Solid state physics. Lecture 2: X-ray diffraction. Prof. Dr. U. Pietsch
|
|
|
- Horatio Singleton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Solid state physics Lecture : X-ray diffraction Prof. Dr. U. Pietsch
2 Die Idee von Max von Laue (9) X-Strahlen sind elektromagnetische Wellen mit einer Wellenlänge viele kürzer als die des sichtbaren Lichtes. X-Strahlen werden an periodisch angeordneten Atomen/Molekülen im Kristall gebeugt 94 Nobelpreis für Physik
3 Originalexperiment von Laue, Friedrich und Knipping Photographic film 0.April 93 X-ray tube Collimator Crystal Ausgestellt im Deutschen Museum in München
4 Erstes Laue Experiment Photographic film Erster Kristall Cu SO 4 5 H O
5 9: Begin der moderen Kristallographie X-Strahlen sind elektromagnetische Wellen mit sehr kurzer Wellenlänge ( ~ Å = 0-0 m). Kristalle sind periodische Strukturen: die innerkristallinen Abstände sind von gleicher Größenordnung wie die Wellenlänge der Röntgenstrahlen. Röntgenbeugung ist eine Methode zur Untersuchung der Struktur von Festkörpern!
6 Erklärung durch Interferenz am 3D Gitter
7 Explanation of Laue pattern
8
9
10 recip. lattice vector
11 a = b = c h² k² l² a a h² k² l² d sin 4 sin sin
12 Alternative description of Laue-pattern by W.H.Bragg und W.L.Bragg Bragg equation N=dsinQ Interference at dense backed lattice planes
13 Reciprocal space, Ewald construction 0,... * 0, * * * * c b b a c c b b a a ) ( * ) ( * ) ( * c b a b a c c b a a c b c b a c b a *) * * ( lc kb ha G K ) ( hkl d G k k f i
14 Setup of modern diffraction experiment Storage ring Monochromator Slits Analysator Q f Detec tor pre-mirror Slits Q i Absorberbox Sample
15 X-ray tube and tube spectrum E = h v = e U min = h c / e U a min =.4/U a Bremsstrahlung Characteristic radiation
16 ESRF
17 Generation of Synchrotron radiation Electron circulates with relatvististic energy in orbit of storage ring with orbit frequency w= 0 6 Hz E e = 5 GeV m0c² m0c² E e v² ß² c² E e is much larger compared to rest mass energy mc², g = 5GeV/ 0.5 GeV 0 4 g Ee m c² ß² o value /g is the vertical open angle Using g one can estimate the electron velocity ß [ ] g ² / g ² 6*0 9 v 6*0 9 c
18 Generation of Synchrotron radiation Supposing the circulating electron emits a photon at point A of orbit. M Elektron proceeds to point C via B on orbit. At point C it emits a second photon. For the electron the length For the photon emitted in A reaches this distance is AC (electron) = v* dt. AC(photon = c *dt The spatial distance between both waves : (c-v) dt An observer at point C the light pulse has a length t ( c v) dt c ( ²) dt
19 Generation of Synchrotron radiation Considering the opening angle a = /g due to electron orbit t a² ( ag)² ( cosa) dt [ ( )( )] dt dt g ² g ² For a =0 t dt 0 8 dt g ² Dilatation of time a consequences for spectral distribution of photon emission Orbit time of electron along AC differs from time of photon t ( electron) t( photon) T 0 g gw T g ² gw 0 s 0 g ³ w 8 s
20 Generation of Synchrotron radiation Inverse pulse length determines the spectral with of light emission w c 3 g ³ w 8 0 Hz The emission spectrum has a critical wave length given by 8 c c This is x-ray range. In energy : 0 m * E e w c wg ³ ( GeV ) B( T )
21 Generation of Synchrotron radiation Bending radius R of electron orbit is gmv Re B R mc g eb Ee mc Ee( GeV) 3.3* mc² eb B( T) Emission power is P( kw).66* Ee ( GeV) B²( T) Ra( m) I( ma) For ESRF, E=6GeV, B=0.8T R= 4.8m P( kw).66*6e ( GeV)0.8²( T)4.8m 0.05mrad *00mA 7. 3W
22 w c Bend magnet spectrum Well predictable ESRF
23 Kinematic X-ray scattering Dipole scattering of x-ray wave by an electron: Electron excites dipole radiation I E² E e² mc² R² cos ² o Superposition of dipole radiation generated by two electrons at positions X and X e² E E0 exp( i[ wt ( X X )]) mc² X For n electrons e² R E E exp( i[ t ] exp( [ S ]) mc² R k 0 S 0 n f k i ( S S 0 ) Stotal scattering amplitude of one atom : atomic form factor
24 Kinematic X-ray scattering Scattering by all electrons of one atom : atomic formfactor e² R E E0 exp( i[ t ] exp( [ S S 0 ]) mc² R n s s0 e * exp( i[ r( S S0 )]) exp(i[ r ] dv n Form factor f[(s-s 0 )/] result from quantun mechanical calculations f(0) = Z ; f[(s-s 0 )/] decays continuosly as function of (s-s 0 )/
25 Kinematic X-ray scattering Scattering by two atoms : E f R R ( S S0 ) R R R exp( i[ t ] f exp( i[ t ]) exp( i[ t ]( f f exp( i[ ( S 0 )]) S Scattering by many disordered atoms : * I E * E f f f f cos[ ( S S0 )] i sin( krnm) exp [ S S0 ] rnm] k kr nm I n, m Debye sche Streugleichung Debye equation f m f n sin( kr kr nm nm )
26 Kinematic X-ray scattering Scattering by small crystal: r nm = R nm +r n distances between unit cells shape factor, distances betwen atoms within one unit cell structure factor R nm m a m a m 3a3 R i E fn exp( iwt)exp( i )exp( ( S S0)[ ma ma m3a3] E I Summation over all unit cells N a, N a, N 3 a 3 K k f k i K sin( NKa) sin( NKa) sin( F² sin( Ka ) sin( Ka ) sin( EE* F² S² N 3 Ka Ka 3 3 ) ) FWHM
27 Kinematic X-ray scattering I <> 0 only in near vicinity of the peak maxima Ka Ka Ka 3 h k l h,k,l integer FWHM of a Bragg peak can be approximated sin ²( Nx) I( x) N² exp( ( xn)² / ) sin ²( x) x ka k B cos Q N ² a² B N ² exp( ( ( )² cos ² Q) ² FWHM B(Q) is inversely proportional to crystal size L B(Q) (ln s) / NacosQ 0.94 NacosQ 0.94 LcosQ
28 Structure factor F F n i f i exp( i( kr i )) k ( ha* kb* lc*) r i x a i y b i z c i F n i f i exp( i( ha * kb* lc*)( x a i y b i z c)) i F n i f i exp( i( hx i ky i lz i )) Examples
29 bcc- structure: xyz = 000, ½ ½ ½ F f ( exp( i( h k l)) F= f if h+k+l = even; F= 0 if h+k+l odd fcc- structure: xyz = 000, ½ ½ 0, ½ 0 ½, 0 ½ ½ F f ( exp( i( h k) exp( i( h l) exp( i( k l)) F= 4f if h,k,l all are even or odd; F= 0 if h,k,l are mixed hcp- structure: xyz = 000, /3 /3 ½ F f ( exp( i(( h k) / 3 l / )) F= f if h+k =3n, l even; F=.73 if h+k= 3n+, l odd F= 0 if h+k= 3n+ l even
30 Extinktion rules Not all combinations of h,k,l are allowed, Bragg peak intensity can be vanishing due to crystal (point group ) symmetry In fcc system, only reflections appear with h²+k²+l² =,4,8,,. =, 00, 0, 3,,.. In NaCl In ZnSe, 3.. Are weak reflectons 0, Are strong reflections 0, 400.strong, 3.middle 00,.weka Structure (point group) identification considering extinktion rules and Bragg peak intensities
31 Powder diffraction pattern from CdSe Nanowires
32 Debye-Waller Factor Due to thermal atom oscillations exp( ik( r r)) exp( ikr) exp( ikr) exp( ix) i x x²... exp( x² ) exp( ikr) exp( k² r² ) exp( M ) M 6 ² u² sin ² ² F( T) F exp( M ) X-ray intensity becomes damped, Bragg peaks exit
33
34
35 Data evaluation
36 Electron charge density distribution from x-ray diffraction data ( r ) F( k)exp( ikr) dk h k l i ( r ) Fi ( H ) exp( Hr); H ( hkl ) V a h k l Electronic charge density of silicon Valence charge density difference charge density (bonding charges) U.Pietsch phys.stat.sol.(b) 37, 44,(986)
37 Electron density distribution of GaAs from x-ray diffraction data Ga As As Ga Valence charge density difference charge density (bonding charges)
Crystal Structure SOLID STATE PHYSICS. Lecture 5. A.H. Harker. thelecture thenextlecture. Physics and Astronomy UCL
 Crystal Structure thelecture thenextlecture SOLID STATE PHYSICS Lecture 5 A.H. Harker Physics and Astronomy UCL Structure & Diffraction Crystal Diffraction (continued) 2.4 Experimental Methods Notes: examples
Crystal Structure thelecture thenextlecture SOLID STATE PHYSICS Lecture 5 A.H. Harker Physics and Astronomy UCL Structure & Diffraction Crystal Diffraction (continued) 2.4 Experimental Methods Notes: examples
Solid State Physics Lecture 3 Diffraction and the Reciprocal Lattice (Kittel Ch. 2)
 Solid State Physics 460 - Lecture 3 Diffraction and the Reciprocal Lattice (Kittel Ch. 2) Diffraction (Bragg Scattering) from a powder of crystallites - real example of image at right from http://www.uni-wuerzburg.de/mineralogie/crystal/teaching/pow.html
Solid State Physics 460 - Lecture 3 Diffraction and the Reciprocal Lattice (Kittel Ch. 2) Diffraction (Bragg Scattering) from a powder of crystallites - real example of image at right from http://www.uni-wuerzburg.de/mineralogie/crystal/teaching/pow.html
X-ray Diffraction. Interaction of Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diffraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity
 X-ray Diraction Interaction o Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity Basic Principles o Interaction o Waves Periodic waves characteristic: Frequency :
X-ray Diraction Interaction o Waves Reciprocal Lattice and Diraction X-ray Scattering by Atoms The Integrated Intensity Basic Principles o Interaction o Waves Periodic waves characteristic: Frequency :
Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction
 Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction Elena Willinger Lecture series: Modern Methods in Heterogeneous Catalysis Research Outline History of X-ray Sources of X-ray radiation Physics of X-ray scattering Fundamentals
Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction Elena Willinger Lecture series: Modern Methods in Heterogeneous Catalysis Research Outline History of X-ray Sources of X-ray radiation Physics of X-ray scattering Fundamentals
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure Lecture 18
 3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure Lecture 18 X-RAYS AT WORK An X-ray diffraction image for the protein myoglobin. Source: Wikipedia. Model of helical domains in myoglobin. Image courtesy of Magnus Manske
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure Lecture 18 X-RAYS AT WORK An X-ray diffraction image for the protein myoglobin. Source: Wikipedia. Model of helical domains in myoglobin. Image courtesy of Magnus Manske
General theory of diffraction
 General theory of diffraction X-rays scatter off the charge density (r), neutrons scatter off the spin density. Coherent scattering (diffraction) creates the Fourier transform of (r) from real to reciprocal
General theory of diffraction X-rays scatter off the charge density (r), neutrons scatter off the spin density. Coherent scattering (diffraction) creates the Fourier transform of (r) from real to reciprocal
Solid State Physics 460- Lecture 5 Diffraction and the Reciprocal Lattice Continued (Kittel Ch. 2)
 Solid State Physics 460- Lecture 5 Diffraction and the Reciprocal Lattice Continued (Kittel Ch. 2) Ewald Construction 2θ k out k in G Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 5 1 Recall from previous lectures Definition
Solid State Physics 460- Lecture 5 Diffraction and the Reciprocal Lattice Continued (Kittel Ch. 2) Ewald Construction 2θ k out k in G Physics 460 F 2006 Lect 5 1 Recall from previous lectures Definition
SOLID STATE 18. Reciprocal Space
 SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
Handout 7 Reciprocal Space
 Handout 7 Reciprocal Space Useful concepts for the analysis of diffraction data http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ Concepts versus reality Reflection from lattice planes is just a concept that helps us
Handout 7 Reciprocal Space Useful concepts for the analysis of diffraction data http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ Concepts versus reality Reflection from lattice planes is just a concept that helps us
Basic Crystallography Part 1. Theory and Practice of X-ray Crystal Structure Determination
 Basic Crystallography Part 1 Theory and Practice of X-ray Crystal Structure Determination We have a crystal How do we get there? we want a structure! The Unit Cell Concept Ralph Krätzner Unit Cell Description
Basic Crystallography Part 1 Theory and Practice of X-ray Crystal Structure Determination We have a crystal How do we get there? we want a structure! The Unit Cell Concept Ralph Krätzner Unit Cell Description
Chap 3 Scattering and structures
 Chap 3 Scattering and structures Dept of Phys M.C. Chang Von Laue was struck in 1912 by the intuition that X-ray might scatter off crystals in the way that ordinary light scatters off a diffraction grating.
Chap 3 Scattering and structures Dept of Phys M.C. Chang Von Laue was struck in 1912 by the intuition that X-ray might scatter off crystals in the way that ordinary light scatters off a diffraction grating.
3.17 Strukturanalyse mit Röntgenstrahlen nach Debye- Scherrer
 3.17 Strukturanalyse mit Röntgenstrahlen nach Debye- Scherrer Ausarbeitung (engl.) Fortgeschrittenenpraktikum an der TU Darmstadt Versuch durchgeführt von: Mussie Beian, Jan Schupp, Florian Wetzel Versuchsdatum:
3.17 Strukturanalyse mit Röntgenstrahlen nach Debye- Scherrer Ausarbeitung (engl.) Fortgeschrittenenpraktikum an der TU Darmstadt Versuch durchgeführt von: Mussie Beian, Jan Schupp, Florian Wetzel Versuchsdatum:
X-ray diffraction geometry
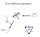 X-ray diffraction geometry Setting controls sample orientation in the diffraction plane. most important for single-crystal diffraction For any poly- (or nano-) crystalline specimen, we usually set: 1 X-ray
X-ray diffraction geometry Setting controls sample orientation in the diffraction plane. most important for single-crystal diffraction For any poly- (or nano-) crystalline specimen, we usually set: 1 X-ray
Chapter 2. X-ray X. Diffraction and Reciprocal Lattice. Scattering from Lattices
 Chapter. X-ray X Diffraction and Reciprocal Lattice Diffraction of waves by crystals Reciprocal Lattice Diffraction of X-rays Powder diffraction Single crystal X-ray diffraction Scattering from Lattices
Chapter. X-ray X Diffraction and Reciprocal Lattice Diffraction of waves by crystals Reciprocal Lattice Diffraction of X-rays Powder diffraction Single crystal X-ray diffraction Scattering from Lattices
Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy
 Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline 1. self-contained introduction neutron scattering and spectroscopy x-ray scattering and spectroscopy 2. application
Neutron and x-ray spectroscopy B. Keimer Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research outline 1. self-contained introduction neutron scattering and spectroscopy x-ray scattering and spectroscopy 2. application
X-ray diffraction is a non-invasive method for determining many types of
 Chapter X-ray Diffraction.1 Introduction X-ray diffraction is a non-invasive method for determining many types of structural features in both crystalline and amorphous materials. In the case of single
Chapter X-ray Diffraction.1 Introduction X-ray diffraction is a non-invasive method for determining many types of structural features in both crystalline and amorphous materials. In the case of single
Fourier Syntheses, Analyses, and Transforms
 Fourier Syntheses, Analyses, and Transforms http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ The electron density The electron density in a crystal can be described as a periodic function - same contents in each unit
Fourier Syntheses, Analyses, and Transforms http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ The electron density The electron density in a crystal can be described as a periodic function - same contents in each unit
Keble College - Hilary 2012 Section VI: Condensed matter physics Tutorial 2 - Lattices and scattering
 Tomi Johnson Keble College - Hilary 2012 Section VI: Condensed matter physics Tutorial 2 - Lattices and scattering Please leave your work in the Clarendon laboratory s J pigeon hole by 5pm on Monday of
Tomi Johnson Keble College - Hilary 2012 Section VI: Condensed matter physics Tutorial 2 - Lattices and scattering Please leave your work in the Clarendon laboratory s J pigeon hole by 5pm on Monday of
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5 detector sample X-ray source monochromator David Ritchie http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home QCMP Lent/Easter 2019 5.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 5 detector sample X-ray source monochromator David Ritchie http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home QCMP Lent/Easter 2019 5.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical
Data processing and reduction
 Data processing and reduction Leopoldo Suescun International School on Fundamental Crystallography 2014 May 1st, 2014 Reciprocal lattice c* b* b * dh' k' l' 1 dh' k' l' * dhkl 1 dhkl a a* 0 d hkl c bc
Data processing and reduction Leopoldo Suescun International School on Fundamental Crystallography 2014 May 1st, 2014 Reciprocal lattice c* b* b * dh' k' l' 1 dh' k' l' * dhkl 1 dhkl a a* 0 d hkl c bc
Crystal planes. Neutrons: magnetic moment - interacts with magnetic materials or nuclei of non-magnetic materials. (in Å)
 Crystallography: neutron, electron, and X-ray scattering from periodic lattice, scattering of waves by periodic structures, Miller indices, reciprocal space, Ewald construction. Diffraction: Specular,
Crystallography: neutron, electron, and X-ray scattering from periodic lattice, scattering of waves by periodic structures, Miller indices, reciprocal space, Ewald construction. Diffraction: Specular,
An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering. School of Chemistry The University of Sydney
 An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering Brendan J. Kennedy School of Chemistry The University of Sydney 1) Strong forces 2) Weak forces Types of Forces 3) Electromagnetic forces 4) Gravity Types
An Introduction to Diffraction and Scattering Brendan J. Kennedy School of Chemistry The University of Sydney 1) Strong forces 2) Weak forces Types of Forces 3) Electromagnetic forces 4) Gravity Types
Roger Johnson Structure and Dynamics: X-ray Diffraction Lecture 6
 6.1. Summary In this Lecture we cover the theory of x-ray diffraction, which gives direct information about the atomic structure of crystals. In these experiments, the wavelength of the incident beam must
6.1. Summary In this Lecture we cover the theory of x-ray diffraction, which gives direct information about the atomic structure of crystals. In these experiments, the wavelength of the incident beam must
Scattering by two Electrons
 Scattering by two Electrons p = -r k in k in p r e 2 q k in /λ θ θ k out /λ S q = r k out p + q = r (k out - k in ) e 1 Phase difference of wave 2 with respect to wave 1: 2π λ (k out - k in ) r= 2π S r
Scattering by two Electrons p = -r k in k in p r e 2 q k in /λ θ θ k out /λ S q = r k out p + q = r (k out - k in ) e 1 Phase difference of wave 2 with respect to wave 1: 2π λ (k out - k in ) r= 2π S r
Protein crystallography. Garry Taylor
 Protein crystallography Garry Taylor X-ray Crystallography - the Basics Grow crystals Collect X-ray data Determine phases Calculate ρ-map Interpret map Refine coordinates Do the biology. Nitrogen at -180
Protein crystallography Garry Taylor X-ray Crystallography - the Basics Grow crystals Collect X-ray data Determine phases Calculate ρ-map Interpret map Refine coordinates Do the biology. Nitrogen at -180
Setting The motor that rotates the sample about an axis normal to the diffraction plane is called (or ).
 X-Ray Diffraction X-ray diffraction geometry A simple X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiment might be set up as shown below. We need a parallel X-ray source, which is usually an X-ray tube in a fixed position
X-Ray Diffraction X-ray diffraction geometry A simple X-ray diffraction (XRD) experiment might be set up as shown below. We need a parallel X-ray source, which is usually an X-ray tube in a fixed position
Analytical Methods for Materials
 Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 15 Reciprocal Lattices and Their Roles in Diffraction Studies Suggested Reading Chs. 2 and 6 in Tilley, Crystals and Crystal Structures, Wiley (2006) Ch. 6 M. DeGraef
Analytical Methods for Materials Lesson 15 Reciprocal Lattices and Their Roles in Diffraction Studies Suggested Reading Chs. 2 and 6 in Tilley, Crystals and Crystal Structures, Wiley (2006) Ch. 6 M. DeGraef
PSD '18 -- Xray lecture 4. Laue conditions Fourier Transform The reciprocal lattice data collection
 PSD '18 -- Xray lecture 4 Laue conditions Fourier Transform The reciprocal lattice data collection 1 Fourier Transform The Fourier Transform is a conversion of one space into another space with reciprocal
PSD '18 -- Xray lecture 4 Laue conditions Fourier Transform The reciprocal lattice data collection 1 Fourier Transform The Fourier Transform is a conversion of one space into another space with reciprocal
Chemical Crystallography
 Chemical Crystallography Prof Andrew Goodwin Michaelmas 2014 Recap: Lecture 1 Why does diffraction give a Fourier transform? k i = k s = 2π/λ k i k s k i k s r l 1 = (λ/2π) k i r l 2 = (λ/2π) k s r Total
Chemical Crystallography Prof Andrew Goodwin Michaelmas 2014 Recap: Lecture 1 Why does diffraction give a Fourier transform? k i = k s = 2π/λ k i k s k i k s r l 1 = (λ/2π) k i r l 2 = (λ/2π) k s r Total
Materials Science and Engineering 102 Structure and Bonding. Prof. Stephen L. Sass. Midterm Examination Duration: 1 hour 20 minutes
 October 9, 008 MSE 0: Structure and Bonding Midterm Exam SOLUTIONS SID: Signature: Materials Science and Engineering 0 Structure and Bonding Prof. Stephen L. Sass Midterm Examination Duration: hour 0 minutes
October 9, 008 MSE 0: Structure and Bonding Midterm Exam SOLUTIONS SID: Signature: Materials Science and Engineering 0 Structure and Bonding Prof. Stephen L. Sass Midterm Examination Duration: hour 0 minutes
17 Finite crystal lattice and its Fourier transform. Lattice amplitude and shape amplitude
 17 FINITE CRYSTAL LATTICE. LATTICE AMPLITUDE AND SHAPE AMPLITUDE 1 17 Finite crystal lattice and its Fourier transform. Lattice amplitude and shape amplitude A finite lattice f x) a regularly distributed
17 FINITE CRYSTAL LATTICE. LATTICE AMPLITUDE AND SHAPE AMPLITUDE 1 17 Finite crystal lattice and its Fourier transform. Lattice amplitude and shape amplitude A finite lattice f x) a regularly distributed
Structure of Surfaces
 Structure of Surfaces C Stepped surface Interference of two waves Bragg s law Path difference = AB+BC =2dsin ( =glancing angle) If, n =2dsin, constructive interference Ex) in a cubic lattice of unit cell
Structure of Surfaces C Stepped surface Interference of two waves Bragg s law Path difference = AB+BC =2dsin ( =glancing angle) If, n =2dsin, constructive interference Ex) in a cubic lattice of unit cell
Accelerator Physics NMI and Synchrotron Radiation. G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 16
 Accelerator Physics NMI and Synchrotron Radiation G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 16 Graduate Accelerator Physics Fall 17 Oscillation Frequency nq I n i Z c E Re Z 1 mode has
Accelerator Physics NMI and Synchrotron Radiation G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 16 Graduate Accelerator Physics Fall 17 Oscillation Frequency nq I n i Z c E Re Z 1 mode has
Neutron Diffraction: a general overview
 RUG1 Neutron Diffraction: a general overview Graeme Blake Zernike Institute for Advanced Materials University of Groningen Outline Elastic scattering of neutrons from matter Comparison of neutron and X-ray
RUG1 Neutron Diffraction: a general overview Graeme Blake Zernike Institute for Advanced Materials University of Groningen Outline Elastic scattering of neutrons from matter Comparison of neutron and X-ray
2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure
 Page 1 of 22 2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure Recall de Broglie matter waves: 2 p h E = where p = 2m λ h 1 E = ( ) 2m λ hc E = hυ = ( photons) λ ( matter wave) He atoms: [E (ev)]
Page 1 of 22 2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure Recall de Broglie matter waves: 2 p h E = where p = 2m λ h 1 E = ( ) 2m λ hc E = hυ = ( photons) λ ( matter wave) He atoms: [E (ev)]
Atomic Physics. Chapter 6 X ray. Jinniu Hu 24/12/ /20/13
 Atomic Physics Chapter 6 X ray 11/20/13 24/12/2018 Jinniu Hu 1!1 6.1 The discovery of X ray X-rays were discovered in 1895 by the German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen. He found that a beam of high-speed electrons
Atomic Physics Chapter 6 X ray 11/20/13 24/12/2018 Jinniu Hu 1!1 6.1 The discovery of X ray X-rays were discovered in 1895 by the German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen. He found that a beam of high-speed electrons
Research with Synchrotron Radiation. Part I
 Research with Synchrotron Radiation Part I Ralf Röhlsberger Generation and properties of synchrotron radiation Radiation sources at DESY Synchrotron Radiation Sources at DESY DORIS III 38 beamlines XFEL
Research with Synchrotron Radiation Part I Ralf Röhlsberger Generation and properties of synchrotron radiation Radiation sources at DESY Synchrotron Radiation Sources at DESY DORIS III 38 beamlines XFEL
Wave diffraction and the reciprocal lattice
 Wave diffraction and the reciprocal lattice Dept of Phys M.C. Chang Braggs theory of diffraction Reciprocal lattice von Laue s theory of diffraction Braggs view of the diffraction (1912, father and son)
Wave diffraction and the reciprocal lattice Dept of Phys M.C. Chang Braggs theory of diffraction Reciprocal lattice von Laue s theory of diffraction Braggs view of the diffraction (1912, father and son)
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 19 Chapter 12. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 19 Chapter 12 There are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry X-ray Techniques include:
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 19 Chapter 12 There are three major techniques used for elemental analysis: Optical spectrometry Mass spectrometry X-ray spectrometry X-ray Techniques include:
Part 1: What is XAFS? What does it tell us? The EXAFS equation. Part 2: Basic steps in the analysis Quick overview of typical analysis
 Introduction to XAFS Part 1: What is XAFS? What does it tell us? The EXAFS equation Part 2: Basic steps in the analysis Quick overview of typical analysis Tomorrow Measurement methods and examples The
Introduction to XAFS Part 1: What is XAFS? What does it tell us? The EXAFS equation Part 2: Basic steps in the analysis Quick overview of typical analysis Tomorrow Measurement methods and examples The
2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure
 2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure Recall de Broglie matter waves: He atoms: [E (ev)] 1/2 = 0.14 / (Å) E 1Å = 0.0196 ev Neutrons: [E (ev)] 1/2 = 0.28 / (Å) E 1Å = 0.0784 ev Electrons:
2. Diffraction as a means to determine crystal structure Recall de Broglie matter waves: He atoms: [E (ev)] 1/2 = 0.14 / (Å) E 1Å = 0.0196 ev Neutrons: [E (ev)] 1/2 = 0.28 / (Å) E 1Å = 0.0784 ev Electrons:
X-ray analysis. 1. Basic crystallography 2. Basic diffraction physics 3. Experimental methods
 X-ray analysis 1. Basic crystallography 2. Basic diffraction physics 3. Experimental methods Introduction Noble prizes associated with X-ray diffraction 1901 W. C. Roentgen (Physics) for the discovery
X-ray analysis 1. Basic crystallography 2. Basic diffraction physics 3. Experimental methods Introduction Noble prizes associated with X-ray diffraction 1901 W. C. Roentgen (Physics) for the discovery
V 11: Electron Diffraction
 Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg Institute of Physics Advanced Practical Lab Course V 11: Electron Diffraction An electron beam conditioned by an electron optical system is diffracted by a polycrystalline,
Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg Institute of Physics Advanced Practical Lab Course V 11: Electron Diffraction An electron beam conditioned by an electron optical system is diffracted by a polycrystalline,
EXAFS data analysis. Extraction of EXAFS signal
 EXAFS data analysis Extraction of EXAFS signal 1 Experimental EXAFS spectrum Φ x Φ µ (ω) source monochromator sample detectors 1 6 1 5 32 - Ge 1 4 1 3 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 Photon energy hω (kev) 1-1 Ge, 1 K µ
EXAFS data analysis Extraction of EXAFS signal 1 Experimental EXAFS spectrum Φ x Φ µ (ω) source monochromator sample detectors 1 6 1 5 32 - Ge 1 4 1 3 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 Photon energy hω (kev) 1-1 Ge, 1 K µ
Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7
 Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7 Due date: June 29th, 2015 Problem 5.1 EXAFS Study of Mn/Fe substitution in Y(Mn 1-x Fe x ) 2 O 5 From article «EXAFS, XANES, and DFT study of the mixed-valence compound
Solid State Spectroscopy Problem Set 7 Due date: June 29th, 2015 Problem 5.1 EXAFS Study of Mn/Fe substitution in Y(Mn 1-x Fe x ) 2 O 5 From article «EXAFS, XANES, and DFT study of the mixed-valence compound
Diffraction Experiments, Data processing and reduction
 Diffraction Experiments, Data processing and reduction Leopoldo Suescun Laboratorio de Cristalografía Química del Estado Sólido y Materiales, Facultad de Química, Universidad de la República, Montevideo,
Diffraction Experiments, Data processing and reduction Leopoldo Suescun Laboratorio de Cristalografía Química del Estado Sólido y Materiales, Facultad de Química, Universidad de la República, Montevideo,
Low Emittance Machines
 Advanced Accelerator Physics Course RHUL, Egham, UK September 2017 Low Emittance Machines Part 1: Beam Dynamics with Synchrotron Radiation Andy Wolski The Cockcroft Institute, and the University of Liverpool,
Advanced Accelerator Physics Course RHUL, Egham, UK September 2017 Low Emittance Machines Part 1: Beam Dynamics with Synchrotron Radiation Andy Wolski The Cockcroft Institute, and the University of Liverpool,
X-ray Spectroscopy. Interaction of X-rays with matter XANES and EXAFS XANES analysis Pre-edge analysis EXAFS analysis
 X-ray Spectroscopy Interaction of X-rays with matter XANES and EXAFS XANES analysis Pre-edge analysis EXAFS analysis Element specific Sensitive to low concentrations (0.01-0.1 %) Why XAS? Applicable under
X-ray Spectroscopy Interaction of X-rays with matter XANES and EXAFS XANES analysis Pre-edge analysis EXAFS analysis Element specific Sensitive to low concentrations (0.01-0.1 %) Why XAS? Applicable under
Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik I + II: Struktur und Dynamik kondensierter Materie
 I + II: Struktur und Dynamik kondensierter Materie Vorlesung zum Haupt/Masterstudiengang Physik SS 2009 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert, W. Wurth 1 Trends in Spectroscopy 23.4. 28.4. 30.4. 5.4. Wolfgang
I + II: Struktur und Dynamik kondensierter Materie Vorlesung zum Haupt/Masterstudiengang Physik SS 2009 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert, W. Wurth 1 Trends in Spectroscopy 23.4. 28.4. 30.4. 5.4. Wolfgang
Materials 286C/UCSB: Class VI Structure factors (continued), the phase problem, Patterson techniques and direct methods
 Materials 286C/UCSB: Class VI Structure factors (continued), the phase problem, Patterson techniques and direct methods Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) Structure factors The structure factor for a
Materials 286C/UCSB: Class VI Structure factors (continued), the phase problem, Patterson techniques and direct methods Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) Structure factors The structure factor for a
Basics of Synchrotron Radiation Beamlines and Detectors. Basics of synchrotron radiation X-ray optics as they apply to EXAFS experiments Detectors
 Basics of Synchrotron Radiation Beamlines and Detectors Basics of synchrotron radiation X-ray optics as they apply to EXAFS experiments Detectors Important properties of Synchrotron Radiation Tunability
Basics of Synchrotron Radiation Beamlines and Detectors Basics of synchrotron radiation X-ray optics as they apply to EXAFS experiments Detectors Important properties of Synchrotron Radiation Tunability
Draft of solution Exam TFY4220, Solid State Physics, 29. May 2015.
 Draft of solution Exam TY40, Solid State Physics, 9. May 05. Problem (5%) Introductory questions (answers can be found in the books) a) Small Ewald sphere, not many reflections in Bragg with a single crystal.
Draft of solution Exam TY40, Solid State Physics, 9. May 05. Problem (5%) Introductory questions (answers can be found in the books) a) Small Ewald sphere, not many reflections in Bragg with a single crystal.
Basics of XRD part III
 Basics of XRD part III Dr. Peter G. Weidler Institute of Functional Interfaces IFG 1 10/31/17 KIT The Research University of the Helmholtz Association Name of Institute, Faculty, Department www.kit.edu
Basics of XRD part III Dr. Peter G. Weidler Institute of Functional Interfaces IFG 1 10/31/17 KIT The Research University of the Helmholtz Association Name of Institute, Faculty, Department www.kit.edu
3.012 Structure An Introduction to X-ray Diffraction
 3.012 Structure An Introduction to X-ray Diffraction This handout summarizes some topics that are important for understanding x-ray diffraction. The following references provide a thorough explanation
3.012 Structure An Introduction to X-ray Diffraction This handout summarizes some topics that are important for understanding x-ray diffraction. The following references provide a thorough explanation
X-ray Diffraction. Diffraction. X-ray Generation. X-ray Generation. X-ray Generation. X-ray Spectrum from Tube
 X-ray Diffraction Mineral identification Mode analysis Structure Studies X-ray Generation X-ray tube (sealed) Pure metal target (Cu) Electrons remover inner-shell electrons from target. Other electrons
X-ray Diffraction Mineral identification Mode analysis Structure Studies X-ray Generation X-ray tube (sealed) Pure metal target (Cu) Electrons remover inner-shell electrons from target. Other electrons
Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung
 Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung Lecture 4 Location Vorlesung zum Haupt- oder Masterstudiengang Physik, SoSe 2015 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert Lecture hall AP, Physics, Jungiusstraße
Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung Lecture 4 Location Vorlesung zum Haupt- oder Masterstudiengang Physik, SoSe 2015 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert Lecture hall AP, Physics, Jungiusstraße
 Name : Roll No. :.... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (NEW)/SEM-2/PH-201/2013 2013 PHYSICS - I Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are
Name : Roll No. :.... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (NEW)/SEM-2/PH-201/2013 2013 PHYSICS - I Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are
Experimental Determination of Crystal Structure
 Experimental Determination of Crystal Structure Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. PHYS 624: Introduction to Solid State Physics http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic/teaching/phys624/phys624.html
Experimental Determination of Crystal Structure Branislav K. Nikolić Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware, U.S.A. PHYS 624: Introduction to Solid State Physics http://www.physics.udel.edu/~bnikolic/teaching/phys624/phys624.html
4. Other diffraction techniques
 4. Other diffraction techniques 4.1 Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction (RHEED) Setup: - Grazing-incidence high energy electron beam (3-5 kev: MEED,
4. Other diffraction techniques 4.1 Reflection High Energy Electron Diffraction (RHEED) Setup: - Grazing-incidence high energy electron beam (3-5 kev: MEED,
The Reciprocal Lattice
 59-553 The Reciprocal Lattice 61 Because of the reciprocal nature of d spacings and θ from Bragg s Law, the pattern of the diffraction we observe can be related to the crystal lattice by a mathematical
59-553 The Reciprocal Lattice 61 Because of the reciprocal nature of d spacings and θ from Bragg s Law, the pattern of the diffraction we observe can be related to the crystal lattice by a mathematical
X-Ray Scattering Studies of Thin Polymer Films
 X-Ray Scattering Studies of Thin Polymer Films Introduction to Neutron and X-Ray Scattering Sunil K. Sinha UCSD/LANL Acknowledgements: Prof. R.Pynn( Indiana U.) Prof. M.Tolan (U. Dortmund) Wilhelm Conrad
X-Ray Scattering Studies of Thin Polymer Films Introduction to Neutron and X-Ray Scattering Sunil K. Sinha UCSD/LANL Acknowledgements: Prof. R.Pynn( Indiana U.) Prof. M.Tolan (U. Dortmund) Wilhelm Conrad
X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Eric Peterson 9/2/2010
 X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Eric Peterson 9/2/2010 Outline Generation/Absorption of X-rays History Synchrotron Light Sources Data reduction/analysis Examples Crystallite size from Coordination Number
X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Eric Peterson 9/2/2010 Outline Generation/Absorption of X-rays History Synchrotron Light Sources Data reduction/analysis Examples Crystallite size from Coordination Number
SOLID STATE 9. Determination of Crystal Structures
 SOLID STATE 9 Determination of Crystal Structures In the diffraction experiment, we measure intensities as a function of d hkl. Intensities are the sum of the x-rays scattered by all the atoms in a crystal.
SOLID STATE 9 Determination of Crystal Structures In the diffraction experiment, we measure intensities as a function of d hkl. Intensities are the sum of the x-rays scattered by all the atoms in a crystal.
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I
 CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle 5.7 Probability,
CHAPTER 5 Wave Properties of Matter and Quantum Mechanics I 5.1 X-Ray Scattering 5.2 De Broglie Waves 5.3 Electron Scattering 5.4 Wave Motion 5.5 Waves or Particles? 5.6 Uncertainty Principle 5.7 Probability,
FROM DIFFRACTION TO STRUCTURE
 3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure Lecture 19 FROM DIFFRACTION TO STRUCTURE Images removed for copyright reasons. 3-fold symmetry in silicon along the [111] direction. Forward (left) and backward (right)
3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure Lecture 19 FROM DIFFRACTION TO STRUCTURE Images removed for copyright reasons. 3-fold symmetry in silicon along the [111] direction. Forward (left) and backward (right)
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B. Tech (New)/SEM-1/PH-101/ PHYSICS-I
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B. Tech (New)/SEM-1/PH-101/2011-12 2011 PHYSICS-I Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B. Tech (New)/SEM-1/PH-101/2011-12 2011 PHYSICS-I Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates
Introduction to crystallography The unitcell The resiprocal space and unitcell Braggs law Structure factor F hkl and atomic scattering factor f zθ
 Introduction to crystallography The unitcell The resiprocal space and unitcell Braggs law Structure factor F hkl and atomic scattering factor f zθ Introduction to crystallography We divide materials into
Introduction to crystallography The unitcell The resiprocal space and unitcell Braggs law Structure factor F hkl and atomic scattering factor f zθ Introduction to crystallography We divide materials into
Chapter 1. From Classical to Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 1. From Classical to Quantum Mechanics Classical Mechanics (Newton): It describes the motion of a classical particle (discrete object). dp F ma, p = m = dt dx m dt F: force (N) a: acceleration
Chapter 1. From Classical to Quantum Mechanics Classical Mechanics (Newton): It describes the motion of a classical particle (discrete object). dp F ma, p = m = dt dx m dt F: force (N) a: acceleration
Polarization is out of the plane
 Physics 055 Lecture 2 Recall from last time the various crystal classes and the dierent translational and rotational symmetry operations which made this enumeration possible. You should also be familiar
Physics 055 Lecture 2 Recall from last time the various crystal classes and the dierent translational and rotational symmetry operations which made this enumeration possible. You should also be familiar
Chapter 1 X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (EXAFS)
 1 Chapter 1 X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (EXAFS) 1.1 What is EXAFS? X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS, XAFS) is an oscillatory modulation in the X-ray absorption coefficient on the high-energy
1 Chapter 1 X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (EXAFS) 1.1 What is EXAFS? X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS, XAFS) is an oscillatory modulation in the X-ray absorption coefficient on the high-energy
Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik I + II: Struktur und Dynamik kondensierter Materie
 I + II: Struktur und Dynamik kondensierter Materie Vorlesung zum Haupt/Masterstudiengang Physik SS 2009 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert, W. Wurth 1 Trends in Spectroscopy 23.4. 28.4. 30.4. 5.4. Wolfgang
I + II: Struktur und Dynamik kondensierter Materie Vorlesung zum Haupt/Masterstudiengang Physik SS 2009 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert, W. Wurth 1 Trends in Spectroscopy 23.4. 28.4. 30.4. 5.4. Wolfgang
David Martin High Precision Beamline Alignment at the ESRF IWAA, Grenoble 3-7 October 2016
 David Martin High Precision Beamline Alignment at the ESRF IWAA, Grenoble 3-7 October 2016 OVERVIEW The ESRF has just completed the Phase I Upgrade programme. The Phase I Upgrade programme was centered
David Martin High Precision Beamline Alignment at the ESRF IWAA, Grenoble 3-7 October 2016 OVERVIEW The ESRF has just completed the Phase I Upgrade programme. The Phase I Upgrade programme was centered
Introduction to XAFS. Grant Bunker Associate Professor, Physics Illinois Institute of Technology. Revised 4/11/97
 Introduction to XAFS Grant Bunker Associate Professor, Physics Illinois Institute of Technology Revised 4/11/97 2 tutorial.nb Outline Overview of Tutorial 1: Overview of XAFS 2: Basic Experimental design
Introduction to XAFS Grant Bunker Associate Professor, Physics Illinois Institute of Technology Revised 4/11/97 2 tutorial.nb Outline Overview of Tutorial 1: Overview of XAFS 2: Basic Experimental design
Laboratory Manual 1.0.6
 Laboratory Manual 1.0.6 Background What is X-ray Diffraction? X-rays scatter off of electrons, in a process of absorption and re-admission. Diffraction is the accumulative result of the x-ray scattering
Laboratory Manual 1.0.6 Background What is X-ray Diffraction? X-rays scatter off of electrons, in a process of absorption and re-admission. Diffraction is the accumulative result of the x-ray scattering
Rajesh Prasad Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology New Delhi
 TEQIP WORKSHOP ON HIGH RESOLUTION X-RAY AND ELECTRON DIFFRACTION, FEB 01, 2016, IIT-K. Introduction to x-ray diffraction Peak Positions and Intensities Rajesh Prasad Department of Applied Mechanics Indian
TEQIP WORKSHOP ON HIGH RESOLUTION X-RAY AND ELECTRON DIFFRACTION, FEB 01, 2016, IIT-K. Introduction to x-ray diffraction Peak Positions and Intensities Rajesh Prasad Department of Applied Mechanics Indian
X-ray Crystallography. Kalyan Das
 X-ray Crystallography Kalyan Das Electromagnetic Spectrum NMR 10 um - 10 mm 700 to 10 4 nm 400 to 700 nm 10 to 400 nm 10-1 to 10 nm 10-4 to 10-1 nm X-ray radiation was discovered by Roentgen in 1895. X-rays
X-ray Crystallography Kalyan Das Electromagnetic Spectrum NMR 10 um - 10 mm 700 to 10 4 nm 400 to 700 nm 10 to 400 nm 10-1 to 10 nm 10-4 to 10-1 nm X-ray radiation was discovered by Roentgen in 1895. X-rays
(Re-write, January 2011, from notes of S. C. Fain Jr., L. Sorensen, O. E. Vilches, J. Stoltenberg and D. B. Pengra, Version 1, preliminary)
 Electron Diffraction (Re-write, January 011, from notes of S. C. Fain Jr., L. Sorensen, O. E. Vilches, J. Stoltenberg and D. B. Pengra, Version 1, preliminary) References: Any introductory physics text
Electron Diffraction (Re-write, January 011, from notes of S. C. Fain Jr., L. Sorensen, O. E. Vilches, J. Stoltenberg and D. B. Pengra, Version 1, preliminary) References: Any introductory physics text
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 9.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 9.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Solid-state physics. Laue diagrams: investigating the lattice structure of monocrystals. LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P
 Solid-state physics Properties of crystals X-ray structural analysis LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P7.1.2.2 Laue diagrams: investigating the lattice structure of monocrystals Objects of the experiment Evaluating
Solid-state physics Properties of crystals X-ray structural analysis LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P7.1.2.2 Laue diagrams: investigating the lattice structure of monocrystals Objects of the experiment Evaluating
X-ray, Neutron and e-beam scattering
 X-ray, Neutron and e-beam scattering Introduction Why scattering? Diffraction basics Neutrons and x-rays Techniques Direct and reciprocal space Single crystals Powders CaFe 2 As 2 an example What is the
X-ray, Neutron and e-beam scattering Introduction Why scattering? Diffraction basics Neutrons and x-rays Techniques Direct and reciprocal space Single crystals Powders CaFe 2 As 2 an example What is the
The Solid State. Phase diagrams Crystals and symmetry Unit cells and packing Types of solid
 The Solid State Phase diagrams Crystals and symmetry Unit cells and packing Types of solid Learning objectives Apply phase diagrams to prediction of phase behaviour Describe distinguishing features of
The Solid State Phase diagrams Crystals and symmetry Unit cells and packing Types of solid Learning objectives Apply phase diagrams to prediction of phase behaviour Describe distinguishing features of
Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric)
 Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric) crystal Y X-ray source 2θ X direct beam tan 2θ = Y X d = resolution 2d sinθ = λ detector 1 Unit Cell: two vectors in plane of image c* Observe: b*
Resolution: maximum limit of diffraction (asymmetric) crystal Y X-ray source 2θ X direct beam tan 2θ = Y X d = resolution 2d sinθ = λ detector 1 Unit Cell: two vectors in plane of image c* Observe: b*
How Does It All Work? A Summary of the IDEAS Beamline at the Canadian Light Source
 How Does It All Work? A Summary of the IDEAS Beamline at the Canadian Light Source What Makes Up The Canadian Light Source? 4. Storage Ring 5. Synchrotron Light 6. Beamline 1. Electron Gun 2. Linear Accelerator
How Does It All Work? A Summary of the IDEAS Beamline at the Canadian Light Source What Makes Up The Canadian Light Source? 4. Storage Ring 5. Synchrotron Light 6. Beamline 1. Electron Gun 2. Linear Accelerator
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 14
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 14 Modern Physics 1. Relativity Einstein s General Relativity 2. Quantum Physics Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect X-Rays Diffraction by Crystals The Compton Effect
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 14 Modern Physics 1. Relativity Einstein s General Relativity 2. Quantum Physics Blackbody Radiation Photoelectric Effect X-Rays Diffraction by Crystals The Compton Effect
Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials
 Brent Fultz James Howe Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials Fourth Edition ~Springer 1 1 Diffraction and the X-Ray Powder Diffractometer 1 1.1 Diffraction... 1 1.1.1 Introduction
Brent Fultz James Howe Transmission Electron Microscopy and Diffractometry of Materials Fourth Edition ~Springer 1 1 Diffraction and the X-Ray Powder Diffractometer 1 1.1 Diffraction... 1 1.1.1 Introduction
EXAFS. Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure
 AOFSRR Cheiron School 2010, SPring-8 EXAFS Oct. 14th, 2010 Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure Iwao Watanabe Ritsumeikan University EXAFS Theory Quantum Mechanics Models Approximations Experiment
AOFSRR Cheiron School 2010, SPring-8 EXAFS Oct. 14th, 2010 Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure Iwao Watanabe Ritsumeikan University EXAFS Theory Quantum Mechanics Models Approximations Experiment
de Broglie Waves h p de Broglie argued Light exhibits both wave and particle properties
 de Broglie argued de Broglie Waves Light exhibits both wave and particle properties Wave interference, diffraction Particle photoelectric effect, Compton effect Then matter (particles) should exhibit both
de Broglie argued de Broglie Waves Light exhibits both wave and particle properties Wave interference, diffraction Particle photoelectric effect, Compton effect Then matter (particles) should exhibit both
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics
 PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Final exam is scheduled on Thursday May 2 @ 8 10 AM In Physics 112 It will cover five Chapters 25, 27, 28, 29, and 30. Review lecture notes,
PHYS 219 General Physics: Electricity, Light and Modern Physics Final exam is scheduled on Thursday May 2 @ 8 10 AM In Physics 112 It will cover five Chapters 25, 27, 28, 29, and 30. Review lecture notes,
Lecture 10. Transition probabilities and photoelectric cross sections
 Lecture 10 Transition probabilities and photoelectric cross sections TRANSITION PROBABILITIES AND PHOTOELECTRIC CROSS SECTIONS Cross section = = Transition probability per unit time of exciting a single
Lecture 10 Transition probabilities and photoelectric cross sections TRANSITION PROBABILITIES AND PHOTOELECTRIC CROSS SECTIONS Cross section = = Transition probability per unit time of exciting a single
Scattering and Diffraction
 Scattering and Diffraction Adventures in k-space, part 1 Lenson Pellouchoud SLAC / SSL XSD summer school 7/16/018 lenson@slac.stanford.edu Outline Elastic Scattering eview / overview and terminology Form
Scattering and Diffraction Adventures in k-space, part 1 Lenson Pellouchoud SLAC / SSL XSD summer school 7/16/018 lenson@slac.stanford.edu Outline Elastic Scattering eview / overview and terminology Form
SLAC Summer School on Electron and Photon Beams. Tor Raubenheimer Lecture #2: Inverse Compton and FEL s
 SLAC Summer School on Electron and Photon Beams Tor Raubenheimer Lecture #: Inverse Compton and FEL s Outline Synchrotron radiation Bending magnets Wigglers and undulators Inverse Compton scattering Free
SLAC Summer School on Electron and Photon Beams Tor Raubenheimer Lecture #: Inverse Compton and FEL s Outline Synchrotron radiation Bending magnets Wigglers and undulators Inverse Compton scattering Free
MP464: Solid State Physics Problem Sheet
 MP464: Solid State Physics Problem Sheet 1 Write down primitive lattice vectors for the -dimensional rectangular lattice, with sides a and b in the x and y-directions respectively, and a face-centred rectangular
MP464: Solid State Physics Problem Sheet 1 Write down primitive lattice vectors for the -dimensional rectangular lattice, with sides a and b in the x and y-directions respectively, and a face-centred rectangular
X-ray Data Collection. Bio5325 Spring 2006
 X-ray Data Collection Bio535 Spring 006 Obtaining I hkl and α (Ihkl) from Frame Images Braggs Law -predicts conditions for in-phase scattering by equivalent atoms lying in planes that transect a crystal.
X-ray Data Collection Bio535 Spring 006 Obtaining I hkl and α (Ihkl) from Frame Images Braggs Law -predicts conditions for in-phase scattering by equivalent atoms lying in planes that transect a crystal.
X-rays. X-ray Radiography - absorption is a function of Z and density. X-ray crystallography. X-ray spectrometry
 X-rays Wilhelm K. Roentgen (1845-1923) NP in Physics 1901 X-ray Radiography - absorption is a function of Z and density X-ray crystallography X-ray spectrometry X-rays Cu K α E = 8.05 kev λ = 1.541 Å Interaction
X-rays Wilhelm K. Roentgen (1845-1923) NP in Physics 1901 X-ray Radiography - absorption is a function of Z and density X-ray crystallography X-ray spectrometry X-rays Cu K α E = 8.05 kev λ = 1.541 Å Interaction
CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy. Diffraction 1
 CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy Diffraction 1 2018-10-15 Yanling Ge Text book: Transmission electron microscopy by David B Williams & C. Barry Carter. 2009, Springer Outline Diffraction in TEM Thinking
CHEM-E5225 :Electron Microscopy Diffraction 1 2018-10-15 Yanling Ge Text book: Transmission electron microscopy by David B Williams & C. Barry Carter. 2009, Springer Outline Diffraction in TEM Thinking
Röntgenpraktikum. M. Oehzelt. (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1])
![Röntgenpraktikum. M. Oehzelt. (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1]) Röntgenpraktikum. M. Oehzelt. (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1])](/thumbs/91/106501237.jpg) Röntgenpraktikum M. Oehzelt (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1]) October 21, 2004 Contents 1 Fundamentals 2 1.1 X-Ray Radiation......................... 2 1.1.1 Bremsstrahlung......................
Röntgenpraktikum M. Oehzelt (based on the diploma thesis of T. Haber [1]) October 21, 2004 Contents 1 Fundamentals 2 1.1 X-Ray Radiation......................... 2 1.1.1 Bremsstrahlung......................
Introduction to Materials Science Graduate students (Applied Physics)
 Introduction to Materials Science Graduate students (Applied Physics) Prof. Michael Roth Chapter Reciprocal Lattice and X-ray Diffraction Reciprocal Lattice - 1 The crystal can be viewed as made up of
Introduction to Materials Science Graduate students (Applied Physics) Prof. Michael Roth Chapter Reciprocal Lattice and X-ray Diffraction Reciprocal Lattice - 1 The crystal can be viewed as made up of
USPAS course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs Ivan Bazarov, Cornell University Geoff Krafft, JLAB. ERL as a X-ray Light Source
 USPAS course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs Ivan Bazarov, Cornell University Geoff Krafft, JLAB ERL as a X-ray Light Source Contents Introduction Light sources landscape General motivation
USPAS course on Recirculated and Energy Recovered Linacs Ivan Bazarov, Cornell University Geoff Krafft, JLAB ERL as a X-ray Light Source Contents Introduction Light sources landscape General motivation
Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung
 . Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung Lecture 5 Vorlesung zum Haupt/Masterstudiengang Physik SS 2014 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert Today: 1 st exercises!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
. Methoden moderner Röntgenphysik II: Streuung und Abbildung Lecture 5 Vorlesung zum Haupt/Masterstudiengang Physik SS 2014 G. Grübel, M. Martins, E. Weckert Today: 1 st exercises!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
CERN Accelerator School. Intermediate Accelerator Physics Course Chios, Greece, September Low Emittance Rings
 CERN Accelerator School Intermediate Accelerator Physics Course Chios, Greece, September 2011 Low Emittance Rings Part 1: Beam Dynamics with Synchrotron Radiation Andy Wolski The Cockcroft Institute, and
CERN Accelerator School Intermediate Accelerator Physics Course Chios, Greece, September 2011 Low Emittance Rings Part 1: Beam Dynamics with Synchrotron Radiation Andy Wolski The Cockcroft Institute, and
