Georgia Online Formative Assessment Resource (GOFAR)
|
|
|
- Wilfred McGee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Water that flows from behind a large dam can cause machines to produce electricity. What change takes place? A)Heat energy changes into mechanical energy. B)Sound energy changes into electrical energy. C)Chemical energy is used to produce electrical energy. D)Mechanical energy is used to produce electrical energy. 2. Through which of the following materials does heat travel the fastest? A)glass B)metal C)plastic D)wood 3. Which of the following is an example of kinetic energy? A)a child jumping rope B)a swimmer ready to dive C)a stuffed toy lying on a table D)firewood stacked in a fireplace 4. When a hair dryer is being used, one of the energy transformations that takes place is A)electrical to chemical. B)electrical to mechanical. C)mechanical to electrical. D)chemical to electrical. 5. When electrical energy is "used" by an electric light, what really happens to the energy? A)It is given off as other forms of energy. B)It changes to matter. C)It stops at the electric light. D)It disappears. 6. A car stopped at the top of a ramp has A)heat energy. B)potential energy. C)kinetic energy. D)mechanical energy. 7. To pull up a bucket of water from a well, George pulled hard on a handle to wind up a rope. Which kind of energy was George applying to the handle? A)chemical energy B)frictional energy C)potential energy Copyright 2015by Georgia Department of Education. Items shall not be used in a third party system or displayed publicly. Page: (2 of 7 )
2 D)mechanical energy 8. Which situation is an example of increasing potential energy? A)pulling a wagon uphill B)emptying a bucket of water C)a cat jumping from a tree D)a bicyclist stopping at a stop sign 9. A pitcher throws a baseball as shown in the diagram below. Which of these has MOSTLY kinetic energy? A)the pitcher B)the ball C)the batter D)the catcher 10. Gasoline, wood, water behind a dam, and a boulder on the edge of a cliff all represent some form of potential energy. What form of potential energy do gasoline and wood have in common? A)heat B)light C)chemical D)mechanical 11. What form of energy is associated with the movement of charges, usually electrons? A)chemical B)electrical C)heat D)sound 12. Burt's mother asked him to use a spoon to stir the stew that was cooking on the stove. Which spoon will stay the coolest while he stirs? A)an iron spoon B)an aluminum spoon C)a wooden spoon D)a silver spoon 13. Which of the following is an example of kinetic energy? Copyright 2015by Georgia Department of Education. Items shall not be used in a third party system or displayed publicly. Page: (3 of 7 )
3 A)A baseball moving from the pitcher to the catcher. B)A rock sitting on the top of a large hill. C)A pendulum at the top of its swing. D)A new flashlight battery. 14. The location on the track where the train has thegreatestpotential energy is A)1. B)2. C)3. D) Students rolled a glass marble and a baseball down an inclined plane, as shown below, and made observations. What is the relationship between the potential and kinetic energy as the objects rolled down the inclined plane? A)As the kinetic energy decreases, the potential energy decreases. B)As the potential energy decreases, the kinetic energy increases. C)When the kinetic energy remained the same, the potential energy increased. Copyright 2015by Georgia Department of Education. Items shall not be used in a third party system or displayed publicly. Page: (4 of 7 )
4 D)When the potential energy remained the same, the kinetic energy increased. 16. What is the negatively charged particle that flows through a circuit? A)electron B)proton C)neutron D)ion 17. Which picture could show the direction of the electrical current in the circuit? A) B) C) D) 18. A(n) circuit has only one path for the current to take. A)open B)parallel C)resistant Copyright 2015by Georgia Department of Education. Items shall not be used in a third party system or displayed publicly. Page: (5 of 7 )
5 D)series 19. A circuit contains four light bulbs. One light bulb goes out but the other three stay lit. This must be a(n) circuit. A)open B)series C)parallel D)resistant 20. In the diagram, what essential part of an electric circuit is missing at position X? A)Load B)On/off switch C)Wires D)Source of electric current Copyright 2015by Georgia Department of Education. Items shall not be used in a third party system or displayed publicly. Page: (6 of 7 )
Hopkins 8th Benchmark Review (Hopkin8BenchmarkReview1)
 Name: Date: 1. Based on the following characteristics, classify the state of matter. A. gas B. solid C. plasma D. liquid high energy found in stars consists of freely moving charged particles 2. What is
Name: Date: 1. Based on the following characteristics, classify the state of matter. A. gas B. solid C. plasma D. liquid high energy found in stars consists of freely moving charged particles 2. What is
2. What would happen to his acceleration if his speed were half? Energy The ability to do work
 1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
Forces and Motion. Vocabulary and Concepts. Name Date
 Edit File Forces and Motion Unit Test Vocabulary and Concepts A push and a pull are two examples of which of the following? a force a power a law of motion a balanced force Which term names a force of
Edit File Forces and Motion Unit Test Vocabulary and Concepts A push and a pull are two examples of which of the following? a force a power a law of motion a balanced force Which term names a force of
Review. 8th grade science STAAR. Name Class. Underline your strong TEKS and circle your weak TEKS: 8.6A Unbalanced Forces
 8th grade science STAAR Review Name Class Underline your strong TEKS and circle your weak TEKS: 8.6A Unbalanced Forces 8.6B Speed, Velocity, & Acceleration 8.6C Newton s Laws 7.7A Work 6.8A Potential and
8th grade science STAAR Review Name Class Underline your strong TEKS and circle your weak TEKS: 8.6A Unbalanced Forces 8.6B Speed, Velocity, & Acceleration 8.6C Newton s Laws 7.7A Work 6.8A Potential and
5 Which of the following is a compound? 6 Erik poured a cup of water onto a pile of dirt, 7 The picture shows the mass, in grams (g), of a
 1 The equation below illustrates a chemical process that involves the elements carbon and oxygen. C + O 2 CO 2 What does this model of a chemical equation illustrate? A. the structure of an atom B. the
1 The equation below illustrates a chemical process that involves the elements carbon and oxygen. C + O 2 CO 2 What does this model of a chemical equation illustrate? A. the structure of an atom B. the
L-8-5 (L-8-5) 1. This graph shows the velocity of a car. Which statement BEST explains how the car is moving?
 Name: Date: 1. This graph shows the velocity of a car. Which statement BEST explains how the car is moving? A. Velocity is increasing, so the car is accelerating. B. Velocity is decreasing, so the car
Name: Date: 1. This graph shows the velocity of a car. Which statement BEST explains how the car is moving? A. Velocity is increasing, so the car is accelerating. B. Velocity is decreasing, so the car
Physics Test Review: Mechanics Session: Name:
 Directions: For each statement or question, write in the answer box, the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The diagram below
Directions: For each statement or question, write in the answer box, the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The diagram below
STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA
 1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
SCI-4 Kaechele_Dix_4.2 force,energy,motion Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-4 Kaechele_Dix_4.2 force,energy,motion Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:21HKN0 1 Speed is a measure of A motion B force C science D solid 2 A boy helped his neighbors pack
SCI-4 Kaechele_Dix_4.2 force,energy,motion Test Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:21HKN0 1 Speed is a measure of A motion B force C science D solid 2 A boy helped his neighbors pack
Georgia Online Formative Assessment Resource (GOFAR) S8P3 SR
 S8P3 SR Name: Date: displayed publicly. Page: (1 of 16 ) Q 1. Shaina uses a shovel to dig a hole to plant a tree. A shovel is an example of a compound machine because it is made up of what two simple machines?
S8P3 SR Name: Date: displayed publicly. Page: (1 of 16 ) Q 1. Shaina uses a shovel to dig a hole to plant a tree. A shovel is an example of a compound machine because it is made up of what two simple machines?
Test Booklet. Subject: SC, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics. Student name:
 Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Test ooklet Subject: S, Grade: HS 2008 Grade High School Physics Student name: uthor: North arolina istrict: North arolina Released Tests Printed: Monday July 09, 2012 1 n object is launched across a room.
Work, Power and Energy Worksheet. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a kg pencil 0.25 m against a force of 23 N.
 Work, Power and Energy Worksheet Work and Power 1. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a 0.025 kg pencil 0.25 m against a
Work, Power and Energy Worksheet Work and Power 1. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a 0.025 kg pencil 0.25 m against a
Energy Unit Test * Required
 Energy Unit Test * Required 1. First and Last Name 2. Class Period 2nd 4th Forms of Energy Standard 6.PS3.1 Analyze the properties and compare sources of kinetic, elastic potential, gravitational potential,
Energy Unit Test * Required 1. First and Last Name 2. Class Period 2nd 4th Forms of Energy Standard 6.PS3.1 Analyze the properties and compare sources of kinetic, elastic potential, gravitational potential,
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic
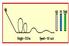 Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Conservation of Energy Review
 onservation of Energy Review Name: ate: 1. An electrostatic force exists between two +3.20 10 19 -coulomb point charges separated by a distance of 0.030 meter. As the distance between the two point charges
onservation of Energy Review Name: ate: 1. An electrostatic force exists between two +3.20 10 19 -coulomb point charges separated by a distance of 0.030 meter. As the distance between the two point charges
4.) A baseball that weighs 1.6 N leaves a bat with a speed of 40.0 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball. 130 J
 AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
FORCES AND MOTION UNIT TEST. Multiple Choice: Draw a Circle Completely around the ONE BEST answer.
 Name: Date: Period: FORCES AND MOTION UNIT TEST Multiple Choice: Draw a Circle Completely around the ONE BEST answer. 1. A force acting on an object does no work if a. a machine is used to move the object.
Name: Date: Period: FORCES AND MOTION UNIT TEST Multiple Choice: Draw a Circle Completely around the ONE BEST answer. 1. A force acting on an object does no work if a. a machine is used to move the object.
Momentum, Work and Energy Review
 Momentum, Work and Energy Review 1.5 Momentum Be able to: o solve simple momentum and impulse problems o determine impulse from the area under a force-time graph o solve problems involving the impulse-momentum
Momentum, Work and Energy Review 1.5 Momentum Be able to: o solve simple momentum and impulse problems o determine impulse from the area under a force-time graph o solve problems involving the impulse-momentum
Physical Science Unit Exam Review. Date Period
 1. Give an example of gravitational potential energy. Frog at the top of its jump Rock at the edge of a hill Skateboarder at the top of the ramp Pendulum at the top of its swing 2. Use Newton s 2 nd law
1. Give an example of gravitational potential energy. Frog at the top of its jump Rock at the edge of a hill Skateboarder at the top of the ramp Pendulum at the top of its swing 2. Use Newton s 2 nd law
Energy can be transformed in to: Mechanical Electrical Thermal Light Sound
 Energy and Force Study Guide CBA 2 STANDARD 5.6A Explore the uses of energy, including mechanical, light, thermal, electrical, and sound energy 5.6B demonstrate that the flow of electricity in circuits
Energy and Force Study Guide CBA 2 STANDARD 5.6A Explore the uses of energy, including mechanical, light, thermal, electrical, and sound energy 5.6B demonstrate that the flow of electricity in circuits
AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name
 AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two objects, one of mass m and the other
AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two objects, one of mass m and the other
Practice - Work. b. Explain the results obtained in part (a).
 Practice - Work 1. A weight lifter, Paul Anderson, used a circular platform attached to a harness to lift a class of 30 children and their teacher. While the children and teacher sat on the platform, Paul
Practice - Work 1. A weight lifter, Paul Anderson, used a circular platform attached to a harness to lift a class of 30 children and their teacher. While the children and teacher sat on the platform, Paul
SPH4U Sample Test - Momentum and Energy
 SPH4U Sample Test - Momentum and Energy Modified True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement
SPH4U Sample Test - Momentum and Energy Modified True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement
3rd Grade Motion and Stability
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction from patterns
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction from patterns
GPE = m g h. GPE = w h. k = f d. PE elastic = ½ k d 2. Work = Force x distance. KE = ½ m v 2
 1 NAME PERIOD PHYSICS GUIDESHEET ENERGY CONVERSIONS POTENTIAL AND KINETIC ENERGY ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT CLASS OVERHEAD NOTES (5 pts/page) (Plus 5 pts/page for sample questions)
1 NAME PERIOD PHYSICS GUIDESHEET ENERGY CONVERSIONS POTENTIAL AND KINETIC ENERGY ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT CLASS OVERHEAD NOTES (5 pts/page) (Plus 5 pts/page for sample questions)
Physics Semester 1 Review
 Physics Semester 1 Review Name: 1. Define: Speed Velocity Acceleration Use the graph to the right to answer questions 2-4. 2. How far did the object travel in 3 seconds? 3. How long did it take for the
Physics Semester 1 Review Name: 1. Define: Speed Velocity Acceleration Use the graph to the right to answer questions 2-4. 2. How far did the object travel in 3 seconds? 3. How long did it take for the
Name: Class: 903 Active Physics Winter Break Regents Prep December 2014
 In this section use the following equations for velocity and displacement to solve: 1. In a drill during basketball practice, a player runs the length of the 30.meter court and back. The player does this
In this section use the following equations for velocity and displacement to solve: 1. In a drill during basketball practice, a player runs the length of the 30.meter court and back. The player does this
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
3rd Grade. Forces and Motion Review. Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106. Slide 4 / 106. Slide 3 / 106. Slide 5 / 106. Slide 6 / 106. Motion and Stability
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Slide 4 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 3rd Grade Motion and Stability 2015-11-09 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 106 Slide 4 / 106 Table of Contents Forces and Motion Review Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Motion prediction
Name: Block: Unit 5 Problems: Energy
 5A: Types of Energy and 5B: Kinetic and Gravitational Potential Energy 1) What type(s) of energy are present in each of the following scenarios? a) Christmas tree lights are powered by a 12 V battery.
5A: Types of Energy and 5B: Kinetic and Gravitational Potential Energy 1) What type(s) of energy are present in each of the following scenarios? a) Christmas tree lights are powered by a 12 V battery.
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
2014 Physics Exam Review
 Name: ate: 1. The diagrams below show a model airplane. Which energy transformation occurs in a rubber band powered model airplane when it is flown?. Thermal energy stored in the rubber band is transformed
Name: ate: 1. The diagrams below show a model airplane. Which energy transformation occurs in a rubber band powered model airplane when it is flown?. Thermal energy stored in the rubber band is transformed
Energy. Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Energy Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 1 Energy is a substance like quantity that can cause change. Makes objects move. Makes things stop. Is needed to do work.
Energy Copyright 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings 1 Energy is a substance like quantity that can cause change. Makes objects move. Makes things stop. Is needed to do work.
Physics Midterm Review KEY
 Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
( ) Physics 201, Final Exam, Fall 2006 PRACTICE EXAMINATION Answer Key. The next three problems refer to the following situation:
 Physics 201, Final Exam, Fall 2006 PRACTICE EXAMINATION Answer Key The next three problems refer to the following situation: Two masses, m 1 and m 2, m 1 > m 2, are suspended by a massless rope over a
Physics 201, Final Exam, Fall 2006 PRACTICE EXAMINATION Answer Key The next three problems refer to the following situation: Two masses, m 1 and m 2, m 1 > m 2, are suspended by a massless rope over a
Q2. A book whose mass is 2 kg rests on a table. Find the magnitude of the force exerted by the table on the book.
 AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems FACT: Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in state of motion. A change in state of motion means a change in an object s velocity, therefore
Potential and Kinetic Energy
 Potential and Kinetic Energy VELOCITY Velocity is a measure of how fast an object is traveling in a certain direction. Example: A bus traveling North at 150 m/s Example: A car is traveling 45 mph South.
Potential and Kinetic Energy VELOCITY Velocity is a measure of how fast an object is traveling in a certain direction. Example: A bus traveling North at 150 m/s Example: A car is traveling 45 mph South.
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Science Physics Energy and Power Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. A woman wants to lift a 10.0-kg rock from the ground to a height of 8.0 m. What is the minimum
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Science Physics Energy and Power Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. A woman wants to lift a 10.0-kg rock from the ground to a height of 8.0 m. What is the minimum
STUDENT NAME DATE ID GRADE 3 SCIENCE
 STUENT NME TE I GRE 3 SIENE dministered ecember 2005 IRETIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. e sure to mark all of your answers. SMPLE Objects That onduct Heat Objects That o Not onduct
STUENT NME TE I GRE 3 SIENE dministered ecember 2005 IRETIONS Read each question and choose the best answer. e sure to mark all of your answers. SMPLE Objects That onduct Heat Objects That o Not onduct
visible light, radio waves, ultra violet light, x-rays, gamma rays
 Energy- Forces Motion Forms of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. There are many forms of energy The sun is a major source of energy for earth. Form of Energy Source Examples Mechanical
Energy- Forces Motion Forms of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. There are many forms of energy The sun is a major source of energy for earth. Form of Energy Source Examples Mechanical
3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy
 3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy STEMscopedia Forms of Energy Addressed Benchmarks: SC.3.P.10.1: Identify some basic forms of energy, such as light, heat, thermal, sound, electrical, and mechanical. SC.3.P.10.2:
3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy STEMscopedia Forms of Energy Addressed Benchmarks: SC.3.P.10.1: Identify some basic forms of energy, such as light, heat, thermal, sound, electrical, and mechanical. SC.3.P.10.2:
1. (P2.1A) The picture below shows a ball rolling along a table at 1 second time intervals. What is the object s average velocity after 6 seconds?
 PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
PHYSICS FINAL EXAM REVIEW FIRST SEMESTER (01/2017) UNIT 1 Motion P2.1 A Calculate the average speed of an object using the change of position and elapsed time. P2.1B Represent the velocities for linear
Projectile motion. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 5/20/14. Identify examples of projectile motion.
 Projectile motion Objectives Identify examples of projectile motion. Solve projectile motion problems. problems Graph the motion of a projectile. 1. Which of the events described below cannot be an example
Projectile motion Objectives Identify examples of projectile motion. Solve projectile motion problems. problems Graph the motion of a projectile. 1. Which of the events described below cannot be an example
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Energy: The ability to do work and the ability to cause change
 Notes: Energy Energy: The ability to do work and the ability to cause change Work: occurs when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force -Work and Energy are expressed in joules (J)
Notes: Energy Energy: The ability to do work and the ability to cause change Work: occurs when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force -Work and Energy are expressed in joules (J)
Mechanical Energy Thermal Energy Chemical Energy Electrical Energy Electromagnetic Energy
 Physical Science PHYSICS UNIT 4 Study Guide. Chapter 15 - Energy Key Terms Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Gravitational Potential Elastic Potential Mechanical Energy Thermal Energy Chemical Energy Electrical
Physical Science PHYSICS UNIT 4 Study Guide. Chapter 15 - Energy Key Terms Energy Kinetic Energy Potential Gravitational Potential Elastic Potential Mechanical Energy Thermal Energy Chemical Energy Electrical
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY
 UNIT 1 - ENERGY SECTION 1 - Background Information Energy can be in one of two states: potential or kinetic. Energy can be transferred from potential to kinetic and between objects. Potential energy is
UNIT 1 - ENERGY SECTION 1 - Background Information Energy can be in one of two states: potential or kinetic. Energy can be transferred from potential to kinetic and between objects. Potential energy is
Efficiency = power out x 100% power in
 Work, Energy and Power Review Package 1) Work: change in energy. Measured in Joules, J. W = Fd W = ΔE Work is scalar, but can be negative. To remember this, ask yourself either: Is the object is losing
Work, Energy and Power Review Package 1) Work: change in energy. Measured in Joules, J. W = Fd W = ΔE Work is scalar, but can be negative. To remember this, ask yourself either: Is the object is losing
STUDENT PACKET # 9 Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics
 STUDENT PACKET # 9 Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics Name: Date: Reporting Category: Physical Science Benchmark SC.7.P.11.2 Investigate and describe the transformation of energy from one form
STUDENT PACKET # 9 Student Exploration: Roller Coaster Physics Name: Date: Reporting Category: Physical Science Benchmark SC.7.P.11.2 Investigate and describe the transformation of energy from one form
Name Period Date. D) density. E) speed.
 Pre-Test - Post-Test 1. In physics, work is defined as. A) force divided by time. B) force times distance. C) distance divided by time. D) force times time. E) force divided by distance. 2. Potential energy
Pre-Test - Post-Test 1. In physics, work is defined as. A) force divided by time. B) force times distance. C) distance divided by time. D) force times time. E) force divided by distance. 2. Potential energy
Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy
 Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy Author: Matthew Kurth Grade Level: pre-ap 6 th grade Science (45 minute class) Sources: CPO Science (Force and Motion) o Curriculum
Calculating Average Speed and Comparing Kinetic and Potential Energy Author: Matthew Kurth Grade Level: pre-ap 6 th grade Science (45 minute class) Sources: CPO Science (Force and Motion) o Curriculum
Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation
 Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled
Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled
Electromagnetism Review Sheet
 Electromagnetism Review Sheet Electricity Atomic basics: Particle name Charge location protons electrons neutrons + in the nucleus - outside of the nucleus neutral in the nucleus What would happen if two
Electromagnetism Review Sheet Electricity Atomic basics: Particle name Charge location protons electrons neutrons + in the nucleus - outside of the nucleus neutral in the nucleus What would happen if two
CHAPTER 5. Chapter 5, Energy
 CHAPTER 5 2. A very light cart holding a 300-N box is moved at constant velocity across a 15-m level surface. What is the net work done in the process? a. zero b. 1/20 J c. 20 J d. 2 000 J 4. An rock is
CHAPTER 5 2. A very light cart holding a 300-N box is moved at constant velocity across a 15-m level surface. What is the net work done in the process? a. zero b. 1/20 J c. 20 J d. 2 000 J 4. An rock is
Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum
 Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC 112.39(c). 4.01 Newton s First Law Physics (4)(D) 4.02 Newton
Section 4: Newton s Laws and Momentum The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Physics TAC 112.39(c). 4.01 Newton s First Law Physics (4)(D) 4.02 Newton
AP Physics II Summer Packet
 Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
Physics 010 Assignments This document contains the five homework assignments given in the Physics 010 course in
 Physics 010 Assignments 2007-2008 This document contains the five homework assignments given in the Physics 010 course in 2007-2008. Physics 010 Assignment #1 1. A car is traveling along a straight road.
Physics 010 Assignments 2007-2008 This document contains the five homework assignments given in the Physics 010 course in 2007-2008. Physics 010 Assignment #1 1. A car is traveling along a straight road.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
1. (P2.2D) Describe the acceleration and speed of an object that is experiencing uniform circular motion.
 UNIT 5 Periodic Motion P2.2D P3.4D P3.6B P3.6d P3.6e P2.1h P2.2f State that uniform circular motion involves acceleration without a change in speed. Identify the force(s) acting on objects moving with
UNIT 5 Periodic Motion P2.2D P3.4D P3.6B P3.6d P3.6e P2.1h P2.2f State that uniform circular motion involves acceleration without a change in speed. Identify the force(s) acting on objects moving with
2 possibilities. 2.) Work is done and... 1.) Work is done and... *** The function of work is to change energy ***
 Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
Chapter 05 Test A. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Chapter 05 Test A Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The SI unit of force preferred by scientists is the: a. kilogram. b. newton.
Class: Date: Chapter 05 Test A Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The SI unit of force preferred by scientists is the: a. kilogram. b. newton.
Physics Fundamentals Study Guide
 Physics Fundamentals Study Guide Items to gather: 1. Any colorful helpful unit sheets 2. All Friday quizzes 3. All free responses from tests On the Day of the Final: May Items to bring: 1. Calculator (using
Physics Fundamentals Study Guide Items to gather: 1. Any colorful helpful unit sheets 2. All Friday quizzes 3. All free responses from tests On the Day of the Final: May Items to bring: 1. Calculator (using
produce sugar, which contains stored chemical energy. Most of the energy that we use on Earth originally came from the Sun.
 Conservation of Energy Energy can be in many different forms. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (energy that is
Conservation of Energy Energy can be in many different forms. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (energy that is
Lesson 40: Conservation of Energy
 Lesson 40: Conservation of Energy Total Mechanical Energy We sometimes call the total energy of an object (potential and kinetic) the total mechanical energy of an object. Mechanical energy doesn t mean
Lesson 40: Conservation of Energy Total Mechanical Energy We sometimes call the total energy of an object (potential and kinetic) the total mechanical energy of an object. Mechanical energy doesn t mean
Lesson 40: Conservation of Energy
 Lesson 40: Conservation of Energy A large number of questions you will do involve the total mechanical energy of a system. As pointed out earlier, the mechanical energy is just the total of all types of
Lesson 40: Conservation of Energy A large number of questions you will do involve the total mechanical energy of a system. As pointed out earlier, the mechanical energy is just the total of all types of
Physics 11 Review Questions
 Physics 11 Review Questions Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled by the
Physics 11 Review Questions Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled by the
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
UNIT 5: WORK and ENERGY RECORD ALL ANSWERS ON ANSWER SHEET.
 PHYSICAL SCIENCE UNIT 5: WORK and ENERGY RECORD ALL ANSWERS ON ANSWER SHEET. name 1. Which of the following processes requires the most work? a. A 10 kg weight rests on a table. b. A person holds a 1 kg
PHYSICAL SCIENCE UNIT 5: WORK and ENERGY RECORD ALL ANSWERS ON ANSWER SHEET. name 1. Which of the following processes requires the most work? a. A 10 kg weight rests on a table. b. A person holds a 1 kg
Exam. Name. 1) For general projectile motion with no air resistance, the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity A) B) C) D)
 Exam Name 1) For general projectile motion with no air resistance, the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity 2) An athlete participates in an interplanetary discus throw competition during an
Exam Name 1) For general projectile motion with no air resistance, the horizontal component of a projectile's velocity 2) An athlete participates in an interplanetary discus throw competition during an
PINBALL MACHINE HOW SCIENTIFIC IS A PINBALL MACHINE? WRITTEN AND CREATED BY: KATHRYN WILMOT JAYCE GRUPPEN LUKE HULSMAN
 PINBALL MACHINE HOW SCIENTIFIC IS A PINBALL MACHINE? WRITTEN AND CREATED BY: LUKE HULSMAN KATHRYN WILMOT JAYCE GRUPPEN Table of Contents Chapter Author Page Marbles on a ramp Kathryn Wilmot 3 Making a
PINBALL MACHINE HOW SCIENTIFIC IS A PINBALL MACHINE? WRITTEN AND CREATED BY: LUKE HULSMAN KATHRYN WILMOT JAYCE GRUPPEN Table of Contents Chapter Author Page Marbles on a ramp Kathryn Wilmot 3 Making a
Section 2. Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down. What Do You See? What Do You Think?
 Thrills and Chills Section Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards: Additional Benchmarks met in Section SC.91.N..4
Thrills and Chills Section Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards: Additional Benchmarks met in Section SC.91.N..4
Equation Sheet for Physics 103 Midterm 1 W = F D. E pot = M g h. E kin = _ M v 2
 Equation Sheet for Physics 103 Midterm 1 Efficiency = Useful Energy Out Total Energy In Efficiency F = M a F = M g s = D t Work Eff = Work out in G M1 M F = 2 D W = F D E pot = M g h E kin = _ M v 2 2
Equation Sheet for Physics 103 Midterm 1 Efficiency = Useful Energy Out Total Energy In Efficiency F = M a F = M g s = D t Work Eff = Work out in G M1 M F = 2 D W = F D E pot = M g h E kin = _ M v 2 2
ì<(sk$m)=bdjabj< +^-Ä-U-Ä-U
 Physical Science Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Captions Labels Call Outs Glossary Motion Scott Foresman Science 4.15 ì
Physical Science Genre Comprehension Skill Text Features Science Content Nonfiction Sequence Captions Labels Call Outs Glossary Motion Scott Foresman Science 4.15 ì
Name Physical Science Final Core Exam Student Study Guide
 Name Physical Science Final Core Exam Student Study Guide Your Physical Science Final Exam addresses the basic study of Physics including the Scientific Method and Laboratory Techniques and Safety. The
Name Physical Science Final Core Exam Student Study Guide Your Physical Science Final Exam addresses the basic study of Physics including the Scientific Method and Laboratory Techniques and Safety. The
Chapter 8: Energy. P = W t. KE = 1 2 mv2. PE = mgh. Text: Chapter 8 (skip sections 8.7 to 8.9) Think and Explain: 1-4 Think and Solve: 1-3
 Text: Chapter 8 (skip sections 8.7 to 8.9) Think and Explain: 1-4 Think and Solve: 1-3 Chapter 8: Energy NAME: Vocabulary: Work, energy, Joule, Watt, kinetic energy, potential energy, mechanical energy,
Text: Chapter 8 (skip sections 8.7 to 8.9) Think and Explain: 1-4 Think and Solve: 1-3 Chapter 8: Energy NAME: Vocabulary: Work, energy, Joule, Watt, kinetic energy, potential energy, mechanical energy,
Name Date P Lesson 4 Forces and Simple Machines
 Lesson 4 Forces and Simple Machines OAA Science Lesson 4 40 Lesson 4: Forces and Simple Machines Student s Reference Sheet: 6 Simple Machines: Screw - Swivel Stool - Spiral Stair Case - Inclined Plane
Lesson 4 Forces and Simple Machines OAA Science Lesson 4 40 Lesson 4: Forces and Simple Machines Student s Reference Sheet: 6 Simple Machines: Screw - Swivel Stool - Spiral Stair Case - Inclined Plane
Energy can change from one form to another without a net loss or gain.
 Energy can change from one form to another without a net loss or gain. Energy may be the most familiar concept in science, yet it is one of the most difficult to define. We observe the effects of energy
Energy can change from one form to another without a net loss or gain. Energy may be the most familiar concept in science, yet it is one of the most difficult to define. We observe the effects of energy
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
Chapter 4 Conservation Laws
 Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 4 Conservation Laws Section Review 4.1 1. List three action and reaction pairs in the picture at right, on page 82 in text. a. Force of paddle on water, and
Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 4 Conservation Laws Section Review 4.1 1. List three action and reaction pairs in the picture at right, on page 82 in text. a. Force of paddle on water, and
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy?
 Name: Date: 1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy? A) a drum of diesel fuel on a parked truck B) a stationary pendulum C) a satellite in geosynchronous
Name: Date: 1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy? A) a drum of diesel fuel on a parked truck B) a stationary pendulum C) a satellite in geosynchronous
Name: ANSWER KEY Quarter 3 Benchmark Review. 3. m/s km/hr. 7. (Vf Vi) / t. 8. m/s m/s F = ma
 Name: ANSWER KEY Quarter 3 Benchmark Review Velocity 1. Define Velocity: Date: Period: 1. Distance divided by time in a specific direction 2. What is the difference between speed and velocity? 2. Velocity
Name: ANSWER KEY Quarter 3 Benchmark Review Velocity 1. Define Velocity: Date: Period: 1. Distance divided by time in a specific direction 2. What is the difference between speed and velocity? 2. Velocity
FORCE AND MOTION. Conceptual Questions F G as seen in the figure. n, and a kinetic frictional force due to the rough table surface f k
 FORCE AND MOTION 5 Conceptual Questions 5.1. Two forces are present, tension T in the cable and gravitational force 5.. F G as seen in the figure. Four forces act on the block: the push of the spring F
FORCE AND MOTION 5 Conceptual Questions 5.1. Two forces are present, tension T in the cable and gravitational force 5.. F G as seen in the figure. Four forces act on the block: the push of the spring F
Dynamics-Newton's 2nd Law
 1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
1. A constant unbalanced force is applied to an object for a period of time. Which graph best represents the acceleration of the object as a function of elapsed time? 2. The diagram below shows a horizontal
Today: Chapter 7 -- Energy
 Today: Chapter 7 -- Energy Energy is a central concept in all of science. We will discuss how energy appears in different forms, but cannot be created or destroyed. Some forms are more useful than others
Today: Chapter 7 -- Energy Energy is a central concept in all of science. We will discuss how energy appears in different forms, but cannot be created or destroyed. Some forms are more useful than others
A) more mass and more inertia C) the same as the magnitude of the rock's weight C) a man standing still on a bathroom scale
 1. A 15-kilogram cart is at rest on a horizontal surface. A 5-kilogram box is placed in the cart. Compared to the mass and inertia of the cart, the cart-box system has A) more mass and more inertia B)
1. A 15-kilogram cart is at rest on a horizontal surface. A 5-kilogram box is placed in the cart. Compared to the mass and inertia of the cart, the cart-box system has A) more mass and more inertia B)
Name. Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL KINETIC
 KINETIC Name Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL Name Period Work and Energy Intro questions Read chapter 9 pages 144 146 (Section 9.1) 1. Define work in terms of physics? 2. In order to do work on an object,
KINETIC Name Honors Physics AND POTENTIAL Name Period Work and Energy Intro questions Read chapter 9 pages 144 146 (Section 9.1) 1. Define work in terms of physics? 2. In order to do work on an object,
RELEASED. Go to next page. 2. The graph shows the acceleration of a car over time.
 1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
1. n object is launched across a room. How can a student determine the average horizontal velocity of the object using a meter stick and a calculator? The student can calculate the object s initial potential
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
Force and Motion Test 2 Review
 Force and Motion Test 2 Review Name: S8P5a. Investigate and explain that electric currents and magnets can exert force on each other. 1. What happens to a compass needle when it is placed next to a wire
Force and Motion Test 2 Review Name: S8P5a. Investigate and explain that electric currents and magnets can exert force on each other. 1. What happens to a compass needle when it is placed next to a wire
Kindergarten. Energy. Slide 1 / 33 Slide 2 / 33. Slide 3 / 33. Slide 4 / 33. Slide 6 / 33. Slide 5 / 33. Energy. Teacher Page.
 Slide 1 / 33 Slide 2 / 33 Kindergarten 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 33 Table of Contents Slide 4 / 33 Types of Transfer Click on the topic to go to that section This presentation is designed to be
Slide 1 / 33 Slide 2 / 33 Kindergarten 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 33 Table of Contents Slide 4 / 33 Types of Transfer Click on the topic to go to that section This presentation is designed to be
Lesson 1: How can you describe motion?
 Lesson 1 Summary Use with pp. 407 409 Lesson 1: How can you describe motion? Vocabulary velocity the speed and direction of an object s motion Types of Motion Motion is movement. When you see something
Lesson 1 Summary Use with pp. 407 409 Lesson 1: How can you describe motion? Vocabulary velocity the speed and direction of an object s motion Types of Motion Motion is movement. When you see something
Energy Notes. Name: Hr:
 Energy Notes Name: Hr: Guided Outline 5-1 Nature of Energy Directions: As you read through Chapter 5 in your textbook, fill in the missing information. I. Section 1: Nature of Energy A. What is Energy?
Energy Notes Name: Hr: Guided Outline 5-1 Nature of Energy Directions: As you read through Chapter 5 in your textbook, fill in the missing information. I. Section 1: Nature of Energy A. What is Energy?
Name Period Date. Record all givens, draw a picture, arrow all vectors, write the formula, substitute and solve. units
 Example Problems 5.1 Force and Acceleration E1. A monkey pushes his pet lemur in a wagon with a net force of 38 N. If the mass of the lemur and wagon combined is 57 kg, calculate the acceleration of the
Example Problems 5.1 Force and Acceleration E1. A monkey pushes his pet lemur in a wagon with a net force of 38 N. If the mass of the lemur and wagon combined is 57 kg, calculate the acceleration of the
