Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3. A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process.
|
|
|
- Claud Stone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Renewal Processes Wednesday, December 16, :02 PM Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3 A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process. The Poisson point process is completely memoryless, and so the probability distribution for the time between incidents is exponentially distributed with some specified mean. A renewal process is memoryless in a more restricted sense: the length of the time intervals between successive incidents are independent, i.e., but need not be exponential. The counting process associated with a renewal process (i.e., is the number of incidents that happen up to time ) need not be a continuous-time Markov chain, as it was for the Poisson point process. That is, we do not lose memory between incidents, only at the moments when incidents happen. Normally we also take the inter-incident times to be iid. delayed renewal process is a variation where the time to first incident may have a different probability distribution than the other. Applications of renewal processes: equipment replacement with nonconstant hazard rate = rate of failure at time given survival up to time the time between spikes (action potentials) sent by a neuron broadly define renewal processes as the times at which a continuous-time Markov chain visits some subset of states. a spatial version of renewal process for car following Just as renewal processes generalize Poisson point process to require the memoryless property to hold only when an incident happens, one can generalize continuous-time Markov chains so they lose memory (other than current state) only when a transition happens. This relaxes the requirement that the time spent in a state is exponentially distributed, and can be a general probability distribution. This is called a semi-markov process; not difficult to simulate but the analytical calculations are much more involved. queueing models with nonexponential service times continuous-time branching processes where the rate of branching depends on the age of an agent Stoch15 Page 1
2 Mathematical Specification of Renewal Processes The key object in defining a renewal process is the CDF (cumulative distribution function) for the interincident time : When the random variable is continuous, then we can relate the CDF and PDF by: and But the CDF formulation is more general; in particular it allows for mixed or hybrid random variables that are both continuous and discrete. CDFs are universal descriptors of arbitrary random variables, no matter how nasty, whereas PMFs only work for discrete random variables, and PDFs only work for continuous random variables. Note that one can in practice work with hybrid/mixture random variables using "generalized PDFs" where the jumps in the CDF (discrete components) are represented in the PDF by Dirac delta functions. CDFs are also complete descriptors of a random variable. How do we compute expectations of a random variable in terms of its CDF? Stieltjes integral: In particular, assuming as we are that, one can write the mean of a random variable in terms of the CDF without a Stieltjes integral: Stoch15 Page 2
3 This follows from integration by parts. Some key quantities associated to renewal processes Counting process Current life: Residual life: Total life: For the special case of a Poisson point process, one can explicitly compute the probability distribution for all these quantities. We already saw that the counting process has a Poisson distribution with mean where is the rate of the Poisson point process. Also, by the memoryless property, one can show that mean is exponentially distributed with Also, because the Markov property works backward in time as well as forward, so the current life has a exponential distribution which is cut off at the value corresponding to no incident having occurred over. (That is, is a hybrid random variable which has a probability to take the value.) But if we take large enough, this cut off plays a small role, and Consequently, we also have that This gives rise to the "Poisson paradox." length-biased sampling is the resolution Stoch15 Page 3
4 Now we turn to how more general renewal processes can be analyzed. simulation is straightforward if one knows how to simulate The basic strategy is the following three steps: 1. Apply a renewal argument to obtain a (recursive) integral equation for the statistical quantity of interest. 2. Arrange this integral equation so that the renewal theorem can be applied to it. 3. Apply the renewal theorem and obtain the resulting behavior at large times. Alternatively, in some simple situations, you can solve the integral equation using Laplace transforms to get finite-time behavior but this is not typical. Renewal Argument This is a generalization of the first-step analysis for Markov chains. We instead will condition on the time of the first incident, which is a time at which memory is lost. Let's apply this first to the mean of the counting process: In general one applies the law of total expectation by partitioning on the time of the first incident: Now compute the conditional expectation: Plug into the law of total expectation: Stoch15 Page 4
5 So we have a recursive integral equation: Sometimes this can be solved analytically via Laplace transform, but can be hard to invert. For the purpose of determining the statistical properties at long time, the renewal theorem gives a systematic way for doing this, but it requires that we put the recursive integral equation into a special form called the renewal equation: We can now apply the "renewal theorem" to this integral equation, which we now formulate. One of the requirements below is that we have to exclude the special case when is arithmetic, meaning that the possible values of fall on some discrete lattice including the origin. Renewal Theorem Suppose that is a nondecreasing function with is not arithmetic, and Then the solution equation): to the following integral equation (the renewal has the following properties: If a(t) is bounded, then the solution A(t) is unique and bounded on finite time intervals. The solution to the integral equation can be expressed as Stoch15 Page 5
6 where M(t) is the renewal function, the solution to: Note this is exactly the integral equation we had for the mean of the counting process. This says that acts as a sort of Green's function for the general renewal equation. 3. If a(t) is integrable ( then where Applying the renewal theorem to the mean of the counting process, we can just use the 4th point to see that at long time where is just the mean time between incidents. A slightly less simple example: Let's derive a formula for the probability distribution of the residual life of a general renewal process, at long time: This could be done by direct conditional probability techniques, but we'll illustrate the 3-step strategy that we outlined above. 1. Renewal argument: Stoch15 Page 6
7 2. Write in the form of a renewal equation to prepare for applying the renewal theorem. We see that this can be done with,. 3. Check the technical conditions of the renewal theorem, particularly the third point regarding the long-time behavior: Stoch15 Page 7
8 which is finite whenever So then the renewal theorem tells us: Karlin and Taylor Sec. 5.8B does a very interesting application of this renewal argument/renewal theorem approach to compute the mean population size of a continuous time branching process for which the time between birth and branching of an agent is given by an arbitrary probability distribution, i.e., CDF. The integral equation you get from the renewal argument doesn t quite satisfy the conditions of the renewal theorem, so you have to twist the integral equation Stoch15 Page 8
9 a little bit by introducing exponential factors with unknown growth rate into the integral equation. There is a unique growth rate which will cause the renewal theorem to work, and it satisfies a sort of eigenvalue problem for the integral equation. And that growth rate is then shown to describe the mean growth rate of the population. Stoch15 Page 9
Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline).
 Large-Time Behavior for Continuous-Time Markov Chains Friday, December 02, 2011 10:58 AM Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline). How are formulas for large-time behavior of discrete-time
Large-Time Behavior for Continuous-Time Markov Chains Friday, December 02, 2011 10:58 AM Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline). How are formulas for large-time behavior of discrete-time
stochnotes Page 1
 stochnotes110308 Page 1 Kolmogorov forward and backward equations and Poisson process Monday, November 03, 2008 11:58 AM How can we apply the Kolmogorov equations to calculate various statistics of interest?
stochnotes110308 Page 1 Kolmogorov forward and backward equations and Poisson process Monday, November 03, 2008 11:58 AM How can we apply the Kolmogorov equations to calculate various statistics of interest?
This is now an algebraic equation that can be solved simply:
 Simulation of CTMC Monday, November 23, 2015 1:55 PM Homework 4 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, December 11 at 5 PM. Let's solve the Kolmogorov forward equation for the Poisson counting
Simulation of CTMC Monday, November 23, 2015 1:55 PM Homework 4 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, December 11 at 5 PM. Let's solve the Kolmogorov forward equation for the Poisson counting
Poisson Point Processes
 Poisson Point Processes Tuesday, April 22, 2014 2:00 PM Homework 4 posted; due Wednesday, May 7. We'll begin with Poisson point processes in one dimension which actually are an example of both a Poisson
Poisson Point Processes Tuesday, April 22, 2014 2:00 PM Homework 4 posted; due Wednesday, May 7. We'll begin with Poisson point processes in one dimension which actually are an example of both a Poisson
Birth-death chain models (countable state)
 Countable State Birth-Death Chains and Branching Processes Tuesday, March 25, 2014 1:59 PM Homework 3 posted, due Friday, April 18. Birth-death chain models (countable state) S = We'll characterize the
Countable State Birth-Death Chains and Branching Processes Tuesday, March 25, 2014 1:59 PM Homework 3 posted, due Friday, April 18. Birth-death chain models (countable state) S = We'll characterize the
1 Delayed Renewal Processes: Exploiting Laplace Transforms
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I Professor Whitt, Tuesday, October 22, 213 Renewal Theory: Proof of Blackwell s theorem 1 Delayed Renewal Processes: Exploiting Laplace Transforms The proof of Blackwell s
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I Professor Whitt, Tuesday, October 22, 213 Renewal Theory: Proof of Blackwell s theorem 1 Delayed Renewal Processes: Exploiting Laplace Transforms The proof of Blackwell s
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains
 Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
So in terms of conditional probability densities, we have by differentiating this relationship:
 Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Let's contemplate a continuous-time limit of the Bernoulli process:
 Mathematical Foundations of Markov Chains Thursday, September 17, 2015 2:04 PM Reading: Lawler Ch. 1 Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM. Office hours today are moved to 6-7 PM. Let's revisit the
Mathematical Foundations of Markov Chains Thursday, September 17, 2015 2:04 PM Reading: Lawler Ch. 1 Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM. Office hours today are moved to 6-7 PM. Let's revisit the
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 2003, Professor Whitt. Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18.
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, :12 PM
 stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
PROBABILITY AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers
 PROBABILITY AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates Rutgers, The State University ofnew Jersey David J. Goodman Rutgers, The State University
PROBABILITY AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES A Friendly Introduction for Electrical and Computer Engineers Roy D. Yates Rutgers, The State University ofnew Jersey David J. Goodman Rutgers, The State University
(implicitly assuming time-homogeneity from here on)
 Continuous-Time Markov Chains Models Tuesday, November 15, 2011 2:02 PM The fundamental object describing the dynamics of a CTMC (continuous-time Markov chain) is the probability transition (matrix) function:
Continuous-Time Markov Chains Models Tuesday, November 15, 2011 2:02 PM The fundamental object describing the dynamics of a CTMC (continuous-time Markov chain) is the probability transition (matrix) function:
Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
 Formulation of Finite State Markov Chains Friday, September 23, 2011 2:04 PM Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
Formulation of Finite State Markov Chains Friday, September 23, 2011 2:04 PM Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
Solutions to Homework Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 2011
 Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1.
 Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
FDST Markov Chain Models
 FDST Markov Chain Models Tuesday, February 11, 2014 2:01 PM Homework 1 due Friday, February 21 at 2 PM. Reading: Karlin and Taylor, Sections 2.1-2.3 Almost all of our Markov chain models will be time-homogenous,
FDST Markov Chain Models Tuesday, February 11, 2014 2:01 PM Homework 1 due Friday, February 21 at 2 PM. Reading: Karlin and Taylor, Sections 2.1-2.3 Almost all of our Markov chain models will be time-homogenous,
f X (x) = λe λx, , x 0, k 0, λ > 0 Γ (k) f X (u)f X (z u)du
 11 COLLECTED PROBLEMS Do the following problems for coursework 1. Problems 11.4 and 11.5 constitute one exercise leading you through the basic ruin arguments. 2. Problems 11.1 through to 11.13 but excluding
11 COLLECTED PROBLEMS Do the following problems for coursework 1. Problems 11.4 and 11.5 constitute one exercise leading you through the basic ruin arguments. 2. Problems 11.1 through to 11.13 but excluding
Recap. Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains. ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks
 Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
Stochastic Renewal Processes in Structural Reliability Analysis:
 Stochastic Renewal Processes in Structural Reliability Analysis: An Overview of Models and Applications Professor and Industrial Research Chair Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University
Stochastic Renewal Processes in Structural Reliability Analysis: An Overview of Models and Applications Professor and Industrial Research Chair Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University
µ n 1 (v )z n P (v, )
 Plan More Examples (Countable-state case). Questions 1. Extended Examples 2. Ideas and Results Next Time: General-state Markov Chains Homework 4 typo Unless otherwise noted, let X be an irreducible, aperiodic
Plan More Examples (Countable-state case). Questions 1. Extended Examples 2. Ideas and Results Next Time: General-state Markov Chains Homework 4 typo Unless otherwise noted, let X be an irreducible, aperiodic
Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, :04 PM
 stochnotes102008 Page 1 Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, 2008 12:04 PM Looking for a detailed balance solution for a stationary distribution is a useful technique. Stationary
stochnotes102008 Page 1 Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, 2008 12:04 PM Looking for a detailed balance solution for a stationary distribution is a useful technique. Stationary
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains
 Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman
 IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman 1. Semi-Markov processes: Consider an irreducible positive recurrent discrete-time Markov chain {X n } with transition matrix P (P i,j ), i, j S, and finite state space.
IEOR 6711, HMWK 5, Professor Sigman 1. Semi-Markov processes: Consider an irreducible positive recurrent discrete-time Markov chain {X n } with transition matrix P (P i,j ), i, j S, and finite state space.
I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30.
 Random Variables Friday, September 09, 2011 2:02 PM I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30. No class or office hours next week. Next class is on Tuesday, September
Random Variables Friday, September 09, 2011 2:02 PM I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30. No class or office hours next week. Next class is on Tuesday, September
Northwestern University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Northwestern University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 454: Modeling and Analysis of Communication Networks Spring 2008 Probability Review As discussed in Lecture 1, probability
Northwestern University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 454: Modeling and Analysis of Communication Networks Spring 2008 Probability Review As discussed in Lecture 1, probability
Adventures in Stochastic Processes
 Sidney Resnick Adventures in Stochastic Processes with Illustrations Birkhäuser Boston Basel Berlin Table of Contents Preface ix CHAPTER 1. PRELIMINARIES: DISCRETE INDEX SETS AND/OR DISCRETE STATE SPACES
Sidney Resnick Adventures in Stochastic Processes with Illustrations Birkhäuser Boston Basel Berlin Table of Contents Preface ix CHAPTER 1. PRELIMINARIES: DISCRETE INDEX SETS AND/OR DISCRETE STATE SPACES
Eulerian (Probability-Based) Approach
 Eulerian (Probability-Based) Approach Tuesday, March 03, 2015 1:59 PM Office hours for Wednesday, March 4 shifted to 5:30-6:30 PM. Homework 2 posted, due Tuesday, March 17 at 2 PM. correction: the drifts
Eulerian (Probability-Based) Approach Tuesday, March 03, 2015 1:59 PM Office hours for Wednesday, March 4 shifted to 5:30-6:30 PM. Homework 2 posted, due Tuesday, March 17 at 2 PM. correction: the drifts
Queueing Theory. VK Room: M Last updated: October 17, 2013.
 Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Birth-Death Processes
 Birth-Death Processes Birth-Death Processes: Transient Solution Poisson Process: State Distribution Poisson Process: Inter-arrival Times Dr Conor McArdle EE414 - Birth-Death Processes 1/17 Birth-Death
Birth-Death Processes Birth-Death Processes: Transient Solution Poisson Process: State Distribution Poisson Process: Inter-arrival Times Dr Conor McArdle EE414 - Birth-Death Processes 1/17 Birth-Death
Basics of Stochastic Modeling: Part II
 Basics of Stochastic Modeling: Part II Continuous Random Variables 1 Sandip Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering, INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR August 10, 2016 1 Reference
Basics of Stochastic Modeling: Part II Continuous Random Variables 1 Sandip Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering, INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY KHARAGPUR August 10, 2016 1 Reference
Stochastic Processes. Theory for Applications. Robert G. Gallager CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Stochastic Processes Theory for Applications Robert G. Gallager CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xv Swgg&sfzoMj ybr zmjfr%cforj owf fmdy xix Acknowledgements xxi 1 Introduction and review
Stochastic Processes Theory for Applications Robert G. Gallager CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xv Swgg&sfzoMj ybr zmjfr%cforj owf fmdy xix Acknowledgements xxi 1 Introduction and review
DISCRETE STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Draft of 2nd Edition
 DISCRETE STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Draft of 2nd Edition R. G. Gallager January 31, 2011 i ii Preface These notes are a draft of a major rewrite of a text [9] of the same name. The notes and the text are outgrowths
DISCRETE STOCHASTIC PROCESSES Draft of 2nd Edition R. G. Gallager January 31, 2011 i ii Preface These notes are a draft of a major rewrite of a text [9] of the same name. The notes and the text are outgrowths
Contents Preface The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process Introduction to Renewal Theory
 Contents Preface... v 1 The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 The Density, the Distribution, the Tail, and the Hazard Functions... 2 1.2.1 The Hazard Function
Contents Preface... v 1 The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 The Density, the Distribution, the Tail, and the Hazard Functions... 2 1.2.1 The Hazard Function
Continuous time Markov chains
 Continuous time Markov chains Alejandro Ribeiro Dept. of Electrical and Systems Engineering University of Pennsylvania aribeiro@seas.upenn.edu http://www.seas.upenn.edu/users/~aribeiro/ October 16, 2017
Continuous time Markov chains Alejandro Ribeiro Dept. of Electrical and Systems Engineering University of Pennsylvania aribeiro@seas.upenn.edu http://www.seas.upenn.edu/users/~aribeiro/ October 16, 2017
Continuous-time Markov Chains
 Continuous-time Markov Chains Gonzalo Mateos Dept. of ECE and Goergen Institute for Data Science University of Rochester gmateosb@ece.rochester.edu http://www.ece.rochester.edu/~gmateosb/ October 23, 2017
Continuous-time Markov Chains Gonzalo Mateos Dept. of ECE and Goergen Institute for Data Science University of Rochester gmateosb@ece.rochester.edu http://www.ece.rochester.edu/~gmateosb/ October 23, 2017
6.041/6.431 Fall 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, December 15, 9:00AM - 12:00noon.
 6.041/6.431 Fall 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, December 15, 9:00AM - 12:00noon. DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE OVER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO Name: Recitation Instructor: TA: Question Score Out of 1.1 4 1.2 4 1.3
6.041/6.431 Fall 2010 Final Exam Wednesday, December 15, 9:00AM - 12:00noon. DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE OVER UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO Name: Recitation Instructor: TA: Question Score Out of 1.1 4 1.2 4 1.3
State-Space Methods for Inferring Spike Trains from Calcium Imaging
 State-Space Methods for Inferring Spike Trains from Calcium Imaging Joshua Vogelstein Johns Hopkins April 23, 2009 Joshua Vogelstein (Johns Hopkins) State-Space Calcium Imaging April 23, 2009 1 / 78 Outline
State-Space Methods for Inferring Spike Trains from Calcium Imaging Joshua Vogelstein Johns Hopkins April 23, 2009 Joshua Vogelstein (Johns Hopkins) State-Space Calcium Imaging April 23, 2009 1 / 78 Outline
6.041/6.431 Fall 2010 Final Exam Solutions Wednesday, December 15, 9:00AM - 12:00noon.
 604/643 Fall 200 Final Exam Solutions Wednesday, December 5, 9:00AM - 2:00noon Problem (32 points) Consider a Markov chain {X n ; n 0,, }, specified by the following transition diagram 06 05 09 04 03 2
604/643 Fall 200 Final Exam Solutions Wednesday, December 5, 9:00AM - 2:00noon Problem (32 points) Consider a Markov chain {X n ; n 0,, }, specified by the following transition diagram 06 05 09 04 03 2
The cost/reward formula has two specific widely used applications:
 Applications of Absorption Probability and Accumulated Cost/Reward Formulas for FDMC Friday, October 21, 2011 2:28 PM No class next week. No office hours either. Next class will be 11/01. The cost/reward
Applications of Absorption Probability and Accumulated Cost/Reward Formulas for FDMC Friday, October 21, 2011 2:28 PM No class next week. No office hours either. Next class will be 11/01. The cost/reward
Glossary availability cellular manufacturing closed queueing network coefficient of variation (CV) conditional probability CONWIP
 Glossary availability The long-run average fraction of time that the processor is available for processing jobs, denoted by a (p. 113). cellular manufacturing The concept of organizing the factory into
Glossary availability The long-run average fraction of time that the processor is available for processing jobs, denoted by a (p. 113). cellular manufacturing The concept of organizing the factory into
2. Transience and Recurrence
 Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Review Quiz. 1. Prove that in a one-dimensional canonical exponential family, the complete and sufficient statistic achieves the
 Review Quiz 1. Prove that in a one-dimensional canonical exponential family, the complete and sufficient statistic achieves the Cramér Rao lower bound (CRLB). That is, if where { } and are scalars, then
Review Quiz 1. Prove that in a one-dimensional canonical exponential family, the complete and sufficient statistic achieves the Cramér Rao lower bound (CRLB). That is, if where { } and are scalars, then
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/39637 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Smit, Laurens Title: Steady-state analysis of large scale systems : the successive
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/39637 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Smit, Laurens Title: Steady-state analysis of large scale systems : the successive
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes Midterm Quiz April 6, 2010 There are 5 questions, each with several parts.
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes Midterm Quiz April 6, 2010 There are 5 questions, each with several parts.
Let's transfer our results for conditional probability for events into conditional probabilities for random variables.
 Kolmogorov/Smoluchowski equation approach to Brownian motion Tuesday, February 12, 2013 1:53 PM Readings: Gardiner, Secs. 1.2, 3.8.1, 3.8.2 Einstein Homework 1 due February 22. Conditional probability
Kolmogorov/Smoluchowski equation approach to Brownian motion Tuesday, February 12, 2013 1:53 PM Readings: Gardiner, Secs. 1.2, 3.8.1, 3.8.2 Einstein Homework 1 due February 22. Conditional probability
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF RELIABILITY AND PROBABILITY MEASURES
 27 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF RELIABILITY AND PROBABILITY MEASURES 3.1 INTRODUCTION The express purpose of this research is to assimilate reliability and its associated probabilistic variables into the Unit
27 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF RELIABILITY AND PROBABILITY MEASURES 3.1 INTRODUCTION The express purpose of this research is to assimilate reliability and its associated probabilistic variables into the Unit
Discrete and Continuous Random Variables
 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables Friday, January 31, 2014 2:03 PM Homework 1 will be posted over the weekend; due in a couple of weeks. Important examples of random variables on discrete state
Discrete and Continuous Random Variables Friday, January 31, 2014 2:03 PM Homework 1 will be posted over the weekend; due in a couple of weeks. Important examples of random variables on discrete state
Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes. Markov Processes Markov Chains. Random Processes
 Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes Definition IID Processes Bernoulli Process Binomial Counting Process Interarrival Time Process Markov Processes Markov Chains Classification of States Steady State Probabilities
Lecture Notes 7 Random Processes Definition IID Processes Bernoulli Process Binomial Counting Process Interarrival Time Process Markov Processes Markov Chains Classification of States Steady State Probabilities
Stochastic Modelling Unit 1: Markov chain models
 Stochastic Modelling Unit 1: Markov chain models Russell Gerrard and Douglas Wright Cass Business School, City University, London June 2004 Contents of Unit 1 1 Stochastic Processes 2 Markov Chains 3 Poisson
Stochastic Modelling Unit 1: Markov chain models Russell Gerrard and Douglas Wright Cass Business School, City University, London June 2004 Contents of Unit 1 1 Stochastic Processes 2 Markov Chains 3 Poisson
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains
 Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Random variables. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Random variables DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Motivation Random variables model numerical quantities
Random variables DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Motivation Random variables model numerical quantities
An M/M/1 Queue in Random Environment with Disasters
 An M/M/1 Queue in Random Environment with Disasters Noam Paz 1 and Uri Yechiali 1,2 1 Department of Statistics and Operations Research School of Mathematical Sciences Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978,
An M/M/1 Queue in Random Environment with Disasters Noam Paz 1 and Uri Yechiali 1,2 1 Department of Statistics and Operations Research School of Mathematical Sciences Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv 69978,
Random Walk on a Graph
 IOR 67: Stochastic Models I Second Midterm xam, hapters 3 & 4, November 2, 200 SOLUTIONS Justify your answers; show your work.. Random Walk on a raph (25 points) Random Walk on a raph 2 5 F B 3 3 2 Figure
IOR 67: Stochastic Models I Second Midterm xam, hapters 3 & 4, November 2, 200 SOLUTIONS Justify your answers; show your work.. Random Walk on a raph (25 points) Random Walk on a raph 2 5 F B 3 3 2 Figure
Markov Chains. X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2 <... < t k < t k+1. If X(t) is discrete-valued. If X(t) is continuous-valued
 Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
Markov Chains X(t) is a Markov Process if, for arbitrary times t 1 < t 2
Lecture 10: Semi-Markov Type Processes
 Lecture 1: Semi-Markov Type Processes 1. Semi-Markov processes (SMP) 1.1 Definition of SMP 1.2 Transition probabilities for SMP 1.3 Hitting times and semi-markov renewal equations 2. Processes with semi-markov
Lecture 1: Semi-Markov Type Processes 1. Semi-Markov processes (SMP) 1.1 Definition of SMP 1.2 Transition probabilities for SMP 1.3 Hitting times and semi-markov renewal equations 2. Processes with semi-markov
Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains. Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan
 Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Continuous-Time Markov Chains Consider a continuous-time stochastic process
Chapter 5. Continuous-Time Markov Chains Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Continuous-Time Markov Chains Consider a continuous-time stochastic process
THE QUEEN S UNIVERSITY OF BELFAST
 THE QUEEN S UNIVERSITY OF BELFAST 0SOR20 Level 2 Examination Statistics and Operational Research 20 Probability and Distribution Theory Wednesday 4 August 2002 2.30 pm 5.30 pm Examiners { Professor R M
THE QUEEN S UNIVERSITY OF BELFAST 0SOR20 Level 2 Examination Statistics and Operational Research 20 Probability and Distribution Theory Wednesday 4 August 2002 2.30 pm 5.30 pm Examiners { Professor R M
Queueing Theory II. Summary. ! M/M/1 Output process. ! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages. ! General Distributions
 Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CONTENTS. Preface Preface to the First Edition
 Preface Preface to the First Edition xi xiii 1 Basic Probability Theory 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Sample Spaces and Events 3 1.3 The Axioms of Probability 7 1.4 Finite Sample Spaces and Combinatorics 15
Preface Preface to the First Edition xi xiii 1 Basic Probability Theory 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Sample Spaces and Events 3 1.3 The Axioms of Probability 7 1.4 Finite Sample Spaces and Combinatorics 15
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes. Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking
 Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models
 Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 Review of PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Hideaki Shimazaki, Ph.D. http://goo.gl/visng Poisson process 1 Probability distribution Probability that a (continuous) random variable X is in (x,x+dx). ( ) P x < X
Review of PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Hideaki Shimazaki, Ph.D. http://goo.gl/visng Poisson process 1 Probability distribution Probability that a (continuous) random variable X is in (x,x+dx). ( ) P x < X
Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis.
 Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 3: Review of Practical Stochastic Processes
 CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 3: Review of Practical Stochastic Processes Definition Stochastic process X = {X(t), t2 T} is a collection of random variables (rvs); one rv
CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 3: Review of Practical Stochastic Processes Definition Stochastic process X = {X(t), t2 T} is a collection of random variables (rvs); one rv
Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29.
 Classification of Birth-Death Chains Tuesday, November 08, 2011 2:02 PM Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29. Continuing with our classification of birth-death chains on nonnegative integers. Last
Classification of Birth-Death Chains Tuesday, November 08, 2011 2:02 PM Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29. Continuing with our classification of birth-death chains on nonnegative integers. Last
Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains
 Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains Friday, February 07, 2014 2:04 PM Stochastic update rule for FSDT Markov Chain requires an initial condition. Most generally, this can
Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains Friday, February 07, 2014 2:04 PM Stochastic update rule for FSDT Markov Chain requires an initial condition. Most generally, this can
Fault-Tolerant Computer System Design ECE 60872/CS 590. Topic 2: Discrete Distributions
 Fault-Tolerant Computer System Design ECE 60872/CS 590 Topic 2: Discrete Distributions Saurabh Bagchi ECE/CS Purdue University Outline Basic probability Conditional probability Independence of events Series-parallel
Fault-Tolerant Computer System Design ECE 60872/CS 590 Topic 2: Discrete Distributions Saurabh Bagchi ECE/CS Purdue University Outline Basic probability Conditional probability Independence of events Series-parallel
Networking = Plumbing. Queueing Analysis: I. Last Lecture. Lecture Outline. Jeremiah Deng. 29 July 2013
 Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012
 SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012 This exam is closed book. YOU NEED TO SHOW YOUR WORK. Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted
SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012 This exam is closed book. YOU NEED TO SHOW YOUR WORK. Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted
At the boundary states, we take the same rules except we forbid leaving the state space, so,.
 Birth-death chains Monday, October 19, 2015 2:22 PM Example: Birth-Death Chain State space From any state we allow the following transitions: with probability (birth) with probability (death) with probability
Birth-death chains Monday, October 19, 2015 2:22 PM Example: Birth-Death Chain State space From any state we allow the following transitions: with probability (birth) with probability (death) with probability
Queues and Queueing Networks
 Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Classification of Countable State Markov Chains
 Classification of Countable State Markov Chains Friday, March 21, 2014 2:01 PM How can we determine whether a communication class in a countable state Markov chain is: transient null recurrent positive
Classification of Countable State Markov Chains Friday, March 21, 2014 2:01 PM How can we determine whether a communication class in a countable state Markov chain is: transient null recurrent positive
HITTING TIME IN AN ERLANG LOSS SYSTEM
 Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences, 16, 2002, 167 184+ Printed in the U+S+A+ HITTING TIME IN AN ERLANG LOSS SYSTEM SHELDON M. ROSS Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations
Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences, 16, 2002, 167 184+ Printed in the U+S+A+ HITTING TIME IN AN ERLANG LOSS SYSTEM SHELDON M. ROSS Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations
M/G/1 and M/G/1/K systems
 M/G/1 and M/G/1/K systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/elt-53606/ OUTLINE: Description of M/G/1 system; Methods of analysis; Residual life approach; Imbedded
M/G/1 and M/G/1/K systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/elt-53606/ OUTLINE: Description of M/G/1 system; Methods of analysis; Residual life approach; Imbedded
Bernoulli Counting Process with p=0.1
 Stat 28 October 29, 21 Today: More Ch 7 (Sections 7.4 and part of 7.) Midterm will cover Ch 7 to section 7.4 Review session will be Nov. Exercises to try (answers in book): 7.1-, 7.2-3, 7.3-3, 7.4-7 Where
Stat 28 October 29, 21 Today: More Ch 7 (Sections 7.4 and part of 7.) Midterm will cover Ch 7 to section 7.4 Review session will be Nov. Exercises to try (answers in book): 7.1-, 7.2-3, 7.3-3, 7.4-7 Where
Transience: Whereas a finite closed communication class must be recurrent, an infinite closed communication class can be transient:
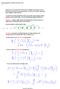 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
The Kemeny constant of a Markov chain
 The Kemeny constant of a Markov chain Peter Doyle Version 1.0 dated 14 September 009 GNU FDL Abstract Given an ergodic finite-state Markov chain, let M iw denote the mean time from i to equilibrium, meaning
The Kemeny constant of a Markov chain Peter Doyle Version 1.0 dated 14 September 009 GNU FDL Abstract Given an ergodic finite-state Markov chain, let M iw denote the mean time from i to equilibrium, meaning
Markov chains. 1 Discrete time Markov chains. c A. J. Ganesh, University of Bristol, 2015
 Markov chains c A. J. Ganesh, University of Bristol, 2015 1 Discrete time Markov chains Example: A drunkard is walking home from the pub. There are n lampposts between the pub and his home, at each of
Markov chains c A. J. Ganesh, University of Bristol, 2015 1 Discrete time Markov chains Example: A drunkard is walking home from the pub. There are n lampposts between the pub and his home, at each of
STAT331 Lebesgue-Stieltjes Integrals, Martingales, Counting Processes
 STAT331 Lebesgue-Stieltjes Integrals, Martingales, Counting Processes This section introduces Lebesgue-Stieltjes integrals, and defines two important stochastic processes: a martingale process and a counting
STAT331 Lebesgue-Stieltjes Integrals, Martingales, Counting Processes This section introduces Lebesgue-Stieltjes integrals, and defines two important stochastic processes: a martingale process and a counting
3 Continuous Random Variables
 Jinguo Lian Math437 Notes January 15, 016 3 Continuous Random Variables Remember that discrete random variables can take only a countable number of possible values. On the other hand, a continuous random
Jinguo Lian Math437 Notes January 15, 016 3 Continuous Random Variables Remember that discrete random variables can take only a countable number of possible values. On the other hand, a continuous random
Finite Markov Information-Exchange processes
 Finite Markov Information-Exchange processes David Aldous March 30, 2011 Note that previous FMIE models were non-equilibrium. We digress to a quite different FMIE model designed to have an equilibrium.
Finite Markov Information-Exchange processes David Aldous March 30, 2011 Note that previous FMIE models were non-equilibrium. We digress to a quite different FMIE model designed to have an equilibrium.
MARKOV PROCESSES. Valerio Di Valerio
 MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Stochastic Petri Nets. Jonatan Lindén. Modelling SPN GSPN. Performance measures. Almost none of the theory. December 8, 2010
 Stochastic Almost none of the theory December 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 Introduction A Petri net (PN) is something like a generalized automata. A Stochastic Petri Net () a stochastic extension to Petri nets,
Stochastic Almost none of the theory December 8, 2010 Outline 1 2 Introduction A Petri net (PN) is something like a generalized automata. A Stochastic Petri Net () a stochastic extension to Petri nets,
Stochastic2010 Page 1
 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, April 02, 2010 2:03 PM Long-time properties for branching processes Clearly state 0 is an absorbing state, forming its own recurrent
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, April 02, 2010 2:03 PM Long-time properties for branching processes Clearly state 0 is an absorbing state, forming its own recurrent
Page 0 of 5 Final Examination Name. Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam.
 Final Examination Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam. To receive full credit, show enough work to indicate your logic. Do not spend time calculating. You will receive full credit
Final Examination Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam. To receive full credit, show enough work to indicate your logic. Do not spend time calculating. You will receive full credit
THE POISSON WAITING TIME DISTRIBUTION: ANALYSIS AND APPLICATION
 THE POISSON WAITING TIME DISTRIBUTION: ANALYSIS AND APPLICATION by Kyle Park ECED 6530 Project Report 12/12/2013 Table of Contents Summary ii Nomenclature ii List of Figures iii 1 The Waiting Time Distribution
THE POISSON WAITING TIME DISTRIBUTION: ANALYSIS AND APPLICATION by Kyle Park ECED 6530 Project Report 12/12/2013 Table of Contents Summary ii Nomenclature ii List of Figures iii 1 The Waiting Time Distribution
Chapter 3 sections. SKIP: 3.10 Markov Chains. SKIP: pages Chapter 3 - continued
 Chapter 3 sections Chapter 3 - continued 3.1 Random Variables and Discrete Distributions 3.2 Continuous Distributions 3.3 The Cumulative Distribution Function 3.4 Bivariate Distributions 3.5 Marginal Distributions
Chapter 3 sections Chapter 3 - continued 3.1 Random Variables and Discrete Distributions 3.2 Continuous Distributions 3.3 The Cumulative Distribution Function 3.4 Bivariate Distributions 3.5 Marginal Distributions
Modelling Complex Queuing Situations with Markov Processes
 Modelling Complex Queuing Situations with Markov Processes Jason Randal Thorne, School of IT, Charles Sturt Uni, NSW 2795, Australia Abstract This article comments upon some new developments in the field
Modelling Complex Queuing Situations with Markov Processes Jason Randal Thorne, School of IT, Charles Sturt Uni, NSW 2795, Australia Abstract This article comments upon some new developments in the field
LECTURE #6 BIRTH-DEATH PROCESS
 LECTURE #6 BIRTH-DEATH PROCESS 204528 Queueing Theory and Applications in Networks Assoc. Prof., Ph.D. (รศ.ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม) Computer Engineering Department, Kasetsart University Outline 2 Birth-Death
LECTURE #6 BIRTH-DEATH PROCESS 204528 Queueing Theory and Applications in Networks Assoc. Prof., Ph.D. (รศ.ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม) Computer Engineering Department, Kasetsart University Outline 2 Birth-Death
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 6.04/6.43: Probabilistic Systems Analysis (Fall 00) Problem Set 7: Solutions. (a) The event of the ith success occuring before the jth failure is equivalent to the ith success occurring within the first
6.04/6.43: Probabilistic Systems Analysis (Fall 00) Problem Set 7: Solutions. (a) The event of the ith success occuring before the jth failure is equivalent to the ith success occurring within the first
Queuing Theory. Richard Lockhart. Simon Fraser University. STAT 870 Summer 2011
 Queuing Theory Richard Lockhart Simon Fraser University STAT 870 Summer 2011 Richard Lockhart (Simon Fraser University) Queuing Theory STAT 870 Summer 2011 1 / 15 Purposes of Today s Lecture Describe general
Queuing Theory Richard Lockhart Simon Fraser University STAT 870 Summer 2011 Richard Lockhart (Simon Fraser University) Queuing Theory STAT 870 Summer 2011 1 / 15 Purposes of Today s Lecture Describe general
Lecture 3. Truncation, length-bias and prevalence sampling
 Lecture 3. Truncation, length-bias and prevalence sampling 3.1 Prevalent sampling Statistical techniques for truncated data have been integrated into survival analysis in last two decades. Truncation in
Lecture 3. Truncation, length-bias and prevalence sampling 3.1 Prevalent sampling Statistical techniques for truncated data have been integrated into survival analysis in last two decades. Truncation in
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART III: HIGHER DIMENSIONAL AND NON-MARKOVIAN QUEUES
 295 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART III: HIGHER DIMENSIONAL AND NON-MARKOVIAN QUEUES 16 Queueing Systems with Two Types of Customers In this section, we discuss queueing systems with two types of customers.
295 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART III: HIGHER DIMENSIONAL AND NON-MARKOVIAN QUEUES 16 Queueing Systems with Two Types of Customers In this section, we discuss queueing systems with two types of customers.
Probability (continued)
 DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 2 September 21, 15 Probability (continued) 1 Random variables (continued) 1.1 Conditioning on an event Given a random variable X with a certain distribution, imagine that it is
DS-GA 1002 Lecture notes 2 September 21, 15 Probability (continued) 1 Random variables (continued) 1.1 Conditioning on an event Given a random variable X with a certain distribution, imagine that it is
MAS1302 Computational Probability and Statistics
 MAS1302 Computational Probability and Statistics April 23, 2008 3. Simulating continuous random behaviour 3.1 The Continuous Uniform U(0,1) Distribution We have already used this random variable a great
MAS1302 Computational Probability and Statistics April 23, 2008 3. Simulating continuous random behaviour 3.1 The Continuous Uniform U(0,1) Distribution We have already used this random variable a great
Probability and Statistics Concepts
 University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
Lecture 3 Continuous Random Variable
 Lecture 3 Continuous Random Variable 1 Cumulative Distribution Function Definition Theorem 3.1 For any random variable X, 2 Continuous Random Variable Definition 3 Example Suppose we have a wheel of circumference
Lecture 3 Continuous Random Variable 1 Cumulative Distribution Function Definition Theorem 3.1 For any random variable X, 2 Continuous Random Variable Definition 3 Example Suppose we have a wheel of circumference
Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
 Mathematical Foundations of Discrete-Time Markov Chains Tuesday, February 04, 2014 2:04 PM Homework 1 posted, due Friday, February 21. Reading: Lawler, Ch. 1 Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
Mathematical Foundations of Discrete-Time Markov Chains Tuesday, February 04, 2014 2:04 PM Homework 1 posted, due Friday, February 21. Reading: Lawler, Ch. 1 Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
