Neutrons as probe particles V pseudo Fermi
|
|
|
- Muriel Walters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neutrons as probe particles V pseudo Fermi Nuclear interaction range (~10-13 cm) b r R b ~ cm 510 thermal neutrons 5 A E ~ 5 mev for thermal neutrons ~ Å for thermal neutrons b
2 Penetration depth of neutrons, X rays and electrons Beam intensities:
3 Cross section and scattering length The interaction of neutrons with matter takes place principally via nuclear forces characterized by a radius of action comparable with the one of the atomic nucleus (10-14 m). The deepness of the potential, V 0 is of the order of few (10-60) MeV. Such value does not vary systematically with atomic number or with atomic weight as in the case of X-Ray scattering where electron density is all that matters. The total electronic function describing the scattering event of the neutron is: ( r) e ik r with f scattering amplitude (a complex number, scattering implies delay and dephasing) independent of the scattering angle θ. The diffusion probability is thus isotropic. f r e The reason for this behavior is connected to the value of the wavelength of the de Broglie wavelength of the thermal neutron which is much larger than the size of the nucleus. The quantity of motion p and the scattering parameter d, yield an angular momentum L L d p L l( l 1) The distance corresponding to l=1 is: d ikr L p l( l 1) l( l 1) 1 many order of magnitude larger than the size of the nucleus for thermal neutrons. scattering in s wave, Born approximation holds Neutrons interact weakly also through their magnetic moments with the electron density. Since the latter extends over all the atom, the resulting scattering intensity will decrease with the scattering angle k 1 5
4 The scattering amplitude f has the dimension of length. scattering length : value of f in the limit of large wavelengths b lim f Once the neutron penetrates into the nucleus its wavefunction can be described by a stationary wave of amplitude /r. Its amplitude and derivative have to match the plane wavefunction outside of the nucleus at the radius of the atomic nucleus, R k. Three possible cases: 1) Neutron does not penetrate into the nucleus cannot b=r k ) Weak interaction: the neutron is scattered b>0 3) Strong interaction: the neutron is initially absorbed and then reemitted b<0 H has a negative value of b, while b is positive for D. An appropriate isotopic mixture can thus give any average value of b. This is very useful when embedding an object in water, since a proper choice of the isotopic mixture can eliminate the contrast in parts of the object, making them invisible.
5 Total and differential cross sections 4 4 f u t r e f r ut ikr outgoing incident outgoing r ik incident e u 4 4 b f t u neutron velocity R position in space (in barn 10-8 m ) Differential cross section ) ( 4 b f d d t t f does not depend on angle scattering potential approximated ) ( ) ( r b m r V by the Fermi pseudopotential Total cross section ) ( ) ( R j r b m r V which for a lattice reads:
6 depends on the nature of the nucleus and on the particluar isotope involved in the collision d d 0 costan te d d d d d I,, dd N I N Total cross section: t = a + s s scattering cross section s d d d a absorption cross section d dd dd Bi The different terms are described by the scattering length, connected to the radius of the potential well and thus of the order of fm. For a composite material the scattering length is the average of the lengths weighted on the density of the components The scattering length depends on energy
7 Coherent and incoherent scattering Since materials correspond to isotopic mixtures with different scattering lengths, the scattering intensity consists of diffraction peaks superposed on an unstructured incoherent background. d d N iqr bje j1 j i iqr ij i b b i j e isotope A with concentration p isotope B with concentration 1-p bb i j pb A ( 1 p) b B p(1 p)( ba b ) B coherent incoherent ij d q ( r r ) d d d coh inc b Np ij e i j diffraction peaks p(1 p) b b ( 1 p)( ba bb ) N A B unstructured background Incoherence results not only the isotopes mixture but also from magnetic scattering (Ni: only 3.4 barn out 18 are coherent, for H only barn out of 80)
8
9 Elastic vs inelastic scattering k 1 k 0 Inelastic scattering corresponds to energy momentum transfer to phonon or magnon baths of the sample. Elastic scattering Inelastic scattering k 1 k 0 q el k 1 q el k 0 k 0 > k 1 E 0 > E 1 E > 0 the neutron looses energy to the sample k 0 sin q k 1 k 0 q k 0 < k 1 E 0 < E 1 E < 0 the neutron gains energy Accessibile kinematic region: q = k 0 k 1 conservation of momentum E s k 1 k0 1 conservation of energy E 0 Scan curve q k 0 k 1 k1 k0 q/k 0 cos Notice: for light and X rays E = ħ c k, = c k: The set of accessible Q and is different than for massive particles E loss /E 0
10 Applications: Neutron radiography:
11 Crystallography Determination of lattice spacing Investigation of Phase Transitions Odd Miller index channels are open for the ordered phase only
12 Lattice dynamics: Phonon dispersion Vertical and horizontal cuts in the -q plane are obtained by changing two parameters at a time as possible using the three axis spectrometer, discussed below
13 Magnetic Scattering the neutron interacts via its magnetic dipole moment n =g n s B expressed in Bohr magnetons, with g n = -1,91 anomalous giromagnetic factor s neutron spin. Atomic scattering length a m = g n r e f(q)m r e =e /mc classical electron radius (g n r e =1, cm) f(q) magnetic form factor M projection of the magnetization in the direction to q. a m is small since it is deterrnined by the weak magnetic interaction with the electronic orbitals of the sample; f(q) is peaked at small q since the orbitals extend over the dimension of the atom. magnon cross section has a strong q dependence.
14 Magnetism Determination of magnetic superlattices Ferro-para magnetic phase transitions and magnetization curves The intensity due to magnetic scattering goes to zero at the Neel temperature, T N. The beams in the example do not vanish above T N since the structure of MnV O 4 is not bcc
15 Magnetic topography Topografia Spin up Spin down Visualization of magnetic domains
16 Magnetic dynamics Magnons, magnetic excitations in which the spin flip is delocalized Magnon dispersion is quadratic in exchanged momentum
17 Neutron Small Angle Scattering Small Angle Scattering relies on diffraction on structures larger than just the atomic size, such as big molecules or clusters that can be hundreds times larger than an atom. Neutron Small Angle Scattering is a non-destructive method for the determination of microstructures with lengths between 0.5 nm and 500 nm. It is based on the principle that an initially parallel neutron beam is scattered by inhomogeneities of a sample. These can be due to fluctuations in density, concentration or magnetisation. The method is widely used in biological structure research (viruses, proteins, enzymes), polymer research (conformation analysis), energy and environmental engineering (porosity and surfaces of filter materials and catalysts) and the development of new materials. Similar and complementar information can be retrieved by Small Angle X-Ray
18 Production of neutron beams Neutrons are generated at high energy by nuclear reactions. The cost of a source depnds on the amount of energy ending up in each neutrone (MeV/n). Neutron beams are expensive. Experiments are approved by international scientific committees SPALLATION to spall = scheggiare Bombarding a heavy nucleus (Uranium/Tantalum) with high energy (~ GeV) protons FISSION Typically of Uranium A thermal neutron hits U. the nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei (e..g Br e La) and releases energy (00 MeV) + ~.5 swift neutrons Chain reaction when more than one neutron per fission is retained in the system. Various particles (protons, neutrinos ) + ~ 0 neutroni(/proton with energies of some MeV ~1 neutron (/fission) with energy of MeV Neutrons must be moderated, i.e. brought to thermal energies (5 mev), by inelastic scattering with light atoms (hydrogen, graphite, methane)
19 Neutron Sources: an important flux of neutrons is available only at large scale facilities, like the Laue-Langevin laboratory in Grenoble. Fission Reactors: The most commonly used reaction to produce neutrons involves fission of 35 U: n+ 35 U= 36 Ba+ 56 Kr+Nn+ +b The cross section is largest for low energy neutrons, i.e. for energies < 1 ev and involves the production on average of N.5 neutrons per fission event. 00 MeV are released, distributed for 10 MeV in rays, MeV in the neutrons and the rest in the other fission products. The emitted neutrons are peaked at 1 MeV, energy at which they are easily captured by the much more abundant U 38 isotope. To maintain the chain reaction the neutrons must be slowed down by immerging the fissile material in water or better heavy water and trying to minimize the lost neutrons. The reactor is screened by a several meter thick concrete, Fe and B wall which blocks rays and neutrons.
20 The beam collimators are of stainless steel and B 4 C, materials with a high stopping power for rays and transparent to neutrons. The experiments are placed at the end of beamlines distributed around the nuclear reactor. The moderator is cooled to room temperature in order to obtain a thermal distribution centered at 5 mev, corresponding to translational velocities of 00 m/sec.
21 Spallation Sources: p +A= Nn+ + pp + spallation products pp stays for small mass particle-antiparticle pairs A is a heavy nucleus. The incident proton must have an energy E>0.5 GeV. It is produced either with a protosincrhotron (diameter 100 m) or by a linear accelerator (length 1 km) or by a combination of both techniques. Typically 10 to 0 high energy neutrons are produced in each collision and fluxes of n/sec concentrated in a small solid angle are generated (high brilliance). The power needed to operate a spallation source is NE 100 kw much smaller than the one of a reactor generating neutron beams with comparable brightness. The spallation source can be operated in continuous or pulsed modes (useful for TOF).
22 Neutron Optics: An efficient use of neutron beams implies waveguides to lead them to the experiment and lenses to focus them on the sample. Lenses and waveguides are possible since neutrons are slowed down inside materials (e.g. quartz) and one can define an effective refraction index. n 1 - (n i b i ) / n i = i th -atomic species density b i = scattering length = neutron wavelewngth Typically : 1-n At =60, the deflection =(n-1) [tg +tg(- )] =3 10-6, Corresponds to just a few arc seconds. prisms are dispersive elements Neutron Lense Since n<1 convergent neutron lenses are concave.
23 Neutron Waveguides are based on total reflection of thermal neutrons for grazing angles c <0.1 ( 56 Ni) n = sen( i )/sen( r ) = sen(/ - c ) = cos c = 1- ½ c = 1 - (n i b i ) / yielding: c = <b>/ Thanks to waveguides the experiments may be placed far away from the nuclear reactor. They are built of quartz covered by a thin film of 58 Ni whose critical angle is even larger than for 56 Ni. Larger critical angles can be reached using non periodic multilayers consisting of materials with different refraction index. This method allows to build neutron mirrors and neutron polarizers, too.
24 Typical set up for a neutron beamline. For = nm the distance between lens and exit slit S 4 is 10 m. The effect of gravitation must be considered in computing the trajectories.
25 Polarization Definition: P=(N + -N - )/(N + +N - ) Polarized neutron beams are obtained by: 1) Transmission through polarizing filters, based a) on the spin dependence of the diffraction cross section (polycristalline iron, P0.6); b) on the difference in the cross section for collisions in singlet and triplet state (crystals doped with Nd 3+, P=100% at E= 5 mev); ) Reflection off a magnetized mirror; critical angle: c = (N(b a m )/ ) with b and a m nuclear and magnetic scattering lengths the highest polarization is obtained for a Ti and Gd mirror. P98% for Ge-Fe multilayers. 3) Bragg reflection from a magnetized single crystal.
26 Neutron detectors: neutrons have no electric charge. Detectors are based on conversion of the energy released in nuclear reactions: Gas phase detectors: 3 He doped with 10 B Reactions: 3 He+n=p+ 3 H 10 B+n 7 Li * + 3 He+n releases 0.8 MeV distributed in a ratio of 3:1 on proton and Tritium. The electrically charged proton ionizes the gas. B +n has a higher cross section. The energetic particle ionizes the gas. The so generated electrons cause further ionizations. The current is collected on a filament. It is proportional to the energy released in the nuclear reaction so that neutron events can be distinguished from those generated by other ionizing particles. Since the ionization potential of 3 He is 0 ev, each events produces 1.6 fc. Assuming that such charge is collected within 1 sec and discharged on a 10 M resistor, one obtains 160 mv impulses. Typically a.5 cm diameter detector with 0 bar pressure has a detection efficiency of 90% for neutrons with =1 Å. 3 He detectors can be made position sensitive by collecting the current with more than one filament.
27 Neutron Monocromators: Neutron monochromators are based on Bragg diffraction on monocrystals typically Cu or pyrolytic graphite. Such crystals have the advantage of being ideally imperfect - (mosaicity 0.1 to 1 ) so that diffraction can occur over a sufficiently large energy window to allow for high beam fluxes (even the most efficient neutron sources are weak!). At =1 Å Cu has a reflectivity peak in the (331) diffraction channel of 30%. Pyrolytic graphite performs even better (70%). Efficiency improves at low temperature, T, because of the Debye Waller factor. I(T)=I o e -WT. Monochromatization can be achieved also with velocity selectors
28 Inelastic diffusion: Time of Flight Chopper
29 3 axis spectrometer It consists of Bragg monochromators used both to monochromatize and to analyze the beam. It can achieve a typical resolution E/E~1% i.e. 0. mev Direct geometry I( S, A ) at fixed M Inverse geometry I( S, M ) at fixed A For both geometries each tern ( S, M, A ) defines a value of Q. ( M, A ) define. It is possible to perform measurements As a function of exchanged energy keeping Q costant.
30 sample Bragg monochromator chopper L 0 L 1 detector M Sample Bragg analyzer A mono M Crystal monochromator ToF spectrometer Detector direct 3-axis geometry inverse 3-axis geometry
31 A 3 1 A A 3 A A A A A cos sin cos sin k d d d E E m m m m M 0 1 M, ~, Q S k k Q I M 3 0 M M cos k d m Q k 0 k 1, ~ cos ) (, A A Q S k k Q I Q k 0 k 1 A A, ~ ) (, Q S k k k Q I Fixed initial energy and scattering angle (direct geometry) Fixed scattering energy (inverse geometry) Incident energy and angle are varied, ~ cos, M 0 M Q S k Q I Three-Axis Spectrometer (constant-q mode)
32 Spin Echo Technique The direction of the neutron spin is preserved in the inelastic interaction with the sample. During the flight time in the magnetic field the spin precess. Inelastic scattered neutrons are slower and precede over a larger angle. Energy Resolution: E/E=10-6 =4 nm E=10-8 mev Typical diffusion energies Apparatus at ILL Grenoble
33 -Spin flipper (campi magnetici incrociati)
34 Larmor precession of the neutron spins
Neutron Instruments I & II. Ken Andersen ESS Instruments Division
 Neutron Instruments I & II ESS Instruments Division Neutron Instruments I & II Overview of source characteristics Bragg s Law Elastic scattering: diffractometers Continuous sources Pulsed sources Inelastic
Neutron Instruments I & II ESS Instruments Division Neutron Instruments I & II Overview of source characteristics Bragg s Law Elastic scattering: diffractometers Continuous sources Pulsed sources Inelastic
Small Angle Neutron Scattering in Different Fields of Research. Henrich Frielinghaus
 Small Angle Neutron Scattering in Different Fields of Research Henrich Frielinghaus Jülich Centre for Neutron Science Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH Lichtenbergstrasse 1 85747 Garching (München) h.frielinghaus@fz-juelich.de
Small Angle Neutron Scattering in Different Fields of Research Henrich Frielinghaus Jülich Centre for Neutron Science Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH Lichtenbergstrasse 1 85747 Garching (München) h.frielinghaus@fz-juelich.de
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter
 Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Chapter V: Interactions of neutrons with matter 1 Content of the chapter Introduction Interaction processes Interaction cross sections Moderation and neutrons path For more details see «Physique des Réacteurs
Neutron facilities and generation. Rob McQueeney, Ames Laboratory and Iowa State University
 Neutron facilities and generation Rob McQueeney, Ames Laboratory and Iowa State University September 12, 2018 19-Sep-18 Physics 502 2 Neutrons compared to other probes of matter Bulk probe Interacts with
Neutron facilities and generation Rob McQueeney, Ames Laboratory and Iowa State University September 12, 2018 19-Sep-18 Physics 502 2 Neutrons compared to other probes of matter Bulk probe Interacts with
An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering. School of Chemistry The University of Sydney
 An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering Brendan J. Kennedy School of Chemistry The University of Sydney 1) Strong forces 2) Weak forces Types of Forces 3) Electromagnetic forces 4) Gravity Types
An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering Brendan J. Kennedy School of Chemistry The University of Sydney 1) Strong forces 2) Weak forces Types of Forces 3) Electromagnetic forces 4) Gravity Types
Neutron Diffraction: a general overview
 RUG1 Neutron Diffraction: a general overview Graeme Blake Zernike Institute for Advanced Materials University of Groningen Outline Elastic scattering of neutrons from matter Comparison of neutron and X-ray
RUG1 Neutron Diffraction: a general overview Graeme Blake Zernike Institute for Advanced Materials University of Groningen Outline Elastic scattering of neutrons from matter Comparison of neutron and X-ray
Nuclear Reactions A Z. Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q > 0. Exothermic Endothermic
 Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
Radioactivity, Spontaneous Decay: Nuclear Reactions A Z 4 P D+ He + Q A 4 Z 2 Q > 0 Nuclear Reaction, Induced Process: x + X Y + y + Q Q = ( m + m m m ) c 2 x X Y y Q > 0 Q < 0 Exothermic Endothermic 2
School on Pulsed Neutrons: Characterization of Materials October Neurton Sources & Scattering Techniques (1-2)
 1866-6 School on Pulsed Neutrons: Characterization of Materials 15-26 October 2007 Neurton Sources & Scattering Techniques (1-2) Guenter Bauer Forschungzentrum Julich GmbH Julich Germany The Abdus Salam
1866-6 School on Pulsed Neutrons: Characterization of Materials 15-26 October 2007 Neurton Sources & Scattering Techniques (1-2) Guenter Bauer Forschungzentrum Julich GmbH Julich Germany The Abdus Salam
Neutron scattering. Niina Jalarvo. SMN/FERMiO, Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo Gaustadalleen 21 NO-0349 Oslo, Norway UNIVERSITY OF OSLO
 Neutron scattering Niina Jalarvo niina.jalarvo@smn.uio.no SMN/FERMiO, Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo Gaustadalleen 21 NO-0349 Oslo, Norway UNIVERSITY OF OSLO NEUTRON what is it? Neutrons are
Neutron scattering Niina Jalarvo niina.jalarvo@smn.uio.no SMN/FERMiO, Department of Chemistry, University of Oslo Gaustadalleen 21 NO-0349 Oslo, Norway UNIVERSITY OF OSLO NEUTRON what is it? Neutrons are
Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy
 Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline 1. self-contained introduction neutron scattering and spectroscopy x-ray scattering and spectroscopy 2. application
Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline 1. self-contained introduction neutron scattering and spectroscopy x-ray scattering and spectroscopy 2. application
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions
 Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Detekce a spektrometrie neutronů. neutron detection and spectroscopy
 Detekce a spektrometrie neutronů neutron detection and spectroscopy 1. Slow neutrons 2. Fast neutrons 1 1. Slow neutrons neutron kinetic energy E a) charged particles are produced, protons, α particle,
Detekce a spektrometrie neutronů neutron detection and spectroscopy 1. Slow neutrons 2. Fast neutrons 1 1. Slow neutrons neutron kinetic energy E a) charged particles are produced, protons, α particle,
1. Nuclear Size. A typical atom radius is a few!10 "10 m (Angstroms). The nuclear radius is a few!10 "15 m (Fermi).
 1. Nuclear Size We have known since Rutherford s! " scattering work at Manchester in 1907, that almost all the mass of the atom is contained in a very small volume with high electric charge. Nucleus with
1. Nuclear Size We have known since Rutherford s! " scattering work at Manchester in 1907, that almost all the mass of the atom is contained in a very small volume with high electric charge. Nucleus with
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface
 Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
Nuclear Physics. (PHY-231) Dr C. M. Cormack. Nuclear Physics This Lecture
 Nuclear Physics (PHY-31) Dr C. M. Cormack 11 Nuclear Physics This Lecture This Lecture We will discuss an important effect in nuclear spectroscopy The Mössbauer Effect and its applications in technology
Nuclear Physics (PHY-31) Dr C. M. Cormack 11 Nuclear Physics This Lecture This Lecture We will discuss an important effect in nuclear spectroscopy The Mössbauer Effect and its applications in technology
APEX CARE INSTITUTE FOR PG - TRB, SLET AND NET IN PHYSICS
 Page 1 1. Within the nucleus, the charge distribution A) Is constant, but falls to zero sharply at the nuclear radius B) Increases linearly from the centre, but falls off exponentially at the surface C)
Page 1 1. Within the nucleus, the charge distribution A) Is constant, but falls to zero sharply at the nuclear radius B) Increases linearly from the centre, but falls off exponentially at the surface C)
SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY
 Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
Section 9: SOURCES of RADIOACTIVITY This section briefly describes various sources of radioactive nuclei, both naturally occurring and those produced artificially (man-made) in, for example, reactors or
SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
Magnetic Neutron Reflectometry. Moses Marsh Shpyrko Group 9/14/11
 Magnetic Neutron Reflectometry Moses Marsh Shpyrko Group 9/14/11 Outline Scattering processes Reflectivity of a slab of material Magnetic scattering Off-specular scattering Source parameters Comparison
Magnetic Neutron Reflectometry Moses Marsh Shpyrko Group 9/14/11 Outline Scattering processes Reflectivity of a slab of material Magnetic scattering Off-specular scattering Source parameters Comparison
= : K A
 Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
U n 3 n Ba Kr (D) Br (C) Kr (B) Rb (E) 94 37
 1984 36. The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) 2.0 37. An object is placed as shown in
1984 36. The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) 2.0 37. An object is placed as shown in
UGC ACADEMY LEADING INSTITUE FOR CSIR-JRF/NET, GATE & JAM PHYSICAL SCIENCE TEST SERIES # 4. Atomic, Solid State & Nuclear + Particle
 UGC ACADEMY LEADING INSTITUE FOR CSIR-JRF/NET, GATE & JAM BOOKLET CODE PH PHYSICAL SCIENCE TEST SERIES # 4 Atomic, Solid State & Nuclear + Particle SUBJECT CODE 05 Timing: 3: H M.M: 200 Instructions 1.
UGC ACADEMY LEADING INSTITUE FOR CSIR-JRF/NET, GATE & JAM BOOKLET CODE PH PHYSICAL SCIENCE TEST SERIES # 4 Atomic, Solid State & Nuclear + Particle SUBJECT CODE 05 Timing: 3: H M.M: 200 Instructions 1.
Introduction to Nuclear Engineering
 2016/9/27 Introduction to Nuclear Engineering Kenichi Ishikawa ( ) http://ishiken.free.fr/english/lecture.html ishiken@n.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp 1 References Nuclear Physics basic properties of nuclei nuclear
2016/9/27 Introduction to Nuclear Engineering Kenichi Ishikawa ( ) http://ishiken.free.fr/english/lecture.html ishiken@n.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp 1 References Nuclear Physics basic properties of nuclei nuclear
1 v. L18.pdf Spring 2010, P627, YK February 22, 2012
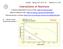 L18.pdf Spring 2010, P627, YK February 22, 2012 18 T2 Nuclear Information Service at LANL: http://t2.lanl.gov/data/ ENDF/B VI Neutron Data : http://t2.lanl.gov/cgi bin/nuclides/endind Thermal neutron x
L18.pdf Spring 2010, P627, YK February 22, 2012 18 T2 Nuclear Information Service at LANL: http://t2.lanl.gov/data/ ENDF/B VI Neutron Data : http://t2.lanl.gov/cgi bin/nuclides/endind Thermal neutron x
22.54 Neutron Interactions and Applications (Spring 2004) Chapter 1 (2/3/04) Overview -- Interactions, Distributions, Cross Sections, Applications
 .54 Neutron Interactions and Applications (Spring 004) Chapter 1 (/3/04) Overview -- Interactions, Distributions, Cross Sections, Applications There are many references in the vast literature on nuclear
.54 Neutron Interactions and Applications (Spring 004) Chapter 1 (/3/04) Overview -- Interactions, Distributions, Cross Sections, Applications There are many references in the vast literature on nuclear
Introduction to Triple Axis Neutron Spectroscopy
 Introduction to Triple Axis Neutron Spectroscopy Bruce D Gaulin McMaster University The triple axis spectrometer Constant-Q and constant E Practical concerns Resolution and Spurions Neutron interactions
Introduction to Triple Axis Neutron Spectroscopy Bruce D Gaulin McMaster University The triple axis spectrometer Constant-Q and constant E Practical concerns Resolution and Spurions Neutron interactions
SAXS and SANS facilities and experimental practice. Clement Blanchet
 SAXS and SANS facilities and experimental practice Clement Blanchet SAS experiment Detector X-ray or neutron Beam Sample 2 s Buffer X-rays Roengten, 1895 Electromagnetic wave The electromagnetic spectrum
SAXS and SANS facilities and experimental practice Clement Blanchet SAS experiment Detector X-ray or neutron Beam Sample 2 s Buffer X-rays Roengten, 1895 Electromagnetic wave The electromagnetic spectrum
Neutron scattering. Max Wolff. Division for Material Physics Department of Physics and Astronomy Uppsala University Uppsala Sweden
 Neutron scattering Max Wolff Division for Material Physics Department of Physics and Astronomy Uppsala University Uppsala Sweden Outline Why is neutron scattering important? Peculiarities of neutrons How
Neutron scattering Max Wolff Division for Material Physics Department of Physics and Astronomy Uppsala University Uppsala Sweden Outline Why is neutron scattering important? Peculiarities of neutrons How
Nuclear Physics 2. D. atomic energy levels. (1) D. scattered back along the original direction. (1)
 Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
Name: Date: Nuclear Physics 2. Which of the following gives the correct number of protons and number of neutrons in the nucleus of B? 5 Number of protons Number of neutrons A. 5 6 B. 5 C. 6 5 D. 5 2. The
Lecture 22 Ion Beam Techniques
 Lecture 22 Ion Beam Techniques Schroder: Chapter 11.3 1/44 Announcements Homework 6/6: Will be online on later today. Due Wednesday June 6th at 10:00am. I will return it at the final exam (14 th June).
Lecture 22 Ion Beam Techniques Schroder: Chapter 11.3 1/44 Announcements Homework 6/6: Will be online on later today. Due Wednesday June 6th at 10:00am. I will return it at the final exam (14 th June).
Chapter 11: Neutrons detectors
 Chapter 11: Neutrons detectors 1 Contents Principles of neutrons detection Slow neutron detection methods Fast neutron detection methods 2 Introduction Neutrons are uncharged particles cannot be directly
Chapter 11: Neutrons detectors 1 Contents Principles of neutrons detection Slow neutron detection methods Fast neutron detection methods 2 Introduction Neutrons are uncharged particles cannot be directly
Transmission Electron Microscopy
 L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
L. Reimer H. Kohl Transmission Electron Microscopy Physics of Image Formation Fifth Edition el Springer Contents 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Transmission Electron Microscopy... 1 1.1.1 Conventional Transmission
MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001 PHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH ASTROPHYSICS PHYSICS WITH SPACE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS WITH MEDICAL PHYSICS
 No. of Pages: 6 No. of Questions: 10 MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001 Subject PHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH ASTROPHYSICS PHYSICS WITH SPACE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS WITH MEDICAL PHYSICS Title of Paper MODULE PA266
No. of Pages: 6 No. of Questions: 10 MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2001 Subject PHYSICS, PHYSICS WITH ASTROPHYSICS PHYSICS WITH SPACE SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS WITH MEDICAL PHYSICS Title of Paper MODULE PA266
Rb, which had been compressed to a density of 1013
 Modern Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Departmental Exam December 3, 2017 1. An electron is initially at rest in a uniform electric field E in the negative y direction and a uniform magnetic
Modern Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Departmental Exam December 3, 2017 1. An electron is initially at rest in a uniform electric field E in the negative y direction and a uniform magnetic
Good Vibrations Studying phonons with momentum resolved spectroscopy. D.J. Voneshen 20/6/2018
 Good Vibrations Studying phonons with momentum resolved spectroscopy D.J. Voneshen 20/6/2018 Overview What probe to use? Types of instruments. Single crystals example Powder example Thing I didn t talk
Good Vibrations Studying phonons with momentum resolved spectroscopy D.J. Voneshen 20/6/2018 Overview What probe to use? Types of instruments. Single crystals example Powder example Thing I didn t talk
Interaction X-rays - Matter
 Interaction X-rays - Matter Pair production hν > M ev Photoelectric absorption hν MATTER hν Transmission X-rays hν' < hν Scattering hν Decay processes hν f Compton Thomson Fluorescence Auger electrons
Interaction X-rays - Matter Pair production hν > M ev Photoelectric absorption hν MATTER hν Transmission X-rays hν' < hν Scattering hν Decay processes hν f Compton Thomson Fluorescence Auger electrons
RFSS: Lecture 2 Nuclear Properties
 RFSS: Lecture 2 Nuclear Properties Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry: Chapter 2 Nuclear Properties Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Chapter 1 Introduction, Chapter 2 Atomic Nuclei Nuclear properties Masses
RFSS: Lecture 2 Nuclear Properties Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry: Chapter 2 Nuclear Properties Nuclear and Radiochemistry: Chapter 1 Introduction, Chapter 2 Atomic Nuclei Nuclear properties Masses
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5 detector sample X-ray source monochromator David Ritchie http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home QCMP Lent/Easter 2019 5.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5 detector sample X-ray source monochromator David Ritchie http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home QCMP Lent/Easter 2019 5.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical
Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials
 Brent Fultz James Howe Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials Fourth Edition ~Springer 1 1 Diffraction and the X-Ray Powder Diffractometer 1 1.1 Diffraction... 1 1.1.1 Introduction
Brent Fultz James Howe Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials Fourth Edition ~Springer 1 1 Diffraction and the X-Ray Powder Diffractometer 1 1.1 Diffraction... 1 1.1.1 Introduction
Nuclear Spin and Stability. PHY 3101 D. Acosta
 Nuclear Spin and Stability PHY 3101 D. Acosta Nuclear Spin neutrons and protons have s = ½ (m s = ± ½) so they are fermions and obey the Pauli- Exclusion Principle The nuclear magneton is eh m µ e eh 1
Nuclear Spin and Stability PHY 3101 D. Acosta Nuclear Spin neutrons and protons have s = ½ (m s = ± ½) so they are fermions and obey the Pauli- Exclusion Principle The nuclear magneton is eh m µ e eh 1
Outline. Chapter 6 The Basic Interactions between Photons and Charged Particles with Matter. Photon interactions. Photoelectric effect
 Chapter 6 The Basic Interactions between Photons and Charged Particles with Matter Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther
Chapter 6 The Basic Interactions between Photons and Charged Particles with Matter Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY. Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University
 DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
DIFFRACTION PHYSICS THIRD REVISED EDITION JOHN M. COWLEY Regents' Professor enzeritus Arizona State University 1995 ELSEVIER Amsterdam Lausanne New York Oxford Shannon Tokyo CONTENTS Preface to the first
Neutron scattering from quantum materials
 Neutron scattering from quantum materials Bernhard Keimer Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research Max Planck UBC UTokyo Center for Quantum Materials Detection of bosonic elementary excitations in
Neutron scattering from quantum materials Bernhard Keimer Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research Max Planck UBC UTokyo Center for Quantum Materials Detection of bosonic elementary excitations in
X-ray diffraction is a non-invasive method for determining many types of
 Chapter X-ray Diffraction.1 Introduction X-ray diffraction is a non-invasive method for determining many types of structural features in both crystalline and amorphous materials. In the case of single
Chapter X-ray Diffraction.1 Introduction X-ray diffraction is a non-invasive method for determining many types of structural features in both crystalline and amorphous materials. In the case of single
object objective lens eyepiece lens
 Advancing Physics G495 June 2015 SET #1 ANSWERS Field and Particle Pictures Seeing with electrons The compound optical microscope Q1. Before attempting this question it may be helpful to review ray diagram
Advancing Physics G495 June 2015 SET #1 ANSWERS Field and Particle Pictures Seeing with electrons The compound optical microscope Q1. Before attempting this question it may be helpful to review ray diagram
Neutron Interactions with Matter
 Radioactivity - Radionuclides - Radiation 8 th Multi-Media Training Course with Nuclides.net (Institute Josžef Stefan, Ljubljana, 13th - 15th September 2006) Thursday, 14 th September 2006 Neutron Interactions
Radioactivity - Radionuclides - Radiation 8 th Multi-Media Training Course with Nuclides.net (Institute Josžef Stefan, Ljubljana, 13th - 15th September 2006) Thursday, 14 th September 2006 Neutron Interactions
EEE4101F / EEE4103F Radiation Interactions & Detection
 EEE4101F / EEE4103F Radiation Interactions & Detection 1. Interaction of Radiation with Matter Dr. Steve Peterson 5.14 RW James Department of Physics University of Cape Town steve.peterson@uct.ac.za March
EEE4101F / EEE4103F Radiation Interactions & Detection 1. Interaction of Radiation with Matter Dr. Steve Peterson 5.14 RW James Department of Physics University of Cape Town steve.peterson@uct.ac.za March
 Atoms and Nuclei 1. The radioactivity of a sample is X at a time t 1 and Y at a time t 2. If the mean life time of the specimen isτ, the number of atoms that have disintegrated in the time interval (t
Atoms and Nuclei 1. The radioactivity of a sample is X at a time t 1 and Y at a time t 2. If the mean life time of the specimen isτ, the number of atoms that have disintegrated in the time interval (t
H2 Physics Set A Paper 3 H2 PHYSICS. Exam papers with worked solutions. (Selected from Top JC) SET A PAPER 3.
 H2 PHYSICS Exam papers with worked solutions (Selected from Top JC) SET A PAPER 3 Compiled by THE PHYSICS CAFE 1 P a g e Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials are required. READ
H2 PHYSICS Exam papers with worked solutions (Selected from Top JC) SET A PAPER 3 Compiled by THE PHYSICS CAFE 1 P a g e Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No Additional Materials are required. READ
MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION. Dr. Flera Rizatdinova
 MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the
MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the
Quasi-specular albedo of cold neutrons from powder of nanoparticles
 Quasi-specular albedo of cold neutrons from powder of nanoparticles R. Cubitt 1, E.V. Lychagin 2, A.Yu. Muzychka 2, G.V. Nekhaev 2, V.V. Nesvizhevsky 1*, G. Pignol 3, K.V. Protasov 3, A.V. Strelkov 2 1
Quasi-specular albedo of cold neutrons from powder of nanoparticles R. Cubitt 1, E.V. Lychagin 2, A.Yu. Muzychka 2, G.V. Nekhaev 2, V.V. Nesvizhevsky 1*, G. Pignol 3, K.V. Protasov 3, A.V. Strelkov 2 1
Topic 7 &13 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics
 Name: Date:. Isotopes provide evidence for the existence of A. protons. B. electrons. C. nuclei. Topic 7 &3 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics D. neutrons.. The atomic line spectra of elements
Name: Date:. Isotopes provide evidence for the existence of A. protons. B. electrons. C. nuclei. Topic 7 &3 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics D. neutrons.. The atomic line spectra of elements
Neutron Sources Fall, 2017 Kyoung-Jae Chung Department of Nuclear Engineering Seoul National University
 Neutron Sources Fall, 2017 Kyoung-Jae Chung Department of Nuclear Engineering Seoul National University Neutrons: discovery In 1920, Rutherford postulated that there were neutral, massive particles in
Neutron Sources Fall, 2017 Kyoung-Jae Chung Department of Nuclear Engineering Seoul National University Neutrons: discovery In 1920, Rutherford postulated that there were neutral, massive particles in
Neutron Interactions Part I. Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics Y2.5321
 Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
Neutron Interactions Part I Rebecca M. Howell, Ph.D. Radiation Physics rhowell@mdanderson.org Y2.5321 Why do we as Medical Physicists care about neutrons? Neutrons in Radiation Therapy Neutron Therapy
A) n L < 1.0 B) n L > 1.1 C) n L > 1.3 D) n L < 1.1 E) n L < 1.3
 1. A beam of light passes from air into water. Which is necessarily true? A) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength increases. B) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength decreases. C) The
1. A beam of light passes from air into water. Which is necessarily true? A) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength increases. B) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength decreases. C) The
General theory of diffraction
 General theory of diffraction X-rays scatter off the charge density (r), neutrons scatter off the spin density. Coherent scattering (diffraction) creates the Fourier transform of (r) from real to reciprocal
General theory of diffraction X-rays scatter off the charge density (r), neutrons scatter off the spin density. Coherent scattering (diffraction) creates the Fourier transform of (r) from real to reciprocal
is the minimum stopping potential for which the current between the plates reduces to zero.
 Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
Module 1 :Quantum Mechanics Chapter 2 : Introduction to Quantum ideas Introduction to Quantum ideas We will now consider some experiments and their implications, which introduce us to quantum ideas. The
6 Neutrons and Neutron Interactions
 6 Neutrons and Neutron Interactions A nuclear reactor will not operate without neutrons. Neutrons induce the fission reaction, which produces the heat in CANDU reactors, and fission creates more neutrons.
6 Neutrons and Neutron Interactions A nuclear reactor will not operate without neutrons. Neutrons induce the fission reaction, which produces the heat in CANDU reactors, and fission creates more neutrons.
INTRODUCTION Strained Silicon Monochromator Magnesium Housing Windows for Monochromator Shutter and Collimator Fission Detector HOPG Monochromator
 Design for a Four-Blade Neutron Interferometer INTRODUCTION Strained Silicon Monochromator The neutron beam used for this interferometer is separated from the NIST reactor's main beam using a strained
Design for a Four-Blade Neutron Interferometer INTRODUCTION Strained Silicon Monochromator The neutron beam used for this interferometer is separated from the NIST reactor's main beam using a strained
Introduction to Neutron Scattering
 Introduction to Neutron Scattering Name: Guorong Li Email: gli6@utk.edu Solid State II, Spring 2008 Instructor: Elbio Dagotto Department of Physics University of Tennessee Introduction to Neutron Scattering
Introduction to Neutron Scattering Name: Guorong Li Email: gli6@utk.edu Solid State II, Spring 2008 Instructor: Elbio Dagotto Department of Physics University of Tennessee Introduction to Neutron Scattering
2. Determine the excess charge on the outer surface of the outer sphere (a distance c from the center of the system).
 Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges will yield
Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges will yield
LECTURE 6: INTERACTION OF RADIATION WITH MATTER
 LCTUR 6: INTRACTION OF RADIATION WITH MATTR All radiation is detected through its interaction with matter! INTRODUCTION: What happens when radiation passes through matter? Interlude The concept of cross-section
LCTUR 6: INTRACTION OF RADIATION WITH MATTR All radiation is detected through its interaction with matter! INTRODUCTION: What happens when radiation passes through matter? Interlude The concept of cross-section
We also find the development of famous Schrodinger equation to describe the quantization of energy levels of atoms.
 Lecture 4 TITLE: Quantization of radiation and matter: Wave-Particle duality Objectives In this lecture, we will discuss the development of quantization of matter and light. We will understand the need
Lecture 4 TITLE: Quantization of radiation and matter: Wave-Particle duality Objectives In this lecture, we will discuss the development of quantization of matter and light. We will understand the need
Structure of Surfaces
 Structure of Surfaces C Stepped surface Interference of two waves Bragg s law Path difference = AB+BC =2dsin ( =glancing angle) If, n =2dsin, constructive interference Ex) in a cubic lattice of unit cell
Structure of Surfaces C Stepped surface Interference of two waves Bragg s law Path difference = AB+BC =2dsin ( =glancing angle) If, n =2dsin, constructive interference Ex) in a cubic lattice of unit cell
Mock Examination Physics 2 nd Book Time 3 Hrs MM : 70
 Mock Examination Physics 2 nd Book Time 3 Hrs MM : 70 SECTION A 1. How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, If the incident violet light is replaced with red light? 2. What is principle
Mock Examination Physics 2 nd Book Time 3 Hrs MM : 70 SECTION A 1. How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, If the incident violet light is replaced with red light? 2. What is principle
Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging
 Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging Contents Introduction Symbols and definitions Part A Diffraction and imaging of elastically scattered electrons Chapter 1. Basic kinematical
Elastic and Inelastic Scattering in Electron Diffraction and Imaging Contents Introduction Symbols and definitions Part A Diffraction and imaging of elastically scattered electrons Chapter 1. Basic kinematical
Putting Neutron Scattering into Perspective
 Putting Neutron Scattering into Perspective H. Schober Institut Laue-Langevin, F-38042 Grenoble, France August 31, 2003 1 Introduction Whenever it is important to know precisely where atoms are or how
Putting Neutron Scattering into Perspective H. Schober Institut Laue-Langevin, F-38042 Grenoble, France August 31, 2003 1 Introduction Whenever it is important to know precisely where atoms are or how
PHYSICS. Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter
 PHYSICS Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter (The first 15 minutes of the examination are for reading the paper only. Candidates must NOT start writing during this time). -------------------------------------------------------------------
PHYSICS Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter (The first 15 minutes of the examination are for reading the paper only. Candidates must NOT start writing during this time). -------------------------------------------------------------------
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI
 UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
Activation Analysis. Characteristic decay mechanisms, α, β, γ Activity A reveals the abundance N:
 2.5. Isotope analysis and neutron activation techniques The previously discussed techniques of material analysis are mainly based on the characteristic atomic structure of the elements and the associated
2.5. Isotope analysis and neutron activation techniques The previously discussed techniques of material analysis are mainly based on the characteristic atomic structure of the elements and the associated
Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, Your Name: Questions
 Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, 1993 Your Name: Questions 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 3. 13. 23. 33. 43. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 8. 18.
Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, 1993 Your Name: Questions 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 3. 13. 23. 33. 43. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 8. 18.
Lectures on Applied Reactor Technology and Nuclear Power Safety. Lecture No 1. Title: Neutron Life Cycle
 Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 1 Title: Neutron Life Cycle Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture Infinite Multiplication Factor, k Four Factor Formula
Lectures on Nuclear Power Safety Lecture No 1 Title: Neutron Life Cycle Department of Energy Technology KTH Spring 2005 Slide No 1 Outline of the Lecture Infinite Multiplication Factor, k Four Factor Formula
The Low Energy Neutron Source at IUCF
 The Low Energy Neutron Source at IUCF David V. Baxter Indiana University 21 September, 2005 Acknowledgments Mike Snow John Cameron Aslam Lone Paul Sokol Hans Otto Meyer Mark Leuschner Helmut Kaiser Laddie
The Low Energy Neutron Source at IUCF David V. Baxter Indiana University 21 September, 2005 Acknowledgments Mike Snow John Cameron Aslam Lone Paul Sokol Hans Otto Meyer Mark Leuschner Helmut Kaiser Laddie
University of California, Berkeley Physics H7C Spring 2011 (Yury Kolomensky) THE FINAL EXAM Monday, May 9, 7 10pm. Maximum score: 200 points
 1 University of California, Berkeley Physics H7C Spring 2011 (Yury Kolomensky) THE FINAL EXAM Monday, May 9, 7 10pm Maximum score: 200 points NAME: SID #: You are given 180 minutes for this exam. You are
1 University of California, Berkeley Physics H7C Spring 2011 (Yury Kolomensky) THE FINAL EXAM Monday, May 9, 7 10pm Maximum score: 200 points NAME: SID #: You are given 180 minutes for this exam. You are
Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016. Lecture 11, MLZ is a cooperation between:
 Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016 Lecture 11, 11.1.2016 MLZ is a cooperation between: Organization Exam (after winter term) Registration: via TUM-Online between 16.11.2015 15.1.2015 Email: sebastian.muehlbauer@frm2.tum.de
Physics with Neutrons I, WS 2015/2016 Lecture 11, 11.1.2016 MLZ is a cooperation between: Organization Exam (after winter term) Registration: via TUM-Online between 16.11.2015 15.1.2015 Email: sebastian.muehlbauer@frm2.tum.de
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions.
 Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
Today, I will present the first of two lectures on neutron interactions. I first need to acknowledge that these two lectures were based on lectures presented previously in Med Phys I by Dr Howell. 1 Before
Hadronic Showers. KIP Journal Club: Calorimetry and Jets 2009/10/28 A.Kaplan & A.Tadday
 Hadronic Showers KIP Journal Club: Calorimetry and Jets 2009/10/28 A.Kaplan & A.Tadday Hadronic Showers em + strong interaction with absorber similarities to em-showers, but much more complex different
Hadronic Showers KIP Journal Club: Calorimetry and Jets 2009/10/28 A.Kaplan & A.Tadday Hadronic Showers em + strong interaction with absorber similarities to em-showers, but much more complex different
Physic 492 Lecture 16
 Physic 492 Lecture 16 Main points of last lecture: Angular momentum dependence. Structure dependence. Nuclear reactions Q-values Kinematics for two body reactions. Main points of today s lecture: Measured
Physic 492 Lecture 16 Main points of last lecture: Angular momentum dependence. Structure dependence. Nuclear reactions Q-values Kinematics for two body reactions. Main points of today s lecture: Measured
NJCTL.org 2015 AP Physics 2 Nuclear Physics
 AP Physics 2 Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
AP Physics 2 Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
Part I. Basics of neutron scattering
 Part I Basics of neutron scattering 13 Chapter 1 Introduction to neutron scattering Neutron scattering is one of the most powerful and versatile experimental methods to study the structure and dynamics
Part I Basics of neutron scattering 13 Chapter 1 Introduction to neutron scattering Neutron scattering is one of the most powerful and versatile experimental methods to study the structure and dynamics
MockTime.com. Ans: (b) Q6. Curie is a unit of [1989] (a) energy of gamma-rays (b) half-life (c) radioactivity (d) intensity of gamma-rays Ans: (c)
![MockTime.com. Ans: (b) Q6. Curie is a unit of [1989] (a) energy of gamma-rays (b) half-life (c) radioactivity (d) intensity of gamma-rays Ans: (c) MockTime.com. Ans: (b) Q6. Curie is a unit of [1989] (a) energy of gamma-rays (b) half-life (c) radioactivity (d) intensity of gamma-rays Ans: (c)](/thumbs/95/125098222.jpg) Chapter Nuclei Q1. A radioactive sample with a half life of 1 month has the label: Activity = 2 micro curies on 1 8 1991. What would be its activity two months earlier? [1988] 1.0 micro curie 0.5 micro
Chapter Nuclei Q1. A radioactive sample with a half life of 1 month has the label: Activity = 2 micro curies on 1 8 1991. What would be its activity two months earlier? [1988] 1.0 micro curie 0.5 micro
Atomic Physics. Chapter 6 X ray. Jinniu Hu 24/12/ /20/13
 Atomic Physics Chapter 6 X ray 11/20/13 24/12/2018 Jinniu Hu 1!1 6.1 The discovery of X ray X-rays were discovered in 1895 by the German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen. He found that a beam of high-speed electrons
Atomic Physics Chapter 6 X ray 11/20/13 24/12/2018 Jinniu Hu 1!1 6.1 The discovery of X ray X-rays were discovered in 1895 by the German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen. He found that a beam of high-speed electrons
Scattering Lecture. February 24, 2014
 Scattering Lecture February 24, 2014 Structure Determination by Scattering Waves of radiation scattered by different objects interfere to give rise to an observable pattern! The wavelength needs to close
Scattering Lecture February 24, 2014 Structure Determination by Scattering Waves of radiation scattered by different objects interfere to give rise to an observable pattern! The wavelength needs to close
energy loss Ionization + excitation of atomic energy levels Mean energy loss rate de /dx proportional to (electric charge) 2 of incident particle
 Lecture 4 Particle physics processes - particles are small, light, energetic à processes described by quantum mechanics and relativity à processes are probabilistic, i.e., we cannot know the outcome of
Lecture 4 Particle physics processes - particles are small, light, energetic à processes described by quantum mechanics and relativity à processes are probabilistic, i.e., we cannot know the outcome of
Neutron interactions and dosimetry. Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland
 Neutron interactions and dosimetry Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland Topics 1. Neutron interactions 1. Scattering 2. Absorption 2. Neutron dosimetry 3. Applications The neutron Uncharged particle, mass close
Neutron interactions and dosimetry Eirik Malinen Einar Waldeland Topics 1. Neutron interactions 1. Scattering 2. Absorption 2. Neutron dosimetry 3. Applications The neutron Uncharged particle, mass close
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis
 Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
Chapter 3: Neutron Activation and Isotope Analysis 3.1. Neutron Activation Techniques 3.2. Neutron Activation of Paintings 3.3. From Qumran to Napoleon 3.4. Neutron Activation with Accelerators 3.5. Isotope
CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions
 CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 10; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 4 Notation Energetics of Nuclear Reactions Reaction Types and Mechanisms
CHEM 312: Lecture 9 Part 1 Nuclear Reactions Readings: Modern Nuclear Chemistry, Chapter 10; Nuclear and Radiochemistry, Chapter 4 Notation Energetics of Nuclear Reactions Reaction Types and Mechanisms
The interaction of radiation with matter
 Basic Detection Techniques 2009-2010 http://www.astro.rug.nl/~peletier/detectiontechniques.html Detection of energetic particles and gamma rays The interaction of radiation with matter Peter Dendooven
Basic Detection Techniques 2009-2010 http://www.astro.rug.nl/~peletier/detectiontechniques.html Detection of energetic particles and gamma rays The interaction of radiation with matter Peter Dendooven
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS)
 CHEM53200: Lecture 10 Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Major reference: Surface Analysis Edited by J. C. Vickerman (1997). 1 Primary particles may be: Secondary particles can be e s, neutral species
CHEM53200: Lecture 10 Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Major reference: Surface Analysis Edited by J. C. Vickerman (1997). 1 Primary particles may be: Secondary particles can be e s, neutral species
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na. Ellen Simmons
 Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
EEE4106Z Radiation Interactions & Detection
 EEE4106Z Radiation Interactions & Detection 2. Radiation Detection Dr. Steve Peterson 5.14 RW James Department of Physics University of Cape Town steve.peterson@uct.ac.za May 06, 2015 EEE4106Z :: Radiation
EEE4106Z Radiation Interactions & Detection 2. Radiation Detection Dr. Steve Peterson 5.14 RW James Department of Physics University of Cape Town steve.peterson@uct.ac.za May 06, 2015 EEE4106Z :: Radiation
PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete
 PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete Written by Jeremy Robinson, Head Instructor Find Out More +Private Instruction +Review Sessions WWW.GRADEPEAK.COM Need Help? Online Private Instruction Anytime, Anywhere
PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete Written by Jeremy Robinson, Head Instructor Find Out More +Private Instruction +Review Sessions WWW.GRADEPEAK.COM Need Help? Online Private Instruction Anytime, Anywhere
Neutron Monochromators. Zahra Yamani Canadian Neutron Beam Centre, Chalk River, Canada
 Neutron Monochromators Zahra Yamani Canadian Neutron Beam Centre, Chalk River, Canada Neutron Scattering Facilities NIST Centre for Neutron Research Canadian Neutron Beam Centre, Chalk River Labs Triple-Axis
Neutron Monochromators Zahra Yamani Canadian Neutron Beam Centre, Chalk River, Canada Neutron Scattering Facilities NIST Centre for Neutron Research Canadian Neutron Beam Centre, Chalk River Labs Triple-Axis
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials
 Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
GAMMA RAY OPTICS. Michael Jentschel Institut Laue-Langevin, Grenoble, France
 GAMMA RAY OPTICS Michael Jentschel Institut Laue-Langevin, Grenoble, France Acknowledgement ILL: W. Urbam M.J Ludwigs Maximilian University Munich D. Habs MPQ Munich M. Guenther Outline Motivation Gamma
GAMMA RAY OPTICS Michael Jentschel Institut Laue-Langevin, Grenoble, France Acknowledgement ILL: W. Urbam M.J Ludwigs Maximilian University Munich D. Habs MPQ Munich M. Guenther Outline Motivation Gamma
The Oxford Solid State Basics
 The Oxford Solid State Basics Steven H. Simon University of Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 About Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.1 What Is Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.2 Why Do We Study Condensed
The Oxford Solid State Basics Steven H. Simon University of Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 About Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.1 What Is Condensed Matter Physics 1 1.2 Why Do We Study Condensed
Chapter 44. Nuclear Structure
 Chapter 44 Nuclear Structure Milestones in the Development of Nuclear Physics 1896: the birth of nuclear physics Becquerel discovered radioactivity in uranium compounds Rutherford showed the radiation
Chapter 44 Nuclear Structure Milestones in the Development of Nuclear Physics 1896: the birth of nuclear physics Becquerel discovered radioactivity in uranium compounds Rutherford showed the radiation
Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter)
 Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Science Physics Department Fourth Grade Nuclear Physics Dr. Ali A. Ridha Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter) Different types of radiation interact
Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Science Physics Department Fourth Grade Nuclear Physics Dr. Ali A. Ridha Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter) Different types of radiation interact
Quantum Mechanics. Exam 3. Photon(or electron) interference? Photoelectric effect summary. Using Quantum Mechanics. Wavelengths of massive objects
 Exam 3 Hour Exam 3: Wednesday, November 29th In-class, Quantum Physics and Nuclear Physics Twenty multiple-choice questions Will cover:chapters 13, 14, 15 and 16 Lecture material You should bring 1 page
Exam 3 Hour Exam 3: Wednesday, November 29th In-class, Quantum Physics and Nuclear Physics Twenty multiple-choice questions Will cover:chapters 13, 14, 15 and 16 Lecture material You should bring 1 page
Lecture 0. NC State University
 Chemistry 736 Lecture 0 Overview NC State University Overview of Spectroscopy Electronic states and energies Transitions between states Absorption and emission Electronic spectroscopy Instrumentation Concepts
Chemistry 736 Lecture 0 Overview NC State University Overview of Spectroscopy Electronic states and energies Transitions between states Absorption and emission Electronic spectroscopy Instrumentation Concepts
