Odd and Even Functions Graphically and Algebraically Use this blank page to compile the most important things you want to remember for cycle 9.5: 181 Even and Odd Functions Even Functions:
9.5 HONORS Determine Odd and Even Functions Graphically and Algebraically Use this blank page to compile the most important things you want to remember for cycle 9.5: 181 Even and Odd Functions Even Functions:
MAA704, Perron-Frobenius theory and Markov chains.
 November 19, 2013 Lecture overview Today we will look at: Permutation and graphs. Perron frobenius for non-negative. Stochastic, and their relation to theory. Hitting and hitting probabilities of chain.
November 19, 2013 Lecture overview Today we will look at: Permutation and graphs. Perron frobenius for non-negative. Stochastic, and their relation to theory. Hitting and hitting probabilities of chain.
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
6.842 Randomness and Computation March 3, Lecture 8
 6.84 Randomness and Computation March 3, 04 Lecture 8 Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribe: Daniel Grier Useful Linear Algebra Let v = (v, v,..., v n ) be a non-zero n-dimensional row vector and P an n n
6.84 Randomness and Computation March 3, 04 Lecture 8 Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribe: Daniel Grier Useful Linear Algebra Let v = (v, v,..., v n ) be a non-zero n-dimensional row vector and P an n n
Probability, Random Processes and Inference
 INSTITUTO POLITÉCNICO NACIONAL CENTRO DE INVESTIGACION EN COMPUTACION Laboratorio de Ciberseguridad Probability, Random Processes and Inference Dr. Ponciano Jorge Escamilla Ambrosio pescamilla@cic.ipn.mx
INSTITUTO POLITÉCNICO NACIONAL CENTRO DE INVESTIGACION EN COMPUTACION Laboratorio de Ciberseguridad Probability, Random Processes and Inference Dr. Ponciano Jorge Escamilla Ambrosio pescamilla@cic.ipn.mx
Random walks, Markov chains, and how to analyse them
 Chapter 12 Random walks, Markov chains, and how to analyse them Today we study random walks on graphs. When the graph is allowed to be directed and weighted, such a walk is also called a Markov Chain.
Chapter 12 Random walks, Markov chains, and how to analyse them Today we study random walks on graphs. When the graph is allowed to be directed and weighted, such a walk is also called a Markov Chain.
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
 http://www.math.uah.edu/stat/markov/.xhtml 1 of 9 7/16/2009 7:20 AM Virtual Laboratories > 16. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. A Markov process is a random process in which the future is
http://www.math.uah.edu/stat/markov/.xhtml 1 of 9 7/16/2009 7:20 AM Virtual Laboratories > 16. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. A Markov process is a random process in which the future is
Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem
 Queuing Analysis: Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. Yannis A. Korilis. Outline Time-Reversal
Queuing Analysis: Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. Yannis A. Korilis. Outline Time-Reversal
Lecture #5. Dependencies along the genome
 Markov Chains Lecture #5 Background Readings: Durbin et. al. Section 3., Polanski&Kimmel Section 2.8. Prepared by Shlomo Moran, based on Danny Geiger s and Nir Friedman s. Dependencies along the genome
Markov Chains Lecture #5 Background Readings: Durbin et. al. Section 3., Polanski&Kimmel Section 2.8. Prepared by Shlomo Moran, based on Danny Geiger s and Nir Friedman s. Dependencies along the genome
Markov Chains. Andreas Klappenecker by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. Texas A&M University
 Markov Chains Andreas Klappenecker Texas A&M University 208 by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. / 58 Stochastic Processes A stochastic process X tx ptq: t P T u is a collection of random variables.
Markov Chains Andreas Klappenecker Texas A&M University 208 by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. / 58 Stochastic Processes A stochastic process X tx ptq: t P T u is a collection of random variables.
Markov chains. Randomness and Computation. Markov chains. Markov processes
 Markov chains Randomness and Computation or, Randomized Algorithms Mary Cryan School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Definition (Definition 7) A discrete-time stochastic process on the state space
Markov chains Randomness and Computation or, Randomized Algorithms Mary Cryan School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Definition (Definition 7) A discrete-time stochastic process on the state space
Some Definition and Example of Markov Chain
 Some Definition and Example of Markov Chain Bowen Dai The Ohio State University April 5 th 2016 Introduction Definition and Notation Simple example of Markov Chain Aim Have some taste of Markov Chain and
Some Definition and Example of Markov Chain Bowen Dai The Ohio State University April 5 th 2016 Introduction Definition and Notation Simple example of Markov Chain Aim Have some taste of Markov Chain and
Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains. Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan
 Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Continuous-Time Markov Chains Consider a continuous-time stochastic process
Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Continuous-Time Markov Chains Consider a continuous-time stochastic process
Machine Learning CPSC 340. Tutorial 12
 Machine Learning CPSC 340 Tutorial 12 Random Walk on Graph Page Rank Algorithm Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected
Machine Learning CPSC 340 Tutorial 12 Random Walk on Graph Page Rank Algorithm Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected
MARKOV PROCESSES. Valerio Di Valerio
 MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains
 Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Introduction to Computational Biology Lecture # 14: MCMC - Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Introduction to Computational Biology Lecture # 14: MCMC - Markov Chain Monte Carlo Assaf Weiner Tuesday, March 13, 2007 1 Introduction Today we will return to the motif finding problem, in lecture 10
Introduction to Computational Biology Lecture # 14: MCMC - Markov Chain Monte Carlo Assaf Weiner Tuesday, March 13, 2007 1 Introduction Today we will return to the motif finding problem, in lecture 10
Chapter 16 focused on decision making in the face of uncertainty about one future
 9 C H A P T E R Markov Chains Chapter 6 focused on decision making in the face of uncertainty about one future event (learning the true state of nature). However, some decisions need to take into account
9 C H A P T E R Markov Chains Chapter 6 focused on decision making in the face of uncertainty about one future event (learning the true state of nature). However, some decisions need to take into account
Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains. Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321
 Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321 Discrete-time random processes A sequence of RVs indexed by a variable n 2 {0, 1, 2,...} forms a discretetime random process
Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321 Discrete-time random processes A sequence of RVs indexed by a variable n 2 {0, 1, 2,...} forms a discretetime random process
STA 414/2104: Machine Learning
 STA 414/2104: Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 9 Sequential Data So far
STA 414/2104: Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 9 Sequential Data So far
Lecture 2: September 8
 CS294 Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Foundations & Applications Fall 2009 Lecture 2: September 8 Lecturer: Prof. Alistair Sinclair Scribes: Anand Bhaskar and Anindya De Disclaimer: These notes have not been
CS294 Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Foundations & Applications Fall 2009 Lecture 2: September 8 Lecturer: Prof. Alistair Sinclair Scribes: Anand Bhaskar and Anindya De Disclaimer: These notes have not been
Lab 2 Worksheet. Problems. Problem 1: Geometry and Linear Equations
 Lab 2 Worksheet Problems Problem : Geometry and Linear Equations Linear algebra is, first and foremost, the study of systems of linear equations. You are going to encounter linear systems frequently in
Lab 2 Worksheet Problems Problem : Geometry and Linear Equations Linear algebra is, first and foremost, the study of systems of linear equations. You are going to encounter linear systems frequently in
SMSTC (2007/08) Probability.
 SMSTC (27/8) Probability www.smstc.ac.uk Contents 12 Markov chains in continuous time 12 1 12.1 Markov property and the Kolmogorov equations.................... 12 2 12.1.1 Finite state space.................................
SMSTC (27/8) Probability www.smstc.ac.uk Contents 12 Markov chains in continuous time 12 1 12.1 Markov property and the Kolmogorov equations.................... 12 2 12.1.1 Finite state space.................................
Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes. Markov Processes Markov Chains. Random Processes
 Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes Definition IID Processes Bernoulli Process Binomial Counting Process Interarrival Time Process Markov Processes Markov Chains Classification of States Steady State Probabilities
Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes Definition IID Processes Bernoulli Process Binomial Counting Process Interarrival Time Process Markov Processes Markov Chains Classification of States Steady State Probabilities
Math Models of OR: Some Definitions
 Math Models of OR: Some Definitions John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 12180 USA September 2018 Mitchell Some Definitions 1 / 20 Active constraints Outline 1 Active constraints
Math Models of OR: Some Definitions John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 12180 USA September 2018 Mitchell Some Definitions 1 / 20 Active constraints Outline 1 Active constraints
Irreducibility. Irreducible. every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that. Absorbing state: p jj =1
 Irreducibility Irreducible every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that i,j are communicate, if the above condition is valid Irreducible: all states are communicate
Irreducibility Irreducible every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that i,j are communicate, if the above condition is valid Irreducible: all states are communicate
INTRODUCTION TO MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV CHAIN MIXING
 INTRODUCTION TO MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV CHAIN MIXING ERIC SHANG Abstract. This paper provides an introduction to Markov chains and their basic classifications and interesting properties. After establishing
INTRODUCTION TO MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV CHAIN MIXING ERIC SHANG Abstract. This paper provides an introduction to Markov chains and their basic classifications and interesting properties. After establishing
Algorithms and Theory of Computation. Lecture 22: NP-Completeness (2)
 Algorithms and Theory of Computation Lecture 22: NP-Completeness (2) Xiaohui Bei MAS 714 November 8, 2018 Nanyang Technological University MAS 714 November 8, 2018 1 / 20 Set Cover Set Cover Input: a set
Algorithms and Theory of Computation Lecture 22: NP-Completeness (2) Xiaohui Bei MAS 714 November 8, 2018 Nanyang Technological University MAS 714 November 8, 2018 1 / 20 Set Cover Set Cover Input: a set
Columbus State Community College Mathematics Department. CREDITS: 5 CLASS HOURS PER WEEK: 5 PREREQUISITES: MATH 2173 with a C or higher
 Columbus State Community College Mathematics Department Course and Number: MATH 2174 - Linear Algebra and Differential Equations for Engineering CREDITS: 5 CLASS HOURS PER WEEK: 5 PREREQUISITES: MATH 2173
Columbus State Community College Mathematics Department Course and Number: MATH 2174 - Linear Algebra and Differential Equations for Engineering CREDITS: 5 CLASS HOURS PER WEEK: 5 PREREQUISITES: MATH 2173
Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming
 CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
Information Theory. Lecture 5 Entropy rate and Markov sources STEFAN HÖST
 Information Theory Lecture 5 Entropy rate and Markov sources STEFAN HÖST Universal Source Coding Huffman coding is optimal, what is the problem? In the previous coding schemes (Huffman and Shannon-Fano)it
Information Theory Lecture 5 Entropy rate and Markov sources STEFAN HÖST Universal Source Coding Huffman coding is optimal, what is the problem? In the previous coding schemes (Huffman and Shannon-Fano)it
Using Markov Chains To Model Human Migration in a Network Equilibrium Framework
 Using Markov Chains To Model Human Migration in a Network Equilibrium Framework Jie Pan Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Saint Joseph s University Philadelphia, PA 19131 Anna Nagurney School
Using Markov Chains To Model Human Migration in a Network Equilibrium Framework Jie Pan Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Saint Joseph s University Philadelphia, PA 19131 Anna Nagurney School
Stochastic Modelling Unit 1: Markov chain models
 Stochastic Modelling Unit 1: Markov chain models Russell Gerrard and Douglas Wright Cass Business School, City University, London June 2004 Contents of Unit 1 1 Stochastic Processes 2 Markov Chains 3 Poisson
Stochastic Modelling Unit 1: Markov chain models Russell Gerrard and Douglas Wright Cass Business School, City University, London June 2004 Contents of Unit 1 1 Stochastic Processes 2 Markov Chains 3 Poisson
Recap. Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains. ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks
 Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
(b) What is the variance of the time until the second customer arrives, starting empty, assuming that we measure time in minutes?
 IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
MATH3200, Lecture 31: Applications of Eigenvectors. Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems
 Lecture 31: Some Applications of Eigenvectors: Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems Winfried Just Department of Mathematics, Ohio University April 9 11, 2018 Review: Eigenvectors and left eigenvectors
Lecture 31: Some Applications of Eigenvectors: Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems Winfried Just Department of Mathematics, Ohio University April 9 11, 2018 Review: Eigenvectors and left eigenvectors
Chapter 10 Markov Chains and Transition Matrices
 Finite Mathematics (Mat 119) Lecture week 3 Dr. Firozzaman Department of Mathematics and Statistics Arizona State University Chapter 10 Markov Chains and Transition Matrices A Markov Chain is a sequence
Finite Mathematics (Mat 119) Lecture week 3 Dr. Firozzaman Department of Mathematics and Statistics Arizona State University Chapter 10 Markov Chains and Transition Matrices A Markov Chain is a sequence
Numerical Solution for Two Dimensional Laplace Equation with Dirichlet Boundary Conditions
 IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728,p-ISSN: 2319-765X, Volume 6, Issue 4 (May. - Jun. 2013), PP 66-75 Numerical Solution for Two Dimensional Laplace Equation with Dirichlet Boundary
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728,p-ISSN: 2319-765X, Volume 6, Issue 4 (May. - Jun. 2013), PP 66-75 Numerical Solution for Two Dimensional Laplace Equation with Dirichlet Boundary
Further Applications of Advanced Mathematics (FP3) THURSDAY 14 JUNE 2007
 ADVANCED GCE UNIT 4757/01 MATHEMATICS (MEI) Further Applications of Advanced Mathematics (FP3) THURSDAY 14 JUNE 2007 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Additional materials: Answer booklet (8 pages) Graph
ADVANCED GCE UNIT 4757/01 MATHEMATICS (MEI) Further Applications of Advanced Mathematics (FP3) THURSDAY 14 JUNE 2007 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Additional materials: Answer booklet (8 pages) Graph
Convex Optimization CMU-10725
 Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Simulated Annealing Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Andrey Markov Markov Chains 2 Markov Chains Markov chain: Homogen Markov chain: 3 Markov Chains Assume that the state
Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Simulated Annealing Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Andrey Markov Markov Chains 2 Markov Chains Markov chain: Homogen Markov chain: 3 Markov Chains Assume that the state
LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION MATRIX OF A CONDENSED FIBONACCI TREE
 International Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 31 No. 18, 41-49 ISSN: 1311-178 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-86 (on-line version) doi: http://dx.doi.org/1.173/ijam.v31i.6 LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION
International Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 31 No. 18, 41-49 ISSN: 1311-178 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-86 (on-line version) doi: http://dx.doi.org/1.173/ijam.v31i.6 LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION
Markov chains and the number of occurrences of a word in a sequence ( , 11.1,2,4,6)
 Markov chains and the number of occurrences of a word in a sequence (4.5 4.9,.,2,4,6) Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 208 Prof. Tesler Markov Chains Math 283 / Fall 208 / 44 Locating overlapping occurrences
Markov chains and the number of occurrences of a word in a sequence (4.5 4.9,.,2,4,6) Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 208 Prof. Tesler Markov Chains Math 283 / Fall 208 / 44 Locating overlapping occurrences
each nonabsorbing state to each absorbing state.
 Chapter 8 Markov Processes Absorbing States Markov Processes Markov process models are useful in studying the evolution of systems over repeated trials or sequential time periods or stages. They have been
Chapter 8 Markov Processes Absorbing States Markov Processes Markov process models are useful in studying the evolution of systems over repeated trials or sequential time periods or stages. They have been
TCOM 501: Networking Theory & Fundamentals. Lecture 6 February 19, 2003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis
 TCOM 50: Networking Theory & Fundamentals Lecture 6 February 9, 003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis 6- Topics Time-Reversal of Markov Chains Reversibility Truncating a Reversible Markov Chain Burke s Theorem Queues
TCOM 50: Networking Theory & Fundamentals Lecture 6 February 9, 003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis 6- Topics Time-Reversal of Markov Chains Reversibility Truncating a Reversible Markov Chain Burke s Theorem Queues
Markov Chains. As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006.
 Markov Chains As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006 1 Introduction A (finite) Markov chain is a process with a finite number of states (or outcomes, or
Markov Chains As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006 1 Introduction A (finite) Markov chain is a process with a finite number of states (or outcomes, or
Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
 Markov Chains Markov chains: 2SAT: Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions rely only on local moves to explore state space. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
Markov Chains Markov chains: 2SAT: Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions rely only on local moves to explore state space. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
Section Notes 9. Midterm 2 Review. Applied Math / Engineering Sciences 121. Week of December 3, 2018
 Section Notes 9 Midterm 2 Review Applied Math / Engineering Sciences 121 Week of December 3, 2018 The following list of topics is an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections
Section Notes 9 Midterm 2 Review Applied Math / Engineering Sciences 121 Week of December 3, 2018 The following list of topics is an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections
Mathematical Methods for Computer Science
 Mathematical Methods for Computer Science Computer Science Tripos, Part IB Michaelmas Term 2016/17 R.J. Gibbens Problem sheets for Probability methods William Gates Building 15 JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge
Mathematical Methods for Computer Science Computer Science Tripos, Part IB Michaelmas Term 2016/17 R.J. Gibbens Problem sheets for Probability methods William Gates Building 15 JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge
Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling
 Part I Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling 1 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 1.1 Structure of Finite Markov Chains We shall only consider Markov chains with a finite, but usually very large,
Part I Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling 1 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 1.1 Structure of Finite Markov Chains We shall only consider Markov chains with a finite, but usually very large,
Transience: Whereas a finite closed communication class must be recurrent, an infinite closed communication class can be transient:
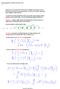 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Introduction to MCMC. DB Breakfast 09/30/2011 Guozhang Wang
 Introduction to MCMC DB Breakfast 09/30/2011 Guozhang Wang Motivation: Statistical Inference Joint Distribution Sleeps Well Playground Sunny Bike Ride Pleasant dinner Productive day Posterior Estimation
Introduction to MCMC DB Breakfast 09/30/2011 Guozhang Wang Motivation: Statistical Inference Joint Distribution Sleeps Well Playground Sunny Bike Ride Pleasant dinner Productive day Posterior Estimation
Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian
 Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian CMPSCI 791BB: Advanced ML Sridhar Mahadevan Random Walks! There is significant interest in the problem of random walks! Markov chain analysis! Computer
Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian CMPSCI 791BB: Advanced ML Sridhar Mahadevan Random Walks! There is significant interest in the problem of random walks! Markov chain analysis! Computer
1.3 Convergence of Regular Markov Chains
 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 3 Applying the same argument to A T, which has the same λ 0 as A, yields the row sum bounds Corollary 0 Let P 0 be the transition matrix of a regular Markov chain
Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 3 Applying the same argument to A T, which has the same λ 0 as A, yields the row sum bounds Corollary 0 Let P 0 be the transition matrix of a regular Markov chain
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
Markov Chains. Contents
 6 Markov Chains Contents 6.1. Discrete-Time Markov Chains............... p. 2 6.2. Classification of States................... p. 9 6.3. Steady-State Behavior.................. p. 13 6.4. Absorption Probabilities
6 Markov Chains Contents 6.1. Discrete-Time Markov Chains............... p. 2 6.2. Classification of States................... p. 9 6.3. Steady-State Behavior.................. p. 13 6.4. Absorption Probabilities
Lecture 1: Brief Review on Stochastic Processes
 Lecture 1: Brief Review on Stochastic Processes A stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X t (s) : t T, s S}, where T is some index set and S is the common sample space of the random variables.
Lecture 1: Brief Review on Stochastic Processes A stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X t (s) : t T, s S}, where T is some index set and S is the common sample space of the random variables.
2. Transience and Recurrence
 Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
MATH 446/546 Test 2 Fall 2014
 MATH 446/546 Test 2 Fall 204 Note the problems are separated into two sections a set for all students and an additional set for those taking the course at the 546 level. Please read and follow all of these
MATH 446/546 Test 2 Fall 204 Note the problems are separated into two sections a set for all students and an additional set for those taking the course at the 546 level. Please read and follow all of these
LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS
 LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS Markov Process and Markov Chains Hidden Markov Models Kalman Filters Types of dynamic systems Problem of future state prediction Predictability Observability Easily
LEARNING DYNAMIC SYSTEMS: MARKOV MODELS Markov Process and Markov Chains Hidden Markov Models Kalman Filters Types of dynamic systems Problem of future state prediction Predictability Observability Easily
8 Wyner Honors Algebra II Fall 2013
 8 Wyner Honors Algebra II Fall 2013 CHAPTER THREE: SOLVING EQUATIONS AND SYSTEMS Summary Terms Objectives The cornerstone of algebra is solving algebraic equations. This can be done with algebraic techniques,
8 Wyner Honors Algebra II Fall 2013 CHAPTER THREE: SOLVING EQUATIONS AND SYSTEMS Summary Terms Objectives The cornerstone of algebra is solving algebraic equations. This can be done with algebraic techniques,
Compartmental modeling
 Compartmental modeling This is a very short summary of the notes from my two-hour lecture. These notes were not originally meant to be distributed, and so they are far from being complete. A comprehensive
Compartmental modeling This is a very short summary of the notes from my two-hour lecture. These notes were not originally meant to be distributed, and so they are far from being complete. A comprehensive
Asymptotic properties of imprecise Markov chains
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING Asymptotic properties of imprecise Markov chains Filip Hermans Gert De Cooman SYSTeMS Ghent University 10 September 2009, München Imprecise Markov chain X 0 X 1 X 2 X 3 Every node
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING Asymptotic properties of imprecise Markov chains Filip Hermans Gert De Cooman SYSTeMS Ghent University 10 September 2009, München Imprecise Markov chain X 0 X 1 X 2 X 3 Every node
MATH 564/STAT 555 Applied Stochastic Processes Homework 2, September 18, 2015 Due September 30, 2015
 ID NAME SCORE MATH 56/STAT 555 Applied Stochastic Processes Homework 2, September 8, 205 Due September 30, 205 The generating function of a sequence a n n 0 is defined as As : a ns n for all s 0 for which
ID NAME SCORE MATH 56/STAT 555 Applied Stochastic Processes Homework 2, September 8, 205 Due September 30, 205 The generating function of a sequence a n n 0 is defined as As : a ns n for all s 0 for which
n α 1 α 2... α m 1 α m σ , A =
 The Leslie Matrix The Leslie matrix is a generalization of the above. It is a matrix which describes the increases in numbers in various age categories of a population year-on-year. As above we write p
The Leslie Matrix The Leslie matrix is a generalization of the above. It is a matrix which describes the increases in numbers in various age categories of a population year-on-year. As above we write p
Probabilistic Model Checking Michaelmas Term Dr. Dave Parker. Department of Computer Science University of Oxford
 Probabilistic Model Checking Michaelmas Term 20 Dr. Dave Parker Department of Computer Science University of Oxford Next few lectures Today: Discrete-time Markov chains (continued) Mon 2pm: Probabilistic
Probabilistic Model Checking Michaelmas Term 20 Dr. Dave Parker Department of Computer Science University of Oxford Next few lectures Today: Discrete-time Markov chains (continued) Mon 2pm: Probabilistic
Lesson Plan. AM 121: Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods. Lecture 17: Markov Chains. Yiling Chen SEAS. Stochastic process Markov Chains
 AM : Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 7: Markov Chains Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Stochastic process Markov Chains n-step probabilities Communicating states, irreducibility Recurrent
AM : Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 7: Markov Chains Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Stochastic process Markov Chains n-step probabilities Communicating states, irreducibility Recurrent
