A Mathematical Study of Germinal Center Formation
|
|
|
- Wilfred Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Mathematical Study of Germinal Center Formation Samantha Erwin Adviser: Dr. Stanca Ciupe Virginia Tech October 1, 2014 Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 1/19
2 1 Biology 2 The Model 3 Results 4 Current Work Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 2/19
3 Biology Long term goal: Develop mathematical models of immune responses to chronic infections. Currently, developing mathematical model of immune responses in non chronic infections. Recently experimentalist discovered T follicular helper cells play a role in adaptive immune responses. Germinal center formations is believed to be dependent on T follicular helper cell and B cell interactions. Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 3/19
4 Biology Image of T follicular helper cell migration, development, and B cell interactions in extra follicular and germinal centers. [ Weinstein, J. S., Hernandez, S. G., and Craft, J. T cells that promote B-cell maturation in systemic autoimmunity. Immunological Reviews, 247: , 2012.] Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 4/19
5 The Model We first look at the host-pathogen dynamics leading to successful antibody response capable of clearing an infection. dn dh dg db 0 db i db n dp = s N d N N α N VN, = α N VN d H H γhb 0, = βγhb 0 d G G ηg = d 0 B 0 σb 0 G, n B i, i=0 = 2ασB i 1 G σb i G d i B i, = 2ασB n 1 G d i B n κb n, = κb n. Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 5/19
6 The Model Our goal for this work is to determine the dynamical evolution of the total B cells in the germinal centers. B T = n i=0 B i for healthy and HIV chronically infected individuals who do and do not control the virus. We have started this work with germinal center formation during non-chronic disease. Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 6/19
7 Known Parameters Name Value Units d N 0.01 per day d H 0.01 per day d G 0.01 per day d 0...d N 0.8 per day α N ml/(virus x day) s N 10 4 cells per ml V 10 4 copes per ml κ 1.2 per day α ml/(cell x day) β 1.97 ml/(cell x day) η ml/(cell x day) Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 7/19
8 Initial Conditions Cells Initial Condition Units N s N d H cells per ml H 0 cells per ml G 0 cells per ml B 0 3 cells per ml B i 0 cells per ml B i 0 cells per ml B n 0 cells per ml P 0 cells per ml Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 8/19
9 Numerical Results Data was gathered from Hollowood & Macartney. They used young, pathogen free mice and measured splenic germinal center cell proliferation responses to a T-dependent antigen. The total number of B cells in a germinal center, B T, versus time (in days). t B T In natural infection germinal center B cells undergo 5 10 steps of somatic hypermutations maturation, or n = 5 to n = 10 in our model. Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 9/19
10 Data Fitting For our results we used n = 8 and fit the parameters σ and γ which represent B cells maturation rate and T FH cells recruitment inside the germinal centers. Parameter Best Fit Description γ γhb 0 σ σb i G 10 4 B T, n=8 Collected Data Total Cells per Germinal Center Days Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 10/19
11 Data Fitting All parts of the model N 10 6 H G P B 0 B 2 B 4 B 6 B n B t Populations Total B Cells in Germinal Center Days Days Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 11/19
12 Germinal Center Formation for Non-Chronic Infection Clone distribution By the time the germinal center becomes extinct, almost all B cells have the highest degree of somatic hypermutation. This results holds even when η = 0, suggesting that B cells do not compete for T FH cells. 1 Distribution of clones at t=10 1 Distribution of clones at t=20 1 Distribution of clones at t= clone number clone number clone number B i /B T B i /B T B i /B T Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 12/19
13 Chronic Infections In HIV patients highly mutated, broadly neutralizing antibodies are formed and an increase in steps of B cells somatic hypermutations occur. We assumed that all parameters are as in the non-chronic case and used n=50 in our model. We predict that B T grows to 10 6 cells and the germinal centers take longer than 30 days to end B T, n=50 Collected Data 10 5 Total Cells per Germinal Center Days Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 13/19
14 Chronic Infections All parts of the model Populations N H G P Total B Cells in Germinal Center B 0 B 20 B 30 B 40 B n B t Days Days Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 14/19
15 The Model We first look at the host-pathogen dynamics leading to successful antibody response capable of clearing an infection. dn dh dg db 0 db i db n dp = s N d N N α N VN, = α N VN d H H γhb 0, = βγhb 0 d G G ηg = d 0 B 0 σb 0 G, n B i, i=0 = 2ασB i 1 G σb i G d i B i, = 2ασB n 1 G d i B n κb n, = κb n. Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 15/19
16 Chronic vs. Nonchronic Infection B, n=8 T 10 6 B, n=50 T 10 3 Collected Data G, n=8 G, n=50 Total Cells per Germinal Center Populations Days Days Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 16/19
17 Germinal Center Formation for Chronic Infection 0.12 B cell competition for T FH cells is important in this scenario, and it leads to a decrease in T FH cell numbers at the peak of B T. As a consequence, B cells of highest somatic hypermutation allowed by the model are not reached. Our future goals are to determine the factors that allow for the emergence and dominance of the high affinity clones. Distribution of clones at t= Distribution of clones at t= Distribution of clones at t= clone number 0.06 clone number 0.06 clone number B i /B T B i /B T B i /B T Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 17/19
18 Mutating Virus dn dh dg db 0 db i db n dv 0 dv i dv n dp i = s N d N N α N Vi N = α N Vi N d H H γhb 0 = βγhb 0 d G G ηg B i = σb 0 GV 0 d 0 B 0 κ 0 B 0 = 2ασB i 1 V i G σb i V i G d i B i k i B i = 2ασB n 1 V ng d nb n κ nb n = d V V 0 µ 0 B 0 V 0 = p i 1 V i 1 d V V i p 0 V 0 µ i B i V i = p n 1 V n 1 d V V n p i V i µ nb nv n = κ i B i d pp i Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 18/19
19 Thank you Thank you! Samantha Erwin Modeling Germinal Center Formation 19/19
Global Dynamics of B Cells and Anti-Idiotipic B Cells and its Application to Autoimmunity
 Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math., 24 (2007), 105 118 Area 1 Global Dynamics of B Cells and Anti-Idiotipic B Cells and its Application to Autoimmunity Toru Sasaki and Tsuyoshi Kajiwara Okayama University E-mail:
Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math., 24 (2007), 105 118 Area 1 Global Dynamics of B Cells and Anti-Idiotipic B Cells and its Application to Autoimmunity Toru Sasaki and Tsuyoshi Kajiwara Okayama University E-mail:
Mathematical Modeling of Immune Responses to Hepatitis C Virus Infection
 East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Electronic Theses and Dissertations 12-2014 Mathematical Modeling of Immune Responses to Hepatitis C Virus Infection Ivan
East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Electronic Theses and Dissertations 12-2014 Mathematical Modeling of Immune Responses to Hepatitis C Virus Infection Ivan
Chapters AP Biology Objectives. Objectives: You should know...
 Objectives: You should know... Notes 1. Scientific evidence supports the idea that evolution has occurred in all species. 2. Scientific evidence supports the idea that evolution continues to occur. 3.
Objectives: You should know... Notes 1. Scientific evidence supports the idea that evolution has occurred in all species. 2. Scientific evidence supports the idea that evolution continues to occur. 3.
Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview
 e Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology How do we keep your body healthy L01 4.3.1.1 Communicable (infectious) disease L02 4.3.1.2 Viral diseases L03 4.3.1.3 Bacterial
e Year 09 Science Learning Cycle 5 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology How do we keep your body healthy L01 4.3.1.1 Communicable (infectious) disease L02 4.3.1.2 Viral diseases L03 4.3.1.3 Bacterial
An Immune System Inspired Approach to Automated Program Verification
 An Immune System Inspired Approach to Automated Program Verification Soumya Banerjee Abstract An immune system inspired Artificial Immune System (AIS) algorithm is presented, and is used for the purposes
An Immune System Inspired Approach to Automated Program Verification Soumya Banerjee Abstract An immune system inspired Artificial Immune System (AIS) algorithm is presented, and is used for the purposes
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
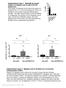 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Global Analysis of a HCV Model with CTL, Antibody Responses and Therapy
 Applied Mathematical Sciences Vol 9 205 no 8 3997-4008 HIKARI Ltd wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/02988/ams20554334 Global Analysis of a HCV Model with CTL Antibody Responses and Therapy Adil Meskaf Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences Vol 9 205 no 8 3997-4008 HIKARI Ltd wwwm-hikaricom http://dxdoiorg/02988/ams20554334 Global Analysis of a HCV Model with CTL Antibody Responses and Therapy Adil Meskaf Department
CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS. Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection
 CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection 1. Genetic variation occurs within and between populations 2. Mutation and sexual recombination
CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection 1. Genetic variation occurs within and between populations 2. Mutation and sexual recombination
Department of Mathematics. Mathematical study of competition between Staphylococcus strains within the host and at the host population level
 Department of Mathematics Mathematical study of competition between Staphylococcus strains within the host and at the host population level MATH554: Main Dissertation Written by Nouf Saleh Alghamdi ID
Department of Mathematics Mathematical study of competition between Staphylococcus strains within the host and at the host population level MATH554: Main Dissertation Written by Nouf Saleh Alghamdi ID
Impact of viral mutation on suppression of infection by cytotoxic T lymphocytes
 Impact of viral mutation on suppression of infection by cytotoxic T lymphocytes Julien Arino Neal Madras Stéphanie Portet Beni Sahai February 11, 2014 Abstract We develop a deterministic model describing
Impact of viral mutation on suppression of infection by cytotoxic T lymphocytes Julien Arino Neal Madras Stéphanie Portet Beni Sahai February 11, 2014 Abstract We develop a deterministic model describing
Host-pathogen coevolution and the emergence of broadly neutralizing antibodies in chronic infections
 Host-pathogen coevolution an the emergence of broaly neutralizing antiboies in chronic infections Armita Nourmohamma 1, Jakub Otwinowski 2, Joshua B Plotkin 2 1 Joseph-Henri Laboratories of Physics an
Host-pathogen coevolution an the emergence of broaly neutralizing antiboies in chronic infections Armita Nourmohamma 1, Jakub Otwinowski 2, Joshua B Plotkin 2 1 Joseph-Henri Laboratories of Physics an
Modelling Within-Host Immune Response to Visceral Helminthiasis and Malaria Co-infection with Prophylaxis
 Modelling Within-Host Immune Response to Visceral Helminthiasis and Malaria Co-infection with Prophylaxis B. Nannyonga, J.Y.T. Mugisha & L.S. Luboobi arxiv:1106.0506v1 [q-bio.pe] 2 Jun 2011 Department
Modelling Within-Host Immune Response to Visceral Helminthiasis and Malaria Co-infection with Prophylaxis B. Nannyonga, J.Y.T. Mugisha & L.S. Luboobi arxiv:1106.0506v1 [q-bio.pe] 2 Jun 2011 Department
STUDY OF THE DYNAMICAL MODEL OF HIV
 STUDY OF THE DYNAMICAL MODEL OF HIV M.A. Lapshova, E.A. Shchepakina Samara National Research University, Samara, Russia Abstract. The paper is devoted to the study of the dynamical model of HIV. An application
STUDY OF THE DYNAMICAL MODEL OF HIV M.A. Lapshova, E.A. Shchepakina Samara National Research University, Samara, Russia Abstract. The paper is devoted to the study of the dynamical model of HIV. An application
Analysis of bacterial population growth using extended logistic Growth model with distributed delay. Abstract INTRODUCTION
 Analysis of bacterial population growth using extended logistic Growth model with distributed delay Tahani Ali Omer Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Missouri-ansas City ansas City,
Analysis of bacterial population growth using extended logistic Growth model with distributed delay Tahani Ali Omer Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Missouri-ansas City ansas City,
Viral evolution model with several time scales
 Viral evolution model with several time scales AA Archibasov Samara National Research University, 4 Moskovskoe Shosse, 4486, Samara, Russia Abstract In this paper a viral evolution model with specific
Viral evolution model with several time scales AA Archibasov Samara National Research University, 4 Moskovskoe Shosse, 4486, Samara, Russia Abstract In this paper a viral evolution model with specific
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY
 B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY What are the 7 components of a healthy diet? 1.. 2.. 3.. 4.. 5.. 6.. 7.. What are the different methods of infection? Describe the issues with being overweight Describe
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY What are the 7 components of a healthy diet? 1.. 2.. 3.. 4.. 5.. 6.. 7.. What are the different methods of infection? Describe the issues with being overweight Describe
CST and FINAL EXAM REVIEW
 Name Date Period CST and FINAL EXAM REVIEW Directions: Both your final exam and the CST (STAR) test are based on the California Standards. There are five major categories and they include: Investigation
Name Date Period CST and FINAL EXAM REVIEW Directions: Both your final exam and the CST (STAR) test are based on the California Standards. There are five major categories and they include: Investigation
ANALYSIS OF A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR INTERACTIONS BETWEEN T CELLS AND MACROPHAGES
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2010(2010), No. 115, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ANALYSIS OF A
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2010(2010), No. 115, pp. 1 10. ISSN: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu ANALYSIS OF A
Analysis and Dynamic Active Subspaces for a Long Term Model of HIV
 Analysis and Dynamic Active Subspaces for a Long Term Model of HIV by Tyson S. Loudon A thesis submitted to the Faculty and the Board of Trustees of the Colorado School of Mines in partial fulfillment
Analysis and Dynamic Active Subspaces for a Long Term Model of HIV by Tyson S. Loudon A thesis submitted to the Faculty and the Board of Trustees of the Colorado School of Mines in partial fulfillment
Detecting the correlated mutations based on selection pressure with CorMut
 Detecting the correlated mutations based on selection pressure with CorMut Zhenpeng Li October 30, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Methods 2 3 Implementation 3 1 Introduction In genetics, the Ka/Ks ratio
Detecting the correlated mutations based on selection pressure with CorMut Zhenpeng Li October 30, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Methods 2 3 Implementation 3 1 Introduction In genetics, the Ka/Ks ratio
Multi-scale problem in the model of RNA virus evolution
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Multi-scale problem in the model of RNA virus evolution To cite this article: Andrei Korobeinikov et al 26 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 727 27 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Multi-scale problem in the model of RNA virus evolution To cite this article: Andrei Korobeinikov et al 26 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 727 27 View the article
Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of Infectious Disease Dynamics
 Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of Infectious Disease Dynamics V. A. Bokil Department of Mathematics Oregon State University Corvallis, OR MTH 323: Mathematical Modeling May 22, 2017 V. A. Bokil (OSU-Math)
Mathematical Modeling and Analysis of Infectious Disease Dynamics V. A. Bokil Department of Mathematics Oregon State University Corvallis, OR MTH 323: Mathematical Modeling May 22, 2017 V. A. Bokil (OSU-Math)
Theoretical advances in artificial immune systems
 Theoretical Computer Science 403 (2008) 11 32 www.elsevier.com/locate/tcs Theoretical advances in artificial immune systems J. Timmis a,b, A. Hone c,, T. Stibor d, E. Clark a a Department of Computer Science,
Theoretical Computer Science 403 (2008) 11 32 www.elsevier.com/locate/tcs Theoretical advances in artificial immune systems J. Timmis a,b, A. Hone c,, T. Stibor d, E. Clark a a Department of Computer Science,
Intermediate Differential Equations. John A. Burns
 Intermediate Differential Equations Delay Differential Equations John A. Burns jaburns@vt.edu Interdisciplinary Center for Applied Mathematics Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg,
Intermediate Differential Equations Delay Differential Equations John A. Burns jaburns@vt.edu Interdisciplinary Center for Applied Mathematics Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg,
A mathematical and computational model of necrotizing enterocolitis
 A mathematical and computational model of necrotizing enterocolitis Ivan Yotov Department of Mathematics, University of Pittsburgh McGowan Institute Scientific Retreat March 10-12, 2008 Acknowledgment:
A mathematical and computational model of necrotizing enterocolitis Ivan Yotov Department of Mathematics, University of Pittsburgh McGowan Institute Scientific Retreat March 10-12, 2008 Acknowledgment:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC
 BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
Numerical computation and series solution for mathematical model of HIV/AIDS
 Journal of Applied Mathematics & Bioinformatics, vol.3, no.4, 3, 69-84 ISSN: 79-66 (print, 79-6939 (online Scienpress Ltd, 3 Numerical computation and series solution for mathematical model of HIV/AIDS
Journal of Applied Mathematics & Bioinformatics, vol.3, no.4, 3, 69-84 ISSN: 79-66 (print, 79-6939 (online Scienpress Ltd, 3 Numerical computation and series solution for mathematical model of HIV/AIDS
A Delayed HIV Infection Model with Specific Nonlinear Incidence Rate and Cure of Infected Cells in Eclipse Stage
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 216, no. 43, 2121-213 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.216.63128 A Delayed HIV Infection Model with Specific Nonlinear Incidence Rate and
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 216, no. 43, 2121-213 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.216.63128 A Delayed HIV Infection Model with Specific Nonlinear Incidence Rate and
7th Grade Life Science Grade Remediation Packet
 7th Grade Life Science Grade Remediation Packet Purpose of this packet If you have received this packet it is because you are currently or in jeopardy of failing this class. This is not a punishment, but
7th Grade Life Science Grade Remediation Packet Purpose of this packet If you have received this packet it is because you are currently or in jeopardy of failing this class. This is not a punishment, but
Life Science FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES
 FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
FROM MOLECULES TO ORGANISMS: STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES HS-LS1-1 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential
Fuzzy modeling and control of HIV infection
 Fuy modeling and control of HIV infection Petrehuş Paul, Zsófia Lendek Department of Automation Technical University of Cluj Napoca Memorandumului 28, 4114, Cluj Napoca, Romania Emails: {paul.petrehus,
Fuy modeling and control of HIV infection Petrehuş Paul, Zsófia Lendek Department of Automation Technical University of Cluj Napoca Memorandumului 28, 4114, Cluj Napoca, Romania Emails: {paul.petrehus,
Approved Courses for General Science students with Major/Minors in Biological Sciences
 Approved Courses for General Science students with Major/Minors in Biological Sciences List C: Physiology, cell and developmental biology BIOIN 301 Bioinformatics. * (fi 6) (first term, 3-0-0). Introduction
Approved Courses for General Science students with Major/Minors in Biological Sciences List C: Physiology, cell and developmental biology BIOIN 301 Bioinformatics. * (fi 6) (first term, 3-0-0). Introduction
Detecting the correlated mutations based on selection pressure with CorMut
 Detecting the correlated mutations based on selection pressure with CorMut Zhenpeng Li April 30, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Methods 2 3 Implementation 3 1 Introduction In genetics, the Ka/Ks ratio
Detecting the correlated mutations based on selection pressure with CorMut Zhenpeng Li April 30, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Methods 2 3 Implementation 3 1 Introduction In genetics, the Ka/Ks ratio
Research Article On the Stability Property of the Infection-Free Equilibrium of a Viral Infection Model
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume, Article ID 644, 9 pages doi:.55//644 Research Article On the Stability Property of the Infection-Free Equilibrium of a Viral
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume, Article ID 644, 9 pages doi:.55//644 Research Article On the Stability Property of the Infection-Free Equilibrium of a Viral
Statistical mechanics of lymphocyte networks modelled with slow and fast variables
 modelled with slow and fast variables Institute for Mathematical and Molecular Biomedicine, King s College London. June 17, 2016 Outline Adaptive Immune System Motivation Dynamics of clonal expansion Statistical
modelled with slow and fast variables Institute for Mathematical and Molecular Biomedicine, King s College London. June 17, 2016 Outline Adaptive Immune System Motivation Dynamics of clonal expansion Statistical
Modeling Disease Transmission in Long-tailed Macaques on Bali
 Modeling Disease Transmission in Long-tailed Macaques on Bali Kelly Lane Gerhard Niederwieser Ryan Kennedy University of Notre Dame Macaque Background Coexisted in temples across the island for at least
Modeling Disease Transmission in Long-tailed Macaques on Bali Kelly Lane Gerhard Niederwieser Ryan Kennedy University of Notre Dame Macaque Background Coexisted in temples across the island for at least
Prereq: Concurrent 3 CH
 0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr. Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences.
 Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences fnasr@ul.edu.lb B3206 Microbial Genetics Eukaryotic M. G. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a genetic model
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences fnasr@ul.edu.lb B3206 Microbial Genetics Eukaryotic M. G. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a genetic model
CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1
 CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 2/13 2/14 - B 2/15 2/16 - B 2/17 2/20 Intro to Viruses Viruses VS Cells 2/21 - B Virus Reproduction Q 1-2 2/22 2/23
CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 2/13 2/14 - B 2/15 2/16 - B 2/17 2/20 Intro to Viruses Viruses VS Cells 2/21 - B Virus Reproduction Q 1-2 2/22 2/23
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW:
 THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
THINGS I NEED TO KNOW: 1. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Both types of cells have ribosomes. Some
Simulation of a Stochastic Cellular Automata HIV/AIDS Model for Investigation of Spatial Pattern Formation Mediated by CD4 + T Cells and HIV Dynamics
 Simulation of a Stochastic Cellular Automata /AIDS Model for Investigation of Spatial Pattern Formation Mediated by CD4 + T Cells and Dynamics MONAMORN PRECHARATTANA 1, WANNAPONG TRIAMPO 1,2,3, CHARIN
Simulation of a Stochastic Cellular Automata /AIDS Model for Investigation of Spatial Pattern Formation Mediated by CD4 + T Cells and Dynamics MONAMORN PRECHARATTANA 1, WANNAPONG TRIAMPO 1,2,3, CHARIN
Lecture 5. October 21, Department of Biostatistics Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Johns Hopkins University.
 Lecture 5 Department of Biostatistics Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Johns Hopkins University October 21, 2007 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 Define conditional probabilities 2 Define conditional mass
Lecture 5 Department of Biostatistics Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health Johns Hopkins University October 21, 2007 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 Define conditional probabilities 2 Define conditional mass
Numerical qualitative analysis of a large-scale model for measles spread
 Numerical qualitative analysis of a large-scale model for measles spread Hossein Zivari-Piran Department of Mathematics and Statistics York University (joint work with Jane Heffernan) p./9 Outline Periodic
Numerical qualitative analysis of a large-scale model for measles spread Hossein Zivari-Piran Department of Mathematics and Statistics York University (joint work with Jane Heffernan) p./9 Outline Periodic
A New Mathematical Approach for. Rabies Endemy
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 2014, no. 2, 59-67 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2014.39525 A New Mathematical Approach for Rabies Endemy Elif Demirci Ankara University
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 2014, no. 2, 59-67 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2014.39525 A New Mathematical Approach for Rabies Endemy Elif Demirci Ankara University
Math 2373: Linear Algebra and Differential Equations
 Math 373: Linear Algebra and Differential Equations Paul Cazeaux* Fraser Hall 1, MW 15:35-1:5 September 7 th, 1 December th, 1 Contents 1 First-order differential equations 1 1.1 Dynamical systems and
Math 373: Linear Algebra and Differential Equations Paul Cazeaux* Fraser Hall 1, MW 15:35-1:5 September 7 th, 1 December th, 1 Contents 1 First-order differential equations 1 1.1 Dynamical systems and
Next-generation genomics technology, Conservation and Extinction
 Next-generation genomics technology, Conservation and Extinction Oliver A. Ryder San Diego Zoo s Institute for Conservation Research www.zooconservation.org Genome 10K http://genome10k.soe.ucsc.edu/ Frozen
Next-generation genomics technology, Conservation and Extinction Oliver A. Ryder San Diego Zoo s Institute for Conservation Research www.zooconservation.org Genome 10K http://genome10k.soe.ucsc.edu/ Frozen
Microbiology BIOL 202 Lecture Course Outcome Guide (COG) Approved 22 MARCH 2012 Pg.1
 Microbiology BIOL 202 Lecture Course Outcome Guide (COG) Approved 22 MARCH 2012 Pg.1 Course: Credits: 3 Instructor: Course Description: Concepts and Issues 1. Microbial Ecology including mineral cycles.
Microbiology BIOL 202 Lecture Course Outcome Guide (COG) Approved 22 MARCH 2012 Pg.1 Course: Credits: 3 Instructor: Course Description: Concepts and Issues 1. Microbial Ecology including mineral cycles.
AQA Biology Year 1 - Topic 2 - Cells
 Section Topic Description You should be able to: 3.2.1.1 Structure of Label the organelles present in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic Cells State the function and structure of the organelles in eukaryotic
Section Topic Description You should be able to: 3.2.1.1 Structure of Label the organelles present in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic Cells State the function and structure of the organelles in eukaryotic
An investigation of viral fitness using statistical and computer models of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus infection
 Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2014 An investigation of viral fitness using statistical and computer models of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus infection Derek Blythe Iowa State University
Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate College 2014 An investigation of viral fitness using statistical and computer models of Equine Infectious Anemia Virus infection Derek Blythe Iowa State University
MAT 2379, Introduction to Biostatistics, Sample Calculator Questions 1. MAT 2379, Introduction to Biostatistics
 MAT 2379, Introduction to Biostatistics, Sample Calculator Questions 1 MAT 2379, Introduction to Biostatistics Sample Calculator Problems for the Final Exam Note: The exam will also contain some problems
MAT 2379, Introduction to Biostatistics, Sample Calculator Questions 1 MAT 2379, Introduction to Biostatistics Sample Calculator Problems for the Final Exam Note: The exam will also contain some problems
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE. Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE)
 Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE) A. Nature of scientific knowledge, inquiry, and historical perspectives 1. Scientific methods...1 2. Processes involved in
Table of Contents I. BASIC PRINCIPLES OF SCIENCE (HISTORY AND NATURAL SCIENCE) A. Nature of scientific knowledge, inquiry, and historical perspectives 1. Scientific methods...1 2. Processes involved in
arxiv: v2 [q-bio.pe] 22 Feb 2018
![arxiv: v2 [q-bio.pe] 22 Feb 2018 arxiv: v2 [q-bio.pe] 22 Feb 2018](/thumbs/80/80765497.jpg) Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Dynamics of Virus and Immune Response in Multi-Epitope Network Cameron J. Browne Hal L. Smith arxiv:75.88v2 [q-bio.pe] 22 Feb 28 the date of receipt
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Dynamics of Virus and Immune Response in Multi-Epitope Network Cameron J. Browne Hal L. Smith arxiv:75.88v2 [q-bio.pe] 22 Feb 28 the date of receipt
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 5 4/27/15 Answer each of the following short answer questions in the space provided, giving explanations when asked to do so. Circle the correct answer or answers
NK cells are part of the innate immune response. Early response to injury and infection
 NK cells are part of the innate immune response Early response to injury and infection Functions: Natural Killer (NK) Cells. Cytolysis: killing infected or damaged cells 2. Cytokine production: IFNγ, GM-CSF,
NK cells are part of the innate immune response Early response to injury and infection Functions: Natural Killer (NK) Cells. Cytolysis: killing infected or damaged cells 2. Cytokine production: IFNγ, GM-CSF,
A Stochastic Viral Infection Model with General Functional Response
 Nonlinear Analysis and Differential Equations, Vol. 4, 16, no. 9, 435-445 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.1988/nade.16.664 A Stochastic Viral Infection Model with General Functional Response
Nonlinear Analysis and Differential Equations, Vol. 4, 16, no. 9, 435-445 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.1988/nade.16.664 A Stochastic Viral Infection Model with General Functional Response
The Fastest Evolutionary Trajectory
 The Fastest Evolutionary Trajectory The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Traulsen, Arne, Yoh Iwasa, and Martin
The Fastest Evolutionary Trajectory The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Traulsen, Arne, Yoh Iwasa, and Martin
On state-space reduction in multi-strain pathogen models, with an application to antigenic drift in influenza A
 On state-space reduction in multi-strain pathogen models, with an application to antigenic drift in influenza A Sergey Kryazhimskiy, Ulf Dieckmann, Simon A. Levin, Jonathan Dushoff Supporting information
On state-space reduction in multi-strain pathogen models, with an application to antigenic drift in influenza A Sergey Kryazhimskiy, Ulf Dieckmann, Simon A. Levin, Jonathan Dushoff Supporting information
Investigating the Effects of Disease on Predator-prey Dynamics in a Protozoan/Bacterial Model System. An Undergraduate Research Thesis.
 Investigating the Effects of Disease on Predator-prey Dynamics in a Protozoan/Bacterial Model System An Undergraduate Research Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty By Carrie Stallings In Partial Fulfillment
Investigating the Effects of Disease on Predator-prey Dynamics in a Protozoan/Bacterial Model System An Undergraduate Research Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty By Carrie Stallings In Partial Fulfillment
Chapter 3. Property Relations The essence of macroscopic thermodynamics Dependence of U, H, S, G, and F on T, P, V, etc.
 Chapter 3 Property Relations The essence of macroscopic thermodynamics Dependence of U, H, S, G, and F on T, P, V, etc. Concepts Energy functions F and G Chemical potential, µ Partial Molar properties
Chapter 3 Property Relations The essence of macroscopic thermodynamics Dependence of U, H, S, G, and F on T, P, V, etc. Concepts Energy functions F and G Chemical potential, µ Partial Molar properties
Biology Scope and Sequence Student Outcomes (Objectives Skills/Verbs)
 C-4 N.12.A 1-6 N.12.B.1-4 Scientific Literacy/ Nature of (embedded throughout course) Scientific Inquiry is the process by which humans systematically examine the natural world. Scientific inquiry is a
C-4 N.12.A 1-6 N.12.B.1-4 Scientific Literacy/ Nature of (embedded throughout course) Scientific Inquiry is the process by which humans systematically examine the natural world. Scientific inquiry is a
A simple model of pathogen-immune dynamics. including specific and non-specific immunity
 A simple model of pathogen-immune dynamics including specific and non-specific immunity Andrea Pugliese 1,, Department of Mathematics, University of Trento, Trento, 38050 Italy Alberto Gandolfi Istituto
A simple model of pathogen-immune dynamics including specific and non-specific immunity Andrea Pugliese 1,, Department of Mathematics, University of Trento, Trento, 38050 Italy Alberto Gandolfi Istituto
Controlling Systemic Inflammation Using NMPC. Using Nonlinear Model Predictive Control with State Estimation
 Controlling Systemic Inflammation Using Nonlinear Model Predictive Control with State Estimation Gregory Zitelli, Judy Day July 2013 With generous support from the NSF, Award 1122462 Motivation We re going
Controlling Systemic Inflammation Using Nonlinear Model Predictive Control with State Estimation Gregory Zitelli, Judy Day July 2013 With generous support from the NSF, Award 1122462 Motivation We re going
A LYAPUNOV-KRASOVSKII FUNCTIONAL FOR A COMPLEX SYSTEM OF DELAY-DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 77, Iss., 015 ISSN 13-707 A LYAPUNOV-KRASOVSKII FUNCTIONAL FOR A COMPLEX SYSTEM OF DELAY-DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Irina Badralexi 1, Andrei Halanay, Ileana Rodica Rădulescu
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 77, Iss., 015 ISSN 13-707 A LYAPUNOV-KRASOVSKII FUNCTIONAL FOR A COMPLEX SYSTEM OF DELAY-DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Irina Badralexi 1, Andrei Halanay, Ileana Rodica Rădulescu
CSISS Center for Spatial Information Science Page 1 and Systems
 Does urbanization play a big role in the rapid increase of Lyme disease cases? Liping Di, Liying Guo Center for Spatial Information Science () George Mason University Fairfax, Virginia, USA ldi@gmu.edu
Does urbanization play a big role in the rapid increase of Lyme disease cases? Liping Di, Liying Guo Center for Spatial Information Science () George Mason University Fairfax, Virginia, USA ldi@gmu.edu
Compiled by GCochrane Half Hollow Hills HS East
 Compiled by GCochrane Half Hollow Hills HS East Regents Exam Format A: 30 Multiple Choice B-1: Multiple Choice B-2: MC and Short constructed response Reading passages, graphing, lab skills C: Constructed
Compiled by GCochrane Half Hollow Hills HS East Regents Exam Format A: 30 Multiple Choice B-1: Multiple Choice B-2: MC and Short constructed response Reading passages, graphing, lab skills C: Constructed
Selection of Proteins for Human MHC Class II Presentation
 Cellular & Molecular Immunology 49 Article Selection of Proteins for Human MHC Class II Presentation Li Jiang 1, 2, Ole Lund 2, 3 and Jinquan Tan 1, 3 We investigated the predicted function of proteins
Cellular & Molecular Immunology 49 Article Selection of Proteins for Human MHC Class II Presentation Li Jiang 1, 2, Ole Lund 2, 3 and Jinquan Tan 1, 3 We investigated the predicted function of proteins
Project 1 Modeling of Epidemics
 532 Chapter 7 Nonlinear Differential Equations and tability ection 7.5 Nonlinear systems, unlike linear systems, sometimes have periodic solutions, or limit cycles, that attract other nearby solutions.
532 Chapter 7 Nonlinear Differential Equations and tability ection 7.5 Nonlinear systems, unlike linear systems, sometimes have periodic solutions, or limit cycles, that attract other nearby solutions.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus?
 Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus? Define virus. What are viruses? Define and translate bacteriophage. Review virus composition. What two classes of compounds are found in all viruses? Define
Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus? Define virus. What are viruses? Define and translate bacteriophage. Review virus composition. What two classes of compounds are found in all viruses? Define
4.6.1 Reproduction Sexual and asexual reproduction Meiosis. Key opportunities for. development. skills development
 4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution In this section we will discover how the number of chromosomes are halved during meiosis and then combined with new genes from the sexual partner to produce unique
4.6 Inheritance, variation and evolution In this section we will discover how the number of chromosomes are halved during meiosis and then combined with new genes from the sexual partner to produce unique
Introduction. Statistical physics: microscopic foundation of thermodynamics degrees of freedom 2 3 state variables!
 Introduction Thermodynamics: phenomenological description of equilibrium bulk properties of matter in terms of only a few state variables and thermodynamical laws. Statistical physics: microscopic foundation
Introduction Thermodynamics: phenomenological description of equilibrium bulk properties of matter in terms of only a few state variables and thermodynamical laws. Statistical physics: microscopic foundation
Living Environment Core Content and Material
 Regents Exam Format A: 30 Multiple Choice B-1: Multiple Choice B-2: MC and Short constructed response Reading passages, graphing, lab skills C: Constructed Responses D: Labs and Lab Skills Making Connections
Regents Exam Format A: 30 Multiple Choice B-1: Multiple Choice B-2: MC and Short constructed response Reading passages, graphing, lab skills C: Constructed Responses D: Labs and Lab Skills Making Connections
Leptospira: The disease and its diagnosis.
 Leptospira: The disease and its diagnosis. Julie Collins-Emerson Lepto forum 06 March 2017 http://r6kbio.wikia.com/wiki/leptospira_interrogans Are bacteria Leptospira Most mammals can be infected A number
Leptospira: The disease and its diagnosis. Julie Collins-Emerson Lepto forum 06 March 2017 http://r6kbio.wikia.com/wiki/leptospira_interrogans Are bacteria Leptospira Most mammals can be infected A number
Master's thesis Longitudinal modeling of antibody dynamics during herpes zoster infection
 2014 2015 FACULTY OF SCIENCES Master of Statistics Master's thesis Longitudinal modeling of antibody dynamics during herpes zoster infection Supervisor : Prof. dr. Niel HENS Supervisor : Dr. BENSON OGUNJIMI
2014 2015 FACULTY OF SCIENCES Master of Statistics Master's thesis Longitudinal modeling of antibody dynamics during herpes zoster infection Supervisor : Prof. dr. Niel HENS Supervisor : Dr. BENSON OGUNJIMI
Oddn ENTRIES. Two New Buildings For County 4-H Fair
 D G N H V G NNG \VH FYXH Y N $40000 b U v v 000 v b vv v vb v v b b x b z b v b b b & K b K G DH F H H /\U F b 80 K b z b bb v $40000 b v x v b bb 8 v b 30 K b b v v b v b b? x v z v b H D N G N H H Fz
D G N H V G NNG \VH FYXH Y N $40000 b U v v 000 v b vv v vb v v b b x b z b v b b b & K b K G DH F H H /\U F b 80 K b z b bb v $40000 b v x v b bb 8 v b 30 K b b v v b v b b? x v z v b H D N G N H H Fz
Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence. Hsin-Jung Joyce Wu "Microbiota and man: the story about us
 Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence Overview q Define microbiota q Learn the tool q Ecological and evolutionary forces in shaping gut microbiota q Gut microbiota versus free-living microbe communities
Microbiota: Its Evolution and Essence Overview q Define microbiota q Learn the tool q Ecological and evolutionary forces in shaping gut microbiota q Gut microbiota versus free-living microbe communities
(c) 4 1. correct derivation of children s genotypes 1. identification of children with cystic fibrosis (dd) 1
 M. (a) 3 a gene allow allele (c) 4 (d) correct derivation of children s genotypes identification of children with cystic fibrosis (dd) 0.5 allow ecf allow ¼ / 5% / in 4 / :3 Page do not accept :4 (e) heterozygous
M. (a) 3 a gene allow allele (c) 4 (d) correct derivation of children s genotypes identification of children with cystic fibrosis (dd) 0.5 allow ecf allow ¼ / 5% / in 4 / :3 Page do not accept :4 (e) heterozygous
Introduction: What one must do to analyze any model Prove the positivity and boundedness of the solutions Determine the disease free equilibrium
 Introduction: What one must do to analyze any model Prove the positivity and boundedness of the solutions Determine the disease free equilibrium point and the model reproduction number Prove the stability
Introduction: What one must do to analyze any model Prove the positivity and boundedness of the solutions Determine the disease free equilibrium point and the model reproduction number Prove the stability
In its most basic terms, the theory of evolution states that species CHANGE over time.
 In its most basic terms, the theory of evolution states that species CHANGE over time. Lamark Use Disuse Hypothesis or Passing on of Acquired Characteristics Summarize how Lamark believes the giraffe got
In its most basic terms, the theory of evolution states that species CHANGE over time. Lamark Use Disuse Hypothesis or Passing on of Acquired Characteristics Summarize how Lamark believes the giraffe got
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Biology 8 Learning Outcomes
 Biology 8 Learning Outcomes CELLS (Bio 8-1) I can connect the names, diagrams, and functions of organelles in a cell I know the major differences between plant and animal cells I can explain cell theory
Biology 8 Learning Outcomes CELLS (Bio 8-1) I can connect the names, diagrams, and functions of organelles in a cell I know the major differences between plant and animal cells I can explain cell theory
Classification and Viruses Practice Test
 Classification and Viruses Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part
Classification and Viruses Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Biologists use a classification system to group organisms in part
Impulsive differential equations with applications to infectious diseases
 Impulsive differential equations with applications to infectious diseases Rachelle Miron Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Impulsive differential equations with applications to infectious diseases Rachelle Miron Thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies in partial fulfillment of the requirements
A Unified Approach to the Statistical Evaluation of Differential Vaccine Efficacy
 A Unified Approach to the Statistical Evaluation of Differential Vaccine Efficacy Erin E Gabriel Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Dean Follmann
A Unified Approach to the Statistical Evaluation of Differential Vaccine Efficacy Erin E Gabriel Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Dean Follmann
Discrete time mathematical models in ecology. Andrew Whittle University of Tennessee Department of Mathematics
 Discrete time mathematical models in ecology Andrew Whittle University of Tennessee Department of Mathematics 1 Outline Introduction - Why use discrete-time models? Single species models Geometric model,
Discrete time mathematical models in ecology Andrew Whittle University of Tennessee Department of Mathematics 1 Outline Introduction - Why use discrete-time models? Single species models Geometric model,
Understanding Recurrent Disease: A Dynamical Systems Approach
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 214 Understanding Recurrent Disease: A Dynamical Systems Approach Wenjing Zhang The University of Western Ontario
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 214 Understanding Recurrent Disease: A Dynamical Systems Approach Wenjing Zhang The University of Western Ontario
Visit to BPRC. Data is crucial! Case study: Evolution of AIRE protein 6/7/13
 Visit to BPRC Adres: Lange Kleiweg 161, 2288 GJ Rijswijk Utrecht CS à Den Haag CS 9:44 Spoor 9a, arrival 10:22 Den Haag CS à Delft 10:28 Spoor 1, arrival 10:44 10:48 Delft Voorzijde à Bushalte TNO/Lange
Visit to BPRC Adres: Lange Kleiweg 161, 2288 GJ Rijswijk Utrecht CS à Den Haag CS 9:44 Spoor 9a, arrival 10:22 Den Haag CS à Delft 10:28 Spoor 1, arrival 10:44 10:48 Delft Voorzijde à Bushalte TNO/Lange
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nature76 Abs V gene D gene J gene CDR CDR length Clone Name Origin Year Acc. No. FI7 IGHV-69* IGHD-* IGHJ* AGSATYYESRFDY BC 8 KJ9 FI6 IGHV-69* IGHD-* IGHJ* AGSGTYFVSRFDY BC 8 KJ98 FI7 IGHV-69* IGHD-6*
doi:.8/nature76 Abs V gene D gene J gene CDR CDR length Clone Name Origin Year Acc. No. FI7 IGHV-69* IGHD-* IGHJ* AGSATYYESRFDY BC 8 KJ9 FI6 IGHV-69* IGHD-* IGHJ* AGSGTYFVSRFDY BC 8 KJ98 FI7 IGHV-69* IGHD-6*
Statistical and Mathematical Modeling in HIV: Estimation and Control
 Statistical and Mathematical Modeling in HIV: Estimation and Control H. T. Banks Center for Research in Scientific Computation Research Team B.M. Adams (Sandia( Sandia) H.T. Banks D. Bortz (U. Michigan)
Statistical and Mathematical Modeling in HIV: Estimation and Control H. T. Banks Center for Research in Scientific Computation Research Team B.M. Adams (Sandia( Sandia) H.T. Banks D. Bortz (U. Michigan)
Mathematical modeling of Toxoplasmosis disease in varying size populations
 Computers and Mathematics with Applications 56 (2008) 690 696 www.elsevier.com/locate/camwa Mathematical modeling of Toxoplasmosis disease in varying size populations Diego F. Aranda a,, Rafael J. Villanueva
Computers and Mathematics with Applications 56 (2008) 690 696 www.elsevier.com/locate/camwa Mathematical modeling of Toxoplasmosis disease in varying size populations Diego F. Aranda a,, Rafael J. Villanueva
Global Analysis of a Mathematical Model of HCV Transmission among Injecting Drug Users and the Impact of Vaccination
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 2014, no. 128, 6379-6388 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2014.48625 Global Analysis of a Mathematical Model of HCV Transmission among
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 2014, no. 128, 6379-6388 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2014.48625 Global Analysis of a Mathematical Model of HCV Transmission among
Station 1 : Evolution KEY
 Station 1 : Evolution KEY Theory of Natural Selection: Use the answers in the bank, to fill in the blanks a. Overproduction b. The spread of an adaptation throughout new generations. c. Variation d. A
Station 1 : Evolution KEY Theory of Natural Selection: Use the answers in the bank, to fill in the blanks a. Overproduction b. The spread of an adaptation throughout new generations. c. Variation d. A
MULTI-SCALE MODELING OF MALARIA: FROM ENDEMICITY TO ELIMINATION
 MULTI-SCALE MODELING OF MALARIA: FROM ENDEMICITY TO ELIMINATION or the DEATH of SEIR models Juan B. Gutierrez UGA s Department of Mathematics & Institute of Bioinformatics December 14, 2012 1 / 19 Collaborators
MULTI-SCALE MODELING OF MALARIA: FROM ENDEMICITY TO ELIMINATION or the DEATH of SEIR models Juan B. Gutierrez UGA s Department of Mathematics & Institute of Bioinformatics December 14, 2012 1 / 19 Collaborators
Evolutionary dynamics on graphs
 Evolutionary dynamics on graphs Laura Hindersin May 4th 2015 Max-Planck-Institut für Evolutionsbiologie, Plön Evolutionary dynamics Main ingredients: Fitness: The ability to survive and reproduce. Selection
Evolutionary dynamics on graphs Laura Hindersin May 4th 2015 Max-Planck-Institut für Evolutionsbiologie, Plön Evolutionary dynamics Main ingredients: Fitness: The ability to survive and reproduce. Selection
Modeling the Immune System W9. Ordinary Differential Equations as Macroscopic Modeling Tool
 Modeling the Immune System W9 Ordinary Differential Equations as Macroscopic Modeling Tool 1 Lecture Notes for ODE Models We use the lecture notes Theoretical Fysiology 2006 by Rob de Boer, U. Utrecht
Modeling the Immune System W9 Ordinary Differential Equations as Macroscopic Modeling Tool 1 Lecture Notes for ODE Models We use the lecture notes Theoretical Fysiology 2006 by Rob de Boer, U. Utrecht
Epidemics in Two Competing Species
 Epidemics in Two Competing Species Litao Han 1 School of Information, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 P. R. China Andrea Pugliese 2 Department of Mathematics, University of Trento, Trento,
Epidemics in Two Competing Species Litao Han 1 School of Information, Renmin University of China, Beijing, 100872 P. R. China Andrea Pugliese 2 Department of Mathematics, University of Trento, Trento,
Understanding relationship between homologous sequences
 Molecular Evolution Molecular Evolution How and when were genes and proteins created? How old is a gene? How can we calculate the age of a gene? How did the gene evolve to the present form? What selective
Molecular Evolution Molecular Evolution How and when were genes and proteins created? How old is a gene? How can we calculate the age of a gene? How did the gene evolve to the present form? What selective
Evolution 1 Star. 6. The different tools used during the beaks of finches lab represented. A. feeding adaptations in finches
 Name: Date: 1. ccording to modern evolutionary theory, genes responsible for new traits that help a species survive in a particular environment will usually. not change in frequency. decrease gradually
Name: Date: 1. ccording to modern evolutionary theory, genes responsible for new traits that help a species survive in a particular environment will usually. not change in frequency. decrease gradually
Mathematical models on Malaria with multiple strains of pathogens
 Mathematical models on Malaria with multiple strains of pathogens Yanyu Xiao Department of Mathematics University of Miami CTW: From Within Host Dynamics to the Epidemiology of Infectious Disease MBI,
Mathematical models on Malaria with multiple strains of pathogens Yanyu Xiao Department of Mathematics University of Miami CTW: From Within Host Dynamics to the Epidemiology of Infectious Disease MBI,
