Stochastic2010 Page 1
|
|
|
- Darleen Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, April 02, :03 PM Long-time properties for branching processes Clearly state 0 is an absorbing state, forming its own recurrent class. The other states in the state space will generically be in a communication class except for unusual choices of offspring distribution (i.e., only even numbers of offspring). In any case, the states 1,2, are all transient since they have one-way communication with the absorbing state 0. This implies in particular that it isn't sensible to talk about stationary distributions -- what will happen, in any realization, is either the branching process will go extinct or will increase indefinitely. This suggests the following questions are relevant for branching processes, for each choice of offspring probability distribution What is the probability to go extinct (rather than to grow indefinitely)? How long does it take to go extinct when the branching process does go extinct? If the branching process goes extinct, how much cost/reward did the branching process incur until it went extinct? When the branching process grows indefinitely, how fast does it grow? These questions find particular application in, for example epidemiology or technology markets. We'll address the first question in detail; the second and third can be attacked by similar methods. The fourth is trickier. Consider the extinction probability, which is same notion as an absorption probability: The special structure of the branching process, namely the independence of each agent, means that:
2 Stochastic2010 Page 2 But each agent has equivalent stochastic rules for its descendants so each of these factors is just the probability for a given single agent to go extinct, namely a(1). Use first-step analysis just as we did for general absorption probability calculation but now exploit special branching process structure. (partition on the state of the Markov chain at epoch 1)
3 Stochastic2010 Page 3 So the extinction probability must satisfy the equation: Does this equation have unique solution, and if not, which solution is the right one? Let's take care of some special cases first: But on the other hand, if This implies that one of the two following graphical possibilities apply:
4 Stochastic2010 Page 4 We see that the possible solutions to are: a=1 (always a solution) nontrivial solution 0<a<1 when One can show (see the references) that when the nontrivial solution exists, it is the correct value for the extinction probability. Notice that this all says the following: When the mean number of offspring per agent is less than one, the population is guaranteed to go extinct. When the mean number of offspring per agent is greater than or equal to one, the population has some nonnegative probability to go extinct, which can be computed by the solution to a nonlinear equation Continuous-time Markov chains References: Lawler Ch. 3, Karlin & Taylor Ch. 4 We now consider how to modify our modeling and analysis when the transitions in state are allowed to happen at moments along a continuous time (parameter) domain rather than at discrete epochs. But state space is still discrete (possibly countably infinite).
5 Stochastic2010 Page 5 state space is still discrete (possibly countably infinite). The realizations of a CTMC will be piecewise constant, with the transition times being random and continuously distributed, and the transitions also being random. By convention, the realizations of a CTMC are taken to be right-continuous (cadlag process). Markov property in continuous time: Notions are easier to work with these finite-time representations of the past; if process is nice (cadlag is enough) then can approximate a complete history with a sufficiently fine finite mesh of points -- passing to the limit involves some measure-theoretic technicalities (see filtrations). Just as for discrete-time Markov chains, many powerful formulas become available if we consider (as we will) time-homogenous CTMC In what situations are CTMC used more modeling? First of all, why would one use a CTMC rather than a DTMC? The reason one should ask this is that for any given CTMC X(t), one can construct some associated DTMC: X n = X(n t) Also we can construct the embedded DTMC : (need strong Markov property which says that Markov property (formulated for deterministic times) carries over to randomly chosen times, provided those random times are Markov times, meaning that they are determined only by information available and up to including the actual time.
6 Stochastic2010 Page 6 So why would a CTMC model be any better than these associated DTMC? one may have a large number of states,some of which are visited sometimes very briefly, and the DTMC obtained from regular time observations may miss it. The embedded DTMC misses timing information; if you augment the embedded DTMC with time spent in each state,then equivalent to a CTMC. CTMC are sometimes good spatial discretizations of continuous-space processes. Simulating a CTMC can actually be easier than simulating a DTMC with regular time steps. Often times in physics and engineering contexts, CTMC models are easier to formulate because it describes instantaneous changes, which can generally be linearly superposed. But finite-time effects generally do not linearly superpose. This explains the kinds of contexts in which one sees CTMCs often used: statistical modeling in atomic and quantum physics chemical reaction networks and biomolecular reaction networks dynamics on more general networks (disease spread on sexual or social networks)
7 Stochastic2010 Page 7
Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, November 11, 2011 2:05 PM Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, November 11, 2011 2:05 PM Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29.
 Classification of Birth-Death Chains Tuesday, November 08, 2011 2:02 PM Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29. Continuing with our classification of birth-death chains on nonnegative integers. Last
Classification of Birth-Death Chains Tuesday, November 08, 2011 2:02 PM Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29. Continuing with our classification of birth-death chains on nonnegative integers. Last
Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline).
 Large-Time Behavior for Continuous-Time Markov Chains Friday, December 02, 2011 10:58 AM Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline). How are formulas for large-time behavior of discrete-time
Large-Time Behavior for Continuous-Time Markov Chains Friday, December 02, 2011 10:58 AM Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline). How are formulas for large-time behavior of discrete-time
Finite-Horizon Statistics for Markov chains
 Analyzing FSDT Markov chains Friday, September 30, 2011 2:03 PM Simulating FSDT Markov chains, as we have said is very straightforward, either by using probability transition matrix or stochastic update
Analyzing FSDT Markov chains Friday, September 30, 2011 2:03 PM Simulating FSDT Markov chains, as we have said is very straightforward, either by using probability transition matrix or stochastic update
The cost/reward formula has two specific widely used applications:
 Applications of Absorption Probability and Accumulated Cost/Reward Formulas for FDMC Friday, October 21, 2011 2:28 PM No class next week. No office hours either. Next class will be 11/01. The cost/reward
Applications of Absorption Probability and Accumulated Cost/Reward Formulas for FDMC Friday, October 21, 2011 2:28 PM No class next week. No office hours either. Next class will be 11/01. The cost/reward
Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, :12 PM
 stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
Birth-death chain models (countable state)
 Countable State Birth-Death Chains and Branching Processes Tuesday, March 25, 2014 1:59 PM Homework 3 posted, due Friday, April 18. Birth-death chain models (countable state) S = We'll characterize the
Countable State Birth-Death Chains and Branching Processes Tuesday, March 25, 2014 1:59 PM Homework 3 posted, due Friday, April 18. Birth-death chain models (countable state) S = We'll characterize the
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains
 Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
This is now an algebraic equation that can be solved simply:
 Simulation of CTMC Monday, November 23, 2015 1:55 PM Homework 4 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, December 11 at 5 PM. Let's solve the Kolmogorov forward equation for the Poisson counting
Simulation of CTMC Monday, November 23, 2015 1:55 PM Homework 4 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, December 11 at 5 PM. Let's solve the Kolmogorov forward equation for the Poisson counting
Classification of Countable State Markov Chains
 Classification of Countable State Markov Chains Friday, March 21, 2014 2:01 PM How can we determine whether a communication class in a countable state Markov chain is: transient null recurrent positive
Classification of Countable State Markov Chains Friday, March 21, 2014 2:01 PM How can we determine whether a communication class in a countable state Markov chain is: transient null recurrent positive
Transience: Whereas a finite closed communication class must be recurrent, an infinite closed communication class can be transient:
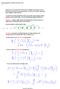 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
At the boundary states, we take the same rules except we forbid leaving the state space, so,.
 Birth-death chains Monday, October 19, 2015 2:22 PM Example: Birth-Death Chain State space From any state we allow the following transitions: with probability (birth) with probability (death) with probability
Birth-death chains Monday, October 19, 2015 2:22 PM Example: Birth-Death Chain State space From any state we allow the following transitions: with probability (birth) with probability (death) with probability
FDST Markov Chain Models
 FDST Markov Chain Models Tuesday, February 11, 2014 2:01 PM Homework 1 due Friday, February 21 at 2 PM. Reading: Karlin and Taylor, Sections 2.1-2.3 Almost all of our Markov chain models will be time-homogenous,
FDST Markov Chain Models Tuesday, February 11, 2014 2:01 PM Homework 1 due Friday, February 21 at 2 PM. Reading: Karlin and Taylor, Sections 2.1-2.3 Almost all of our Markov chain models will be time-homogenous,
2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains
 2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains Angela Peace Biomathematics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology. CRC Press,
2 Discrete-Time Markov Chains Angela Peace Biomathematics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology. CRC Press,
Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, :04 PM
 stochnotes102008 Page 1 Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, 2008 12:04 PM Looking for a detailed balance solution for a stationary distribution is a useful technique. Stationary
stochnotes102008 Page 1 Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, 2008 12:04 PM Looking for a detailed balance solution for a stationary distribution is a useful technique. Stationary
2. Transience and Recurrence
 Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Outlines. Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC)
 Markov Chains (2) Outlines Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC) 2 pj ( n) denotes the pmf of the random variable p ( n) P( X j) j We will only be concerned with homogenous
Markov Chains (2) Outlines Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) Continuous Time Markov Chain (CTMC) 2 pj ( n) denotes the pmf of the random variable p ( n) P( X j) j We will only be concerned with homogenous
Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread
 Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread Julien Arino Centre for Research on Inner City Health St Michael s Hospital Toronto On leave from Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba Julien Arino@umanitoba.ca
Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread Julien Arino Centre for Research on Inner City Health St Michael s Hospital Toronto On leave from Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba Julien Arino@umanitoba.ca
IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt. Introduction to Markov Chains
 IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt Introduction to Markov Chains 1. Markov Mouse: The Closed Maze We start by considering how to model a mouse moving around in a maze. The maze is a closed space containing nine
IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt Introduction to Markov Chains 1. Markov Mouse: The Closed Maze We start by considering how to model a mouse moving around in a maze. The maze is a closed space containing nine
Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread
 Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread Julien Arino Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba Winnipeg Julien Arino@umanitoba.ca 19 May 2012 1 Introduction 2 Stochastic processes 3 The SIS model
Stochastic modelling of epidemic spread Julien Arino Department of Mathematics University of Manitoba Winnipeg Julien Arino@umanitoba.ca 19 May 2012 1 Introduction 2 Stochastic processes 3 The SIS model
Let's contemplate a continuous-time limit of the Bernoulli process:
 Mathematical Foundations of Markov Chains Thursday, September 17, 2015 2:04 PM Reading: Lawler Ch. 1 Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM. Office hours today are moved to 6-7 PM. Let's revisit the
Mathematical Foundations of Markov Chains Thursday, September 17, 2015 2:04 PM Reading: Lawler Ch. 1 Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM. Office hours today are moved to 6-7 PM. Let's revisit the
So in terms of conditional probability densities, we have by differentiating this relationship:
 Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
MARKOV PROCESSES. Valerio Di Valerio
 MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
(b) What is the variance of the time until the second customer arrives, starting empty, assuming that we measure time in minutes?
 IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1.
 Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
 Formulation of Finite State Markov Chains Friday, September 23, 2011 2:04 PM Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
Formulation of Finite State Markov Chains Friday, September 23, 2011 2:04 PM Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30.
 Random Variables Friday, September 09, 2011 2:02 PM I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30. No class or office hours next week. Next class is on Tuesday, September
Random Variables Friday, September 09, 2011 2:02 PM I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30. No class or office hours next week. Next class is on Tuesday, September
(implicitly assuming time-homogeneity from here on)
 Continuous-Time Markov Chains Models Tuesday, November 15, 2011 2:02 PM The fundamental object describing the dynamics of a CTMC (continuous-time Markov chain) is the probability transition (matrix) function:
Continuous-Time Markov Chains Models Tuesday, November 15, 2011 2:02 PM The fundamental object describing the dynamics of a CTMC (continuous-time Markov chain) is the probability transition (matrix) function:
Markov Model. Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states
 Markov Model Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states (applicable to repairable, as well as non-repairable systems) System behavior
Markov Model Model representing the different resident states of a system, and the transitions between the different states (applicable to repairable, as well as non-repairable systems) System behavior
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 2
 MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 2 2. Countable Markov Chains I started Chapter 2 which talks about Markov chains with a countably infinite number of states. I did my favorite example which is on
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 2 2. Countable Markov Chains I started Chapter 2 which talks about Markov chains with a countably infinite number of states. I did my favorite example which is on
STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions
 J. Virtamo 38.3143 Queueing Theory / Stochastic processes 1 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions Often the systems we consider evolve in time and we are interested in their dynamic behaviour, usually involving
J. Virtamo 38.3143 Queueing Theory / Stochastic processes 1 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Basic notions Often the systems we consider evolve in time and we are interested in their dynamic behaviour, usually involving
Convergence of Feller Processes
 Chapter 15 Convergence of Feller Processes This chapter looks at the convergence of sequences of Feller processes to a iting process. Section 15.1 lays some ground work concerning weak convergence of processes
Chapter 15 Convergence of Feller Processes This chapter looks at the convergence of sequences of Feller processes to a iting process. Section 15.1 lays some ground work concerning weak convergence of processes
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains
 Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee
 Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee Overview Markov Property Markov Chains Definition Stationary Property Paths in Markov Chains Classification of States Steady States in MCs. 2 Markov Property A discrete
Markov Processes Hamid R. Rabiee Overview Markov Property Markov Chains Definition Stationary Property Paths in Markov Chains Classification of States Steady States in MCs. 2 Markov Property A discrete
Lecture 1: Brief Review on Stochastic Processes
 Lecture 1: Brief Review on Stochastic Processes A stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X t (s) : t T, s S}, where T is some index set and S is the common sample space of the random variables.
Lecture 1: Brief Review on Stochastic Processes A stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X t (s) : t T, s S}, where T is some index set and S is the common sample space of the random variables.
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations
 Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains. Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321
 Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321 Discrete-time random processes A sequence of RVs indexed by a variable n 2 {0, 1, 2,...} forms a discretetime random process
Lecture 11: Introduction to Markov Chains Copyright G. Caire (Sample Lectures) 321 Discrete-time random processes A sequence of RVs indexed by a variable n 2 {0, 1, 2,...} forms a discretetime random process
MATH 56A SPRING 2008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 65
 MATH 56A SPRING 2008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 65 2.2.5. proof of extinction lemma. The proof of Lemma 2.3 is just like the proof of the lemma I did on Wednesday. It goes like this. Suppose that â is the smallest
MATH 56A SPRING 2008 STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 65 2.2.5. proof of extinction lemma. The proof of Lemma 2.3 is just like the proof of the lemma I did on Wednesday. It goes like this. Suppose that â is the smallest
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 2003, Professor Whitt. Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18.
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
The SIS and SIR stochastic epidemic models revisited
 The SIS and SIR stochastic epidemic models revisited Jesús Artalejo Faculty of Mathematics, University Complutense of Madrid Madrid, Spain jesus_artalejomat.ucm.es BCAM Talk, June 16, 2011 Talk Schedule
The SIS and SIR stochastic epidemic models revisited Jesús Artalejo Faculty of Mathematics, University Complutense of Madrid Madrid, Spain jesus_artalejomat.ucm.es BCAM Talk, June 16, 2011 Talk Schedule
Statistics 150: Spring 2007
 Statistics 150: Spring 2007 April 23, 2008 0-1 1 Limiting Probabilities If the discrete-time Markov chain with transition probabilities p ij is irreducible and positive recurrent; then the limiting probabilities
Statistics 150: Spring 2007 April 23, 2008 0-1 1 Limiting Probabilities If the discrete-time Markov chain with transition probabilities p ij is irreducible and positive recurrent; then the limiting probabilities
Let (Ω, F) be a measureable space. A filtration in discrete time is a sequence of. F s F t
 2.2 Filtrations Let (Ω, F) be a measureable space. A filtration in discrete time is a sequence of σ algebras {F t } such that F t F and F t F t+1 for all t = 0, 1,.... In continuous time, the second condition
2.2 Filtrations Let (Ω, F) be a measureable space. A filtration in discrete time is a sequence of σ algebras {F t } such that F t F and F t F t+1 for all t = 0, 1,.... In continuous time, the second condition
Probability Distributions
 Lecture 1: Background in Probability Theory Probability Distributions The probability mass function (pmf) or probability density functions (pdf), mean, µ, variance, σ 2, and moment generating function
Lecture 1: Background in Probability Theory Probability Distributions The probability mass function (pmf) or probability density functions (pdf), mean, µ, variance, σ 2, and moment generating function
Lecture 20 : Markov Chains
 CSCI 3560 Probability and Computing Instructor: Bogdan Chlebus Lecture 0 : Markov Chains We consider stochastic processes. A process represents a system that evolves through incremental changes called
CSCI 3560 Probability and Computing Instructor: Bogdan Chlebus Lecture 0 : Markov Chains We consider stochastic processes. A process represents a system that evolves through incremental changes called
88 CONTINUOUS MARKOV CHAINS
 88 CONTINUOUS MARKOV CHAINS 3.4. birth-death. Continuous birth-death Markov chains are very similar to countable Markov chains. One new concept is explosion which means that an infinite number of state
88 CONTINUOUS MARKOV CHAINS 3.4. birth-death. Continuous birth-death Markov chains are very similar to countable Markov chains. One new concept is explosion which means that an infinite number of state
Markov chains. Randomness and Computation. Markov chains. Markov processes
 Markov chains Randomness and Computation or, Randomized Algorithms Mary Cryan School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Definition (Definition 7) A discrete-time stochastic process on the state space
Markov chains Randomness and Computation or, Randomized Algorithms Mary Cryan School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Definition (Definition 7) A discrete-time stochastic process on the state space
1 Stochastic Dynamic Programming
 1 Stochastic Dynamic Programming Formally, a stochastic dynamic program has the same components as a deterministic one; the only modification is to the state transition equation. When events in the future
1 Stochastic Dynamic Programming Formally, a stochastic dynamic program has the same components as a deterministic one; the only modification is to the state transition equation. When events in the future
Let's transfer our results for conditional probability for events into conditional probabilities for random variables.
 Kolmogorov/Smoluchowski equation approach to Brownian motion Tuesday, February 12, 2013 1:53 PM Readings: Gardiner, Secs. 1.2, 3.8.1, 3.8.2 Einstein Homework 1 due February 22. Conditional probability
Kolmogorov/Smoluchowski equation approach to Brownian motion Tuesday, February 12, 2013 1:53 PM Readings: Gardiner, Secs. 1.2, 3.8.1, 3.8.2 Einstein Homework 1 due February 22. Conditional probability
Availability. M(t) = 1 - e -mt
 Availability Availability - A(t) the probability that the system is operating correctly and is available to perform its functions at the instant of time t More general concept than reliability: failure
Availability Availability - A(t) the probability that the system is operating correctly and is available to perform its functions at the instant of time t More general concept than reliability: failure
Stability of the two queue system
 Stability of the two queue system Iain M. MacPhee and Lisa J. Müller University of Durham Department of Mathematical Science Durham, DH1 3LE, UK (e-mail: i.m.macphee@durham.ac.uk, l.j.muller@durham.ac.uk)
Stability of the two queue system Iain M. MacPhee and Lisa J. Müller University of Durham Department of Mathematical Science Durham, DH1 3LE, UK (e-mail: i.m.macphee@durham.ac.uk, l.j.muller@durham.ac.uk)
Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3. A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process.
 Renewal Processes Wednesday, December 16, 2015 1:02 PM Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3 A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process. The Poisson point process is completely
Renewal Processes Wednesday, December 16, 2015 1:02 PM Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3 A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process. The Poisson point process is completely
IEOR 4106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Spring 2011, Professor Whitt Class Lecture Notes: Tuesday, March 1.
 IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Spring, Professor Whitt Class Lecture Notes: Tuesday, March. Continuous-Time Markov Chains, Ross Chapter 6 Problems for Discussion and Solutions.
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Spring, Professor Whitt Class Lecture Notes: Tuesday, March. Continuous-Time Markov Chains, Ross Chapter 6 Problems for Discussion and Solutions.
1 Types of stochastic models
 1 Types of stochastic models Models so far discussed are all deterministic, meaning that, if the present state were perfectly known, it would be possible to predict exactly all future states. We have seen
1 Types of stochastic models Models so far discussed are all deterministic, meaning that, if the present state were perfectly known, it would be possible to predict exactly all future states. We have seen
Irreducibility. Irreducible. every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that. Absorbing state: p jj =1
 Irreducibility Irreducible every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that i,j are communicate, if the above condition is valid Irreducible: all states are communicate
Irreducibility Irreducible every state can be reached from every other state For any i,j, exist an m 0, such that i,j are communicate, if the above condition is valid Irreducible: all states are communicate
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER 1
 MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER. Finite Markov chains For the sake of completeness of these notes I decided to write a summary of the basic concepts of finite Markov chains. The topics in this chapter
MATH 56A: STOCHASTIC PROCESSES CHAPTER. Finite Markov chains For the sake of completeness of these notes I decided to write a summary of the basic concepts of finite Markov chains. The topics in this chapter
Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor, Sec. 2.3)
 stochnotes091108 Page 1 Markov Chain Models and Basic Computations Thursday, September 11, 2008 11:50 AM Homework 1 is posted, due Monday, September 22. Two more examples. Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor,
stochnotes091108 Page 1 Markov Chain Models and Basic Computations Thursday, September 11, 2008 11:50 AM Homework 1 is posted, due Monday, September 22. Two more examples. Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor,
Probability Distributions
 Lecture : Background in Probability Theory Probability Distributions The probability mass function (pmf) or probability density functions (pdf), mean, µ, variance, σ 2, and moment generating function (mgf)
Lecture : Background in Probability Theory Probability Distributions The probability mass function (pmf) or probability density functions (pdf), mean, µ, variance, σ 2, and moment generating function (mgf)
Stochastic Models: Markov Chains and their Generalizations
 Scuola di Dottorato in Scienza ed Alta Tecnologia Dottorato in Informatica Universita di Torino Stochastic Models: Markov Chains and their Generalizations Gianfranco Balbo e Andras Horvath Outline Introduction
Scuola di Dottorato in Scienza ed Alta Tecnologia Dottorato in Informatica Universita di Torino Stochastic Models: Markov Chains and their Generalizations Gianfranco Balbo e Andras Horvath Outline Introduction
Markov Chains (Part 3)
 Markov Chains (Part 3) State Classification Markov Chains - State Classification Accessibility State j is accessible from state i if p ij (n) > for some n>=, meaning that starting at state i, there is
Markov Chains (Part 3) State Classification Markov Chains - State Classification Accessibility State j is accessible from state i if p ij (n) > for some n>=, meaning that starting at state i, there is
Lecture 5. If we interpret the index n 0 as time, then a Markov chain simply requires that the future depends only on the present and not on the past.
 1 Markov chain: definition Lecture 5 Definition 1.1 Markov chain] A sequence of random variables (X n ) n 0 taking values in a measurable state space (S, S) is called a (discrete time) Markov chain, if
1 Markov chain: definition Lecture 5 Definition 1.1 Markov chain] A sequence of random variables (X n ) n 0 taking values in a measurable state space (S, S) is called a (discrete time) Markov chain, if
Chapter 2 SOME ANALYTICAL TOOLS USED IN THE THESIS
 Chapter 2 SOME ANALYTICAL TOOLS USED IN THE THESIS 63 2.1 Introduction In this chapter we describe the analytical tools used in this thesis. They are Markov Decision Processes(MDP), Markov Renewal process
Chapter 2 SOME ANALYTICAL TOOLS USED IN THE THESIS 63 2.1 Introduction In this chapter we describe the analytical tools used in this thesis. They are Markov Decision Processes(MDP), Markov Renewal process
Stochastic Petri Nets. Jonatan Lindén. Modelling SPN GSPN. Performance measures. Almost none of the theory. December 8, 2010
 Stochastic Almost none of the theory December 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 Introduction A Petri net (PN) is something like a generalized automata. A Stochastic Petri Net () a stochastic extension to Petri nets,
Stochastic Almost none of the theory December 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 Introduction A Petri net (PN) is something like a generalized automata. A Stochastic Petri Net () a stochastic extension to Petri nets,
Question Points Score Total: 70
 The University of British Columbia Final Examination - April 204 Mathematics 303 Dr. D. Brydges Time: 2.5 hours Last Name First Signature Student Number Special Instructions: Closed book exam, no calculators.
The University of British Columbia Final Examination - April 204 Mathematics 303 Dr. D. Brydges Time: 2.5 hours Last Name First Signature Student Number Special Instructions: Closed book exam, no calculators.
EE 550: Notes on Markov chains, Travel Times, and Opportunistic Routing
 EE 550: Notes on Markov chains, Travel Times, and Opportunistic Routing Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/ mjneely 1 Abstract This collection of notes provides a
EE 550: Notes on Markov chains, Travel Times, and Opportunistic Routing Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/ mjneely 1 Abstract This collection of notes provides a
 http://www.math.uah.edu/stat/markov/.xhtml 1 of 9 7/16/2009 7:20 AM Virtual Laboratories > 16. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. A Markov process is a random process in which the future is
http://www.math.uah.edu/stat/markov/.xhtml 1 of 9 7/16/2009 7:20 AM Virtual Laboratories > 16. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1. A Markov process is a random process in which the future is
6 Continuous-Time Birth and Death Chains
 6 Continuous-Time Birth and Death Chains Angela Peace Biomathematics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology.
6 Continuous-Time Birth and Death Chains Angela Peace Biomathematics II MATH 5355 Spring 2017 Lecture notes follow: Allen, Linda JS. An introduction to stochastic processes with applications to biology.
Discrete time Markov chains. Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting. Limiting Distribution and Classification. Regular Transition Probability Matrices
 Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting Distribution and Classification DTU Informatics 02407 Stochastic Processes 3, September 9 207 Today: Discrete time Markov chains - invariant
Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Limiting Distribution and Classification DTU Informatics 02407 Stochastic Processes 3, September 9 207 Today: Discrete time Markov chains - invariant
4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes
 Math Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes Page 1 4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes Introduction A stochastic model is one in which random effects are incorporated into the model.
Math Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes Page 1 4452 Mathematical Modeling Lecture 16: Markov Processes Introduction A stochastic model is one in which random effects are incorporated into the model.
Stochastic processes. MAS275 Probability Modelling. Introduction and Markov chains. Continuous time. Markov property
 Chapter 1: and Markov chains Stochastic processes We study stochastic processes, which are families of random variables describing the evolution of a quantity with time. In some situations, we can treat
Chapter 1: and Markov chains Stochastic processes We study stochastic processes, which are families of random variables describing the evolution of a quantity with time. In some situations, we can treat
MATH3200, Lecture 31: Applications of Eigenvectors. Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems
 Lecture 31: Some Applications of Eigenvectors: Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems Winfried Just Department of Mathematics, Ohio University April 9 11, 2018 Review: Eigenvectors and left eigenvectors
Lecture 31: Some Applications of Eigenvectors: Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems Winfried Just Department of Mathematics, Ohio University April 9 11, 2018 Review: Eigenvectors and left eigenvectors
IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman
 IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman 1. Semi-Markov processes: Consider an irreducible positive recurrent discrete-time Markov chain {X n } with transition matrix P (P i,j ), i, j S, and finite state space.
IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman 1. Semi-Markov processes: Consider an irreducible positive recurrent discrete-time Markov chain {X n } with transition matrix P (P i,j ), i, j S, and finite state space.
Markov Chains. X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2 <... < t k < t k+1. If X(t) is discrete-valued. If X(t) is continuous-valued
 Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
1 IEOR 4701: Continuous-Time Markov Chains
 Copyright c 2006 by Karl Sigman 1 IEOR 4701: Continuous-Time Markov Chains A Markov chain in discrete time, {X n : n 0}, remains in any state for exactly one unit of time before making a transition (change
Copyright c 2006 by Karl Sigman 1 IEOR 4701: Continuous-Time Markov Chains A Markov chain in discrete time, {X n : n 0}, remains in any state for exactly one unit of time before making a transition (change
Markov Chains. As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006.
 Markov Chains As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006 1 Introduction A (finite) Markov chain is a process with a finite number of states (or outcomes, or
Markov Chains As part of Interdisciplinary Mathematical Modeling, By Warren Weckesser Copyright c 2006 1 Introduction A (finite) Markov chain is a process with a finite number of states (or outcomes, or
Recap. Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains. ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks
 Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
Markov Chains CK eqns Classes Hitting times Rec./trans. Strong Markov Stat. distr. Reversibility * Markov Chains
 Markov Chains A random process X is a family {X t : t T } of random variables indexed by some set T. When T = {0, 1, 2,... } one speaks about a discrete-time process, for T = R or T = [0, ) one has a continuous-time
Markov Chains A random process X is a family {X t : t T } of random variables indexed by some set T. When T = {0, 1, 2,... } one speaks about a discrete-time process, for T = R or T = [0, ) one has a continuous-time
AARMS Homework Exercises
 1 For the gamma distribution, AARMS Homework Exercises (a) Show that the mgf is M(t) = (1 βt) α for t < 1/β (b) Use the mgf to find the mean and variance of the gamma distribution 2 A well-known inequality
1 For the gamma distribution, AARMS Homework Exercises (a) Show that the mgf is M(t) = (1 βt) α for t < 1/β (b) Use the mgf to find the mean and variance of the gamma distribution 2 A well-known inequality
Lectures on Markov Chains
 Lectures on Markov Chains David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 2016 edition 1 Contents Contents 2 1 Markov chains 4 1.1 The definition of a Markov chain.....................
Lectures on Markov Chains David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 2016 edition 1 Contents Contents 2 1 Markov chains 4 1.1 The definition of a Markov chain.....................
An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling
 F An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling Fourth Edition Mark A. Pinsky Department of Mathematics Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois Samuel Karlin Department of Mathematics Stanford University Stanford,
F An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling Fourth Edition Mark A. Pinsky Department of Mathematics Northwestern University Evanston, Illinois Samuel Karlin Department of Mathematics Stanford University Stanford,
MS&E 321 Spring Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10
 MS&E 321 Spring 12-13 Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10 Section 3: Regenerative Processes Contents 3.1 Regeneration: The Basic Idea............................... 1 3.2
MS&E 321 Spring 12-13 Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10 Section 3: Regenerative Processes Contents 3.1 Regeneration: The Basic Idea............................... 1 3.2
Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM.
 Stationary Distributions: Application Monday, October 05, 2015 2:04 PM Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM. To prepare to describe the conditions under which the
Stationary Distributions: Application Monday, October 05, 2015 2:04 PM Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM. To prepare to describe the conditions under which the
LECTURE 10: REVIEW OF POWER SERIES. 1. Motivation
 LECTURE 10: REVIEW OF POWER SERIES By definition, a power series centered at x 0 is a series of the form where a 0, a 1,... and x 0 are constants. For convenience, we shall mostly be concerned with the
LECTURE 10: REVIEW OF POWER SERIES By definition, a power series centered at x 0 is a series of the form where a 0, a 1,... and x 0 are constants. For convenience, we shall mostly be concerned with the
Modelling Complex Queuing Situations with Markov Processes
 Modelling Complex Queuing Situations with Markov Processes Jason Randal Thorne, School of IT, Charles Sturt Uni, NSW 2795, Australia Abstract This article comments upon some new developments in the field
Modelling Complex Queuing Situations with Markov Processes Jason Randal Thorne, School of IT, Charles Sturt Uni, NSW 2795, Australia Abstract This article comments upon some new developments in the field
Lecturer: Olga Galinina
 Renewal models Lecturer: Olga Galinina E-mail: olga.galinina@tut.fi Outline Reminder. Exponential models definition of renewal processes exponential interval distribution Erlang distribution hyperexponential
Renewal models Lecturer: Olga Galinina E-mail: olga.galinina@tut.fi Outline Reminder. Exponential models definition of renewal processes exponential interval distribution Erlang distribution hyperexponential
Data analysis and stochastic modeling
 Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
STA 624 Practice Exam 2 Applied Stochastic Processes Spring, 2008
 Name STA 624 Practice Exam 2 Applied Stochastic Processes Spring, 2008 There are five questions on this test. DO use calculators if you need them. And then a miracle occurs is not a valid answer. There
Name STA 624 Practice Exam 2 Applied Stochastic Processes Spring, 2008 There are five questions on this test. DO use calculators if you need them. And then a miracle occurs is not a valid answer. There
Math Homework 5 Solutions
 Math 45 - Homework 5 Solutions. Exercise.3., textbook. The stochastic matrix for the gambler problem has the following form, where the states are ordered as (,, 4, 6, 8, ): P = The corresponding diagram
Math 45 - Homework 5 Solutions. Exercise.3., textbook. The stochastic matrix for the gambler problem has the following form, where the states are ordered as (,, 4, 6, 8, ): P = The corresponding diagram
Basic Probability space, sample space concepts and order of a Stochastic Process
 The Lecture Contains: Basic Introduction Basic Probability space, sample space concepts and order of a Stochastic Process Examples Definition of Stochastic Process Marginal Distributions Moments Gaussian
The Lecture Contains: Basic Introduction Basic Probability space, sample space concepts and order of a Stochastic Process Examples Definition of Stochastic Process Marginal Distributions Moments Gaussian
Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains. Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan
 Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Continuous-Time Markov Chains Consider a continuous-time stochastic process
Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Continuous-Time Markov Chains Consider a continuous-time stochastic process
Markov decision processes and interval Markov chains: exploiting the connection
 Markov decision processes and interval Markov chains: exploiting the connection Mingmei Teo Supervisors: Prof. Nigel Bean, Dr Joshua Ross University of Adelaide July 10, 2013 Intervals and interval arithmetic
Markov decision processes and interval Markov chains: exploiting the connection Mingmei Teo Supervisors: Prof. Nigel Bean, Dr Joshua Ross University of Adelaide July 10, 2013 Intervals and interval arithmetic
LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION MATRIX OF A CONDENSED FIBONACCI TREE
 International Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 31 No. 18, 41-49 ISSN: 1311-178 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-86 (on-line version) doi: http://dx.doi.org/1.173/ijam.v31i.6 LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION
International Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 31 No. 18, 41-49 ISSN: 1311-178 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-86 (on-line version) doi: http://dx.doi.org/1.173/ijam.v31i.6 LIMITING PROBABILITY TRANSITION
LECTURE NOTES: Discrete time Markov Chains (2/24/03; SG)
 LECTURE NOTES: Discrete time Markov Chains (2/24/03; SG) A discrete time Markov Chains is a stochastic dynamical system in which the probability of arriving in a particular state at a particular time moment
LECTURE NOTES: Discrete time Markov Chains (2/24/03; SG) A discrete time Markov Chains is a stochastic dynamical system in which the probability of arriving in a particular state at a particular time moment
Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models. Winter Midterm Exam Monday, Feb 10, 2014
 Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models Winter 2014 - Midterm Exam Monday, Feb 10, 2014 Student Name (print): (a) Do not sit directly next to another student. (b) This is a closed-book, closed-note
Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models Winter 2014 - Midterm Exam Monday, Feb 10, 2014 Student Name (print): (a) Do not sit directly next to another student. (b) This is a closed-book, closed-note
Matrix analytic methods. Lecture 1: Structured Markov chains and their stationary distribution
 1/29 Matrix analytic methods Lecture 1: Structured Markov chains and their stationary distribution Sophie Hautphenne and David Stanford (with thanks to Guy Latouche, U. Brussels and Peter Taylor, U. Melbourne
1/29 Matrix analytic methods Lecture 1: Structured Markov chains and their stationary distribution Sophie Hautphenne and David Stanford (with thanks to Guy Latouche, U. Brussels and Peter Taylor, U. Melbourne
Basic Definitions: Indexed Collections and Random Functions
 Chapter 1 Basic Definitions: Indexed Collections and Random Functions Section 1.1 introduces stochastic processes as indexed collections of random variables. Section 1.2 builds the necessary machinery
Chapter 1 Basic Definitions: Indexed Collections and Random Functions Section 1.1 introduces stochastic processes as indexed collections of random variables. Section 1.2 builds the necessary machinery
Positive and null recurrent-branching Process
 December 15, 2011 In last discussion we studied the transience and recurrence of Markov chains There are 2 other closely related issues about Markov chains that we address Is there an invariant distribution?
December 15, 2011 In last discussion we studied the transience and recurrence of Markov chains There are 2 other closely related issues about Markov chains that we address Is there an invariant distribution?
MS&E 321 Spring Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10. x n+1 = f(x n ),
 MS&E 321 Spring 12-13 Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10 Section 4: Steady-State Theory Contents 4.1 The Concept of Stochastic Equilibrium.......................... 1 4.2
MS&E 321 Spring 12-13 Stochastic Systems June 1, 2013 Prof. Peter W. Glynn Page 1 of 10 Section 4: Steady-State Theory Contents 4.1 The Concept of Stochastic Equilibrium.......................... 1 4.2
ECE-517: Reinforcement Learning in Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 4: Discrete-Time Markov Chains
 ECE-517: Reinforcement Learning in Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4: Discrete-Time Markov Chains September 1, 215 Dr. Itamar Arel College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer
ECE-517: Reinforcement Learning in Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4: Discrete-Time Markov Chains September 1, 215 Dr. Itamar Arel College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer
Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC)
 Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) John Boccio February 3, 204 Sources Taylor & Karlin, An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling, 3rd edition. Chapters 3-4. Ross, Introduction to Probability Models, 8th edition,
Discrete Time Markov Chain (DTMC) John Boccio February 3, 204 Sources Taylor & Karlin, An Introduction to Stochastic Modeling, 3rd edition. Chapters 3-4. Ross, Introduction to Probability Models, 8th edition,
Discrete time Markov chains. Discrete Time Markov Chains, Definition and classification. Probability axioms and first results
 Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Definition and classification 1 1 Applied Mathematics and Computer Science 02407 Stochastic Processes 1, September 5 2017 Today: Short recap of
Discrete time Markov chains Discrete Time Markov Chains, Definition and classification 1 1 Applied Mathematics and Computer Science 02407 Stochastic Processes 1, September 5 2017 Today: Short recap of
