No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1.
|
|
|
- Charla Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, :02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly prefer printed copy in my mailbox in Amos Eaton 310 acknowledge collaborations! Last time we described how to compute arbitrary finite horizon statistics for a FSDT MC. But many questions of interest don't have a prescribed finite horizon: long run behavior questions about whether certain states are eventually achieved, and if so, how long does it take to happen To begin to address these questions, we must develop some other characterizations and mathematical structures associated with Markov chains. We saw last time that we could compute finite horizon statistics for both time-homogenous and timeinhomogenous Markov chains. However, for indefinite horizon calculations, very few mathematical formulas are available for time-inhomogenous Markov chains, so we will restrict consideration going forward to time-homogenous Markov chains. A stationary distribution of a time-homogenous FSDT Markov chain is defined to be a probability distribution which is preserved by the dynamics of the Markov chain. Specifically, it can encoded as a (column) vector: with the following properties (where is the probability transition matrix of the MC) Stoch15 Page 1
2 The first property is the essential one: Suppose that we define the probaiblity distribution for the state of a FSDT MC after epochs by the vector: From last time, we know that the probability distribution for the state of FSDT MC updates as follows: (just refer to the calculation at end of last lecture with ) So, if, then as well. And in particular, if, then for all So we see the analogy stationary distribution : FSDT MCs :: fixed points/equilibria : dynamical systems In particular, the stationary distribution gives a probability distribution for the state of a FSDT MC which is determined by the dynamics, and so is somehow "natural." Note that what is fixed under the evolution of the stationary distribution are Stoch15 Page 2
3 the probabilities, not the state variable itself which certainly changes. Note that a FSDT MC which is initialized by a stationary distribution will give rise to a statistically stationary Markov process which means that the Markov process itself has statistics which are invariant under time translation to be distinguished by a general solution to a time-homogenous FSDT MC which has evolution rules that don't depend on time, but which can fail to be statistically stationary because the initial condition breaks time translation invariance. Note also that an important modern example of the use of stationary distributions is in the PageRank algorithm, based on a "random surfer" model Markov chain for the network under consideration. Key mathematical questions pertaining to stationary distributions: Under what conditions are we guaranteed that a stationary distribution for a FSDT MC exists? Under what conditions is the stationary distribution for a FSDT MC uniquely determined? Under what conditions does the stationary distribution serve as a limit distribution, meaning that the probability distribution for the Markov chain initialized arbitrarily will, after many epochs, approach the limit distribution? Existence: Every FSDT MC is guaranteed to have a stationary distribution. The proof is based on the observation that, because all row sums of the probability transition matrix must, then: Stoch15 Page 3
4 That means that has a right eigenvector with eigenvalue 1. Then linear algebra tells us also has a left eigenvector with eigenvalue 1. equivalently observe that is singular But then how do we guarantee the other two properties of stationary distribution? The Perron-Frobenius Theorem (Karlin and Taylor, Appendix B), which describes the properties of eigenvalues/eigenvectors of matrices with nonnegative entries, can be applied to guarantee that the left eigenvector can be chosen to have all nonnegative entries. Once we have a left eigenvector of eigenvalue 1 with nonnegative entries, we can just divide it by the sum of its entries so the normalization condition is satisfied. Uniqueness? See Resnick Secs for formal proofs of statements. One requires a classification of the topology of the Markov chain in order to answer whether or not the stationary distribution is unique. topology of a Markov chain simply means the properties of the graph whose adjacency matrix if and otherwise. In other words, draw a directed graph on the state space with directed edges everywhere that. Two states of a Markov chain are said to communicate provided there exist nonnegative integers such that: and Recalling that describes the matrix of probabilities to go from one state to another in exactly epochs, this statement just means: "It is possible to go from state to state, and from state to state." (Except state always communicates with state, even if ; choose.) Stoch15 Page 4
5 Every node corresponds to a state in the state space A directed edge exists from node i to node if and only if Notationally we write with state. for the statement that state communicates We can also write a notation to mean that it is possible to go from state to state, but not necessarily from state to state. (This is not enough for communication.) Communication is an equivalence relation, and a consequence from algebra is that the state space can be decomposed into communication classes such that all states within a communication class communicate with each other, but states in different communication classes do not communicate with each other. A communication class is said to be closed provided there exist no pair of states, such that. In other words, there is no way to leave a closed communication class. A Markov chain is said to be irreducible if it has a single communication class (meaning that all states communicate with each other.) Stoch15 Page 5
6 Note that if one restricts a reducible Markov chain to a closed communication class, the result is an irreducible Markov chain with state space equal to that closed communication class. this will be useful in applying some results for irreducible Markov chains to reducible Markov chains The key uniqueness result for FSDT MCs is: Any irreducible FSDT MC has a unique stationary distribution, which moreover can be expressed by the following formula: where is the first passage time for state (usually called first return time if, which is a random variable. The conditional expectation of random variables can be computed by using the conditional probabilities: The intuition behind the linkage between the stationary distribution and first return time is as follows: Suppose we have a statistically stationary Markov chain initialized by the stationary distribution. Then for any epoch, we have, which means that the MC will be in state roughly a fraction of the time. So if we record the states visited by a realization of the MC with stationary distribution Stoch15 Page 6
7 The connection between the stationary distribution and the average first return time is usually used as a means to compute average first return times. Stoch15 Page 7
Finite-Horizon Statistics for Markov chains
 Analyzing FSDT Markov chains Friday, September 30, 2011 2:03 PM Simulating FSDT Markov chains, as we have said is very straightforward, either by using probability transition matrix or stochastic update
Analyzing FSDT Markov chains Friday, September 30, 2011 2:03 PM Simulating FSDT Markov chains, as we have said is very straightforward, either by using probability transition matrix or stochastic update
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains
 Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Transience: Whereas a finite closed communication class must be recurrent, an infinite closed communication class can be transient:
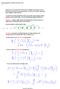 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Let's contemplate a continuous-time limit of the Bernoulli process:
 Mathematical Foundations of Markov Chains Thursday, September 17, 2015 2:04 PM Reading: Lawler Ch. 1 Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM. Office hours today are moved to 6-7 PM. Let's revisit the
Mathematical Foundations of Markov Chains Thursday, September 17, 2015 2:04 PM Reading: Lawler Ch. 1 Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM. Office hours today are moved to 6-7 PM. Let's revisit the
Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM.
 Stationary Distributions: Application Monday, October 05, 2015 2:04 PM Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM. To prepare to describe the conditions under which the
Stationary Distributions: Application Monday, October 05, 2015 2:04 PM Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM. To prepare to describe the conditions under which the
Classification of Countable State Markov Chains
 Classification of Countable State Markov Chains Friday, March 21, 2014 2:01 PM How can we determine whether a communication class in a countable state Markov chain is: transient null recurrent positive
Classification of Countable State Markov Chains Friday, March 21, 2014 2:01 PM How can we determine whether a communication class in a countable state Markov chain is: transient null recurrent positive
Birth-death chain models (countable state)
 Countable State Birth-Death Chains and Branching Processes Tuesday, March 25, 2014 1:59 PM Homework 3 posted, due Friday, April 18. Birth-death chain models (countable state) S = We'll characterize the
Countable State Birth-Death Chains and Branching Processes Tuesday, March 25, 2014 1:59 PM Homework 3 posted, due Friday, April 18. Birth-death chain models (countable state) S = We'll characterize the
Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
 Formulation of Finite State Markov Chains Friday, September 23, 2011 2:04 PM Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
Formulation of Finite State Markov Chains Friday, September 23, 2011 2:04 PM Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains
 Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains Friday, February 07, 2014 2:04 PM Stochastic update rule for FSDT Markov Chain requires an initial condition. Most generally, this can
Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains Friday, February 07, 2014 2:04 PM Stochastic update rule for FSDT Markov Chain requires an initial condition. Most generally, this can
FDST Markov Chain Models
 FDST Markov Chain Models Tuesday, February 11, 2014 2:01 PM Homework 1 due Friday, February 21 at 2 PM. Reading: Karlin and Taylor, Sections 2.1-2.3 Almost all of our Markov chain models will be time-homogenous,
FDST Markov Chain Models Tuesday, February 11, 2014 2:01 PM Homework 1 due Friday, February 21 at 2 PM. Reading: Karlin and Taylor, Sections 2.1-2.3 Almost all of our Markov chain models will be time-homogenous,
Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, :12 PM
 stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
 Mathematical Foundations of Discrete-Time Markov Chains Tuesday, February 04, 2014 2:04 PM Homework 1 posted, due Friday, February 21. Reading: Lawler, Ch. 1 Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
Mathematical Foundations of Discrete-Time Markov Chains Tuesday, February 04, 2014 2:04 PM Homework 1 posted, due Friday, February 21. Reading: Lawler, Ch. 1 Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Uncertainty and Randomization
 Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30.
 Random Variables Friday, September 09, 2011 2:02 PM I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30. No class or office hours next week. Next class is on Tuesday, September
Random Variables Friday, September 09, 2011 2:02 PM I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30. No class or office hours next week. Next class is on Tuesday, September
Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29.
 Classification of Birth-Death Chains Tuesday, November 08, 2011 2:02 PM Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29. Continuing with our classification of birth-death chains on nonnegative integers. Last
Classification of Birth-Death Chains Tuesday, November 08, 2011 2:02 PM Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29. Continuing with our classification of birth-death chains on nonnegative integers. Last
The cost/reward formula has two specific widely used applications:
 Applications of Absorption Probability and Accumulated Cost/Reward Formulas for FDMC Friday, October 21, 2011 2:28 PM No class next week. No office hours either. Next class will be 11/01. The cost/reward
Applications of Absorption Probability and Accumulated Cost/Reward Formulas for FDMC Friday, October 21, 2011 2:28 PM No class next week. No office hours either. Next class will be 11/01. The cost/reward
So in terms of conditional probability densities, we have by differentiating this relationship:
 Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline).
 Large-Time Behavior for Continuous-Time Markov Chains Friday, December 02, 2011 10:58 AM Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline). How are formulas for large-time behavior of discrete-time
Large-Time Behavior for Continuous-Time Markov Chains Friday, December 02, 2011 10:58 AM Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline). How are formulas for large-time behavior of discrete-time
MATH3200, Lecture 31: Applications of Eigenvectors. Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems
 Lecture 31: Some Applications of Eigenvectors: Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems Winfried Just Department of Mathematics, Ohio University April 9 11, 2018 Review: Eigenvectors and left eigenvectors
Lecture 31: Some Applications of Eigenvectors: Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems Winfried Just Department of Mathematics, Ohio University April 9 11, 2018 Review: Eigenvectors and left eigenvectors
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks
 ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian
 Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian CMPSCI 791BB: Advanced ML Sridhar Mahadevan Random Walks! There is significant interest in the problem of random walks! Markov chain analysis! Computer
Markov Chains, Random Walks on Graphs, and the Laplacian CMPSCI 791BB: Advanced ML Sridhar Mahadevan Random Walks! There is significant interest in the problem of random walks! Markov chain analysis! Computer
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm
 Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
Convex Optimization CMU-10725
 Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Simulated Annealing Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Andrey Markov Markov Chains 2 Markov Chains Markov chain: Homogen Markov chain: 3 Markov Chains Assume that the state
Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Simulated Annealing Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Andrey Markov Markov Chains 2 Markov Chains Markov chain: Homogen Markov chain: 3 Markov Chains Assume that the state
Announcements Monday, September 18
 Announcements Monday, September 18 WeBWorK 1.4, 1.5 are due on Wednesday at 11:59pm. The first midterm is on this Friday, September 22. Midterms happen during recitation. The exam covers through 1.5. About
Announcements Monday, September 18 WeBWorK 1.4, 1.5 are due on Wednesday at 11:59pm. The first midterm is on this Friday, September 22. Midterms happen during recitation. The exam covers through 1.5. About
Lecture Notes: Markov chains Tuesday, September 16 Dannie Durand
 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Lecture Notes: Markov chains Tuesday, September 6 Dannie Durand In the last lecture, we introduced Markov chains, a mathematical formalism for modeling how
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Lecture Notes: Markov chains Tuesday, September 6 Dannie Durand In the last lecture, we introduced Markov chains, a mathematical formalism for modeling how
Calculating Web Page Authority Using the PageRank Algorithm
 Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming
 CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
MATH36001 Perron Frobenius Theory 2015
 MATH361 Perron Frobenius Theory 215 In addition to saying something useful, the Perron Frobenius theory is elegant. It is a testament to the fact that beautiful mathematics eventually tends to be useful,
MATH361 Perron Frobenius Theory 215 In addition to saying something useful, the Perron Frobenius theory is elegant. It is a testament to the fact that beautiful mathematics eventually tends to be useful,
Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
 Review of Probability Theory Tuesday, September 06, 2011 2:05 PM Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
Review of Probability Theory Tuesday, September 06, 2011 2:05 PM Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor, Sec. 2.3)
 stochnotes091108 Page 1 Markov Chain Models and Basic Computations Thursday, September 11, 2008 11:50 AM Homework 1 is posted, due Monday, September 22. Two more examples. Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor,
stochnotes091108 Page 1 Markov Chain Models and Basic Computations Thursday, September 11, 2008 11:50 AM Homework 1 is posted, due Monday, September 22. Two more examples. Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor,
Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, November 11, 2011 2:05 PM Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, November 11, 2011 2:05 PM Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, :04 PM
 stochnotes102008 Page 1 Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, 2008 12:04 PM Looking for a detailed balance solution for a stationary distribution is a useful technique. Stationary
stochnotes102008 Page 1 Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, 2008 12:04 PM Looking for a detailed balance solution for a stationary distribution is a useful technique. Stationary
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
Note that. No office hours on Monday October 15 or Wednesday October 17. No class Tuesday October 16
 advprobnotes101207b Page 1 CDFS and coping with random variables that are not purely discrete nor absolutely continuouss Friday, October 12, 2007 2:10 PM Note that No office hours on Monday October 15
advprobnotes101207b Page 1 CDFS and coping with random variables that are not purely discrete nor absolutely continuouss Friday, October 12, 2007 2:10 PM Note that No office hours on Monday October 15
MAT 211, Spring 2015, Introduction to Linear Algebra.
 MAT 211, Spring 2015, Introduction to Linear Algebra. Lecture 04, 53103: MWF 10-10:53 AM. Location: Library W4535 Contact: mtehrani@scgp.stonybrook.edu Final Exam: Monday 5/18/15 8:00 AM-10:45 AM The aim
MAT 211, Spring 2015, Introduction to Linear Algebra. Lecture 04, 53103: MWF 10-10:53 AM. Location: Library W4535 Contact: mtehrani@scgp.stonybrook.edu Final Exam: Monday 5/18/15 8:00 AM-10:45 AM The aim
Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
 Probability Theory Foundations Thursday, September 03, 2015 1:57 PM Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
Probability Theory Foundations Thursday, September 03, 2015 1:57 PM Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
Definition A finite Markov chain is a memoryless homogeneous discrete stochastic process with a finite number of states.
 Chapter 8 Finite Markov Chains A discrete system is characterized by a set V of states and transitions between the states. V is referred to as the state space. We think of the transitions as occurring
Chapter 8 Finite Markov Chains A discrete system is characterized by a set V of states and transitions between the states. V is referred to as the state space. We think of the transitions as occurring
MAA704, Perron-Frobenius theory and Markov chains.
 November 19, 2013 Lecture overview Today we will look at: Permutation and graphs. Perron frobenius for non-negative. Stochastic, and their relation to theory. Hitting and hitting probabilities of chain.
November 19, 2013 Lecture overview Today we will look at: Permutation and graphs. Perron frobenius for non-negative. Stochastic, and their relation to theory. Hitting and hitting probabilities of chain.
Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 7 Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains Daniel A Spielman September 9, 202 7 About these notes These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation of what happened in
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 7 Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains Daniel A Spielman September 9, 202 7 About these notes These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation of what happened in
This is now an algebraic equation that can be solved simply:
 Simulation of CTMC Monday, November 23, 2015 1:55 PM Homework 4 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, December 11 at 5 PM. Let's solve the Kolmogorov forward equation for the Poisson counting
Simulation of CTMC Monday, November 23, 2015 1:55 PM Homework 4 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, December 11 at 5 PM. Let's solve the Kolmogorov forward equation for the Poisson counting
SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices)
 Chapter 14 SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Today we continue the topic of low-dimensional approximation to datasets and matrices. Last time we saw the singular
Chapter 14 SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Today we continue the topic of low-dimensional approximation to datasets and matrices. Last time we saw the singular
Lecture 14: SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Lecturer: Sanjeev Arora
 princeton univ. F 13 cos 521: Advanced Algorithm Design Lecture 14: SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Lecturer: Sanjeev Arora Scribe: Today we continue the
princeton univ. F 13 cos 521: Advanced Algorithm Design Lecture 14: SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Lecturer: Sanjeev Arora Scribe: Today we continue the
Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling
 Part I Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling 1 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 1.1 Structure of Finite Markov Chains We shall only consider Markov chains with a finite, but usually very large,
Part I Markov Chains and Stochastic Sampling 1 Markov Chains and Random Walks on Graphs 1.1 Structure of Finite Markov Chains We shall only consider Markov chains with a finite, but usually very large,
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 110
 Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
As it is not necessarily possible to satisfy this equation, we just ask for a solution to the more general equation
 Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Section 1.7: Properties of the Leslie Matrix
 Section 1.7: Properties of the Leslie Matrix Definition: A matrix A whose entries are nonnegative (positive) is called a nonnegative (positive) matrix, denoted as A 0 (A > 0). Definition: A square m m
Section 1.7: Properties of the Leslie Matrix Definition: A matrix A whose entries are nonnegative (positive) is called a nonnegative (positive) matrix, denoted as A 0 (A > 0). Definition: A square m m
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 7 Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains Daniel A. Spielman September 19, 2018 7.1 Overview In today s lecture we will justify some of the behavior we observed when using eigenvectors
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 7 Fiedler s Theorems on Nodal Domains Daniel A. Spielman September 19, 2018 7.1 Overview In today s lecture we will justify some of the behavior we observed when using eigenvectors
Markov Chains. As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006.
 Markov Chains As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006 1 Introduction A (finite) Markov chain is a process with a finite number of states (or outcomes, or
Markov Chains As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006 1 Introduction A (finite) Markov chain is a process with a finite number of states (or outcomes, or
DATA MINING LECTURE 13. Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
 DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions
 J. Virtamo 38.3143 Queueing Theory / Stochastic processes 1 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions Often the systems we consider evolve in time and we are interested in their dynamic behaviour, usually involving
J. Virtamo 38.3143 Queueing Theory / Stochastic processes 1 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions Often the systems we consider evolve in time and we are interested in their dynamic behaviour, usually involving
Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain
 Spectral Graph Theory and Applications WS 20/202 Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Sun Introduction to Markov Chains Definition 5.. A sequence of random variables
Spectral Graph Theory and Applications WS 20/202 Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Sun Introduction to Markov Chains Definition 5.. A sequence of random variables
 http://www.math.uah.edu/stat/markov/.xhtml 1 of 9 7/16/2009 7:20 AM Virtual Laboratories > 16. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. A Markov process is a random process in which the future is
http://www.math.uah.edu/stat/markov/.xhtml 1 of 9 7/16/2009 7:20 AM Virtual Laboratories > 16. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. A Markov process is a random process in which the future is
At the boundary states, we take the same rules except we forbid leaving the state space, so,.
 Birth-death chains Monday, October 19, 2015 2:22 PM Example: Birth-Death Chain State space From any state we allow the following transitions: with probability (birth) with probability (death) with probability
Birth-death chains Monday, October 19, 2015 2:22 PM Example: Birth-Death Chain State space From any state we allow the following transitions: with probability (birth) with probability (death) with probability
MAT1302F Mathematical Methods II Lecture 19
 MAT302F Mathematical Methods II Lecture 9 Aaron Christie 2 April 205 Eigenvectors, Eigenvalues, and Diagonalization Now that the basic theory of eigenvalues and eigenvectors is in place most importantly
MAT302F Mathematical Methods II Lecture 9 Aaron Christie 2 April 205 Eigenvectors, Eigenvalues, and Diagonalization Now that the basic theory of eigenvalues and eigenvectors is in place most importantly
Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4)
 Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
7.1 Coupling from the Past
 Georgia Tech Fall 2006 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Lecture 7: September 12, 2006 Coupling from the Past Eric Vigoda 7.1 Coupling from the Past 7.1.1 Introduction We saw in the last lecture how Markov
Georgia Tech Fall 2006 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Lecture 7: September 12, 2006 Coupling from the Past Eric Vigoda 7.1 Coupling from the Past 7.1.1 Introduction We saw in the last lecture how Markov
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method
 eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701
 Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Goal & Motivation Sampling Rejection Importance Markov
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Goal & Motivation Sampling Rejection Importance Markov
IR: Information Retrieval
 / 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
/ 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
Social network analysis: social learning
 Social network analysis: social learning Donglei Du (ddu@unb.edu) Faculty of Business Administration, University of New Brunswick, NB Canada Fredericton E3B 9Y2 October 20, 2016 Donglei Du (UNB) AlgoTrading
Social network analysis: social learning Donglei Du (ddu@unb.edu) Faculty of Business Administration, University of New Brunswick, NB Canada Fredericton E3B 9Y2 October 20, 2016 Donglei Du (UNB) AlgoTrading
A Note on Google s PageRank
 A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis. Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa
 Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Announcements: Nov 10
 Announcements: Nov 10 WebWork 5.3, 5.5 due Wednesday Midterm 3 on Friday Nov 17 Upcoming Office Hours Me: Monday 1-2 and Wednesday 3-4, Skiles 234 Bharat: Tuesday 1:45-2:45, Skiles 230 Qianli: Wednesday
Announcements: Nov 10 WebWork 5.3, 5.5 due Wednesday Midterm 3 on Friday Nov 17 Upcoming Office Hours Me: Monday 1-2 and Wednesday 3-4, Skiles 234 Bharat: Tuesday 1:45-2:45, Skiles 230 Qianli: Wednesday
stochnotes Page 1
 stochnotes110308 Page 1 Kolmogorov forward and backward equations and Poisson process Monday, November 03, 2008 11:58 AM How can we apply the Kolmogorov equations to calculate various statistics of interest?
stochnotes110308 Page 1 Kolmogorov forward and backward equations and Poisson process Monday, November 03, 2008 11:58 AM How can we apply the Kolmogorov equations to calculate various statistics of interest?
How works. or How linear algebra powers the search engine. M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University
 How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions
 CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions Instructor: Erik Sudderth Brown University Computer Science April 14, 215 Review: Discrete Markov Chains Some
CS145: Probability & Computing Lecture 18: Discrete Markov Chains, Equilibrium Distributions Instructor: Erik Sudderth Brown University Computer Science April 14, 215 Review: Discrete Markov Chains Some
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
642:550, Summer 2004, Supplement 6 The Perron-Frobenius Theorem. Summer 2004
 642:550, Summer 2004, Supplement 6 The Perron-Frobenius Theorem. Summer 2004 Introduction Square matrices whose entries are all nonnegative have special properties. This was mentioned briefly in Section
642:550, Summer 2004, Supplement 6 The Perron-Frobenius Theorem. Summer 2004 Introduction Square matrices whose entries are all nonnegative have special properties. This was mentioned briefly in Section
2. Transience and Recurrence
 Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 1
 MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER. Finite Markov chains For the sake of completeness of these notes I decided to write a summary of the basic concepts of finite Markov chains. The topics in this chapter
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER. Finite Markov chains For the sake of completeness of these notes I decided to write a summary of the basic concepts of finite Markov chains. The topics in this chapter
Lecture 15 Perron-Frobenius Theory
 EE363 Winter 2005-06 Lecture 15 Perron-Frobenius Theory Positive and nonnegative matrices and vectors Perron-Frobenius theorems Markov chains Economic growth Population dynamics Max-min and min-max characterization
EE363 Winter 2005-06 Lecture 15 Perron-Frobenius Theory Positive and nonnegative matrices and vectors Perron-Frobenius theorems Markov chains Economic growth Population dynamics Max-min and min-max characterization
Matrix analytic methods. Lecture 1: Structured Markov chains and their stationary distribution
 1/29 Matrix analytic methods Lecture 1: Structured Markov chains and their stationary distribution Sophie Hautphenne and David Stanford (with thanks to Guy Latouche, U. Brussels and Peter Taylor, U. Melbourne
1/29 Matrix analytic methods Lecture 1: Structured Markov chains and their stationary distribution Sophie Hautphenne and David Stanford (with thanks to Guy Latouche, U. Brussels and Peter Taylor, U. Melbourne
Discrete time Markov chains. Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting. Limiting Distribution and Classification. Regular Transition Probability Matrices
 Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting Distribution and Classification DTU Informatics 02407 Stochastic Processes 3, September 9 207 Today: Discrete time Markov chains - invariant
Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting Distribution and Classification DTU Informatics 02407 Stochastic Processes 3, September 9 207 Today: Discrete time Markov chains - invariant
MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II
 MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Alistair Savage Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa Winter 2015 Lecture 19 Alistair Savage (uottawa) MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Winter 2015 Lecture
MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Alistair Savage Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa Winter 2015 Lecture 19 Alistair Savage (uottawa) MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Winter 2015 Lecture
CS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #8: How PCA Works
 CS68: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #8: How PCA Works Tim Roughgarden & Gregory Valiant April 20, 206 Introduction Last lecture introduced the idea of principal components analysis (PCA). The
CS68: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #8: How PCA Works Tim Roughgarden & Gregory Valiant April 20, 206 Introduction Last lecture introduced the idea of principal components analysis (PCA). The
Perron Frobenius Theory
 Perron Frobenius Theory Oskar Perron Georg Frobenius (1880 1975) (1849 1917) Stefan Güttel Perron Frobenius Theory 1 / 10 Positive and Nonnegative Matrices Let A, B R m n. A B if a ij b ij i, j, A > B
Perron Frobenius Theory Oskar Perron Georg Frobenius (1880 1975) (1849 1917) Stefan Güttel Perron Frobenius Theory 1 / 10 Positive and Nonnegative Matrices Let A, B R m n. A B if a ij b ij i, j, A > B
Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm Anthony Trubiano April 11th, 2018 1 Introduction Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are a class of algorithms for sampling from a probability
Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm Anthony Trubiano April 11th, 2018 1 Introduction Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are a class of algorithms for sampling from a probability
COMPSCI 514: Algorithms for Data Science
 COMPSCI 514: Algorithms for Data Science Arya Mazumdar University of Massachusetts at Amherst Fall 2018 Lecture 4 Markov Chain & Pagerank Homework Announcement Show your work in the homework Write the
COMPSCI 514: Algorithms for Data Science Arya Mazumdar University of Massachusetts at Amherst Fall 2018 Lecture 4 Markov Chain & Pagerank Homework Announcement Show your work in the homework Write the
Math 304 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks.
 Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
(implicitly assuming time-homogeneity from here on)
 Continuous-Time Markov Chains Models Tuesday, November 15, 2011 2:02 PM The fundamental object describing the dynamics of a CTMC (continuous-time Markov chain) is the probability transition (matrix) function:
Continuous-Time Markov Chains Models Tuesday, November 15, 2011 2:02 PM The fundamental object describing the dynamics of a CTMC (continuous-time Markov chain) is the probability transition (matrix) function:
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
INVARIANTS OF TWIST-WISE FLOW EQUIVALENCE
 ELECTRONIC RESEARCH ANNOUNCEMENTS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 3, Pages 126 130 (December 17, 1997) S 1079-6762(97)00037-1 INVARIANTS OF TWIST-WISE FLOW EQUIVALENCE MICHAEL C. SULLIVAN (Communicated
ELECTRONIC RESEARCH ANNOUNCEMENTS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 3, Pages 126 130 (December 17, 1997) S 1079-6762(97)00037-1 INVARIANTS OF TWIST-WISE FLOW EQUIVALENCE MICHAEL C. SULLIVAN (Communicated
Announcements Monday, November 13
 Announcements Monday, November 13 The third midterm is on this Friday, November 17. The exam covers 3.1, 3.2, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 5.5. About half the problems will be conceptual, and the other half computational.
Announcements Monday, November 13 The third midterm is on this Friday, November 17. The exam covers 3.1, 3.2, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 5.5. About half the problems will be conceptual, and the other half computational.
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Daily Update. Math 290: Elementary Linear Algebra Fall 2018
 Daily Update Math 90: Elementary Linear Algebra Fall 08 Lecture 7: Tuesday, December 4 After reviewing the definitions of a linear transformation, and the kernel and range of a linear transformation, we
Daily Update Math 90: Elementary Linear Algebra Fall 08 Lecture 7: Tuesday, December 4 After reviewing the definitions of a linear transformation, and the kernel and range of a linear transformation, we
Probability & Computing
 Probability & Computing Stochastic Process time t {X t t 2 T } state space Ω X t 2 state x 2 discrete time: T is countable T = {0,, 2,...} discrete space: Ω is finite or countably infinite X 0,X,X 2,...
Probability & Computing Stochastic Process time t {X t t 2 T } state space Ω X t 2 state x 2 discrete time: T is countable T = {0,, 2,...} discrete space: Ω is finite or countably infinite X 0,X,X 2,...
Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search
 CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
On the mathematical background of Google PageRank algorithm
 Working Paper Series Department of Economics University of Verona On the mathematical background of Google PageRank algorithm Alberto Peretti, Alberto Roveda WP Number: 25 December 2014 ISSN: 2036-2919
Working Paper Series Department of Economics University of Verona On the mathematical background of Google PageRank algorithm Alberto Peretti, Alberto Roveda WP Number: 25 December 2014 ISSN: 2036-2919
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3. A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process.
 Renewal Processes Wednesday, December 16, 2015 1:02 PM Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3 A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process. The Poisson point process is completely
Renewal Processes Wednesday, December 16, 2015 1:02 PM Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3 A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process. The Poisson point process is completely
Stochastic2010 Page 1
 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, April 02, 2010 2:03 PM Long-time properties for branching processes Clearly state 0 is an absorbing state, forming its own recurrent
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, April 02, 2010 2:03 PM Long-time properties for branching processes Clearly state 0 is an absorbing state, forming its own recurrent
Announcements Wednesday, November 01
 Announcements Wednesday, November 01 WeBWorK 3.1, 3.2 are due today at 11:59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 3.1, 3.2. My office is Skiles 244. Rabinoffice hours are Monday, 1 3pm and Tuesday, 9 11am. Section
Announcements Wednesday, November 01 WeBWorK 3.1, 3.2 are due today at 11:59pm. The quiz on Friday covers 3.1, 3.2. My office is Skiles 244. Rabinoffice hours are Monday, 1 3pm and Tuesday, 9 11am. Section
Detailed Proof of The PerronFrobenius Theorem
 Detailed Proof of The PerronFrobenius Theorem Arseny M Shur Ural Federal University October 30, 2016 1 Introduction This famous theorem has numerous applications, but to apply it you should understand
Detailed Proof of The PerronFrobenius Theorem Arseny M Shur Ural Federal University October 30, 2016 1 Introduction This famous theorem has numerous applications, but to apply it you should understand
Majorizations for the Eigenvectors of Graph-Adjacency Matrices: A Tool for Complex Network Design
 Majorizations for the Eigenvectors of Graph-Adjacency Matrices: A Tool for Complex Network Design Rahul Dhal Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Pullman, WA rdhal@eecs.wsu.edu
Majorizations for the Eigenvectors of Graph-Adjacency Matrices: A Tool for Complex Network Design Rahul Dhal Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Pullman, WA rdhal@eecs.wsu.edu
Today. Next lecture. (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models
 Today (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models Graphical representation Transition probability matrix Propagating state distributions The stationary distribution Next lecture (Ch 14) Markov chains
Today (Ch 14) Markov chains and hidden Markov models Graphical representation Transition probability matrix Propagating state distributions The stationary distribution Next lecture (Ch 14) Markov chains
Stochastic processes. MAS275 Probability Modelling. Introduction and Markov chains. Continuous time. Markov property
 Chapter 1: and Markov chains Stochastic processes We study stochastic processes, which are families of random variables describing the evolution of a quantity with time. In some situations, we can treat
Chapter 1: and Markov chains Stochastic processes We study stochastic processes, which are families of random variables describing the evolution of a quantity with time. In some situations, we can treat
Markov Chains, Stochastic Processes, and Matrix Decompositions
 Markov Chains, Stochastic Processes, and Matrix Decompositions 5 May 2014 Outline 1 Markov Chains Outline 1 Markov Chains 2 Introduction Perron-Frobenius Matrix Decompositions and Markov Chains Spectral
Markov Chains, Stochastic Processes, and Matrix Decompositions 5 May 2014 Outline 1 Markov Chains Outline 1 Markov Chains 2 Introduction Perron-Frobenius Matrix Decompositions and Markov Chains Spectral
