Superconductivity controlled by the magnetic state of ferromagnetic nanoparticles
|
|
|
- Kory Fletcher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
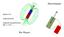
1 Superconductivity controlled by the magnetic state of ferromagnetic nanoparticles A.A. Fraerman 1, B.A. Gribkov 1, S.A. Gusev 1, E. Il ichev 2, A.Yu. Klimov 1, Yu.N. Nozdrin 1, G.L. Pakhomov 1, V.V. Rogov 1, R. Stolz 2 and S.N. Vdovichev 1 1 Institute for Physics of Microstructures RAS, GSP 15, 6395 Nizhny Novgorod, Russia 2 Institute for Physical High Technology, Jena, Germany (Dated: July 9, 24) Novel hybrid superconductor/ferromagnetic particles structures are presented. Arrays of Co submicron particles were fabricated on overlap, edge type Josephson junctions and on a narrow Nb microbridge by means of high-resolution e-beam lithography. We observed a strong dependence between the magnetic state of the particles and the field-dependent critical I c (H) of these structures. PACS numbers: r, a, d INTRODUCTION Recent advances in microfabrication techniques have increased the interest in application of submicron sized patterned magnetic elements. The prospective usage of patterned ferromagnetic particles of submicron sizes is accounted for by the well defined local magnetic fields. In particular, magnetic dots arrays can be used as artificial pinning centers in a superconductor thin film. Experimental investigation of such a hybrid superconductor/ferromagnetic particles system was begun in the last decade from pioneer works of D. Givord et al. [1,2] and is underway currently, for example [3,4]. Transport properties of a superconducting layer may also assist in determining the magnetic states of a ferromagnetic particles array [2]. However, the magnetic mechanism of pinning in thin films works close to T c, when natural pinning forces are insignificant [4,5]. Another way for controlling the superconducting state of a film by magnetic circuit is through modulating the superconducting order parameter and creating weak links [6]. This device can work as a superconductor switch. In this paper, we present three novel hybrid structures: weak links - Josephson junctions (overlap and edge type) and a narrow superconductor microbridge patterned by magnetic dots arrays. The influence of the particle magnetization distribution on the static field-dependent critical current I c (H) of these structures has been investigated. All measurements were done at temperatures well below the superconducting transition. EDGE-TYPE JOSEPSON JUNCTION Theory. We propose to use the influence of a stray magnetic field of nanoparticles on quantum interference in a Josephson junction. We model a real structure as an infinite strip of superconductor cut by a narrow slot, see Fig. 1. Assuming a sinusoidal current-phase relationship, the field-dependent total current I(H) of the junction is expressed as I( H ) = S j e c iϕ ( H ) ds,
2 2 z H j y x Fig. 1. Schematic and SEM image of an edge-type Josephson junction with a chain of magnetic nanoparticles. where ϕ is the phase differences, j c is the critical current density [7]. If the ferromagnetic particles are placed near the barrier, see Fig. 1, ϕ can be written as ϕ = ϕ ext + ϕ particle, where ϕ ext, ϕ particle are the phase differences due to the external magnetic field and the magnetic field of the particles, respectively. It means that the magnetic field of the particles can change the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern I c (H). We now assume that the spatial distribution of the Josephson phase difference ϕ(x) across the junction barrier can be written as ϕ = x 2π Λ Φ ( H + H ), p where Λ is the effective thickness of the junction (Λ 2λ L, λ L is the London penetration depth), H is the external magnetic field, H p is the magnetic field induced by the magnetic particles, Φ =hc/e=2 1-7 Oe cm 2 is the magnetic flux quantum. In particular, if the magnetic moment of a single particle in the chain has a uniform distribution, H p (x), ϕ particle are periodic functions. The results of numeric simulation of I c (H) for a junction with five dipoles is shown on Fig. 2a. In this case the fielddependent critical current should have a maximum when the magnetic flux per period of the array of nanoparticles at the Josephson junction contains an integer number of flux quanta Φ d = nφ, (Φ d = HΛd, n is integer). A more explicit model for this case confirmed the same result [8]. Experiment. For experimental investigation of the dependence of the particles magnetization distribution on the critical current we fabricated a series of Nb\SiN x \Nb edge-type Josephson junctions [9] with chains of ferromagnetic Co nanoparticles with a typical lateral size of 3-6 nm and a height of 25 nm (see Fig. 1). Measurements of the critical current I c (H) were performed by a standard fourterminal method at T=4.2K, in the magnetic field normal to the plane of the junction. The particles were magnetized at room temperature either by applying a magnetic field of 2 koe or by the MFM tip [1]. The magnetic state of the nanoparticles was controlled by MFM before and after the low temperature experiments. We present two series of experiments. 1). All particles were magnetized as dipoles (see inset on Fig. 2b) 2). All particles were magnetized close to the vortex state. In the case of the dipole magnetic states, we 2
3 3 1.9 I c /I - junction with particles - particles-free junction I C, µa Φ/Φ a) b) Fig. 2. Dependence I c (H) of the junction with dipoles a) the numeric simulation b) the experiment (on the inset MFM image of the junction) observed an increase in the additional I c (H) maxima whose position depends on a period of the particles chain, as theory predicted, see Fig. 2. In the case of the vortex magnetic states of the particles, the resonance effects were absent. This result is brought about by the weak magnetic field induced by the particles with a curling magnetization distribution. makes easier the entrance of the Abrikosov vortices. The particles array was fabricated on the top of the junction, using electron beam lithography, see Fig. 3. OVERLAP JOSEPHSON JUNCTION The basic idea of this experiment is to trap a regular lattice of the Abrikosov vortices in the top electrode of the overlap junction perpendicularly to the junction surface. This is a unique way for controlling the properties of the overlap type junction because neither the magnetic field induced by particles, nor the aligned vortices trapped in both electrodes affect the phase differences, i.e., properties of the junction. A special series of overlap geometry junctions Nb\Al\AlO x \Nb with a thin top electrode (3 nm) was produced by IPHT (Jene, Germany). The width and length of the junctions is about 2 µm. The top electrode thickness is smaller than λ L of the Nb, which Fig. 3. SEM image of the overlap Josephson junction with an array of magnetic nanoparticles. Measurements of the critical current I c (H) were performed by the four-terminal method for helium temperature, in the magnetic field within the plane of the junction. It is evident that the trapping of vortices is controlled by the magnetic state of the particles. We also present two series of 3
4 I, ua I, ua a) b) Fig. 4. Dependence I c (H) of the overlap junction with a) prevalence of dipoles states, b) prevalence of vortex magnetic states. experiments. 1). About 8% of the particles were magnetized as dipoles. 2). About 8% of the particles were magnetized as vortices. The Fraunhofer pattern for the vortex magnetic state of the particles and for junction without particles is the same, see Fig. 4a. The diffraction pattern for the dipole magnetic state of the dots has changed considerably, see Fig. 4b. The critical current has been suppressed; the form of the Fraunhofer pattern has changed and become different from zero at a high magnetic field. There are no resonance effects that can be explained by the absence of the regular vortex lattice. The results observed in this experiment slightly resemble those obtained in a special experiment for a single vortex motion [11]. NARROW SUPERCONUCTOR MICROBRIDGE We fabricated a series of 1 µm wide Nb microbridges with the Nb thickness of about.1 µm (Т с ~9 К) and formed a chain of Co nanoparticles with a typical lateral size of 3*6 nm and a height of 1 nm (Fig. 5a). The remanent magnetic state of the particles is inhomogeneous; particles can be magnetized to a uniform state by the field of 5-1 Gs [13]. The density of the critical current for our Nb films is about A/cm 2, which implies deep centers of pinning [14]. We performed standard measurements of the critical current I c (H) at T=4.2K in an external magnetic field normal to the plane of the microbridge. Fig. 5. SEM image of microbridges with ferromagnetic nanoparticles. The critical current dramatically decreased with an increasing magnetic field and this dependence was the same for samples with and without particles. If a magnetic field is applied in the plane of a particle-free microbridge (up to 2.5 koe), the critical current remains unaffected. For a microbridge with magnetic particles we observed the 4
5 5 I c, ma H, koe Fig. 6. Dependence I c (H) of the microbridge with ferromagnetic nanoparticles. following effects, see Fig. 6: enhancement of the critical current I c to 2% with an increasing magnetic field H; strong dependence of the critical current on the magnetic field sign, the difference between I c (H) and I c (-H) reached 7% ( diode effect ). In addition, the critical current has a periodical component with a period about 5 Oe, see Fig. 6. Today we do not have a clear understanding of the mechanism behind the magnetic particles effect on the critical current of a microbridge, all existing hypotheses have some imperfections. It seems important, though, that our Nb film is polycrystalline and features a high density of the critical current, and the microbridge of our make is narrow, which determines the boundary condition for entrance of the vortices. CONCLUSION We investigated novel types of hybrid structures composed of ferromagnetic nanoparticles on superconductor, which can be used without control of the temperature. The transport properties of superconductors are well controlled by the magnetic state of the particles. For the case of the edge-type Josephson junction a simple model of the influence produced by magnetic particles is proposed. The experiments confirmed susceptibility of the Josephson junctions to the magnetic state of nanoparticles, which can be used in low temperature electronic devices. The experimental results obtained in the study of overlap geometry junction and narrow microbridge are novel, and there is no theory interpreting these effects nowadays. However, the observed effects are interesting both from the fundamental point of view and for prospective application. This work was supported by the RFBR, Grant number , , and INTAS, Grant number , REFERENCE [1] Y. Otani, B. Pannetier, J.P. Nozieres, D. Givord. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 126 (1993) 622. [2] O. Geoffroy, D. Givord, Y. Otany et al. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 121 (1993) 223. [3] J.I. Martin, M. Velez, J. Nogues and I.K. Shuller. Phys. Rev. Lett. 79 (1997) [4] A.V. Silhanek, L. Van Look, S. Raedts et al. Phys. Rev. B 68 (23) [5] I.D. Tokman. Phys. Let. A 166 (1992) 412. [6] T.W. Clinton, M. Johnson. J. Appl. Phys. 83 (1998) [7] A. Barone and G.Paterno. Phisics and Applications of the Josephson Effect (Wiley, New York, 1982; Mir, Moscow, 1984). [8] A.V. Samohkvalov. J. Exp. Tech. Phys. Lett. 78 (23) 369. [9] S.N. Vdovichev, A.Yu. Klimov, Yu.N. Nozdrin, V.V. Rogov. Tech. Phys. Lett. 3 (24). [1] A.A. Fraerman, B.A. Gribkov, S.A. Gusev et al. Low Dim. Struc. To be published. [11] O.B.Hyun, J.R.Clem, D.KJ.Finnemore. Phys.Rev. B 4 (1989) 175. [12] A. Alexeev. Private communication. [13] V.V. Schmidt. The physics of Superconductors.(MCNMO,Moscow,2; Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg, 1997). 5
University of Antwerp Condensed Matter Theory Group Vortices in superconductors IV. Hybrid systems
 Vortices in superconductors IV. Hybrid systems François Peeters Magnetic impurities T c decreases with increasing impurity density Origin: exchange interaction between electron and impurity: Γ(r i -r e
Vortices in superconductors IV. Hybrid systems François Peeters Magnetic impurities T c decreases with increasing impurity density Origin: exchange interaction between electron and impurity: Γ(r i -r e
Configuration-induced vortex motion in type II superconducting films with periodic magnetic dot arrays
 Configuration-induced vortex motion in type II superconducting films with periodic magnetic dot arrays Qinghua Chen Prof. Shi Xue Dou 1 Outline: I. An Introduction of superconductor II. Overview of vortex
Configuration-induced vortex motion in type II superconducting films with periodic magnetic dot arrays Qinghua Chen Prof. Shi Xue Dou 1 Outline: I. An Introduction of superconductor II. Overview of vortex
Vortex lattice channeling effects in Nb films induced by anisotropic arrays of mesoscopic pinning centers
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 65, 104511 Vortex lattice channeling effects in Nb films induced by anisotropic arrays of mesoscopic pinning centers M. Velez Depto. Física, F. Ciencias, Universidad de Oviedo,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 65, 104511 Vortex lattice channeling effects in Nb films induced by anisotropic arrays of mesoscopic pinning centers M. Velez Depto. Física, F. Ciencias, Universidad de Oviedo,
Enhanced pinning in high-temperature superconducting cuprate single crystals at low DC magnetic field
 Enhanced pinning in high-temperature superconducting cuprate single crystals at low DC magnetic field V.Yu.Monarkha, Yu.A.Savina, V.P.Timofeev B.Verkin Institute for Low Temperature Physics & Engineering
Enhanced pinning in high-temperature superconducting cuprate single crystals at low DC magnetic field V.Yu.Monarkha, Yu.A.Savina, V.P.Timofeev B.Verkin Institute for Low Temperature Physics & Engineering
Electrodynamics of superconductor-ferromagnet hybrid structures
 Electrodynamics of superconductor-ferromagnet hybrid structures A.S.Mel nikov Institute for Physics of Microstructures RAS IPM RAS S.V.Mironov A.V.Samokhvalov D.Vodolazov Yu.Erin A.Bespalov V.Vadimov M.Sapozhnikov
Electrodynamics of superconductor-ferromagnet hybrid structures A.S.Mel nikov Institute for Physics of Microstructures RAS IPM RAS S.V.Mironov A.V.Samokhvalov D.Vodolazov Yu.Erin A.Bespalov V.Vadimov M.Sapozhnikov
Vortex matter in nanostructured and hybrid superconductors
 Vortex matter in nanostructured and hybrid superconductors François Peeters University of Antwerp In collaboration with: B. Baelus, M. Miloševic V.A. Schweigert (Russian Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk)
Vortex matter in nanostructured and hybrid superconductors François Peeters University of Antwerp In collaboration with: B. Baelus, M. Miloševic V.A. Schweigert (Russian Academy of Sciences, Novosibirsk)
Magnetic relaxation of superconducting YBCO samples in weak magnetic fields
 Magnetic relaxation of superconducting YBCO samples in weak magnetic fields V.P. Timofeev, A.N. Omelyanchouk B.Verkin Institute for Low Temperature Physics & Engineering National Academy of Sciences of
Magnetic relaxation of superconducting YBCO samples in weak magnetic fields V.P. Timofeev, A.N. Omelyanchouk B.Verkin Institute for Low Temperature Physics & Engineering National Academy of Sciences of
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Feb 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Feb 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Feb 2011](/thumbs/94/118065177.jpg) Mesoscopic cross film cryotrons: Vortex trapping and dc Josephson like oscillations of the critical current arxiv:112.4545v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Feb 211 A.Yu. Aladyshkin, 1,2 G.W. Ataklti, 1 W. Gillijns,
Mesoscopic cross film cryotrons: Vortex trapping and dc Josephson like oscillations of the critical current arxiv:112.4545v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Feb 211 A.Yu. Aladyshkin, 1,2 G.W. Ataklti, 1 W. Gillijns,
Control of the Magnetic State of Massifs of Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles with the Aid of the Inhomogeneous Field of a Magnetic-Force-Microscope Probe 1
 ISSN 0031-918X, The Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2010, Vol. 110, No. 7, pp. 1 27. Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2010. Control of the Magnetic State of Massifs of Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles with the
ISSN 0031-918X, The Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2010, Vol. 110, No. 7, pp. 1 27. Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2010. Control of the Magnetic State of Massifs of Ferromagnetic Nanoparticles with the
Commensurability effects induced by a periodic array of nanoscale anti-dots in Nb superconductor
 Physica C 404 (2004) 166 170 www.elsevier.com/locate/physc Commensurability effects induced by a periodic array of nanoscale anti-dots in Nb superconductor A.A. Zhukov a, *, E.T. Filby a, P.A.J. de Groot
Physica C 404 (2004) 166 170 www.elsevier.com/locate/physc Commensurability effects induced by a periodic array of nanoscale anti-dots in Nb superconductor A.A. Zhukov a, *, E.T. Filby a, P.A.J. de Groot
Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets. A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems
 Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems Dr. J. Sort Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA)
Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems Dr. J. Sort Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA)
smaller mfp coh L type II
 Type II superconductors Superconductivity: outline of 10.10 Superconductor in magnetic field Thin superconductor in magnetic field Interface energy Type II superconductors Mixed phase Abrikosov vortices
Type II superconductors Superconductivity: outline of 10.10 Superconductor in magnetic field Thin superconductor in magnetic field Interface energy Type II superconductors Mixed phase Abrikosov vortices
Superconducting films with antidot arrays Novel behavior of the critical current
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 May 2006 Europhys. Lett., 74 (3), pp. 493 499 (2006) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2006-10013-1 Superconducting films with antidot arrays Novel behavior of the critical current G. R. Berdiyorov,
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 1 May 2006 Europhys. Lett., 74 (3), pp. 493 499 (2006) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2006-10013-1 Superconducting films with antidot arrays Novel behavior of the critical current G. R. Berdiyorov,
Introduction to Superconductivity. Superconductivity was discovered in 1911 by Kamerlingh Onnes. Zero electrical resistance
 Introduction to Superconductivity Superconductivity was discovered in 1911 by Kamerlingh Onnes. Zero electrical resistance Meissner Effect Magnetic field expelled. Superconducting surface current ensures
Introduction to Superconductivity Superconductivity was discovered in 1911 by Kamerlingh Onnes. Zero electrical resistance Meissner Effect Magnetic field expelled. Superconducting surface current ensures
Antivortex state in crosslike nanomagnets
 Antivortex state in crosslike nanomagnets V. L. Mironov,* O. L. Ermolaeva, S. A. Gusev, A. Yu. Klimov, V. V. Rogov, B. A. Gribkov, O. G. Udalov, and A. A. Fraerman Institute for Physics of Microstructures,
Antivortex state in crosslike nanomagnets V. L. Mironov,* O. L. Ermolaeva, S. A. Gusev, A. Yu. Klimov, V. V. Rogov, B. A. Gribkov, O. G. Udalov, and A. A. Fraerman Institute for Physics of Microstructures,
Zurich Open Repository and Archive. Current-Induced Critical State in NbN Thin-Film Structures
 University of Zurich Zurich Open Repository and Archive Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich http://www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2008 Current-Induced Critical State in NbN Thin-Film Structures Il in, K; Siegel,
University of Zurich Zurich Open Repository and Archive Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich http://www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2008 Current-Induced Critical State in NbN Thin-Film Structures Il in, K; Siegel,
MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS
 MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS Christian L. Petersen, Rong Lin, Dirch H. Petersen, Peter F. Nielsen CAPRES A/S, Burnaby, BC, Canada CAPRES A/S, Lyngby, Denmark We
MICRO-SCALE SHEET RESISTANCE MEASUREMENTS ON ULTRA SHALLOW JUNCTIONS Christian L. Petersen, Rong Lin, Dirch H. Petersen, Peter F. Nielsen CAPRES A/S, Burnaby, BC, Canada CAPRES A/S, Lyngby, Denmark We
From Last Time. Partially full bands = metal Bands completely full or empty = insulator / seminconductor
 From Last Time Solids are large numbers of atoms arranged in a regular crystal structure. Each atom has electron quantum states, but interactions shift the energies. End result is each type atomic electron
From Last Time Solids are large numbers of atoms arranged in a regular crystal structure. Each atom has electron quantum states, but interactions shift the energies. End result is each type atomic electron
Heterogeneous vortex dynamics in high temperature superconductors
 Heterogeneous vortex dynamics in high temperature superconductors Feng YANG Laboratoire des Solides Irradiés, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau, France. June 18, 2009/PhD thesis defense Outline 1 Introduction
Heterogeneous vortex dynamics in high temperature superconductors Feng YANG Laboratoire des Solides Irradiés, Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau, France. June 18, 2009/PhD thesis defense Outline 1 Introduction
Superconducting Pinning by Magnetic Domains in a Ferromagnet-Superconductor Bilayer
 Vol. 106 (2004) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the School Superconductivity and Other Phenomena in Perovskites, Warsaw 2004 Superconducting Pinning by Magnetic Domains in a Ferromagnet-Superconductor
Vol. 106 (2004) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 5 Proceedings of the School Superconductivity and Other Phenomena in Perovskites, Warsaw 2004 Superconducting Pinning by Magnetic Domains in a Ferromagnet-Superconductor
Magnetic imaging and dissipation force microscopy of vortices on superconducting Nb films
 Applied Surface Science 188 (2002) 416 420 Magnetic imaging and dissipation force microscopy of vortices on superconducting Nb films M. Roseman *,P.Grütter Department of Physics, Centre for the Physics
Applied Surface Science 188 (2002) 416 420 Magnetic imaging and dissipation force microscopy of vortices on superconducting Nb films M. Roseman *,P.Grütter Department of Physics, Centre for the Physics
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 10 Oct 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 10 Oct 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 10 Oct 2005](/thumbs/73/69263403.jpg) Magnetic dipole vortex interaction in a bilayer superconductor/soft-magnet heterostructure arxiv:cond-mat/5151v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 1 Oct 5 S. V. Yampolskii and G. I. Yampolskaya Institut für Materialwissenschaft
Magnetic dipole vortex interaction in a bilayer superconductor/soft-magnet heterostructure arxiv:cond-mat/5151v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 1 Oct 5 S. V. Yampolskii and G. I. Yampolskaya Institut für Materialwissenschaft
M.C. Escher. Angels and devils (detail), 1941
 M.C. Escher Angels and devils (detail), 1941 1 Coherent Quantum Phase Slip: Exact quantum dual to Josephson Tunneling (Coulomb blockade is a partial dual) Degree of freedom in superconductor: Phase and
M.C. Escher Angels and devils (detail), 1941 1 Coherent Quantum Phase Slip: Exact quantum dual to Josephson Tunneling (Coulomb blockade is a partial dual) Degree of freedom in superconductor: Phase and
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 27 Jul 1999
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 27 Jul 1999 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 27 Jul 1999](/thumbs/72/66877043.jpg) Shapiro steps in a superconducting film with an antidot lattice arxiv:cond-mat/9907410v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 27 Jul 1999 L. Van Look, E. Rosseel, M. J. Van Bael, K. Temst, V. V. Moshchalkov and Y. Bruynseraede
Shapiro steps in a superconducting film with an antidot lattice arxiv:cond-mat/9907410v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 27 Jul 1999 L. Van Look, E. Rosseel, M. J. Van Bael, K. Temst, V. V. Moshchalkov and Y. Bruynseraede
Cryogenic memory element based on a single Abrikosov vortex
 Cryogenic memory element based on a single Abrikosov vortex Vladimir Krasnov, T. Golod and A. Iovan Experimental Condensed Matter Physics Group Department of Physics Stockholm University AlbaNova University
Cryogenic memory element based on a single Abrikosov vortex Vladimir Krasnov, T. Golod and A. Iovan Experimental Condensed Matter Physics Group Department of Physics Stockholm University AlbaNova University
The Nanotube SQUID. uhu,, M. Monthioux,, V. Bouchiat, W. Wernsdorfer, CEMES-Toulouse, CRTBT & LLN Grenoble
 The Nanotube SQUID J.-P. Cleuziou,, Th. Ondarçuhu uhu,, M. Monthioux,, V. Bouchiat, W. Wernsdorfer, CEMES-Toulouse, CRTBT & LLN Grenoble Outline Sample fabrication Proximity effect in CNT The CNT superconducting
The Nanotube SQUID J.-P. Cleuziou,, Th. Ondarçuhu uhu,, M. Monthioux,, V. Bouchiat, W. Wernsdorfer, CEMES-Toulouse, CRTBT & LLN Grenoble Outline Sample fabrication Proximity effect in CNT The CNT superconducting
Shapiro steps in Josephson junctions with alternating critical current density
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 5458 27 Shapiro steps in Josephson junctions with alternating critical current density M. Moshe and R. G. Mints* School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and Beverly Sackler Faculty
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 76, 5458 27 Shapiro steps in Josephson junctions with alternating critical current density M. Moshe and R. G. Mints* School of Physics and Astronomy, Raymond and Beverly Sackler Faculty
TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 25 Apr 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 25 Apr 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 25 Apr 2005](/thumbs/91/107362925.jpg) Europhysics Letters PREPRINT arxiv:cond-mat/0504645v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 25 Apr 2005 Field-enhanced critical parameters in magnetically nanostructured superconductors M. V. Milošević and F. M. Peeters
Europhysics Letters PREPRINT arxiv:cond-mat/0504645v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 25 Apr 2005 Field-enhanced critical parameters in magnetically nanostructured superconductors M. V. Milošević and F. M. Peeters
Hole-arrays. U. Welp, Z. L. Xiao, J. S. Jiang, V. K. Vlasko-Vlasov, S. D. Bader, G. W. Crabtree
 Superconducting Transition and Vortex Pinning in Nb Films Patterned with Nano-scale ole-arrays U. Welp, Z. L. Xiao, J. S. Jiang, V. K. Vlasko-Vlasov, S. D. Bader, G. W. Crabtree Materials Science Division,
Superconducting Transition and Vortex Pinning in Nb Films Patterned with Nano-scale ole-arrays U. Welp, Z. L. Xiao, J. S. Jiang, V. K. Vlasko-Vlasov, S. D. Bader, G. W. Crabtree Materials Science Division,
Introduction Critical state models Pinning regimes Kinds of pinning sites HTS Results on YBCO Conclusions. Flux pinning.
 Department of Physics and Astronomy 14.6.2011 Contents Introduction Critical state models Pinning regimes Kinds of pinning sites HTS Results on YBCO Type II superconductors and vortices Type I ξ < λ S/N
Department of Physics and Astronomy 14.6.2011 Contents Introduction Critical state models Pinning regimes Kinds of pinning sites HTS Results on YBCO Type II superconductors and vortices Type I ξ < λ S/N
cond-mat/ May 1998
 Magnetic field dependence of the critical current in stacked Josephson junctions. Evidence for fluxon modes in Bi Sr CaCu O 8+x mesas. V.M.Krasnov a,b, N.Mros a, A.Yurgens a,c, and D.Winkler a a) Department
Magnetic field dependence of the critical current in stacked Josephson junctions. Evidence for fluxon modes in Bi Sr CaCu O 8+x mesas. V.M.Krasnov a,b, N.Mros a, A.Yurgens a,c, and D.Winkler a a) Department
Phase diagram of a superconductorõferromagnet bilayer
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 68, 174522 2003 Phase diagram of a superconductorõferromagnet bilayer M. Lange,* M. J. Van Bael, and V. V. Moshchalkov Laboratory for Solid State Physics and Magnetism, Nanoscale Superconductivity
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 68, 174522 2003 Phase diagram of a superconductorõferromagnet bilayer M. Lange,* M. J. Van Bael, and V. V. Moshchalkov Laboratory for Solid State Physics and Magnetism, Nanoscale Superconductivity
Using SQUID VSM Superconducting Magnets at Low Fields
 Application Note 1500-011 Using SQUID VSM Superconducting Magnets at Low Fields Abstract The superconducting magnet used in SQUID VSM is capable of generating fields up to 7 tesla (7x10 4 gauss) with the
Application Note 1500-011 Using SQUID VSM Superconducting Magnets at Low Fields Abstract The superconducting magnet used in SQUID VSM is capable of generating fields up to 7 tesla (7x10 4 gauss) with the
Determination of the Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Impurity Magnetic Susceptibility in Ge:As near the Metal Insulator phase Transition
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Determination of the Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Impurity Magnetic Susceptibility in Ge:As near the Metal Insulator phase Transition To cite this
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Determination of the Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Impurity Magnetic Susceptibility in Ge:As near the Metal Insulator phase Transition To cite this
Formation of vortex clusters and giant vortices in mesoscopic superconducting disks with strong disorder
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Formation of vortex clusters and giant vortices in mesoscopic superconducting disks with strong disorder To cite this article: W Escoffier et al 2008 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Formation of vortex clusters and giant vortices in mesoscopic superconducting disks with strong disorder To cite this article: W Escoffier et al 2008 J. Phys.: Conf.
Periodic Oscillations of Josephson-Vortex Flow Resistance in Oxygen-Deficient Y 1 Ba 2 Cu 3 O x
 1 Periodic Oscillations of Josephson-Vortex Flow Resistance in Oxygen-Deficient Y 1 Ba 2 Cu 3 O x M. Nagao, S. Urayama, S. M. Kim, H. B. Wang, K. S. Yun, Y. Takano, T. Hatano, I. Iguchi, T. Yamashita,
1 Periodic Oscillations of Josephson-Vortex Flow Resistance in Oxygen-Deficient Y 1 Ba 2 Cu 3 O x M. Nagao, S. Urayama, S. M. Kim, H. B. Wang, K. S. Yun, Y. Takano, T. Hatano, I. Iguchi, T. Yamashita,
Modeling of Magnetisation and Intrinsic Properties of Ideal Type-II Superconductor in External Magnetic Field
 Modeling of Magnetisation and Intrinsic Properties of Ideal Type-II Superconductor in External Magnetic Field Oleg A. Chevtchenko *1, Johan J. Smit 1, D.J. de Vries 2, F.W.A. de Pont 2 1 Technical University
Modeling of Magnetisation and Intrinsic Properties of Ideal Type-II Superconductor in External Magnetic Field Oleg A. Chevtchenko *1, Johan J. Smit 1, D.J. de Vries 2, F.W.A. de Pont 2 1 Technical University
Self-Induced Resonances in Asymmetric Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices
 Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 1 Proceedings of the XIII National School of Superconductivity, L adek Zdrój 2007 Self-Induced Resonances in Asymmetric Superconducting Quantum Interference
Vol. 114 (2008) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 1 Proceedings of the XIII National School of Superconductivity, L adek Zdrój 2007 Self-Induced Resonances in Asymmetric Superconducting Quantum Interference
Pinning-induced formation of vortex clusters and giant vortices in mesoscopic. superconducting disks
 Pinning-induced formation of vortex clusters and giant vortices in mesoscopic superconducting disks W. Escoffier, I.V. Grigorieva School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester, Manchester M13
Pinning-induced formation of vortex clusters and giant vortices in mesoscopic superconducting disks W. Escoffier, I.V. Grigorieva School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester, Manchester M13
Vortex pinning in a superconducting film due to in-plane magnetized ferromagnets of different shapes: The London approximation
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 69, 104522 2004 Vortex pinning in a superconducting film due to in-plane magnetized ferromagnets of different shapes: The London approximation M. V. Milošević and F. M. Peeters* Departement
PHYSICAL REVIEW B 69, 104522 2004 Vortex pinning in a superconducting film due to in-plane magnetized ferromagnets of different shapes: The London approximation M. V. Milošević and F. M. Peeters* Departement
Magnetic Shielding for Improvement of Superconductor Performance
 phys. stat. sol. (a) 189, No. 2, 469 473 (2002) Magnetic Shielding for Improvement of Superconductor Performance Y. A. Genenko 1 ) Institut für Materialwissenschaft, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Petersenstr.
phys. stat. sol. (a) 189, No. 2, 469 473 (2002) Magnetic Shielding for Improvement of Superconductor Performance Y. A. Genenko 1 ) Institut für Materialwissenschaft, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Petersenstr.
Enhanced vortex pinning by a composite antidot lattice in a superconducting Pb film
 Enhanced vortex pinning by a composite antidot lattice in a superconducting Pb film A. V. Silhanek, 1, * L. Van Look, 2 R. Jonckheere, 2 B. Y. Zhu, 1, S. Raedts, 1 and V. V. Moshchalkov 1 1 Nanoscale Superconductivity
Enhanced vortex pinning by a composite antidot lattice in a superconducting Pb film A. V. Silhanek, 1, * L. Van Look, 2 R. Jonckheere, 2 B. Y. Zhu, 1, S. Raedts, 1 and V. V. Moshchalkov 1 1 Nanoscale Superconductivity
Advanced Lab Course. Tunneling Magneto Resistance
 Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
1 Quantum Dynamics of Vortices and Vortex Qubits
 1 Quantum Dynamics of Vortices and Vortex Qubits A. Wallraff 1, A. Kemp, and A. V. Ustinov Physikalisches Institut III Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg D-9158 Erlangen, Germany 1.1 Introduction Vortices appear
1 Quantum Dynamics of Vortices and Vortex Qubits A. Wallraff 1, A. Kemp, and A. V. Ustinov Physikalisches Institut III Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg D-9158 Erlangen, Germany 1.1 Introduction Vortices appear
Quantitative magneto-optical investigation of S/F hybrid structures
 Quantitative magneto-optical investigation of S/F hybrid structures Jérémy Brisbois Experimental Physics of Nanostructured Materials University of Liège, Belgium Collaborators Prof. Alejandro Silhanek
Quantitative magneto-optical investigation of S/F hybrid structures Jérémy Brisbois Experimental Physics of Nanostructured Materials University of Liège, Belgium Collaborators Prof. Alejandro Silhanek
Focused-ion-beam milling based nanostencil mask fabrication for spin transfer torque studies. Güntherodt
 Focused-ion-beam milling based nanostencil mask fabrication for spin transfer torque studies B. Özyilmaz a, G. Richter, N. Müsgens, M. Fraune, M. Hawraneck, B. Beschoten b, and G. Güntherodt Physikalisches
Focused-ion-beam milling based nanostencil mask fabrication for spin transfer torque studies B. Özyilmaz a, G. Richter, N. Müsgens, M. Fraune, M. Hawraneck, B. Beschoten b, and G. Güntherodt Physikalisches
MO-IMAGING OF GRANULAR AND STRUCTURED HIGH-T C SUPERCONDUCTORS
 MO-IMAGING OF GRANULAR AND STRUCTURED HIGH-T C SUPERCONDUCTORS Michael R. Koblischka and Anjela Koblischka-Veneva 1 Institute of Experimental Physics, University of the Saarland, P.O. Box 151150, D-66041
MO-IMAGING OF GRANULAR AND STRUCTURED HIGH-T C SUPERCONDUCTORS Michael R. Koblischka and Anjela Koblischka-Veneva 1 Institute of Experimental Physics, University of the Saarland, P.O. Box 151150, D-66041
Intrinsic Josephson π-junctions for novel devices
 Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II Dottorato in Tecnologie Innovative per Materiali, Sensori e Imaging - 2 ciclo - Intrinsic Josephson π-junctions for novel devices Karin Cedergren Coordinatore:
Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II Dottorato in Tecnologie Innovative per Materiali, Sensori e Imaging - 2 ciclo - Intrinsic Josephson π-junctions for novel devices Karin Cedergren Coordinatore:
Electronic transport in low dimensional systems
 Electronic transport in low dimensional systems For example: 2D system l
Electronic transport in low dimensional systems For example: 2D system l
Artificial pinning arrays investigated by scanning Hall probe microscopy
 Ž. Physica C 332 2000 20 26 www.elsevier.nlrlocaterphysc Artificial pinning arrays investigated by scanning Hall probe microscopy S.J. Bending a,), G.D. Howells a, A.N. Grigorenko a, M.J. Van Bael b, J.
Ž. Physica C 332 2000 20 26 www.elsevier.nlrlocaterphysc Artificial pinning arrays investigated by scanning Hall probe microscopy S.J. Bending a,), G.D. Howells a, A.N. Grigorenko a, M.J. Van Bael b, J.
FYSZ 460 Advanced laboratory work: Superconductivity and high T C superconductor Y 1 Ba 2 Cu 3 O 6+y
 FYSZ 460 Advanced laboratory work: Superconductivity and high T C superconductor Y 1 Ba 2 Cu 3 O 6+y Laboratory Instructions Minna Nevala minna.nevala@phys.jyu.fi November 15, 2010 Contents 1 Introduction
FYSZ 460 Advanced laboratory work: Superconductivity and high T C superconductor Y 1 Ba 2 Cu 3 O 6+y Laboratory Instructions Minna Nevala minna.nevala@phys.jyu.fi November 15, 2010 Contents 1 Introduction
There are two main theories in superconductivity: Ginzburg-Landau Theory. Outline of the Lecture. Ginzburg-Landau theory
 Ginzburg-Landau Theory There are two main theories in superconductivity: i Microscopic theory describes why materials are superconducting Prof. Damian Hampshire Durham University ii Ginzburg-Landau Theory
Ginzburg-Landau Theory There are two main theories in superconductivity: i Microscopic theory describes why materials are superconducting Prof. Damian Hampshire Durham University ii Ginzburg-Landau Theory
Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes
 Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes Supplemental Material L. Shi, T. K. Hakala, H. T. Rekola, J. -P.
Spatial Coherence Properties of Organic Molecules Coupled to Plasmonic Surface Lattice Resonances in the Weak and Strong Coupling Regimes Supplemental Material L. Shi, T. K. Hakala, H. T. Rekola, J. -P.
A new approach to AFM investigation of buried Al/In x Ga 1-x As/GaAs interfaces and quantum dots
 A new approach to AFM investigation of buried Al/In x Ga 1-x As/GaAs interfaces and quantum dots V. M. Danil tsev, M. N. Drozdov, Yu. N. Drozdov, O. I. Khrykin, V. I. Shashkin, I. Yu. Shuleshova, N. V.
A new approach to AFM investigation of buried Al/In x Ga 1-x As/GaAs interfaces and quantum dots V. M. Danil tsev, M. N. Drozdov, Yu. N. Drozdov, O. I. Khrykin, V. I. Shashkin, I. Yu. Shuleshova, N. V.
Superconducting Metamaterials
 Superconducting Metamaterials P. Jung 1, S. Butz 1, N. Maleeva 1,2, A. Averkin 2, N. Abramov 2, K. Shulga 2,3 V. P. Koshelets 2,4, L. V. Filippenko 2,4, V. Chichkov 2 A. Karpov 2, S. V. Shitov 2,4, V.
Superconducting Metamaterials P. Jung 1, S. Butz 1, N. Maleeva 1,2, A. Averkin 2, N. Abramov 2, K. Shulga 2,3 V. P. Koshelets 2,4, L. V. Filippenko 2,4, V. Chichkov 2 A. Karpov 2, S. V. Shitov 2,4, V.
Superconducting Vortex Noise Measurements on Niobium Films with Periodic Pinning Sites
 Superconducting Vortex Noise Measurements on Niobium Films with Periodic Pinning Sites A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Tanner Franz Schulz
Superconducting Vortex Noise Measurements on Niobium Films with Periodic Pinning Sites A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Tanner Franz Schulz
Magnetic field dependence of kinetic inductance in. applications
 Magnetic field dependence of kinetic inductance in Bi 2 Sr 2 Ca 2 Cu 3 O 10 superconducting strip and its feasible applications S. Sarangi *, S. P. Chockalingam, S. V. Bhat Department of Physics, Indian
Magnetic field dependence of kinetic inductance in Bi 2 Sr 2 Ca 2 Cu 3 O 10 superconducting strip and its feasible applications S. Sarangi *, S. P. Chockalingam, S. V. Bhat Department of Physics, Indian
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.supr-con] 29 Mar 2007
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.supr-con] 29 Mar 2007 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.supr-con] 29 Mar 2007](/thumbs/74/71377257.jpg) Critical fields for vortex expulsion from narrow superconducting strips P. Sánchez-Lotero and J. J. Palacios Departamento de Física Aplicada, Universidad de Alicante, San Vicente del Raspeig, Alicante
Critical fields for vortex expulsion from narrow superconducting strips P. Sánchez-Lotero and J. J. Palacios Departamento de Física Aplicada, Universidad de Alicante, San Vicente del Raspeig, Alicante
Scanning Probe Microscopy. L. J. Heyderman
 1 Scanning Probe Microscopy 2 Scanning Probe Microscopy If an atom was as large as a ping-pong ball......the tip would have the size of the Matterhorn! 3 Magnetic Force Microscopy Stray field interaction
1 Scanning Probe Microscopy 2 Scanning Probe Microscopy If an atom was as large as a ping-pong ball......the tip would have the size of the Matterhorn! 3 Magnetic Force Microscopy Stray field interaction
Electric current crowding in nanostructured conductors. Alejandro V. Silhanek
 XXXVIII National Meeting on Condensed Matter Physics May 24-28, 2015, Foz do Iguaçu, PR, Brazil Electric current crowding in nanostructured conductors Alejandro V. Silhanek Experimental physics of nanostructured
XXXVIII National Meeting on Condensed Matter Physics May 24-28, 2015, Foz do Iguaçu, PR, Brazil Electric current crowding in nanostructured conductors Alejandro V. Silhanek Experimental physics of nanostructured
Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers
 Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers M. E. Gracheva, V. A. Kashurnikov, a) and I. A. Rudnev Moscow State Engineering Physics
Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers M. E. Gracheva, V. A. Kashurnikov, a) and I. A. Rudnev Moscow State Engineering Physics
Fluxon dynamics in long Josephson junctions in the presence of a temperature gradient or spatial nonuniformity
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 31, 2019 Fluxon dynamics in long Josephson junctions in the presence of a temperature gradient or spatial nonuniformity Krasnov, V.M.; Oboznov, V.A.; Pedersen, Niels
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 31, 2019 Fluxon dynamics in long Josephson junctions in the presence of a temperature gradient or spatial nonuniformity Krasnov, V.M.; Oboznov, V.A.; Pedersen, Niels
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail.
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Title: Kemppinen, Antti
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Title: Kemppinen, Antti
Effect of swift heavy ion irradiation on surface resistance of DyBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 δ thin films at microwave frequencies
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 8, Nos & journal of May & June physics pp. 99 9 Effect of swift heavy ion irradiation on surface resistance of DyBa Cu O 7 δ thin films at microwave frequencies
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 8, Nos & journal of May & June physics pp. 99 9 Effect of swift heavy ion irradiation on surface resistance of DyBa Cu O 7 δ thin films at microwave frequencies
Proceedings of SPIE, Micro- and Nanoelectronics -2003, Vol. 5401, pp (2003).
 Proceedings of SPIE, Micro- and Nanoelectronics -2003, Vol. 5401, pp 555-560 (2003). Magnetic force microscopy of magnetization reversal of microstructures in situ in the external field of up to 2000Oe
Proceedings of SPIE, Micro- and Nanoelectronics -2003, Vol. 5401, pp 555-560 (2003). Magnetic force microscopy of magnetization reversal of microstructures in situ in the external field of up to 2000Oe
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 320 (2008) 2547 2562 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Topical
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 320 (2008) 2547 2562 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Topical
Lecture 6. Josephson junction circuits. Simple current-biased junction Assume for the moment that the only source of current is the bulk leads, and
 Lecture 6. Josephson junction circuits Simple current-biased junction Assume for the moment that the only source of current is the bulk leads, and I(t) its only destination is as supercurrent through the
Lecture 6. Josephson junction circuits Simple current-biased junction Assume for the moment that the only source of current is the bulk leads, and I(t) its only destination is as supercurrent through the
A Superfluid Universe
 A Superfluid Universe Lecture 2 Quantum field theory & superfluidity Kerson Huang MIT & IAS, NTU Lecture 2. Quantum fields The dynamical vacuum Vacuumscalar field Superfluidity Ginsburg Landau theory BEC
A Superfluid Universe Lecture 2 Quantum field theory & superfluidity Kerson Huang MIT & IAS, NTU Lecture 2. Quantum fields The dynamical vacuum Vacuumscalar field Superfluidity Ginsburg Landau theory BEC
Demonstration of conditional gate operation using superconducting charge qubits
 Demonstration of conditional gate operation using superconducting charge qubits T. Yamamoto, Yu. A. Pashkin, * O. Astafiev, Y. Nakamura, & J. S. Tsai NEC Fundamental Research Laboratories, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
Demonstration of conditional gate operation using superconducting charge qubits T. Yamamoto, Yu. A. Pashkin, * O. Astafiev, Y. Nakamura, & J. S. Tsai NEC Fundamental Research Laboratories, Tsukuba, Ibaraki
Presented by: Göteborg University, Sweden
 SMR 1760-3 COLLEGE ON PHYSICS OF NANO-DEVICES 10-21 July 2006 Nanoelectromechanics of Magnetic and Superconducting Tunneling Devices Presented by: Robert Shekhter Göteborg University, Sweden * Mechanically
SMR 1760-3 COLLEGE ON PHYSICS OF NANO-DEVICES 10-21 July 2006 Nanoelectromechanics of Magnetic and Superconducting Tunneling Devices Presented by: Robert Shekhter Göteborg University, Sweden * Mechanically
Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films
 Hans Lüth Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films Fifth Edition With 427 Figures.2e Springer Contents 1 Surface and Interface Physics: Its Definition and Importance... 1 Panel I: Ultrahigh Vacuum (UHV)
Hans Lüth Solid Surfaces, Interfaces and Thin Films Fifth Edition With 427 Figures.2e Springer Contents 1 Surface and Interface Physics: Its Definition and Importance... 1 Panel I: Ultrahigh Vacuum (UHV)
Magnetic resonance studies of the fundamental spin-wave modes in individual submicron Cu/NiFe/Cu perpendicularly magnetized disks.
 Magnetic resonance studies of the fundamental spin-wave modes in individual submicron Cu/NiFe/Cu perpendicularly magnetized disks. G. de Loubens, V. V. Naletov, and O. Klein arxiv:cond-mat/0606245v3 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci]
Magnetic resonance studies of the fundamental spin-wave modes in individual submicron Cu/NiFe/Cu perpendicularly magnetized disks. G. de Loubens, V. V. Naletov, and O. Klein arxiv:cond-mat/0606245v3 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci]
Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS. An Introduction to Theory and Experiment
 Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS An Introduction to Theory and Experiment With 230 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Harald Ibach Hans Lüth SOLID-STATE PHYSICS An Introduction to Theory and Experiment With 230 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Paolo Vavassori. Ikerbasque, Basque Fundation for Science and CIC nanogune Consolider, San Sebastian, Spain.
 Magnetic nanostructures Paolo Vavassori Ikerbasque, Basque Fundation for Science and CIC nanogune Consolider, San Sebastian, Spain. P. Vavassori nano@nanogune.eu I www.nanogune.eu 1 Outline Part I Introduction.
Magnetic nanostructures Paolo Vavassori Ikerbasque, Basque Fundation for Science and CIC nanogune Consolider, San Sebastian, Spain. P. Vavassori nano@nanogune.eu I www.nanogune.eu 1 Outline Part I Introduction.
Transport properties of sub-micron YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ step-edge Josephson junctions
 1 Transport properties of sub-micron YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ step-edge Josephson junctions Peter Larsson *, Alexander Ya. Tzalenchuk, and Zdravko G. Ivanov MINA, School of Physics and Engineering Physics, Chalmers
1 Transport properties of sub-micron YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7-δ step-edge Josephson junctions Peter Larsson *, Alexander Ya. Tzalenchuk, and Zdravko G. Ivanov MINA, School of Physics and Engineering Physics, Chalmers
Magnetic Force Microscopy practical
 European School on Magnetism 2015 From basic magnetic concepts to spin currents Magnetic Force Microscopy practical Organized by: Yann Perrin, Michal Staňo and Olivier Fruchart Institut NEEL (CNRS & Univ.
European School on Magnetism 2015 From basic magnetic concepts to spin currents Magnetic Force Microscopy practical Organized by: Yann Perrin, Michal Staňo and Olivier Fruchart Institut NEEL (CNRS & Univ.
The change in conductivity anisotropy due to 1 superconductivity onset in the form of rare isolated islands: the theory and its application to FeSe
 A.A. Sinchenko, PG et al., Phys.Rev. B 95,165120 (2017); PG et al., JETP Lett. 105 (12), 786 (2017) The change in conductivity anisotropy due to 1 superconductivity onset in the form of rare isolated islands:
A.A. Sinchenko, PG et al., Phys.Rev. B 95,165120 (2017); PG et al., JETP Lett. 105 (12), 786 (2017) The change in conductivity anisotropy due to 1 superconductivity onset in the form of rare isolated islands:
Broadband ESR from 500 MHz to 40 GHz using superconducting coplanar waveguides
 Broadband ESR from 500 MHz to 40 GHz using superconducting coplanar waveguides Martin Dressel 1. Physikalisches Institut, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Outline 1. Introduction ESR resonators 2. Strip
Broadband ESR from 500 MHz to 40 GHz using superconducting coplanar waveguides Martin Dressel 1. Physikalisches Institut, Universität Stuttgart, Germany Outline 1. Introduction ESR resonators 2. Strip
Nanoscale magnetic imaging with single spins in diamond
 Nanoscale magnetic imaging with single spins in diamond Ania Bleszynski Jayich UC Santa Barbara Physics AFOSR Nanoelectronics Review Oct 24, 2016 Single spin scanning magnetometer Variable temperature
Nanoscale magnetic imaging with single spins in diamond Ania Bleszynski Jayich UC Santa Barbara Physics AFOSR Nanoelectronics Review Oct 24, 2016 Single spin scanning magnetometer Variable temperature
physics 590 ruslan prozorov magnetic measurements Nov 9,
 physics 590 ruslan prozorov magnetic measurements Nov 9, 2009 - magnetic moment of free currents Magnetic moment of a closed loop carrying current I: Magnetic field on the axis of a loop of radius R at
physics 590 ruslan prozorov magnetic measurements Nov 9, 2009 - magnetic moment of free currents Magnetic moment of a closed loop carrying current I: Magnetic field on the axis of a loop of radius R at
Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization. Yuri S. Kivshar
 Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia St. Petersburg University of Information Technologies,
Effect of nonlinearity on wave scattering and localization Yuri S. Kivshar Nonlinear Physics Centre, Australian National University, Canberra, Australia St. Petersburg University of Information Technologies,
Interference phenomena and long-range proximity effect in superconductor/ferromagnet systems
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Interference phenomena and long-range proximity effect in superconductor/ferromagnet systems To cite this article: A I Buzdin et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Interference phenomena and long-range proximity effect in superconductor/ferromagnet systems To cite this article: A I Buzdin et al 2014 J. Phys.: Conf.
Interplay between static and dynamic properties of semifluxons in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 δ 0 π Josephson junctions
 Interplay between static and dynamic properties of semifluxons in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 δ 0 π Josephson junctions K. Cedergren 1, J.R. Kirtley 2, T. Bauch 1, G. Rotoli 3, A. Troeman 4, H. Hilgenkamp 4, F. Tafuri
Interplay between static and dynamic properties of semifluxons in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 δ 0 π Josephson junctions K. Cedergren 1, J.R. Kirtley 2, T. Bauch 1, G. Rotoli 3, A. Troeman 4, H. Hilgenkamp 4, F. Tafuri
Direct Measurement of Penetration Length in Ultra-Thin and/or Mesoscopic Superconducting Structures
 Direct Measurement of Penetration Length in Ultra-Thin and/or Mesoscopic Superconducting Structures L. Hao National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, TW11 0LW, United Kingdom; J.C. Macfarlane Department
Direct Measurement of Penetration Length in Ultra-Thin and/or Mesoscopic Superconducting Structures L. Hao National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, TW11 0LW, United Kingdom; J.C. Macfarlane Department
Noise effects and thermally induced switching errors in Josephson junctions
 3479 Noise effects and thermally induced switching errors in Josephson junctions Andrey L. Pankratov 1 and Bernardo Spagnolo 2 1 Institute for Physics of Microstructures of RAS, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia
3479 Noise effects and thermally induced switching errors in Josephson junctions Andrey L. Pankratov 1 and Bernardo Spagnolo 2 1 Institute for Physics of Microstructures of RAS, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/content/349/6253/1202/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Critical behavior at a dynamic vortex insulator-to-metal transition Nicola Poccia, Tatyana I. Baturina, Francesco Coneri,
www.sciencemag.org/content/349/6253/1202/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Critical behavior at a dynamic vortex insulator-to-metal transition Nicola Poccia, Tatyana I. Baturina, Francesco Coneri,
For a complex order parameter the Landau expansion of the free energy for small would be. hc A. (9)
 Physics 17c: Statistical Mechanics Superconductivity: Ginzburg-Landau Theory Some of the key ideas for the Landau mean field description of phase transitions were developed in the context of superconductivity.
Physics 17c: Statistical Mechanics Superconductivity: Ginzburg-Landau Theory Some of the key ideas for the Landau mean field description of phase transitions were developed in the context of superconductivity.
Effect of Photodoping on the Fiske Resonances of YBa2Cu3Ox Grain Boundary Josephson Junctions
 Journal of Superconductivity, Vol. 11, No. 2, 1998 Effect of Photodoping on the Fiske Resonances of YBa2Cu3Ox Grain Boundary Josephson Junctions M. G. Medici,1 J. Elly,1 M. Razani,1 A. Gilabert,1 F. Schmidl,2
Journal of Superconductivity, Vol. 11, No. 2, 1998 Effect of Photodoping on the Fiske Resonances of YBa2Cu3Ox Grain Boundary Josephson Junctions M. G. Medici,1 J. Elly,1 M. Razani,1 A. Gilabert,1 F. Schmidl,2
Superconducting qubits (Phase qubit) Quantum informatics (FKA 172)
 Superconducting qubits (Phase qubit) Quantum informatics (FKA 172) Thilo Bauch (bauch@chalmers.se) Quantum Device Physics Laboratory, MC2, Chalmers University of Technology Qubit proposals for implementing
Superconducting qubits (Phase qubit) Quantum informatics (FKA 172) Thilo Bauch (bauch@chalmers.se) Quantum Device Physics Laboratory, MC2, Chalmers University of Technology Qubit proposals for implementing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Collapse of superconductivity in a hybrid tin graphene Josephson junction array by Zheng Han et al. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. Determination of the electronic mobility of graphene. 1.a extraction from
Collapse of superconductivity in a hybrid tin graphene Josephson junction array by Zheng Han et al. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. Determination of the electronic mobility of graphene. 1.a extraction from
B. Y. Zhu National Laboratory for Superconductivity, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing , China.
 Enhanced pinning and proliferation of matching effects in a superconducting film with a Penrose array of magnetic dots arxiv:cond-mat/0611173v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 7 Nov 2006 A. V. Silhanek, W. Gillijns,
Enhanced pinning and proliferation of matching effects in a superconducting film with a Penrose array of magnetic dots arxiv:cond-mat/0611173v1 [cond-mat.supr-con] 7 Nov 2006 A. V. Silhanek, W. Gillijns,
Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment
 Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment Christian Beck Queen Mary, University of London 1 Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment Christian Beck Queen Mary, University
Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment Christian Beck Queen Mary, University of London 1 Testing axion physics in a Josephson junction environment Christian Beck Queen Mary, University
Principles and Applications of Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUIDs)
 Principles and Applications of Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUIDs) PHY 300 - Junior Phyics Laboratory Syed Ali Raza Roll no: 2012-10-0124 LUMS School of Science and Engineering Thursday,
Principles and Applications of Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUIDs) PHY 300 - Junior Phyics Laboratory Syed Ali Raza Roll no: 2012-10-0124 LUMS School of Science and Engineering Thursday,
SOLID STATE PHYSICS. Second Edition. John Wiley & Sons. J. R. Hook H. E. Hall. Department of Physics, University of Manchester
 SOLID STATE PHYSICS Second Edition J. R. Hook H. E. Hall Department of Physics, University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Contents Flow diagram Inside front
SOLID STATE PHYSICS Second Edition J. R. Hook H. E. Hall Department of Physics, University of Manchester John Wiley & Sons CHICHESTER NEW YORK BRISBANE TORONTO SINGAPORE Contents Flow diagram Inside front
SPECTRUM of electromagnetic radiation from a type-ii
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITY, VOL. 19, NO. 4, AUGUST 2009 3653 A Superconductor THz Modulator Based on Vortex Flux Flow Farrokh Sarreshtedari, Mehdi Hosseini, Hamid Reza Chalabi, Ali
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON APPLIED SUPERCONDUCTIVITY, VOL. 19, NO. 4, AUGUST 2009 3653 A Superconductor THz Modulator Based on Vortex Flux Flow Farrokh Sarreshtedari, Mehdi Hosseini, Hamid Reza Chalabi, Ali
The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other
 1 The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other phases of matter that have been experimentally observed,
1 The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other phases of matter that have been experimentally observed,
GaAs and InGaAs Single Electron Hex. Title. Author(s) Kasai, Seiya; Hasegawa, Hideki. Citation 13(2-4): Issue Date DOI
 Title GaAs and InGaAs Single Electron Hex Circuits Based on Binary Decision D Author(s) Kasai, Seiya; Hasegawa, Hideki Citation Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems 3(2-4): 925-929 Issue Date 2002-03 DOI
Title GaAs and InGaAs Single Electron Hex Circuits Based on Binary Decision D Author(s) Kasai, Seiya; Hasegawa, Hideki Citation Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems 3(2-4): 925-929 Issue Date 2002-03 DOI
single-electron electron tunneling (SET)
 single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
single-electron electron tunneling (SET) classical dots (SET islands): level spacing is NOT important; only the charging energy (=classical effect, many electrons on the island) quantum dots: : level spacing
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jul 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jul 2008 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 28 Jul 2008](/thumbs/88/117898456.jpg) Current induced resistance change of magnetic tunnel junctions with ultra-thin MgO tunnel barriers Patryk Krzysteczko, 1, Xinli Kou, 2 Karsten Rott, 1 Andy Thomas, 1 and Günter Reiss 1 1 Bielefeld University,
Current induced resistance change of magnetic tunnel junctions with ultra-thin MgO tunnel barriers Patryk Krzysteczko, 1, Xinli Kou, 2 Karsten Rott, 1 Andy Thomas, 1 and Günter Reiss 1 1 Bielefeld University,
