Avalanches in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium In the same Universality Class???
|
|
|
- Tobias Rodgers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Avalanches in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium In the same Universality Class??? UIUC: John Carpenter (now Sandia), Amit Mehta, Robert White (now San Diego), Matthew Delgado, Yang Liu, Andrew Missel, Geoffrey Poore, Alex Travesset (now Assis. Prof. Iowa/Ames Lab) REU s: Ma ayan Bresler (Princeton), Sharon Loverde (now Northwestern), Riva Vanderveld (now Cornell) Jim Sethna, M. Kuntz, O. Perkovic (Cornell University), A. Middleton -- theory Yehuda Ben Zion (USC, Earth and Planetary Sciences), (D.S. Fisher (Harvard)) - earthquakes A. Berger, O. Hellwig (IBM/Hitachi) -- exp. Gianfranco Durin (Turino, Italy) -- exp. Andrea Mills, Mike Weissman (UIUC) -- exp. Funding/Equipment: NSF, MCC, SLOAN, UIUC, IBM, SANDIA E. Carlson (Perdue), E. Fradkin (UIUC), S. Kivelson (Stanford), D. VanHarlingen (UIUC), M. Weissman (UIUC), C.Panagopoulos (Cambridge) -- superconductors C. Marchetti (Syr.)-- plastic CDW D. Nelson (Harvard) and N. Shnerb (Israel) - spreading Bacteria Colonies
2 Magnets and Barkhausen Noise- or Martensites and acc. emission Crackling noise Sample Volt H(t)
3 Crackling Noise / Avalanches: Barkhausen Noise (magnets) Acoustic emission (Martensites( Martensites) (Ortin, Vives,... ) Superconductors (P.Adams; Field,Witt,Nori,...) Liquid He invading Nuclepore (Hallock, Lilly,Wooters...) Rupture of fibrous Materials Earthquakes Broad Range of s -τ sizes & durations
4 The Zero Temperature Non-equilibrium Random Field Ising Model Random Field Distribution H ρ(h i ) R= strength of the disorder Each Ηspin systemis = always J aligned S i S j with the direction + S iof the H local " force" ( H(t) hi ) Zero Temperature : (Equilibration time scale) >> (Experimental time scale) n. n. = H ( t ) + i h i + J n. n. S j Jumps = Avalanches = Barkhausen noise
5 The Disorder Induced Critical Point Seen also in experiments: Berger et al, PRL 2000, J.Appl.Phys H Up Down Clean critical Dirty disorder R Log(#) τ+σβδ=2.03±0.03, 1/σ=4.2 ±0.3,... Dirty critical Vary Disorder by 50% of critical amount: still find 2 decades of powerlaw scaling! HUGE scaling region!!! LOG (AVALANCHE SIZE)
6 Self-similarity at critical disorder R c =2.16J (Cross-sections of avalanches during magnetization) CRITICAL POINT: system is at a fixed point under coarse graining transformation (Renormalization Group)
7 Why powerlaw at (H c, R c )? Renormalization Group (Wilson, Fisher, Kadanoff) history dependent, deterministic time dependent description: H=H(t)= Ωt with Ω 0 Random fields probability distribution for paths Average and expand around mean field theory Martin Siggia Rose / Bausch Janssen Wagner Formalismus soft spins: Renormalization group: (6-ε) expansion Langevin dynamics:
8 Generating Functional: Path integral: Narayan, Middleton PRB 1993, Narayan, Fisher, PRB 1992, Zippelius PRB 1984, Sompolinsky, Zippelius PRB 1992, De Dominicis, PRB 1978, Bausch, Janssen, Wagner, ZPB 1976, Martin Siggia Rose, PRA 1973 Product over all times, average over the random fields: Transformation to local fields: Random field averaged probability distribution for path η : P( η )
9 Effective Action: Momentum Shell Renormalization: 1. Integrate over momentum shell 2.rescale New Fixed Point (to O(ε)) a
10 Huge Universality Class!!! (Details don t matter!) H Η system = J S i S j + n. n. ( H(t) hi ) i S i Replace J by random couplings Use different distribution of h i or replace h i by random anisotropies Magnets (Sethna,KD,Myers, Nature 2001), plastic charge density wave depinning (Marchetti, KD PRB 2002), earthquakes (Mehta, BenZion, KD 2005), maybe superconductors (Carlson, KD, Fradkin, Kivelson, PRL 2005), others? H Η system = With nucleation of new domains J Other Universality classes? S is j + n. n. ( H(t) hi ) i + 2 Dynamics S i + long range forces Single domain wall; Nattermann, Robbins, Ji, Zapperi, Ciseau, Durin, Stanley, Urbach et al., Narayan, Sethna,...
11 RESULTS Simulation 6-ε expansion (Renormalization Group) 1/ν = 2 - ε/3-0.1ε ε 3-0.3ε 4 + ε 5 + O(ε 6 ) (PRL 93, 95, 2003 PRB 96, 99, 2002 (R)) Nature 410, 242 (2001) Experiments and Simulations in 3 dim. (Barkhausen Noise): Need Noise Exp. Tuning disorder!!!
12 SURPRIZINGLY SIMILAR: EQUILIBRIUM and NONEQUILIBRIUM RFIM: 1. SAME MEAN FIELD EXPONENTS (β=1/2, ν=1/2, δ=3) τ=3/2 and σ=1/2 (Liu, KD) 2. ABOUT SAME SIMULATION EXPONENTS in 3D and even in 4D (WITHIN ERRORBARS) 3. 6-ε expansion of noneq. mapped to all orders in ε to wrong eq. expansion (KD, Sethna) 4. SAME SIMULATION EXPONENTS for GROUND STATE & DEMAGN. STATE (Zapperi et al.) 5. SAME EXP. AND SCALING FUNCTS FOR DEMAGN. CURVE & SAT. LOOP (Carpenter, KD) 6. Middleton's no-passing rule: flipped spin cannot flip back with increasing field. (Liu, KD)
13 Surprizing Result: same Avalanche Exponents And Scaling Function In Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Ground state Avalanches : Liu, KD 2006
14 Result: ~Same scaling of Avalanche Surface Area Distribution Integrated avalanche surface distribution for avalanche size S Liu, KD, 2006
15 Demagnetizing curves in the T=0 Random Field Ising Model: John Carpenter, KD, PRB 2003 (R) Same disorder induced critical point as saturation loop: Need: Experiments on Barkhausen Noise for various disorders??? Avalanche Size Distribution ΔM vs R R=3.3 R=
16 Conclusions Avalanche exponents and spatial structures (fractal dimensions and anisotropy measures), etc. all strongly suggest that the equilibrium and non-equilibrium transition of the T=0 RFIM belong to the same universality class!!!??? Thanks to A. A. Middleton and J.P. Sethna (Yang Liu, KD, condmat 2006)
Complex dynamics ofmagnetic domain walls
 Physica A 314 (2002) 230 234 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Complex dynamics ofmagnetic domain walls G. Durin a;, S. Zapperi b a Istituto Elettrotecnico Nazionale, Galileo Ferraris and INFM, str. delle
Physica A 314 (2002) 230 234 www.elsevier.com/locate/physa Complex dynamics ofmagnetic domain walls G. Durin a;, S. Zapperi b a Istituto Elettrotecnico Nazionale, Galileo Ferraris and INFM, str. delle
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 6 Jun 2001
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 6 Jun 2001 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 6 Jun 2001](/thumbs/93/117977348.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0106113v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 6 Jun 2001 On the power spectrum of magnetization noise G. Durin a,, S. Zapperi b a Istituto Elettrotecnico Nazionale Galileo Ferraris and INFM, Corso M. d
arxiv:cond-mat/0106113v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 6 Jun 2001 On the power spectrum of magnetization noise G. Durin a,, S. Zapperi b a Istituto Elettrotecnico Nazionale Galileo Ferraris and INFM, Corso M. d
Crackling Noise, Power Spectra and Disorder Induced Critical Scaling
 arxiv:cond-mat/0112133v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Dec 2001 Crackling Noise, Power Spectra and Disorder Induced Critical Scaling A. Travesset, R.A. White, and K.A. Dahmen Loomis Laboratory, University of
arxiv:cond-mat/0112133v2 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 14 Dec 2001 Crackling Noise, Power Spectra and Disorder Induced Critical Scaling A. Travesset, R.A. White, and K.A. Dahmen Loomis Laboratory, University of
Noise in disordered systems: The power spectrum and dynamic exponents in avalanche models
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 17 1 NOVEMBER 2-I Noise in disordered systems: The power spectrum and dynamic exponents in avalanche models Matthew C. Kuntz* and James P. Sethna LASSP, Department of
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 62, NUMBER 17 1 NOVEMBER 2-I Noise in disordered systems: The power spectrum and dynamic exponents in avalanche models Matthew C. Kuntz* and James P. Sethna LASSP, Department of
James P. Sethna*, Karin A. Dahmen, and Christopher R. Myers. * Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics, Clark Hall, Cornell University, Ithaca,
 1 Crackling noise James P. Sethna*, Karin A. Dahmen, and Christopher R. Myers * Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics, Clark Hall, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853-2501, sethna@lassp.cornell.edu.
1 Crackling noise James P. Sethna*, Karin A. Dahmen, and Christopher R. Myers * Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics, Clark Hall, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853-2501, sethna@lassp.cornell.edu.
Continuous Phase Transitions
 Continuous Phase Transitions Jim Sethna, Physics 653, Fall 2010 Experiment Theory Yanjiun Chen, Stefanos Papanikolaou, Karin Dahmen, Olga Perković, Chris Myers, Matt Kuntz, Gianfranco Durin, Stefano Zapperi,
Continuous Phase Transitions Jim Sethna, Physics 653, Fall 2010 Experiment Theory Yanjiun Chen, Stefanos Papanikolaou, Karin Dahmen, Olga Perković, Chris Myers, Matt Kuntz, Gianfranco Durin, Stefano Zapperi,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jun 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jun 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jun 2005](/thumbs/94/118222547.jpg) Random Field Ising Models of Hysteresis arxiv:cond-mat/0406320v3 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jun 2005 Contents James P. Sethna Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics (LASSP), Clark Hall, Cornell University,
Random Field Ising Models of Hysteresis arxiv:cond-mat/0406320v3 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jun 2005 Contents James P. Sethna Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics (LASSP), Clark Hall, Cornell University,
In the past decade or so, science has broadened its
 Crackling noise James P. Sethna*, Karin A. Dahmen & Christopher R. Myers *Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics, Clark Hall, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853-2501, USA (sethna@lassp.cornell.edu)
Crackling noise James P. Sethna*, Karin A. Dahmen & Christopher R. Myers *Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics, Clark Hall, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853-2501, USA (sethna@lassp.cornell.edu)
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 7 Jan 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 7 Jan 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 7 Jan 2002](/thumbs/93/113743173.jpg) Microscopic foundations of the Rayleigh law of hysteresis arxiv:cond-mat/0106332v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 7 Jan 2002 Stefano Zapperi a, Alessandro Magni b Gianfranco Durin b a INFM sezione di Roma 1, Dipartimento
Microscopic foundations of the Rayleigh law of hysteresis arxiv:cond-mat/0106332v2 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 7 Jan 2002 Stefano Zapperi a, Alessandro Magni b Gianfranco Durin b a INFM sezione di Roma 1, Dipartimento
Dynamics of Ising models with damping
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 77, 094437 2008 Dynamics of Ising models with damping J. M. Deutsch Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, California 95064, USA A. Berger CIC nanogune Consolider,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 77, 094437 2008 Dynamics of Ising models with damping J. M. Deutsch Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, California 95064, USA A. Berger CIC nanogune Consolider,
Domain wall in a ferromagnetic Ising Co thin film
 Domain wall in a ferromagnetic Ising Co thin film Lemerle, Ferre, Chappert, Mathe, Giamarchi, PLD (Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998) D =1+1 interface (d=1,n=1) x x D =1+1 interface (d=1,n=1) short-range disorder
Domain wall in a ferromagnetic Ising Co thin film Lemerle, Ferre, Chappert, Mathe, Giamarchi, PLD (Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998) D =1+1 interface (d=1,n=1) x x D =1+1 interface (d=1,n=1) short-range disorder
Josh Deutsch. University of California. Santa Cruz
 Nonequilibrium symmetry breaking and pattern formation in magnetic films. p. 1/6 Nonequilibrium symmetry breaking and pattern formation in magnetic films Josh Deutsch University of California Santa Cruz
Nonequilibrium symmetry breaking and pattern formation in magnetic films. p. 1/6 Nonequilibrium symmetry breaking and pattern formation in magnetic films Josh Deutsch University of California Santa Cruz
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 15 Dec 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 15 Dec 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 15 Dec 2006](/thumbs/94/118485128.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0612418v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 15 Dec 2006 CRACKLING NOISE AND AVALANCHES: SCALING, CRITICAL PHENOMENA, AND THE RENORMALIZATION GROUP James P. Sethna Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics,
arxiv:cond-mat/0612418v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 15 Dec 2006 CRACKLING NOISE AND AVALANCHES: SCALING, CRITICAL PHENOMENA, AND THE RENORMALIZATION GROUP James P. Sethna Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics,
SWEEPRATE AND TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON CRACKLING NOISE ROBERT ALLEN WHITE
 SWEEPRATE AND TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON CRACKLING NOISE BY ROBERT ALLEN WHITE B.S., California State University, Chico, 1998 M.S., University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2001 DISSERTATION Submitted in
SWEEPRATE AND TEMPERATURE EFFECTS ON CRACKLING NOISE BY ROBERT ALLEN WHITE B.S., California State University, Chico, 1998 M.S., University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2001 DISSERTATION Submitted in
The Study of Magnetization Processes. Using Monte Carlo Methods
 Faculty of Physics, Babeş-Bolyai University Cluj-Napoca, România The Study of Magnetization Processes Using Monte Carlo Methods Kovács Katalin PhD Thesis Presented at Faculty of Physics, Babeş-Bolyai University
Faculty of Physics, Babeş-Bolyai University Cluj-Napoca, România The Study of Magnetization Processes Using Monte Carlo Methods Kovács Katalin PhD Thesis Presented at Faculty of Physics, Babeş-Bolyai University
Using Disorder to Detect Order: Hysteresis and Noise of Nematic Stripe Domains in High Temperature Superconductors
 Using Disorder to Detect Order: Hysteresis and Noise of Nematic Stripe Domains in High Temperature Superconductors Erica Carlson Karin Dahmen Eduardo Fradkin Steven Kivelson Dale Van Harlingen Michael
Using Disorder to Detect Order: Hysteresis and Noise of Nematic Stripe Domains in High Temperature Superconductors Erica Carlson Karin Dahmen Eduardo Fradkin Steven Kivelson Dale Van Harlingen Michael
Functional RG for disordered elastic systems: what is it? what is it useful for?
 Functional RG for disordered elastic systems: what is it? what is it useful for? tests and applications model: elastic manifolds statics Functional RG measuring R(u) depinning transition activated dynamics
Functional RG for disordered elastic systems: what is it? what is it useful for? tests and applications model: elastic manifolds statics Functional RG measuring R(u) depinning transition activated dynamics
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Aug 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Aug 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Aug 2007](/thumbs/89/98418196.jpg) Ising Dynamics with Damping J. M. Deutsch Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA 95064. A. Berger CIC Nanogune, Mikeletegi Pasealekua 56, 301 E-20009 Donostia Spain arxiv:0708.3855v1
Ising Dynamics with Damping J. M. Deutsch Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA 95064. A. Berger CIC Nanogune, Mikeletegi Pasealekua 56, 301 E-20009 Donostia Spain arxiv:0708.3855v1
Equilibrium and non-equilibrium Mott transitions at finite temperatures
 Equilibrium and non-equilibrium Mott transitions at finite temperatures Stefanos Papanikolaou Department of Physics, Cornell University Collaborators A. Shekhawat (Cornell), S. Zapperi (U. Milan), J. P.
Equilibrium and non-equilibrium Mott transitions at finite temperatures Stefanos Papanikolaou Department of Physics, Cornell University Collaborators A. Shekhawat (Cornell), S. Zapperi (U. Milan), J. P.
FRACTAL CONCEPT S IN SURFACE GROWT H
 FRACTAL CONCEPT S IN SURFACE GROWT H Albert-Läszlö Barabäs i H. Eugene Stanley Preface Notation guide x v xi x PART 1 Introduction 1 1 Interfaces in nature 1 1.1 Interface motion in disordered media 3
FRACTAL CONCEPT S IN SURFACE GROWT H Albert-Läszlö Barabäs i H. Eugene Stanley Preface Notation guide x v xi x PART 1 Introduction 1 1 Interfaces in nature 1 1.1 Interface motion in disordered media 3
The Last Survivor: a Spin Glass Phase in an External Magnetic Field.
 The Last Survivor: a Spin Glass Phase in an External Magnetic Field. J. J. Ruiz-Lorenzo Dep. Física, Universidad de Extremadura Instituto de Biocomputación y Física de los Sistemas Complejos (UZ) http://www.eweb.unex.es/eweb/fisteor/juan
The Last Survivor: a Spin Glass Phase in an External Magnetic Field. J. J. Ruiz-Lorenzo Dep. Física, Universidad de Extremadura Instituto de Biocomputación y Física de los Sistemas Complejos (UZ) http://www.eweb.unex.es/eweb/fisteor/juan
A Theory of Spatiotemporal Chaos: What s it mean, and how close are we?
 A Theory of Spatiotemporal Chaos: What s it mean, and how close are we? Michael Dennin UC Irvine Department of Physics and Astronomy Funded by: NSF DMR9975497 Sloan Foundation Research Corporation Outline
A Theory of Spatiotemporal Chaos: What s it mean, and how close are we? Michael Dennin UC Irvine Department of Physics and Astronomy Funded by: NSF DMR9975497 Sloan Foundation Research Corporation Outline
the renormalization group (RG) idea
 the renormalization group (RG) idea Block Spin Partition function Z =Tr s e H. block spin transformation (majority rule) T (s, if s i ; s,...,s 9 )= s i > 0; 0, otherwise. b Block Spin (block-)transformed
the renormalization group (RG) idea Block Spin Partition function Z =Tr s e H. block spin transformation (majority rule) T (s, if s i ; s,...,s 9 )= s i > 0; 0, otherwise. b Block Spin (block-)transformed
Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University
 PY502, Computational Physics, December 12, 2017 Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Advancing Research in Basic Science and Mathematics Example:
PY502, Computational Physics, December 12, 2017 Quantum Annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Advancing Research in Basic Science and Mathematics Example:
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 13 May 1999
 Numerical signs for a transition in the 2d Random Field Ising Model at T = 0 arxiv:cond-mat/9905188v1 13 May 1999 Carlos Frontera and Eduard Vives Departament d Estructura i Constituents de la Matèria,
Numerical signs for a transition in the 2d Random Field Ising Model at T = 0 arxiv:cond-mat/9905188v1 13 May 1999 Carlos Frontera and Eduard Vives Departament d Estructura i Constituents de la Matèria,
The Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld sandpile model around the upper critical dimension
 Phys. Rev. E 56, 518 (1997. 518 The Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld sandpile model around the upper critical dimension S. Lübeck and K. D. Usadel Theoretische Tieftemperaturphysik, Gerhard-Mercator-Universität Duisburg,
Phys. Rev. E 56, 518 (1997. 518 The Bak-Tang-Wiesenfeld sandpile model around the upper critical dimension S. Lübeck and K. D. Usadel Theoretische Tieftemperaturphysik, Gerhard-Mercator-Universität Duisburg,
Quantum and classical annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing. Anders W Sandvik, Boston University
 NATIONAL TAIWAN UNIVERSITY, COLLOQUIUM, MARCH 10, 2015 Quantum and classical annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Cheng-Wei Liu (BU) Anatoli Polkovnikov (BU)
NATIONAL TAIWAN UNIVERSITY, COLLOQUIUM, MARCH 10, 2015 Quantum and classical annealing in spin glasses and quantum computing Anders W Sandvik, Boston University Cheng-Wei Liu (BU) Anatoli Polkovnikov (BU)
Dynamics of polar nanodomains and critical behavior of the uniaxial relaxor SBN
 Dynamics of polar nanodomains and critical behavior of the uniaxial relaxor SBN W. Kleemann, Th. Braun, Angewandte Physik, Univ. Duisburg, Germany J. Banys, Physics Department, University of Vilnius, Lithuania
Dynamics of polar nanodomains and critical behavior of the uniaxial relaxor SBN W. Kleemann, Th. Braun, Angewandte Physik, Univ. Duisburg, Germany J. Banys, Physics Department, University of Vilnius, Lithuania
Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians. Renormalization Group without Field Theory
 Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians Renormalization Group without Field Theory Alberto Parola Università dell Insubria (Como - Italy) Renormalization Group Universality Only dimensionality and
Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians Renormalization Group without Field Theory Alberto Parola Università dell Insubria (Como - Italy) Renormalization Group Universality Only dimensionality and
Dispersion and Scaling Law of Dynamic Hysteresis Based on the Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert Model
 Dispersion and Scaling Law of Dynamic Hysteresis Based on the Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert Model Siying Liu, Hongyi Zhang, Hao Yu * Department of Mathematical Sciences, Xi an Jiaotong-Liverpool University,
Dispersion and Scaling Law of Dynamic Hysteresis Based on the Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert Model Siying Liu, Hongyi Zhang, Hao Yu * Department of Mathematical Sciences, Xi an Jiaotong-Liverpool University,
L. Laurson and M. J. Alava f noise and avalanche scaling in plastic deformation. Physical Review E, volume 74, , 5 pages.
 L. Laurson and M. J. Alava. 2006. 1 f noise and avalanche scaling in plastic deformation. Physical Review E, volume 74, 066106, 5 pages. 2006 American Physical Society Reprinted with permission. Readers
L. Laurson and M. J. Alava. 2006. 1 f noise and avalanche scaling in plastic deformation. Physical Review E, volume 74, 066106, 5 pages. 2006 American Physical Society Reprinted with permission. Readers
Avalanches, transport, and local equilibrium in self-organized criticality
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 998 Avalanches, transport, and local equilibrium in self-organized criticality Afshin Montakhab and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 58, NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 998 Avalanches, transport, and local equilibrium in self-organized criticality Afshin Montakhab and J. M. Carlson Department of Physics, University of California,
Magnetic-field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in underdoped La 2-x Sr x CuO 4
 Magnetic-field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in underdoped La 2-x Sr x CuO 4 Dragana Popović National High Magnetic Field Laboratory Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA Collaborators
Magnetic-field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in underdoped La 2-x Sr x CuO 4 Dragana Popović National High Magnetic Field Laboratory Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA Collaborators
Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field
 Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field University of Illinois at Chicago May 25, 2018 INT Workshop Multi Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Reference: Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.5,
Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field University of Illinois at Chicago May 25, 2018 INT Workshop Multi Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Reference: Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.5,
Quantitative scaling of magnetic avalanches
 Quantitative scaling of magnetic avalanches G. Durin, 1, 2 F. Bohn, 3 M. A. Corrêa, 3 R. L. Sommer, 4 P. Le Doussal, 5 and K. J. Wiese 5 1 Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica, Strada delle Cacce
Quantitative scaling of magnetic avalanches G. Durin, 1, 2 F. Bohn, 3 M. A. Corrêa, 3 R. L. Sommer, 4 P. Le Doussal, 5 and K. J. Wiese 5 1 Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica, Strada delle Cacce
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point
 Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Universal Post-quench Dynamics at a Quantum Critical Point Peter P. Orth University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA Rutgers University, 10 March 2016 References: P. Gagel, P. P. Orth, J. Schmalian Phys.
Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics.
 Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics. Bertrand Delamotte Saclay, march 3, 2009 Introduction Field theory: - infinitely many degrees of
Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics. Bertrand Delamotte Saclay, march 3, 2009 Introduction Field theory: - infinitely many degrees of
Physics 212: Statistical mechanics II Lecture XI
 Physics 212: Statistical mechanics II Lecture XI The main result of the last lecture was a calculation of the averaged magnetization in mean-field theory in Fourier space when the spin at the origin is
Physics 212: Statistical mechanics II Lecture XI The main result of the last lecture was a calculation of the averaged magnetization in mean-field theory in Fourier space when the spin at the origin is
Non-equilibrium phase transitions
 Non-equilibrium phase transitions An Introduction Lecture III Haye Hinrichsen University of Würzburg, Germany March 2006 Third Lecture: Outline 1 Directed Percolation Scaling Theory Langevin Equation 2
Non-equilibrium phase transitions An Introduction Lecture III Haye Hinrichsen University of Würzburg, Germany March 2006 Third Lecture: Outline 1 Directed Percolation Scaling Theory Langevin Equation 2
Phase-slip avalanches in superflow through nano-apertures
 Phase-slip avalanches in the superflow of 4 He through arrays of nano-apertures David Pekker, Roman Barankov & Paul M. Goldbart Department of Physics & Seitz Materials Research Laboratory University of
Phase-slip avalanches in the superflow of 4 He through arrays of nano-apertures David Pekker, Roman Barankov & Paul M. Goldbart Department of Physics & Seitz Materials Research Laboratory University of
Determinationoftheuniversalityclassofcrystalplasticity
 February0 EPL, 0(0)600 doi:0.09/095-5075/0/600 www.epljournal.org Determinationoftheuniversalityclassofcrystalplasticity G.Tsekenis,J.T.Uhl,N.GoldenfeldandK.A.Dahmen DepartmentofPhysics,UniversityofIllinoisatUrbana-Champaign,LoomisLaboratoryofPhysics
February0 EPL, 0(0)600 doi:0.09/095-5075/0/600 www.epljournal.org Determinationoftheuniversalityclassofcrystalplasticity G.Tsekenis,J.T.Uhl,N.GoldenfeldandK.A.Dahmen DepartmentofPhysics,UniversityofIllinoisatUrbana-Champaign,LoomisLaboratoryofPhysics
Emergent phenomena in large interacting communities
 Emergent phenomena in large interacting communities Giulio Biroli Institute for Theoretical Physics, CEA Saclay, France Statistical Physics Lab- ENS Paris Joint works with G. Bunin, C. Cammarota, V. Ros,
Emergent phenomena in large interacting communities Giulio Biroli Institute for Theoretical Physics, CEA Saclay, France Statistical Physics Lab- ENS Paris Joint works with G. Bunin, C. Cammarota, V. Ros,
Statistical Mechanics
 Statistical Mechanics Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity James P. Sethna Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics Cornell University, Ithaca, NY OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of figures
Statistical Mechanics Entropy, Order Parameters, and Complexity James P. Sethna Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics Cornell University, Ithaca, NY OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of figures
Scaling Theory. Roger Herrigel Advisor: Helmut Katzgraber
 Scaling Theory Roger Herrigel Advisor: Helmut Katzgraber 7.4.2007 Outline The scaling hypothesis Critical exponents The scaling hypothesis Derivation of the scaling relations Heuristic explanation Kadanoff
Scaling Theory Roger Herrigel Advisor: Helmut Katzgraber 7.4.2007 Outline The scaling hypothesis Critical exponents The scaling hypothesis Derivation of the scaling relations Heuristic explanation Kadanoff
Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene
 Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene Markus Müller in collaboration with Lars Fritz (Harvard) Subir Sachdev (Harvard) Jörg Schmalian (Iowa) Landau Memorial Conference June 6, 008 Outline Relativistic
Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene Markus Müller in collaboration with Lars Fritz (Harvard) Subir Sachdev (Harvard) Jörg Schmalian (Iowa) Landau Memorial Conference June 6, 008 Outline Relativistic
Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation
 Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation Katharina Vollmayr-Lee, Robin Bjorkquist, Landon M. Chambers Bucknell University & Göttingen 7 td tb r n (t) 6 R 5 4 3 2 ti t [ns] waiting
Microscopic Picture of Aging in SiO 2 : A Computer Simulation Katharina Vollmayr-Lee, Robin Bjorkquist, Landon M. Chambers Bucknell University & Göttingen 7 td tb r n (t) 6 R 5 4 3 2 ti t [ns] waiting
Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Homework 5, due Wednesday, April 2 Latest revision: April 4, 2003, 8:53 am
 Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Homework 5, due Wednesday, April 2 Latest revision: April 4, 2003, 8:53 am Reading David Chandler, Introduction to Modern Statistical Mechanics,
Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Homework 5, due Wednesday, April 2 Latest revision: April 4, 2003, 8:53 am Reading David Chandler, Introduction to Modern Statistical Mechanics,
THREE-BODY INTERACTIONS DRIVE THE TRANSITION TO POLAR ORDER IN A SIMPLE FLOCKING MODEL
 THREE-BODY INTERACTIONS DRIVE THE TRANSITION TO POLAR ORDER IN A SIMPLE FLOCKING MODEL Purba Chatterjee and Nigel Goldenfeld Department of Physics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Flocking in
THREE-BODY INTERACTIONS DRIVE THE TRANSITION TO POLAR ORDER IN A SIMPLE FLOCKING MODEL Purba Chatterjee and Nigel Goldenfeld Department of Physics University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Flocking in
Slightly off-equilibrium dynamics
 Slightly off-equilibrium dynamics Giorgio Parisi Many progresses have recently done in understanding system who are slightly off-equilibrium because their approach to equilibrium is quite slow. In this
Slightly off-equilibrium dynamics Giorgio Parisi Many progresses have recently done in understanding system who are slightly off-equilibrium because their approach to equilibrium is quite slow. In this
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 18 Oct 1996
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 18 Oct 1996 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 18 Oct 1996](/thumbs/91/104506699.jpg) Stability of Elastic Glass Phases in Random Field XY Magnets and Vortex Lattices in Type II Superconductors arxiv:cond-mat/9610146v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 18 Oct 1996 Daniel S. Fisher Department of Physics,
Stability of Elastic Glass Phases in Random Field XY Magnets and Vortex Lattices in Type II Superconductors arxiv:cond-mat/9610146v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 18 Oct 1996 Daniel S. Fisher Department of Physics,
Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications
 Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications Román Orús School of Physical Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane (Australia) Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Quantum many-body systems and tensor networks: simulation methods and applications Román Orús School of Physical Sciences, University of Queensland, Brisbane (Australia) Department of Physics and Astronomy,
QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydrodynamics
 QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydrodynamics M. Stephanov M. Stephanov QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydro Oxford 2017 1 / 32 History Cagniard de la Tour (1822): discovered continuos transition
QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydrodynamics M. Stephanov M. Stephanov QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydro Oxford 2017 1 / 32 History Cagniard de la Tour (1822): discovered continuos transition
Magnetic domain theory in dynamics
 Chapter 3 Magnetic domain theory in dynamics Microscale magnetization reversal dynamics is one of the hot issues, because of a great demand for fast response and high density data storage devices, for
Chapter 3 Magnetic domain theory in dynamics Microscale magnetization reversal dynamics is one of the hot issues, because of a great demand for fast response and high density data storage devices, for
Renormalization of Tensor Network States
 Renormalization of Tensor Network States I. Coarse Graining Tensor Renormalization Tao Xiang Institute of Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences txiang@iphy.ac.cn Numerical Renormalization Group brief introduction
Renormalization of Tensor Network States I. Coarse Graining Tensor Renormalization Tao Xiang Institute of Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences txiang@iphy.ac.cn Numerical Renormalization Group brief introduction
Phase Transitions and Renormalization:
 Phase Transitions and Renormalization: Using quantum techniques to understand critical phenomena. Sean Pohorence Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge CAPS 2013
Phase Transitions and Renormalization: Using quantum techniques to understand critical phenomena. Sean Pohorence Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge CAPS 2013
In-class exercises. Day 1
 Physics 4488/6562: Statistical Mechanics http://www.physics.cornell.edu/sethna/teaching/562/ Material for Week 13 Exercises due Mon Apr 30 Last correction at April 24, 2018, 12:59 pm c 2018, James Sethna,
Physics 4488/6562: Statistical Mechanics http://www.physics.cornell.edu/sethna/teaching/562/ Material for Week 13 Exercises due Mon Apr 30 Last correction at April 24, 2018, 12:59 pm c 2018, James Sethna,
Complex Systems Methods 9. Critical Phenomena: The Renormalization Group
 Complex Systems Methods 9. Critical Phenomena: The Renormalization Group Eckehard Olbrich e.olbrich@gmx.de http://personal-homepages.mis.mpg.de/olbrich/complex systems.html Potsdam WS 2007/08 Olbrich (Leipzig)
Complex Systems Methods 9. Critical Phenomena: The Renormalization Group Eckehard Olbrich e.olbrich@gmx.de http://personal-homepages.mis.mpg.de/olbrich/complex systems.html Potsdam WS 2007/08 Olbrich (Leipzig)
Introduction to Phase Transitions in Statistical Physics and Field Theory
 Introduction to Phase Transitions in Statistical Physics and Field Theory Motivation Basic Concepts and Facts about Phase Transitions: Phase Transitions in Fluids and Magnets Thermodynamics and Statistical
Introduction to Phase Transitions in Statistical Physics and Field Theory Motivation Basic Concepts and Facts about Phase Transitions: Phase Transitions in Fluids and Magnets Thermodynamics and Statistical
Effect of Diffusing Disorder on an. Absorbing-State Phase Transition
 Effect of Diffusing Disorder on an Absorbing-State Phase Transition Ronald Dickman Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil Support: CNPq & Fapemig, Brazil OUTLINE Introduction: absorbing-state phase
Effect of Diffusing Disorder on an Absorbing-State Phase Transition Ronald Dickman Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil Support: CNPq & Fapemig, Brazil OUTLINE Introduction: absorbing-state phase
Simulation of Hysteresis In Permalloy Films
 GQ-02 1 Simulation of Hysteresis In Permalloy Films Andrew Kunz and Chuck Campbell Magnetic Microscopy Center University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN Introduction 2 Looking for the classical behavior of
GQ-02 1 Simulation of Hysteresis In Permalloy Films Andrew Kunz and Chuck Campbell Magnetic Microscopy Center University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN Introduction 2 Looking for the classical behavior of
Kondo Physics in Nanostructures. A.Abdelrahman Department of Physics University of Basel Date: 27th Nov. 2006/Monday meeting
 Kondo Physics in Nanostructures A.Abdelrahman Department of Physics University of Basel Date: 27th Nov. 2006/Monday meeting Kondo Physics in Nanostructures Kondo Effects in Metals: magnetic impurities
Kondo Physics in Nanostructures A.Abdelrahman Department of Physics University of Basel Date: 27th Nov. 2006/Monday meeting Kondo Physics in Nanostructures Kondo Effects in Metals: magnetic impurities
Avalanches in mean-field models and the Barkhausen noise in spin-glasses
 OFFPRINT Avalanches in mean-field models and the Barkhausen noise in spin-glasses P. Le Doussal, M. Müller and K. J. Wiese EPL, 91 2010 57004 Please visit the new website www.epljournal.org TARGET YOUR
OFFPRINT Avalanches in mean-field models and the Barkhausen noise in spin-glasses P. Le Doussal, M. Müller and K. J. Wiese EPL, 91 2010 57004 Please visit the new website www.epljournal.org TARGET YOUR
theory, which can be quite useful in more complex systems.
 Physics 7653: Statistical Physics http://www.physics.cornell.edu/sethna/teaching/653/ In Class Exercises Last correction at August 30, 2018, 11:55 am c 2017, James Sethna, all rights reserved 9.5 Landau
Physics 7653: Statistical Physics http://www.physics.cornell.edu/sethna/teaching/653/ In Class Exercises Last correction at August 30, 2018, 11:55 am c 2017, James Sethna, all rights reserved 9.5 Landau
Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets
 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets theory and application to YbMgGaO 4 Yukawa Institute, Kyoto, November 2017 Itamar Kimchi I.K., Adam Nahum, T. Senthil, arxiv:1710.06860 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum
Valence Bonds in Random Quantum Magnets theory and application to YbMgGaO 4 Yukawa Institute, Kyoto, November 2017 Itamar Kimchi I.K., Adam Nahum, T. Senthil, arxiv:1710.06860 Valence Bonds in Random Quantum
The glass transition as a spin glass problem
 The glass transition as a spin glass problem Mike Moore School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester UBC 2007 Co-Authors: Joonhyun Yeo, Konkuk University Marco Tarzia, Saclay Mike Moore (Manchester)
The glass transition as a spin glass problem Mike Moore School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester UBC 2007 Co-Authors: Joonhyun Yeo, Konkuk University Marco Tarzia, Saclay Mike Moore (Manchester)
Disordered Elastic s s y t s em e s stems T. Giamarchi h c / h/gr_gi hi/ amarc
 Disordered Elastic sstems systems T. Giamarchi http://dpmc.unige.ch/gr_giamarchi/ h/ i hi/ P. Le Doussal (ENS) S. SB Barnes (Miami iu) U.) S. Bustingorry (Bariloche Bariloche) D. Carpentier (ENS Lyon)
Disordered Elastic sstems systems T. Giamarchi http://dpmc.unige.ch/gr_giamarchi/ h/ i hi/ P. Le Doussal (ENS) S. SB Barnes (Miami iu) U.) S. Bustingorry (Bariloche Bariloche) D. Carpentier (ENS Lyon)
Introduction to the Renormalization Group
 Introduction to the Renormalization Group Gregory Petropoulos University of Colorado Boulder March 4, 2015 1 / 17 Summary Flavor of Statistical Physics Universality / Critical Exponents Ising Model Renormalization
Introduction to the Renormalization Group Gregory Petropoulos University of Colorado Boulder March 4, 2015 1 / 17 Summary Flavor of Statistical Physics Universality / Critical Exponents Ising Model Renormalization
Deconfined Quantum Critical Points
 Deconfined Quantum Critical Points Leon Balents T. Senthil, MIT A. Vishwanath, UCB S. Sachdev, Yale M.P.A. Fisher, UCSB Outline Introduction: what is a DQCP Disordered and VBS ground states and gauge theory
Deconfined Quantum Critical Points Leon Balents T. Senthil, MIT A. Vishwanath, UCB S. Sachdev, Yale M.P.A. Fisher, UCSB Outline Introduction: what is a DQCP Disordered and VBS ground states and gauge theory
Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms
 Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: Ehud Altman, Anton Burkov, Robert Cherng, Adilet Imambekov, Vladimir Gritsev, Mikhail Lukin,
Nonequilibrium dynamics of interacting systems of cold atoms Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: Ehud Altman, Anton Burkov, Robert Cherng, Adilet Imambekov, Vladimir Gritsev, Mikhail Lukin,
Metal-Insulator Transitions in a model for magnetic Weyl semimetal and graphite under high magnetic field
 Metal-Insulator Transitions in a model for magnetic Weyl semimetal and graphite under high magnetic field Disorder-driven quantum phase transition in Weyl fermion semimetal Luo, Xu, Ohtsuki and RS, ArXiv:1710.00572v2,
Metal-Insulator Transitions in a model for magnetic Weyl semimetal and graphite under high magnetic field Disorder-driven quantum phase transition in Weyl fermion semimetal Luo, Xu, Ohtsuki and RS, ArXiv:1710.00572v2,
Models of collective displacements: from microscopic to macroscopic description
 Models of collective displacements: from microscopic to macroscopic description Sébastien Motsch CSCAMM, University of Maryland joint work with : P. Degond, L. Navoret (IMT, Toulouse) SIAM Analysis of
Models of collective displacements: from microscopic to macroscopic description Sébastien Motsch CSCAMM, University of Maryland joint work with : P. Degond, L. Navoret (IMT, Toulouse) SIAM Analysis of
Phase transitions and finite-size scaling
 Phase transitions and finite-size scaling Critical slowing down and cluster methods. Theory of phase transitions/ RNG Finite-size scaling Detailed treatment: Lectures on Phase Transitions and the Renormalization
Phase transitions and finite-size scaling Critical slowing down and cluster methods. Theory of phase transitions/ RNG Finite-size scaling Detailed treatment: Lectures on Phase Transitions and the Renormalization
Crack growth in brittle heterogeneous materials
 Crack growth in brittle heterogeneous materials D. Bonamy 1, S. Santucci, L. Ponson 3, K.-J. Måløy 4 1 CEA, IRAMIS, SPCSI, Grp. Comple Systems & Fracture, F-91191 Gif sur Yvette France; Physics of Geological
Crack growth in brittle heterogeneous materials D. Bonamy 1, S. Santucci, L. Ponson 3, K.-J. Måløy 4 1 CEA, IRAMIS, SPCSI, Grp. Comple Systems & Fracture, F-91191 Gif sur Yvette France; Physics of Geological
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
J. Stat. Mech. (2009) P01020
 Journal of Statistical Mechanics: An IOP and SISSA journal Theory and Experiment Visualization of avalanches in magnetic thin films: temporal processing Alessandro Magni 1, Gianfranco Durin 1,2, Stefano
Journal of Statistical Mechanics: An IOP and SISSA journal Theory and Experiment Visualization of avalanches in magnetic thin films: temporal processing Alessandro Magni 1, Gianfranco Durin 1,2, Stefano
Various Facets of Chalker- Coddington network model
 Various Facets of Chalker- Coddington network model V. Kagalovsky Sami Shamoon College of Engineering Beer-Sheva Israel Context Integer quantum Hall effect Semiclassical picture Chalker-Coddington Coddington
Various Facets of Chalker- Coddington network model V. Kagalovsky Sami Shamoon College of Engineering Beer-Sheva Israel Context Integer quantum Hall effect Semiclassical picture Chalker-Coddington Coddington
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 8 Nov 2016](/thumbs/90/102460254.jpg) Noise, diffusion, and hyperuniformity Daniel Hexner 1,2 and Dov Levine 1 1. Department of Physics, Technion, Haifa 32000, Israel and 2. James Franck Institute, The University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois
Noise, diffusion, and hyperuniformity Daniel Hexner 1,2 and Dov Levine 1 1. Department of Physics, Technion, Haifa 32000, Israel and 2. James Franck Institute, The University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois
The Ising model Summary of L12
 The Ising model Summary of L2 Aim: Study connections between macroscopic phenomena and the underlying microscopic world for a ferromagnet. How: Study the simplest possible model of a ferromagnet containing
The Ising model Summary of L2 Aim: Study connections between macroscopic phenomena and the underlying microscopic world for a ferromagnet. How: Study the simplest possible model of a ferromagnet containing
Active Matter Lectures for the 2011 ICTP School on Mathematics and Physics of Soft and Biological Matter Lecture 3: Hydrodynamics of SP Hard Rods
 Active Matter Lectures for the 2011 ICTP School on Mathematics and Physics of Soft and Biological Matter Lecture 3: of SP Hard Rods M. Cristina Marchetti Syracuse University Baskaran & MCM, PRE 77 (2008);
Active Matter Lectures for the 2011 ICTP School on Mathematics and Physics of Soft and Biological Matter Lecture 3: of SP Hard Rods M. Cristina Marchetti Syracuse University Baskaran & MCM, PRE 77 (2008);
Computer Simulation of Glasses: Jumps and Self-Organized Criticality
 Computer Simulation of Glasses: Jumps and Self-Organized Criticality Katharina Vollmayr-Lee Bucknell University November 2, 2007 Thanks: E. A. Baker, A. Zippelius, K. Binder, and J. Horbach V glass crystal
Computer Simulation of Glasses: Jumps and Self-Organized Criticality Katharina Vollmayr-Lee Bucknell University November 2, 2007 Thanks: E. A. Baker, A. Zippelius, K. Binder, and J. Horbach V glass crystal
 Avalanche criticality in externally driven materials Antoni Planes (antoniplanes@ub.edu) Departamentde Físicade la Matèria Condensada Universitat de Barcelona Collaborators E. Vives, Ll. Mañosa, J. Baró
Avalanche criticality in externally driven materials Antoni Planes (antoniplanes@ub.edu) Departamentde Físicade la Matèria Condensada Universitat de Barcelona Collaborators E. Vives, Ll. Mañosa, J. Baró
Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 12, 2014
 Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 1, 014 What is role of (dis)order for mechanical behavior? Andrea J. Liu Carl Goodrich Justin
Relevance of jamming to the mechanical properties of solids Sidney Nagel University of Chicago Capri; September 1, 014 What is role of (dis)order for mechanical behavior? Andrea J. Liu Carl Goodrich Justin
Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999
![Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999](/thumbs/71/65846802.jpg) Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/9909323v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 B. Zheng FB Physik, Universität Halle, 06099 Halle, Germany Abstract Numerically we
Microscopic Deterministic Dynamics and Persistence Exponent arxiv:cond-mat/9909323v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 22 Sep 1999 B. Zheng FB Physik, Universität Halle, 06099 Halle, Germany Abstract Numerically we
Today: 5 July 2008 ٢
 Anderson localization M. Reza Rahimi Tabar IPM 5 July 2008 ١ Today: 5 July 2008 ٢ Short History of Anderson Localization ٣ Publication 1) F. Shahbazi, etal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 165505 (2005) 2) A. Esmailpour,
Anderson localization M. Reza Rahimi Tabar IPM 5 July 2008 ١ Today: 5 July 2008 ٢ Short History of Anderson Localization ٣ Publication 1) F. Shahbazi, etal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 165505 (2005) 2) A. Esmailpour,
Crackling dynamics during the failure of heterogeneous material: Optical and acoustic tracking of slow interfacial crack growth
 Crackling dynamics during the failure of heterogeneous material: Optical and acoustic tracking of slow interfacial crack growth S. Santucci 1,2,3, M. Grob 4, R.Toussaint 4,5, J. Schmittbuhl 4,5, A. Hansen
Crackling dynamics during the failure of heterogeneous material: Optical and acoustic tracking of slow interfacial crack growth S. Santucci 1,2,3, M. Grob 4, R.Toussaint 4,5, J. Schmittbuhl 4,5, A. Hansen
Mesoscopic physics: normal metals, ferromagnets, and magnetic semiconductors
 Mesoscopic physics: normal metals, ferromagnets, and magnetic semiconductors Douglas Natelson Department of Physics and Astronomy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rice Quantum Institute
Mesoscopic physics: normal metals, ferromagnets, and magnetic semiconductors Douglas Natelson Department of Physics and Astronomy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Rice Quantum Institute
Different types of phase transitions for a simple model of alignment of oriented particles
 Different types of phase transitions for a simple model of alignment of oriented particles Amic Frouvelle CEREMADE Université Paris Dauphine Joint work with Jian-Guo Liu (Duke University, USA) and Pierre
Different types of phase transitions for a simple model of alignment of oriented particles Amic Frouvelle CEREMADE Université Paris Dauphine Joint work with Jian-Guo Liu (Duke University, USA) and Pierre
Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Final Exam, due Wednesday, May 14 Latest revision: May 11, 2003, 6:00 pm
 Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Final Exam, due Wednesday, May 14 Latest revision: May 11, 2003, 6:00 pm Open Book Exam Workon your own for this exam. You may consult your
Physics 562: Statistical Mechanics Spring 2003, James P. Sethna Final Exam, due Wednesday, May 14 Latest revision: May 11, 2003, 6:00 pm Open Book Exam Workon your own for this exam. You may consult your
Electronic Noise Due to Thermal Stripe Switching
 Electronic Noise Due to Thermal Stripe Switching E. W. Carlson B. Phillabaum Y. L. Loh D. X. Yao Research Corporation Solid Liquid Gas www.stonecropgallery.com/artists/caleb/01-solidliquidgas.jpg Crystals
Electronic Noise Due to Thermal Stripe Switching E. W. Carlson B. Phillabaum Y. L. Loh D. X. Yao Research Corporation Solid Liquid Gas www.stonecropgallery.com/artists/caleb/01-solidliquidgas.jpg Crystals
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Renormalization Group: 1d Ising Model. Perturbation expansion
 Physics 17b: Statistical Mechanics Renormalization Group: 1d Ising Model The ReNormalization Group (RNG) gives an understanding of scaling and universality, and provides various approximation schemes to
Physics 17b: Statistical Mechanics Renormalization Group: 1d Ising Model The ReNormalization Group (RNG) gives an understanding of scaling and universality, and provides various approximation schemes to
Renormalization of Tensor Network States. Partial order and finite temperature phase transition in the Potts model on irregular lattice
 Renormalization of Tensor Network States Partial order and finite temperature phase transition in the Potts model on irregular lattice Tao Xiang Institute of Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences Background:
Renormalization of Tensor Network States Partial order and finite temperature phase transition in the Potts model on irregular lattice Tao Xiang Institute of Physics Chinese Academy of Sciences Background:
An Introduction to Disordered Elastic Systems. T. Giamarchi
 An Introduction to Disordered Elastic Systems T. Giamarchi Many Physical Systems Interfaces Classical Crystals Quantum crystals Interfaces Magnetic domain walls Ferroelectrics Contact line in wetting Epitaxial
An Introduction to Disordered Elastic Systems T. Giamarchi Many Physical Systems Interfaces Classical Crystals Quantum crystals Interfaces Magnetic domain walls Ferroelectrics Contact line in wetting Epitaxial
Universal scaling behavior of directed percolation and the pair contact process in an external field
 Journal of Physics A 35, 005, (00) Universal scaling behavior of directed percolation and the pair contact process in an external field S. Lübeck, and R. D. Willmann,3 Weizmann Institute, Department of
Journal of Physics A 35, 005, (00) Universal scaling behavior of directed percolation and the pair contact process in an external field S. Lübeck, and R. D. Willmann,3 Weizmann Institute, Department of
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
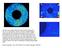 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
Outline for Fundamentals of Statistical Physics Leo P. Kadanoff
 Outline for Fundamentals of Statistical Physics Leo P. Kadanoff text: Statistical Physics, Statics, Dynamics, Renormalization Leo Kadanoff I also referred often to Wikipedia and found it accurate and helpful.
Outline for Fundamentals of Statistical Physics Leo P. Kadanoff text: Statistical Physics, Statics, Dynamics, Renormalization Leo Kadanoff I also referred often to Wikipedia and found it accurate and helpful.
Emergent light and the high temperature superconductors
 HARVARD Emergent light and the high temperature superconductors Pennsylvania State University State College, January 21, 2016 Subir Sachdev Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu Maxwell's equations:
HARVARD Emergent light and the high temperature superconductors Pennsylvania State University State College, January 21, 2016 Subir Sachdev Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu Maxwell's equations:
Quantum noise studies of ultracold atoms
 Quantum noise studies of ultracold atoms Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: Ehud Altman, Robert Cherng, Adilet Imambekov, Vladimir Gritsev, Mikhail Lukin, Anatoli Polkovnikov Funded by NSF,
Quantum noise studies of ultracold atoms Eugene Demler Harvard University Collaborators: Ehud Altman, Robert Cherng, Adilet Imambekov, Vladimir Gritsev, Mikhail Lukin, Anatoli Polkovnikov Funded by NSF,
Phase transitions and critical phenomena
 Phase transitions and critical phenomena Classification of phase transitions. Discontinous (st order) transitions Summary week -5 st derivatives of thermodynamic potentials jump discontinously, e.g. (
Phase transitions and critical phenomena Classification of phase transitions. Discontinous (st order) transitions Summary week -5 st derivatives of thermodynamic potentials jump discontinously, e.g. (
Universality in Soft Active Matter
 Universality in Soft Active Matter Chiu Fan Lee Department of Bioengineering, Imperial College London, UK M.C. Escher (1938) Day and Night Universality in soft living matter Amyloid fibrils RNA granules
Universality in Soft Active Matter Chiu Fan Lee Department of Bioengineering, Imperial College London, UK M.C. Escher (1938) Day and Night Universality in soft living matter Amyloid fibrils RNA granules
Optimization in random field Ising models by quantum annealing
 Optimization in random field Ising models by quantum annealing Matti Sarjala, 1 Viljo Petäjä, 1 and Mikko Alava 1 1 Helsinki University of Techn., Lab. of Physics, P.O.Box 1100, 02015 HUT, Finland We investigate
Optimization in random field Ising models by quantum annealing Matti Sarjala, 1 Viljo Petäjä, 1 and Mikko Alava 1 1 Helsinki University of Techn., Lab. of Physics, P.O.Box 1100, 02015 HUT, Finland We investigate
