Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee
|
|
|
- Jayson Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee
2 Overview Markov Property Markov Chains Definition Stationary Property Paths in Markov Chains Classification of States Steady States in MCs. 2
3 Markov Property A discrete process has the Markov property if given its value at time t, the value at time t+ is independent of values at times before t. That is: Pr X t+ = x t+ X t = x t, X t = x t,, X = x = Pr X t+ = x t+ X t = x t For all t, x t+, x t, x t, x t 2,, x. 3
4 Stationary Property A Markov Process is called stationary if Pr X t+ = u X t = v = Pr X = u X 0 = v for all t. The evolution of stationary processes don t change over time. For defining the complete joint distribution of a stationary Markov Process it is sufficient to define Pr X = u X 0 = v and Pr X 0 = v for all u and v. (why?) We will mainly consider stationary Markov processes here. 4
5 Example (Coin Tossing Game) Consider a single player game in which at every step a biased coin is tossed and according to the result, the score will be increased or decreased by one point. The game ends if either the score reaches 00 (winning) or -00 (losing). Score of the player at each step t 0 is a random variable and the sequence of scores as the game progresses forms a random process X 0, X,, X t. 5
6 Example (Coin Tossing Game) It is easy to verify that X is a stationary Markov chain: At the end of each step the score solely depends on the current score s c and the result of tossing the coin (which is independent of time and previous tosses). Stating this mathematically (for s c { 00,00}): Pr X t+ = s X t = s c, X t = s t,, X 0 = 0 = p ; s = s c + p ; s = s c 0 ; otherwise = Pr X t+ = s X t = s c = Pr X = s X 0 = s c If value of p was subject to change in time, the process would not be stationary. In the formulation we would have p t instead of p. Independent of t and s 0,, s t 6
7 Example (Tracking) Assume we want to track a target in XY plane, and so we need to model its movement. Assuming that current position and speed of the target describes everything about its future movements, we can consider the 4- dimensional state: S t = (X t, Y t, X t, Y t ) It is common to consider linear relation between S t and S t with a Gaussian additive noise: S t = A t S t + v t ; v t ~N(0, Σ) Or equivalently: f St S t s t s t = N(s t ; A t s t, Σ) There exists efficient algorithms to work with these linear- Gaussian models. 7
8 Example (Tracking) Considering the kinematics relations of a moving object we can define linear relation as: 0 Δt Δt A t = This approach can not model Acceleration the speed is changed only because of noise. Independent of t (stationary) We can model arbitrary speed change by appropriately setting the 3 rd and 4 th rows of the matrix at each time. An example of a non stationary Markov process. Another approach is to extend the states to 6- dimensions containing X t and Y t. 8
9 Example (Speech) A basic model for speech signal considers the value at time t to be a linear combination of its d previous values with a Gaussian additive noise: S t = d i= α i S t i S t is not a Markov process. + v t ; v t ~N(0, Σ) 9
10 Example (Speech) We can make a stationary Markov process by considering the d-dimensional state U t = S t, S t, S t d T : Where: A = U t = AU t + v k B α α 2 α d , B = Equivalently: f Ut U t u t u t = N u t ; A t u t, Σ I i d u t i = u t i Which (x) i is the ith dimension of vector x and I is the indicator function (used for guaranteeing consistency). Note that we have repeated X t in d consecutive states of U and there should be no inconsistency between those values. 0 0
11 Markov Process Types Two types of Markov processes based on domain of X t values: Discrete Continuous Discrete Markov processes are called Markov Chains (MC). In this session we will focus on stationary MCs.
12 Transition matrix According to the Markov property and stationary property, at each time step the process moves according to a fixed transition matrix: P X t+ = j X t = i = p ij Stochastic matrix: Rows sum up to Double stochastic matrix: Rows and columns sum up to 2
13 State Graph It is convenient to visualize a stationary Markov Chain with a transition diagram: A node represents a possible value of X t. At each time t, we say the process is in state s if X t =s. Each edge represents the probability of going from one state to another (we omit edges with zero weight). We should also specify the vector of initial probabilities π = π,, π n where π i = Pr(X 0 = i). So a stationary discrete process could be described as a person walking randomly on a graph (considering each step to depend only on the state he is currently in). The result path is called a Random Walk. 3
14 Example The transition diagram of the coin tossing game: p p p p p -p -p -p -p We modeled winning and losing by states which when we get into, we never get out. Note that if the process was not stationary we were not able to visualize it in this way: For example consider the case that p is changing in time. 4
15 Example (Modeling Weather) Example: Each day is sunny or rainy. If a day is rainy, the next day is rainy with probability α (and sunny with probability α). If the day is sunny, the next day is rainy with probability β (and sunny with probability β). S = {rainy, sunny}, P = α α β β α α β R S β 5
16 Paths If the state space is {0,} we have: pr x 2 = 0 x 0 = 0 = Pr x = x 0 = 0 p x 2 = 0 x = +Pr x = 0 x 0 = 0 p x 2 = 0 x = 0 (n) Define p ij as the probability that starting from state i, the process stops at state j after n time steps. (2) = r pik p kj p ij k= 6
17 Paths Theorem: (n) p ij = r k= (n ) pik pkj To simplify the notation we define the matrix P (n) such that (n) the value at the i th row and j th column is p ij. Corollary : P (n) can be calculated by: P (n) = P n Corollary 2: If the process starts at time 0 with distribution π on the states then after n steps the distribution is πp n. 7
18 Absorbing Markov Chain An absorbing state is one in which the probability that the process remains in that state once it enters the state is (i.e., p ii = ). A Markov chain is absorbing if it has at least one absorbing state, and if from every state it is possible to go to an absorbing state (not necessarily in one step). An absorbing Markov chain will eventually enter one of the absorbing states and never leave it. Example: The 00 and -00 states in coin tossing game Note: After playing ling enough, the player will either win or lose (with probability ). p p p p p -p -p -p -p 8
19 Absorption theorem In an absorbing Markov chain the probability that the process will be absorbed is. Proof: From each non-absorbing state s j it is possible to reach an absorbing state starting from s j. Therefore there exists p and m, such that the probability of not absorbing after m steps is at most p, in 2m steps at most p 2, etc. Since the probability of not being absorbed is monotonically decreasing, we have: lim n Pr(not absorbed after n steps) =0 9
20 Classification of States Accessibility: State j is said to be accessible from state i if starting in i it is possible that the process will ever enter state j: (P n ) ij > 0. Communication: Two states i and j that are accessible to each other are said to communicate. Every node communicates with itself: p ii 0 = Pr X 0 = i X 0 = i = Communication is an equivalence relation: It divides the state space up into a number of separate classes in which every pair of states communicate. (why?) The Markov chain is said to be irreducible if it has only one class. 20
21 Transient and Recurrent states For any state i we let f i denote the probability that, starting in state i, the process will ever reenter state i : f i = Pr n: X n = i X 0 = i) State i is said to be recurrent if f i = and transient if f i <. Theorem : State i is recurrent if and only if, starting in state i, the expected number of time periods that the process is in state i is infinite: Corollary : A transient state will only be visited a finite number of times Proof: E size n: X n = i X 0 = i = k= k Pr(size n: X n = i = k X 0 = i) = + prob size n: X n = i = X 0 = i < prob size n: X n = i = X 0 = i = 0 2
22 Transient and Recurrent states Theorem 2: State i is recurrent iff n=(p n ) ii =. Look at the text book for proof. Corollary 2: A finite state Markov chain has at least one recurrent state. If all states are transient there will be a finite number of steps that after that the process should not be in any state (which is a contradiction). 22
23 Ergodic states If state i is recurrent, then it is said to be positive recurrent if, starting in i, the expected time until the process returns to state i is finite. In a finite-state MC, all recurrent states are positive recurrent. State i is said to have period d if p n ii=0 whenever n is not divisible by d, and d is the largest integer with this property. Equivalently: d = gcd n: Pr X n = i X 0 = i > 0} A state with period is said to be aperiodic. We call an MC aperiodic if all its states are aperiodic. A state i is said to be ergodic if it is aperiodic and positive recurrent. Period, recurrence and positive recurrence are all class properties. They are shared between states of a class. 23
24 Example 0.25 Classes: {},{2,3},{4,5},{6},{7.8} Recurrent states: 6, 7, 8 => all positive Periodic states: 2, 3, 7, 8 (with period 2) Absorbing state(s): 6 Ergodic state(s): As time goes to infinity, what is the probability of being in each class? Answer: The process will be in transient classes {},{2,3},{4,5} with probability 0. Problem is symmetric for entering classes {6} and {7,8} as their only input edge is one from 5 with equal probabilities 0.25, and once it enters them, there is no way out. So at infinity probability of being in each of these two classes is
25 Example 0.25 Classes: {},{2,3},{4,5},{6},{7.8} Recurrent states: 6, 7, 8 => all positive Periodic states: 2, 3, 7, 8 (with period 2) Absorbing state(s): 6 Ergodic state(s): If the process is absorbed in {7,8} (which could be considered as an absorbing super state) what will happen after that? It will alternate between 7 and 8 to the end. So at time t probability of being in 7 (or 8) will depend on the parity of t. In general finding the exact behavior of non-ergodic states as t is not easy. (try it!) We will talk about the ergodic cases in next slides
26 Steady State Theorem: For an irreducible ergodic Markov chain lim n P n ij exists and is independent of i. Furthermore, letting π j = lim n P n ij Then π = π, π d t is unique nonnegative solution of π = π P d j= π j If the ergodicity condition is removed, lim n P n ij does not exist in general but the given equations yet have a unique solution π = π, π d t in which π j will be equal to the long run proportion of time that the Markov chain is in state j. = 26
27 Example Consider the weather model example discussed before. We want to see how will the weather be when time goes to infinity: P = α α β π 0 = απ 0 + βπ π = α π 0 + β π π 0 + π = β One of these equations is redundant. (why?) Which yields that π 0 = β and π +β α = α. +β α Exercise: In each of the following cases investigate the existence of solution and its meaning: ) α=0 and β = 2) α= and β = 0 27
28 Acknowledge Thanks to Hassan Hafez and Abbas Hosseini for preparation of slides 28
29 References Ross, Sheldon M. Introduction to probability models. 29
Markov Chains (Part 3)
 Markov Chains (Part 3) State Classification Markov Chains - State Classification Accessibility State j is accessible from state i if p ij (n) > for some n>=, meaning that starting at state i, there is
Markov Chains (Part 3) State Classification Markov Chains - State Classification Accessibility State j is accessible from state i if p ij (n) > for some n>=, meaning that starting at state i, there is
Markov Chains (Part 4)
 Markov Chains (Part 4) Steady State Probabilities and First Passage Times Markov Chains - 1 Steady-State Probabilities Remember, for the inventory example we had (8) P &.286 =.286.286 %.286 For an irreducible
Markov Chains (Part 4) Steady State Probabilities and First Passage Times Markov Chains - 1 Steady-State Probabilities Remember, for the inventory example we had (8) P &.286 =.286.286 %.286 For an irreducible
Lesson Plan. AM 121: Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods. Lecture 17: Markov Chains. Yiling Chen SEAS. Stochastic process Markov Chains
 AM : Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 7: Markov Chains Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Stochastic process Markov Chains n-step probabilities Communicating states, irreducibility Recurrent
AM : Introduction to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 7: Markov Chains Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Stochastic process Markov Chains n-step probabilities Communicating states, irreducibility Recurrent
ISM206 Lecture, May 12, 2005 Markov Chain
 ISM206 Lecture, May 12, 2005 Markov Chain Instructor: Kevin Ross Scribe: Pritam Roy May 26, 2005 1 Outline of topics for the 10 AM lecture The topics are: Discrete Time Markov Chain Examples Chapman-Kolmogorov
ISM206 Lecture, May 12, 2005 Markov Chain Instructor: Kevin Ross Scribe: Pritam Roy May 26, 2005 1 Outline of topics for the 10 AM lecture The topics are: Discrete Time Markov Chain Examples Chapman-Kolmogorov
Markov Chains Absorption (cont d) Hamid R. Rabiee
 Markov Chains Absorption (cont d) Hamid R. Rabiee 1 Absorbing Markov Chain An absorbing state is one in which the probability that the process remains in that state once it enters the state is 1 (i.e.,
Markov Chains Absorption (cont d) Hamid R. Rabiee 1 Absorbing Markov Chain An absorbing state is one in which the probability that the process remains in that state once it enters the state is 1 (i.e.,
Markov Chains. As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006.
 Markov Chains As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006 1 Introduction A (finite) Markov chain is a process with a finite number of states (or outcomes, or
Markov Chains As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006 1 Introduction A (finite) Markov chain is a process with a finite number of states (or outcomes, or
8. Statistical Equilibrium and Classification of States: Discrete Time Markov Chains
 8. Statistical Equilibrium and Classification of States: Discrete Time Markov Chains 8.1 Review 8.2 Statistical Equilibrium 8.3 Two-State Markov Chain 8.4 Existence of P ( ) 8.5 Classification of States
8. Statistical Equilibrium and Classification of States: Discrete Time Markov Chains 8.1 Review 8.2 Statistical Equilibrium 8.3 Two-State Markov Chain 8.4 Existence of P ( ) 8.5 Classification of States
Markov Chains Absorption Hamid R. Rabiee
 Markov Chains Absorption Hamid R. Rabiee Absorbing Markov Chain An absorbing state is one in which the probability that the process remains in that state once it enters the state is (i.e., p ii = ). A
Markov Chains Absorption Hamid R. Rabiee Absorbing Markov Chain An absorbing state is one in which the probability that the process remains in that state once it enters the state is (i.e., p ii = ). A
Chapter 16 focused on decision making in the face of uncertainty about one future
 9 C H A P T E R Markov Chains Chapter 6 focused on decision making in the face of uncertainty about one future event (learning the true state of nature). However, some decisions need to take into account
9 C H A P T E R Markov Chains Chapter 6 focused on decision making in the face of uncertainty about one future event (learning the true state of nature). However, some decisions need to take into account
Lecture 20 : Markov Chains
 CSCI 3560 Probability and Computing Instructor: Bogdan Chlebus Lecture 0 : Markov Chains We consider stochastic processes. A process represents a system that evolves through incremental changes called
CSCI 3560 Probability and Computing Instructor: Bogdan Chlebus Lecture 0 : Markov Chains We consider stochastic processes. A process represents a system that evolves through incremental changes called
IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt. Introduction to Markov Chains
 IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt Introduction to Markov Chains 1. Markov Mouse: The Closed Maze We start by considering how to model a mouse moving around in a maze. The maze is a closed space containing nine
IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt Introduction to Markov Chains 1. Markov Mouse: The Closed Maze We start by considering how to model a mouse moving around in a maze. The maze is a closed space containing nine
Probability, Random Processes and Inference
 INSTITUTO POLITÉCNICO NACIONAL CENTRO DE INVESTIGACION EN COMPUTACION Laboratorio de Ciberseguridad Probability, Random Processes and Inference Dr. Ponciano Jorge Escamilla Ambrosio pescamilla@cic.ipn.mx
INSTITUTO POLITÉCNICO NACIONAL CENTRO DE INVESTIGACION EN COMPUTACION Laboratorio de Ciberseguridad Probability, Random Processes and Inference Dr. Ponciano Jorge Escamilla Ambrosio pescamilla@cic.ipn.mx
Markov Chains. X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2 <... < t k < t k+1. If X(t) is discrete-valued. If X(t) is continuous-valued
 Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions
 J. Virtamo 38.3143 Queueing Theory / Stochastic processes 1 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions Often the systems we consider evolve in time and we are interested in their dynamic behaviour, usually involving
J. Virtamo 38.3143 Queueing Theory / Stochastic processes 1 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions Often the systems we consider evolve in time and we are interested in their dynamic behaviour, usually involving
1.3 Convergence of Regular Markov Chains
 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 3 Applying the same argument to A T, which has the same λ 0 as A, yields the row sum bounds Corollary 0 Let P 0 be the transition matrix of a regular Markov chain
Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 3 Applying the same argument to A T, which has the same λ 0 as A, yields the row sum bounds Corollary 0 Let P 0 be the transition matrix of a regular Markov chain
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 1
 MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER. Finite Markov chains For the sake of completeness of these notes I decided to write a summary of the basic concepts of finite Markov chains. The topics in this chapter
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER. Finite Markov chains For the sake of completeness of these notes I decided to write a summary of the basic concepts of finite Markov chains. The topics in this chapter
Markov Chains CK eqns Classes Hitting times Rec./trans. Strong Markov Stat. distr. Reversibility * Markov Chains
 Markov Chains A random process X is a family {X t : t T } of random variables indexed by some set T. When T = {0, 1, 2,... } one speaks about a discrete-time process, for T = R or T = [0, ) one has a continuous-time
Markov Chains A random process X is a family {X t : t T } of random variables indexed by some set T. When T = {0, 1, 2,... } one speaks about a discrete-time process, for T = R or T = [0, ) one has a continuous-time
Outlines. Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC)
 Markov Chains (2) Outlines Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC) 2 pj ( n) denotes the pmf of the random variable p ( n) P( X j) j We will only be concerned with homogenous
Markov Chains (2) Outlines Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC) 2 pj ( n) denotes the pmf of the random variable p ( n) P( X j) j We will only be concerned with homogenous
2. Transience and Recurrence
 Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Markov chains. Randomness and Computation. Markov chains. Markov processes
 Markov chains Randomness and Computation or, Randomized Algorithms Mary Cryan School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Definition (Definition 7) A discrete-time stochastic process on the state space
Markov chains Randomness and Computation or, Randomized Algorithms Mary Cryan School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Definition (Definition 7) A discrete-time stochastic process on the state space
Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains. Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321
 Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321 Discrete-time random processes A sequence of RVs indexed by a variable n 2 {0, 1, 2,...} forms a discretetime random process
Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321 Discrete-time random processes A sequence of RVs indexed by a variable n 2 {0, 1, 2,...} forms a discretetime random process
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 110
 Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Statistics 150: Spring 2007
 Statistics 150: Spring 2007 April 23, 2008 0-1 1 Limiting Probabilities If the discrete-time Markov chain with transition probabilities p ij is irreducible and positive recurrent; then the limiting probabilities
Statistics 150: Spring 2007 April 23, 2008 0-1 1 Limiting Probabilities If the discrete-time Markov chain with transition probabilities p ij is irreducible and positive recurrent; then the limiting probabilities
ISE/OR 760 Applied Stochastic Modeling
 ISE/OR 760 Applied Stochastic Modeling Topic 2: Discrete Time Markov Chain Yunan Liu Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering NC State University Yunan Liu (NC State University) ISE/OR 760 1 /
ISE/OR 760 Applied Stochastic Modeling Topic 2: Discrete Time Markov Chain Yunan Liu Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering NC State University Yunan Liu (NC State University) ISE/OR 760 1 /
CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions
 CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions Instructor: Erik Sudderth Brown University Computer Science April 14, 215 Review: Discrete Markov Chains Some
CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions Instructor: Erik Sudderth Brown University Computer Science April 14, 215 Review: Discrete Markov Chains Some
ISyE 6650 Probabilistic Models Fall 2007
 ISyE 6650 Probabilistic Models Fall 2007 Homework 4 Solution 1. (Ross 4.3) In this case, the state of the system is determined by the weather conditions in the last three days. Letting D indicate a dry
ISyE 6650 Probabilistic Models Fall 2007 Homework 4 Solution 1. (Ross 4.3) In this case, the state of the system is determined by the weather conditions in the last three days. Letting D indicate a dry
Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes. Markov Processes Markov Chains. Random Processes
 Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes Definition IID Processes Bernoulli Process Binomial Counting Process Interarrival Time Process Markov Processes Markov Chains Classification of States Steady State Probabilities
Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes Definition IID Processes Bernoulli Process Binomial Counting Process Interarrival Time Process Markov Processes Markov Chains Classification of States Steady State Probabilities
Classification of Countable State Markov Chains
 Classification of Countable State Markov Chains Friday, March 21, 2014 2:01 PM How can we determine whether a communication class in a countable state Markov chain is: transient null recurrent positive
Classification of Countable State Markov Chains Friday, March 21, 2014 2:01 PM How can we determine whether a communication class in a countable state Markov chain is: transient null recurrent positive
MAS275 Probability Modelling Exercises
 MAS75 Probability Modelling Exercises Note: these questions are intended to be of variable difficulty. In particular: Questions or part questions labelled (*) are intended to be a bit more challenging.
MAS75 Probability Modelling Exercises Note: these questions are intended to be of variable difficulty. In particular: Questions or part questions labelled (*) are intended to be a bit more challenging.
Irreducibility. Irreducible. every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that. Absorbing state: p jj =1
 Irreducibility Irreducible every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that i,j are communicate, if the above condition is valid Irreducible: all states are communicate
Irreducibility Irreducible every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that i,j are communicate, if the above condition is valid Irreducible: all states are communicate
Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian
 Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian CMPSCI 791BB: Advanced ML Sridhar Mahadevan Random Walks! There is significant interest in the problem of random walks! Markov chain analysis! Computer
Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian CMPSCI 791BB: Advanced ML Sridhar Mahadevan Random Walks! There is significant interest in the problem of random walks! Markov chain analysis! Computer
Markov Chains Introduction
 Markov Chains 4 4.1. Introduction In this chapter, we consider a stochastic process {X n,n= 0, 1, 2,...} that takes on a finite or countable number of possible values. Unless otherwise mentioned, this
Markov Chains 4 4.1. Introduction In this chapter, we consider a stochastic process {X n,n= 0, 1, 2,...} that takes on a finite or countable number of possible values. Unless otherwise mentioned, this
Discrete time Markov chains. Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting. Limiting Distribution and Classification. Regular Transition Probability Matrices
 Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting Distribution and Classification DTU Informatics 02407 Stochastic Processes 3, September 9 207 Today: Discrete time Markov chains - invariant
Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting Distribution and Classification DTU Informatics 02407 Stochastic Processes 3, September 9 207 Today: Discrete time Markov chains - invariant
1 Ways to Describe a Stochastic Process
 purdue university cs 59000-nmc networks & matrix computations LECTURE NOTES David F. Gleich September 22, 2011 Scribe Notes: Debbie Perouli 1 Ways to Describe a Stochastic Process We will use the biased
purdue university cs 59000-nmc networks & matrix computations LECTURE NOTES David F. Gleich September 22, 2011 Scribe Notes: Debbie Perouli 1 Ways to Describe a Stochastic Process We will use the biased
Treball final de grau GRAU DE MATEMÀTIQUES Facultat de Matemàtiques Universitat de Barcelona MARKOV CHAINS
 Treball final de grau GRAU DE MATEMÀTIQUES Facultat de Matemàtiques Universitat de Barcelona MARKOV CHAINS Autor: Anna Areny Satorra Director: Dr. David Márquez Carreras Realitzat a: Departament de probabilitat,
Treball final de grau GRAU DE MATEMÀTIQUES Facultat de Matemàtiques Universitat de Barcelona MARKOV CHAINS Autor: Anna Areny Satorra Director: Dr. David Márquez Carreras Realitzat a: Departament de probabilitat,
Markov Chains on Countable State Space
 Markov Chains on Countable State Space 1 Markov Chains Introduction 1. Consider a discrete time Markov chain {X i, i = 1, 2,...} that takes values on a countable (finite or infinite) set S = {x 1, x 2,...},
Markov Chains on Countable State Space 1 Markov Chains Introduction 1. Consider a discrete time Markov chain {X i, i = 1, 2,...} that takes values on a countable (finite or infinite) set S = {x 1, x 2,...},
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 2
 MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 2 2. Countable Markov Chains I started Chapter 2 which talks about Markov chains with a countably infinite number of states. I did my favorite example which is on
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 2 2. Countable Markov Chains I started Chapter 2 which talks about Markov chains with a countably infinite number of states. I did my favorite example which is on
Recap. Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains. ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks
 Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
TMA 4265 Stochastic Processes Semester project, fall 2014 Student number and
 TMA 4265 Stochastic Processes Semester project, fall 2014 Student number 730631 and 732038 Exercise 1 We shall study a discrete Markov chain (MC) {X n } n=0 with state space S = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
TMA 4265 Stochastic Processes Semester project, fall 2014 Student number 730631 and 732038 Exercise 1 We shall study a discrete Markov chain (MC) {X n } n=0 with state space S = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling
 Part I Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling 1 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 1.1 Structure of Finite Markov Chains We shall only consider Markov chains with a finite, but usually very large,
Part I Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling 1 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 1.1 Structure of Finite Markov Chains We shall only consider Markov chains with a finite, but usually very large,
Lecture 9 Classification of States
 Lecture 9: Classification of States of 27 Course: M32K Intro to Stochastic Processes Term: Fall 204 Instructor: Gordan Zitkovic Lecture 9 Classification of States There will be a lot of definitions and
Lecture 9: Classification of States of 27 Course: M32K Intro to Stochastic Processes Term: Fall 204 Instructor: Gordan Zitkovic Lecture 9 Classification of States There will be a lot of definitions and
CHAPTER 6. Markov Chains
 CHAPTER 6 Markov Chains 6.1. Introduction A(finite)Markovchainisaprocess withafinitenumberofstates (or outcomes, or events) in which the probability of being in a particular state at step n+1depends only
CHAPTER 6 Markov Chains 6.1. Introduction A(finite)Markovchainisaprocess withafinitenumberofstates (or outcomes, or events) in which the probability of being in a particular state at step n+1depends only
Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain
 Spectral Graph Theory and Applications WS 20/202 Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Sun Introduction to Markov Chains Definition 5.. A sequence of random variables
Spectral Graph Theory and Applications WS 20/202 Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Sun Introduction to Markov Chains Definition 5.. A sequence of random variables
Transience: Whereas a finite closed communication class must be recurrent, an infinite closed communication class can be transient:
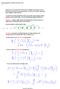 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Stochastic process. X, a series of random variables indexed by t
 Stochastic process X, a series of random variables indexed by t X={X(t), t 0} is a continuous time stochastic process X={X(t), t=0,1, } is a discrete time stochastic process X(t) is the state at time t,
Stochastic process X, a series of random variables indexed by t X={X(t), t 0} is a continuous time stochastic process X={X(t), t=0,1, } is a discrete time stochastic process X(t) is the state at time t,
Interlude: Practice Final
 8 POISSON PROCESS 08 Interlude: Practice Final This practice exam covers the material from the chapters 9 through 8. Give yourself 0 minutes to solve the six problems, which you may assume have equal point
8 POISSON PROCESS 08 Interlude: Practice Final This practice exam covers the material from the chapters 9 through 8. Give yourself 0 minutes to solve the six problems, which you may assume have equal point
2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains
 2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains Angela Peace Biomathematics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology. CRC Press,
2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains Angela Peace Biomathematics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology. CRC Press,
Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol
 Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol Laila Daniel and Krishnan Narayanan April 22, 2012 Outline of the talk A Markov chain (MC) model for Slotted ALOHA Basic properties of Discrete-time Markov Chain Stability
Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol Laila Daniel and Krishnan Narayanan April 22, 2012 Outline of the talk A Markov chain (MC) model for Slotted ALOHA Basic properties of Discrete-time Markov Chain Stability
T 1. The value function v(x) is the expected net gain when using the optimal stopping time starting at state x:
 108 OPTIMAL STOPPING TIME 4.4. Cost functions. The cost function g(x) gives the price you must pay to continue from state x. If T is your stopping time then X T is your stopping state and f(x T ) is your
108 OPTIMAL STOPPING TIME 4.4. Cost functions. The cost function g(x) gives the price you must pay to continue from state x. If T is your stopping time then X T is your stopping state and f(x T ) is your
INTRODUCTION TO MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV CHAIN MIXING
 INTRODUCTION TO MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV CHAIN MIXING ERIC SHANG Abstract. This paper provides an introduction to Markov chains and their basic classifications and interesting properties. After establishing
INTRODUCTION TO MARKOV CHAINS AND MARKOV CHAIN MIXING ERIC SHANG Abstract. This paper provides an introduction to Markov chains and their basic classifications and interesting properties. After establishing
Discrete Markov Chain. Theory and use
 Discrete Markov Chain. Theory and use Andres Vallone PhD Student andres.vallone@predoc.uam.es 2016 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Concept and definition Examples Transitions Matrix Chains Classification 3 Empirical
Discrete Markov Chain. Theory and use Andres Vallone PhD Student andres.vallone@predoc.uam.es 2016 Contents 1 Introduction 2 Concept and definition Examples Transitions Matrix Chains Classification 3 Empirical
Probability & Computing
 Probability & Computing Stochastic Process time t {X t t 2 T } state space Ω X t 2 state x 2 discrete time: T is countable T = {0,, 2,...} discrete space: Ω is finite or countably infinite X 0,X,X 2,...
Probability & Computing Stochastic Process time t {X t t 2 T } state space Ω X t 2 state x 2 discrete time: T is countable T = {0,, 2,...} discrete space: Ω is finite or countably infinite X 0,X,X 2,...
The Theory behind PageRank
 The Theory behind PageRank Mauro Sozio Telecom ParisTech May 21, 2014 Mauro Sozio (LTCI TPT) The Theory behind PageRank May 21, 2014 1 / 19 A Crash Course on Discrete Probability Events and Probability
The Theory behind PageRank Mauro Sozio Telecom ParisTech May 21, 2014 Mauro Sozio (LTCI TPT) The Theory behind PageRank May 21, 2014 1 / 19 A Crash Course on Discrete Probability Events and Probability
The cost/reward formula has two specific widely used applications:
 Applications of Absorption Probability and Accumulated Cost/Reward Formulas for FDMC Friday, October 21, 2011 2:28 PM No class next week. No office hours either. Next class will be 11/01. The cost/reward
Applications of Absorption Probability and Accumulated Cost/Reward Formulas for FDMC Friday, October 21, 2011 2:28 PM No class next week. No office hours either. Next class will be 11/01. The cost/reward
Markov Model. Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states
 Markov Model Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states (applicable to repairable, as well as non-repairable systems) System behavior
Markov Model Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states (applicable to repairable, as well as non-repairable systems) System behavior
MARKOV PROCESSES. Valerio Di Valerio
 MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
30 Classification of States
 30 Classification of States In a Markov chain, each state can be placed in one of the three classifications. 1 Since each state falls into one and only one category, these categories partition the states.
30 Classification of States In a Markov chain, each state can be placed in one of the three classifications. 1 Since each state falls into one and only one category, these categories partition the states.
Markov Chains. Chapter 16. Markov Chains - 1
 Markov Chains Chapter 16 Markov Chains - 1 Why Study Markov Chains? Decision Analysis focuses on decision making in the face of uncertainty about one future event. However, many decisions need to consider
Markov Chains Chapter 16 Markov Chains - 1 Why Study Markov Chains? Decision Analysis focuses on decision making in the face of uncertainty about one future event. However, many decisions need to consider
Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
 Markov Chains Markov chains: 2SAT: Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions rely only on local moves to explore state space. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
Markov Chains Markov chains: 2SAT: Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions rely only on local moves to explore state space. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
STOCHASTIC MODELS LECTURE 1 MARKOV CHAINS. Nan Chen MSc Program in Financial Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong (ShenZhen) Sept.
 STOCHASTIC MODELS LECTURE 1 MARKOV CHAINS Nan Chen MSc Program in Financial Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong (ShenZhen) Sept. 6, 2016 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Chapman-Kolmogrov Equations
STOCHASTIC MODELS LECTURE 1 MARKOV CHAINS Nan Chen MSc Program in Financial Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong (ShenZhen) Sept. 6, 2016 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Chapman-Kolmogrov Equations
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains
 Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
APPM 4/5560 Markov Processes Fall 2019, Some Review Problems for Exam One
 APPM /556 Markov Processes Fall 9, Some Review Problems for Exam One (Note: You will not have to invert any matrices on the exam and you will not be expected to solve systems of or more unknowns. There
APPM /556 Markov Processes Fall 9, Some Review Problems for Exam One (Note: You will not have to invert any matrices on the exam and you will not be expected to solve systems of or more unknowns. There
Social network analysis: social learning
 Social network analysis: social learning Donglei Du (ddu@unb.edu) Faculty of Business Administration, University of New Brunswick, NB Canada Fredericton E3B 9Y2 October 20, 2016 Donglei Du (UNB) AlgoTrading
Social network analysis: social learning Donglei Du (ddu@unb.edu) Faculty of Business Administration, University of New Brunswick, NB Canada Fredericton E3B 9Y2 October 20, 2016 Donglei Du (UNB) AlgoTrading
Let (Ω, F) be a measureable space. A filtration in discrete time is a sequence of. F s F t
 2.2 Filtrations Let (Ω, F) be a measureable space. A filtration in discrete time is a sequence of σ algebras {F t } such that F t F and F t F t+1 for all t = 0, 1,.... In continuous time, the second condition
2.2 Filtrations Let (Ω, F) be a measureable space. A filtration in discrete time is a sequence of σ algebras {F t } such that F t F and F t F t+1 for all t = 0, 1,.... In continuous time, the second condition
Math Homework 5 Solutions
 Math 45 - Homework 5 Solutions. Exercise.3., textbook. The stochastic matrix for the gambler problem has the following form, where the states are ordered as (,, 4, 6, 8, ): P = The corresponding diagram
Math 45 - Homework 5 Solutions. Exercise.3., textbook. The stochastic matrix for the gambler problem has the following form, where the states are ordered as (,, 4, 6, 8, ): P = The corresponding diagram
Chapter 11 Advanced Topic Stochastic Processes
 Chapter 11 Advanced Topic Stochastic Processes CHAPTER OUTLINE Section 1 Simple Random Walk Section 2 Markov Chains Section 3 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Section 4 Martingales Section 5 Brownian Motion Section
Chapter 11 Advanced Topic Stochastic Processes CHAPTER OUTLINE Section 1 Simple Random Walk Section 2 Markov Chains Section 3 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Section 4 Martingales Section 5 Brownian Motion Section
Chapter 35 out of 37 from Discrete Mathematics for Neophytes: Number Theory, Probability, Algorithms, and Other Stuff by J. M. Cargal.
 35 Mixed Chains In this chapter we learn how to analyze Markov chains that consists of transient and absorbing states. Later we will see that this analysis extends easily to chains with (nonabsorbing)
35 Mixed Chains In this chapter we learn how to analyze Markov chains that consists of transient and absorbing states. Later we will see that this analysis extends easily to chains with (nonabsorbing)
Markov Chains. Andreas Klappenecker by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. Texas A&M University
 Markov Chains Andreas Klappenecker Texas A&M University 208 by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. / 58 Stochastic Processes A stochastic process X tx ptq: t P T u is a collection of random variables.
Markov Chains Andreas Klappenecker Texas A&M University 208 by Andreas Klappenecker. All rights reserved. / 58 Stochastic Processes A stochastic process X tx ptq: t P T u is a collection of random variables.
Lecture 6: Entropy Rate
 Lecture 6: Entropy Rate Entropy rate H(X) Random walk on graph Dr. Yao Xie, ECE587, Information Theory, Duke University Coin tossing versus poker Toss a fair coin and see and sequence Head, Tail, Tail,
Lecture 6: Entropy Rate Entropy rate H(X) Random walk on graph Dr. Yao Xie, ECE587, Information Theory, Duke University Coin tossing versus poker Toss a fair coin and see and sequence Head, Tail, Tail,
Definition A finite Markov chain is a memoryless homogeneous discrete stochastic process with a finite number of states.
 Chapter 8 Finite Markov Chains A discrete system is characterized by a set V of states and transitions between the states. V is referred to as the state space. We think of the transitions as occurring
Chapter 8 Finite Markov Chains A discrete system is characterized by a set V of states and transitions between the states. V is referred to as the state space. We think of the transitions as occurring
18.175: Lecture 30 Markov chains
 18.175: Lecture 30 Markov chains Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Review what you know about finite state Markov chains Finite state ergodicity and stationarity More general setup Outline Review what you know
18.175: Lecture 30 Markov chains Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Review what you know about finite state Markov chains Finite state ergodicity and stationarity More general setup Outline Review what you know
Stochastic Processes
 Stochastic Processes 8.445 MIT, fall 20 Mid Term Exam Solutions October 27, 20 Your Name: Alberto De Sole Exercise Max Grade Grade 5 5 2 5 5 3 5 5 4 5 5 5 5 5 6 5 5 Total 30 30 Problem :. True / False
Stochastic Processes 8.445 MIT, fall 20 Mid Term Exam Solutions October 27, 20 Your Name: Alberto De Sole Exercise Max Grade Grade 5 5 2 5 5 3 5 5 4 5 5 5 5 5 6 5 5 Total 30 30 Problem :. True / False
Lecture #5. Dependencies along the genome
 Markov Chains Lecture #5 Background Readings: Durbin et. al. Section 3., Polanski&Kimmel Section 2.8. Prepared by Shlomo Moran, based on Danny Geiger s and Nir Friedman s. Dependencies along the genome
Markov Chains Lecture #5 Background Readings: Durbin et. al. Section 3., Polanski&Kimmel Section 2.8. Prepared by Shlomo Moran, based on Danny Geiger s and Nir Friedman s. Dependencies along the genome
LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION MATRIX OF A CONDENSED FIBONACCI TREE
 International Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 31 No. 18, 41-49 ISSN: 1311-178 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-86 (on-line version) doi: http://dx.doi.org/1.173/ijam.v31i.6 LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION
International Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 31 No. 18, 41-49 ISSN: 1311-178 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-86 (on-line version) doi: http://dx.doi.org/1.173/ijam.v31i.6 LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION
1 Gambler s Ruin Problem
 1 Gambler s Ruin Problem Consider a gambler who starts with an initial fortune of $1 and then on each successive gamble either wins $1 or loses $1 independent of the past with probabilities p and q = 1
1 Gambler s Ruin Problem Consider a gambler who starts with an initial fortune of $1 and then on each successive gamble either wins $1 or loses $1 independent of the past with probabilities p and q = 1
MATH 56A SPRING 2008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES
 MATH 56A SPRING 008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES KIYOSHI IGUSA Contents 4. Optimal Stopping Time 95 4.1. Definitions 95 4.. The basic problem 95 4.3. Solutions to basic problem 97 4.4. Cost functions 101 4.5.
MATH 56A SPRING 008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES KIYOSHI IGUSA Contents 4. Optimal Stopping Time 95 4.1. Definitions 95 4.. The basic problem 95 4.3. Solutions to basic problem 97 4.4. Cost functions 101 4.5.
Quantitative Evaluation of Emedded Systems Solution 2: Discrete Time Markov Chains (DTMC)
 Quantitative Evaluation of Emedded Systems Solution 2: Discrete Time Markov Chains (DTMC) 2.1 Classification of DTMC states Prof. Dr. Anne Remke Design and Analysis of Communication Systems University
Quantitative Evaluation of Emedded Systems Solution 2: Discrete Time Markov Chains (DTMC) 2.1 Classification of DTMC states Prof. Dr. Anne Remke Design and Analysis of Communication Systems University
STAT STOCHASTIC PROCESSES. Contents
 STAT 3911 - STOCHASTIC PROCESSES ANDREW TULLOCH Contents 1. Stochastic Processes 2 2. Classification of states 2 3. Limit theorems for Markov chains 4 4. First step analysis 5 5. Branching processes 5
STAT 3911 - STOCHASTIC PROCESSES ANDREW TULLOCH Contents 1. Stochastic Processes 2 2. Classification of states 2 3. Limit theorems for Markov chains 4 4. First step analysis 5 5. Branching processes 5
P i [B k ] = lim. n=1 p(n) ii <. n=1. V i :=
![P i [B k ] = lim. n=1 p(n) ii <. n=1. V i := P i [B k ] = lim. n=1 p(n) ii <. n=1. V i :=](/thumbs/92/110148679.jpg) 2.7. Recurrence and transience Consider a Markov chain {X n : n N 0 } on state space E with transition matrix P. Definition 2.7.1. A state i E is called recurrent if P i [X n = i for infinitely many n]
2.7. Recurrence and transience Consider a Markov chain {X n : n N 0 } on state space E with transition matrix P. Definition 2.7.1. A state i E is called recurrent if P i [X n = i for infinitely many n]
1 Random Walks and Electrical Networks
 CME 305: Discrete Mathematics and Algorithms Random Walks and Electrical Networks Random walks are widely used tools in algorithm design and probabilistic analysis and they have numerous applications.
CME 305: Discrete Mathematics and Algorithms Random Walks and Electrical Networks Random walks are widely used tools in algorithm design and probabilistic analysis and they have numerous applications.
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 20, 4/11/2017
 COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 20, 4/11/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University SEQUENTIAL DATA So far, when thinking
COMS 4721: Machine Learning for Data Science Lecture 20, 4/11/2017 Prof. John Paisley Department of Electrical Engineering & Data Science Institute Columbia University SEQUENTIAL DATA So far, when thinking
Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Chapter 5 Markov Chain Monte Carlo MCMC is a kind of improvement of the Monte Carlo method By sampling from a Markov chain whose stationary distribution is the desired sampling distributuion, it is possible
Chapter 5 Markov Chain Monte Carlo MCMC is a kind of improvement of the Monte Carlo method By sampling from a Markov chain whose stationary distribution is the desired sampling distributuion, it is possible
18.600: Lecture 32 Markov Chains
 18.600: Lecture 32 Markov Chains Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Markov chains Examples Ergodicity and stationarity Outline Markov chains Examples Ergodicity and stationarity Markov chains Consider a sequence
18.600: Lecture 32 Markov Chains Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Markov chains Examples Ergodicity and stationarity Outline Markov chains Examples Ergodicity and stationarity Markov chains Consider a sequence
18.440: Lecture 33 Markov Chains
 18.440: Lecture 33 Markov Chains Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline Markov chains Examples Ergodicity and stationarity 2 Outline Markov chains Examples Ergodicity and stationarity 3 Markov chains Consider a
18.440: Lecture 33 Markov Chains Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline Markov chains Examples Ergodicity and stationarity 2 Outline Markov chains Examples Ergodicity and stationarity 3 Markov chains Consider a
Stochastic Models: Markov Chains and their Generalizations
 Scuola di Dottorato in Scienza ed Alta Tecnologia Dottorato in Informatica Universita di Torino Stochastic Models: Markov Chains and their Generalizations Gianfranco Balbo e Andras Horvath Outline Introduction
Scuola di Dottorato in Scienza ed Alta Tecnologia Dottorato in Informatica Universita di Torino Stochastic Models: Markov Chains and their Generalizations Gianfranco Balbo e Andras Horvath Outline Introduction
Today. Next lecture. (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models
 Today (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models Graphical representation Transition probability matrix Propagating state distributions The stationary distribution Next lecture (Ch 14) Markov chains
Today (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models Graphical representation Transition probability matrix Propagating state distributions The stationary distribution Next lecture (Ch 14) Markov chains
6 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)
 6 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) The underlying idea in MCMC is to replace the iid samples of basic MC methods, with dependent samples from an ergodic Markov chain, whose limiting (stationary) distribution
6 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) The underlying idea in MCMC is to replace the iid samples of basic MC methods, with dependent samples from an ergodic Markov chain, whose limiting (stationary) distribution
Lecture notes for Analysis of Algorithms : Markov decision processes
 Lecture notes for Analysis of Algorithms : Markov decision processes Lecturer: Thomas Dueholm Hansen June 6, 013 Abstract We give an introduction to infinite-horizon Markov decision processes (MDPs) with
Lecture notes for Analysis of Algorithms : Markov decision processes Lecturer: Thomas Dueholm Hansen June 6, 013 Abstract We give an introduction to infinite-horizon Markov decision processes (MDPs) with
25.1 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)
 CS880: Approximations Algorithms Scribe: Dave Andrzejewski Lecturer: Shuchi Chawla Topic: Approx counting/sampling, MCMC methods Date: 4/4/07 The previous lecture showed that, for self-reducible problems,
CS880: Approximations Algorithms Scribe: Dave Andrzejewski Lecturer: Shuchi Chawla Topic: Approx counting/sampling, MCMC methods Date: 4/4/07 The previous lecture showed that, for self-reducible problems,
4.7.1 Computing a stationary distribution
 At a high-level our interest in the rest of this section will be to understand the limiting distribution, when it exists and how to compute it To compute it, we will try to reason about when the limiting
At a high-level our interest in the rest of this section will be to understand the limiting distribution, when it exists and how to compute it To compute it, we will try to reason about when the limiting
The Markov Chain Monte Carlo Method
 The Markov Chain Monte Carlo Method Idea: define an ergodic Markov chain whose stationary distribution is the desired probability distribution. Let X 0, X 1, X 2,..., X n be the run of the chain. The Markov
The Markov Chain Monte Carlo Method Idea: define an ergodic Markov chain whose stationary distribution is the desired probability distribution. Let X 0, X 1, X 2,..., X n be the run of the chain. The Markov
2 DISCRETE-TIME MARKOV CHAINS
 1 2 DISCRETE-TIME MARKOV CHAINS 21 FUNDAMENTAL DEFINITIONS AND PROPERTIES From now on we will consider processes with a countable or finite state space S {0, 1, 2, } Definition 1 A discrete-time discrete-state
1 2 DISCRETE-TIME MARKOV CHAINS 21 FUNDAMENTAL DEFINITIONS AND PROPERTIES From now on we will consider processes with a countable or finite state space S {0, 1, 2, } Definition 1 A discrete-time discrete-state
Markov Chains and Pandemics
 Markov Chains and Pandemics Caleb Dedmore and Brad Smith December 8, 2016 Page 1 of 16 Abstract Markov Chain Theory is a powerful tool used in statistical analysis to make predictions about future events
Markov Chains and Pandemics Caleb Dedmore and Brad Smith December 8, 2016 Page 1 of 16 Abstract Markov Chain Theory is a powerful tool used in statistical analysis to make predictions about future events
MATH 56A SPRING 2008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 65
 MATH 56A SPRING 2008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 65 2.2.5. proof of extinction lemma. The proof of Lemma 2.3 is just like the proof of the lemma I did on Wednesday. It goes like this. Suppose that â is the smallest
MATH 56A SPRING 2008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 65 2.2.5. proof of extinction lemma. The proof of Lemma 2.3 is just like the proof of the lemma I did on Wednesday. It goes like this. Suppose that â is the smallest
= P{X 0. = i} (1) If the MC has stationary transition probabilities then, = i} = P{X n+1
 Properties of Markov Chains and Evaluation of Steady State Transition Matrix P ss V. Krishnan - 3/9/2 Property 1 Let X be a Markov Chain (MC) where X {X n : n, 1, }. The state space is E {i, j, k, }. The
Properties of Markov Chains and Evaluation of Steady State Transition Matrix P ss V. Krishnan - 3/9/2 Property 1 Let X be a Markov Chain (MC) where X {X n : n, 1, }. The state space is E {i, j, k, }. The
Essentials on the Analysis of Randomized Algorithms
 Essentials on the Analysis of Randomized Algorithms Dimitris Diochnos Feb 0, 2009 Abstract These notes were written with Monte Carlo algorithms primarily in mind. Topics covered are basic (discrete) random
Essentials on the Analysis of Randomized Algorithms Dimitris Diochnos Feb 0, 2009 Abstract These notes were written with Monte Carlo algorithms primarily in mind. Topics covered are basic (discrete) random
Homework set 2 - Solutions
 Homework set 2 - Solutions Math 495 Renato Feres Simulating a Markov chain in R Generating sample sequences of a finite state Markov chain. The following is a simple program for generating sample sequences
Homework set 2 - Solutions Math 495 Renato Feres Simulating a Markov chain in R Generating sample sequences of a finite state Markov chain. The following is a simple program for generating sample sequences
Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread
 Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread Julien Arino Centre for Research on Inner City Health St Michael s Hospital Toronto On leave from Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba Julien Arino@umanitoba.ca
Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread Julien Arino Centre for Research on Inner City Health St Michael s Hospital Toronto On leave from Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba Julien Arino@umanitoba.ca
Midterm 2 Review. CS70 Summer Lecture 6D. David Dinh 28 July UC Berkeley
 Midterm 2 Review CS70 Summer 2016 - Lecture 6D David Dinh 28 July 2016 UC Berkeley Midterm 2: Format 8 questions, 190 points, 110 minutes (same as MT1). Two pages (one double-sided sheet) of handwritten
Midterm 2 Review CS70 Summer 2016 - Lecture 6D David Dinh 28 July 2016 UC Berkeley Midterm 2: Format 8 questions, 190 points, 110 minutes (same as MT1). Two pages (one double-sided sheet) of handwritten
Note that in the example in Lecture 1, the state Home is recurrent (and even absorbing), but all other states are transient. f ii (n) f ii = n=1 < +
 Random Walks: WEEK 2 Recurrence and transience Consider the event {X n = i for some n > 0} by which we mean {X = i}or{x 2 = i,x i}or{x 3 = i,x 2 i,x i},. Definition.. A state i S is recurrent if P(X n
Random Walks: WEEK 2 Recurrence and transience Consider the event {X n = i for some n > 0} by which we mean {X = i}or{x 2 = i,x i}or{x 3 = i,x 2 i,x i},. Definition.. A state i S is recurrent if P(X n
