Exchange biasing and electric polarization with YMnO 3
|
|
|
- Martha McDonald
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applied Physics Letters, in press Exchange biasing and electric polarization with YMnO 3 X. Martí, F. Sánchez, D. Hrabovsky, L. Fàbrega, A. Ruyter, J. Fontcuberta Institut de Ciència de Materials de Barcelona - CSIC, Campus U.A.B., Bellaterra 08193, Spain V. Laukhin Institut de Ciència de Materials de Barcelona - CSIC, Campus U.A.B., Bellaterra 08193, and Institut Català de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA), Barcelona, Spain V. Skumryev Departament de Física, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra 08193, and Institut Català de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA), Barcelona, Spain M.V. García-Cuenca, C. Ferrater, M. Varela Departament de Física Aplicada i Òptica, Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 647, Barcelona 08028, Spain A. Vilà Departament d Electrònica. Universitat de Barcelona, Diagonal 647, Barcelona 08028, Spain U. Lüders, J.F. Bobo LNMH CNRS-ONERA, BP Toulouse Cedex 4, France 1
2 Abstract We report on the growth and functional characterization of epitaxial thin films of the multiferroic YMnO 3. We show that using Pt as a seed layer on SrTiO 3 (111) substrates, epitaxial YMnO 3 films (0001) textured are obtained. An atomic force microscope has been used to polarize electric domains revealing the ferroelectric nature of the film. When a Permalloy layer is grown on top of the YMnO 3 (0001) film, clear indications of exchange bias and enhanced coercivity are observed at low temperature. The observation of coexisting antiferromagnetism and electrical polarization suggests that the biferroic character of YMnO 3 can be exploited in novel devices. 2
3 Multiferroic materials, displaying simultaneously the occurrence of magnetic and ferroelectric orders, are nowadays of the highest interest because of possible applications where dual tuning of the magnetic and electric response could be of relevance [1,2]. Whereas much effort is being focused to the scarce materials displaying ferromagnetic and ferroelectric response [3], the functional exploitation of the more abundant materials displaying antiferromagnetic (AF) and ferroelectric (FE) orders has received less attention. Hexagonal YMnO 3 (YMO) belongs to this class of materials. It displays a high temperature FE transition (at about 900 ºC) and a low temperature AF transition (T N 70 K). Possible use of the FE properties of YMO in ferroelectric devices has been already highlighted [4] and YMO thin films have been subsequently grown with a variety of techniques [4,5]. Electrical polarization in YMO is along the hexagonal c-axis [6] whereas the magnetic moments of Mn 3+ lie in the perpendicular plane, forming a triangular, geometrically frustrated, network of AF coupled spins [7,8]. Antiferromagnets are used in spintronics by exploiting the exchange bias (EB) with suitable ferromagnets. Therefore, YMO could be also used as pinning layer if significant EB could be stimulated across an interface with a ferromagnet. Indeed, it has been recently proposed that YMO displays EB when grown textured along the [1121] direction but almost no exchange bias was observed for [0001] films [9]. As the [0001] direction is the polarization direction it seemed that prospectives of YMO for multifunctional devices were rather limited. In this paper we will show that YMO films with a unique [0001]-axis texture can be grown on (111)-oriented SrTiO 3 (STO) single crystalline substrates when buffered with a thin Pt layer and that these films display both ferroelectric character and a substantial EB. As FE and AF domains are coupled in YMO [10] it turns out that YMO could be exploited for multifunctional operation. 3
4 Pt films were deposited on a STO(111) substrate by dc sputtering. Previous to the deposition, substrates were annealed in-situ during 5 min at 800 ºC and, afterwards, Pt ( 8 nm thick) was deposited at mbar pure Ar and at substrate temperature of 500 ºC. The Pt buffered substrate was transferred to a pulsed laser deposition chamber and the YMO was subsequently grown, using a stoichiometric YMnO 3 target. Films were deposited at a substrate temperature of 800 ºC in 0.2 mbar of oxygen pressure. At the end of the growth the samples were cooled down and 1 atm of oxygen was introduced in the chamber at 500 ºC. A Permalloy (Ni 81 Fe 19, Py) layer, 15 nm thick, was subsequently grown by dc sputtering at room temperature, under a magnetic field of 100 Oe, in order to build the Py/YMO/Pt//STO(111) heterostructure. The crystal structure was investigated by X-ray diffractometry (XRD) using Cu K α radiation. Pt film thickness was determined by modeling Laue fringes observed in XRD patterns, whereas profilometry was used in other cases. Magnetic and electric transport properties were measured by using a superconducting quantum interference device and a PPMS from Quantum Design. Piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM) with a Nanoscope Dimension 3100 microscope (Digital Instruments) was used to measure the piezoelectric response. The bottom Pt electrode was connected to ground by using silver paste, while the voltages V DC, V AC, to polarize the sample and characterize the response respectively, were applied to the upper surface of the YMO film through the microscope tip. In Fig. 1a we show a XRD θ/2θ scan corresponding to a Py/YMO(90nm)/Pt//STO(111) sample. Diffraction peaks from the substrate and the Pt and YMO layers are found. Inspection of the Pt reflections indicates that the Pt film has a (111) texture and the observation of the associated Laue fringes reflects the flatness and crystal quality of the Pt films. The reflections (0001) of the hexagonal YMO phase 4
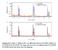
5 are well visible. Interestingly, no traces of orthorhombic phase are found in spite of being the stable phase when YMO grows directly on STO(111) substrates [11]. Out-ofplane lattice distances were evaluated from Bragg s peaks positions. The out-of-plane parameter of Pt is d (111) = 2.27Å, almost coincident with that of bulk Pt whereas the outof-plane d (0001) c parameter of YMO is 11.45Å, somewhat expanded with respect to c bulk = 11.40Å; the strain is ε (0001) = 0.44%, suggesting an in-plane compression. Indeed, the in-plane parameter of the YMO film, determined from XRD φ-scans, matches that of Pt thus reflecting the epitaxial compressive stress on the YMO films. In Fig. 1b we have collected the pole figures of the STO(110), Pt(111), and YMO(1124) reflections measured along the pole [111] STO direction. Considering the poles of the Pt(111) reflections, one notices the existence of two sets of peaks (labeled A and B) corresponding to the family of planes {111} and {111} respectively. It indicates that the Pt epitaxial film has grown in two domains, 180º in-plane rotated; the epitaxial relationships with the substrate are [112]Pt(111)/[112]STO(111) and [112]Pt(111)/[112]STO(111). The pole figure of the YMO(1124) reflections shows six peaks as expected due to the P6 3 cm symmetry of YMO. Notice that this symmetry does not allow to discern the presence of one or two domains (60º in-plane rotated). However, since YMO grows on bi-domained Pt layer, two domains also in the YMO layer are expected. The corresponding epitaxial relationships are [1010]YMO/[112]Pt and [1010]YMO/[112]Pt. The magnetic hysteresis loops, measured at 100 K and 2 K after a magnetic field (3 koe) cooling procedure, are displayed in Fig. 2. The loop measured at 100 K is symmetric with coercivity (H C ) of only 10 Oe, very similar to the loops measured at higher temperature. In contrast, the loop measured at 2 K is asymmetric, revealing that an exchange bias (H EB 61Oe) accompanied by a significant coercivity enhancement 5
6 (H C 98Oe) develops at low temperatures. Fig. 2 includes two magnetization loops measured consecutively (denoted 1 st and 2 nd ). It can be appreciated that there is a significant reduction of H EB upon cycling the field. This training effect [12] is characteristic of AF systems with low or multiaxial anisotropy [13], which likely contributes to the fast decay of H EB upon heating. The temperature dependence of H EB and H C are shown in Fig. 2 (inset). We notice that H EB decays rapidly when increasing the temperature and vanishs at 10 K. The existence of EB also provokes changes of the anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) of the upper-lying Py layer [14,15]. AMR was measured by rotating the magnetic field in the film plane while recording the film resistance R as a function of the angle θ between the measuring current and the applied magnetic field (H a ). In Fig. 3a we include the R(θ) cycles recorded at several temperatures (100 K, 50 K and 2 K), above and below T N ( 70 K). Prior to any measurement, the sample was field cooled (3 koe) from room temperature to the measuring temperature and then the field was reduced to the selected H a value. Data included in Fig. 3 were obtained when the cooling field was fixed at 45º from the current direction and H a = 40 Oe. We note that this value is smaller that the largest H c value determined from the magnetization loops (Fig. 2). At T = 100 K, R(θ) displays the common cos 2 θ dependence expected for a system where the magnetization follows the magnetic field (Fig. 3a). However, at 50K, R(θ) displays a clear departure of the cos 2 θ dependence due to the presence of the H EB, which becomes more prominent when cooling down (Fig. 3b). In fact, at 2 K the presence of an H EB has dramatically modified the magnetization response when H a is rotated (Fig. 3c). The strong departure of the R(θ) curve from the cos 2 θ dependence indicates that, at 2K, the H EB should be much larger than the measuring field (40 Oe), 6
7 and then larger than the values extracted from the magnetization loops. Observation of larger H EB values in transport measurements results from the different way in which the presence of an H EB is revealed [14]. Notice that in transport measurements exchange bias is monitored via its impact on the magnetization when rotating H a but there is no need to switch the magnetization as in the common magnetic measurements and thus training effects are less important. We turn now to the ferroelectric response. First, a background was set over a 2x2 μm 2 square by scanning it with V DC = +6 V, in contact mode using a tip velocity of 0.8 μm/s. Inside, a smaller square (1x1μm 2 ) was polarized with V DC = -6V, using the same tip velocity. Finally, the PFM response is recorded by using an AC signal (V AC = 3.5V), and scanning over the outer square with a tip velocity of 0.4 μm/s. In Fig. 4 we show the PFM phase image of a YMO(150nm)/Pt//STO sample. As expected, it displays contrast over the polarized square (bright area, 1x1 μm 2 at the center), due to the different phase of the PFM response for the up and down domains; although the observed phase-contrast is rather small (~3º), the obvious change of contrast confirms the piezoresponse of the film. Traces of the substrate-induced steps are well visible in the PFM image (as well as in the topographic image not show-). We stress that contrast in the PFM image remains roughly constant for several hour after poling, thus suggesting a low leakage. In summary, we have shown that YMO films can be used to induce exchange bias on suitable ferromagnetic layers while preserving the electric polarization. As magnetic and ferroelectric domains in YMO are coupled [10] our results strongly suggest that multiferroic materials with antiferromagnetic and ferroelectric orders can be 7
8 successfully used to modify the exchange bias, and subsequently the transport and magnetic properties of a ferromagnetic layer, by electric fields. Financial support by the MEC of the Spanish Government (projects NAN and MAT ), and FEDER and the STREP project (Nº ) of the E.U. are acknowledged. A.R. (permanent address: LEMA Laboratory, UMR 6157 CNRS- CEA, and Faculté des Sciences et Techniques, University of Tours, France) acknowledges Generalitat de Catalunya for a grant. We are thankful to J.M. Pérez for technical support. 8
9 References 1. M. Fiebig, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 38, R123 (2005) 2. Ch. Binek and B. Doudin, J. Phys.: Conds. Matter 17, L39 (2005) 3. N.A. Hill, J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6694 (2000) 4. S. Imada, T. Kurakova, E. Tokumitsu, and H. Ishiwara, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40, 666 (2001); A. Posadas, J.B. Yau, C.H. Ahn, J. Han, S. Gariglio, K. Johnston, K.M. Rabe, and J.B. Neaton, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, (2005); D. Ito, N. Fujimura, T. Yoshimura, and T. Ito, J. Appl. Phys. 93, 5563 (2003) 5. J. Dho, C.W. Leung, J.L. Driscoll, and M.G. Blamire, J. Cryst. Growth 267, 548 (2004) 6. see for instance, B.B. van Aken, T.T.M. Palstra, A. Filippetti, and N.A. Spaldin, Nature Mat. 3, 164 (2004) 7. A, Muñoz, J.A. Alonso, M.J. Martínez-Lope, M.T. Casáis, J.L. Martínez, and M.T. Fernández-Díaz, Phys. Rev. B 62, 9498 (2000) 8. M. Fiebig, D. Frölich, K. Kohn, St. Leute, Th. Lottermoser, V.V. Pavlov, and R.V. Pisarev, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 5620 (2000) 9. J. Dho and M. G. Blamire, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, (2005) 10. M. Fiebig, T. Lottermoser, D. Frohlich, A.V. Goltsev, and R.V. Pisarev, Nature 419, 818 (2002) 11. X. Martí, F. Sánchez, J. Fontcuberta, M.V. García-Cuenca, C. Ferrater, and M. Varela, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 08P302 (2006) 12. J. Nogués and I.K. Schuller, J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 192, 203 (1999) 9
10 13. A. Hoffmann, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, (2004) 14. B.H. Miller and E.Dan Dahlberg, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 3932 (1996) 15. H. L. Brown, E. Dan Dahlberg, M. Kief, and Ch. Hou, J. Appl. Phys. 91, 7415 (2002) 10
11 Figure captions Figure 1: (a) XRD θ/2θ scan of Py/YMO(0001)/Pt(111)//STO(111). Dashed line indicates the angular position where the orthorhombic peaks should appear. (b) Pole figure collecting the STO(110), YMO(1124), and Pt(111) reflections. The two families of {111} and {111} planes of Pt are labeled as A and B, respectively. Figure 2 Magnetization loops vs applied magnetic field, measured at 100 K (open symbols) and 2 K (close symbols), after cooling the sample from 150 K in a field of 3kOe. Two consecutive loops recorded at 2 K are displayed. Inset: temperature dependence of the exchange bias (closed squares) and the coercivity (open circles) fields. Figure 3: Angular dependence of the magnetoresistance (AMR) of the Py film at (a) 100 K, (b) 50 K and (c) 2 K. Measurements were done using a magnetic field of 40 Oe, and after field-cooling (3 koe) applied at 45º with respect to the measuring current. Figure 4 Piezoresponse image of YMnO/Pt//STO(111) after poling an area of 2x2μm 2 with +6V and repolarizing an areas of 1x1μm 2 with -6V. 11
12 Figure 1 12
13 Figure 2 13
14 Figure 3 14
15 Figure
Electric field effects on magnetotransport properties of multiferroic Py/YMnO 3 /Pt heterostructures
 Electric field effects on magnetotransport properties of multiferroic Py/YMnO 3 /Pt heterostructures V. Laukhin 1,2, X. Martí 1, V. Skumryev 2,3, D. Hrabovsky 1, F. Sánchez 1, M.V. García-Cuenca 4, C.
Electric field effects on magnetotransport properties of multiferroic Py/YMnO 3 /Pt heterostructures V. Laukhin 1,2, X. Martí 1, V. Skumryev 2,3, D. Hrabovsky 1, F. Sánchez 1, M.V. García-Cuenca 4, C.
Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets. A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems
 Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems Dr. J. Sort Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA)
Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems Dr. J. Sort Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA)
Electric field control of magnetization using AFM/FM interfaces. Xiaoshan Xu
 Electric field control of magnetization using AFM/FM interfaces Xiaoshan Xu Magnetoelectric effects α = μ 0 M E H M H = 0, E = 0 = 0 (General magnetoelectrics) M H = 0, E = 0 0, P H = 0, E = 0 0, (Multiferroics)
Electric field control of magnetization using AFM/FM interfaces Xiaoshan Xu Magnetoelectric effects α = μ 0 M E H M H = 0, E = 0 = 0 (General magnetoelectrics) M H = 0, E = 0 0, P H = 0, E = 0 0, (Multiferroics)
THERE are many possibilities by which the hysteresis loop
 1968 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 44, NO. 7, JULY 2008 Exchange-Biased Magnetic Vortices Axel Hoffmann 1;2, Jordi Sort 3, Kristen S. Buchanan 2, and Josep Nogués 4 Materials Science Division, Argonne
1968 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MAGNETICS, VOL. 44, NO. 7, JULY 2008 Exchange-Biased Magnetic Vortices Axel Hoffmann 1;2, Jordi Sort 3, Kristen S. Buchanan 2, and Josep Nogués 4 Materials Science Division, Argonne
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
"Oxygen-vacancy effect on structural, magnetic, and ferroelectric properties in multiferroic YMnO3 single crystals"
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2012 "Oxygen-vacancy effect on structural, magnetic, and ferroelectric
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2012 "Oxygen-vacancy effect on structural, magnetic, and ferroelectric
Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2. Elke Arenholz
 Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2 Elke Arenholz Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720 Kai Liu Department of Physics,
Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2 Elke Arenholz Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720 Kai Liu Department of Physics,
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar
 Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers
 Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers S. M. Zhou, 1,2 L. Sun, 3 P. C. Searson, 3 and C. L. Chien 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University,
Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers S. M. Zhou, 1,2 L. Sun, 3 P. C. Searson, 3 and C. L. Chien 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University,
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films
 Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Magneto-optical study of magnetization reversal asymmetry in exchange bias
 Magneto-optical study of magnetization reversal asymmetry in exchange bias A. Tillmanns, S. Oertker*, B. Beschoten**, and G. Güntherodt. Physikalisches nstitut, RWTH Aachen, 5256 Aachen, Germany C. eighton***,
Magneto-optical study of magnetization reversal asymmetry in exchange bias A. Tillmanns, S. Oertker*, B. Beschoten**, and G. Güntherodt. Physikalisches nstitut, RWTH Aachen, 5256 Aachen, Germany C. eighton***,
Chapter 103 Spin-Polarized Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 Chapter 103 Spin-Polarized Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Toyo Kazu Yamada Keywords Spin-polarized tunneling current Spin polarization Magnetism 103.1 Principle Spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy
Chapter 103 Spin-Polarized Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Toyo Kazu Yamada Keywords Spin-polarized tunneling current Spin polarization Magnetism 103.1 Principle Spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multiphase Nanodomains in a Strained BaTiO3 Film on a GdScO3 Substrate Shunsuke Kobayashi 1*, Kazutoshi Inoue 2, Takeharu Kato 1, Yuichi Ikuhara 1,2,3 and Takahisa Yamamoto 1, 4
Spinel ferrites: old materials bring new opportunities for spintronics
 Spinel ferrites: old materials bring new opportunities for spintronics Ulrike Lüders 1,2, Agnès Barthélémy 3 *, Manuel Bibes 4, Karim Bouzehouane 3, Stéphane Fusil 5, Eric Jacquet 3, Jean-Pierre Contour
Spinel ferrites: old materials bring new opportunities for spintronics Ulrike Lüders 1,2, Agnès Barthélémy 3 *, Manuel Bibes 4, Karim Bouzehouane 3, Stéphane Fusil 5, Eric Jacquet 3, Jean-Pierre Contour
MAGNETO-RESISTANCE AND INDUCED DOMAIN STRUCTURE IN TUNNEL JUNCTIONS
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 001 Materials Research Society MAGNETO-RESISTANCE AND INDUCED DOMAIN STRUCTURE IN TUNNEL JUNCTIONS M. Hehn, O. Lenoble, D. Lacour and A. Schuhl Laboratoire de Physique
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 001 Materials Research Society MAGNETO-RESISTANCE AND INDUCED DOMAIN STRUCTURE IN TUNNEL JUNCTIONS M. Hehn, O. Lenoble, D. Lacour and A. Schuhl Laboratoire de Physique
Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple perovskite manganite NdMnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface
 What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations
 Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations Xavier Batlle, A. Labarta, Ò. Iglesias, M. García del Muro and M. Kovylina Goup of Magnetic Nanomaterials
Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations Xavier Batlle, A. Labarta, Ò. Iglesias, M. García del Muro and M. Kovylina Goup of Magnetic Nanomaterials
ANGULAR DEPENDENCE OF MAGNETIC PROPERTIES IN Co/Pt MULTILAYERS WITH PERPENDICULAR MAGNETIC ANISOTROPY
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 19, Nos. 15, 16 & 17 (2005) 2562-2567 World Scientific Publishing Company World Scientific V www.worldscientific.com ANGULAR DEPENDENCE OF MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 19, Nos. 15, 16 & 17 (2005) 2562-2567 World Scientific Publishing Company World Scientific V www.worldscientific.com ANGULAR DEPENDENCE OF MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic
 Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic sublattices Y. Sun, 1,a) J.-Z. Cong, 1 Y.-S. Chai, 1 L.-Q. Yan, 1 Y.-L. Zhao, 1 S.-G. Wang, 1 W. Ning, 2 and Y.-H Zhang 2 1 Beijing National
Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic sublattices Y. Sun, 1,a) J.-Z. Cong, 1 Y.-S. Chai, 1 L.-Q. Yan, 1 Y.-L. Zhao, 1 S.-G. Wang, 1 W. Ning, 2 and Y.-H Zhang 2 1 Beijing National
TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
Lateral length scales in exchange bias
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2005 Europhys. Lett., 71 (2), pp. 297 303 (2005) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10078-2 Lateral length scales in exchange bias I. V. Roshchin 1,O.Petracic 1,2,R.Morales 1,3,Z.-P.Li
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2005 Europhys. Lett., 71 (2), pp. 297 303 (2005) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10078-2 Lateral length scales in exchange bias I. V. Roshchin 1,O.Petracic 1,2,R.Morales 1,3,Z.-P.Li
Influence of ferromagnetic antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in Ni/Fe x Mn 1 x bilayers
 Influence of ferromagnetic antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in Ni/Fe x Mn 1 x bilayers M. Stampe, P. Stoll, T. Homberg, K. Lenz, and W. Kuch Institut für Experimentalphysik,
Influence of ferromagnetic antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in Ni/Fe x Mn 1 x bilayers M. Stampe, P. Stoll, T. Homberg, K. Lenz, and W. Kuch Institut für Experimentalphysik,
Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates.
 Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates. Abstract S. Dunn and R. W. Whatmore Building 70, Nanotechnology,
Transformation dependence of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) as shown by PiezoAFM surface mapping of Sol-gel produced PZT on various substrates. Abstract S. Dunn and R. W. Whatmore Building 70, Nanotechnology,
Ferroelectric Characterization of La BiFeO3/ Bi0.5(Na0.85K0.15)0.5TiO3 Nano-composite Films
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2016 Ferroelectric Characterization of La BiFeO3/ Bi0.5(Na0.85K0.15)0.5TiO3
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2016 Ferroelectric Characterization of La BiFeO3/ Bi0.5(Na0.85K0.15)0.5TiO3
Ferromagnetic Domain Distribution in Thin Films During Magnetization Reversal. and E. D. Dahlberg 3. Abstract
 Ferromagnetic Domain Distribution in Thin Films During Magnetization Reversal W.-T. Lee 1, S. G. E. te Velthuis 2, G. P. Felcher 2, F. Klose 1, T. Gredig 3, and E. D. Dahlberg 3. 1 Spallation Neutron Source,
Ferromagnetic Domain Distribution in Thin Films During Magnetization Reversal W.-T. Lee 1, S. G. E. te Velthuis 2, G. P. Felcher 2, F. Klose 1, T. Gredig 3, and E. D. Dahlberg 3. 1 Spallation Neutron Source,
Influence of Size on the Properties of Materials
 Influence of Size on the Properties of Materials M. J. O Shea Kansas State University mjoshea@phys.ksu.edu If you cannot get the papers connected to this work, please e-mail me for a copy 1. General Introduction
Influence of Size on the Properties of Materials M. J. O Shea Kansas State University mjoshea@phys.ksu.edu If you cannot get the papers connected to this work, please e-mail me for a copy 1. General Introduction
Novel Field-Induced Phases in HoMnO 3 at Low Temperatures
 Novel Field-Induced Phases in HoMnO 3 at Low Temperatures B. Lorenz 1, F. Yen 1, M. M. Gospodinov 2, and C. W. Chu 1,3,4 1 Department of Physics and TCSAM, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204-5002
Novel Field-Induced Phases in HoMnO 3 at Low Temperatures B. Lorenz 1, F. Yen 1, M. M. Gospodinov 2, and C. W. Chu 1,3,4 1 Department of Physics and TCSAM, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204-5002
Influence of ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in NiÕFe x Mn 1 x bilayers
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 81, 1442 21 Influence of ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in NiÕFe x Mn 1 x bilayers M. Stampe,* P. Stoll, T. Homberg, K. Lenz, and
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 81, 1442 21 Influence of ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic coupling on the antiferromagnetic ordering temperature in NiÕFe x Mn 1 x bilayers M. Stampe,* P. Stoll, T. Homberg, K. Lenz, and
Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor. (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction
 Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction D. Chiba 1, 2*, Y. Sato 1, T. Kita 2, 1, F. Matsukura 1, 2, and H. Ohno 1, 2 1 Laboratory
Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction D. Chiba 1, 2*, Y. Sato 1, T. Kita 2, 1, F. Matsukura 1, 2, and H. Ohno 1, 2 1 Laboratory
Isothermal anisotropic magnetoresistance in antiferromagnetic metallic IrMn
 Isothermal anisotropic magnetoresistance in antiferromagnetic metallic IrMn R. Galceran 1, I.Fina 1,2, *, J. Cisneros-Fernández 1, B. Bozzo 1, C. Frontera 1, L. López-Mir 1, H. Deniz 3, K.-W. Park 4, B.-G.
Isothermal anisotropic magnetoresistance in antiferromagnetic metallic IrMn R. Galceran 1, I.Fina 1,2, *, J. Cisneros-Fernández 1, B. Bozzo 1, C. Frontera 1, L. López-Mir 1, H. Deniz 3, K.-W. Park 4, B.-G.
Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering
 Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering G.J. Mankey, V.V. Krishnamurthy, F.D. Mackey and I. Zoto University of Alabama in collaboration with J.L. Robertson and M.L. Crow Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering G.J. Mankey, V.V. Krishnamurthy, F.D. Mackey and I. Zoto University of Alabama in collaboration with J.L. Robertson and M.L. Crow Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Region mapping. a Pristine and b Mn-doped Bi 2 Te 3. Arrows point at characteristic defects present on the pristine surface which have been used as markers
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Region mapping. a Pristine and b Mn-doped Bi 2 Te 3. Arrows point at characteristic defects present on the pristine surface which have been used as markers
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.
![Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998. Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.](/thumbs/90/104152266.jpg) Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Magnetoelectric Effects in Multiferroics
 Magnetoelectric Effects in Multiferroics Th. Lottermoser, M. Fiebig, T. Arima, Y. Tokura PROMOX2, APRIL 2005 ERATO-SSS Magnetoelectric Effects in Multiferroics Introduction: Magnetoelectric Effect & Multiferroics
Magnetoelectric Effects in Multiferroics Th. Lottermoser, M. Fiebig, T. Arima, Y. Tokura PROMOX2, APRIL 2005 ERATO-SSS Magnetoelectric Effects in Multiferroics Introduction: Magnetoelectric Effect & Multiferroics
Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 690 2002 Materials Research Society Imaging Self-Organized Domains at the Micron Scale in Antiferromagnetic Elemental Cr Using Magnetic X-ray Microscopy P. G. Evans, 1 E.
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study
 Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions
 Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions Ryan Stearrett Ryan Stearrett, W. G. Wang, Xiaoming Kou, J. F. Feng, J. M. D. Coey, J. Q. Xiao, and E. R. Nowak, Physical
Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions Ryan Stearrett Ryan Stearrett, W. G. Wang, Xiaoming Kou, J. F. Feng, J. M. D. Coey, J. Q. Xiao, and E. R. Nowak, Physical
Electric-field control of magnetic domain wall motion and local magnetization reversal
 Electric-field control of magnetic domain wall motion and local magnetization reversal Tuomas H. E. Lahtinen, Kévin J. A. Franke and Sebastiaan van Dijken* NanoSpin, Department of Applied Physics, Aalto
Electric-field control of magnetic domain wall motion and local magnetization reversal Tuomas H. E. Lahtinen, Kévin J. A. Franke and Sebastiaan van Dijken* NanoSpin, Department of Applied Physics, Aalto
Solid State Science and Technology, Vol. 13, No 1 & 2 (2005) ISSN
 FABRICATION OF Bi-Ti-O THIN FILM PRESSURE SENSOR PREPARED BY ELECTRON BEAM EVAPORATION METHOD Chong Cheong Wei, Muhammad Yahaya and Muhamad Mat Salleh Institue of Microengineering and Nanoelectronics,
FABRICATION OF Bi-Ti-O THIN FILM PRESSURE SENSOR PREPARED BY ELECTRON BEAM EVAPORATION METHOD Chong Cheong Wei, Muhammad Yahaya and Muhamad Mat Salleh Institue of Microengineering and Nanoelectronics,
Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface
 Submitted to Applied Physics Letters 09/22/03 Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface N. Haberkorn Universidad Nacional del Sur, Avda. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, 8000 Bs.
Submitted to Applied Physics Letters 09/22/03 Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface N. Haberkorn Universidad Nacional del Sur, Avda. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, 8000 Bs.
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore.
 This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Author(s) Citation Wang, J.; Neaton, J. B.;
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Author(s) Citation Wang, J.; Neaton, J. B.;
5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes
 5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes 5.1 New candidates for nanoelectronics: ferroelectric nanotubes In this chapter, one of the core elements for a complex building
5. Building Blocks I: Ferroelectric inorganic micro- and nano(shell) tubes 5.1 New candidates for nanoelectronics: ferroelectric nanotubes In this chapter, one of the core elements for a complex building
Holcomb Group Capabilities
 Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy
 Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy Application Notes Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy experiments were performed in an experimental station consisting of an analysis and a preparation chamber.
Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy Application Notes Spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy experiments were performed in an experimental station consisting of an analysis and a preparation chamber.
Magnetostatic Coupling in CoFe 2 O 4 /Pb(Zr 0.53 Ti 0.47 )O 3 Magnetoelectric Composite Thin Films of 2-2 Type Structure
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 25, NUMBER 1 FEBRUARY 27, 2012 ARTICLE Magnetostatic Coupling in CoFe 2 O 4 /Pb(Zr 0.53 Ti 0.47 )O 3 Magnetoelectric Composite Thin Films of 2-2 Type Structure
CHINESE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 25, NUMBER 1 FEBRUARY 27, 2012 ARTICLE Magnetostatic Coupling in CoFe 2 O 4 /Pb(Zr 0.53 Ti 0.47 )O 3 Magnetoelectric Composite Thin Films of 2-2 Type Structure
Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves
 Supplementary Information Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves Shiheng Liang 1, Rugang Geng 1, Baishun Yang 2, Wenbo Zhao 3, Ram Chandra Subedi 1,
Supplementary Information Curvature-enhanced Spin-orbit Coupling and Spinterface Effect in Fullerene-based Spin Valves Shiheng Liang 1, Rugang Geng 1, Baishun Yang 2, Wenbo Zhao 3, Ram Chandra Subedi 1,
HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2002, p. 79-84 HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS M. Volmer, J. Neamtu
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials, Vol. 4, No. 1, March 2002, p. 79-84 HALL EFFECT AND MAGNETORESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON PERMALLOY Py THIN FILMS AND Py/Cu/Py MULTILAYERS M. Volmer, J. Neamtu
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Exchange coupling mechanism for magnetization reversal and thermal stability of Co nanoparticles embedded in a CoO matrix
 Exchange coupling mechanism for magnetization reversal and thermal stability of Co nanoparticles embedded in a CoO matrix Dominique Givord, Vassil Skumryev, Josep Nogués To cite this version: Dominique
Exchange coupling mechanism for magnetization reversal and thermal stability of Co nanoparticles embedded in a CoO matrix Dominique Givord, Vassil Skumryev, Josep Nogués To cite this version: Dominique
Fabrication and Domain Imaging of Iron Magnetic Nanowire Arrays
 Abstract #: 983 Program # MI+NS+TuA9 Fabrication and Domain Imaging of Iron Magnetic Nanowire Arrays D. A. Tulchinsky, M. H. Kelley, J. J. McClelland, R. Gupta, R. J. Celotta National Institute of Standards
Abstract #: 983 Program # MI+NS+TuA9 Fabrication and Domain Imaging of Iron Magnetic Nanowire Arrays D. A. Tulchinsky, M. H. Kelley, J. J. McClelland, R. Gupta, R. J. Celotta National Institute of Standards
Newcastle University eprints
 Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
Newcastle University eprints Ponon NK, Appleby DJR, Arac E, Kwa KSK, Goss JP, Hannemann U, Petrov PK, Alford NM, O'Neill A. Impact of Crystalline Orientation on the Switching Field in Barium Titanate Using
Supplementary Figures:
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Cross-sectional morphology and Chemical composition. (a) A low-magnification dark-field TEM image shows the cross-sectional morphology of the BWO thin film
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1 Cross-sectional morphology and Chemical composition. (a) A low-magnification dark-field TEM image shows the cross-sectional morphology of the BWO thin film
Advanced Lab Course. Tunneling Magneto Resistance
 Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of
 Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2 artificial lattices by polarized neutron reflection
 Proc. Int. Conf. and Summer School on Advanced Silicide Technology 2014 JJAP Conf. Proc. 3 (2015) 011503 2015 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2
Proc. Int. Conf. and Summer School on Advanced Silicide Technology 2014 JJAP Conf. Proc. 3 (2015) 011503 2015 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 -
 Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
Combined neutron and synchrotron studies of magnetic films
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 1 journal of July 2006 physics pp. 47 55 Combined neutron and synchrotron studies of magnetic films SUNIL K SINHA 1,2, S ROY 1, M R FITZSIMMONS 2, S PARK
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 1 journal of July 2006 physics pp. 47 55 Combined neutron and synchrotron studies of magnetic films SUNIL K SINHA 1,2, S ROY 1, M R FITZSIMMONS 2, S PARK
Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional Oxide p-n Heterojunctions
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Synthesizing and Characterizing Sr 2 FeMoO 6 Bulk and Thin Films
 Undergraduate Review Volume 4 Article 14 2008 Synthesizing and Characterizing Sr 2 Bulk and Thin Films Louis Bianchini Follow this and additional works at: http://vc.bridgew.edu/undergrad_rev Part of the
Undergraduate Review Volume 4 Article 14 2008 Synthesizing and Characterizing Sr 2 Bulk and Thin Films Louis Bianchini Follow this and additional works at: http://vc.bridgew.edu/undergrad_rev Part of the
Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 300 (2006) 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers D. Repetto, A. Enders, K. Kern Max Planck Institut
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 300 (2006) 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers D. Repetto, A. Enders, K. Kern Max Planck Institut
Piezoelectric properties of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 thin films annealed in different atmospheres
 Materials Research Bulletin 42 (2007) 967 974 www.elsevier.com/locate/matresbu Piezoelectric properties of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 thin films annealed in different atmospheres A.Z. Simões *, C.S. Riccardi, A.H.M.
Materials Research Bulletin 42 (2007) 967 974 www.elsevier.com/locate/matresbu Piezoelectric properties of Bi 4 Ti 3 O 12 thin films annealed in different atmospheres A.Z. Simões *, C.S. Riccardi, A.H.M.
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1. SEM images of perovskite single-crystal patterned thin film with
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary References Supplementary Figure 1. SEM images of perovskite single-crystal patterned thin film with
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials
 Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques
 Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques James Vale October 25, 2011 Abstract Multiferroic materials have significant potential for both the scientific
Observation of ferroelectric domains in bismuth ferrite using coherent diffraction techniques James Vale October 25, 2011 Abstract Multiferroic materials have significant potential for both the scientific
Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 11 1 DECEMBER 2002 Depth profile study of ferroelectric PbZr 0.2 Ti 0.8 O 3 films Y. Li, V. Nagarajan, S. Aggarwal, R. Ramesh, L. G. Salamanca-Riba, and L.
Highly efficient electrochemical and chemical hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol using recyclable narrow mesoporous magnetic CoPt nanowires
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2016 not adjust margins Highly efficient electrochemical and chemical hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry Please do 2016 not adjust margins Highly efficient electrochemical and chemical hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol
Contents. Acknowledgments
 MAGNETIC MATERIALS Fundamentals and Applications Second edition NICOLA A. SPALDIN University of California, Santa Barbara CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Acknowledgments page xiii I Basics 1 Review
MAGNETIC MATERIALS Fundamentals and Applications Second edition NICOLA A. SPALDIN University of California, Santa Barbara CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Acknowledgments page xiii I Basics 1 Review
Hidden Interfaces and High-Temperature Magnetism in Intrinsic Topological Insulator - Ferromagnetic Insulator Heterostructures
 Hidden Interfaces and High-Temperature Magnetism in Intrinsic Topological Insulator - Ferromagnetic Insulator Heterostructures Valeria Lauter Quantum Condensed Matter Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Hidden Interfaces and High-Temperature Magnetism in Intrinsic Topological Insulator - Ferromagnetic Insulator Heterostructures Valeria Lauter Quantum Condensed Matter Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. A, Schematic of a Au/SRO113/SRO214 junction. A 15-nm thick SRO113 layer was etched along with 30-nm thick SRO214 substrate layer. To isolate the top Au electrodes
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. A, Schematic of a Au/SRO113/SRO214 junction. A 15-nm thick SRO113 layer was etched along with 30-nm thick SRO214 substrate layer. To isolate the top Au electrodes
Multiferroics for spintronics Manuel Bibes
 Multiferroics for spintronics Manuel Bibes 2 H. Béa 1, M. Gajek 1, X.-H. Zhu 1, S. Fusil 1, G. Herranz 1, M. Basletic 1, B. Warot-Fonrose 3, S. Petit 4, P. Bencok 6, K. Bouzehouane 1, C. Deranlot 1, E.
Multiferroics for spintronics Manuel Bibes 2 H. Béa 1, M. Gajek 1, X.-H. Zhu 1, S. Fusil 1, G. Herranz 1, M. Basletic 1, B. Warot-Fonrose 3, S. Petit 4, P. Bencok 6, K. Bouzehouane 1, C. Deranlot 1, E.
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Magnetic and ferroelectric properties of multiferroic Bi2NiMnO6 nanoparticles
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Magnetic and ferroelectric properties of multiferroic Bi2NiMnO6 nanoparticles
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Magnetic and ferroelectric properties of multiferroic Bi2NiMnO6 nanoparticles
Giant Magnetoresistance
 Giant Magnetoresistance This is a phenomenon that produces a large change in the resistance of certain materials as a magnetic field is applied. It is described as Giant because the observed effect is
Giant Magnetoresistance This is a phenomenon that produces a large change in the resistance of certain materials as a magnetic field is applied. It is described as Giant because the observed effect is
Reinforced magnetic properties of Ni-doped BiFeO 3 ceramic
 Reinforced magnetic properties of Ni-doped BiFe ceramic J. S. Hwang, Y. J. Yoo and Y. P. Lee Department of Physics, Hanyang University, Seoul 04763, Korea J.-H. Kang Dept. of Nano and Electronic Physics,
Reinforced magnetic properties of Ni-doped BiFe ceramic J. S. Hwang, Y. J. Yoo and Y. P. Lee Department of Physics, Hanyang University, Seoul 04763, Korea J.-H. Kang Dept. of Nano and Electronic Physics,
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012267 TITLE: Exchange Coupling and Spin-Flip Transition of CoFe204/alpha-Fe2O3 Bilayered Films DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012267 TITLE: Exchange Coupling and Spin-Flip Transition of CoFe204/alpha-Fe2O3 Bilayered Films DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public
Title: Ferroelectric YMnO 3 films deposited on n-type Si (111) substrates
 Title: Ferroelectric YMnO 3 films deposited on n-type Si (111) substrates Authors: S Parashar, A R Raju P Victor and S B Krupanidhi and C N R Rao Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru
Title: Ferroelectric YMnO 3 films deposited on n-type Si (111) substrates Authors: S Parashar, A R Raju P Victor and S B Krupanidhi and C N R Rao Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light. Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film
 Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
Photovoltaic Enhancement Due to Surface-Plasmon Assisted Visible-Light Absorption at the Inartificial Surface of Lead Zirconate-Titanate Film Fengang Zheng, a,b, * Peng Zhang, a Xiaofeng Wang, a Wen Huang,
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION 2. EXPERIMENT
 Fabrication of Nanostructured Heterojunction LEDs Using Self-Forming Moth-Eye Type Arrays of n-zno Nanocones Grown on p-si (111) Substrates by Pulsed Laser Deposition D. J. Rogers 1, V. E. Sandana 1,2,3,
Fabrication of Nanostructured Heterojunction LEDs Using Self-Forming Moth-Eye Type Arrays of n-zno Nanocones Grown on p-si (111) Substrates by Pulsed Laser Deposition D. J. Rogers 1, V. E. Sandana 1,2,3,
Supplementary Information for Optical and magneto-optical behavior of Cerium Yttrium Iron Garnet thin films at wavelengths of nm
 Supplementary Information for Optical and magneto-optical behavior of Cerium Yttrium Iron Garnet thin films at wavelengths of 200-1770 nm Mehmet C. Onbasli 1,a), Lukáš Beran 2,a), Martin Zahradník 2, Miroslav
Supplementary Information for Optical and magneto-optical behavior of Cerium Yttrium Iron Garnet thin films at wavelengths of 200-1770 nm Mehmet C. Onbasli 1,a), Lukáš Beran 2,a), Martin Zahradník 2, Miroslav
Universal valence-band picture of. the ferromagnetic semiconductor GaMnAs
 Universal valence-band picture of the ferromagnetic semiconductor GaMnAs Shinobu Ohya *, Kenta Takata, and Masaaki Tanaka Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Systems, The University of
Universal valence-band picture of the ferromagnetic semiconductor GaMnAs Shinobu Ohya *, Kenta Takata, and Masaaki Tanaka Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Systems, The University of
The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials
 Chapter 1 The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials When the ferromagnetic (FM) materials are contacted with antiferromagnetic (AFM) materials, the magnetic properties of FM materials are drastically
Chapter 1 The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials When the ferromagnetic (FM) materials are contacted with antiferromagnetic (AFM) materials, the magnetic properties of FM materials are drastically
Nanoxide electronics
 Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Infrastructure of Thin Films Laboratory in Institute of Molecular Physics Polish Academy of Sciences
 Infrastructure of Thin Films Laboratory in Institute of Molecular Physics Polish Academy of Sciences Outline Sample preparation Magnetron sputtering Ion-beam sputtering Pulsed laser deposition Electron-beam
Infrastructure of Thin Films Laboratory in Institute of Molecular Physics Polish Academy of Sciences Outline Sample preparation Magnetron sputtering Ion-beam sputtering Pulsed laser deposition Electron-beam
Tuning the magnetic properties of Co nanoparticles by Pt capping
 1 Tuning the magnetic properties of Co nanoparticles by Pt capping A. Ebbing, 1,a) O. Hellwig, 2 L. Agudo, 3 G. Eggeler, 3 and O. Petracic 1,b) 1 Institute of Experimental Physics/Condensed Matter Physics,
1 Tuning the magnetic properties of Co nanoparticles by Pt capping A. Ebbing, 1,a) O. Hellwig, 2 L. Agudo, 3 G. Eggeler, 3 and O. Petracic 1,b) 1 Institute of Experimental Physics/Condensed Matter Physics,
Part IV Multiferroic RMnO 3. Ferroelectric & magnetic ordering SHG spectroscopy SHG topography Identification of multiferroic interactions
 Part IV Multiferroic RMnO 3 Ferroelectric & magnetic ordering SHG spectroscopy SHG topography Identification of multiferroic interactions Multiferroic Hexagonal Manganites RMnO 3 Hexagonal manganites RMnO
Part IV Multiferroic RMnO 3 Ferroelectric & magnetic ordering SHG spectroscopy SHG topography Identification of multiferroic interactions Multiferroic Hexagonal Manganites RMnO 3 Hexagonal manganites RMnO
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE-
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE- NOMENOLOGY In the main text we introduce anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in analogy to ferromagnets where non-crystalline and crystalline contributions
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 1: ANISOTROPIC MAGNETORESISTANCE PHE- NOMENOLOGY In the main text we introduce anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in analogy to ferromagnets where non-crystalline and crystalline contributions
Magnon-drag thermopile
 Magnon-drag thermopile I. DEVICE FABRICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION Our devices consist of a large number of pairs of permalloy (NiFe) wires (30 nm wide, 20 nm thick and 5 µm long) connected in a zigzag
Magnon-drag thermopile I. DEVICE FABRICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION Our devices consist of a large number of pairs of permalloy (NiFe) wires (30 nm wide, 20 nm thick and 5 µm long) connected in a zigzag
A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode
 (a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of changing po 2 on the field-enhanced conductance A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode configuration is shown
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of changing po 2 on the field-enhanced conductance A constant potential of 0.4 V was maintained between electrodes 5 and 6 (the electrode configuration is shown
Application of density functional theory to real materials problems. Nicola Spaldin Materials Department, UCSB
 Application of density functional theory to real materials problems Nicola Spaldin Materials Department, UCSB From Harry Suhl s lecture notes: In theoretical physics, one obective is to explain what has
Application of density functional theory to real materials problems Nicola Spaldin Materials Department, UCSB From Harry Suhl s lecture notes: In theoretical physics, one obective is to explain what has
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum Wells
 Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proc. XXXVII International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2008 Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum
Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proc. XXXVII International School of Semiconducting Compounds, Jaszowiec 2008 Ferroelectric Field Effect Transistor Based on Modulation Doped CdTe/CdMgTe Quantum
Observation of magnetism in Au thin films.
 Observation of magnetism in Au thin films. S. Reich*, G. Leitus and Y. Feldman. Department of Materials and Interfaces, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovoth, Israel. *e-mail: shimon.reich@weizmann.ac.il
Observation of magnetism in Au thin films. S. Reich*, G. Leitus and Y. Feldman. Department of Materials and Interfaces, The Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovoth, Israel. *e-mail: shimon.reich@weizmann.ac.il
ELECTRIC FIELD-DRIVEN TUNING OF MULTIFERROIC TRANSDUCERS AND ANTENNAS THROUGH CHANGES IN FIELD STRENGTH AND MATERIAL MORPHOLOGY
 ELECTRIC FIELD-DRIVEN TUNING OF MULTIFERROIC TRANSDUCERS AND ANTENNAS THROUGH CHANGES IN FIELD STRENGTH AND MATERIAL MORPHOLOGY A Dissertation Presented by Trifon Ivanov Fitchorov to The Department of
ELECTRIC FIELD-DRIVEN TUNING OF MULTIFERROIC TRANSDUCERS AND ANTENNAS THROUGH CHANGES IN FIELD STRENGTH AND MATERIAL MORPHOLOGY A Dissertation Presented by Trifon Ivanov Fitchorov to The Department of
Superconducting Pinning by Magnetic Domains in a Ferromagnet-Superconductor Bilayer
 Vol. 106 (2004) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the School Superconductivity and Other Phenomena in Perovskites, Warsaw 2004 Superconducting Pinning by Magnetic Domains in a Ferromagnet-Superconductor
Vol. 106 (2004) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the School Superconductivity and Other Phenomena in Perovskites, Warsaw 2004 Superconducting Pinning by Magnetic Domains in a Ferromagnet-Superconductor
Tailoring the magnetization reversal of elliptical dots using exchange bias (invited)
 Tailoring the magnetization reversal of elliptical dots using exchange bias (invited) J. Sort, K. S. Buchanan, J. E. Pearson, A. Hoffmann, E. Menéndez, G. Salazar-Alvarez, M. D. Baró, M. Miron, B. Rodmacq,
Tailoring the magnetization reversal of elliptical dots using exchange bias (invited) J. Sort, K. S. Buchanan, J. E. Pearson, A. Hoffmann, E. Menéndez, G. Salazar-Alvarez, M. D. Baró, M. Miron, B. Rodmacq,
Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 114107 2006 Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films J. H. Hao a Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS 100, 114107 2006 Effects of substrate on the dielectric and tunable properties of epitaxial SrTiO 3 thin films J. H. Hao a Department of Applied Physics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic
Si, X. X. Xi, and Q. X. JIA
 LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
Supplementary Information. Spin coupling and relaxation inside molecule-metal contacts
 Supplementary Information Spin coupling and relaxation inside molecule-metal contacts Aitor Mugarza 1,2*, Cornelius Krull 1,2, Roberto Robles 2, Sebastian Stepanow 1,2, Gustavo Ceballos 1,2, Pietro Gambardella
Supplementary Information Spin coupling and relaxation inside molecule-metal contacts Aitor Mugarza 1,2*, Cornelius Krull 1,2, Roberto Robles 2, Sebastian Stepanow 1,2, Gustavo Ceballos 1,2, Pietro Gambardella
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.16 Electrical detection of charge current-induced spin polarization due to spin-momentum locking in Bi 2 Se 3 by C.H. Li, O.M.J. van t Erve, J.T. Robinson,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.16 Electrical detection of charge current-induced spin polarization due to spin-momentum locking in Bi 2 Se 3 by C.H. Li, O.M.J. van t Erve, J.T. Robinson,
