Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field
|
|
|
- Lewis Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hydrodynamics and QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field University of Illinois at Chicago May 25, 2018 INT Workshop Multi Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Reference: Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.5, (with Shiyong Li) and Phys.Rev. D97 (2018) no.1, and arxiv: (with K. Hattori, Y. Hirono, Y. Yin)
2 The magnetic field in heavy-ion collisions In heavy-ion collisions, two magnetic fields from the projectiles overlap along the same direction out of reaction plane eb (300 MeV) 2 T 2, but the life time may be short τ 1 fm/c
3 Variables in hydrodynamics Variables of hydrodynamics are local equilibrium parameters related to conserved quantities Eg: T (x), u µ (x), µ(x), etc, such that when they are constant, the system doesn t evolve The system changes arbitrarily slowly when these parameters vary arbitrary small in gradient expansion
4 Hydrodynamics with External, Non-dynamic Magnetic Field? We will see that the transverse components of fluid velocity perpendicular to the magnetic field is not a hydrodynamic variable in a new emerging hydrodynamics at sufficiently low energy regime Remark: This is not the case when we have dynamical electromagnetic fields in magneto-hydrodynamics
5 Let us start from the conventional hydrodynamics with a background magnetic field B j µ = σe µ, E µ = F µν u ν In non-relativistic limit u µ = γ(1, v) (1, v) we have j = σv B This can be understood from the fact that in the rest frame of the fluid with velocity v, there is an electric field E = v B, so there is an Ohmic current j = σe. Or simply, the microscopic origin is the Lorentz force. B J=σ(VxB) V
6 From the spatial component of the energy-momentum conservation µ T µν = F να j α with the constitutive relation T 0 = (ɛ + p)v, we get t v = B 1 (ɛ + p) j B = σ B 2 (ɛ + p) v 1 τ R v This is also the Lorentz force J=σ(VxB) F=JxB V
7 We see that the transverse velocity v relaxes to zero with a relaxation time τ R = (ɛ+p) σ B 2 They are no longer the hydrodynamic variables below this time scale, rather they are quasi-normal modes The basic reason is the loss of conservation of transverse momentum in a background magnetic field
8 Absence of Transverse Conductivity Suppose we apply a small transverse electric field E. From J µ = σf µν u ν, we have j = σ(e + v B) and the energy-momentum conservation gives t v = 1 (ɛ + p) j B = σ ( ) E B B 2 v (ɛ + p) = 1 τ R (v eq v ), v eq E B B 2 that is, v relaxes to v eq with the same relaxation time τ R. At equilibrium v = v eq, the current vanishes j = σ(e + v eq B) = 0
9 B E V->Veq=ExB/B^2
10 The charged particles get momentum kicks to the Poynting vector direction E B, and the fluid moves along that direction until it reaches v eq. In the frame with v eq, E = γ(e + v eq B) vanishes. This is impossible when E > B. In this case the fluid moves with v eq = E B where the magnetic field E 2 vanishes in the fluid rest frame, and the electric field is E = E (1 B 2 /E 2 ). We have a current ( ) j = σe = σe 1 B2 Θ(E E 2 B)
11 Dynamical Electromagnetism: Magnetohydrodynamics B E=VxB V The situation is different in magnetohydrodynamics. Since EM fields are dynamical, the E and v can coordinate with each other to achieve an equilibrium E + v B = 0 v is now a dynamical variable, and E is slaved to v.
12 Given v, from Maxwell eq, t E = j = σ(e + v B) = σ(e E eq ) where E eq = v B. The E relaxes to the equilibrium value with the relaxation time 1/σ. From t n = j = σ E = σn, the charge density n is also not a variable in magnetohydrodynamics. The variables in magnetohydrodynamics below the scale of σ are T (x), v(x) (or u µ (x)) and B(x), whereas the electric field is slaved to be E = v B + 1 σ B +
13 Alfven Waves In the presence of background B 0, consider a transverse velocity fluctuation δv, and the electric field is δe = δv B 0. This implies a magnetic field fluctuation by t δb = δe and the current by δj = δb. From the Lorentz force t v = 1 ɛ + p δj B 0 2 t v = = we have 1 ɛ + p ( δe ) B 0 1 ɛ + p ( (δv B 0 )) B 0 = B2 0 ɛ + p 2 v, v 2 Alfven = B2 0 ɛ + p
14 Back to non-dynamical B case: Reduction of hydro variables in the new low energy hydrodynamics below τ R We have T (x) and 1+1 dimensional longitudinal velocity u µ (x), but note that x contains all directions The most general constitutive relation for the energy-momentum tensor T µν = (ɛ + p )u µ uν + p g µν + p g µν η( µ uν + u ν µ ) (ζ(uµ uν + g µν ) + ζ g µν )( αu α ) with one shear viscosity η and two bulk viscosities (ζ, ζ )
15 Computation of η in finite T perturbative QCD in leading log The QCD Boltzmann eq. in leading log is well known (Monien-Pethick-Ravenhall-Baym, Arnold-Moore-Yaffe, Hong-Teaney). f t + ˆp f x + ṗ f p = C[f ] ṗ = ±q F ˆp (eb), C[f ] g 4 T log(1/g)
16 We assume eb g 4 log(1/g)t 2 so that the cyclotron orbit size is comparable to the mean-free path l cyclo p/(eb) 1/(g 4 log(1/g)t ) l mfp C 1 1/(g 4 log(1/g)t ) The collision time is shorter than this l coll 1/(gT ), so there is no effect from the magnetic field to the collision term The result depends on the dimensionless strength of magnetic field B = (eb)/(g 4 log(1/g)t 2 ) l mfp /l cyclo
17 The shear viscosity is obtained from T z = η v z in the presence of slowly varying v z (x ). The distribution functions are f (x, p) = f eq (u µ (x)) + δf where C[f eq ] = 0 and we obtain the disturbance δf from solving the Boltzmann equation that is linear in the gradient of u µ (x) δf C 1 ( v z ) T z = d 3 p (2π) 3 p p z E p Then ( ) ν q (δf q + δf q ) + ν g δf g F
18 η(b) B T 3 η = η( B) g 4 log(1/g)
19 QCD Critical Point in Magnetic Field: Dynamic Universality Class The static universality class of QCD critical point is the 3D Ising class (or "λφ 4 theory", Wilson-Fisher) This is only about the thermal equilibrium distribution of order parameter fluctuations averaged in time. How fast the system approaches to this equilibrium distribution when it is perturbed, say relaxation rates, or how in real-time this distribution is realized is a completely independent "dynamics" questions. In the critical regime k ξ 1 (ξ: correlation length), many systems show "dynamical critical behaviors" with the scaling law for the relaxation frequency ω k z, with z: dynamic critical exponent
20 This dynamical evolution is heavily dependent of conservation laws: for example, the order parameter may or may not be conserved. In the former case, we will have a diffusion-type relaxation with ω D(ξ)k 2 in the hydro-regime of k ξ 1, while in the latter case, ω f (ξ, k 0) is a finite constant even in k 0 limit. The static universality class has no information about this: it is an additional information on the system Two systems with the same static universality class can belong to the different dynamic universality classes
21 Eg. 1) The 3D Ising model: The order parameter is the net spin density. Since the spin density is conserved locally, spin fluctuations can only diffuse. However, there is no "fluid motion" since there is no notion of conserved momentum. This gives the Model C
22 Eg. 2) Gas-Liquid Critical Point: The order parameter is the relative portion of gas-liquid, equivalently the mass density. Since the mass is locally conserved, its fluctuations can only diffuse. In addition, there are fluctuations of "fluid motions" due to momentum conservation which also can only diffuse. The fluid motions can deliver the mass fluctuations from one place to another place, enhancing the mass diffusion. This mode-coupling dynamics becomes important in the critical regime, mutually enhancing the mass and the momentum diffusion constants. This gives the Model H
23 The QCD critical point belongs to the dynamic universality class of "model H" (Son-Stephanov) The model H : 1) the order parameter is conserved, 2) the total momentum of the fluid is conserved From 1), the order parameter relaxes by a diffusion-type ω λ χ k 2 where λ is the conductivity and χ is the susceptibility From 2), the shear component of velocity fluctuations relax with the shear diffusion-type ω ηk 2 But, all these coefficients are "running" with the scales k itself, due to non-linear couplings in the dynamics λ(k), η(k)
24 With λ(k) k z 4 and χ(k) k 2 in the scaling regime k ξ 1 ω λ(k) χ(k) k 2 k z The RG running of these transport coefficients are obtained by doing Wilsonian momentum shell integration between bλ < k < Λ with b < 1. For z > 1, the ω range is elongated quickly to [, + ] Smaller scale fluctuations affect the larger scale properties and renormalize the transport coefficients at larger scales. The same physics as in the static RG, but applied to dynamical equations
25 The detailed model equations are diffusion-type with Langevin thermal noise to satisfy fluctuation-dissipation to reproduce the static universality class thermal probability P = e F ψ t j t F = = λλ z 4 2 δf δψ gλz 3+ɛ/2 ψ δf + θ δj ( = P ηλ z 2 2 j + gλ z 3+ɛ/2 ψ δf ) δψ + ξ d 4 ɛ x ( 1 2 ( ψ)2 + rλ2 2 ψ2 + uλɛ 4! ψ4 + 1 ) 2 j j We use the ɛ-expansion as in the static case, since it turns out that the dynamic fixed point constant f = 1 g 2 is order ɛ and we can do perturbation theory 8π 2 λ η on this small coupling
26 It is easiest to do momentum-shell integration after going to the path integral formulation in the Schwinger-Keldysh After all, we get z 4 Cɛ = 3.05 with C = and ɛ = 1 The conductivity diverges as λ ξ Cɛ, the shear viscosity η ξ (1 C)ɛ
27 Back to non-dynamical B We observe that the transverse component of velocity is not a critical variable any more due to a finite relaxation time τ R 1/(λ B 2 0 ) (λ : transverse conductivity) This implies that there is no non-linear dynamics between λ and v fluctuations to give rise to the previous diverging λ, and λ is expected to remain constant as in the model C. Since λ is expected to diverge, we can neglect λ in the scaling analysis. We consider a modification of model H without any diffusion along d T = 2 transverse dimensions: this implies a reduction of phase space volume for the critical non-linear dynamics
28 ψ t j t = λ Λ z 4 2 δf δψ gλz 3+ɛ/2 ψ δf + θ δj ( = P η Λ z 2 2 j + η Λ z 2 2 j + gλ z 3+ɛ/2 ψ δf ) δψ + ξ This is also obvious since we loose the momentum conservation in the transverse dimensions. After all computations, we get z 4 Cɛ = 3.15 with C = and ɛ = 1 The C gets smaller than the original model H value of due to the reduced phase space volume for the critical non-linear coupling dynamics
29 Thank you!
Transport Properties in Magnetic Field
 University of Illinois at Chicago/ RIKEN-BNL Research Center The Phases of Dense Matter, July 11-Aug 12 INT, July 28, 2016 The magnetic field in heavy-ion collisions In heavy-ion collisions, two magnetic
University of Illinois at Chicago/ RIKEN-BNL Research Center The Phases of Dense Matter, July 11-Aug 12 INT, July 28, 2016 The magnetic field in heavy-ion collisions In heavy-ion collisions, two magnetic
Collaborators: Aleksas Mazeliauskas (Heidelberg) & Derek Teaney (Stony Brook) Refs: , /25
 2017 8 28 30 @ Collaborators: Aleksas Mazeliauskas (Heidelberg) & Derek Teaney (Stony Brook) Refs: 1606.07742, 1708.05657 1/25 1. Introduction 2/25 Ultra-relativistic heavy-ion collisions and the Bjorken
2017 8 28 30 @ Collaborators: Aleksas Mazeliauskas (Heidelberg) & Derek Teaney (Stony Brook) Refs: 1606.07742, 1708.05657 1/25 1. Introduction 2/25 Ultra-relativistic heavy-ion collisions and the Bjorken
QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydrodynamics
 QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydrodynamics M. Stephanov M. Stephanov QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydro Oxford 2017 1 / 32 History Cagniard de la Tour (1822): discovered continuos transition
QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydrodynamics M. Stephanov M. Stephanov QCD critical point, fluctuations and hydro Oxford 2017 1 / 32 History Cagniard de la Tour (1822): discovered continuos transition
Lifshitz Hydrodynamics
 Lifshitz Hydrodynamics Yaron Oz (Tel-Aviv University) With Carlos Hoyos and Bom Soo Kim, arxiv:1304.7481 Outline Introduction and Summary Lifshitz Hydrodynamics Strange Metals Open Problems Strange Metals
Lifshitz Hydrodynamics Yaron Oz (Tel-Aviv University) With Carlos Hoyos and Bom Soo Kim, arxiv:1304.7481 Outline Introduction and Summary Lifshitz Hydrodynamics Strange Metals Open Problems Strange Metals
Chiral Magnetic and Vortical Effects at Weak Coupling
 Chiral Magnetic and Vortical Effects at Weak Coupling University of Illinois at Chicago and RIKEN-BNL Research Center June 19, 2014 XQCD 2014 Stonybrook University, June 19-20, 2014 Chiral Magnetic and
Chiral Magnetic and Vortical Effects at Weak Coupling University of Illinois at Chicago and RIKEN-BNL Research Center June 19, 2014 XQCD 2014 Stonybrook University, June 19-20, 2014 Chiral Magnetic and
Hydrodynamics of the superfluid CFL phase and r-mode instabilities
 Hydrodynamics of the superfluid CFL phase and r-mode instabilities Cristina Manuel Instituto de Ciencias del Espacio (IEEC-CSIC) Barcelona Hirschegg 2009 Outline Introduction Superfluid hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics
Hydrodynamics of the superfluid CFL phase and r-mode instabilities Cristina Manuel Instituto de Ciencias del Espacio (IEEC-CSIC) Barcelona Hirschegg 2009 Outline Introduction Superfluid hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics
Finite Temperature Field Theory
 Finite Temperature Field Theory Dietrich Bödeker, Universität Bielefeld 1. Thermodynamics (better: thermo-statics) (a) Imaginary time formalism (b) free energy: scalar particles, resummation i. pedestrian
Finite Temperature Field Theory Dietrich Bödeker, Universität Bielefeld 1. Thermodynamics (better: thermo-statics) (a) Imaginary time formalism (b) free energy: scalar particles, resummation i. pedestrian
Fluid dynamic propagation of initial baryon number perturbations
 Fluid dynamic propagation of initial baryon number perturbations Stefan Flörchinger (Heidelberg U.) Initial Stages 2016, Lisbon, mainly based on S. Floerchinger & M. Martinez: Fluid dynamic propagation
Fluid dynamic propagation of initial baryon number perturbations Stefan Flörchinger (Heidelberg U.) Initial Stages 2016, Lisbon, mainly based on S. Floerchinger & M. Martinez: Fluid dynamic propagation
The critical point in QCD
 The critical point in QCD Thomas Scha fer North Carolina State University The phase diagram of QCD L = q f (id/ m f )q f 1 4g 2 Ga µνg a µν 2000: Dawn of the collider era at RHIC Au + Au @200 AGeV What
The critical point in QCD Thomas Scha fer North Carolina State University The phase diagram of QCD L = q f (id/ m f )q f 1 4g 2 Ga µνg a µν 2000: Dawn of the collider era at RHIC Au + Au @200 AGeV What
Waves in plasma. Denis Gialis
 Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
Waves in plasma Denis Gialis This is a short introduction on waves in a non-relativistic plasma. We will consider a plasma of electrons and protons which is fully ionized, nonrelativistic and homogeneous.
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 9 Jun 2008
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 9 Jun 2008 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 9 Jun 2008](/thumbs/74/69739854.jpg) Dissipative effects from transport and viscous hydrodynamics arxiv:0806.1367v1 [nucl-th] 9 Jun 2008 1. Introduction Denes Molnar 1,2 and Pasi Huovinen 1 1 Purdue University, Physics Department, 525 Northwestern
Dissipative effects from transport and viscous hydrodynamics arxiv:0806.1367v1 [nucl-th] 9 Jun 2008 1. Introduction Denes Molnar 1,2 and Pasi Huovinen 1 1 Purdue University, Physics Department, 525 Northwestern
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019](/thumbs/93/113658716.jpg) arxiv:1901.01924v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019 E-mail: sigtryggur.hauksson@mail.mcgill.ca Sangyong Jeon E-mail: jeon@physics.mcgill.ca Charles Gale E-mail: gale@physics.mcgill.ca Jets are a promising way to probe
arxiv:1901.01924v1 [nucl-th] 7 Jan 2019 E-mail: sigtryggur.hauksson@mail.mcgill.ca Sangyong Jeon E-mail: jeon@physics.mcgill.ca Charles Gale E-mail: gale@physics.mcgill.ca Jets are a promising way to probe
Hydrodynamic Fluctuations in relativistic heavy ion collisions
 Hydrodynamic Fluctuations in relativistic heavy ion collisions J.I. Kapusta, BM & M. Stephanov, PRC 85, 054906 (2012) Berndt Müller INT Workshop on the Ridge 5-11 May 2012 Sources of fluctuations Initial-state
Hydrodynamic Fluctuations in relativistic heavy ion collisions J.I. Kapusta, BM & M. Stephanov, PRC 85, 054906 (2012) Berndt Müller INT Workshop on the Ridge 5-11 May 2012 Sources of fluctuations Initial-state
Off-equilibrium Non-Gaussian Cumulants: criticality, complexity, and universality
 Off-equilibrium Non-Gaussian Cumulants: criticality, complexity, and universality Swagato Mukherjee SM, R. Venugopalan, Y. Yin: arxiv:1605.09341 & arxiv:1506.00645 June 2016, Wroclaw hope: observe something
Off-equilibrium Non-Gaussian Cumulants: criticality, complexity, and universality Swagato Mukherjee SM, R. Venugopalan, Y. Yin: arxiv:1605.09341 & arxiv:1506.00645 June 2016, Wroclaw hope: observe something
Chiral kinetic theory and magnetic effect. Yoshimasa Hidaka (RIKEN)
 Chiral kinetic theory and magnetic effect Yoshimasa Hidaka (RIKEN) What is chiral kinetic theory? Relativistic Boltzmann equation (v µ @ µ + v µ F µ @ p )f = C[f] widely used in plasma physics Transport
Chiral kinetic theory and magnetic effect Yoshimasa Hidaka (RIKEN) What is chiral kinetic theory? Relativistic Boltzmann equation (v µ @ µ + v µ F µ @ p )f = C[f] widely used in plasma physics Transport
Fluid dynamics of electrons in graphene. Andrew Lucas
 Fluid dynamics of electrons in graphene Andrew Lucas Stanford Physics Condensed Matter Seminar, Princeton October 17, 2016 Collaborators 2 Subir Sachdev Harvard Physics & Perimeter Institute Philip Kim
Fluid dynamics of electrons in graphene Andrew Lucas Stanford Physics Condensed Matter Seminar, Princeton October 17, 2016 Collaborators 2 Subir Sachdev Harvard Physics & Perimeter Institute Philip Kim
Longitudinal thermalization via the chromo-weibel instability
 Longitudinal thermalization via the chromo-weibel instability Maximilian Attems Frankfurt Institute of Advanced Studies 1207.5795, 1301.7749 Collaborators: Anton Rebhan, Michael Strickland Schladming,
Longitudinal thermalization via the chromo-weibel instability Maximilian Attems Frankfurt Institute of Advanced Studies 1207.5795, 1301.7749 Collaborators: Anton Rebhan, Michael Strickland Schladming,
Hydrodynamics. Stefan Flörchinger (Heidelberg) Heidelberg, 3 May 2010
 Hydrodynamics Stefan Flörchinger (Heidelberg) Heidelberg, 3 May 2010 What is Hydrodynamics? Describes the evolution of physical systems (classical or quantum particles, fluids or fields) close to thermal
Hydrodynamics Stefan Flörchinger (Heidelberg) Heidelberg, 3 May 2010 What is Hydrodynamics? Describes the evolution of physical systems (classical or quantum particles, fluids or fields) close to thermal
Classical YM Dynamics and Turbulence Diffusion
 Classical YM Dynamics and Turbulence Diffusion Kenji Fukushima Department of Physics, Keio University 1 Transverse Pattern Formation Central Results g 2 μ t=0.1 g 2 μ t=30 g 2 μ t=10 June 18, 2013g@2 μ
Classical YM Dynamics and Turbulence Diffusion Kenji Fukushima Department of Physics, Keio University 1 Transverse Pattern Formation Central Results g 2 μ t=0.1 g 2 μ t=30 g 2 μ t=10 June 18, 2013g@2 μ
(Super) Fluid Dynamics. Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University
 (Super) Fluid Dynamics Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University Hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics (undergraduate version): Newton s law for continuous, deformable media. Fluids: Gases, liquids, plasmas,...
(Super) Fluid Dynamics Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University Hydrodynamics Hydrodynamics (undergraduate version): Newton s law for continuous, deformable media. Fluids: Gases, liquids, plasmas,...
Macroscopic plasma description
 Macroscopic plasma description Macroscopic plasma theories are fluid theories at different levels single fluid (magnetohydrodynamics MHD) two-fluid (multifluid, separate equations for electron and ion
Macroscopic plasma description Macroscopic plasma theories are fluid theories at different levels single fluid (magnetohydrodynamics MHD) two-fluid (multifluid, separate equations for electron and ion
Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics.
 Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics. Bertrand Delamotte Saclay, march 3, 2009 Introduction Field theory: - infinitely many degrees of
Renormalization Group: non perturbative aspects and applications in statistical and solid state physics. Bertrand Delamotte Saclay, march 3, 2009 Introduction Field theory: - infinitely many degrees of
Anisotropic fluid dynamics. Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University
 Anisotropic fluid dynamics Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University Outline We wish to extract the properties of nearly perfect (low viscosity) fluids from experiments with trapped gases, colliding
Anisotropic fluid dynamics Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University Outline We wish to extract the properties of nearly perfect (low viscosity) fluids from experiments with trapped gases, colliding
Hybrid Model of Heavy-Ion Collisions at BES Energies with Dynamical Sources
 Hybrid Model of Heavy-Ion Collisions at BES Energies with Dynamical Sources Lipei Du In collaboration with Gojko Vujanovic and Ulrich Heinz Department of Physics, The Ohio State University, USA May 14,
Hybrid Model of Heavy-Ion Collisions at BES Energies with Dynamical Sources Lipei Du In collaboration with Gojko Vujanovic and Ulrich Heinz Department of Physics, The Ohio State University, USA May 14,
2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1. Waves in plasmas. T. Johnson
 2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasma physics Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas Transverse waves
2/8/16 Dispersive Media, Lecture 5 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasma physics Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas Transverse waves
the renormalization group (RG) idea
 the renormalization group (RG) idea Block Spin Partition function Z =Tr s e H. block spin transformation (majority rule) T (s, if s i ; s,...,s 9 )= s i > 0; 0, otherwise. b Block Spin (block-)transformed
the renormalization group (RG) idea Block Spin Partition function Z =Tr s e H. block spin transformation (majority rule) T (s, if s i ; s,...,s 9 )= s i > 0; 0, otherwise. b Block Spin (block-)transformed
Hydrodynamical description of ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions
 Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies June 27, 2011 with G. Denicol, E. Molnar, P. Huovinen, D. H. Rischke 1 Fluid dynamics (Navier-Stokes equations) Conservation laws momentum conservation Thermal
Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies June 27, 2011 with G. Denicol, E. Molnar, P. Huovinen, D. H. Rischke 1 Fluid dynamics (Navier-Stokes equations) Conservation laws momentum conservation Thermal
Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1. Waves in plasmas. T. Johnson
 2017-02-14 Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasmas as a coupled system Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas
2017-02-14 Dispersive Media, Lecture 7 - Thomas Johnson 1 Waves in plasmas T. Johnson Introduction to plasmas as a coupled system Magneto-Hydro Dynamics, MHD Plasmas without magnetic fields Cold plasmas
Towards new relativistic hydrodynamcis from AdS/CFT
 Towards new relativistic hydrodynamcis from AdS/CFT Michael Lublinsky Stony Brook with Edward Shuryak QGP is Deconfined QGP is strongly coupled (sqgp) behaves almost like a perfect liquid (Navier-Stokes
Towards new relativistic hydrodynamcis from AdS/CFT Michael Lublinsky Stony Brook with Edward Shuryak QGP is Deconfined QGP is strongly coupled (sqgp) behaves almost like a perfect liquid (Navier-Stokes
Nearly Perfect Fluidity: From Cold Atoms to Hot Quarks. Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University
 Nearly Perfect Fluidity: From Cold Atoms to Hot Quarks Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University RHIC serves the perfect fluid Experiments at RHIC are consistent with the idea that a thermalized
Nearly Perfect Fluidity: From Cold Atoms to Hot Quarks Thomas Schaefer, North Carolina State University RHIC serves the perfect fluid Experiments at RHIC are consistent with the idea that a thermalized
Status of viscous hydrodynamic code development
 Status of viscous hydrodynamic code development Yuriy KARPENKO Transport group meeting, Jan 17, 2013 Yuriy Karpenko (FIAS/BITP) Status of viscous hydro code Transport group meeting, Jan 17, 2013 1 / 21
Status of viscous hydrodynamic code development Yuriy KARPENKO Transport group meeting, Jan 17, 2013 Yuriy Karpenko (FIAS/BITP) Status of viscous hydro code Transport group meeting, Jan 17, 2013 1 / 21
Strongly interacting quantum fluids: Transport theory
 Strongly interacting quantum fluids: Transport theory Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University Fluids: Gases, Liquids, Plasmas,... Hydrodynamics: Long-wavelength, low-frequency dynamics of conserved
Strongly interacting quantum fluids: Transport theory Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University Fluids: Gases, Liquids, Plasmas,... Hydrodynamics: Long-wavelength, low-frequency dynamics of conserved
Dynamics of net-baryon density correlations near the QCD critical point
 Dynamics of net-baryon density correlations near the QCD critical point Marcus Bluhm and Marlene Nahrgang The work of M.B. is funded by the European Union s Horizon 22 research and innovation programme
Dynamics of net-baryon density correlations near the QCD critical point Marcus Bluhm and Marlene Nahrgang The work of M.B. is funded by the European Union s Horizon 22 research and innovation programme
Constraining the QCD equation of state in hadron colliders
 Constraining the QCD equation of state in hadron colliders Akihiko Monnai (KEK, Japan) with Jean-Yves Ollitrault (IPhT Saclay, France) AM and J.-Y. Ollitrault, Phys. Rev. C 96, 044902 (2017) New Frontiers
Constraining the QCD equation of state in hadron colliders Akihiko Monnai (KEK, Japan) with Jean-Yves Ollitrault (IPhT Saclay, France) AM and J.-Y. Ollitrault, Phys. Rev. C 96, 044902 (2017) New Frontiers
Modelling Early Time Dynamics of Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions
 Kyoto, 2015/10/05 Modelling Early Time Dynamics of Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions Dr. Marco Ruggieri Physics and Astronomy Department, Catania University, Catania (Italy) Collaborators: Vincenzo Greco
Kyoto, 2015/10/05 Modelling Early Time Dynamics of Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions Dr. Marco Ruggieri Physics and Astronomy Department, Catania University, Catania (Italy) Collaborators: Vincenzo Greco
Thermalization of Color Glass Condensate within Partonic Cascade BAMPS and Comparison with Bottom-Up Scenario.
 Thermalization of Color Glass Condensate within Partonic Cascade BAMPS and Comparison with Bottom-Up Scenario. Shear viscosity from BAMPS Andrej El Zhe Xu Carsten Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik
Thermalization of Color Glass Condensate within Partonic Cascade BAMPS and Comparison with Bottom-Up Scenario. Shear viscosity from BAMPS Andrej El Zhe Xu Carsten Greiner Institut für Theoretische Physik
Relativistic Viscous Hydrodynamics for Multi-Component Systems with Multiple Conserved Currents
 Reference: AM and T. Hirano, arxiv:1003:3087 Relativistic Viscous Hydrodynamics for Multi-Component Systems with Multiple Conserved Currents Akihiko Monnai Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo
Reference: AM and T. Hirano, arxiv:1003:3087 Relativistic Viscous Hydrodynamics for Multi-Component Systems with Multiple Conserved Currents Akihiko Monnai Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo
Divergence of the gradient expansion and the applicability of fluid dynamics Gabriel S. Denicol (IF-UFF)
 Divergence of the gradient expansion and the applicability of fluid dynamics Gabriel S. Denicol (IF-UFF) arxiv:1608.07869, arxiv:1711.01657, arxiv:1709.06644 Frankfurt University 1.February.2018 Preview
Divergence of the gradient expansion and the applicability of fluid dynamics Gabriel S. Denicol (IF-UFF) arxiv:1608.07869, arxiv:1711.01657, arxiv:1709.06644 Frankfurt University 1.February.2018 Preview
Relativistic hydrodynamics for heavy-ion physics
 heavy-ion physics Universität Heidelberg June 27, 2014 1 / 26 Collision time line 2 / 26 3 / 26 4 / 26 Space-time diagram proper time: τ = t 2 z 2 space-time rapidity η s : t = τ cosh(η s ) z = τ sinh(η
heavy-ion physics Universität Heidelberg June 27, 2014 1 / 26 Collision time line 2 / 26 3 / 26 4 / 26 Space-time diagram proper time: τ = t 2 z 2 space-time rapidity η s : t = τ cosh(η s ) z = τ sinh(η
Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram
 Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram Raju Venugopalan BNL/Heidelberg arxiv:1310.1600 [cond-mat.stat-mech] Heidelberg Seminar, June 8 th, 2016
Kibble-Zurek dynamics and off-equilibrium scaling of critical cumulants in the QCD phase diagram Raju Venugopalan BNL/Heidelberg arxiv:1310.1600 [cond-mat.stat-mech] Heidelberg Seminar, June 8 th, 2016
Fundamental equations of relativistic fluid dynamics
 CHAPTER VI Fundamental equations of relativistic fluid dynamics When the energy density becomes large as may happen for instance in compact astrophysical objects, in the early Universe, or in high-energy
CHAPTER VI Fundamental equations of relativistic fluid dynamics When the energy density becomes large as may happen for instance in compact astrophysical objects, in the early Universe, or in high-energy
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 19 Feb 1999
 ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION IN THE EARLY UNIVERSE arxiv:hep-ph/9902398v1 19 Feb 1999 H. HEISELBERG Nordita, Blegdamsvej 17, 2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark E-mail: hh@nordita.dk The electrical conductivity has been
ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION IN THE EARLY UNIVERSE arxiv:hep-ph/9902398v1 19 Feb 1999 H. HEISELBERG Nordita, Blegdamsvej 17, 2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark E-mail: hh@nordita.dk The electrical conductivity has been
No-drag frame for anomalous chiral fluid
 No-drag frame for anomalous chiral fluid M. Stephanov University of Illinois at Chicago M. Stephanov (UIC) No-drag frame UCLA 2016 1 / 15 Based on arxiv:1508.02396 with Ho-Ung Yee. M. Stephanov (UIC) No-drag
No-drag frame for anomalous chiral fluid M. Stephanov University of Illinois at Chicago M. Stephanov (UIC) No-drag frame UCLA 2016 1 / 15 Based on arxiv:1508.02396 with Ho-Ung Yee. M. Stephanov (UIC) No-drag
Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Equilibrium Properties
 Quantum Liquids LECTURE I-II Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Phenomenology and Microscopic Foundations LECTURE III Superfluidity. Bogoliubov theory. Bose-Einstein condensation. LECTURE IV Luttinger Liquids.
Quantum Liquids LECTURE I-II Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Phenomenology and Microscopic Foundations LECTURE III Superfluidity. Bogoliubov theory. Bose-Einstein condensation. LECTURE IV Luttinger Liquids.
Transport phenomena in strong magnetic fields
 Transport phenomena in strong magnetic fields Koichi Hattori Shanghai Fudan University Seminar in INT Program INT-18-1b Week 1 Multi-Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Strong magnetic fields
Transport phenomena in strong magnetic fields Koichi Hattori Shanghai Fudan University Seminar in INT Program INT-18-1b Week 1 Multi-Scale Problems Using Effective Field Theories Strong magnetic fields
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 2 Mar 2015
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 2 Mar 2015 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 2 Mar 2015](/thumbs/71/65578601.jpg) The domain of validity of fluid dynamics and the onset of cavitation in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions arxiv:503.0053v [nucl-th] 2 Mar 205 Department of Physics, McGill University, 3600 University
The domain of validity of fluid dynamics and the onset of cavitation in ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions arxiv:503.0053v [nucl-th] 2 Mar 205 Department of Physics, McGill University, 3600 University
The Big Picture. Thomas Schaefer. North Carolina State University
 The Big Picture Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University 1 Big Questions What is QCD? What is a Phase of QCD? What is a Plasma? What is a (perfect) Liquid? What is a wqgp/sqgp? 2 What is QCD (Quantum
The Big Picture Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University 1 Big Questions What is QCD? What is a Phase of QCD? What is a Plasma? What is a (perfect) Liquid? What is a wqgp/sqgp? 2 What is QCD (Quantum
Past, Present, and Future of the QGP Physics
 Past, Present, and Future of the QGP Physics Masayuki Asakawa Department of Physics, Osaka University November 8, 2018 oward Microscopic Understanding In Condensed Matter Physics 1st Macroscopic Properties
Past, Present, and Future of the QGP Physics Masayuki Asakawa Department of Physics, Osaka University November 8, 2018 oward Microscopic Understanding In Condensed Matter Physics 1st Macroscopic Properties
Hadronic equation of state and relativistic heavy-ion collisions
 Hadronic equation of state and relativistic heavy-ion collisions Pasi Huovinen J. W. Goethe Universität Workshop on Excited Hadronic States and the Deconfinement Transition Feb 23, 2011, Thomas Jefferson
Hadronic equation of state and relativistic heavy-ion collisions Pasi Huovinen J. W. Goethe Universität Workshop on Excited Hadronic States and the Deconfinement Transition Feb 23, 2011, Thomas Jefferson
Entropy current and equilibrium partition function in fluid dynam
 Entropy current and equilibrium partition function in fluid dynamics December 18, 2014 Aim of the talk In this talk we would analyse the relation between two apparently disjoint physical conditions that
Entropy current and equilibrium partition function in fluid dynamics December 18, 2014 Aim of the talk In this talk we would analyse the relation between two apparently disjoint physical conditions that
Fermi Liquid and BCS Phase Transition
 Fermi Liquid and BCS Phase Transition Yu, Zhenhua November 2, 25 Abstract Landau fermi liquid theory is introduced as a successful theory describing the low energy properties of most fermi systems. Besides
Fermi Liquid and BCS Phase Transition Yu, Zhenhua November 2, 25 Abstract Landau fermi liquid theory is introduced as a successful theory describing the low energy properties of most fermi systems. Besides
Effective Field Theory of Dissipative Fluids
 Effective Field Theory of Dissipative Fluids Hong Liu Paolo Glorioso Michael Crossley arxiv: 1511.03646 Conserved quantities Consider a long wavelength disturbance of a system in thermal equilibrium non-conserved
Effective Field Theory of Dissipative Fluids Hong Liu Paolo Glorioso Michael Crossley arxiv: 1511.03646 Conserved quantities Consider a long wavelength disturbance of a system in thermal equilibrium non-conserved
Transport coefficients from Kinetic Theory: Bulk viscosity, Diffusion, Thermal conductivity. Debarati Chatterjee
 Transport coefficients from Kinetic Theory: Bulk viscosity, Diffusion, Thermal conductivity Debarati Chatterjee Recap: Hydrodynamics of nearly perfect fluids Hydrodynamics: correlation functions at low
Transport coefficients from Kinetic Theory: Bulk viscosity, Diffusion, Thermal conductivity Debarati Chatterjee Recap: Hydrodynamics of nearly perfect fluids Hydrodynamics: correlation functions at low
CHAPMAN-ENSKOG EXPANSION OF THE BOLTZMANN EQUATION AND ITS DIAGRAMMATIC INTERPRETATION
 CHAPMAN-ENSKOG EXPANSION OF THE BOLTZMANN EQUATION AND ITS DIAGRAMMATIC INTERPRETATION M.E. CARRINGTON A,B,HOUDEFU A,B,C AND R. KOBES B,D a Department of Physics, Brandon University, Brandon, MB,R7A 6A9
CHAPMAN-ENSKOG EXPANSION OF THE BOLTZMANN EQUATION AND ITS DIAGRAMMATIC INTERPRETATION M.E. CARRINGTON A,B,HOUDEFU A,B,C AND R. KOBES B,D a Department of Physics, Brandon University, Brandon, MB,R7A 6A9
The direct photon puzzle
 The direct photon puzzle Jean-François Paquet January 16, 2017 ALICE Journal Club Jean-François Paquet (Stony Brook) 2 What is the direct photon puzzle? > Background
The direct photon puzzle Jean-François Paquet January 16, 2017 ALICE Journal Club Jean-François Paquet (Stony Brook) 2 What is the direct photon puzzle? > Background
AdS/CFT and Second Order Viscous Hydrodynamics
 AdS/CFT and Second Order Viscous Hydrodynamics Micha l P. Heller Institute of Physics Jagiellonian University, Cracow Cracow School of Theoretical Physics XLVII Course Zakopane, 20.06.2007 Based on [hep-th/0703243]
AdS/CFT and Second Order Viscous Hydrodynamics Micha l P. Heller Institute of Physics Jagiellonian University, Cracow Cracow School of Theoretical Physics XLVII Course Zakopane, 20.06.2007 Based on [hep-th/0703243]
J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2)
 Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
Critical Region of the QCD Phase Transition
 Critical Region of the QCD Phase Transition Mean field vs. Renormalization group B.-J. Schaefer 1 and J. Wambach 1,2 1 Institut für Kernphysik TU Darmstadt 2 GSI Darmstadt 18th August 25 Uni. Graz B.-J.
Critical Region of the QCD Phase Transition Mean field vs. Renormalization group B.-J. Schaefer 1 and J. Wambach 1,2 1 Institut für Kernphysik TU Darmstadt 2 GSI Darmstadt 18th August 25 Uni. Graz B.-J.
Relativistic magnetohydrodynamics. Abstract
 Relativistic magnetohydrodynamics R. D. Hazeltine and S. M. Mahajan Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas, Austin, Texas 78712 (October 19, 2000) Abstract The lowest-order description of
Relativistic magnetohydrodynamics R. D. Hazeltine and S. M. Mahajan Institute for Fusion Studies, The University of Texas, Austin, Texas 78712 (October 19, 2000) Abstract The lowest-order description of
Probing Universality in AdS/CFT
 1 / 24 Probing Universality in AdS/CFT Adam Ritz University of Victoria with P. Kovtun [0801.2785, 0806.0110] and J. Ward [0811.4195] Shifmania workshop Minneapolis May 2009 2 / 24 Happy Birthday Misha!
1 / 24 Probing Universality in AdS/CFT Adam Ritz University of Victoria with P. Kovtun [0801.2785, 0806.0110] and J. Ward [0811.4195] Shifmania workshop Minneapolis May 2009 2 / 24 Happy Birthday Misha!
CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI. INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY
 CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY E-mail: pietroni@pd.infn.it The formation of topological defects in a second order
CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY E-mail: pietroni@pd.infn.it The formation of topological defects in a second order
Effective field theory, holography, and non-equilibrium physics. Hong Liu
 Effective field theory, holography, and non-equilibrium physics Hong Liu Equilibrium systems Microscopic description low energy effective field theory: Macroscopic phenomena Renormalization group, universality
Effective field theory, holography, and non-equilibrium physics Hong Liu Equilibrium systems Microscopic description low energy effective field theory: Macroscopic phenomena Renormalization group, universality
Anomalous hydrodynamics and gravity. Dam T. Son (INT, University of Washington)
 Anomalous hydrodynamics and gravity Dam T. Son (INT, University of Washington) Summary of the talk Hydrodynamics: an old theory, describing finite temperature systems The presence of anomaly modifies hydrodynamics
Anomalous hydrodynamics and gravity Dam T. Son (INT, University of Washington) Summary of the talk Hydrodynamics: an old theory, describing finite temperature systems The presence of anomaly modifies hydrodynamics
Quantum critical transport and AdS/CFT
 Quantum critical transport and AdS/CFT Lars Fritz, Harvard Sean Hartnoll, Harvard Christopher Herzog, Princeton Pavel Kovtun, Victoria Markus Mueller, Trieste Joerg Schmalian, Iowa Dam Son, Washington
Quantum critical transport and AdS/CFT Lars Fritz, Harvard Sean Hartnoll, Harvard Christopher Herzog, Princeton Pavel Kovtun, Victoria Markus Mueller, Trieste Joerg Schmalian, Iowa Dam Son, Washington
Heavy-Quark Transport in the QGP
 Heavy-Quark Transport in the QGP Hendrik van Hees Justus-Liebig Universität Gießen October 13, 29 Institut für Theoretische Physik JUSTUS-LIEBIG- UNIVERSITÄT GIESSEN Hendrik van Hees (JLU Gießen) Heavy-Quark
Heavy-Quark Transport in the QGP Hendrik van Hees Justus-Liebig Universität Gießen October 13, 29 Institut für Theoretische Physik JUSTUS-LIEBIG- UNIVERSITÄT GIESSEN Hendrik van Hees (JLU Gießen) Heavy-Quark
Gerry and Fermi Liquid Theory. Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State
 Ë Ë Ë³ Gerry and Fermi Liquid Theory Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State Introduction I learned about Fermi liquid theory (FLT from Gerry. I was under the imression that the theory amounted to the oeration
Ë Ë Ë³ Gerry and Fermi Liquid Theory Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State Introduction I learned about Fermi liquid theory (FLT from Gerry. I was under the imression that the theory amounted to the oeration
Effective Field Theory
 Effective Field Theory Iain Stewart MIT The 19 th Taiwan Spring School on Particles and Fields April, 2006 Physics compartmentalized Quantum Field Theory String Theory? General Relativity short distance
Effective Field Theory Iain Stewart MIT The 19 th Taiwan Spring School on Particles and Fields April, 2006 Physics compartmentalized Quantum Field Theory String Theory? General Relativity short distance
QGP, Hydrodynamics and the AdS/CFT correspondence
 QGP, Hydrodynamics and the AdS/CFT correspondence Adrián Soto Stony Brook University October 25th 2010 Adrián Soto (Stony Brook University) QGP, Hydrodynamics and AdS/CFT October 25th 2010 1 / 18 Outline
QGP, Hydrodynamics and the AdS/CFT correspondence Adrián Soto Stony Brook University October 25th 2010 Adrián Soto (Stony Brook University) QGP, Hydrodynamics and AdS/CFT October 25th 2010 1 / 18 Outline
Equation of state and transport coefficients at finite baryo-chemical potential
 Equation of state and transport coefficients at finite baryo-chemical potential Jacquelyn Noronha-Hostler University of Houston: Israel Portillo, Paolo Parotto, Claudia Ratti University of Sao Paulo: Romulo
Equation of state and transport coefficients at finite baryo-chemical potential Jacquelyn Noronha-Hostler University of Houston: Israel Portillo, Paolo Parotto, Claudia Ratti University of Sao Paulo: Romulo
Holography and (Lorentzian) black holes
 Holography and (Lorentzian) black holes Simon Ross Centre for Particle Theory The State of the Universe, Cambridge, January 2012 Simon Ross (Durham) Holography and black holes Cambridge 7 January 2012
Holography and (Lorentzian) black holes Simon Ross Centre for Particle Theory The State of the Universe, Cambridge, January 2012 Simon Ross (Durham) Holography and black holes Cambridge 7 January 2012
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing.
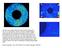 This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
This false color image is taken from Dan Howell's experiments. This is a 2D experiment in which a collection of disks undergoes steady shearing. The red regions mean large local force, and the blue regions
Electrical Transport in Nanoscale Systems
 Electrical Transport in Nanoscale Systems Description This book provides an in-depth description of transport phenomena relevant to systems of nanoscale dimensions. The different viewpoints and theoretical
Electrical Transport in Nanoscale Systems Description This book provides an in-depth description of transport phenomena relevant to systems of nanoscale dimensions. The different viewpoints and theoretical
Relativistic hydrodynamics at large gradients
 Relativistic hydrodynamics at large gradients Michał P. Heller Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Canada National Centre for Nuclear Research, Poland based on 03.3452, 302.0697, 409.5087 & 503.0754
Relativistic hydrodynamics at large gradients Michał P. Heller Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Canada National Centre for Nuclear Research, Poland based on 03.3452, 302.0697, 409.5087 & 503.0754
Boost-invariant dynamics near and far from equilibrium physics and AdS/CFT.
 Boost-invariant dynamics near and far from equilibrium physics and AdS/CFT. Micha l P. Heller michal.heller@uj.edu.pl Department of Theory of Complex Systems Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University
Boost-invariant dynamics near and far from equilibrium physics and AdS/CFT. Micha l P. Heller michal.heller@uj.edu.pl Department of Theory of Complex Systems Institute of Physics, Jagiellonian University
Plasma waves in the fluid picture I
 Plasma waves in the fluid picture I Langmuir oscillations and waves Ion-acoustic waves Debye length Ordinary electromagnetic waves General wave equation General dispersion equation Dielectric response
Plasma waves in the fluid picture I Langmuir oscillations and waves Ion-acoustic waves Debye length Ordinary electromagnetic waves General wave equation General dispersion equation Dielectric response
In this chapter we will discuss the effect of shear viscosity on evolution of fluid, p T
 Chapter 3 Shear viscous evolution In this chapter we will discuss the effect of shear viscosity on evolution of fluid, p T spectra, and elliptic flow (v ) of pions using a +1D relativistic viscous hydrodynamics
Chapter 3 Shear viscous evolution In this chapter we will discuss the effect of shear viscosity on evolution of fluid, p T spectra, and elliptic flow (v ) of pions using a +1D relativistic viscous hydrodynamics
Diffusive Transport Enhanced by Thermal Velocity Fluctuations
 Diffusive Transport Enhanced by Thermal Velocity Fluctuations Aleksandar Donev 1 Courant Institute, New York University & Alejandro L. Garcia, San Jose State University John B. Bell, Lawrence Berkeley
Diffusive Transport Enhanced by Thermal Velocity Fluctuations Aleksandar Donev 1 Courant Institute, New York University & Alejandro L. Garcia, San Jose State University John B. Bell, Lawrence Berkeley
Laszlo P. Csernai, University of Bergen, Norway. COST-THOR Working Group Meeting, Lisboa, June 11-14, 2018
 Laszlo P. Csernai, University of Bergen, Norway COST-THOR Working Group Meeting, Lisboa, June 11-14, 2018 [ F. Becattini, QM18] One of the most important new results in last year: Global Λ hyperon polarization
Laszlo P. Csernai, University of Bergen, Norway COST-THOR Working Group Meeting, Lisboa, June 11-14, 2018 [ F. Becattini, QM18] One of the most important new results in last year: Global Λ hyperon polarization
Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays
 Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays DESY Summer Student Programme, 2016 Olga Lebiga Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisors Reinaldo
Linear and non-linear evolution of the gyroresonance instability in Cosmic Rays DESY Summer Student Programme, 2016 Olga Lebiga Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukraine Supervisors Reinaldo
Stable Propagating Waves and Wake Fields in Relativistic Electromagnetic Plasma
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 49 (2008) pp. 753 758 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 49, No. 3, March 15, 2008 Stable Propagating Waves and Wake Fields in Relativistic Electromagnetic Plasma XIE
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 49 (2008) pp. 753 758 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 49, No. 3, March 15, 2008 Stable Propagating Waves and Wake Fields in Relativistic Electromagnetic Plasma XIE
6.2 Governing Equations for Natural Convection
 6. Governing Equations for Natural Convection 6..1 Generalized Governing Equations The governing equations for natural convection are special cases of the generalized governing equations that were discussed
6. Governing Equations for Natural Convection 6..1 Generalized Governing Equations The governing equations for natural convection are special cases of the generalized governing equations that were discussed
The Nernst effect in high-temperature superconductors
 The Nernst effect in high-temperature superconductors Iddo Ussishkin (University of Minnesota) with Shivaji Sondhi David Huse Vadim Oganesyan Outline Introduction: - High-temperature superconductors: physics
The Nernst effect in high-temperature superconductors Iddo Ussishkin (University of Minnesota) with Shivaji Sondhi David Huse Vadim Oganesyan Outline Introduction: - High-temperature superconductors: physics
Fluid equations, magnetohydrodynamics
 Fluid equations, magnetohydrodynamics Multi-fluid theory Equation of state Single-fluid theory Generalised Ohm s law Magnetic tension and plasma beta Stationarity and equilibria Validity of magnetohydrodynamics
Fluid equations, magnetohydrodynamics Multi-fluid theory Equation of state Single-fluid theory Generalised Ohm s law Magnetic tension and plasma beta Stationarity and equilibria Validity of magnetohydrodynamics
On the effective action in hydrodynamics
 On the effective action in hydrodynamics Pavel Kovtun, University of Victoria arxiv: 1502.03076 August 2015, Seattle Outline Introduction Effective action: Phenomenology Effective action: Bottom-up Effective
On the effective action in hydrodynamics Pavel Kovtun, University of Victoria arxiv: 1502.03076 August 2015, Seattle Outline Introduction Effective action: Phenomenology Effective action: Bottom-up Effective
Introduction to Relativistic Hydrodynamics
 Introduction to Relativistic Hydrodynamics Heavy Ion Collisions and Hydrodynamics modified from B. Schenke, S. Jeon, C. Gale, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 042301 (2011), http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/ schenke/,
Introduction to Relativistic Hydrodynamics Heavy Ion Collisions and Hydrodynamics modified from B. Schenke, S. Jeon, C. Gale, Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 042301 (2011), http://www.physics.mcgill.ca/ schenke/,
Direct drive by cyclotron heating can explain spontaneous rotation in tokamaks
 Direct drive by cyclotron heating can explain spontaneous rotation in tokamaks J. W. Van Dam and L.-J. Zheng Institute for Fusion Studies University of Texas at Austin 12th US-EU Transport Task Force Annual
Direct drive by cyclotron heating can explain spontaneous rotation in tokamaks J. W. Van Dam and L.-J. Zheng Institute for Fusion Studies University of Texas at Austin 12th US-EU Transport Task Force Annual
Bulk and shear viscosities for the Gribov-Zwanziger plasma
 EPJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 215 Bulk and shear viscosities for the Gribov-Zwanziger plasma Wojciech
EPJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 215 Bulk and shear viscosities for the Gribov-Zwanziger plasma Wojciech
Hydrodynamics in the Dirac fluid in graphene. Andrew Lucas
 Hydrodynamics in the Dirac fluid in graphene Andrew Lucas Stanford Physics Fluid flows from graphene to planet atmospheres; Simons Center for Geometry and Physics March 20, 2017 Collaborators 2 Subir Sachdev
Hydrodynamics in the Dirac fluid in graphene Andrew Lucas Stanford Physics Fluid flows from graphene to planet atmospheres; Simons Center for Geometry and Physics March 20, 2017 Collaborators 2 Subir Sachdev
ECT*, Trento December 3, Collaborators: Vincenzo Greco Salvo Plumari Armando Puglisi Marco Ruggieri Francesco Scardina
 ECT*, Trento December 3, 2015 Collaborators: Vincenzo Greco Salvo Plumari Armando Puglisi Marco Ruggieri Francesco Scardina initial stage pre-equilibrium hydrodynamical evolution hadronization freeze-out
ECT*, Trento December 3, 2015 Collaborators: Vincenzo Greco Salvo Plumari Armando Puglisi Marco Ruggieri Francesco Scardina initial stage pre-equilibrium hydrodynamical evolution hadronization freeze-out
Toward a unified description of equilibrium and dynamics of neutron star matter
 Toward a unified description of equilibrium and dynamics of neutron star matter Omar Benhar INFN and Department of Physics Sapienza Università di Roma I-00185 Roma, Italy Based on work done in collaboration
Toward a unified description of equilibrium and dynamics of neutron star matter Omar Benhar INFN and Department of Physics Sapienza Università di Roma I-00185 Roma, Italy Based on work done in collaboration
Talk based on: arxiv: arxiv: arxiv: arxiv: arxiv:1106.xxxx. In collaboration with:
 Talk based on: arxiv:0812.3572 arxiv:0903.3244 arxiv:0910.5159 arxiv:1007.2963 arxiv:1106.xxxx In collaboration with: A. Buchel (Perimeter Institute) J. Liu, K. Hanaki, P. Szepietowski (Michigan) The behavior
Talk based on: arxiv:0812.3572 arxiv:0903.3244 arxiv:0910.5159 arxiv:1007.2963 arxiv:1106.xxxx In collaboration with: A. Buchel (Perimeter Institute) J. Liu, K. Hanaki, P. Szepietowski (Michigan) The behavior
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 30 Nov 2001
 CHAPMAN-ENSKOG EXPANSION OF THE BOLTZMANN EQUATION AND ITS DIAGRAMMATIC INTERPRETATION arxiv:hep-ph/0446v 30 Nov 00 M.E. CARRINGTON A,B, HOU DEFU A,B,C AND R. KOBES B,D a Department of Physics, Brandon
CHAPMAN-ENSKOG EXPANSION OF THE BOLTZMANN EQUATION AND ITS DIAGRAMMATIC INTERPRETATION arxiv:hep-ph/0446v 30 Nov 00 M.E. CARRINGTON A,B, HOU DEFU A,B,C AND R. KOBES B,D a Department of Physics, Brandon
Hydrodynamic transport in the Dirac fluid in graphene. Andrew Lucas
 Hydrodynamic transport in the Dirac fluid in graphene Andrew Lucas Harvard Physics Condensed Matter Seminar, MIT November 4, 2015 Collaborators 2 Subir Sachdev Harvard Physics & Perimeter Institute Philip
Hydrodynamic transport in the Dirac fluid in graphene Andrew Lucas Harvard Physics Condensed Matter Seminar, MIT November 4, 2015 Collaborators 2 Subir Sachdev Harvard Physics & Perimeter Institute Philip
From spectral functions to viscosity in the QuarkGluon Plasma
 From spectral functions to viscosity in the QuarkGluon Plasma N.C., Haas, Pawlowski, Strodthoff: Phys. Rev. Lett. 115.112002, 2015 Hirschegg 21.1.2016 Outline Introduction Framework for transport coefficients
From spectral functions to viscosity in the QuarkGluon Plasma N.C., Haas, Pawlowski, Strodthoff: Phys. Rev. Lett. 115.112002, 2015 Hirschegg 21.1.2016 Outline Introduction Framework for transport coefficients
Scale invariant fluid dynamics for the dilute Fermi gas at unitarity
 Scale invariant fluid dynamics for the dilute Fermi gas at unitarity Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University Fluids: Gases, Liquids, Plasmas,... Hydrodynamics: Long-wavelength, low-frequency dynamics
Scale invariant fluid dynamics for the dilute Fermi gas at unitarity Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State University Fluids: Gases, Liquids, Plasmas,... Hydrodynamics: Long-wavelength, low-frequency dynamics
Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene
 Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene Markus Müller in collaboration with Lars Fritz (Harvard) Subir Sachdev (Harvard) Jörg Schmalian (Iowa) Landau Memorial Conference June 6, 008 Outline Relativistic
Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene Markus Müller in collaboration with Lars Fritz (Harvard) Subir Sachdev (Harvard) Jörg Schmalian (Iowa) Landau Memorial Conference June 6, 008 Outline Relativistic
Phase Transitions and Renormalization:
 Phase Transitions and Renormalization: Using quantum techniques to understand critical phenomena. Sean Pohorence Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge CAPS 2013
Phase Transitions and Renormalization: Using quantum techniques to understand critical phenomena. Sean Pohorence Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge CAPS 2013
Anisotropic Hydrodynamics
 Anisotropic Hydrodynamics Is early isotropization Lecture 1 Michael Strickland Kent State University JET Summer School June 13, 2013 References: arxiv:1204.1473 (Martinez, Ryblewski, and MS) arxiv:1204.2624
Anisotropic Hydrodynamics Is early isotropization Lecture 1 Michael Strickland Kent State University JET Summer School June 13, 2013 References: arxiv:1204.1473 (Martinez, Ryblewski, and MS) arxiv:1204.2624
The Superfluid-Insulator transition
 The Superfluid-Insulator transition Boson Hubbard model M.P. A. Fisher, P.B. Weichmann, G. Grinstein, and D.S. Fisher, Phys. Rev. B 40, 546 (1989). Superfluid-insulator transition Ultracold 87 Rb atoms
The Superfluid-Insulator transition Boson Hubbard model M.P. A. Fisher, P.B. Weichmann, G. Grinstein, and D.S. Fisher, Phys. Rev. B 40, 546 (1989). Superfluid-insulator transition Ultracold 87 Rb atoms
Isotropization from Color Field Condensate in heavy ion collisions
 Isotropization from Color Field Condensate in heavy ion collisions Stefan Flörchinger (CERN) RBRC Workshop on The Approach to Equilibrium in Strongly Interacting Matter, BNL, April 2, 2014. based on: S.
Isotropization from Color Field Condensate in heavy ion collisions Stefan Flörchinger (CERN) RBRC Workshop on The Approach to Equilibrium in Strongly Interacting Matter, BNL, April 2, 2014. based on: S.
