Poisson Point Processes
|
|
|
- Scarlett Lawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Poisson Point Processes Tuesday, April 22, :00 PM Homework 4 posted; due Wednesday, May 7. We'll begin with Poisson point processes in one dimension which actually are an example of both a Poisson point process and a renewal process. One convenient way to define a Poisson point process in one dimension is the set of moments in time where the Poisson counting process changes state. We can label the Poisson point process as the sequence of times generated in this way: The statistics of these times (which are random) can be most conveniently characterized in terms of the interval between successive times: Using the results we computed from the Poisson counting process and mapping them to the Poisson point process, we have the following characterizing property of the Poisson point process: are iid random variables which are exponentially distributed with mean where was the "birth rate" in the associated Poisson counting process. When referring to the Poisson point process, the parameter is referred to as the intensity (or rate or density) of the Poisson point process. The reason for this terminology is that we can alternatively view point processes in terms of how many points are generated in a fixed interval. For the Poisson point process, the number of points in such an interval is a Poisson random variable with mean, so we see that is the average density of the Poisson point process. Also, one can show (again by referring to the Poisson counting process associated to the Poisson point process) that the number of Poisson points in nonoverlapping (Borel) sets is independent. This follows from the Markov property of the Poisson counting process (future and past is conditionally independent, given the present, and choose the present moment to be "between" the two sets for the case those sets are intervals.) Poisson point processes are widely used in modeling the times of random incidents in dynamical models: Arrivals of demand in a queueing model Stoch14 Page 1
2 Arrival of cars at an intersection or an entry ramp to an expressway Arrival of input signals to neurons in a network Times at which claims are filed at an insurance company More broadly, Poisson point processes turn out to be good models for systems where the incidents can be viewed as a superposition of a large number of processes which generate incidents rarely, and are independent of each other. this is the modeling interpretation of the Poisson limit theorem see Karlin and Taylor Sec. 5.9 Queueing model: The demands are arising from a large pool of noninteracting potential clients who each are making rare demands Seasonal variations (i.e., holidays, sales, etc.) can actually still be accounted for by a nonhomogenous Poisson point process which has an intensity that depends on time t. The above formulas need to be modified, i.e., with hazard functions for the time delay between successive incidents, and the number of points in an interval is Poisson distributed with mean Traffic model: Independent large number of cars except in cases like: regulation by traffic lights or police shortly before the entrance random accident causes many cars to divert behavior rush hour and other regular variations in traffic behavior can be modeled as nonhomogenous Poisson point process funerals and other coordinated random traffic activity Neuronal networks: Violations of Poisson point process model when inputs are only determined by a small number of neurons upstream and/or synchronization upstream some statistics look robustly like Poisson point process while others (in frequency domain) do not B. Lindner, "Superposition of many independent spike trains is not generally a Poisson process," Physical Review E 73 (2006), /PhysRevE Insurance claims: large-scale disasters would violate the assumption because it's an unpredictable source to generate many claims together. Multidimensional Poisson Point Processes To make this extension, we will characterize the properties of the one-dimensional point process within a Poisson random measure framework. = # Poisson points in a Borel set A. (As usual in measure theory, one has to prescribe a suitably cooperative to work with, and we'll take Borel sets). algebra of sets Stoch14 Page 2
3 Recall that in one dimension we have the following properties: 1. Countable additivity (true of all measures) if A is the disjoint union of. Also true of finite unions For Poisson random measure, under the above relationship between A and, are independent of each other. The mean number of Poisson points in a set A is, where is the Lebesgue measure of set A, which is just a generalization of the notion of length. These properties are actually sufficient to uniquely prescribe the Poisson point process in one dimension (alternative to the prescription regarding the time intervals between incidents). Note that we did not have to assume that the number of points in a given set are given by the Poisson distribution. That is in fact a consequence of the assumptions above, as we'll argue a little later. Proceeding for now with the practical side of Poisson point processes, the importance of the above characterization is that it extends to multiple dimensions (unlike the characterization in terms of interincident times). To generate a multidimensional Poisson point process in practice, one can show that the basic assumptions imply that you should do the following: Organize your simulation or (Monte Carlo) calculation so that it is referring to disjoint sets with finite measure (length/volume/area). For each disjoint region generate a Poisson random variable for the number of points in that region: Stoch14 Page 3
4 and these random variables are independent across disjoint regions. Then distribute these points uniformly over that region, with the location of each point independent of the location of other points. How simulate this for irregular regions? Use rejection method which is a way of using sampling of simple probability distributions to sample from complicated probability distributions. To employ it, one has to choose a simple probability distribution that "bounds: the complicated probability distribution. Enclose the domain in some cuboid (multidimensional rectangle). Generate random uniform points in the cuboid. If it falls within the set then accept the point, otherwise, reject and redo. One can show by a conditional probability calculation that this will generate points uniformly in the set. Note the rejection method also can be used to sample from complicated probability distributions by sampling with rejection from simpler probability distributions. Note sampling from a PDF is choosing a uniform random point under the graph of the PDF! Applications of multidimensional Poisson point process are typically to generate random locations in space with density/intensity. defects in materials vortices in fluid food sources in an ecosystem baseline for distribution of stars/galaxies Why is the Poisson distribution associated with simple point processes? Because the Poisson distribution is the simplest discrete probability distribution that has the property of being infinitely divisible. Let's see what the defining property of the multidimensional Poisson point process implies about the random variable characterizing the number of points in sets. Stoch14 Page 4
5 And in fact, this relationship must remain true if I choose finer and finer subdivisions of the form This is what is meant by infinite divisibility of a random variable, that it can be expressed as a sum of arbitrarily many independent random variables. This is a restrictive condition, as I'll argue in a minute, and is satisfied by some special probability distributions, among which are Poisson and Gaussian (continuous), but not binomial. How can you actually check whether a probability distribution is infinitely divisible? Use probability generating functions. So one can check whether the family of probability distributions being referred to in a stochastic model satisfies this infinite divisibility condition. For a Poisson distribution, we'd want and in any case, we would need that would have to satisfy Stoch14 Page 5
6 Infinite divisibility: Stoch14 Page 6
I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30.
 Random Variables Friday, September 09, 2011 2:02 PM I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30. No class or office hours next week. Next class is on Tuesday, September
Random Variables Friday, September 09, 2011 2:02 PM I will post Homework 1 soon, probably over the weekend, due Friday, September 30. No class or office hours next week. Next class is on Tuesday, September
Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3. A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process.
 Renewal Processes Wednesday, December 16, 2015 1:02 PM Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3 A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process. The Poisson point process is completely
Renewal Processes Wednesday, December 16, 2015 1:02 PM Reading: Karlin and Taylor Ch. 5 Resnick Ch. 3 A renewal process is a generalization of the Poisson point process. The Poisson point process is completely
This is now an algebraic equation that can be solved simply:
 Simulation of CTMC Monday, November 23, 2015 1:55 PM Homework 4 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, December 11 at 5 PM. Let's solve the Kolmogorov forward equation for the Poisson counting
Simulation of CTMC Monday, November 23, 2015 1:55 PM Homework 4 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, December 11 at 5 PM. Let's solve the Kolmogorov forward equation for the Poisson counting
FDST Markov Chain Models
 FDST Markov Chain Models Tuesday, February 11, 2014 2:01 PM Homework 1 due Friday, February 21 at 2 PM. Reading: Karlin and Taylor, Sections 2.1-2.3 Almost all of our Markov chain models will be time-homogenous,
FDST Markov Chain Models Tuesday, February 11, 2014 2:01 PM Homework 1 due Friday, February 21 at 2 PM. Reading: Karlin and Taylor, Sections 2.1-2.3 Almost all of our Markov chain models will be time-homogenous,
Discrete and Continuous Random Variables
 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables Friday, January 31, 2014 2:03 PM Homework 1 will be posted over the weekend; due in a couple of weeks. Important examples of random variables on discrete state
Discrete and Continuous Random Variables Friday, January 31, 2014 2:03 PM Homework 1 will be posted over the weekend; due in a couple of weeks. Important examples of random variables on discrete state
Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
 Formulation of Finite State Markov Chains Friday, September 23, 2011 2:04 PM Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
Formulation of Finite State Markov Chains Friday, September 23, 2011 2:04 PM Note special lecture series by Emmanuel Candes on compressed sensing Monday and Tuesday 4-5 PM (room information on rpinfo)
Birth-death chain models (countable state)
 Countable State Birth-Death Chains and Branching Processes Tuesday, March 25, 2014 1:59 PM Homework 3 posted, due Friday, April 18. Birth-death chain models (countable state) S = We'll characterize the
Countable State Birth-Death Chains and Branching Processes Tuesday, March 25, 2014 1:59 PM Homework 3 posted, due Friday, April 18. Birth-death chain models (countable state) S = We'll characterize the
Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline).
 Large-Time Behavior for Continuous-Time Markov Chains Friday, December 02, 2011 10:58 AM Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline). How are formulas for large-time behavior of discrete-time
Large-Time Behavior for Continuous-Time Markov Chains Friday, December 02, 2011 10:58 AM Homework 4 due on Thursday, December 15 at 5 PM (hard deadline). How are formulas for large-time behavior of discrete-time
Let's contemplate a continuous-time limit of the Bernoulli process:
 Mathematical Foundations of Markov Chains Thursday, September 17, 2015 2:04 PM Reading: Lawler Ch. 1 Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM. Office hours today are moved to 6-7 PM. Let's revisit the
Mathematical Foundations of Markov Chains Thursday, September 17, 2015 2:04 PM Reading: Lawler Ch. 1 Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM. Office hours today are moved to 6-7 PM. Let's revisit the
SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012
 SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012 This exam is closed book. YOU NEED TO SHOW YOUR WORK. Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted
SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012 This exam is closed book. YOU NEED TO SHOW YOUR WORK. Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains
 Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains Friday, February 07, 2014 2:04 PM Stochastic update rule for FSDT Markov Chain requires an initial condition. Most generally, this can
Mathematical Foundations of Finite State Discrete Time Markov Chains Friday, February 07, 2014 2:04 PM Stochastic update rule for FSDT Markov Chain requires an initial condition. Most generally, this can
(implicitly assuming time-homogeneity from here on)
 Continuous-Time Markov Chains Models Tuesday, November 15, 2011 2:02 PM The fundamental object describing the dynamics of a CTMC (continuous-time Markov chain) is the probability transition (matrix) function:
Continuous-Time Markov Chains Models Tuesday, November 15, 2011 2:02 PM The fundamental object describing the dynamics of a CTMC (continuous-time Markov chain) is the probability transition (matrix) function:
So in terms of conditional probability densities, we have by differentiating this relationship:
 Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Modeling with Finite State Markov Chains Tuesday, September 27, 2011 1:54 PM Homework 1 due Friday, September 30 at 2 PM. Office hours on 09/28: Only 11 AM-12 PM (not at 3 PM) Important side remark about
Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
 Probability Theory Foundations Thursday, September 03, 2015 1:57 PM Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
Probability Theory Foundations Thursday, September 03, 2015 1:57 PM Office hours: Mondays 5-6 PM (undergraduate class preference) Tuesdays 5-6 PM (this class preference) Thursdays 5-6 PM (free-for-all)
Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor, Sec. 2.3)
 stochnotes091108 Page 1 Markov Chain Models and Basic Computations Thursday, September 11, 2008 11:50 AM Homework 1 is posted, due Monday, September 22. Two more examples. Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor,
stochnotes091108 Page 1 Markov Chain Models and Basic Computations Thursday, September 11, 2008 11:50 AM Homework 1 is posted, due Monday, September 22. Two more examples. Inventory Model (Karlin and Taylor,
stochnotes Page 1
 stochnotes110308 Page 1 Kolmogorov forward and backward equations and Poisson process Monday, November 03, 2008 11:58 AM How can we apply the Kolmogorov equations to calculate various statistics of interest?
stochnotes110308 Page 1 Kolmogorov forward and backward equations and Poisson process Monday, November 03, 2008 11:58 AM How can we apply the Kolmogorov equations to calculate various statistics of interest?
Poisson Processes. Stochastic Processes. Feb UC3M
 Poisson Processes Stochastic Processes UC3M Feb. 2012 Exponential random variables A random variable T has exponential distribution with rate λ > 0 if its probability density function can been written
Poisson Processes Stochastic Processes UC3M Feb. 2012 Exponential random variables A random variable T has exponential distribution with rate λ > 0 if its probability density function can been written
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I SOLUTIONS to the First Midterm Exam, October 7, 2008
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I SOLUTIONS to the First Midterm Exam, October 7, 2008 Justify your answers; show your work. 1. A sequence of Events. (10 points) Let {B n : n 1} be a sequence of events in
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I SOLUTIONS to the First Midterm Exam, October 7, 2008 Justify your answers; show your work. 1. A sequence of Events. (10 points) Let {B n : n 1} be a sequence of events in
Stochastic-Process Limits
 Ward Whitt Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues With 68 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vii 1 Experiencing Statistical Regularity
Ward Whitt Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues With 68 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vii 1 Experiencing Statistical Regularity
Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM.
 Stationary Distributions: Application Monday, October 05, 2015 2:04 PM Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM. To prepare to describe the conditions under which the
Stationary Distributions: Application Monday, October 05, 2015 2:04 PM Homework 2 will be posted by tomorrow morning, due Friday, October 16 at 5 PM. To prepare to describe the conditions under which the
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains
 Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Countable state discrete time Markov Chains Tuesday, March 18, 2014 2:12 PM Readings: Lawler Ch. 2 Karlin & Taylor Chs. 2 & 3 Resnick Ch. 1 Countably infinite state spaces are of practical utility in situations
Q = (c) Assuming that Ricoh has been working continuously for 7 days, what is the probability that it will remain working at least 8 more days?
 IEOR 4106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Spring 2005, Professor Whitt, Second Midterm Exam Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, March 31, 11:00am-1:00pm Open Book: but only the Ross
IEOR 4106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Spring 2005, Professor Whitt, Second Midterm Exam Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, March 31, 11:00am-1:00pm Open Book: but only the Ross
Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
 Mathematical Foundations of Discrete-Time Markov Chains Tuesday, February 04, 2014 2:04 PM Homework 1 posted, due Friday, February 21. Reading: Lawler, Ch. 1 Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
Mathematical Foundations of Discrete-Time Markov Chains Tuesday, February 04, 2014 2:04 PM Homework 1 posted, due Friday, February 21. Reading: Lawler, Ch. 1 Mathematical Framework for Stochastic Processes
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 2003, Professor Whitt. Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18.
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
Eulerian (Probability-Based) Approach
 Eulerian (Probability-Based) Approach Tuesday, March 03, 2015 1:59 PM Office hours for Wednesday, March 4 shifted to 5:30-6:30 PM. Homework 2 posted, due Tuesday, March 17 at 2 PM. correction: the drifts
Eulerian (Probability-Based) Approach Tuesday, March 03, 2015 1:59 PM Office hours for Wednesday, March 4 shifted to 5:30-6:30 PM. Homework 2 posted, due Tuesday, March 17 at 2 PM. correction: the drifts
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Temporal Point Processes the Conditional Intensity Function
 Temporal Point Processes the Conditional Intensity Function Jakob G. Rasmussen Department of Mathematics Aalborg University Denmark February 8, 2010 1/10 Temporal point processes A temporal point process
Temporal Point Processes the Conditional Intensity Function Jakob G. Rasmussen Department of Mathematics Aalborg University Denmark February 8, 2010 1/10 Temporal point processes A temporal point process
So we will instead use the Jacobian method for inferring the PDF of functionally related random variables; see Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis Sec. 4.1.
 2011 Page 1 Simulating Gaussian Random Variables Monday, February 14, 2011 2:00 PM Readings: Kloeden and Platen Sec. 1.3 Why does the Box Muller method work? How was it derived? The basic idea involves
2011 Page 1 Simulating Gaussian Random Variables Monday, February 14, 2011 2:00 PM Readings: Kloeden and Platen Sec. 1.3 Why does the Box Muller method work? How was it derived? The basic idea involves
Chapter 8: Continuous Probability Distributions
 Chapter 8: Continuous Probability Distributions 8.1 Introduction This chapter continued our discussion of probability distributions. It began by describing continuous probability distributions in general,
Chapter 8: Continuous Probability Distributions 8.1 Introduction This chapter continued our discussion of probability distributions. It began by describing continuous probability distributions in general,
STAT 7032 Probability Spring Wlodek Bryc
 STAT 7032 Probability Spring 2018 Wlodek Bryc Created: Friday, Jan 2, 2014 Revised for Spring 2018 Printed: January 9, 2018 File: Grad-Prob-2018.TEX Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Cincinnati,
STAT 7032 Probability Spring 2018 Wlodek Bryc Created: Friday, Jan 2, 2014 Revised for Spring 2018 Printed: January 9, 2018 File: Grad-Prob-2018.TEX Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Cincinnati,
Why study probability? Set theory. ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables
 ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables Readings from G&S: Chapter 1. Section 2.1, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.5, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section
ECE 6010 Lecture 1 Introduction; Review of Random Variables Readings from G&S: Chapter 1. Section 2.1, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 3.1, Section 3.2, Section 3.5, Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section
Let's transfer our results for conditional probability for events into conditional probabilities for random variables.
 Kolmogorov/Smoluchowski equation approach to Brownian motion Tuesday, February 12, 2013 1:53 PM Readings: Gardiner, Secs. 1.2, 3.8.1, 3.8.2 Einstein Homework 1 due February 22. Conditional probability
Kolmogorov/Smoluchowski equation approach to Brownian motion Tuesday, February 12, 2013 1:53 PM Readings: Gardiner, Secs. 1.2, 3.8.1, 3.8.2 Einstein Homework 1 due February 22. Conditional probability
STAT 7032 Probability. Wlodek Bryc
 STAT 7032 Probability Wlodek Bryc Revised for Spring 2019 Printed: January 14, 2019 File: Grad-Prob-2019.TEX Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH 45221 E-mail address:
STAT 7032 Probability Wlodek Bryc Revised for Spring 2019 Printed: January 14, 2019 File: Grad-Prob-2019.TEX Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH 45221 E-mail address:
Probability and Statistics Concepts
 University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
Stochastic Integration (Simple Version)
 Stochastic Integration (Simple Version) Tuesday, March 17, 2015 2:03 PM Reading: Gardiner Secs. 4.1-4.3, 4.4.4 But there are boundary issues when (if ) so we can't apply the standard delta function integration
Stochastic Integration (Simple Version) Tuesday, March 17, 2015 2:03 PM Reading: Gardiner Secs. 4.1-4.3, 4.4.4 But there are boundary issues when (if ) so we can't apply the standard delta function integration
Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29.
 Classification of Birth-Death Chains Tuesday, November 08, 2011 2:02 PM Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29. Continuing with our classification of birth-death chains on nonnegative integers. Last
Classification of Birth-Death Chains Tuesday, November 08, 2011 2:02 PM Homework 3 posted, due Tuesday, November 29. Continuing with our classification of birth-death chains on nonnegative integers. Last
Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
 Review of Probability Theory Tuesday, September 06, 2011 2:05 PM Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
Review of Probability Theory Tuesday, September 06, 2011 2:05 PM Office hours: Wednesdays 11 AM- 12 PM (this class preference), Mondays 2 PM - 3 PM (free-for-all), Wednesdays 3 PM - 4 PM (DE class preference)
Solutions to Homework Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 2011
 Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Chapter 8 - Extensions of the basic HMM
 Chapter 8 - Extensions of the basic HMM 02433 - Hidden Markov Models Martin Wæver Pedersen, Henrik Madsen 28 March, 2011 MWP, compiled March 31, 2011 Extensions Second-order underlying Markov chain. Multinomial-like
Chapter 8 - Extensions of the basic HMM 02433 - Hidden Markov Models Martin Wæver Pedersen, Henrik Madsen 28 March, 2011 MWP, compiled March 31, 2011 Extensions Second-order underlying Markov chain. Multinomial-like
Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, :12 PM
 stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
stochnotes101608 Page 1 Examples of Countable State Markov Chains Thursday, October 16, 2008 12:12 PM Homework 2 solutions will be posted later today. A couple of quick examples. Queueing model (without
(b) What is the variance of the time until the second customer arrives, starting empty, assuming that we measure time in minutes?
 IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
Random Variables. Definition: A random variable (r.v.) X on the probability space (Ω, F, P) is a mapping
 Random Variables Example: We roll a fair die 6 times. Suppose we are interested in the number of 5 s in the 6 rolls. Let X = number of 5 s. Then X could be 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. X = 0 corresponds to the
Random Variables Example: We roll a fair die 6 times. Suppose we are interested in the number of 5 s in the 6 rolls. Let X = number of 5 s. Then X could be 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. X = 0 corresponds to the
Theorem 2.1 (Caratheodory). A (countably additive) probability measure on a field has an extension. n=1
 Chapter 2 Probability measures 1. Existence Theorem 2.1 (Caratheodory). A (countably additive) probability measure on a field has an extension to the generated σ-field Proof of Theorem 2.1. Let F 0 be
Chapter 2 Probability measures 1. Existence Theorem 2.1 (Caratheodory). A (countably additive) probability measure on a field has an extension to the generated σ-field Proof of Theorem 2.1. Let F 0 be
Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
 Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, November 11, 2011 2:05 PM Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
Extinction Probability for Branching Processes Friday, November 11, 2011 2:05 PM Continuing the calculation of the absorption probability for a branching process. Homework 3 is due Tuesday, November 29.
Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation. Lectures Definition 6.1. Two random variables defined on a probability space are said to be
 Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation Lectures 24-30 In this chapter, we introduce expected value or the mean of a random variable. First we define expectation for discrete random variables
Chapter 6 Expectation and Conditional Expectation Lectures 24-30 In this chapter, we introduce expected value or the mean of a random variable. First we define expectation for discrete random variables
Random variables. DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science.
 Random variables DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Motivation Random variables model numerical quantities
Random variables DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Motivation Random variables model numerical quantities
The main results about probability measures are the following two facts:
 Chapter 2 Probability measures The main results about probability measures are the following two facts: Theorem 2.1 (extension). If P is a (continuous) probability measure on a field F 0 then it has a
Chapter 2 Probability measures The main results about probability measures are the following two facts: Theorem 2.1 (extension). If P is a (continuous) probability measure on a field F 0 then it has a
No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1.
 Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Modelling the risk process
 Modelling the risk process Krzysztof Burnecki Hugo Steinhaus Center Wroc law University of Technology www.im.pwr.wroc.pl/ hugo Modelling the risk process 1 Risk process If (Ω, F, P) is a probability space
Modelling the risk process Krzysztof Burnecki Hugo Steinhaus Center Wroc law University of Technology www.im.pwr.wroc.pl/ hugo Modelling the risk process 1 Risk process If (Ω, F, P) is a probability space
Convergence of Random Processes
 Convergence of Random Processes DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Aim Define convergence for random
Convergence of Random Processes DS GA 1002 Probability and Statistics for Data Science http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/dsga1002_fall17 Carlos Fernandez-Granda Aim Define convergence for random
Chapter 1 Statistical Reasoning Why statistics? Section 1.1 Basics of Probability Theory
 Chapter 1 Statistical Reasoning Why statistics? Uncertainty of nature (weather, earth movement, etc. ) Uncertainty in observation/sampling/measurement Variability of human operation/error imperfection
Chapter 1 Statistical Reasoning Why statistics? Uncertainty of nature (weather, earth movement, etc. ) Uncertainty in observation/sampling/measurement Variability of human operation/error imperfection
18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions
 18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Extension theorems Characterizing measures on R d Random variables Outline Extension theorems Characterizing
18.175: Lecture 2 Extension theorems, random variables, distributions Scott Sheffield MIT Outline Extension theorems Characterizing measures on R d Random variables Outline Extension theorems Characterizing
Recap. Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains. ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks
 Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997
 57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997 Part: I II III IV V VI Total Possible Pts: 52 10 12 16 13 12 115 PART ONE Indicate "+" if True and "o" if False: + a. If a component's
57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997 Part: I II III IV V VI Total Possible Pts: 52 10 12 16 13 12 115 PART ONE Indicate "+" if True and "o" if False: + a. If a component's
Simulation. Where real stuff starts
 Simulation Where real stuff starts March 2019 1 ToC 1. What is a simulation? 2. Accuracy of output 3. Random Number Generators 4. How to sample 5. Monte Carlo 6. Bootstrap 2 1. What is a simulation? 3
Simulation Where real stuff starts March 2019 1 ToC 1. What is a simulation? 2. Accuracy of output 3. Random Number Generators 4. How to sample 5. Monte Carlo 6. Bootstrap 2 1. What is a simulation? 3
CAS Exam MAS-1. Howard Mahler. Stochastic Models
 CAS Exam MAS-1 Howard Mahler Stochastic Models 2019 Stochastic Models, HCM 12/31/18, Page 1 The slides are in the same order as the sections of my study guide. Section # Section Name 1 Introduction 2 Exponential
CAS Exam MAS-1 Howard Mahler Stochastic Models 2019 Stochastic Models, HCM 12/31/18, Page 1 The slides are in the same order as the sections of my study guide. Section # Section Name 1 Introduction 2 Exponential
Introduction and Overview STAT 421, SP Course Instructor
 Introduction and Overview STAT 421, SP 212 Prof. Prem K. Goel Mon, Wed, Fri 3:3PM 4:48PM Postle Hall 118 Course Instructor Prof. Goel, Prem E mail: goel.1@osu.edu Office: CH 24C (Cockins Hall) Phone: 614
Introduction and Overview STAT 421, SP 212 Prof. Prem K. Goel Mon, Wed, Fri 3:3PM 4:48PM Postle Hall 118 Course Instructor Prof. Goel, Prem E mail: goel.1@osu.edu Office: CH 24C (Cockins Hall) Phone: 614
IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 7, 2013
 IEOR 316: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 7, 13 SOLUTIONS Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted code of academic honesty. You may keep the exam itself.
IEOR 316: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 7, 13 SOLUTIONS Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted code of academic honesty. You may keep the exam itself.
L06. Chapter 6: Continuous Probability Distributions
 L06 Chapter 6: Continuous Probability Distributions Probability Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Recall Discrete Probability Distributions Could only take on particular values Continuous
L06 Chapter 6: Continuous Probability Distributions Probability Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions Recall Discrete Probability Distributions Could only take on particular values Continuous
Session-Based Queueing Systems
 Session-Based Queueing Systems Modelling, Simulation, and Approximation Jeroen Horters Supervisor VU: Sandjai Bhulai Executive Summary Companies often offer services that require multiple steps on the
Session-Based Queueing Systems Modelling, Simulation, and Approximation Jeroen Horters Supervisor VU: Sandjai Bhulai Executive Summary Companies often offer services that require multiple steps on the
Continuous-time Markov Chains
 Continuous-time Markov Chains Gonzalo Mateos Dept. of ECE and Goergen Institute for Data Science University of Rochester gmateosb@ece.rochester.edu http://www.ece.rochester.edu/~gmateosb/ October 23, 2017
Continuous-time Markov Chains Gonzalo Mateos Dept. of ECE and Goergen Institute for Data Science University of Rochester gmateosb@ece.rochester.edu http://www.ece.rochester.edu/~gmateosb/ October 23, 2017
6 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)
 6 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) The underlying idea in MCMC is to replace the iid samples of basic MC methods, with dependent samples from an ergodic Markov chain, whose limiting (stationary) distribution
6 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) The underlying idea in MCMC is to replace the iid samples of basic MC methods, with dependent samples from an ergodic Markov chain, whose limiting (stationary) distribution
Figure 10.1: Recording when the event E occurs
 10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
Discrete probability distributions
 Discrete probability s BSAD 30 Dave Novak Fall 08 Source: Anderson et al., 05 Quantitative Methods for Business th edition some slides are directly from J. Loucks 03 Cengage Learning Covered so far Chapter
Discrete probability s BSAD 30 Dave Novak Fall 08 Source: Anderson et al., 05 Quantitative Methods for Business th edition some slides are directly from J. Loucks 03 Cengage Learning Covered so far Chapter
Computer Applications for Engineers ET 601
 Computer Applications for Engineers ET 601 Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Random Variables (Con t) 1 Office Hours: (BKD 3601-7) Wednesday 9:30-11:30 Wednesday 16:00-17:00 Thursday
Computer Applications for Engineers ET 601 Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th Random Variables (Con t) 1 Office Hours: (BKD 3601-7) Wednesday 9:30-11:30 Wednesday 16:00-17:00 Thursday
IEOR 4106: Spring Solutions to Homework Assignment 7: Due on Tuesday, March 22.
 IEOR 46: Spring Solutions to Homework Assignment 7: Due on Tuesday, March. More of Chapter 5: Read the rest of Section 5.3, skipping Examples 5.7 (Coupon Collecting), 5. (Insurance claims)and Subsection
IEOR 46: Spring Solutions to Homework Assignment 7: Due on Tuesday, March. More of Chapter 5: Read the rest of Section 5.3, skipping Examples 5.7 (Coupon Collecting), 5. (Insurance claims)and Subsection
6. Bernoulli Trials and the Poisson Process
 1 of 5 7/16/2009 7:09 AM Virtual Laboratories > 14. The Poisson Process > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 6. Bernoulli Trials and the Poisson Process Basic Comparison In some sense, the Poisson process is a continuous time
1 of 5 7/16/2009 7:09 AM Virtual Laboratories > 14. The Poisson Process > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 6. Bernoulli Trials and the Poisson Process Basic Comparison In some sense, the Poisson process is a continuous time
Randomized Algorithms
 Randomized Algorithms Prof. Tapio Elomaa tapio.elomaa@tut.fi Course Basics A new 4 credit unit course Part of Theoretical Computer Science courses at the Department of Mathematics There will be 4 hours
Randomized Algorithms Prof. Tapio Elomaa tapio.elomaa@tut.fi Course Basics A new 4 credit unit course Part of Theoretical Computer Science courses at the Department of Mathematics There will be 4 hours
Northwestern University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Northwestern University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 454: Modeling and Analysis of Communication Networks Spring 2008 Probability Review As discussed in Lecture 1, probability
Northwestern University Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EECS 454: Modeling and Analysis of Communication Networks Spring 2008 Probability Review As discussed in Lecture 1, probability
POISSON PROCESSES 1. THE LAW OF SMALL NUMBERS
 POISSON PROCESSES 1. THE LAW OF SMALL NUMBERS 1.1. The Rutherford-Chadwick-Ellis Experiment. About 90 years ago Ernest Rutherford and his collaborators at the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge conducted
POISSON PROCESSES 1. THE LAW OF SMALL NUMBERS 1.1. The Rutherford-Chadwick-Ellis Experiment. About 90 years ago Ernest Rutherford and his collaborators at the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge conducted
Probability and Statistics for Data Science. Carlos Fernandez-Granda
 Probability and Statistics for Data Science Carlos Fernandez-Granda Preface These notes were developed for the course Probability and Statistics for Data Science at the Center for Data Science in NYU.
Probability and Statistics for Data Science Carlos Fernandez-Granda Preface These notes were developed for the course Probability and Statistics for Data Science at the Center for Data Science in NYU.
Independent random variables
 CHAPTER 2 Independent random variables 2.1. Product measures Definition 2.1. Let µ i be measures on (Ω i,f i ), 1 i n. Let F F 1... F n be the sigma algebra of subsets of Ω : Ω 1... Ω n generated by all
CHAPTER 2 Independent random variables 2.1. Product measures Definition 2.1. Let µ i be measures on (Ω i,f i ), 1 i n. Let F F 1... F n be the sigma algebra of subsets of Ω : Ω 1... Ω n generated by all
Random Variables Example:
 Random Variables Example: We roll a fair die 6 times. Suppose we are interested in the number of 5 s in the 6 rolls. Let X = number of 5 s. Then X could be 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. X = 0 corresponds to the
Random Variables Example: We roll a fair die 6 times. Suppose we are interested in the number of 5 s in the 6 rolls. Let X = number of 5 s. Then X could be 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. X = 0 corresponds to the
Basic Measure and Integration Theory. Michael L. Carroll
 Basic Measure and Integration Theory Michael L. Carroll Sep 22, 2002 Measure Theory: Introduction What is measure theory? Why bother to learn measure theory? 1 What is measure theory? Measure theory is
Basic Measure and Integration Theory Michael L. Carroll Sep 22, 2002 Measure Theory: Introduction What is measure theory? Why bother to learn measure theory? 1 What is measure theory? Measure theory is
Abstract Measure Theory
 2 Abstract Measure Theory Lebesgue measure is one of the premier examples of a measure on R d, but it is not the only measure and certainly not the only important measure on R d. Further, R d is not the
2 Abstract Measure Theory Lebesgue measure is one of the premier examples of a measure on R d, but it is not the only measure and certainly not the only important measure on R d. Further, R d is not the
CS 361: Probability & Statistics
 February 26, 2018 CS 361: Probability & Statistics Random variables The discrete uniform distribution If every value of a discrete random variable has the same probability, then its distribution is called
February 26, 2018 CS 361: Probability & Statistics Random variables The discrete uniform distribution If every value of a discrete random variable has the same probability, then its distribution is called
2. Transience and Recurrence
 Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
Virtual Laboratories > 15. Markov Chains > 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. Transience and Recurrence The study of Markov chains, particularly the limiting behavior, depends critically on the random times
3 Continuous Random Variables
 Jinguo Lian Math437 Notes January 15, 016 3 Continuous Random Variables Remember that discrete random variables can take only a countable number of possible values. On the other hand, a continuous random
Jinguo Lian Math437 Notes January 15, 016 3 Continuous Random Variables Remember that discrete random variables can take only a countable number of possible values. On the other hand, a continuous random
Section 2: Classes of Sets
 Section 2: Classes of Sets Notation: If A, B are subsets of X, then A \ B denotes the set difference, A \ B = {x A : x B}. A B denotes the symmetric difference. A B = (A \ B) (B \ A) = (A B) \ (A B). Remarks
Section 2: Classes of Sets Notation: If A, B are subsets of X, then A \ B denotes the set difference, A \ B = {x A : x B}. A B denotes the symmetric difference. A B = (A \ B) (B \ A) = (A B) \ (A B). Remarks
Classical Queueing Models.
 Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Simulation. Where real stuff starts
 1 Simulation Where real stuff starts ToC 1. What is a simulation? 2. Accuracy of output 3. Random Number Generators 4. How to sample 5. Monte Carlo 6. Bootstrap 2 1. What is a simulation? 3 What is a simulation?
1 Simulation Where real stuff starts ToC 1. What is a simulation? 2. Accuracy of output 3. Random Number Generators 4. How to sample 5. Monte Carlo 6. Bootstrap 2 1. What is a simulation? 3 What is a simulation?
STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes. Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed.
 STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed. Chapter 1: Combinatorial Analysis Demonstrate the ability to solve combinatorial
STAT 302 Introduction to Probability Learning Outcomes Textbook: A First Course in Probability by Sheldon Ross, 8 th ed. Chapter 1: Combinatorial Analysis Demonstrate the ability to solve combinatorial
Page 0 of 5 Final Examination Name. Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam.
 Final Examination Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam. To receive full credit, show enough work to indicate your logic. Do not spend time calculating. You will receive full credit
Final Examination Closed book. 120 minutes. Cover page plus five pages of exam. To receive full credit, show enough work to indicate your logic. Do not spend time calculating. You will receive full credit
Errata for the ASM Study Manual for Exam P, Fourth Edition By Dr. Krzysztof M. Ostaszewski, FSA, CFA, MAAA
 Errata for the ASM Study Manual for Exam P, Fourth Edition By Dr. Krzysztof M. Ostaszewski, FSA, CFA, MAAA (krzysio@krzysio.net) Effective July 5, 3, only the latest edition of this manual will have its
Errata for the ASM Study Manual for Exam P, Fourth Edition By Dr. Krzysztof M. Ostaszewski, FSA, CFA, MAAA (krzysio@krzysio.net) Effective July 5, 3, only the latest edition of this manual will have its
References: Shreve Secs. 1.1, 1.2 Gardiner Secs. 2.1, 2.2 Grigoriu Secs , 2.10
 2011 Page 1 Random Variables Monday, January 31, 2011 2:09 PM References: Shreve Secs. 1.1, 1.2 Gardiner Secs. 2.1, 2.2 Grigoriu Secs. 2.1-2.5, 2.10 We will introduce the measure-theoretic formulation
2011 Page 1 Random Variables Monday, January 31, 2011 2:09 PM References: Shreve Secs. 1.1, 1.2 Gardiner Secs. 2.1, 2.2 Grigoriu Secs. 2.1-2.5, 2.10 We will introduce the measure-theoretic formulation
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design
 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
Supratim Ray
 Supratim Ray sray@cns.iisc.ernet.in Biophysics of Action Potentials Passive Properties neuron as an electrical circuit Passive Signaling cable theory Active properties generation of action potential Techniques
Supratim Ray sray@cns.iisc.ernet.in Biophysics of Action Potentials Passive Properties neuron as an electrical circuit Passive Signaling cable theory Active properties generation of action potential Techniques
Homework 4 Math 11, UCSD, Winter 2018 Due on Tuesday, 13th February
 PID: Last Name, First Name: Section: Approximate time spent to complete this assignment: hour(s) Homework 4 Math 11, UCSD, Winter 2018 Due on Tuesday, 13th February Readings: Chapters 16.6-16.7 and the
PID: Last Name, First Name: Section: Approximate time spent to complete this assignment: hour(s) Homework 4 Math 11, UCSD, Winter 2018 Due on Tuesday, 13th February Readings: Chapters 16.6-16.7 and the
Transience: Whereas a finite closed communication class must be recurrent, an infinite closed communication class can be transient:
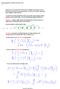 Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Stochastic2010 Page 1 Long-Time Properties of Countable-State Markov Chains Tuesday, March 23, 2010 2:14 PM Homework 2: if you turn it in by 5 PM on 03/25, I'll grade it by 03/26, but you can turn it in
Minicourse on: Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Simulation Techniques in Statistics
 Minicourse on: Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Simulation Techniques in Statistics Eric Slud, Statistics Program Lecture 1: Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm, plus background in Simulation and Markov Chains. Lecture
Minicourse on: Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Simulation Techniques in Statistics Eric Slud, Statistics Program Lecture 1: Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm, plus background in Simulation and Markov Chains. Lecture
Temporal point processes: the conditional intensity function
 Temporal point processes: the conditional intensity function Jakob Gulddahl Rasmussen December 21, 2009 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Evolutionary point processes 2 2.1 Evolutionarity..............................
Temporal point processes: the conditional intensity function Jakob Gulddahl Rasmussen December 21, 2009 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Evolutionary point processes 2 2.1 Evolutionarity..............................
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran November 13, 2014.
 EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran November 13, 2014 Midterm Exam 2 Last name First name SID Rules. DO NOT open the exam until instructed
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran November 13, 2014 Midterm Exam 2 Last name First name SID Rules. DO NOT open the exam until instructed
Writing proofs for MATH 51H Section 2: Set theory, proofs of existential statements, proofs of uniqueness statements, proof by cases
 Writing proofs for MATH 51H Section 2: Set theory, proofs of existential statements, proofs of uniqueness statements, proof by cases September 22, 2018 Recall from last week that the purpose of a proof
Writing proofs for MATH 51H Section 2: Set theory, proofs of existential statements, proofs of uniqueness statements, proof by cases September 22, 2018 Recall from last week that the purpose of a proof
Continuum Probability and Sets of Measure Zero
 Chapter 3 Continuum Probability and Sets of Measure Zero In this chapter, we provide a motivation for using measure theory as a foundation for probability. It uses the example of random coin tossing to
Chapter 3 Continuum Probability and Sets of Measure Zero In this chapter, we provide a motivation for using measure theory as a foundation for probability. It uses the example of random coin tossing to
1 Delayed Renewal Processes: Exploiting Laplace Transforms
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I Professor Whitt, Tuesday, October 22, 213 Renewal Theory: Proof of Blackwell s theorem 1 Delayed Renewal Processes: Exploiting Laplace Transforms The proof of Blackwell s
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I Professor Whitt, Tuesday, October 22, 213 Renewal Theory: Proof of Blackwell s theorem 1 Delayed Renewal Processes: Exploiting Laplace Transforms The proof of Blackwell s
MAT SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions.
 MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, :04 PM
 stochnotes102008 Page 1 Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, 2008 12:04 PM Looking for a detailed balance solution for a stationary distribution is a useful technique. Stationary
stochnotes102008 Page 1 Detailed Balance and Branching Processes Monday, October 20, 2008 12:04 PM Looking for a detailed balance solution for a stationary distribution is a useful technique. Stationary
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research
 PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
Introduction to Rare Event Simulation
 Introduction to Rare Event Simulation Brown University: Summer School on Rare Event Simulation Jose Blanchet Columbia University. Department of Statistics, Department of IEOR. Blanchet (Columbia) 1 / 31
Introduction to Rare Event Simulation Brown University: Summer School on Rare Event Simulation Jose Blanchet Columbia University. Department of Statistics, Department of IEOR. Blanchet (Columbia) 1 / 31
