An FPGA Implementation of Reciprocal Sums for SPME
|
|
|
- Bryce Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An FPGA Implementation of Reciprocal Sums for SPME Sam Lee and Paul Chow Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto
2 Objectives Accelerate part of Molecular Dynamics Simulation Smooth Particle Mesh Ewald Implementation FPGA based Try it and learn Investigation Acceleration bottleneck Precision requirement Parallelization strategy
3 Presentation Outline Molecular Dynamics SPME The Reciprocal Sum Compute Engine Speedup and Parallelization Precision Future work
4 Molecular Dynamics Simulation 4
5 Molecular Dynamics Combines empirical force calculations with Newton s equations of motion. Predict the time trajectory of small atomic systems. Computationally demanding.. Calculate interatomic forces.. Calculate the net force.. Integrate Newton s equations of motion. a r = F m ( t + δt ) = r () t + δt v () t + 0.5δt a () t v ( t + δt ) = v () t δt a () t + a ( t + δt ) F 5
6 Molecular Dynamics k Θ All Angles + + k ( l b l o All Bonds ( Θ Θ ) o ) U = A [ + cos( nτ + φ)] All Torsions + + All Pairs All Pairs q q r σ 4ε r 6 σ r + δ δ 6
7 MD Simulation Problem scientists are facing: SLOW! O(N ) complexity. 0 CPU Years 7
8 Solutions Parallelize to more compute engines Accelerate with FPGA Especially: The non-bonded calculations To be more specific, this paper addresses: Electrostatic interaction (Reciprocal space) Smooth Particle Mesh Ewald algorithm. 8
9 Previous Work Software SPME Implementations: Original PME Package written by Toukmaji. Used in NAMD. Hardware Implementations: No previous hardware implementation of reciprocal sums calculation. MD-Grape & MD-Engine uses Ewald Summation. Ewald Summation is O(N ); SPME is O(NLogN)! 9
10 Smooth Particle Mesh Ewald 0
11 Electrostatic Interaction Coulombic equation: qq = 4πε r v coulomb 0 Under the Periodic Boundary Condition, the summation to calculate Electrostatic energy is only Conditionally Convergent. U = ' n N N q q i= j= ij, n i r j
12 Periodic Boundary Condition A 4 5 B 4 5 C 4 5 D 4 5 E 4 5 F 4 5 G 4 5 H 4 5 I 4 5 To combat Surface Effect 4 5 Replication
13 Ewald Summation Used For PBC To calculate the Coulombic Interactions O(N ) Direct Sum + O(N ) Reciprocal Sum q r Direct Sum q Reciprocal Sum q r r
14 Smooth Particle Mesh Ewald Shift the workload to the Reciprocal Sum. Use Fast Fourier Transform. O(N) Real + O(NLogN) Reciprocal. RSCE calculates the Reciprocal Sums using the SPME algorithm. 4
15 5 SPME Reciprocal Contribution ),m,m m Q)( (θ ),m,m (m r Q r E F K m K m rec K m αi αi rec ~ = = = = = ) (m b ) (m b ) b (m ),m,m B(m = 0 exp exp = + = n k i i n i i i i ) K πim k ( ) (k M ) K )m πi(n ( ) b (m exp m ) /β m π ( πv ),m,m C(m = = ),,,c( m ) m, m, m )F(Q)(,m,m F(Q)(m ),m,m B(m m ) /β m π ( πv E m ~ 0 exp = FFT FFT Energy: Force: ),m,m m Q)( (θ ),m,m Q(m E K m K m rec K m ~ = = = =
16 Charge Interpolation F D A C B E 6
17 Reciprocal Sum Compute Engine 7
18 RSCE Architecture 8
19 RSCE Verification Testbench 9
20 RSCE Validation Environment 0
21 Speedup Estimate RSCE vs. Software Implementation
22 RSCE Speedup 00MHz vs. P4 Speedup: x to 4x Why so insignificant? Reciprocal Sums calculations not easily parallelizable. QMM memory bandwidth limitation. Improvement: Using more QMM memories can improve the speedup. Slight design modifications are required.
23 Parallelization Strategy Multiple RSCE
24 RSCE Parallelization Strategy Assume a -D simulation system. Assume P=, K=8, N=6. Assume NumP = 4. An 8x8x8 mesh Four 4x4x4 Mini Meshes 4
25 RSCE Parallelization Strategy Mini-mesh composed -> D-IFFT D-IFFT = two passes of D-FFT (X and Y). X Direction FFT Y Direction FFT Ky Ky P P P P P P P4 D FFT Y direction P4 0 Kx D FFT X direction 0 Kx 5
26 Parallelization Strategy D-IFFT -> Energy Calculation -> D-FFT D-FFT -> Force Calculation Energy Calculation Force Calculation E Total = E P P= 0 D-FFT 6
27 MD Simulations RSCE + NAMD 7
28 RSCE Precision Precision goal: Relative error bound < 0-5. Two major calculation steps: B-Spline Calculation. D-FFT/IFFT Calculation. Due to the limited logic resource & limited precision FFT LogiCore. => Precision goal cannot be achieved. 8
29 RSCE Precision To achieve the relative error bound of < 0-5. Minimum calculation precision: FFT {4.0}, B-Spline {.7} 9
30 MD Simulation with RSCE RMS Energy Error Fluctuation: RMS Energy Fluctuatio n = E E E 0
31 FFT Precision Vs. Energy Fluctuation
32 Summary Implementation of FPGA-based Reciprocal Sums Compute Engine and its SystemC model. Integration of the RSCE into a widely used Molecular Dynamics program called NAMD for verification RSCE Speedup Estimate x to 4x Precision Requirement B-Spline: {.7} & FFT: {4:0} => 0-5 rel. error Parallelization Strategy
33 Future Work More in-depth precision analysis. Investigation on how to further speedup the SPME algorithm with FPGA.
34 Questions 4
Non-bonded interactions
 speeding up the number-crunching continued Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař December 3, 2013 why care? number of individual pair-wise interactions bonded interactions proportional to N: O(N) non-bonded interactions
speeding up the number-crunching continued Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař December 3, 2013 why care? number of individual pair-wise interactions bonded interactions proportional to N: O(N) non-bonded interactions
Advanced Molecular Molecular Dynamics
 Advanced Molecular Molecular Dynamics Technical details May 12, 2014 Integration of harmonic oscillator r m period = 2 k k and the temperature T determine the sampling of x (here T is related with v 0
Advanced Molecular Molecular Dynamics Technical details May 12, 2014 Integration of harmonic oscillator r m period = 2 k k and the temperature T determine the sampling of x (here T is related with v 0
Non-bonded interactions
 speeding up the number-crunching Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař May 8, 2015 why care? key to understand biomolecular structure and function binding of a ligand efficiency of a reaction color of a chromophore
speeding up the number-crunching Marcus Elstner and Tomáš Kubař May 8, 2015 why care? key to understand biomolecular structure and function binding of a ligand efficiency of a reaction color of a chromophore
Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar.
 Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar. 25, 2002 Molecular Dynamics: Introduction At physiological conditions, the
Why Proteins Fold? (Parts of this presentation are based on work of Ashok Kolaskar) CS490B: Introduction to Bioinformatics Mar. 25, 2002 Molecular Dynamics: Introduction At physiological conditions, the
Optimizing GROMACS for parallel performance
 Optimizing GROMACS for parallel performance Outline 1. Why optimize? Performance status quo 2. GROMACS as a black box. (PME) 3. How does GROMACS spend its time? (MPE) 4. What you can do What I want to
Optimizing GROMACS for parallel performance Outline 1. Why optimize? Performance status quo 2. GROMACS as a black box. (PME) 3. How does GROMACS spend its time? (MPE) 4. What you can do What I want to
Seminar in Particles Simulations. Particle Mesh Ewald. Theodora Konstantinidou
 Seminar in Particles Simulations Particle Mesh Ewald Theodora Konstantinidou This paper is part of the course work: seminar 2 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Role of Molecular Dynamics - MD.......................
Seminar in Particles Simulations Particle Mesh Ewald Theodora Konstantinidou This paper is part of the course work: seminar 2 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Role of Molecular Dynamics - MD.......................
Introduction to molecular dynamics
 1 Introduction to molecular dynamics Yves Lansac Université François Rabelais, Tours, France Visiting MSE, GIST for the summer Molecular Simulation 2 Molecular simulation is a computational experiment.
1 Introduction to molecular dynamics Yves Lansac Université François Rabelais, Tours, France Visiting MSE, GIST for the summer Molecular Simulation 2 Molecular simulation is a computational experiment.
Parallelization of Molecular Dynamics (with focus on Gromacs) SeSE 2014 p.1/29
 Parallelization of Molecular Dynamics (with focus on Gromacs) SeSE 2014 p.1/29 Outline A few words on MD applications and the GROMACS package The main work in an MD simulation Parallelization Stream computing
Parallelization of Molecular Dynamics (with focus on Gromacs) SeSE 2014 p.1/29 Outline A few words on MD applications and the GROMACS package The main work in an MD simulation Parallelization Stream computing
Efficient Parallelization of Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Hybrid CPU/GPU Supercoputers
 Efficient Parallelization of Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Hybrid CPU/GPU Supercoputers Jaewoon Jung (RIKEN, RIKEN AICS) Yuji Sugita (RIKEN, RIKEN AICS, RIKEN QBiC, RIKEN ithes) Molecular Dynamics
Efficient Parallelization of Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Hybrid CPU/GPU Supercoputers Jaewoon Jung (RIKEN, RIKEN AICS) Yuji Sugita (RIKEN, RIKEN AICS, RIKEN QBiC, RIKEN ithes) Molecular Dynamics
Molecular Dynamics Simulations
 Molecular Dynamics Simulations Dr. Kasra Momeni www.knanosys.com Outline Long-range Interactions Ewald Sum Fast Multipole Method Spherically Truncated Coulombic Potential Speeding up Calculations SPaSM
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Dr. Kasra Momeni www.knanosys.com Outline Long-range Interactions Ewald Sum Fast Multipole Method Spherically Truncated Coulombic Potential Speeding up Calculations SPaSM
Lecture 12: Solvation Models: Molecular Mechanics Modeling of Hydration Effects
 Statistical Thermodynamics Lecture 12: Solvation Models: Molecular Mechanics Modeling of Hydration Effects Dr. Ronald M. Levy ronlevy@temple.edu Bare Molecular Mechanics Atomistic Force Fields: torsion
Statistical Thermodynamics Lecture 12: Solvation Models: Molecular Mechanics Modeling of Hydration Effects Dr. Ronald M. Levy ronlevy@temple.edu Bare Molecular Mechanics Atomistic Force Fields: torsion
A Fast N-Body Solver for the Poisson(-Boltzmann) Equation
 A Fast N-Body Solver for the Poisson(-Boltzmann) Equation Robert D. Skeel Departments of Computer Science (and Mathematics) Purdue University http://bionum.cs.purdue.edu/2008december.pdf 1 Thesis Poisson(-Boltzmann)
A Fast N-Body Solver for the Poisson(-Boltzmann) Equation Robert D. Skeel Departments of Computer Science (and Mathematics) Purdue University http://bionum.cs.purdue.edu/2008december.pdf 1 Thesis Poisson(-Boltzmann)
Large-Scale Hydrodynamic Brownian Simulations on Multicore and Manycore Architectures
 Large-Scale Hydrodynamic Brownian Simulations on Multicore and Manycore Architectures Xing Liu School of Computational Science and Engineering College of Computing, Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Large-Scale Hydrodynamic Brownian Simulations on Multicore and Manycore Architectures Xing Liu School of Computational Science and Engineering College of Computing, Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Molecular dynamics simulation. CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 5 and 10, 2017 Ron Dror
 Molecular dynamics simulation CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 5 and 10, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Molecular dynamics (MD): The basic idea Equations of motion Key properties of MD simulations Sample applications
Molecular dynamics simulation CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 5 and 10, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Molecular dynamics (MD): The basic idea Equations of motion Key properties of MD simulations Sample applications
The Fast Multipole Method in molecular dynamics
 The Fast Multipole Method in molecular dynamics Berk Hess KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden ADAC6 workshop Zurich, 20-06-2018 Slide BioExcel Slide Molecular Dynamics of biomolecules
The Fast Multipole Method in molecular dynamics Berk Hess KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden ADAC6 workshop Zurich, 20-06-2018 Slide BioExcel Slide Molecular Dynamics of biomolecules
RWTH Aachen University
 IPCC @ RWTH Aachen University Optimization of multibody and long-range solvers in LAMMPS Rodrigo Canales William McDoniel Markus Höhnerbach Ahmed E. Ismail Paolo Bientinesi IPCC Showcase November 2016
IPCC @ RWTH Aachen University Optimization of multibody and long-range solvers in LAMMPS Rodrigo Canales William McDoniel Markus Höhnerbach Ahmed E. Ismail Paolo Bientinesi IPCC Showcase November 2016
Building a Multi-FPGA Virtualized Restricted Boltzmann Machine Architecture Using Embedded MPI
 Building a Multi-FPGA Virtualized Restricted Boltzmann Machine Architecture Using Embedded MPI Charles Lo and Paul Chow {locharl1, pc}@eecg.toronto.edu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Building a Multi-FPGA Virtualized Restricted Boltzmann Machine Architecture Using Embedded MPI Charles Lo and Paul Chow {locharl1, pc}@eecg.toronto.edu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Explore Computational Power of GPU in Electromagnetics and Micromagnetics
 Explore Computational Power of GPU in Electromagnetics and Micromagnetics Presenter: Sidi Fu, PhD candidate, UC San Diego Advisor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Center of Magnetic Recording Research, Department
Explore Computational Power of GPU in Electromagnetics and Micromagnetics Presenter: Sidi Fu, PhD candidate, UC San Diego Advisor: Prof. Vitaliy Lomakin Center of Magnetic Recording Research, Department
Why study protein dynamics?
 Why study protein dynamics? Protein flexibility is crucial for function. One average structure is not enough. Proteins constantly sample configurational space. Transport - binding and moving molecules
Why study protein dynamics? Protein flexibility is crucial for function. One average structure is not enough. Proteins constantly sample configurational space. Transport - binding and moving molecules
FENZI: GPU-enabled Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Large Membrane Regions based on the CHARMM force field and PME
 211 IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium : GPU-enabled Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Large Membrane Regions based on the force field and PME Narayan Ganesan, Michela Taufer
211 IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium : GPU-enabled Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Large Membrane Regions based on the force field and PME Narayan Ganesan, Michela Taufer
Long-range interactions: P 3 M, MMMxD, ELC, MEMD and ICC
 Long-range interactions: P 3 M, MMMxD, ELC, MEMD and ICC Axel Arnold Institute for Computational Physics Universität Stuttgart October 10, 2012 Long-range interactions gravity Coulomb interaction dipolar
Long-range interactions: P 3 M, MMMxD, ELC, MEMD and ICC Axel Arnold Institute for Computational Physics Universität Stuttgart October 10, 2012 Long-range interactions gravity Coulomb interaction dipolar
CE 530 Molecular Simulation
 1 CE 530 Molecular Simulation Lecture 14 Molecular Models David A. Kofke Department of Chemical Engineering SUNY Buffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu 2 Review Monte Carlo ensemble averaging, no dynamics easy
1 CE 530 Molecular Simulation Lecture 14 Molecular Models David A. Kofke Department of Chemical Engineering SUNY Buffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu 2 Review Monte Carlo ensemble averaging, no dynamics easy
Coarse-Grained Models!
 Coarse-Grained Models! Large and complex molecules (e.g. long polymers) can not be simulated on the all-atom level! Requires coarse-graining of the model! Coarse-grained models are usually also particles
Coarse-Grained Models! Large and complex molecules (e.g. long polymers) can not be simulated on the all-atom level! Requires coarse-graining of the model! Coarse-grained models are usually also particles
SP-CNN: A Scalable and Programmable CNN-based Accelerator. Dilan Manatunga Dr. Hyesoon Kim Dr. Saibal Mukhopadhyay
 SP-CNN: A Scalable and Programmable CNN-based Accelerator Dilan Manatunga Dr. Hyesoon Kim Dr. Saibal Mukhopadhyay Motivation Power is a first-order design constraint, especially for embedded devices. Certain
SP-CNN: A Scalable and Programmable CNN-based Accelerator Dilan Manatunga Dr. Hyesoon Kim Dr. Saibal Mukhopadhyay Motivation Power is a first-order design constraint, especially for embedded devices. Certain
Tutorial on the smooth particle-mesh Ewald algorithm
 Tutorial on the smooth particle-mesh Ewald algorithm These notes explain the smooth particle-mesh Ewald algorithm (SPME) in detail. The accompanying library libpme6 is a fully-featured implementation of
Tutorial on the smooth particle-mesh Ewald algorithm These notes explain the smooth particle-mesh Ewald algorithm (SPME) in detail. The accompanying library libpme6 is a fully-featured implementation of
Janus: FPGA Based System for Scientific Computing Filippo Mantovani
 Janus: FPGA Based System for Scientific Computing Filippo Mantovani Physics Department Università degli Studi di Ferrara Ferrara, 28/09/2009 Overview: 1. The physical problem: - Ising model and Spin Glass
Janus: FPGA Based System for Scientific Computing Filippo Mantovani Physics Department Università degli Studi di Ferrara Ferrara, 28/09/2009 Overview: 1. The physical problem: - Ising model and Spin Glass
A Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Homogeneous Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Silica Membrane
 A Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Homogeneous Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Silica Membrane Supplementary Information: Simulation Procedure and Physical Property Analysis Simulation Procedure The molecular
A Molecular Dynamics Simulation of a Homogeneous Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Silica Membrane Supplementary Information: Simulation Procedure and Physical Property Analysis Simulation Procedure The molecular
Anton: A Specialized ASIC for Molecular Dynamics
 Anton: A Specialized ASIC for Molecular Dynamics Martin M. Deneroff, David E. Shaw, Ron O. Dror, Jeffrey S. Kuskin, Richard H. Larson, John K. Salmon, and Cliff Young D. E. Shaw Research Marty.Deneroff@DEShawResearch.com
Anton: A Specialized ASIC for Molecular Dynamics Martin M. Deneroff, David E. Shaw, Ron O. Dror, Jeffrey S. Kuskin, Richard H. Larson, John K. Salmon, and Cliff Young D. E. Shaw Research Marty.Deneroff@DEShawResearch.com
Gromacs Workshop Spring CSC
 Gromacs Workshop Spring 2007 @ CSC Erik Lindahl Center for Biomembrane Research Stockholm University, Sweden David van der Spoel Dept. Cell & Molecular Biology Uppsala University, Sweden Berk Hess Max-Planck-Institut
Gromacs Workshop Spring 2007 @ CSC Erik Lindahl Center for Biomembrane Research Stockholm University, Sweden David van der Spoel Dept. Cell & Molecular Biology Uppsala University, Sweden Berk Hess Max-Planck-Institut
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATIONS OF BIOMOLECULES: Long-Range Electrostatic Effects
 Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1999. 28:155 79 Copyright c 1999 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATIONS OF BIOMOLECULES: Long-Range Electrostatic Effects Celeste Sagui
Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1999. 28:155 79 Copyright c 1999 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATIONS OF BIOMOLECULES: Long-Range Electrostatic Effects Celeste Sagui
An introduction to Molecular Dynamics. EMBO, June 2016
 An introduction to Molecular Dynamics EMBO, June 2016 What is MD? everything that living things do can be understood in terms of the jiggling and wiggling of atoms. The Feynman Lectures in Physics vol.
An introduction to Molecular Dynamics EMBO, June 2016 What is MD? everything that living things do can be understood in terms of the jiggling and wiggling of atoms. The Feynman Lectures in Physics vol.
Linear Scale-Space. Algorithms for Linear Scale-Space. Gaussian Image Derivatives. Rein van den Boomgaard University of Amsterdam.
 $ ( Linear Scale-Space Linear scale-space is constructed by embedding an image family of images that satisfy the diffusion equation: into a one parameter with initial condition convolution: The solution
$ ( Linear Scale-Space Linear scale-space is constructed by embedding an image family of images that satisfy the diffusion equation: into a one parameter with initial condition convolution: The solution
Multiple time step Monte Carlo simulations: Application to charged systems with Ewald summation
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 1 1 JULY 004 Multiple time step Monte Carlo simulations: Application to charged systems with Ewald summation Katarzyna Bernacki a) Department of Chemistry
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 1 1 JULY 004 Multiple time step Monte Carlo simulations: Application to charged systems with Ewald summation Katarzyna Bernacki a) Department of Chemistry
Computer simulation methods (2) Dr. Vania Calandrini
 Computer simulation methods (2) Dr. Vania Calandrini in the previous lecture: time average versus ensemble average MC versus MD simulations equipartition theorem (=> computing T) virial theorem (=> computing
Computer simulation methods (2) Dr. Vania Calandrini in the previous lecture: time average versus ensemble average MC versus MD simulations equipartition theorem (=> computing T) virial theorem (=> computing
Graphics Card Computing for Materials Modelling
 Graphics Card Computing for Materials Modelling Case study: Analytic Bond Order Potentials B. Seiser, T. Hammerschmidt, R. Drautz, D. Pettifor Funded by EPSRC within the collaborative multi-scale project
Graphics Card Computing for Materials Modelling Case study: Analytic Bond Order Potentials B. Seiser, T. Hammerschmidt, R. Drautz, D. Pettifor Funded by EPSRC within the collaborative multi-scale project
Introduction to Benchmark Test for Multi-scale Computational Materials Software
 Introduction to Benchmark Test for Multi-scale Computational Materials Software Shun Xu*, Jian Zhang, Zhong Jin xushun@sccas.cn Computer Network Information Center Chinese Academy of Sciences (IPCC member)
Introduction to Benchmark Test for Multi-scale Computational Materials Software Shun Xu*, Jian Zhang, Zhong Jin xushun@sccas.cn Computer Network Information Center Chinese Academy of Sciences (IPCC member)
arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 19 Oct 2008
![arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 19 Oct 2008 arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 19 Oct 2008](/thumbs/96/128248023.jpg) P 3 M algorithm for dipolar interactions Juan J. Cerdà, 1, V. Ballenegger, 2 O. Lenz, 1, 3 and C. Holm 1, 3 1 Frankfurt Inst. for Advanced Studies, (FIAS), arxiv:0805.4783v2 [physics.comp-ph] 19 Oct 2008
P 3 M algorithm for dipolar interactions Juan J. Cerdà, 1, V. Ballenegger, 2 O. Lenz, 1, 3 and C. Holm 1, 3 1 Frankfurt Inst. for Advanced Studies, (FIAS), arxiv:0805.4783v2 [physics.comp-ph] 19 Oct 2008
A reciprocal space based method for treating long range interactions in ab initio and force-field-based calculations in clusters
 A reciprocal space based method for treating long range interactions in ab initio and force-field-based calculations in clusters Glenn J. Martyna and Mark E. Tuckerman Citation: The Journal of Chemical
A reciprocal space based method for treating long range interactions in ab initio and force-field-based calculations in clusters Glenn J. Martyna and Mark E. Tuckerman Citation: The Journal of Chemical
Computational Molecular Biophysics. Computational Biophysics, GRS Jülich SS 2013
 Computational Molecular Biophysics Computational Biophysics, GRS Jülich SS 2013 Computational Considerations Number of terms for different energy contributions / E el ~N ~N ~N ~N 2 Computational cost for
Computational Molecular Biophysics Computational Biophysics, GRS Jülich SS 2013 Computational Considerations Number of terms for different energy contributions / E el ~N ~N ~N ~N 2 Computational cost for
Molecular Dynamics. A very brief introduction
 Molecular Dynamics A very brief introduction Sander Pronk Dept. of Theoretical Physics KTH Royal Institute of Technology & Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm, Sweden Why computer simulations? Two primary
Molecular Dynamics A very brief introduction Sander Pronk Dept. of Theoretical Physics KTH Royal Institute of Technology & Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm, Sweden Why computer simulations? Two primary
Astronomical Computer Simulations. Aaron Smith
 Astronomical Computer Simulations Aaron Smith 1 1. The Purpose and History of Astronomical Computer Simulations 2. Algorithms 3. Systems/Architectures 4. Simulation/Projects 2 The Purpose of Astronomical
Astronomical Computer Simulations Aaron Smith 1 1. The Purpose and History of Astronomical Computer Simulations 2. Algorithms 3. Systems/Architectures 4. Simulation/Projects 2 The Purpose of Astronomical
Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Dr. Noelia Faginas Lago Dipartimento di Chimica,Biologia e Biotecnologie Università di Perugia
 Molecular Dynamics Simulations Dr. Noelia Faginas Lago Dipartimento di Chimica,Biologia e Biotecnologie Università di Perugia 1 An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Simulations Macroscopic properties
Molecular Dynamics Simulations Dr. Noelia Faginas Lago Dipartimento di Chimica,Biologia e Biotecnologie Università di Perugia 1 An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Simulations Macroscopic properties
ab initio Electronic Structure Calculations
 ab initio Electronic Structure Calculations New scalability frontiers using the BG/L Supercomputer C. Bekas, A. Curioni and W. Andreoni IBM, Zurich Research Laboratory Rueschlikon 8803, Switzerland ab
ab initio Electronic Structure Calculations New scalability frontiers using the BG/L Supercomputer C. Bekas, A. Curioni and W. Andreoni IBM, Zurich Research Laboratory Rueschlikon 8803, Switzerland ab
Bioengineering 215. An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules
 Bioengineering 215 An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules David Parker May 18, 2007 ntroduction A principal tool to study biological molecules is molecular dynamics simulations (MD). MD
Bioengineering 215 An Introduction to Molecular Dynamics for Biomolecules David Parker May 18, 2007 ntroduction A principal tool to study biological molecules is molecular dynamics simulations (MD). MD
Molecular Mechanics, Dynamics & Docking
 Molecular Mechanics, Dynamics & Docking Lawrence Hunter, Ph.D. Director, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter
Molecular Mechanics, Dynamics & Docking Lawrence Hunter, Ph.D. Director, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter
Exam 2. Average: 85.6 Median: 87.0 Maximum: Minimum: 55.0 Standard Deviation: Numerical Methods Fall 2011 Lecture 20
 Exam 2 Average: 85.6 Median: 87.0 Maximum: 100.0 Minimum: 55.0 Standard Deviation: 10.42 Fall 2011 1 Today s class Multiple Variable Linear Regression Polynomial Interpolation Lagrange Interpolation Newton
Exam 2 Average: 85.6 Median: 87.0 Maximum: 100.0 Minimum: 55.0 Standard Deviation: 10.42 Fall 2011 1 Today s class Multiple Variable Linear Regression Polynomial Interpolation Lagrange Interpolation Newton
Cider Seminar, University of Toronto DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AWGN COMMUNICATION CHANNEL EMULATOR
 Cider Seminar, University of Toronto DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AWGN COMMUNICATION CHANNEL EMULATOR Prof. Emmanuel Boutillon LESTER South Brittany University emmanuel.boutillon@univ-ubs.fr
Cider Seminar, University of Toronto DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF A HIGH SPEED AWGN COMMUNICATION CHANNEL EMULATOR Prof. Emmanuel Boutillon LESTER South Brittany University emmanuel.boutillon@univ-ubs.fr
All-atom Molecular Mechanics. Trent E. Balius AMS 535 / CHE /27/2010
 All-atom Molecular Mechanics Trent E. Balius AMS 535 / CHE 535 09/27/2010 Outline Molecular models Molecular mechanics Force Fields Potential energy function functional form parameters and parameterization
All-atom Molecular Mechanics Trent E. Balius AMS 535 / CHE 535 09/27/2010 Outline Molecular models Molecular mechanics Force Fields Potential energy function functional form parameters and parameterization
XXL-BIOMD. Large Scale Biomolecular Dynamics Simulations. onsdag, 2009 maj 13
 XXL-BIOMD Large Scale Biomolecular Dynamics Simulations David van der Spoel, PI Aatto Laaksonen Peter Coveney Siewert-Jan Marrink Mikael Peräkylä Uppsala, Sweden Stockholm, Sweden London, UK Groningen,
XXL-BIOMD Large Scale Biomolecular Dynamics Simulations David van der Spoel, PI Aatto Laaksonen Peter Coveney Siewert-Jan Marrink Mikael Peräkylä Uppsala, Sweden Stockholm, Sweden London, UK Groningen,
Set the initial conditions r i. Update neighborlist. Get new forces F i
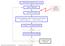 Set the initial conditions r i ( t 0 ), v i ( t 0 ) Update neighborlist Potential models ionic compounds Get new forces F i ( r i ) Solve the equations of motion numerically over time step Δt : r i ( t
Set the initial conditions r i ( t 0 ), v i ( t 0 ) Update neighborlist Potential models ionic compounds Get new forces F i ( r i ) Solve the equations of motion numerically over time step Δt : r i ( t
Computational Chemistry - MD Simulations
 Computational Chemistry - MD Simulations P. Ojeda-May pedro.ojeda-may@umu.se Department of Chemistry/HPC2N, Umeå University, 901 87, Sweden. May 2, 2017 Table of contents 1 Basics on MD simulations Accelerated
Computational Chemistry - MD Simulations P. Ojeda-May pedro.ojeda-may@umu.se Department of Chemistry/HPC2N, Umeå University, 901 87, Sweden. May 2, 2017 Table of contents 1 Basics on MD simulations Accelerated
Simulations of bulk phases. Periodic boundaries. Cubic boxes
 Simulations of bulk phases ChE210D Today's lecture: considerations for setting up and running simulations of bulk, isotropic phases (e.g., liquids and gases) Periodic boundaries Cubic boxes In simulations
Simulations of bulk phases ChE210D Today's lecture: considerations for setting up and running simulations of bulk, isotropic phases (e.g., liquids and gases) Periodic boundaries Cubic boxes In simulations
Accelerating Model Reduction of Large Linear Systems with Graphics Processors
 Accelerating Model Reduction of Large Linear Systems with Graphics Processors P. Benner 1, P. Ezzatti 2, D. Kressner 3, E.S. Quintana-Ortí 4, Alfredo Remón 4 1 Max-Plank-Institute for Dynamics of Complex
Accelerating Model Reduction of Large Linear Systems with Graphics Processors P. Benner 1, P. Ezzatti 2, D. Kressner 3, E.S. Quintana-Ortí 4, Alfredo Remón 4 1 Max-Plank-Institute for Dynamics of Complex
Classical Electrostatics for Biomolecular Simulations
 pubs.acs.org/cr Classical Electrostatics for Biomolecular Simulations G. Andreś Cisneros, Mikko Karttunen, Pengyu Ren, and Celeste Sagui*, Department of Chemistry, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan
pubs.acs.org/cr Classical Electrostatics for Biomolecular Simulations G. Andreś Cisneros, Mikko Karttunen, Pengyu Ren, and Celeste Sagui*, Department of Chemistry, Wayne State University, Detroit, Michigan
Force Field for Water Based on Neural Network
 Force Field for Water Based on Neural Network Hao Wang Department of Chemistry, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708, USA Weitao Yang* Department of Chemistry, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708, USA Department
Force Field for Water Based on Neural Network Hao Wang Department of Chemistry, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708, USA Weitao Yang* Department of Chemistry, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708, USA Department
Charge equilibration
 Charge equilibration Taylor expansion of energy of atom A @E E A (Q) =E A0 + Q A + 1 @Q A 0 2 Q2 A @ 2 E @Q 2 A 0 +... The corresponding energy of cation/anion and neutral atom E A (+1) = E A0 + @E @Q
Charge equilibration Taylor expansion of energy of atom A @E E A (Q) =E A0 + Q A + 1 @Q A 0 2 Q2 A @ 2 E @Q 2 A 0 +... The corresponding energy of cation/anion and neutral atom E A (+1) = E A0 + @E @Q
1/11/12. A Scalar Field. The Electric Field + + A Vector Field
 The lectric ield q Coulomb s Law of lectro-static orce: qq k r How does q know of the presence of q? q rˆ A Scalar ield 77 7 7 75 8 7 84 77 8 68 64 8 8 55 7 66 75 8 8 9 9 9 These isolated temperatures
The lectric ield q Coulomb s Law of lectro-static orce: qq k r How does q know of the presence of q? q rˆ A Scalar ield 77 7 7 75 8 7 84 77 8 68 64 8 8 55 7 66 75 8 8 9 9 9 These isolated temperatures
Parameter Estimation for the Dirichlet-Multinomial Distribution
 Parameter Estimation for the Dirichlet-Multinomial Distribution Amanda Peterson Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County May 20, 2011 Abstract. In the 1998 paper
Parameter Estimation for the Dirichlet-Multinomial Distribution Amanda Peterson Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County May 20, 2011 Abstract. In the 1998 paper
Multiscale Materials Modeling
 Multiscale Materials Modeling Lecture 09 Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) Techniques Fundamentals of Sustainable Technology These notes created by David Keffer, University of Tennessee, Knoxville,
Multiscale Materials Modeling Lecture 09 Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) Techniques Fundamentals of Sustainable Technology These notes created by David Keffer, University of Tennessee, Knoxville,
PHY 114 A General Physics II 11 AM-12:15 PM TR Olin 101. Plan for Lecture 1:
 PHY 4 A General Physics II AM-:5 PM TR Olin Plan for Lecture :. Welcome & overview. Class structure & announcements 3. Electrical charges and forces /8/0 PHY 4 A Spring 0 -- Lecture PHY 4 A General Physics
PHY 4 A General Physics II AM-:5 PM TR Olin Plan for Lecture :. Welcome & overview. Class structure & announcements 3. Electrical charges and forces /8/0 PHY 4 A Spring 0 -- Lecture PHY 4 A General Physics
Introduction to Molecular Dynamics
 Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Dr. Kasra Momeni www.knanosys.com Overview of the MD Classical Dynamics Outline Basics and Terminology Pairwise interacting objects Interatomic potentials (short-range
Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Dr. Kasra Momeni www.knanosys.com Overview of the MD Classical Dynamics Outline Basics and Terminology Pairwise interacting objects Interatomic potentials (short-range
Andrew Morton University of Waterloo Canada
 EDF Feasibility and Hardware Accelerators Andrew Morton University of Waterloo Canada Outline 1) Introduction and motivation 2) Review of EDF and feasibility analysis 3) Hardware accelerators and scheduling
EDF Feasibility and Hardware Accelerators Andrew Morton University of Waterloo Canada Outline 1) Introduction and motivation 2) Review of EDF and feasibility analysis 3) Hardware accelerators and scheduling
Scalable and Power-Efficient Data Mining Kernels
 Scalable and Power-Efficient Data Mining Kernels Alok Choudhary, John G. Searle Professor Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and Professor, Kellogg School of Management Director of the
Scalable and Power-Efficient Data Mining Kernels Alok Choudhary, John G. Searle Professor Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and Professor, Kellogg School of Management Director of the
How to Avoid Butchering S-parameters
 How to Avoid Butchering S-parameters Course Number: TP-T3 Yuriy Shlepnev, Simberian Inc. shlepnev@simberian.com +1-(702)-876-2882 1 Introduction Outline Quality of S-parameter models Rational macro-models
How to Avoid Butchering S-parameters Course Number: TP-T3 Yuriy Shlepnev, Simberian Inc. shlepnev@simberian.com +1-(702)-876-2882 1 Introduction Outline Quality of S-parameter models Rational macro-models
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT)
 Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 9 1) Coulomb s Law and Field Intensity 2) Electric Fields Due to Continuous Charge Distributions Line Charge Surface Charge Volume Charge Coulomb's Law Coulomb's
Electromagnetic Field Theory (EMT) Lecture # 9 1) Coulomb s Law and Field Intensity 2) Electric Fields Due to Continuous Charge Distributions Line Charge Surface Charge Volume Charge Coulomb's Law Coulomb's
Neighbor Tables Long-Range Potentials
 Neighbor Tables Long-Range Potentials Today we learn how we can handle long range potentials. Neighbor tables Long-range potential Ewald sums MSE485/PHY466/CSE485 1 Periodic distances Minimum Image Convention:
Neighbor Tables Long-Range Potentials Today we learn how we can handle long range potentials. Neighbor tables Long-range potential Ewald sums MSE485/PHY466/CSE485 1 Periodic distances Minimum Image Convention:
Computation Time Assessment of a Galerkin Finite Volume Method (GFVM) for Solving Time Solid Mechanics Problems under Dynamic Loads
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Civil, Structural and Transportation Engineering Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, May 4 5, 215 Paper o. 31 Computation Time Assessment of a Galerkin Finite Volume
Proceedings of the International Conference on Civil, Structural and Transportation Engineering Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, May 4 5, 215 Paper o. 31 Computation Time Assessment of a Galerkin Finite Volume
Fondamenti di Chimica Farmaceutica. Computer Chemistry in Drug Research: Introduction
 Fondamenti di Chimica Farmaceutica Computer Chemistry in Drug Research: Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction Computer Chemistry in Drug Design Drug Discovery: Target identification Lead
Fondamenti di Chimica Farmaceutica Computer Chemistry in Drug Research: Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction Computer Chemistry in Drug Design Drug Discovery: Target identification Lead
Example questions for Molecular modelling (Level 4) Dr. Adrian Mulholland
 Example questions for Molecular modelling (Level 4) Dr. Adrian Mulholland 1) Question. Two methods which are widely used for the optimization of molecular geometies are the Steepest descents and Newton-Raphson
Example questions for Molecular modelling (Level 4) Dr. Adrian Mulholland 1) Question. Two methods which are widely used for the optimization of molecular geometies are the Steepest descents and Newton-Raphson
Reflections on S-parameter Quality DesignCon IBIS Summit, Santa Clara, February 3, 2011
 Reflections on S-parameter Quality DesignCon IBIS Summit, Santa Clara, February 3, 2011 Yuriy Shlepnev shlepnev@simberian.com Copyright 2011 by Simberian Inc. Reuse by written permission only. All rights
Reflections on S-parameter Quality DesignCon IBIS Summit, Santa Clara, February 3, 2011 Yuriy Shlepnev shlepnev@simberian.com Copyright 2011 by Simberian Inc. Reuse by written permission only. All rights
Concept of Statistical Model Checking. Presented By: Diana EL RABIH
 Concept of Statistical Model Checking Presented By: Diana EL RABIH Introduction Model checking of stochastic systems Continuous-time Markov chains Continuous Stochastic Logic (CSL) Probabilistic time-bounded
Concept of Statistical Model Checking Presented By: Diana EL RABIH Introduction Model checking of stochastic systems Continuous-time Markov chains Continuous Stochastic Logic (CSL) Probabilistic time-bounded
Using Molecular Dynamics to Compute Properties CHEM 430
 Using Molecular Dynamics to Compute Properties CHEM 43 Heat Capacity and Energy Fluctuations Running an MD Simulation Equilibration Phase Before data-collection and results can be analyzed the system
Using Molecular Dynamics to Compute Properties CHEM 43 Heat Capacity and Energy Fluctuations Running an MD Simulation Equilibration Phase Before data-collection and results can be analyzed the system
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Molecular Mechanics
 Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Molecular Mechanics How to Calculate Energies Calculation of molecular energies is of key importance in protein folding, molecular modelling etc. There are two main computational
Structural Bioinformatics (C3210) Molecular Mechanics How to Calculate Energies Calculation of molecular energies is of key importance in protein folding, molecular modelling etc. There are two main computational
Material Surfaces, Grain Boundaries and Interfaces: Structure-Property Relationship Predictions
 Material Surfaces, Grain Boundaries and Interfaces: Structure-Property Relationship Predictions Susan B. Sinnott Department of Materials Science and Engineering Penn State University September 16, 2016
Material Surfaces, Grain Boundaries and Interfaces: Structure-Property Relationship Predictions Susan B. Sinnott Department of Materials Science and Engineering Penn State University September 16, 2016
New Algorithms for Conventional and. Jing Kong ( 孔静 ) Q-Chem Inc. Pittsburgh, PA
 New Algorithms for Conventional and Nondynamic DFT Jing Kong ( 孔静 ) Q-Chem Inc. Pittsburgh, PA XC Numerical Integration mrxc: multiresolution exchage-correlation Chunming Chang Nick Russ Phys. Rev. A.,
New Algorithms for Conventional and Nondynamic DFT Jing Kong ( 孔静 ) Q-Chem Inc. Pittsburgh, PA XC Numerical Integration mrxc: multiresolution exchage-correlation Chunming Chang Nick Russ Phys. Rev. A.,
Molecular Dynamics Simulations
 MDGRAPE-3 chip: A 165- Gflops application-specific LSI for Molecular Dynamics Simulations Makoto Taiji High-Performance Biocomputing Research Team Genomic Sciences Center, RIKEN Molecular Dynamics Simulations
MDGRAPE-3 chip: A 165- Gflops application-specific LSI for Molecular Dynamics Simulations Makoto Taiji High-Performance Biocomputing Research Team Genomic Sciences Center, RIKEN Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Long range interactions in computer simulations. 1 (Part 3)
 Long range interactions in computer simulations. 1 (Part 3) Laboratoire de Physique Théorique (UMR-867), Université Paris-Sud 11 et CNRS, Bâtiment 10, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France. (.@th.u-psud.fr) 1 st Workshop
Long range interactions in computer simulations. 1 (Part 3) Laboratoire de Physique Théorique (UMR-867), Université Paris-Sud 11 et CNRS, Bâtiment 10, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France. (.@th.u-psud.fr) 1 st Workshop
Lecture 27: Hardware Acceleration. James C. Hoe Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon University
 18 447 Lecture 27: Hardware Acceleration James C. Hoe Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon niversity 18 447 S18 L27 S1, James C. Hoe, CM/ECE/CALCM, 2018 18 447 S18 L27 S2, James C. Hoe, CM/ECE/CALCM, 2018
18 447 Lecture 27: Hardware Acceleration James C. Hoe Department of ECE Carnegie Mellon niversity 18 447 S18 L27 S1, James C. Hoe, CM/ECE/CALCM, 2018 18 447 S18 L27 S2, James C. Hoe, CM/ECE/CALCM, 2018
Efficient multiple time step method for use with Ewald and particle mesh Ewald for large biomolecular systems
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 115, NUMBER 5 1 AUGUST 2001 Efficient multiple time step method for use with Ewald and particle mesh Ewald for large biomolecular systems Ruhong Zhou IBM Thomas J. Watson
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 115, NUMBER 5 1 AUGUST 2001 Efficient multiple time step method for use with Ewald and particle mesh Ewald for large biomolecular systems Ruhong Zhou IBM Thomas J. Watson
arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 22 Nov 2012
![arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 22 Nov 2012 arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 22 Nov 2012](/thumbs/93/111410153.jpg) A Customized 3D GPU Poisson Solver for Free BCs Nazim Dugan a, Luigi Genovese b, Stefan Goedecker a, a Department of Physics, University of Basel, Klingelbergstr. 82, 4056 Basel, Switzerland b Laboratoire
A Customized 3D GPU Poisson Solver for Free BCs Nazim Dugan a, Luigi Genovese b, Stefan Goedecker a, a Department of Physics, University of Basel, Klingelbergstr. 82, 4056 Basel, Switzerland b Laboratoire
Beam dynamics calculation
 September 6 Beam dynamics calculation S.B. Vorozhtsov, Е.Е. Perepelkin and V.L. Smirnov Dubna, JINR http://parallel-compute.com Outline Problem formulation Numerical methods OpenMP and CUDA realization
September 6 Beam dynamics calculation S.B. Vorozhtsov, Е.Е. Perepelkin and V.L. Smirnov Dubna, JINR http://parallel-compute.com Outline Problem formulation Numerical methods OpenMP and CUDA realization
CS 179: GPU Programming. Lecture 9 / Homework 3
 CS 179: GPU Programming Lecture 9 / Homework 3 Recap Some algorithms are less obviously parallelizable : Reduction Sorts FFT (and certain recursive algorithms) Parallel FFT structure (radix-2) Bit-reversed
CS 179: GPU Programming Lecture 9 / Homework 3 Recap Some algorithms are less obviously parallelizable : Reduction Sorts FFT (and certain recursive algorithms) Parallel FFT structure (radix-2) Bit-reversed
Econometrics I. Lecture 10: Nonparametric Estimation with Kernels. Paul T. Scott NYU Stern. Fall 2018
 Econometrics I Lecture 10: Nonparametric Estimation with Kernels Paul T. Scott NYU Stern Fall 2018 Paul T. Scott NYU Stern Econometrics I Fall 2018 1 / 12 Nonparametric Regression: Intuition Let s get
Econometrics I Lecture 10: Nonparametric Estimation with Kernels Paul T. Scott NYU Stern Fall 2018 Paul T. Scott NYU Stern Econometrics I Fall 2018 1 / 12 Nonparametric Regression: Intuition Let s get
Simulation of molecular systems by molecular dynamics
 Simulation of molecular systems by molecular dynamics Yohann Moreau yohann.moreau@ujf-grenoble.fr November 26, 2015 Yohann Moreau (UJF) Molecular Dynamics, Label RFCT 2015 November 26, 2015 1 / 35 Introduction
Simulation of molecular systems by molecular dynamics Yohann Moreau yohann.moreau@ujf-grenoble.fr November 26, 2015 Yohann Moreau (UJF) Molecular Dynamics, Label RFCT 2015 November 26, 2015 1 / 35 Introduction
Development of Molecular Dynamics Simulation System for Large-Scale Supra-Biomolecules, PABIOS (PArallel BIOmolecular Simulator)
 Development of Molecular Dynamics Simulation System for Large-Scale Supra-Biomolecules, PABIOS (PArallel BIOmolecular Simulator) Group Representative Hisashi Ishida Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute
Development of Molecular Dynamics Simulation System for Large-Scale Supra-Biomolecules, PABIOS (PArallel BIOmolecular Simulator) Group Representative Hisashi Ishida Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute
FDTD for 1D wave equation. Equation: 2 H Notations: o o. discretization. ( t) ( x) i i i i i
 FDTD for 1D wave equation Equation: 2 H = t 2 c2 2 H x 2 Notations: o t = nδδ, x = iδx o n H nδδ, iδx = H i o n E nδδ, iδx = E i discretization H 2H + H H 2H + H n+ 1 n n 1 n n n i i i 2 i+ 1 i i 1 = c
FDTD for 1D wave equation Equation: 2 H = t 2 c2 2 H x 2 Notations: o t = nδδ, x = iδx o n H nδδ, iδx = H i o n E nδδ, iδx = E i discretization H 2H + H H 2H + H n+ 1 n n 1 n n n i i i 2 i+ 1 i i 1 = c
ACCELERATED LEARNING OF GAUSSIAN PROCESS MODELS
 ACCELERATED LEARNING OF GAUSSIAN PROCESS MODELS Bojan Musizza, Dejan Petelin, Juš Kocijan, Jožef Stefan Institute Jamova 39, Ljubljana, Slovenia University of Nova Gorica Vipavska 3, Nova Gorica, Slovenia
ACCELERATED LEARNING OF GAUSSIAN PROCESS MODELS Bojan Musizza, Dejan Petelin, Juš Kocijan, Jožef Stefan Institute Jamova 39, Ljubljana, Slovenia University of Nova Gorica Vipavska 3, Nova Gorica, Slovenia
A smooth particle-mesh Ewald algorithm for Stokes suspension simulations: The sedimentation of fibers
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 7, 03330 2005 A smooth particle-mesh Ewald algorithm for Stokes suspension simulations: The sedimentation of fibers David Saintillan and Eric Darve a Department of Mechanical Engineering,
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 7, 03330 2005 A smooth particle-mesh Ewald algorithm for Stokes suspension simulations: The sedimentation of fibers David Saintillan and Eric Darve a Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Week 4. Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential
 Week 4 Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential Electric Charge - A property of matter Matter is made up of two kinds of electric charges (positive and negative). Like charges repel, unlike
Week 4 Outline Review electric Forces Review electric Potential Electric Charge - A property of matter Matter is made up of two kinds of electric charges (positive and negative). Like charges repel, unlike
ARTICLES. Constant Temperature Constrained Molecular Dynamics: The Newton-Euler Inverse Mass Operator Method
 10508 J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 10508-10517 ARTICLES Constant Temperature Constrained Molecular Dynamics: The Newton-Euler Inverse Mass Operator Method Nagarajan Vaidehi, Abhinandan Jain, and William A.
10508 J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 10508-10517 ARTICLES Constant Temperature Constrained Molecular Dynamics: The Newton-Euler Inverse Mass Operator Method Nagarajan Vaidehi, Abhinandan Jain, and William A.
Analysis of Software Artifacts
 Analysis of Software Artifacts System Performance I Shu-Ngai Yeung (with edits by Jeannette Wing) Department of Statistics Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 2001 by Carnegie Mellon University
Analysis of Software Artifacts System Performance I Shu-Ngai Yeung (with edits by Jeannette Wing) Department of Statistics Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 2001 by Carnegie Mellon University
Reading: Chapter 28. 4πε r. For r > a. Gauss s Law
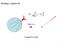 Reading: Chapter 8 Q 4πε r o k Q r e For r > a Gauss s Law 1 Chapter 8 Gauss s Law lectric Flux Definition: lectric flux is the product of the magnitude of the electric field and the surface area, A, perpendicular
Reading: Chapter 8 Q 4πε r o k Q r e For r > a Gauss s Law 1 Chapter 8 Gauss s Law lectric Flux Definition: lectric flux is the product of the magnitude of the electric field and the surface area, A, perpendicular
GPU acceleration of Newton s method for large systems of polynomial equations in double double and quad double arithmetic
 GPU acceleration of Newton s method for large systems of polynomial equations in double double and quad double arithmetic Jan Verschelde joint work with Xiangcheng Yu University of Illinois at Chicago
GPU acceleration of Newton s method for large systems of polynomial equations in double double and quad double arithmetic Jan Verschelde joint work with Xiangcheng Yu University of Illinois at Chicago
Faster Kinetics: Accelerate Your Finite-Rate Combustion Simulation with GPUs
 Faster Kinetics: Accelerate Your Finite-Rate Combustion Simulation with GPUs Christopher P. Stone, Ph.D. Computational Science and Engineering, LLC Kyle Niemeyer, Ph.D. Oregon State University 2 Outline
Faster Kinetics: Accelerate Your Finite-Rate Combustion Simulation with GPUs Christopher P. Stone, Ph.D. Computational Science and Engineering, LLC Kyle Niemeyer, Ph.D. Oregon State University 2 Outline
Supporting Information. for An atomistic modeling of F-actin mechanical responses and determination of. mechanical properties
 Supporting Information for An atomistic modeling of F-actin mechanical responses and determination of mechanical properties Authors: Si Li 1, Jin Zhang 2, Chengyuan Wang 1, Perumal Nithiarasu 1 1. Zienkiewicz
Supporting Information for An atomistic modeling of F-actin mechanical responses and determination of mechanical properties Authors: Si Li 1, Jin Zhang 2, Chengyuan Wang 1, Perumal Nithiarasu 1 1. Zienkiewicz
PanHomc'r I'rui;* :".>r '.a'' W"»' I'fltolt. 'j'l :. r... Jnfii<on. Kslaiaaac. <.T i.. %.. 1 >
 5 28 (x / &» )»(»»» Q ( 3 Q» (» ( (3 5» ( q 2 5 q 2 5 5 8) 5 2 2 ) ~ ( / x {» /»»»»» (»»» ( 3 ) / & Q ) X ] Q & X X X x» 8 ( &» 2 & % X ) 8 x & X ( #»»q 3 ( ) & X 3 / Q X»»» %» ( z 22 (»» 2» }» / & 2 X
5 28 (x / &» )»(»»» Q ( 3 Q» (» ( (3 5» ( q 2 5 q 2 5 5 8) 5 2 2 ) ~ ( / x {» /»»»»» (»»» ( 3 ) / & Q ) X ] Q & X X X x» 8 ( &» 2 & % X ) 8 x & X ( #»»q 3 ( ) & X 3 / Q X»»» %» ( z 22 (»» 2» }» / & 2 X
Forces, Energy and Equations of Motion
 Forces, Energy and Equations of Motion Chapter 1 P. J. Grandinetti Chem. 4300 Jan. 8, 2019 P. J. Grandinetti (Chem. 4300) Forces, Energy and Equations of Motion Jan. 8, 2019 1 / 50 Galileo taught us how
Forces, Energy and Equations of Motion Chapter 1 P. J. Grandinetti Chem. 4300 Jan. 8, 2019 P. J. Grandinetti (Chem. 4300) Forces, Energy and Equations of Motion Jan. 8, 2019 1 / 50 Galileo taught us how
Notes for Lecture 10
 February 2, 26 Notes for Lecture Introduction to grid-based methods for solving Poisson and Laplace Equations Finite difference methods The basis for most grid-based finite difference methods is the Taylor
February 2, 26 Notes for Lecture Introduction to grid-based methods for solving Poisson and Laplace Equations Finite difference methods The basis for most grid-based finite difference methods is the Taylor
Quantum computing with superconducting qubits Towards useful applications
 Quantum computing with superconducting qubits Towards useful applications Stefan Filipp IBM Research Zurich Switzerland Forum Teratec 2018 June 20, 2018 Palaiseau, France Why Quantum Computing? Why now?
Quantum computing with superconducting qubits Towards useful applications Stefan Filipp IBM Research Zurich Switzerland Forum Teratec 2018 June 20, 2018 Palaiseau, France Why Quantum Computing? Why now?
