Three right directions and three wrong directions for tensor research
|
|
|
- Clifton Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Three right directions and three wrong directions for tensor research Michael W. Mahoney Stanford University ( For more info, see: cs.stanford.edu/people/mmahoney/ or Google on Michael Mahoney )
2 Lots and lots of large data! High energy physics experimental data Hyperspectral medical and astronomical image data DNA microarray data and DNA SNP data Medical literature analysis data Collaboration and citation networks Internet networks and web graph data Advertiser-bidded phrase data Static and dynamic social network data
3 Scientific and Internet data individuals SNPs AG AG AG AG AA CC GG AG CG AC CC AA CC AA GG TT AG CT CG CG CG AT CT CT AG CT AA AG AG AG AA CC AG GG CC AC CC AA CG AA GG TT AG CT CG CG CG AT CT CT AG CT AA GG GG GG AA CT GG AA CC AC CG AA CC AA GG TT GG CC CG CG CG AT CT CT AG CT AG AG AG AG AA CT GG AG CC CC CG AA CC AA GT TT AG CT CG CG CG AT CT CT AG CT AA AG AG AG AA CC AG AG CG AA CC AA CG AA GG TT AA TT GG GG GG TT TT CC GG TT
4 Algorithmic vs. Statistical Perspectives Lambert (2000) Computer Scientists Data: are a record of everything that happened. Goal: process the data to find interesting patterns and associations. Methodology: Develop approximation algorithms under different models of data access since the goal is typically computationally hard. Statisticians Data: are a particular random instantiation of an underlying process describing unobserved patterns in the world. Goal: is to extract information about the world from noisy data. Methodology: Make inferences (perhaps about unseen events) by positing a model that describes the random variability of the data around the deterministic model.
5 Matrices and Data individuals SNPs AG AG AG AG AA CC GG AG CG AC CC AA CC AA GG TT AG CT CG CG CG AT CT CT AG CT AA AG AG AG AA CC AG GG CC AC CC AA CG AA GG TT AG CT CG CG CG AT CT CT AG CT AA GG GG GG AA CT GG AA CC AC CG AA CC AA GG TT GG CC CG CG CG AT CT CT AG CT AG AG AG AG AA CT GG AG CC CC CG AA CC AA GT TT AG CT CG CG CG AT CT CT AG CT AA AG AG AG AA CC AG AG CG AA CC AA CG AA GG TT AA TT GG GG GG TT TT CC GG TT Matrices provide simple representations of data: A ij = 0 or 1 (perhaps then weighted), depending on whether word i appears in document j A ij = -1,0,+1, if homozygous for the major allele, heterozygous, or homozygous for the minor allele Can take advantage of nice properties of vector spaces: structural properties: SVD, Euclidean geometry algorithmic properties: everything is O(n 3 ) statistical properties: PCA, regularization, etc.
6 Graphs and Data Interaction graph model of networks: Nodes represent entities Edges represent interaction between pairs of entities Common variations include: Directed graphs Weighted graphs Bipartite graphs
7 Why model data as graphs and matrices? Graphs and matrices - provide natural mathematical structures that provide algorithmic, statistical, and geometric benefits provide nice tradeoff between rich descriptive framework and sufficient algorithmic structure provide regularization due to geometry, either explicitly due to R n or implicitly due to approximation algorithms
8 What if graphs/matrices don t work? Employ more general mathematical structures: Hypergraphs Attributes associated with nodes Kernelize the data using, e.g., a similarity notion Generalized linear or hierarchical models Tensors!! These structures provide greater descriptive flexibility, that typically comes at a (moderate or severe) computational cost.
9 What is a tensor? (1 of 3) See L.H.Lim s tutorial on tensors at MMDS 2006.
10 What is a tensor? (2 of 3)
11 What is a tensor? (3 of 3) IMPORTANT: This is similar to NLA --- but, there is no reason to expect the subscript manipulation methods, so useful in NLA, to yield anything meaningful for more general algebraic structures.
12 Tensor ranks and data analysis (1 of 3)
13 Tensor ranks and data analysis (2 of 3) IMPORTANT: These ill-posedness results are NOT pathological--- they are ubiquitous and essential properties of tensors.
14 Tensor ranks and data analysis (3 of 3) THAT IS: To get a simple or low-rank tensor approximation, we focus on exceptions to fundamental ill-posedness properties of tensors (i.e., rank-1 tensors and 2-mode tensors).
15 Historical Perspective on NLA NLA grew out of statistics (among other areas) (40s and 50s) NLA focuses on numerical issues (60s, 70s, and 80s) Large-scale data generation increasingly common (90s and 00s) NLA has suffered due to the success of PageRank and HITS. Large-scale scientific and Internet data problems invite us to take a broader perspective on traditional NLA: revisit algorithmic basis of common NLA matrix algorithms revisit statistical underpinnings of NLA expand traditional NLA view of tensors
16 The gap between NLA and TCS Matrix factorizations: in NLA and scientific computing - used to express a problem s.t. it can be solved more easily. in TCS and statistical data analysis - used to represent structure that may be present in a matrix obtained from object-feature observations. NLA: emphasis on optimal conditioning, backward error analysis issues, is running time a large or small constant multiplied by n 2 or n 3. TCS: motivated by large data applications space-constrained or pass-efficient models over-sampling and randomness as computational resources. MMDS06, MMDS08, were designed to bridge the gap between NLA, TCS, and data applications.
17 How to bridge the gap (Lessons from MMDS) In a vector space, everything is easy, multi-linear captures the inherent intractability of NP-hardness. Convexity is an appropriate generalization of linear nice algorithmic framework, as with kernels in Machine Learning Randomness, over-sampling, approximation... are powerful algorithmic resources but you need to have a clear objective you are solving Geometry of combinatorial objects (e.g., graphs, tensors, etc.) has positive algorithmic, statistical, and conceptual benefits Approximate computation induces implicit statistical regularization
18 Examples of tensor data (Acar and Yener 2008) Chemistry: model fluorescence excitation-emission data in food science: A ijk is samples x emission x excitation. Neuroscience: EEG data as patients, doses, conditions, etc. varied: A ijk is time samples x frequency x electrodes. Social network and Web analysis: to discover hidden structures: A ijk is webpages x webpages x anchor text. A ijk is users x queries x webpages. A ijk is advertisers x bidded-phrases x time. Computer Vision: image compression and face recognition: A ijk is pixel x illumination x expression x viewpoint x person. Quantum mechanics, large-scale computation, hyperspectral data, climate data, ICA, nonnegative data, blind source separation, NP-hard problems, Tensor-based data are particularly challenging due to their size and since many data analysis tools based on graph theory and linear algebra do not easily generalize. -- MMD06
19 Three Right Directions
20 Three Right Directions 1. Understand statistical and algorithmic assumptions s.t. tensor methods work. (NOT just independence.)
21 Three Right Directions 1. Understand statistical and algorithmic assumptions s.t. tensor methods work. (NOT just independence.) 2. Understand the geometry of tensors. (NOT of vector spaces you unfold to.)
22 Three Right Directions 1. Understand statistical and algorithmic assumptions s.t. tensor methods work. (NOT just independence.) 2. Understand the geometry of tensors. (NOT of vector spaces you unfold to.) 3. Understand WHY tensors work in physical applications and what this says about less structured data applications (and vice-versa, which has been very fruitful for matrices*.) *(E.g., low-rank off-diagonal blocks are common in matrices -- since the world is 3D, which is not true in less structured applications -- this has significant algorithmic implications.)
23 Four! Right Directions 1. Understand statistical and algorithmic assumptions s.t. tensor methods work. (NOT just independence.) 2. Understand the geometry of tensors. (NOT of vector spaces you unfold to.) 3. Understand WHY tensors work in physical applications and what this says about less structured data applications (and vice-versa, which has been very fruitful for matrices*.) 4. Understand unfolding as a process of defining features. (Since this puts you in a nice algorithmic place.) *(E.g., low-rank off-diagonal blocks are common in matrices -- since the world is 3D, which is not true in less structured applications -- this has significant algorithmic implications.)
24 Three Wrong directions
25 Three Wrong directions 1. Viewing tensors as matrices with additional subscripts. (That may be true, but it hampers you, since R n is so nice.)
26 Three Wrong directions 1. Viewing tensors as matrices with additional subscripts. (That may be true, but it hampers you, since R n is so nice.) 2. Using methods that damage geometry and enhance sparsity. (BTW, you will do this if you don t understand the underlying geometric and sparsity structure.)
27 Three Wrong directions 1. Viewing tensors as matrices with additional subscripts. (That may be true, but it hampers you, since R n is so nice.) 2. Using methods that damage geometry and enhance sparsity. (BTW, you will do this if you don t understand the underlying geometric and sparsity structure.) 3. Doing Applied Ramsey Theory : Theorem: Given a large enough universe of data, then for any algorithm there exists a data set s.t. it performs well. (Show me where your method fails AND where it succeeds! Otherwise, is your result about your data or your method? Of course, this applies more generally in data analysis.)
28 Conclusions Large-scale data applications have been the main driver for a lot of the interest in tensors. Tensors are tricky to deal with, both algorithmically and statistically. Let s use this meeting to refine my directions in light of motivating data applications.
Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4)
 Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Linear Algebra and Robot Modeling
 Linear Algebra and Robot Modeling Nathan Ratliff Abstract Linear algebra is fundamental to robot modeling, control, and optimization. This document reviews some of the basic kinematic equations and uses
Linear Algebra and Robot Modeling Nathan Ratliff Abstract Linear algebra is fundamental to robot modeling, control, and optimization. This document reviews some of the basic kinematic equations and uses
Locally-biased analytics
 Locally-biased analytics You have BIG data and want to analyze a small part of it: Solution 1: Cut out small part and use traditional methods Challenge: cutting out may be difficult a priori Solution 2:
Locally-biased analytics You have BIG data and want to analyze a small part of it: Solution 1: Cut out small part and use traditional methods Challenge: cutting out may be difficult a priori Solution 2:
Using Local Spectral Methods in Theory and in Practice
 Using Local Spectral Methods in Theory and in Practice Michael W. Mahoney ICSI and Dept of Statistics, UC Berkeley ( For more info, see: http: // www. stat. berkeley. edu/ ~ mmahoney or Google on Michael
Using Local Spectral Methods in Theory and in Practice Michael W. Mahoney ICSI and Dept of Statistics, UC Berkeley ( For more info, see: http: // www. stat. berkeley. edu/ ~ mmahoney or Google on Michael
Machine Learning. Principal Components Analysis. Le Song. CSE6740/CS7641/ISYE6740, Fall 2012
 Machine Learning CSE6740/CS7641/ISYE6740, Fall 2012 Principal Components Analysis Le Song Lecture 22, Nov 13, 2012 Based on slides from Eric Xing, CMU Reading: Chap 12.1, CB book 1 2 Factor or Component
Machine Learning CSE6740/CS7641/ISYE6740, Fall 2012 Principal Components Analysis Le Song Lecture 22, Nov 13, 2012 Based on slides from Eric Xing, CMU Reading: Chap 12.1, CB book 1 2 Factor or Component
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012
 Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Google Page Rank Project Linear Algebra Summer 2012 How does an internet search engine, like Google, work? In this project you will discover how the Page Rank algorithm works to give the most relevant
Notes on Latent Semantic Analysis
 Notes on Latent Semantic Analysis Costas Boulis 1 Introduction One of the most fundamental problems of information retrieval (IR) is to find all documents (and nothing but those) that are semantically
Notes on Latent Semantic Analysis Costas Boulis 1 Introduction One of the most fundamental problems of information retrieval (IR) is to find all documents (and nothing but those) that are semantically
1 Searching the World Wide Web
 Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Quick Introduction to Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
 Quick Introduction to Nonnegative Matrix Factorization Norm Matloff University of California at Davis 1 The Goal Given an u v matrix A with nonnegative elements, we wish to find nonnegative, rank-k matrices
Quick Introduction to Nonnegative Matrix Factorization Norm Matloff University of California at Davis 1 The Goal Given an u v matrix A with nonnegative elements, we wish to find nonnegative, rank-k matrices
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Lecture: Face Recognition and Feature Reduction
 Lecture: Face Recognition and Feature Reduction Juan Carlos Niebles and Ranjay Krishna Stanford Vision and Learning Lab Lecture 11-1 Recap - Curse of dimensionality Assume 5000 points uniformly distributed
Lecture: Face Recognition and Feature Reduction Juan Carlos Niebles and Ranjay Krishna Stanford Vision and Learning Lab Lecture 11-1 Recap - Curse of dimensionality Assume 5000 points uniformly distributed
Discriminative Direction for Kernel Classifiers
 Discriminative Direction for Kernel Classifiers Polina Golland Artificial Intelligence Lab Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 polina@ai.mit.edu Abstract In many scientific and engineering
Discriminative Direction for Kernel Classifiers Polina Golland Artificial Intelligence Lab Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 polina@ai.mit.edu Abstract In many scientific and engineering
Data Mining and Matrices
 Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
CS 277: Data Mining. Mining Web Link Structure. CS 277: Data Mining Lectures Analyzing Web Link Structure Padhraic Smyth, UC Irvine
 CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
a Short Introduction
 Collaborative Filtering in Recommender Systems: a Short Introduction Norm Matloff Dept. of Computer Science University of California, Davis matloff@cs.ucdavis.edu December 3, 2016 Abstract There is a strong
Collaborative Filtering in Recommender Systems: a Short Introduction Norm Matloff Dept. of Computer Science University of California, Davis matloff@cs.ucdavis.edu December 3, 2016 Abstract There is a strong
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations Abelino Jimenez (slides from Bhiksha Raj and Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 1, 217 1 So far Weights Data Basis Data Independent ICA
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations Abelino Jimenez (slides from Bhiksha Raj and Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 1, 217 1 So far Weights Data Basis Data Independent ICA
Lecture: Face Recognition and Feature Reduction
 Lecture: Face Recognition and Feature Reduction Juan Carlos Niebles and Ranjay Krishna Stanford Vision and Learning Lab 1 Recap - Curse of dimensionality Assume 5000 points uniformly distributed in the
Lecture: Face Recognition and Feature Reduction Juan Carlos Niebles and Ranjay Krishna Stanford Vision and Learning Lab 1 Recap - Curse of dimensionality Assume 5000 points uniformly distributed in the
The Kernel Trick, Gram Matrices, and Feature Extraction. CS6787 Lecture 4 Fall 2017
 The Kernel Trick, Gram Matrices, and Feature Extraction CS6787 Lecture 4 Fall 2017 Momentum for Principle Component Analysis CS6787 Lecture 3.1 Fall 2017 Principle Component Analysis Setting: find the
The Kernel Trick, Gram Matrices, and Feature Extraction CS6787 Lecture 4 Fall 2017 Momentum for Principle Component Analysis CS6787 Lecture 3.1 Fall 2017 Principle Component Analysis Setting: find the
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Recap: Inference Example
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture 19: Decision Diagrams 11/01/2007 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Recap: Inference Example Find P( F=bad) Restrict all factors P() P(F=bad ) P() 0.7 0.3 eather 0.7
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2007 Lecture 19: Decision Diagrams 11/01/2007 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Recap: Inference Example Find P( F=bad) Restrict all factors P() P(F=bad ) P() 0.7 0.3 eather 0.7
Conditional probabilities and graphical models
 Conditional probabilities and graphical models Thomas Mailund Bioinformatics Research Centre (BiRC), Aarhus University Probability theory allows us to describe uncertainty in the processes we model within
Conditional probabilities and graphical models Thomas Mailund Bioinformatics Research Centre (BiRC), Aarhus University Probability theory allows us to describe uncertainty in the processes we model within
TENSOR LAYERS FOR COMPRESSION OF DEEP LEARNING NETWORKS. Cris Cecka Senior Research Scientist, NVIDIA GTC 2018
 TENSOR LAYERS FOR COMPRESSION OF DEEP LEARNING NETWORKS Cris Cecka Senior Research Scientist, NVIDIA GTC 2018 Tensors Computations and the GPU AGENDA Tensor Networks and Decompositions Tensor Layers in
TENSOR LAYERS FOR COMPRESSION OF DEEP LEARNING NETWORKS Cris Cecka Senior Research Scientist, NVIDIA GTC 2018 Tensors Computations and the GPU AGENDA Tensor Networks and Decompositions Tensor Layers in
Scalable Tensor Factorizations with Incomplete Data
 Scalable Tensor Factorizations with Incomplete Data Tamara G. Kolda & Daniel M. Dunlavy Sandia National Labs Evrim Acar Information Technologies Institute, TUBITAK-UEKAE, Turkey Morten Mørup Technical
Scalable Tensor Factorizations with Incomplete Data Tamara G. Kolda & Daniel M. Dunlavy Sandia National Labs Evrim Acar Information Technologies Institute, TUBITAK-UEKAE, Turkey Morten Mørup Technical
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3
 Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Data Mining Recitation Notes Week 3 Jack Rae January 28, 2013 1 Information Retrieval Given a set of documents, pull the (k) most similar document(s) to a given query. 1.1 Setup Say we have D documents
Convex sets, conic matrix factorizations and conic rank lower bounds
 Convex sets, conic matrix factorizations and conic rank lower bounds Pablo A. Parrilo Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute
Convex sets, conic matrix factorizations and conic rank lower bounds Pablo A. Parrilo Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute
Approximate Principal Components Analysis of Large Data Sets
 Approximate Principal Components Analysis of Large Data Sets Daniel J. McDonald Department of Statistics Indiana University mypage.iu.edu/ dajmcdon April 27, 2016 Approximation-Regularization for Analysis
Approximate Principal Components Analysis of Large Data Sets Daniel J. McDonald Department of Statistics Indiana University mypage.iu.edu/ dajmcdon April 27, 2016 Approximation-Regularization for Analysis
CVPR A New Tensor Algebra - Tutorial. July 26, 2017
 CVPR 2017 A New Tensor Algebra - Tutorial Lior Horesh lhoresh@us.ibm.com Misha Kilmer misha.kilmer@tufts.edu July 26, 2017 Outline Motivation Background and notation New t-product and associated algebraic
CVPR 2017 A New Tensor Algebra - Tutorial Lior Horesh lhoresh@us.ibm.com Misha Kilmer misha.kilmer@tufts.edu July 26, 2017 Outline Motivation Background and notation New t-product and associated algebraic
Opportunities and challenges in quantum-enhanced machine learning in near-term quantum computers
 Opportunities and challenges in quantum-enhanced machine learning in near-term quantum computers Alejandro Perdomo-Ortiz Senior Research Scientist, Quantum AI Lab. at NASA Ames Research Center and at the
Opportunities and challenges in quantum-enhanced machine learning in near-term quantum computers Alejandro Perdomo-Ortiz Senior Research Scientist, Quantum AI Lab. at NASA Ames Research Center and at the
Introduction to Machine Learning
 10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning PCA Slides based on 18-661 Fall 2018 PCA Raw data can be Complex, High-dimensional To understand a phenomenon we measure various related quantities If we knew what
10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning PCA Slides based on 18-661 Fall 2018 PCA Raw data can be Complex, High-dimensional To understand a phenomenon we measure various related quantities If we knew what
Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making A. Week #1
 Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making 80-629-17A Week #1 Today Introduction to machine learning The course (syllabus) Math review (probability + linear algebra) The future
Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making 80-629-17A Week #1 Today Introduction to machine learning The course (syllabus) Math review (probability + linear algebra) The future
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Structured matrix factorizations. Example: Eigenfaces
 Structured matrix factorizations Example: Eigenfaces An extremely large variety of interesting and important problems in machine learning can be formulated as: Given a matrix, find a matrix and a matrix
Structured matrix factorizations Example: Eigenfaces An extremely large variety of interesting and important problems in machine learning can be formulated as: Given a matrix, find a matrix and a matrix
A New Space for Comparing Graphs
 A New Space for Comparing Graphs Anshumali Shrivastava and Ping Li Cornell University and Rutgers University August 18th 2014 Anshumali Shrivastava and Ping Li ASONAM 2014 August 18th 2014 1 / 38 Main
A New Space for Comparing Graphs Anshumali Shrivastava and Ping Li Cornell University and Rutgers University August 18th 2014 Anshumali Shrivastava and Ping Li ASONAM 2014 August 18th 2014 1 / 38 Main
Introduction to the Tensor Train Decomposition and Its Applications in Machine Learning
 Introduction to the Tensor Train Decomposition and Its Applications in Machine Learning Anton Rodomanov Higher School of Economics, Russia Bayesian methods research group (http://bayesgroup.ru) 14 March
Introduction to the Tensor Train Decomposition and Its Applications in Machine Learning Anton Rodomanov Higher School of Economics, Russia Bayesian methods research group (http://bayesgroup.ru) 14 March
CS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #6: Regularization
 CS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #6: Regularization Tim Roughgarden & Gregory Valiant April 18, 2018 1 The Context and Intuition behind Regularization Given a dataset, and some class of models
CS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #6: Regularization Tim Roughgarden & Gregory Valiant April 18, 2018 1 The Context and Intuition behind Regularization Given a dataset, and some class of models
Practical Linear Algebra: A Geometry Toolbox
 Practical Linear Algebra: A Geometry Toolbox Third edition Chapter 12: Gauss for Linear Systems Gerald Farin & Dianne Hansford CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, An A K Peters Book www.farinhansford.com/books/pla
Practical Linear Algebra: A Geometry Toolbox Third edition Chapter 12: Gauss for Linear Systems Gerald Farin & Dianne Hansford CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, An A K Peters Book www.farinhansford.com/books/pla
Singular Value Decompsition
 Singular Value Decompsition Massoud Malek One of the most useful results from linear algebra, is a matrix decomposition known as the singular value decomposition It has many useful applications in almost
Singular Value Decompsition Massoud Malek One of the most useful results from linear algebra, is a matrix decomposition known as the singular value decomposition It has many useful applications in almost
DATA MINING LECTURE 13. Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
 DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Faloutsos, Tong ICDE, 2009
 Large Graph Mining: Patterns, Tools and Case Studies Christos Faloutsos Hanghang Tong CMU Copyright: Faloutsos, Tong (29) 2-1 Outline Part 1: Patterns Part 2: Matrix and Tensor Tools Part 3: Proximity
Large Graph Mining: Patterns, Tools and Case Studies Christos Faloutsos Hanghang Tong CMU Copyright: Faloutsos, Tong (29) 2-1 Outline Part 1: Patterns Part 2: Matrix and Tensor Tools Part 3: Proximity
DATA MINING LECTURE 8. Dimensionality Reduction PCA -- SVD
 DATA MINING LECTURE 8 Dimensionality Reduction PCA -- SVD The curse of dimensionality Real data usually have thousands, or millions of dimensions E.g., web documents, where the dimensionality is the vocabulary
DATA MINING LECTURE 8 Dimensionality Reduction PCA -- SVD The curse of dimensionality Real data usually have thousands, or millions of dimensions E.g., web documents, where the dimensionality is the vocabulary
Fitting a Tensor Decomposition is a Nonlinear Optimization Problem
 Fitting a Tensor Decomposition is a Nonlinear Optimization Problem Evrim Acar, Daniel M. Dunlavy, and Tamara G. Kolda* Sandia National Laboratories Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia
Fitting a Tensor Decomposition is a Nonlinear Optimization Problem Evrim Acar, Daniel M. Dunlavy, and Tamara G. Kolda* Sandia National Laboratories Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia
Statistical Issues in Searches: Photon Science Response. Rebecca Willett, Duke University
 Statistical Issues in Searches: Photon Science Response Rebecca Willett, Duke University 1 / 34 Photon science seen this week Applications tomography ptychography nanochrystalography coherent diffraction
Statistical Issues in Searches: Photon Science Response Rebecca Willett, Duke University 1 / 34 Photon science seen this week Applications tomography ptychography nanochrystalography coherent diffraction
Collaborative topic models: motivations cont
 Collaborative topic models: motivations cont Two topics: machine learning social network analysis Two people: " boy Two articles: article A! girl article B Preferences: The boy likes A and B --- no problem.
Collaborative topic models: motivations cont Two topics: machine learning social network analysis Two people: " boy Two articles: article A! girl article B Preferences: The boy likes A and B --- no problem.
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Announcements
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2011 Lecture 18: HMMs and Particle Filtering 4/4/2011 Pieter Abbeel --- UC Berkeley Many slides over this course adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2011 Lecture 18: HMMs and Particle Filtering 4/4/2011 Pieter Abbeel --- UC Berkeley Many slides over this course adapted from Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, Andrew Moore
Lecture 21: Spectral Learning for Graphical Models
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 Lecture 21: Spectral Learning for Graphical Models Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Maruan Al-Shedivat, Wei-Cheng Chang, Frederick Liu 1 Motivation
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2016 Lecture 21: Spectral Learning for Graphical Models Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Maruan Al-Shedivat, Wei-Cheng Chang, Frederick Liu 1 Motivation
Approximate Computation and Implicit Regularization for Very Large-scale Data Analysis
 Approximate Computation and Implicit Regularization for Very Large-scale Data Analysis Michael W. Mahoney Department of Mathematics Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 mmahoney@cs.stanford.edu ABSTRACT
Approximate Computation and Implicit Regularization for Very Large-scale Data Analysis Michael W. Mahoney Department of Mathematics Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 mmahoney@cs.stanford.edu ABSTRACT
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis. Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa
 Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Computational Linear Algebra
 Computational Linear Algebra PD Dr. rer. nat. habil. Ralf-Peter Mundani Computation in Engineering / BGU Scientific Computing in Computer Science / INF Winter Term 2018/19 Part 6: Some Other Stuff PD Dr.
Computational Linear Algebra PD Dr. rer. nat. habil. Ralf-Peter Mundani Computation in Engineering / BGU Scientific Computing in Computer Science / INF Winter Term 2018/19 Part 6: Some Other Stuff PD Dr.
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. Sparse Matrix Factorization Fall 2018
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Sparse Matrix Factorization Fall 2018 Last Time: PCA with Orthogonal/Sequential Basis When k = 1, PCA has a scaling problem. When k > 1, have scaling, rotation,
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Sparse Matrix Factorization Fall 2018 Last Time: PCA with Orthogonal/Sequential Basis When k = 1, PCA has a scaling problem. When k > 1, have scaling, rotation,
Introduction to Information Retrieval
 Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2013-07-10 1/43
Introduction to Information Retrieval http://informationretrieval.org IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Hinrich Schütze Center for Information and Language Processing, University of Munich 2013-07-10 1/43
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors
 MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
COMP61011! Probabilistic Classifiers! Part 1, Bayes Theorem!
 COMP61011 Probabilistic Classifiers Part 1, Bayes Theorem Reverend Thomas Bayes, 1702-1761 p ( T W ) W T ) T ) W ) Bayes Theorem forms the backbone of the past 20 years of ML research into probabilistic
COMP61011 Probabilistic Classifiers Part 1, Bayes Theorem Reverend Thomas Bayes, 1702-1761 p ( T W ) W T ) T ) W ) Bayes Theorem forms the backbone of the past 20 years of ML research into probabilistic
CS264: Beyond Worst-Case Analysis Lecture #15: Topic Modeling and Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
 CS264: Beyond Worst-Case Analysis Lecture #15: Topic Modeling and Nonnegative Matrix Factorization Tim Roughgarden February 28, 2017 1 Preamble This lecture fulfills a promise made back in Lecture #1,
CS264: Beyond Worst-Case Analysis Lecture #15: Topic Modeling and Nonnegative Matrix Factorization Tim Roughgarden February 28, 2017 1 Preamble This lecture fulfills a promise made back in Lecture #1,
Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces
 9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 10th, 2010 Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces Lecturer: Lorenzo Rosasco Scribe: Greg Durrett 1 Introduction In the previous two lectures, we
9.520: Statistical Learning Theory and Applications February 10th, 2010 Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Spaces Lecturer: Lorenzo Rosasco Scribe: Greg Durrett 1 Introduction In the previous two lectures, we
PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval https://www.fi.muni.cz/~sojka/pv211
 PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval https://www.fi.muni.cz/~sojka/pv211 IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Handout version Petr Sojka, Hinrich Schütze et al. Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University,
PV211: Introduction to Information Retrieval https://www.fi.muni.cz/~sojka/pv211 IIR 18: Latent Semantic Indexing Handout version Petr Sojka, Hinrich Schütze et al. Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University,
Stat 315c: Introduction
 Stat 315c: Introduction Art B. Owen Stanford Statistics Art B. Owen (Stanford Statistics) Stat 315c: Introduction 1 / 14 Stat 315c Analysis of Transposable Data Usual Statistics Setup there s Y (we ll
Stat 315c: Introduction Art B. Owen Stanford Statistics Art B. Owen (Stanford Statistics) Stat 315c: Introduction 1 / 14 Stat 315c Analysis of Transposable Data Usual Statistics Setup there s Y (we ll
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Modern Algebra Prof. Manindra Agrawal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Modern Algebra Prof. Manindra Agrawal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 02 Groups: Subgroups and homomorphism (Refer Slide Time: 00:13) We looked
Modern Algebra Prof. Manindra Agrawal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 02 Groups: Subgroups and homomorphism (Refer Slide Time: 00:13) We looked
Linear Algebra & Geometry why is linear algebra useful in computer vision?
 Linear Algebra & Geometry why is linear algebra useful in computer vision? References: -Any book on linear algebra! -[HZ] chapters 2, 4 Some of the slides in this lecture are courtesy to Prof. Octavia
Linear Algebra & Geometry why is linear algebra useful in computer vision? References: -Any book on linear algebra! -[HZ] chapters 2, 4 Some of the slides in this lecture are courtesy to Prof. Octavia
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017
 Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017 1 Vectors k is a scalar (a number) c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, c = ( c1 c 2 ) (Advanced: More precisely, a vector is defined in a vector space.
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2017 1 Vectors k is a scalar (a number) c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, c = ( c1 c 2 ) (Advanced: More precisely, a vector is defined in a vector space.
Approximate Inference
 Approximate Inference Simulation has a name: sampling Sampling is a hot topic in machine learning, and it s really simple Basic idea: Draw N samples from a sampling distribution S Compute an approximate
Approximate Inference Simulation has a name: sampling Sampling is a hot topic in machine learning, and it s really simple Basic idea: Draw N samples from a sampling distribution S Compute an approximate
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
A primer on matrices
 A primer on matrices Stephen Boyd August 4, 2007 These notes describe the notation of matrices, the mechanics of matrix manipulation, and how to use matrices to formulate and solve sets of simultaneous
A primer on matrices Stephen Boyd August 4, 2007 These notes describe the notation of matrices, the mechanics of matrix manipulation, and how to use matrices to formulate and solve sets of simultaneous
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
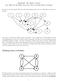 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
Towards a Regression using Tensors
 February 27, 2014 Outline Background 1 Background Linear Regression Tensorial Data Analysis 2 Definition Tensor Operation Tensor Decomposition 3 Model Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Data Analysis
February 27, 2014 Outline Background 1 Background Linear Regression Tensorial Data Analysis 2 Definition Tensor Operation Tensor Decomposition 3 Model Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Data Analysis
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval
 Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009 Lecture 21: Hidden Markov Models 4/7/2009 John DeNero UC Berkeley Slides adapted from Dan Klein Announcements Written 3 deadline extended! Posted last Friday
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2009 Lecture 21: Hidden Markov Models 4/7/2009 John DeNero UC Berkeley Slides adapted from Dan Klein Announcements Written 3 deadline extended! Posted last Friday
RandNLA: Randomized Numerical Linear Algebra
 RandNLA: Randomized Numerical Linear Algebra Petros Drineas Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Computer Science Department To access my web page: drineas RandNLA: sketch a matrix by row/ column sampling
RandNLA: Randomized Numerical Linear Algebra Petros Drineas Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Computer Science Department To access my web page: drineas RandNLA: sketch a matrix by row/ column sampling
Machine Learning CPSC 340. Tutorial 12
 Machine Learning CPSC 340 Tutorial 12 Random Walk on Graph Page Rank Algorithm Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected
Machine Learning CPSC 340 Tutorial 12 Random Walk on Graph Page Rank Algorithm Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected graph G = (V, A) Label Propagation on Graph Assume a strongly connected
Regression. Goal: Learn a mapping from observations (features) to continuous labels given a training set (supervised learning)
 Linear Regression Regression Goal: Learn a mapping from observations (features) to continuous labels given a training set (supervised learning) Example: Height, Gender, Weight Shoe Size Audio features
Linear Regression Regression Goal: Learn a mapping from observations (features) to continuous labels given a training set (supervised learning) Example: Height, Gender, Weight Shoe Size Audio features
CS246 Final Exam, Winter 2011
 CS246 Final Exam, Winter 2011 1. Your name and student ID. Name:... Student ID:... 2. I agree to comply with Stanford Honor Code. Signature:... 3. There should be 17 numbered pages in this exam (including
CS246 Final Exam, Winter 2011 1. Your name and student ID. Name:... Student ID:... 2. I agree to comply with Stanford Honor Code. Signature:... 3. There should be 17 numbered pages in this exam (including
Regression. Goal: Learn a mapping from observations (features) to continuous labels given a training set (supervised learning)
 Linear Regression Regression Goal: Learn a mapping from observations (features) to continuous labels given a training set (supervised learning) Example: Height, Gender, Weight Shoe Size Audio features
Linear Regression Regression Goal: Learn a mapping from observations (features) to continuous labels given a training set (supervised learning) Example: Height, Gender, Weight Shoe Size Audio features
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018
 Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018 1 Vectors k, M, N are scalars A one-dimensional array c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, ( ) c1 c = c 2 c i is the i-th component of c c T = (c 1, c
Linear Algebra (Review) Volker Tresp 2018 1 Vectors k, M, N are scalars A one-dimensional array c is a column vector. Thus in two dimensions, ( ) c1 c = c 2 c i is the i-th component of c c T = (c 1, c
MATH36061 Convex Optimization
 M\cr NA Manchester Numerical Analysis MATH36061 Convex Optimization Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Manchester, September 26, 2017 Outline General information What is optimization?
M\cr NA Manchester Numerical Analysis MATH36061 Convex Optimization Martin Lotz School of Mathematics The University of Manchester Manchester, September 26, 2017 Outline General information What is optimization?
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall VPI Example. VPI Properties. Reasoning over Time. Markov Models. Lecture 19: HMMs 11/4/2008
 CS 88: Artificial Intelligence Fall 28 Lecture 9: HMMs /4/28 Announcements Midterm solutions up, submit regrade requests within a week Midterm course evaluation up on web, please fill out! Dan Klein UC
CS 88: Artificial Intelligence Fall 28 Lecture 9: HMMs /4/28 Announcements Midterm solutions up, submit regrade requests within a week Midterm course evaluation up on web, please fill out! Dan Klein UC
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations. Bhiksha Raj (slides from Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 22, 2013
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations Bhiksha Raj (slides from Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 22, 2013 1 Key Topics in this Lecture Basics Component-based representations
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations Bhiksha Raj (slides from Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 22, 2013 1 Key Topics in this Lecture Basics Component-based representations
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
1 Undirected Graphical Models. 2 Markov Random Fields (MRFs)
 Machine Learning (ML, F16) Lecture#07 (Thursday Nov. 3rd) Lecturer: Byron Boots Undirected Graphical Models 1 Undirected Graphical Models In the previous lecture, we discussed directed graphical models.
Machine Learning (ML, F16) Lecture#07 (Thursday Nov. 3rd) Lecturer: Byron Boots Undirected Graphical Models 1 Undirected Graphical Models In the previous lecture, we discussed directed graphical models.
Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10715
 Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10715 Independent Component Analysis Barnabás Póczos Independent Component Analysis 2 Independent Component Analysis Model original signals Observations (Mixtures)
Advanced Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10715 Independent Component Analysis Barnabás Póczos Independent Component Analysis 2 Independent Component Analysis Model original signals Observations (Mixtures)
Learning Query and Document Similarities from Click-through Bipartite Graph with Metadata
 Learning Query and Document Similarities from Click-through Bipartite Graph with Metadata Wei Wu a, Hang Li b, Jun Xu b a Department of Probability and Statistics, Peking University b Microsoft Research
Learning Query and Document Similarities from Click-through Bipartite Graph with Metadata Wei Wu a, Hang Li b, Jun Xu b a Department of Probability and Statistics, Peking University b Microsoft Research
STA 414/2104: Machine Learning
 STA 414/2104: Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 9 Sequential Data So far
STA 414/2104: Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 9 Sequential Data So far
Analysis and synthesis: a complexity perspective
 Analysis and synthesis: a complexity perspective Pablo A. Parrilo ETH ZürichZ control.ee.ethz.ch/~parrilo Outline System analysis/design Formal and informal methods SOS/SDP techniques and applications
Analysis and synthesis: a complexity perspective Pablo A. Parrilo ETH ZürichZ control.ee.ethz.ch/~parrilo Outline System analysis/design Formal and informal methods SOS/SDP techniques and applications
Wiki Definition. Reputation Systems I. Outline. Introduction to Reputations. Yury Lifshits. HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte
 Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
Linear dimensionality reduction for data analysis
 Linear dimensionality reduction for data analysis Nicolas Gillis Joint work with Robert Luce, François Glineur, Stephen Vavasis, Robert Plemmons, Gabriella Casalino The setup Dimensionality reduction for
Linear dimensionality reduction for data analysis Nicolas Gillis Joint work with Robert Luce, François Glineur, Stephen Vavasis, Robert Plemmons, Gabriella Casalino The setup Dimensionality reduction for
Index. Copyright (c)2007 The Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics From: Matrix Methods in Data Mining and Pattern Recgonition By: Lars Elden
 Index 1-norm, 15 matrix, 17 vector, 15 2-norm, 15, 59 matrix, 17 vector, 15 3-mode array, 91 absolute error, 15 adjacency matrix, 158 Aitken extrapolation, 157 algebra, multi-linear, 91 all-orthogonality,
Index 1-norm, 15 matrix, 17 vector, 15 2-norm, 15, 59 matrix, 17 vector, 15 3-mode array, 91 absolute error, 15 adjacency matrix, 158 Aitken extrapolation, 157 algebra, multi-linear, 91 all-orthogonality,
Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search
 CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
Graph Partitioning Using Random Walks
 Graph Partitioning Using Random Walks A Convex Optimization Perspective Lorenzo Orecchia Computer Science Why Spectral Algorithms for Graph Problems in practice? Simple to implement Can exploit very efficient
Graph Partitioning Using Random Walks A Convex Optimization Perspective Lorenzo Orecchia Computer Science Why Spectral Algorithms for Graph Problems in practice? Simple to implement Can exploit very efficient
Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix. Steve Kirkland University of Regina
 Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix Steve Kirkland University of Regina June 5, 2006 Motivation: Google s PageRank algorithm finds the stationary vector of a stochastic
Conditioning of the Entries in the Stationary Vector of a Google-Type Matrix Steve Kirkland University of Regina June 5, 2006 Motivation: Google s PageRank algorithm finds the stationary vector of a stochastic
The core of solving constraint problems using Constraint Programming (CP), with emphasis on:
 What is it about? l Theory The core of solving constraint problems using Constraint Programming (CP), with emphasis on: l Modeling l Solving: Local consistency and propagation; Backtracking search + heuristics.
What is it about? l Theory The core of solving constraint problems using Constraint Programming (CP), with emphasis on: l Modeling l Solving: Local consistency and propagation; Backtracking search + heuristics.
Latent Semantic Analysis. Hongning Wang
 Latent Semantic Analysis Hongning Wang CS@UVa Recap: vector space model Represent both doc and query by concept vectors Each concept defines one dimension K concepts define a high-dimensional space Element
Latent Semantic Analysis Hongning Wang CS@UVa Recap: vector space model Represent both doc and query by concept vectors Each concept defines one dimension K concepts define a high-dimensional space Element
Introduction to Graphical Models. Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah
 Introduction to Graphical Models Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Reference Christopher M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Jonathan S. Yedidia, William T. Freeman,
Introduction to Graphical Models Srikumar Ramalingam School of Computing University of Utah Reference Christopher M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, Jonathan S. Yedidia, William T. Freeman,
BOOLEAN MATRIX AND TENSOR DECOMPOSITIONS. Pauli Miettinen TML September 2013
 BOOLEAN MATRIX AND TENSOR DECOMPOSITIONS Pauli Miettinen TML 2013 27 September 2013 BOOLEAN MATRIX AND TENSOR DECOMPOSITIONS Boolean decompositions are like normal decompositions, except that Input is
BOOLEAN MATRIX AND TENSOR DECOMPOSITIONS Pauli Miettinen TML 2013 27 September 2013 BOOLEAN MATRIX AND TENSOR DECOMPOSITIONS Boolean decompositions are like normal decompositions, except that Input is
Nonlinear Optimization Methods for Machine Learning
 Nonlinear Optimization Methods for Machine Learning Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University University of California, Davis, Sept 2018 1 Introduction We don t really know, do we? a) Deep neural networks
Nonlinear Optimization Methods for Machine Learning Jorge Nocedal Northwestern University University of California, Davis, Sept 2018 1 Introduction We don t really know, do we? a) Deep neural networks
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
9.2 Support Vector Machines 159
 9.2 Support Vector Machines 159 9.2.3 Kernel Methods We have all the tools together now to make an exciting step. Let us summarize our findings. We are interested in regularized estimation problems of
9.2 Support Vector Machines 159 9.2.3 Kernel Methods We have all the tools together now to make an exciting step. Let us summarize our findings. We are interested in regularized estimation problems of
Lecture 5 : Projections
 Lecture 5 : Projections EE227C. Lecturer: Professor Martin Wainwright. Scribe: Alvin Wan Up until now, we have seen convergence rates of unconstrained gradient descent. Now, we consider a constrained minimization
Lecture 5 : Projections EE227C. Lecturer: Professor Martin Wainwright. Scribe: Alvin Wan Up until now, we have seen convergence rates of unconstrained gradient descent. Now, we consider a constrained minimization
Hidden Markov Models. Hal Daumé III. Computer Science University of Maryland CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 19 Apr 2012
 Hidden Markov Models Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 19 Apr 2012 Many slides courtesy of Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, or
Hidden Markov Models Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 19 Apr 2012 Many slides courtesy of Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, or
Latent Semantic Analysis. Hongning Wang
 Latent Semantic Analysis Hongning Wang CS@UVa VS model in practice Document and query are represented by term vectors Terms are not necessarily orthogonal to each other Synonymy: car v.s. automobile Polysemy:
Latent Semantic Analysis Hongning Wang CS@UVa VS model in practice Document and query are represented by term vectors Terms are not necessarily orthogonal to each other Synonymy: car v.s. automobile Polysemy:
The Learning Problem and Regularization
 9.520 Class 02 February 2011 Computational Learning Statistical Learning Theory Learning is viewed as a generalization/inference problem from usually small sets of high dimensional, noisy data. Learning
9.520 Class 02 February 2011 Computational Learning Statistical Learning Theory Learning is viewed as a generalization/inference problem from usually small sets of high dimensional, noisy data. Learning
