DATA MINING LECTURE 13. Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
|
|
|
- Maude Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
2 How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories
3 How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates: Find relevant docs in a small and trusted set e.g., Newspaper articles, Patents, etc. ( needle-in-a-haystack ) Limitation of keywords (synonyms, polysemy, etc) But: Web is huge, full of untrusted documents, random things, web spam, etc. Everyone can create a web page of high production value Rich diversity of people issuing queries Dynamic and constantly-changing nature of web content
4 How to organize the web Third try (the Google era): using the web graph Sift from relevance to authoritativeness It is not only important that a page is relevant, but that it is also important on the web For example, what kind of results would we like to get for the query greek newspapers?
5 Link Analysis Ranking Use the graph structure in order to determine the relative importance of the nodes Applications: Ranking on graphs (Web, Twitter, FB, etc) Intuition: An edge from node p to node q denotes endorsement Node p endorses/recommends/confirms the authority/centrality/importance of node q Use the graph of recommendations to assign an authority value to every node
6 Link Analysis Not all web pages are equal on the web What is the simplest way to measure importance of a page on the web?
7 Rank by Popularity Rank pages according to the number of incoming edges (in-degree, degree centrality) v v v 3. Red Page. Yellow Page 3. Blue Page 4. Purple Page. Green Page v v 4
8 Popularity It is not important only how many link to you, but how important are the people that link to you. Good authorities are pointed by good authorities Recursive definition of importance
9 PAGERANK
10 PageRank Good authorities should be pointed by good authorities The value of a node is the value of the nodes that point to it. How do we implement that? Assume that we have a unit of authority to distribute to all nodes. Initially each node gets n amount of authority Each node distributes the authority value they have to their neighbors The authority value of each node is the sum of the authority fractions it collects from its neighbors. w v = d out u w u w v : the PageRank value of node v u v Recursive definition
11 Example v w = /3 w 4 + / w w = / w + w 3 + /3 w 4 w 3 = / w + /3 w 4 w 4 = / w w = w v v 3 w v = u v d out u w u v v 4
12 Computing PageRank weights A simple way to compute the weights is by iteratively updating the weights PageRank Algorithm Initialize all PageRank weights to n Repeat: w v = u v d out u w u Until the weights do not change This process converges
13 Example w = /3 w 4 + / w w v = u v d out u w u v w = / w + w 3 + /3 w 4 v v 3 w 3 = / w + /3 w 4 w 4 = / w w = w w w w 3 w 4 w t=..... t= t= t= t= v v 4 Think of the weight as a fluid: there is constant amount of it in the graph, but it moves around until it stabilizes
14 Example w = /3 w 4 + / w w v = u v d out u w u v w = / w + w 3 + /3 w 4 v v 3 w 3 = / w + /3 w 4 w 4 = / w w = w v v 4 w w w 3 w 4 w t= Think of the weight as a fluid: there is constant amount of it in the graph, but it moves around until it stabilizes
15 Random Walks on Graphs The algorithm defines a random walk on the graph Random walk: Start from a node chosen uniformly at random with probability n. Pick one of the outgoing edges uniformly at random Move to the destination of the edge Repeat. The Random Surfer model Users wander on the web, following links.
16 Example Step v v v 3 v v 4
17 Example Step v v v 3 v v 4
18 Example Step v v v 3 v v 4
19 Example Step v v v 3 v v 4
20 Example Step v v v 3 v v 4
21 Example Step v v v 3 v v 4
22 Example Step 3 v v v 3 v v 4
23 Example Step 3 v v v 3 v v 4
24 Example Step 4 v v v 3 v v 4
25 Random walk Question: what is the probability p i t of being at node i after t steps? v p = p t = 3 p 4 t + p t v v 3 p = p t = p t + p 3 t + 3 p 4 t p 3 = p 3 t = p t + 3 p 4 t p 4 = p 4 t = p t v v 4 p = p t = p t The equations are the same as those for the PageRank computation
26 Markov chains A Markov chain describes a discrete time stochastic process over a set of states S = {s, s,, s n } according to a transition probability matrix P = {P ij } P ij = probability of moving to state j when at state i Matrix P has the property that the entries of all rows sum to j P i, j = A matrix with this property is called stochastic State probability distribution: The vector p t probability of being at state s i after t steps = (p i t, p t,, p n t ) that stores the Memorylessness property: The next state of the chain depends only at the current state and not on the past of the process (first order MC) Higher order MCs are also possible Markov Chain Theory: After infinite steps the state probability vector converges to a unique distribution if the chain is irreducible and aperiodic
27 Random walks Random walks on graphs correspond to Markov Chains The set of states S is the set of nodes of the graph G The transition probability matrix is the probability that we follow an edge from one node to another P i, j = deg out i We can compute the vector p t at step t using a vector-matrix multiplication p t+ = p t P
28 An example P v v 3 v 4 v v A
29 An example P v v v 3 p t = 3 p 4 t + p t p t = p t + p 3 t + 3 p 4 t v v 4 p 3 t = p t + 3 p 4 t p 4 t = p t p t = p t
30 Stationary distribution The stationary distribution of a random walk with transition matrix P, is a probability distribution π, such that π = πp The stationary distribution is an eigenvector of matrix P the principal left eigenvector of P stochastic matrices have maximum eigenvalue The probability π i is the fraction of times that we visited state i as t Markov Chain Theory: The random walk converges to a unique stationary distribution independent of the initial vector if the graph is strongly connected, and not bipartite.
31 Computing the stationary distribution The Power Method Initialize p to some distribution Repeat p t = p t P Until convergence After many iterations p t π regardless of the initial vector p Power method because it computes p t = p P t Rate of convergence determined by the second eigenvalue λ
32 The stationary distribution What is the meaning of the stationary distribution π of a random walk? π(i): the probability of being at node i after very large (infinite) number of steps π is the left eigenvector of transition matrix P π = p P, where P is the transition matrix, p the original vector P i, j : probability of going from i to j in one step P (i, j): probability of going from i to j in two steps (probability of all paths of length ) P i, j = π(j): probability of going from i to j in infinite steps starting point does not matter.
33 The PageRank random walk Vanilla random walk make the adjacency matrix stochastic and run a random walk P
34 The PageRank random walk What about sink nodes? what happens when the random walk moves to a node without any outgoing inks? P
35 3 3 3 P' The PageRank random walk Replace these row vectors with a vector v typically, the uniform vector P = P + dv T otherwise sink is i if d
36 The PageRank random walk What about loops? Spider traps
37 3 3 3 P'' ) ( The PageRank random walk Add a random jump to vector v with prob -α typically, to a uniform vector Restarts after /(-α) steps in expectation Guarantees irreducibility, convergence P = αp + (-α)uv T, where u is the vector of all s Random walk with restarts
38 PageRank algorithm [BP98] The Random Surfer model pick a page at random with probability - α jump to a random page with probability α follow a random outgoing link Rank according to the stationary distribution PR( q) PR( p) Out ( q ) n q p α =.8 in most cases. Red Page. Purple Page 3. Yellow Page 4. Blue Page. Green Page
39 PageRank: Example
40 Stationary distribution with random jump If v is the jump vector p = v p = αp P + α v = αvp + α v p = αp P + α v = α vp + α vαp + α v p = α v + α vαp + α vα P + = α I αp With the random jump the shorter paths are more important, since the weight decreases exponentially makes sense when thought of as a restart If v is not uniform, we can bias the random walk towards the nodes that are close to v Personalized and Topic-Specific Pagerank.
41 Effects of random jump Guarantees convergence to unique distribution Motivated by the concept of random surfer Offers additional flexibility personalization anti-spam Controls the rate of convergence the second eigenvalue of matrix P is α
42 Random walks on undirected graphs For undirected graphs, the stationary distribution is proportional to the degrees of the nodes Thus in this case a random walk is the same as degree popularity This is no longer true if we do random jumps Now the short paths play a greater role, and the previous distribution does not hold.
43 Pagerank implementation Store the graph in adjacency list, or list of edges Keep current pagerank values and new pagerank values Go through edges and update the values of the destination nodes. Repeat until the difference (L or L difference) is below some small value ε.
44 A (Matlab-friendly) PageRank algorithm Performing vanilla power method is now too expensive the matrix is not sparse q = v t = repeat t q δ t = t + until δ < ε T t P'' q q t q t Efficient computation of y = (P ) T x y αp β x T x y y y βv P = normalized adjacency matrix P = P + dv T, where d i is if i is sink and o.w. P = αp + (-α)uv T, where u is the vector of all s
45 Pagerank history Huge advantage for Google in the early days It gave a way to get an idea for the value of a page, which was useful in many different ways Put an order to the web. After a while it became clear that the anchor text was probably more important for ranking Also, link spam became a new (dark) art Flood of research Numerical analysis got rejuvenated Huge number of variations Efficiency became a great issue. Huge number of applications in different fields Random walk is often referred to as PageRank.
46 THE HITS ALGORITHM
47 The HITS algorithm Another algorithm proposed around the same time as Pagerank for using the hyperlinks to rank pages Kleinberg: then an intern at IBM Almaden IBM never made anything out of it
48 Query dependent input Root set obtained from a text-only search engine Root Set
49 Query dependent input IN Root Set OUT
50 Query dependent input IN Root Set OUT
51 Query dependent input Base Set IN Root Set OUT
52 Hubs and Authorities [K98] Authority is not necessarily transferred directly between authorities Pages have double identity hub identity authority identity Good hubs point to good authorities Good authorities are pointed by good hubs hubs authorities
53 Hubs and Authorities Two kind of weights: Hub weight Authority weight The hub weight is the sum of the authority weights of the authorities pointed to by the hub The authority weight is the sum of the hub weights that point to this authority.
54 HITS Algorithm Initialize all weights to. Repeat until convergence O operation : hubs collect the weight of the authorities h i a j j: i j I operation: authorities collect the weight of the hubs a i h j j: ji Normalize weights under some norm
55 HITS and eigenvectors The HITS algorithm is a power-method eigenvector computation In vector terms a t = A T h t and h t = Aa t a t = A T Aa t and h t = AA T h t Repeated iterations will converge to the eigenvectors The authority weight vector a is the eigenvector of A T A The hub weight vector h is the eigenvector of AA T The vectors a and h are called the singular vectors of the matrix A
56 Singular Value Decomposition r : rank of matrix A σ σ σ r : singular values (square roots of eig-vals AA T, A T A) : left singular vectors (eig-vectors of AA T ) : right singular vectors (eig-vectors of A T A) r r r T v v v σ σ σ u u u V Σ U A [n r] [r r] [r n] r u,,,u u r v,,,v v T r r r T T v σ u v u σ v σ u A
57 Why does the Power Method work? If a matrix R is real and symmetric, it has real eigenvalues and eigenvectors: λ, w, λ, w,, (λ r, w r ) r is the rank of the matrix λ λ λ r For any matrix R, the eigenvectors w, w,, w r of R define a basis of the vector space For any vector x, Rx = α w + a w + + a r w r After t multiplications we have: R t x = λ t α w + λ t a w + + λ t a r w r Normalizing leaves only the term w.
58 Example Initialize hubs authorities
59 Example Step : O operation 3 hubs authorities
60 Example Step : I operation 3 6 hubs authorities
61 Example Step : Normalization (Max norm) /3 /3 /3 /3 hubs /6 /6 /6 /6 authorities
62 Example Step : O step /6 6/6 7/6 /6 hubs /6 /6 /6 /6 authorities
63 Example Step : I step /6 6/6 7/6 /6 hubs 33/6 7/6 3/6 7/6 /6 authorities
64 Example Step : Normalization 6/6 /6 7/6 /6 7/33 3/33 7/33 /33 hubs authorities
65 Example Convergence hubs authorities
66 OTHER ALGORITHMS
67 The SALSA algorithm [LM] Perform a random walk alternating between hubs and authorities What does this random walk converge to? hubs authorities The graph is essentially undirected, so it will be proportional to the degree.
68 Social network analysis Evaluate the centrality of individuals in social networks degree centrality the (weighted) degree of a node distance centrality the average (weighted) distance of a node to the rest in the graph v betweenness centrality D c u v d(v,u) the average number of (weighted) shortest paths that use node v B c v svt σst(v) σ st
69 Counting paths Katz 3 The importance of a node is measured by the weighted sum of paths that lead to this node A m [i,j] = number of paths of length m from i to j Compute m P ba b A b A converges when b < λ (A) I ba I Rank nodes according to the column sums of the matrix P m
70 Bibliometrics Impact factor (E. Garfield 7) counts the number of citations received for papers of the journal in the previous two years Pinsky-Narin 76 perform a random walk on the set of journals P ij = the fraction of citations from journal i that are directed to journal j
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Mining PageRank. From Stanford C246
 Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Link Mining PageRank From Stanford C246 Broad Question: How to organize the Web? First try: Human curated Web dictionaries Yahoo, DMOZ LookSmart Second try: Web Search Information Retrieval investigates
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University.
 Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Slides based on those in:
 Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Data Mining and Matrices
 Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
Models and Algorithms for Complex Networks. Link Analysis Ranking
 Models and Algorithms for Complex Networks Link Analysis Ranking Why Link Analysis? First generation search engines view documents as flat text files could not cope with size, spamming, user needs Second
Models and Algorithms for Complex Networks Link Analysis Ranking Why Link Analysis? First generation search engines view documents as flat text files could not cope with size, spamming, user needs Second
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval
 Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Link Analysis. Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016
 Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University.
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
LINK ANALYSIS. Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS
 LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis. Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa
 Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
PageRank algorithm Hubs and Authorities. Data mining. Web Data Mining PageRank, Hubs and Authorities. University of Szeged.
 Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
CS 277: Data Mining. Mining Web Link Structure. CS 277: Data Mining Lectures Analyzing Web Link Structure Padhraic Smyth, UC Irvine
 CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK. Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech. Lecture for CS 6505
 INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
IR: Information Retrieval
 / 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
/ 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
Link Analysis. Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze
 Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK. Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech. Lecture for CS 6505
 INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
INTRODUCTION TO MCMC AND PAGERANK Eric Vigoda Georgia Tech Lecture for CS 6505 1 MARKOV CHAIN BASICS 2 ERGODICITY 3 WHAT IS THE STATIONARY DISTRIBUTION? 4 PAGERANK 5 MIXING TIME 6 PREVIEW OF FURTHER TOPICS
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3
 Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks
 ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence
 Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks
 Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social
Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social
1998: enter Link Analysis
 1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
Wiki Definition. Reputation Systems I. Outline. Introduction to Reputations. Yury Lifshits. HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte
 Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
PageRank. Ryan Tibshirani /36-662: Data Mining. January Optional reading: ESL 14.10
 PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Data and Algorithms of the Web
 Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
1 Searching the World Wide Web
 Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval. PageRank Con+nued. with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma
 IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval PageRank Con+nued with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma Exercise: Assump0ons underlying PageRank Assump0on 1: A link on the web is a quality signal the
IS4200/CS6200 Informa0on Retrieval PageRank Con+nued with slides from Hinrich Schütze and Chris6na Lioma Exercise: Assump0ons underlying PageRank Assump0on 1: A link on the web is a quality signal the
Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
 Markov Chains Markov chains: 2SAT: Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions rely only on local moves to explore state space. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
Markov Chains Markov chains: 2SAT: Powerful tool for sampling from complicated distributions rely only on local moves to explore state space. Many use Markov chains to model events that arise in nature.
Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4)
 Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Node and Link Analysis
 Node and Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Applied Mathematics and Information Science National Research University Higher School of Economics 10.02.2014 Leonid E. Zhukov (HSE) Lecture 5 10.02.2014
Node and Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Applied Mathematics and Information Science National Research University Higher School of Economics 10.02.2014 Leonid E. Zhukov (HSE) Lecture 5 10.02.2014
A Note on Google s PageRank
 A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
How does Google rank webpages?
 Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Math 304 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks.
 Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
Information Retrieval and Search. Web Linkage Mining. Miłosz Kadziński
 Web Linkage Analysis D24 D4 : Web Linkage Mining Miłosz Kadziński Institute of Computing Science Poznan University of Technology, Poland www.cs.put.poznan.pl/mkadzinski/wpi Web mining: Web Mining Discovery
Web Linkage Analysis D24 D4 : Web Linkage Mining Miłosz Kadziński Institute of Computing Science Poznan University of Technology, Poland www.cs.put.poznan.pl/mkadzinski/wpi Web mining: Web Mining Discovery
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68
 CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
Complex Social System, Elections. Introduction to Network Analysis 1
 Complex Social System, Elections Introduction to Network Analysis 1 Complex Social System, Network I person A voted for B A is more central than B if more people voted for A In-degree centrality index
Complex Social System, Elections Introduction to Network Analysis 1 Complex Social System, Network I person A voted for B A is more central than B if more people voted for A In-degree centrality index
Uncertainty and Randomization
 Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
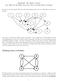 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
CS 3750 Advanced Machine Learning. Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya
 CS 375 Advanced Machine Learning Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya Outline SVD and LSI Kleinberg s Algorithm PageRank Algorithm Vector Space Model Vector space model represents
CS 375 Advanced Machine Learning Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya Outline SVD and LSI Kleinberg s Algorithm PageRank Algorithm Vector Space Model Vector space model represents
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm
 Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
Graph Models The PageRank Algorithm Anna-Karin Tornberg Mathematical Models, Analysis and Simulation Fall semester, 2013 The PageRank Algorithm I Invented by Larry Page and Sergey Brin around 1998 and
25.1 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)
 CS880: Approximations Algorithms Scribe: Dave Andrzejewski Lecturer: Shuchi Chawla Topic: Approx counting/sampling, MCMC methods Date: 4/4/07 The previous lecture showed that, for self-reducible problems,
CS880: Approximations Algorithms Scribe: Dave Andrzejewski Lecturer: Shuchi Chawla Topic: Approx counting/sampling, MCMC methods Date: 4/4/07 The previous lecture showed that, for self-reducible problems,
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 110
 Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks
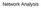 Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation
 Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation Taher Haveliwala, Sepandar Kamvar, Dan Klein, Chris Manning, and Gene Golub Stanford University Abstract. We present a novel technique for speeding up the computation
Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation Taher Haveliwala, Sepandar Kamvar, Dan Klein, Chris Manning, and Gene Golub Stanford University Abstract. We present a novel technique for speeding up the computation
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a
 Journal of Web Engineering, Vol. 0, No. 0 (2003) 000 000 c Rinton Press The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a Vassilis Plachouras University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ UK vassilis@dcs.gla.ac.uk Iadh
Journal of Web Engineering, Vol. 0, No. 0 (2003) 000 000 c Rinton Press The Static Absorbing Model for the Web a Vassilis Plachouras University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ UK vassilis@dcs.gla.ac.uk Iadh
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012
 Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain
 Spectral Graph Theory and Applications WS 20/202 Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Sun Introduction to Markov Chains Definition 5.. A sequence of random variables
Spectral Graph Theory and Applications WS 20/202 Lecture 5: Random Walks and Markov Chain Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Sun Introduction to Markov Chains Definition 5.. A sequence of random variables
6.842 Randomness and Computation March 3, Lecture 8
 6.84 Randomness and Computation March 3, 04 Lecture 8 Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribe: Daniel Grier Useful Linear Algebra Let v = (v, v,..., v n ) be a non-zero n-dimensional row vector and P an n n
6.84 Randomness and Computation March 3, 04 Lecture 8 Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribe: Daniel Grier Useful Linear Algebra Let v = (v, v,..., v n ) be a non-zero n-dimensional row vector and P an n n
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y
 Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds
 MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, 2008 Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds Search for information Assume some resource of interest is stored at the vertices of a network: Web pages Files in a file-sharing
MAE 298, Lecture 8 Feb 4, 2008 Web search and decentralized search on small-worlds Search for information Assume some resource of interest is stored at the vertices of a network: Web pages Files in a file-sharing
SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices)
 Chapter 14 SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Today we continue the topic of low-dimensional approximation to datasets and matrices. Last time we saw the singular
Chapter 14 SVD, Power method, and Planted Graph problems (+ eigenvalues of random matrices) Today we continue the topic of low-dimensional approximation to datasets and matrices. Last time we saw the singular
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method
 eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
eigenvalues, markov matrices, and the power method Slides by Olson. Some taken loosely from Jeff Jauregui, Some from Semeraro L. Olson Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University 2 Web pages are important if people visit them a lot. But we can t watch everybody using the Web. A good surrogate for visiting pages is to assume people follow links
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University 2 Web pages are important if people visit them a lot. But we can t watch everybody using the Web. A good surrogate for visiting pages is to assume people follow links
Faloutsos, Tong ICDE, 2009
 Large Graph Mining: Patterns, Tools and Case Studies Christos Faloutsos Hanghang Tong CMU Copyright: Faloutsos, Tong (29) 2-1 Outline Part 1: Patterns Part 2: Matrix and Tensor Tools Part 3: Proximity
Large Graph Mining: Patterns, Tools and Case Studies Christos Faloutsos Hanghang Tong CMU Copyright: Faloutsos, Tong (29) 2-1 Outline Part 1: Patterns Part 2: Matrix and Tensor Tools Part 3: Proximity
Probability & Computing
 Probability & Computing Stochastic Process time t {X t t 2 T } state space Ω X t 2 state x 2 discrete time: T is countable T = {0,, 2,...} discrete space: Ω is finite or countably infinite X 0,X,X 2,...
Probability & Computing Stochastic Process time t {X t t 2 T } state space Ω X t 2 state x 2 discrete time: T is countable T = {0,, 2,...} discrete space: Ω is finite or countably infinite X 0,X,X 2,...
Google PageRank. Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano
 Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
The Theory behind PageRank
 The Theory behind PageRank Mauro Sozio Telecom ParisTech May 21, 2014 Mauro Sozio (LTCI TPT) The Theory behind PageRank May 21, 2014 1 / 19 A Crash Course on Discrete Probability Events and Probability
The Theory behind PageRank Mauro Sozio Telecom ParisTech May 21, 2014 Mauro Sozio (LTCI TPT) The Theory behind PageRank May 21, 2014 1 / 19 A Crash Course on Discrete Probability Events and Probability
Finding central nodes in large networks
 Finding central nodes in large networks Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands Woudschoten Conference 2017 Complex networks Networks: Internet, WWW, social
Finding central nodes in large networks Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands Woudschoten Conference 2017 Complex networks Networks: Internet, WWW, social
Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page
![Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies. authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page](/thumbs/95/125556981.jpg) IV.3 HITS Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) hubs as good link sources (~high outdegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page a
IV.3 HITS Hyperlinked-Induced Topic Search (HITS) identifies authorities as good content sources (~high indegree) hubs as good link sources (~high outdegree) HITS [Kleinberg 99] considers a web page a
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors
 MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING
 CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING Graph and Network Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu May 31, 2017 Methods Learnt Classification Clustering Vector Data Text Data Recommender System Decision Tree; Naïve
CS249: ADVANCED DATA MINING Graph and Network Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu May 31, 2017 Methods Learnt Classification Clustering Vector Data Text Data Recommender System Decision Tree; Naïve
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
As it is not necessarily possible to satisfy this equation, we just ask for a solution to the more general equation
 Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
The Google Markov Chain: convergence speed and eigenvalues
 U.U.D.M. Project Report 2012:14 The Google Markov Chain: convergence speed and eigenvalues Fredrik Backåker Examensarbete i matematik, 15 hp Handledare och examinator: Jakob Björnberg Juni 2012 Department
U.U.D.M. Project Report 2012:14 The Google Markov Chain: convergence speed and eigenvalues Fredrik Backåker Examensarbete i matematik, 15 hp Handledare och examinator: Jakob Björnberg Juni 2012 Department
Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming
 CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
CSE 521: Design and Analysis of Algorithms I Winter 2017 Lecture 14: Random Walks, Local Graph Clustering, Linear Programming Lecturer: Shayan Oveis Gharan 3/01/17 Scribe: Laura Vonessen Disclaimer: These
Calculating Web Page Authority Using the PageRank Algorithm
 Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Algebraic Representation of Networks
 Algebraic Representation of Networks 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu Describing networks with matrices (1) Adjacency matrix A matrix with rows and columns labeled by
Algebraic Representation of Networks 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 Hiroki Sayama sayama@binghamton.edu Describing networks with matrices (1) Adjacency matrix A matrix with rows and columns labeled by
CS47300: Web Information Search and Management
 CS473: Web Information Search and Management Using Graph Structure for Retrieval Prof. Chris Clifton 24 September 218 Material adapted from slides created by Dr. Rong Jin (formerly Michigan State, now
CS473: Web Information Search and Management Using Graph Structure for Retrieval Prof. Chris Clifton 24 September 218 Material adapted from slides created by Dr. Rong Jin (formerly Michigan State, now
How works. or How linear algebra powers the search engine. M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University
 How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
Definition A finite Markov chain is a memoryless homogeneous discrete stochastic process with a finite number of states.
 Chapter 8 Finite Markov Chains A discrete system is characterized by a set V of states and transitions between the states. V is referred to as the state space. We think of the transitions as occurring
Chapter 8 Finite Markov Chains A discrete system is characterized by a set V of states and transitions between the states. V is referred to as the state space. We think of the transitions as occurring
Introduction to Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2013-07-10 1/43
Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2013-07-10 1/43
6.842 Randomness and Computation February 24, Lecture 6
 6.8 Randomness and Computation February, Lecture 6 Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribe: Mutaamba Maasha Outline Random Walks Markov Chains Stationary Distributions Hitting, Cover, Commute times Markov Chains
6.8 Randomness and Computation February, Lecture 6 Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribe: Mutaamba Maasha Outline Random Walks Markov Chains Stationary Distributions Hitting, Cover, Commute times Markov Chains
CS54701 Information Retrieval. Link Analysis. Luo Si. Department of Computer Science Purdue University. Borrowed Slides from Prof.
 CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU) Citation Analysis Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site
CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU) Citation Analysis Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site
Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search
 CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (2 of 4) 19 Computing spectral ranking with the push procedure
 Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 19-04/02/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (2 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 19-04/02/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (2 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1.
 Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Stationary Distributions Monday, September 28, 2015 2:02 PM No class on Thursday, October 1. No office hours on Tuesday, September 29 and Thursday, October 1. Homework 1 due Friday, October 2 at 5 PM strongly
Intelligent Data Analysis. PageRank. School of Computer Science University of Birmingham
 Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
Intelligent Data Analysis PageRank Peter Tiňo School of Computer Science University of Birmingham Information Retrieval on the Web Most scoring methods on the Web have been derived in the context of Information
Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test]
![Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test] Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test] = Pr[positive test]](/thumbs/77/74699650.jpg) 146 Probability Pr[virus] = 0.00001 Pr[no virus] = 0.99999 Pr[positive test virus] = 0.99 Pr[positive test no virus] = 0.01 Pr[virus positive test] = Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] = 0.99 0.00001 =
146 Probability Pr[virus] = 0.00001 Pr[no virus] = 0.99999 Pr[positive test virus] = 0.99 Pr[positive test no virus] = 0.01 Pr[virus positive test] = Pr[positive test virus] Pr[virus] = 0.99 0.00001 =
Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm Anthony Trubiano April 11th, 2018 1 Introduction Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are a class of algorithms for sampling from a probability
Markov Chain Monte Carlo The Metropolis-Hastings Algorithm Anthony Trubiano April 11th, 2018 1 Introduction Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods are a class of algorithms for sampling from a probability
The Dynamic Absorbing Model for the Web
 The Dynamic Absorbing Model for the Web Gianni Amati, Iadh Ounis, Vassilis Plachouras Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ, U.K. Abstract In this paper we propose a new
The Dynamic Absorbing Model for the Web Gianni Amati, Iadh Ounis, Vassilis Plachouras Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow Glasgow G12 8QQ, U.K. Abstract In this paper we propose a new
Inf 2B: Ranking Queries on the WWW
 Inf B: Ranking Queries on the WWW Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Queries Suppose we have an Inverted Index for a set of webpages. Disclaimer Not really the scenario of
Inf B: Ranking Queries on the WWW Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Queries Suppose we have an Inverted Index for a set of webpages. Disclaimer Not really the scenario of
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity. Due July 18, 2014
 Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
