ELEG 479 Lecture #6. Mark Mirotznik, Ph.D. Associate Professor The University of Delaware
|
|
|
- Gavin Norton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELEG 479 Lecture #6 Mark Mirotznik, Ph.D. Associate Professor The University of Delaware
2 Summary of Last Lecture X-ray Physics What are X-rays and when are they useful for medical imaging? How are X-rays generated? How do X-rays interact with matter (tissue)? How do we detect X-rays How do we mathematically model X-ray projection radiography
3 X-rays Wavelength: nm Frequency: 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz (3x10 16 to 3x10 19 ) Energies: 120 ev to 120 kev Soft X-rays: Hard X-rays: 0.12 kev to 30 kev 30 kev to 120 kev Soft X-rays do not penetrate matter where hard X-rays do
4
5 Interaction of Photons with Matter
6
7 Interaction of Photons with Matter: Attenuation x I o µ I
8 Interaction of Photons with Matter: Attenuation Lower energies can distinguish different material better than higher energies
9
10
11 Interaction of Photons with Matter: Attenuation x I o µ(x) I(x)
12 Interaction of Photons with Matter: Attenuation x S o (E) µ(x,e) I(x)
13
14
15 * FDA Study
16 & Inevitable problems of not fully understanding the effects of ionizing radiation
17 Today s Lecture Projection Radiography Overview of different systems for projection radiography Instrumentation Overall system layout X-ray sources grids and filters detectors Imaging Equations Basic equations Geometrical distortions More complicated imaging equations
18 Projection Radiography Traditional chest x-ray 2-3 mrem ~100 kev Static X-ray Systems (snap shots) Traditional dental x-ray 2-3 mrem kev Mammography 70 mrem ~30 kev
19 Digital Fluoroscopy 10 mrem/min ~50 kev Projection Radiography Dynamic X-ray Systems (Fluoroscopic) Angiogram 460-1,580 mrem ~50 kev Barium Colon Image 700 mrem ~30 kev
20 Projection Radiography Some new stuff Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
21 Projection Radiography Generic System Description
22 xrays
23 Amount of radiation for a fixed voltage is proportional to the current in the tube. Radiation exposure is often given in units of mas (milliampere-seconds). This gives an idea of how much current was used in the tube for how long. While mas is usually proportional to dose (rems or rads) it is not easy to equate the two however
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 X-Ray Detectors Screen or Film Image Intensifier Storage Phosphors Direct Flat Panel Radiography
31 X-Ray Detectors
32
33
34
35
36
37 X-Ray Detectors What do we do in dynamic systems that can t use film?
38
39
40 10 x12 85 micron pixel pitch 3600 x 3000 pixels (10.8 Mpixels)
41
42 Quiz #1: March 18 th, 2014 (1) Determine the transfer function of an imaging system defined by the following PSF x y h ( x, y) = rect(, ) 2 2 Recall: rect( p, q) = 1 p < 0.5, q < 0 else 0.5 (2) Calculate the value of the transfer function at u=0.25 rad/cm and v=0.25 rad/cm. In words tell me what the value you just calculated means physically. Equations: H ( u, v) = h( x, y) = h( x, y) e H ( u, v) e j2π j2π ( ux+ vy ) ( ux+ vy ) dxdy dudv
43 Quiz #1: March 18 th, 2014 (1) Determine the transfer function of an imaging system defined by the following PSF Recall: rect( p, q) H ( u, v) = = = = = h ( x, y) = 1 p < 0.5, q < 0.5 = 0 else πju e e j2π h( x, y) e j2π ( ux+ vy) x rect(, 2 y ) 2 ( ux+ vy) j2π ( ux) 1 j2π ( vy) [ e dx] [ e dy] j2π ( u ) j2π ( u ) 1 j2π ( v) j2π ( v) [ e e ] e e ( u ) j2π ( u ) j2π ( v) j2π ( v) e 2πju j2π dxdy e dxdy 2πjv e 2πjv 2 j sin(2πu) 2 j sin(2πv) 2πju 2πjv = [ ] = 4 sin c(2π u) sin c(2π v)
44 Quiz #1: March 18 th, 2014 (2) Calculate the value of the transfer function at u=0.25 rad/cm and v=0.25 rad/cm. In words tell me what the value you just calculated means physically. H ( u, v) = 4 sin c(2π u) sin c(2π v) H (0.25,0.25) = 4 sin c(2π 0.25) sin c(2π 0.25) sin( π / 2) sin( π / 2) 16 = 4 = 2 π / 2 π / 2 π If a sinusoidal input of spatial frequencies u=0.25 rad/cm and v=0.25 rad/cm is inputted into the system the output s magnitude will be 16/pi^2 less and in phase.
45
46 Monochromatic = ), ( 0 ), ; ( ), ( y x r ds y x s I o e y x I µ Polychromatic ' ),, ; ( ' ' ), ( 0 ' max min ) ( ), ( de e E E S y x I y x r ds E y x s E E o = µ
47
48 I = I e min ( ) o I o I = I e max Local contrast: Global contrast: ( ) o I o C l = C = I I I I I max min = max max I + I max min = min
49 I = I e min ( ) o I o I = I e max Local contrast: Global contrast: ( ) o I o C l = C = I I I I I max min = max max I + I max min = min
50 Geometric Effects X-rays are diverging from source Undesirable effects cos 3 (θ) fall off in intensity across detector magnification
51 Geometric Effects
52 I s = photon flux at source I o = photon flux at detector origin I r = photon flux at (x,y) point on detector
53
54 Inverse Square Law +Obliquity How big of a deal is this?
55 Inverse Square Law +Obliquity How big of a deal is this? Depends on (1) how far away is the detector from the source and (2) how large of a field of view are we looking at.
56 Inverse Square Law +Obliquity Example How big of a deal is this? Depends on (1) how far away is the detector from the source and (2) how large of a field of view are we looking at. Chest x-ray system has a detector of 18 x 18 The source is placed a distance of 6 (72 ) away What is the maximum change in intensity across the detector? 1 9 θ = tan ( ) = cos( θ ) = I = I min o o Usually not that big of a problem
57 Path Length Variation Uniform (or homogenous) slab of material. Since the rays are going at different angles the amount of material they go through varies depending on the location through the tissue. This difference in path length means more attenuation for points away from the origin.
58 Path Length Variation This results in a prism effect if you are imaging a cube. How big of a deal is this?
59 Inverse Square Law +Obliquity+Path Length I d ( x, y) = I o cos 3 ( θ ) e µ L / cosθ
60
61 x d = x z ' o x ' = x z d o = x M ( z)
62 ) ( ) ( ' ' z M y d z y y z M x d z x x o o = = = = ) ) (, ) ( ( ) ( cos ), ( 3 z M y z M x t I y x I z o d = θ ), ( ' ' y x t z Let transmittvity given as Then at the detector we get ), ( ) ( ), ( d yz d xz t y x d d I y x I z o d + + = After substitution we get: be transmission through an infinitely thin object (e.g. thin piece of paper with a lead pattern printed on it)
63 Not done yet! There are additional factors (1) X-rays source are not really a point source but an extended source. This causes blurring (2)X-ray films are not perfect! A single x-ray photon causes a blurry spot on the film. This is equivalent to the impulse response or PSF of the film h(x,y)
64 When we add all that together ), ( ), (, 4 1 ) ( cos ), ( y x h M y M x t m y m x s m d I y x I z o d = π θ Inverse square +obliquity Extended source m=source magnification s=source intensity distribution. Transmittivity of object PSF of film M m z d M o = = 1 where
1-D Fourier Transform Pairs
 1-D Fourier Transform Pairs The concept of the PSF is most easily explained by considering a very small point source being placed in the imaging field-of-view The relationship between the image, I, and
1-D Fourier Transform Pairs The concept of the PSF is most easily explained by considering a very small point source being placed in the imaging field-of-view The relationship between the image, I, and
Midterm Review. Yao Wang Polytechnic University, Brooklyn, NY 11201
 Midterm Review Yao Wang Polytechnic University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on J. L. Prince and J. M. Links, Medical maging Signals and Systems, and lecture notes by Prince. Figures are from the textbook.
Midterm Review Yao Wang Polytechnic University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on J. L. Prince and J. M. Links, Medical maging Signals and Systems, and lecture notes by Prince. Figures are from the textbook.
Topics. EM spectrum. X-Rays Computed Tomography Direct Inverse and Iterative Inverse Backprojection Projection Theorem Filtered Backprojection
 Bioengineering 28A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 24 X-Rays/CT Lecture Topics X-Rays Computed Tomography Direct Inverse and Iterative Inverse Backprojection Projection Theorem Filtered Backprojection
Bioengineering 28A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 24 X-Rays/CT Lecture Topics X-Rays Computed Tomography Direct Inverse and Iterative Inverse Backprojection Projection Theorem Filtered Backprojection
1. Which of the following statements is true about Bremsstrahlung and Characteristic Radiation?
 BioE 1330 - Review Chapters 4, 5, and 6 (X-ray and CT) 9/27/2018 Instructions: On the Answer Sheet, enter your 2-digit ID number (with a leading 0 if needed) in the boxes of the ID section. Fill in the
BioE 1330 - Review Chapters 4, 5, and 6 (X-ray and CT) 9/27/2018 Instructions: On the Answer Sheet, enter your 2-digit ID number (with a leading 0 if needed) in the boxes of the ID section. Fill in the
Topics. EM spectrum. X-Rays Computed Tomography Direct Inverse and Iterative Inverse Backprojection Projection Theorem Filtered Backprojection
 Bioengineering 28A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 25 X-Rays/CT Lecture Topics X-Rays Computed Tomography Direct Inverse and Iterative Inverse Backprojection Projection Theorem Filtered Backprojection
Bioengineering 28A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 25 X-Rays/CT Lecture Topics X-Rays Computed Tomography Direct Inverse and Iterative Inverse Backprojection Projection Theorem Filtered Backprojection
Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging. Fall Quarter 2005 X-Rays/CT Lecture 1. Topics
 Bioengineering 28A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 25 X-Rays/CT Lecture Topics X-Rays Computed Tomography Direct Inverse and Iterative Inverse Backprojection Projection Theorem Filtered Backprojection
Bioengineering 28A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 25 X-Rays/CT Lecture Topics X-Rays Computed Tomography Direct Inverse and Iterative Inverse Backprojection Projection Theorem Filtered Backprojection
11/10/2014. Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Imaging. Projection (Transmission) vs. Emission Imaging. Emission Imaging
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Imaging Overview of Modalities Properties of an Image: Limitations on Information Content Contrast (both object & image): Brightness difference Sharpness (blur): Smallest
Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Imaging Overview of Modalities Properties of an Image: Limitations on Information Content Contrast (both object & image): Brightness difference Sharpness (blur): Smallest
MIT 2.71/2.710 Optics 10/31/05 wk9-a-1. The spatial frequency domain
 10/31/05 wk9-a-1 The spatial frequency domain Recall: plane wave propagation x path delay increases linearly with x λ z=0 θ E 0 x exp i2π sinθ + λ z i2π cosθ λ z plane of observation 10/31/05 wk9-a-2 Spatial
10/31/05 wk9-a-1 The spatial frequency domain Recall: plane wave propagation x path delay increases linearly with x λ z=0 θ E 0 x exp i2π sinθ + λ z i2π cosθ λ z plane of observation 10/31/05 wk9-a-2 Spatial
October 4th, Bioengineering 508: Physical Aspects of Medical Imaging Some Elementary Particles
 Bioengineering 508: Physical Aspects of Medical Imaging http://courses.washington.edu/bioen508/ For questions, remarks, discussions, errors in the book: Class Discussion Board (link from class website)
Bioengineering 508: Physical Aspects of Medical Imaging http://courses.washington.edu/bioen508/ For questions, remarks, discussions, errors in the book: Class Discussion Board (link from class website)
BioE Exam 1 10/9/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions. 1. The sagittal plane
 BioE 1330 - Exam 1 10/9/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. The sagittal plane A. is perpendicular to the coronal plane. B. is parallel to the top of the head. C. represents a
BioE 1330 - Exam 1 10/9/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. The sagittal plane A. is perpendicular to the coronal plane. B. is parallel to the top of the head. C. represents a
Biomedical Imaging. X ray imaging. Patrícia Figueiredo IST
 Biomedical Imaging X ray imaging Patrícia Figueiredo IST 2013-2014 Overview Production of X rays Interaction of electrons with matter X ray spectrum X ray tube Interaction of X rays with matter Photoelectric
Biomedical Imaging X ray imaging Patrícia Figueiredo IST 2013-2014 Overview Production of X rays Interaction of electrons with matter X ray spectrum X ray tube Interaction of X rays with matter Photoelectric
Projection Radiography
 Projection Radiography Yao Wang Polytechnic University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on J. L. Prince and J. M. Links, Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, and lecture notes by Prince. Figures are from the
Projection Radiography Yao Wang Polytechnic University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on J. L. Prince and J. M. Links, Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, and lecture notes by Prince. Figures are from the
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS OPTION I-2 MEDICAL IMAGING Reading Activity Answers IB Assessment Statements Option I-2, Medical Imaging: X-Rays I.2.1. I.2.2. I.2.3. Define
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging. Outline
 A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
A Brief Introduction to Medical Imaging Outline General Goals Linear Imaging Systems An Example, The Pin Hole Camera Radiations and Their Interactions with Matter Coherent vs. Incoherent Imaging Length
Production of X-rays. Radiation Safety Training for Analytical X-Ray Devices Module 9
 Module 9 This module presents information on what X-rays are and how they are produced. Introduction Module 9, Page 2 X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Other types of electromagnetic radiation
Module 9 This module presents information on what X-rays are and how they are produced. Introduction Module 9, Page 2 X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. Other types of electromagnetic radiation
5. LIGHT MICROSCOPY Abbe s theory of imaging
 5. LIGHT MICROSCOPY. We use Fourier optics to describe coherent image formation, imaging obtained by illuminating the specimen with spatially coherent light. We define resolution, contrast, and phase-sensitive
5. LIGHT MICROSCOPY. We use Fourier optics to describe coherent image formation, imaging obtained by illuminating the specimen with spatially coherent light. We define resolution, contrast, and phase-sensitive
ABSOLUTE AIR-KERMA MEASUREMENT IN A SYNCHROTRON LIGHT BEAM BY IONIZATION FREE-AIR CHAMBER
 ABSOLUTE AIR-KERMA MEASUREMENT IN A SYNCHROTRON LIGHT BEAM BY IONIZATION FREE-AIR CHAMBER M. Bovi (1), R.F. Laitano (1), M. Pimpinella (1), M. P. Toni (1), K. Casarin(2), E. Quai(2), G. Tromba(2), A. Vascotto(2),
ABSOLUTE AIR-KERMA MEASUREMENT IN A SYNCHROTRON LIGHT BEAM BY IONIZATION FREE-AIR CHAMBER M. Bovi (1), R.F. Laitano (1), M. Pimpinella (1), M. P. Toni (1), K. Casarin(2), E. Quai(2), G. Tromba(2), A. Vascotto(2),
Basic principles of x-ray production
 Production of X-Rays part 1 George Starkschall, Ph.D. Lecture Objectives Identify what is needed to produce x-rays Describe how a diagnostic x-ray tube produces x-rays Describe the types of interactions
Production of X-Rays part 1 George Starkschall, Ph.D. Lecture Objectives Identify what is needed to produce x-rays Describe how a diagnostic x-ray tube produces x-rays Describe the types of interactions
Optical/IR Observational Astronomy Telescopes I: Optical Principles. David Buckley, SAAO. 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1
 David Buckley, SAAO 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1 1 What Do Telescopes Do? They collect light They form images of distant objects The images are analyzed by instruments The human eye Photographic
David Buckley, SAAO 24 Feb 2012 NASSP OT1: Telescopes I-1 1 What Do Telescopes Do? They collect light They form images of distant objects The images are analyzed by instruments The human eye Photographic
Rad T 290 Worksheet 2
 Class: Date: Rad T 290 Worksheet 2 1. Projectile electrons travel from a. anode to cathode. c. target to patient. b. cathode to anode. d. inner shell to outer shell. 2. At the target, the projectile electrons
Class: Date: Rad T 290 Worksheet 2 1. Projectile electrons travel from a. anode to cathode. c. target to patient. b. cathode to anode. d. inner shell to outer shell. 2. At the target, the projectile electrons
Tomography and Reconstruction
 Tomography and Reconstruction Lecture Overview Applications Background/history of tomography Radon Transform Fourier Slice Theorem Filtered Back Projection Algebraic techniques Measurement of Projection
Tomography and Reconstruction Lecture Overview Applications Background/history of tomography Radon Transform Fourier Slice Theorem Filtered Back Projection Algebraic techniques Measurement of Projection
FXA UNIT G485 Module X-Rays. Candidates should be able to : I = I 0 e -μx
 1 Candidates should be able to : HISTORY Describe the nature of X-rays. Describe in simple terms how X-rays are produced. X-rays were discovered by Wilhelm Röntgen in 1865, when he found that a fluorescent
1 Candidates should be able to : HISTORY Describe the nature of X-rays. Describe in simple terms how X-rays are produced. X-rays were discovered by Wilhelm Röntgen in 1865, when he found that a fluorescent
2015 Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination III. Radiological Sciences - Medical Physics
 January 2015 2015 Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination III Radiological Sciences - Medical Physics In this three-hour exam, you are required to answer all of the questions in Part A and any two (2) out of the
January 2015 2015 Ph.D. Comprehensive Examination III Radiological Sciences - Medical Physics In this three-hour exam, you are required to answer all of the questions in Part A and any two (2) out of the
Physics of Radiography
 EL-GY 6813 / BE-GY 6203 / G16.4426 Medical Imaging Physics of Radiography Jonathan Mamou and Yao Wang Polytechnic School of Engineering New York University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on Prince and Links,
EL-GY 6813 / BE-GY 6203 / G16.4426 Medical Imaging Physics of Radiography Jonathan Mamou and Yao Wang Polytechnic School of Engineering New York University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on Prince and Links,
X ray physics. Two types of x-ray imaging,- and two lectures
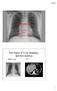 X ray physics Lectures DTU Mikael Jensen oct.2017. Two types of x-ray imaging,- and two lectures Planar x-ray CT 1 Why use x-rays? Non invasive, high resolution Quick, widespread Konrad Røntgen, 1896 X-rays
X ray physics Lectures DTU Mikael Jensen oct.2017. Two types of x-ray imaging,- and two lectures Planar x-ray CT 1 Why use x-rays? Non invasive, high resolution Quick, widespread Konrad Røntgen, 1896 X-rays
AQA Physics /7408
 AQA Physics - 7407/7408 Module 10: Medical physics You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 10.1 Physics of the eye 10.1.1 Physics of vision The eye as an optical refracting system,
AQA Physics - 7407/7408 Module 10: Medical physics You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 10.1 Physics of the eye 10.1.1 Physics of vision The eye as an optical refracting system,
G52IVG, School of Computer Science, University of Nottingham
 Image Transforms Fourier Transform Basic idea 1 Image Transforms Fourier transform theory Let f(x) be a continuous function of a real variable x. The Fourier transform of f(x) is F ( u) f ( x)exp[ j2πux]
Image Transforms Fourier Transform Basic idea 1 Image Transforms Fourier transform theory Let f(x) be a continuous function of a real variable x. The Fourier transform of f(x) is F ( u) f ( x)exp[ j2πux]
For the next several lectures, we will be looking at specific photon interactions with matter. In today s lecture, we begin with the photoelectric
 For the next several lectures, we will be looking at specific photon interactions with matter. In today s lecture, we begin with the photoelectric effect. 1 The objectives of today s lecture are to identify
For the next several lectures, we will be looking at specific photon interactions with matter. In today s lecture, we begin with the photoelectric effect. 1 The objectives of today s lecture are to identify
Basic physics Questions
 Chapter1 Basic physics Questions S. Ilyas 1. Which of the following statements regarding protons are correct? a. They have a negative charge b. They are equal to the number of electrons in a non-ionized
Chapter1 Basic physics Questions S. Ilyas 1. Which of the following statements regarding protons are correct? a. They have a negative charge b. They are equal to the number of electrons in a non-ionized
Projection Radiography
 EL-GY 6813 / BE-GY 6203 / G16.4426 Medical maging Projection Radiography Jonathan Mamou and Yao Wang Tandon School of Engineering New York University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on Prince and Links, Medical
EL-GY 6813 / BE-GY 6203 / G16.4426 Medical maging Projection Radiography Jonathan Mamou and Yao Wang Tandon School of Engineering New York University, Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on Prince and Links, Medical
We have seen how the Brems and Characteristic interactions work when electrons are accelerated by kilovolts and the electrons impact on the target
 We have seen how the Brems and Characteristic interactions work when electrons are accelerated by kilovolts and the electrons impact on the target focal spot. This discussion will center over how x-ray
We have seen how the Brems and Characteristic interactions work when electrons are accelerated by kilovolts and the electrons impact on the target focal spot. This discussion will center over how x-ray
INTERACTIONS OF RADIATION WITH MATTER
 INTERACTIONS OF RADIATION WITH MATTER Renée Dickinson, MS, DABR Medical Physicist University of Washington Medical Center Department of Radiology Diagnostic Physics Section Outline Describe the various
INTERACTIONS OF RADIATION WITH MATTER Renée Dickinson, MS, DABR Medical Physicist University of Washington Medical Center Department of Radiology Diagnostic Physics Section Outline Describe the various
Comparison of Polychromatic and Monochromatic X-rays for Imaging
 Comparison of Polychromatic and Monochromatic X-rays for Imaging M. Hoheisel 1, P. Bernhardt 1, R. Lawaczeck 2, and H. Pietsch 2 1 Siemens AG Medical Solutions, Forchheim, Germany 2 Schering AG Imaging
Comparison of Polychromatic and Monochromatic X-rays for Imaging M. Hoheisel 1, P. Bernhardt 1, R. Lawaczeck 2, and H. Pietsch 2 1 Siemens AG Medical Solutions, Forchheim, Germany 2 Schering AG Imaging
11/19/2014. Chapter 3: Interaction of Radiation with Matter in Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. Nuclide Families. Family Nuclides with Same: Example
 2014-2015 Residents' Core Physics Lectures Mondays 7:00-8:00 am in VA Radiology and UCSDMC Lasser Conference Rooms Topic Chapters Date Faculty 1 Introduction and Basic Physics 1, 2 M 11/17 Andre 2 Interaction
2014-2015 Residents' Core Physics Lectures Mondays 7:00-8:00 am in VA Radiology and UCSDMC Lasser Conference Rooms Topic Chapters Date Faculty 1 Introduction and Basic Physics 1, 2 M 11/17 Andre 2 Interaction
X-ray Interaction with Matter
 X-ray Interaction with Matter 10-526-197 Rhodes Module 2 Interaction with Matter kv & mas Peak kilovoltage (kvp) controls Quality, or penetrating power, Limited effects on quantity or number of photons
X-ray Interaction with Matter 10-526-197 Rhodes Module 2 Interaction with Matter kv & mas Peak kilovoltage (kvp) controls Quality, or penetrating power, Limited effects on quantity or number of photons
Warm-up Which of the following is NOT made up of photons?
 Warm-up Which of the following is NOT made up of photons? 1. Laser light 2. Radio waves 3. Ultrasonic waves 4. X-rays Radio µwaves fir IR uv x-ray gamma-ray... Xrays Discovered by Wm. Roentgen in 1895
Warm-up Which of the following is NOT made up of photons? 1. Laser light 2. Radio waves 3. Ultrasonic waves 4. X-rays Radio µwaves fir IR uv x-ray gamma-ray... Xrays Discovered by Wm. Roentgen in 1895
Take-Home Final Exam Last Possible Due Date: Dec. 21, 2004, 5 p.m.
 Take-Home Final Exam Last Possible Due Date: Dec 1, 004, 5 pm Your solutions to the exam should be handed in to the instructor (BIRB 1088) or to Eve Gochis, the MRI lab administrator (BIRB 107) no later
Take-Home Final Exam Last Possible Due Date: Dec 1, 004, 5 pm Your solutions to the exam should be handed in to the instructor (BIRB 1088) or to Eve Gochis, the MRI lab administrator (BIRB 107) no later
GBS765 Electron microscopy
 GBS765 Electron microscopy Lecture 1 Waves and Fourier transforms 10/14/14 9:05 AM Some fundamental concepts: Periodicity! If there is some a, for a function f(x), such that f(x) = f(x + na) then function
GBS765 Electron microscopy Lecture 1 Waves and Fourier transforms 10/14/14 9:05 AM Some fundamental concepts: Periodicity! If there is some a, for a function f(x), such that f(x) = f(x + na) then function
MAC2313 Final A. (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative.
 MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative. ii. The vector field F = 5(x 2 + y 2 ) 3/2 x, y is radial. iii. All constant
MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. How many of the following are necessarily true? i. The vector field F = 2x + 3y, 3x 5y is conservative. ii. The vector field F = 5(x 2 + y 2 ) 3/2 x, y is radial. iii. All constant
NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal
 NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal Ionizing Radiation and Hazard Potential John R. Frazier, Ph.D. Certified Health Physicist May 12, 2014 Radiation Radiation is a word that
NORM and TENORM: Occurrence, Characterizing, Handling and Disposal Ionizing Radiation and Hazard Potential John R. Frazier, Ph.D. Certified Health Physicist May 12, 2014 Radiation Radiation is a word that
Introduction to the Fourier transform. Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing. The Fourier transform (continued) The Fourier transform (continued)
 Introduction to the Fourier transform Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Fourier Transform Let f(x) be a continuous function of a real variable x The Fourier transform of f(x), denoted by I {f(x)}
Introduction to the Fourier transform Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Fourier Transform Let f(x) be a continuous function of a real variable x The Fourier transform of f(x), denoted by I {f(x)}
Semiconductor Optoelectronics Prof. M. R. Shenoy Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Semiconductor Optoelectronics Prof. M. R. Shenoy Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 20 Amplification by Stimulated Emission (Refer Slide Time: 00:37) So, we start today
Semiconductor Optoelectronics Prof. M. R. Shenoy Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 20 Amplification by Stimulated Emission (Refer Slide Time: 00:37) So, we start today
SPARCLAB. Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam
 SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X Introduction to SPARC_LAB 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current can be
SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X Introduction to SPARC_LAB 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current can be
SPARCLAB. Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton. On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration
 SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current
SPARCLAB Source For Plasma Accelerators and Radiation Compton with Laser And Beam On behalf of SPARCLAB collaboration EMITTANCE X X X X X X X X 2 BRIGHTNESS (electrons) B n 2I nx ny A m 2 rad 2 The current
Applications of Low KeV Imaging in Abdomen
 Applications of Low KeV Imaging in Abdomen Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
Applications of Low KeV Imaging in Abdomen Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
Nuclear Fusion and Radiation
 Nuclear Fusion and Radiation Lecture 9 (Meetings 23 & 24) Eugenio Schuster schuster@lehigh.edu Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics Lehigh University Nuclear Fusion and Radiation p. 1/42 Radiation Interactions
Nuclear Fusion and Radiation Lecture 9 (Meetings 23 & 24) Eugenio Schuster schuster@lehigh.edu Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics Lehigh University Nuclear Fusion and Radiation p. 1/42 Radiation Interactions
Diffractometer. Geometry Optics Detectors
 Diffractometer Geometry Optics Detectors Diffractometers Debye Scherrer Camera V.K. Pecharsky and P.Y. Zavalij Fundamentals of Powder Diffraction and Structural Characterization of Materials. Diffractometers
Diffractometer Geometry Optics Detectors Diffractometers Debye Scherrer Camera V.K. Pecharsky and P.Y. Zavalij Fundamentals of Powder Diffraction and Structural Characterization of Materials. Diffractometers
Astronomy 114. Lecture 26: Telescopes. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture 26: Telescopes Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 26 17 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 6,26 Astronomy 114 1/17 Announcements Quiz #2: we re aiming
Astronomy 114 Lecture 26: Telescopes Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 26 17 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 6,26 Astronomy 114 1/17 Announcements Quiz #2: we re aiming
Compton Storage Rings
 Compton Polarimetry @ Storage Rings Wolfgang Hillert ELectron Stretcher Accelerator Physics Institute of Bonn University Møller-Polarimeter Compton-Polarimeter Mott-Polarimeter Compton Scattering Differential
Compton Polarimetry @ Storage Rings Wolfgang Hillert ELectron Stretcher Accelerator Physics Institute of Bonn University Møller-Polarimeter Compton-Polarimeter Mott-Polarimeter Compton Scattering Differential
11/23/2014 RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS. Units of Radioactivity
 CHAPTER 4 RADIATION UNITS RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS 1 Units of Radioactivity 2 1 Radiation Units There are specific units for the amount of radiation you receive in a given time and for the total
CHAPTER 4 RADIATION UNITS RADIATION AND DOSE MEASUREMENTS 1 Units of Radioactivity 2 1 Radiation Units There are specific units for the amount of radiation you receive in a given time and for the total
Physics of Radiography
 Physics of Radiography Yao Wang Polytechnic Institute of NYU Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on J L Prince and J M Links Medical Imaging Signals and Based on J. L. Prince and J. M. Links, Medical Imaging Signals
Physics of Radiography Yao Wang Polytechnic Institute of NYU Brooklyn, NY 11201 Based on J L Prince and J M Links Medical Imaging Signals and Based on J. L. Prince and J. M. Links, Medical Imaging Signals
Telescopes (Chapter 6)
 Telescopes (Chapter 6) Based on Chapter 6 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 7 and 10 on Our planetary system and Jovian planet systems Chapter 5 on Light will be useful for understanding
Telescopes (Chapter 6) Based on Chapter 6 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 7 and 10 on Our planetary system and Jovian planet systems Chapter 5 on Light will be useful for understanding
Fig. 2 The image will be in focus everywhere. It's size changes based on the position of the focal plane.
 Instruments 1. Basic Optics 1. Rays of Light 2. Waves of light 3. Basic Imaging Systems 4. A Basic Telescope 5. Aberrations 6. Mirrors 2. Some Real Instruments 1. Galileo's Telescope 2. Keplerian Optics
Instruments 1. Basic Optics 1. Rays of Light 2. Waves of light 3. Basic Imaging Systems 4. A Basic Telescope 5. Aberrations 6. Mirrors 2. Some Real Instruments 1. Galileo's Telescope 2. Keplerian Optics
Image Reconstruction from Projection
 Image Reconstruction from Projection Reconstruct an image from a series of projections X-ray computed tomography (CT) Computed tomography is a medical imaging method employing tomography where digital
Image Reconstruction from Projection Reconstruct an image from a series of projections X-ray computed tomography (CT) Computed tomography is a medical imaging method employing tomography where digital
Medical Applications of Compact Laser-Compton Light Source
 Medical Applications of Compact Laser-Compton Light Source Y. Hwang 1, D. J. Gibson 2, R. A. Marsh 2, G. G. Anderson 2, T. Tajima 1, C. P. J. Barty 2 1 University of California, Irvine 2 Lawrence Livermore
Medical Applications of Compact Laser-Compton Light Source Y. Hwang 1, D. J. Gibson 2, R. A. Marsh 2, G. G. Anderson 2, T. Tajima 1, C. P. J. Barty 2 1 University of California, Irvine 2 Lawrence Livermore
What I Forgot Over My Summer Vacation A Review of Oral Radiology I. Steven R. Singer, DDS
 What I Forgot Over My Summer Vacation A Review of Oral Radiology I Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen 1845-1923 The Discovery Roentgen discovered x-rays on November 8 th, 1895
What I Forgot Over My Summer Vacation A Review of Oral Radiology I Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen 1845-1923 The Discovery Roentgen discovered x-rays on November 8 th, 1895
LECTURE 4 PRINCIPLE OF IMAGE FORMATION KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH
 LECTURE 4 PRINCIPLE OF IMAGE FORMATION KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, student should able to: Define attenuation Explain interactions between x-rays and matter in
LECTURE 4 PRINCIPLE OF IMAGE FORMATION KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH Lesson Objectives At the end of the lesson, student should able to: Define attenuation Explain interactions between x-rays and matter in
A Parameterization of the Chandra Point Spread Function
 Christopher L. Allen, Diab Jerius, and Terry Gaetz SAO 27 Oct 2003 Overview The off-axis Chandra PSF is a complex function of source position and energy: It is roughly elliptical, more so as off-axis angle
Christopher L. Allen, Diab Jerius, and Terry Gaetz SAO 27 Oct 2003 Overview The off-axis Chandra PSF is a complex function of source position and energy: It is roughly elliptical, more so as off-axis angle
Chapter 30 X Rays GOALS. When you have mastered the material in this chapter, you will be able to:
 Chapter 30 X Rays GOALS When you have mastered the material in this chapter, you will be able to: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it in an operational definition: hard and soft
Chapter 30 X Rays GOALS When you have mastered the material in this chapter, you will be able to: Definitions Define each of the following terms, and use it in an operational definition: hard and soft
X-ray imaging with amorphous selenium: Theoretical feasibility of the liquid crystal light valve for radiography
 X-ray imaging with amorphous selenium: Theoretical feasibility of the liquid crystal light valve for radiography Pia-Krista Rieppo and J. A. Rowlands a) Departments of Medical Biophysics and Medical Imaging,
X-ray imaging with amorphous selenium: Theoretical feasibility of the liquid crystal light valve for radiography Pia-Krista Rieppo and J. A. Rowlands a) Departments of Medical Biophysics and Medical Imaging,
( ) ( ) numerically using the DFT. The DTFT is defined. [ ]e. [ ] = x n. [ ]e j 2π Fn and the DFT is defined by X k. [ ]e j 2π kn/n with N = 5.
![( ) ( ) numerically using the DFT. The DTFT is defined. [ ]e. [ ] = x n. [ ]e j 2π Fn and the DFT is defined by X k. [ ]e j 2π kn/n with N = 5. ( ) ( ) numerically using the DFT. The DTFT is defined. [ ]e. [ ] = x n. [ ]e j 2π Fn and the DFT is defined by X k. [ ]e j 2π kn/n with N = 5.](/thumbs/88/116792961.jpg) ( /13) in the Ω form. ind the DTT of 8rect 3 n 2 8rect ( 3( n 2) /13) 40drcl(,5)e j 4π Let = Ω / 2π. Then 8rect 3 n 2 40 drcl( Ω / 2π,5)e j 2Ω ( /13) ind the DTT of 8rect 3( n 2) /13 by X = x n numerically
( /13) in the Ω form. ind the DTT of 8rect 3 n 2 8rect ( 3( n 2) /13) 40drcl(,5)e j 4π Let = Ω / 2π. Then 8rect 3 n 2 40 drcl( Ω / 2π,5)e j 2Ω ( /13) ind the DTT of 8rect 3( n 2) /13 by X = x n numerically
EE 230 Lecture 40. Data Converters. Amplitude Quantization. Quantization Noise
 EE 230 Lecture 40 Data Converters Amplitude Quantization Quantization Noise Review from Last Time: Time Quantization Typical ADC Environment Review from Last Time: Time Quantization Analog Signal Reconstruction
EE 230 Lecture 40 Data Converters Amplitude Quantization Quantization Noise Review from Last Time: Time Quantization Typical ADC Environment Review from Last Time: Time Quantization Analog Signal Reconstruction
Radiation and Radioactivity. PHYS 0219 Radiation and Radioactivity
 Radiation and Radioactivity 1 Radiation and Radioactivity This experiment has four parts: 1. Counting Statistics 2. Gamma (g) Ray Absorption Half-length and shielding 3. 137 Ba Decay Half-life 4. Dosimetry
Radiation and Radioactivity 1 Radiation and Radioactivity This experiment has four parts: 1. Counting Statistics 2. Gamma (g) Ray Absorption Half-length and shielding 3. 137 Ba Decay Half-life 4. Dosimetry
The Divergence Theorem
 Math 1a The Divergence Theorem 1. Parameterize the boundary of each of the following with positive orientation. (a) The solid x + 4y + 9z 36. (b) The solid x + y z 9. (c) The solid consisting of all points
Math 1a The Divergence Theorem 1. Parameterize the boundary of each of the following with positive orientation. (a) The solid x + 4y + 9z 36. (b) The solid x + y z 9. (c) The solid consisting of all points
BI-LAYER PROTECTION AGAINST SCATTER RADIATION
 BI-LAYER PROTECTION AGAINST SCATTER RADIATION An all new innovation in radiation protection core material THE STORY Kiarmor is an all new innovation in radiation protection core material, the combination
BI-LAYER PROTECTION AGAINST SCATTER RADIATION An all new innovation in radiation protection core material THE STORY Kiarmor is an all new innovation in radiation protection core material, the combination
MEDICAL IMAGING. METHODS OF MODERN IMAGING, BASED ON ELECTRO-MAGNETIC RADIATION (radiowaves, infrared radiation, X-rays, γ-rays ) AND ULTRASOUND
 MEDICAL IMAGING MEDICAL IMAGING METHODS OF MODERN IMAGING, BASED ON ELECTRO-MAGNETIC RADIATION (radiowaves, infrared radiation, X-rays, γ-rays ) AND ULTRASOUND MEDICAL IMAGING RADIOLOGY NUCLEAR MEDICINE
MEDICAL IMAGING MEDICAL IMAGING METHODS OF MODERN IMAGING, BASED ON ELECTRO-MAGNETIC RADIATION (radiowaves, infrared radiation, X-rays, γ-rays ) AND ULTRASOUND MEDICAL IMAGING RADIOLOGY NUCLEAR MEDICINE
Principles of Neutron Imaging
 Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Manuel Morgano Neutron Imaging & Activation Group, Paul Scherrer Institut, Switzerland Principles of Neutron Imaging PSI, 8. Oktober 2015 1. Absorption-based imaging
Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Manuel Morgano Neutron Imaging & Activation Group, Paul Scherrer Institut, Switzerland Principles of Neutron Imaging PSI, 8. Oktober 2015 1. Absorption-based imaging
Chap. 15 Radiation Imaging
 Chap. 15 Radiation Imaging 15.1 INTRODUCTION Modern Medical Imaging Devices Incorporating fundamental concepts in physical science and innovations in computer technology Nobel prize (physics) : 1895 Wilhelm
Chap. 15 Radiation Imaging 15.1 INTRODUCTION Modern Medical Imaging Devices Incorporating fundamental concepts in physical science and innovations in computer technology Nobel prize (physics) : 1895 Wilhelm
(i.e. what you should be able to answer at end of lecture)
 Today s Announcements 1. Test given back next Wednesday 2. HW assigned next Wednesday. 3. Next Monday 1 st discussion about Individual Projects. Today s take-home lessons (i.e. what you should be able
Today s Announcements 1. Test given back next Wednesday 2. HW assigned next Wednesday. 3. Next Monday 1 st discussion about Individual Projects. Today s take-home lessons (i.e. what you should be able
Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors
 King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa
King Saud University College of Applied Studies and Community Service Department of Natural Sciences Nuclear Reaction and Radiation Detectors General Physics II PHYS 111 Nouf Alkathran nalkathran@ksu.edu.sa
Radioactivity. Lecture 7 Dosimetry and Exposure Limits
 Radioactivity Lecture 7 Dosimetry and Exposure Limits Radiation Exposure - Radiology The radiation impact on biological and genetic materials requires some protective measures! Units for scaling the decay
Radioactivity Lecture 7 Dosimetry and Exposure Limits Radiation Exposure - Radiology The radiation impact on biological and genetic materials requires some protective measures! Units for scaling the decay
Possible Interactions. Possible Interactions. X-ray Interaction (Part I) Possible Interactions. Possible Interactions. section
 Possible Interactions X-ray Interaction (Part I) Three types of interaction 1. Scattering Interaction with an atom Deflected May or may not loss of energy 1 Possible Interactions Three types of interaction
Possible Interactions X-ray Interaction (Part I) Three types of interaction 1. Scattering Interaction with an atom Deflected May or may not loss of energy 1 Possible Interactions Three types of interaction
Notes on the point spread function and resolution for projection lens/corf. 22 April 2009 Dr. Raymond Browning
 Notes on the point spread function and resolution for projection lens/corf Abstract April 009 Dr. Raymond Browning R. Browning Consultants, 4 John Street, Shoreham, NY 786 Tel: (63) 8 348 This is a calculation
Notes on the point spread function and resolution for projection lens/corf Abstract April 009 Dr. Raymond Browning R. Browning Consultants, 4 John Street, Shoreham, NY 786 Tel: (63) 8 348 This is a calculation
University Environmental Health & Safety
 University Environmental Health & Safety X-rays were discovered in 1895 when William Conrad Roentgen observed that a screen coated with a barium salt fluoresced when placed near a cathode ray tube. Roentgen
University Environmental Health & Safety X-rays were discovered in 1895 when William Conrad Roentgen observed that a screen coated with a barium salt fluoresced when placed near a cathode ray tube. Roentgen
Radiation and the Atom
 Radiation and the Atom PHYS Lecture Departamento de Física Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto cav@isep.ipp.pt Overview SI Units and Prefixes Radiation Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum
Radiation and the Atom PHYS Lecture Departamento de Física Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto cav@isep.ipp.pt Overview SI Units and Prefixes Radiation Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic Spectrum
Radiation Dose, Biology & Risk
 ENGG 167 MEDICAL IMAGING Lecture 2: Sept. 27 Radiation Dosimetry & Risk References: The Essential Physics of Medical Imaging, Bushberg et al, 2 nd ed. Radiation Detection and Measurement, Knoll, 2 nd Ed.
ENGG 167 MEDICAL IMAGING Lecture 2: Sept. 27 Radiation Dosimetry & Risk References: The Essential Physics of Medical Imaging, Bushberg et al, 2 nd ed. Radiation Detection and Measurement, Knoll, 2 nd Ed.
Outline. Radiation Interactions. Spurs, Blobs and Short Tracks. Introduction. Radiation Interactions 1
 Outline Radiation Interactions Introduction Interaction of Heavy Charged Particles Interaction of Fast Electrons Interaction of Gamma Rays Interactions of Neutrons Radiation Exposure & Dose Sources of
Outline Radiation Interactions Introduction Interaction of Heavy Charged Particles Interaction of Fast Electrons Interaction of Gamma Rays Interactions of Neutrons Radiation Exposure & Dose Sources of
X-rays. X-ray Radiography - absorption is a function of Z and density. X-ray crystallography. X-ray spectrometry
 X-rays Wilhelm K. Roentgen (1845-1923) NP in Physics 1901 X-ray Radiography - absorption is a function of Z and density X-ray crystallography X-ray spectrometry X-rays Cu K α E = 8.05 kev λ = 1.541 Å Interaction
X-rays Wilhelm K. Roentgen (1845-1923) NP in Physics 1901 X-ray Radiography - absorption is a function of Z and density X-ray crystallography X-ray spectrometry X-rays Cu K α E = 8.05 kev λ = 1.541 Å Interaction
Solid-state physics. Laue diagrams: investigating the lattice structure of monocrystals. LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P
 Solid-state physics Properties of crystals X-ray structural analysis LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P7.1.2.2 Laue diagrams: investigating the lattice structure of monocrystals Objects of the experiment Evaluating
Solid-state physics Properties of crystals X-ray structural analysis LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P7.1.2.2 Laue diagrams: investigating the lattice structure of monocrystals Objects of the experiment Evaluating
Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8. θ (radians) θ (degrees) cos θ sin θ π/ /2 1/2 π/4 45 2/2 2/2 π/3 60 1/2 3/2 π/
 Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8 Trigonometric Identities ( cos(θ) = cos(θ) sin(θ) = sin(θ) sin(θ) = cos θ π ) 2 Cosines and Sines of common angles Euler s Formula θ (radians) θ (degrees)
Name (print): Lab (circle): W8 Th8 Th11 Th2 F8 Trigonometric Identities ( cos(θ) = cos(θ) sin(θ) = sin(θ) sin(θ) = cos θ π ) 2 Cosines and Sines of common angles Euler s Formula θ (radians) θ (degrees)
X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
 X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Nikki Truss November 26, 2012 Abstract In these experiments, some aspects of x-ray absorption spectroscopy were investigated. The x-ray spectrum of molybdenum was recorded
X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Nikki Truss November 26, 2012 Abstract In these experiments, some aspects of x-ray absorption spectroscopy were investigated. The x-ray spectrum of molybdenum was recorded
Detection of X-Rays. Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics
 Detection of X-Rays Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics Solid State X-ray Detectors X-ray interacts in material to produce photoelectrons which are collected
Detection of X-Rays Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics Solid State X-ray Detectors X-ray interacts in material to produce photoelectrons which are collected
Training program for x-ray inspection film (RT)
 of MTU Aero Engines AG Training program for x-ray inspection film (RT) In the NDT training course the following knowledge will be educated. approved by NANDTB Germany Preface + + + Introduction + + + Properties
of MTU Aero Engines AG Training program for x-ray inspection film (RT) In the NDT training course the following knowledge will be educated. approved by NANDTB Germany Preface + + + Introduction + + + Properties
Atomic and nuclear physics
 Atomic and nuclear physics X-ray physics Attenuation of x-rays LD Physics Leaflets P6.3.2.1 Investigating the attenuation of x-rays as a function of the absorber material and absorber thickness Objects
Atomic and nuclear physics X-ray physics Attenuation of x-rays LD Physics Leaflets P6.3.2.1 Investigating the attenuation of x-rays as a function of the absorber material and absorber thickness Objects
Pixels GaAs Detectors for Digital Radiography. M.E. Fantacci. and. Abstract
 Pixels GaAs Detectors for Digital Radiography M.E. Fantacci Dipartimento di Fisica dell'universita and Sezione I.N.F.N., Pisa, Italy and European Laboratory for Particle Physics (CERN), Geneve, Switzerland
Pixels GaAs Detectors for Digital Radiography M.E. Fantacci Dipartimento di Fisica dell'universita and Sezione I.N.F.N., Pisa, Italy and European Laboratory for Particle Physics (CERN), Geneve, Switzerland
In today s lecture, we want to see what happens when we hit the target.
 In the previous lecture, we identified three requirements for the production of x- rays. We need a source of electrons, we need something to accelerate electrons, and we need something to slow the electrons
In the previous lecture, we identified three requirements for the production of x- rays. We need a source of electrons, we need something to accelerate electrons, and we need something to slow the electrons
CHAPTER 4 RADIATION ATTENUATION
 HDR202 PHYSICS FOR RADIOGRAPHERS 2 CHAPTER 4 RADIATION ATTENUATION PREPARED BY: MR KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH SCHOOL OF MEDICAL IMAGING FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES Learning Objectives At the end of the lesson,
HDR202 PHYSICS FOR RADIOGRAPHERS 2 CHAPTER 4 RADIATION ATTENUATION PREPARED BY: MR KAMARUL AMIN BIN ABDULLAH SCHOOL OF MEDICAL IMAGING FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES Learning Objectives At the end of the lesson,
Setting The motor that rotates the sample about an axis normal to the diffraction plane is called (or ).
 X-Ray Diffraction X-ray diffraction geometry A simple X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiment might be set up as shown below. We need a parallel X-ray source, which is usually an X-ray tube in a fixed position
X-Ray Diffraction X-ray diffraction geometry A simple X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiment might be set up as shown below. We need a parallel X-ray source, which is usually an X-ray tube in a fixed position
GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY
 GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY ABSORBED DOSE: The amount of energy absorbed, as a result of radiation passing through a material, per unit mass of material. Measured in rads (1 rad
GLOSSARY OF BASIC RADIATION PROTECTION TERMINOLOGY ABSORBED DOSE: The amount of energy absorbed, as a result of radiation passing through a material, per unit mass of material. Measured in rads (1 rad
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 10 pages Written test, 12 December 2012 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: None. Pocket calculator not allowed "Weighting":
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 10 pages Written test, 12 December 2012 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: None. Pocket calculator not allowed "Weighting":
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 417 (1998) 86 94
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 417 (1998) 86 94 Experimental determination of detector gain, zero frequency detective quantum efficiency, and spectral compatibility of phosphor screens:
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 417 (1998) 86 94 Experimental determination of detector gain, zero frequency detective quantum efficiency, and spectral compatibility of phosphor screens:
Radiation Protection & Radiation Therapy
 Radiation Protection & Radiation Therapy For Medical Students Professor of Medical Physics Radiation Units Activity Number disintegrations per second (Curie, Becquerel) Exposure (Roentgen, C/kg) Absorbed
Radiation Protection & Radiation Therapy For Medical Students Professor of Medical Physics Radiation Units Activity Number disintegrations per second (Curie, Becquerel) Exposure (Roentgen, C/kg) Absorbed
This is the third of three lectures on cavity theory.
 This is the third of three lectures on cavity theory. 1 In this lecture, we are going to go over what is meant by charged particle equilibrium and look at the dose and kerma when you have charged particle
This is the third of three lectures on cavity theory. 1 In this lecture, we are going to go over what is meant by charged particle equilibrium and look at the dose and kerma when you have charged particle
Physics Modern Physics Professor Jodi Cooley. Welcome back. to PHY Arthur Compton
 Welcome back to PHY 3305 Today s Lecture: X-ray Production Compton Scattering Dual Nature of Light Arthur Compton 1892-1962 The Production of xrays X-rays were discovered in 1895 by German physicist Wihelm
Welcome back to PHY 3305 Today s Lecture: X-ray Production Compton Scattering Dual Nature of Light Arthur Compton 1892-1962 The Production of xrays X-rays were discovered in 1895 by German physicist Wihelm
Medical Physics. Image Quality 1) Ho Kyung Kim. Pusan National University
 Medical Physics Prince & Links 3 Image Quality 1) Ho Kyung Kim hokyung@pusan.ac.kr Pusan National University 1) The degree to which an image allows medical professionals to accomplish their goals (e.g.,
Medical Physics Prince & Links 3 Image Quality 1) Ho Kyung Kim hokyung@pusan.ac.kr Pusan National University 1) The degree to which an image allows medical professionals to accomplish their goals (e.g.,
X-Ray Emission and Absorption
 X-Ray Emission and Absorption Author: Mike Nill Alex Bryant February 6, 20 Abstract X-rays were produced by two bench-top diffractometers using a copper target. Various nickel filters were placed in front
X-Ray Emission and Absorption Author: Mike Nill Alex Bryant February 6, 20 Abstract X-rays were produced by two bench-top diffractometers using a copper target. Various nickel filters were placed in front
Name Final Exam May 1, 2017
 Name Final Exam May 1, 217 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Some possibly useful formulas appear below. Constants, etc.
Name Final Exam May 1, 217 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Some possibly useful formulas appear below. Constants, etc.
How we wanted to revolutionize X-ray radiography, and how we then "accidentally" discovered single-photon CMOS imaging
 How we wanted to revolutionize X-ray radiography, and how we then "accidentally" discovered single-photon CMOS imaging Stanford University EE Computer Systems Colloquium February 23 rd, 2011 EE380 Peter
How we wanted to revolutionize X-ray radiography, and how we then "accidentally" discovered single-photon CMOS imaging Stanford University EE Computer Systems Colloquium February 23 rd, 2011 EE380 Peter
6: Positron Emission Tomography
 6: Positron Emission Tomography. What is the principle of PET imaging? Positron annihilation Electronic collimation coincidence detection. What is really measured by the PET camera? True, scatter and random
6: Positron Emission Tomography. What is the principle of PET imaging? Positron annihilation Electronic collimation coincidence detection. What is really measured by the PET camera? True, scatter and random
INDUSTRIAL RADIOGRAPHY
 1 BASICS INDUSTRIAL RADIOGRAPHY -Dr.O.Prabhakar, OP-TECH INTRODUCTION From the time Roentgen discovered X-rays and used it to radiograph his rifle, X-rays are being used in the industry to reveal internal
1 BASICS INDUSTRIAL RADIOGRAPHY -Dr.O.Prabhakar, OP-TECH INTRODUCTION From the time Roentgen discovered X-rays and used it to radiograph his rifle, X-rays are being used in the industry to reveal internal
