Linear Classification
|
|
|
- Anis Carter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Linear Classification by Prof. Seungchul Lee isystems Design Lab UNIS able of Contents I.. Supervised Learning II.. Classification III. 3. Perceptron I. 3.. Linear Classifier II. 3.. Perceptron Algorithm III Iterations of Perceptron IV Perceptron loss function V he best hyperplane separator? VI Python Example
2 . Supervised Learning. Classification where y is a discrete value develop the classification algorithm to determine which class a new input should fall into start with binary class problems Later look at multiclass classification problem, although this is just an extension of binary classification We could use linear regression hen, threshold the classifier output (i.e. anything over some value is yes, else no) linear regression with thresholding seems to work We will learn perceptron support vector machine logistic regression
3 3. Perceptron x For input x = x d ω weights ω = ω d 'attributes of a customer' Approve credit if Deny credit if d ω i x i i= d ω i x i i= > threshold, < threshold. d h(x) = sign (( ) threshold) = sign (( ) + ) ω i x i i= = Introduce an artificial coordinate x 0 : In vector form, the perceptron implements d h(x) = sign ( ) ω i x i i=0 h(x) = sign ( ω x) d ω i x i ω 0 i=
4 Hyperplane Separates a D-dimensional space into two half-spaces Defined by an outward pointing normal vector ω ω is orthogonal to any vector lying on the hyperplane assume the hyperplane passes through origin, ω x = 0 with x 0 =
5 3.. Linear Classifier represent the decision boundary by a hyperplane ω he linear classifier is a way of combining expert opinion. In this case, each opinion is made by a binary "expert" Goal: to learn the hyperplane ω using the training data 3.. Perceptron Algorithm he perceptron implements h(x) = sign ( ω x) Given the training set (, ), (, ),, (, ) where {, } x y x y x N y N y i ) pick a misclassified point sign ( ω x n ) y n ) and update the weight vector ω ω + y n x n
6 Why perceptron updates work? = + Let's look at a misclassified positive example ( ) perceptron (wrongly) thinks ω old x n < 0 y n updates would be ω new ω new x n = + = + ω old y n x n ω old x n = ( + = + ω old x n ) x n ω old x n x n x n hus ω new x n is less negative than ω old x n
7 3.3. Iterations of Perceptron. Randomly assign ω. One iteration of the PLA (perceptron learning algorithm) where (x, y) is a misclassified training point t =,, 3,, ω ω + yx 3. At iteration pick a misclassified point from x y x y x N y N (, ), (, ),, (, ) 4. and run a PLA iteration on it 5. hat's it! 3.4. Perceptron loss function m L(ω) = max {0, ( )} n= Loss = 0 on examples where perceptron is correct, i.e., Loss > 0 on examples where perceptron misclassified, i.e., y n y n ω x n ( ) > 0 y n ω x n ( ) < 0 ω x n note: sign ( ω x n ) y n is equivalent to y n ( ω x n ) < 0
8 3.5. he best hyperplane separator? Perceptron finds one of the many possible hyperplanes separating the data if one exists Of the many possible choices, which one is the best? Utilize distance information as well Intuitively we want the hyperplane having the maximum margin Large margin leads to good generalization on the test data we will see this formally when we cover Support Vector Machine 3.6. Python Example ω = ω ω ω 3 ( x () ) x y ( x () ) = = = ( x (3) ) ( x (m) ) y () y () y (3) y (m) x () x () x (3) x (m) x () x () x (3) x (m) In []: import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt % matplotlib inline In []: #training data gerneration m = 00 x = 8*np.random.rand(m, ) x = 7*np.random.rand(m, ) - 4 g0 = 0.8*x + x - 3 g = g0 - g = g0 +
9 In [3]: C = np.where(g >= 0) C = np.where(g < 0) print(c) (array([ 0,, 5, 8, 6, 8, 9,, 3, 6, 30, 3, 33, 4, 46, 55, 5 9, 6, 64, 67, 7, 77, 83, 99]), array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])) In [4]: C = np.where(g >= 0)[0] C = np.where(g < 0)[0] print(c.shape) print(c.shape) (4,) (45,) In [6]: plt.figure(figsize=(0, 6)) plt.plot(x[c], x[c], 'ro', label='c') plt.plot(x[c], x[c], 'bo', label='c') plt.title('linearly seperable classes', fontsize=5) plt.legend(loc='upper left', fontsize=5) plt.xlabel(r'$x_$', fontsize=0) plt.ylabel(r'$x_$', fontsize=0) plt.show()
10 x y ( x () ) ( x () ) = = = ( x (3) ) ( x (m) ) y () y () y (3) y (m) x () x () x (3) x (m) x () x () x (3) x (m) In [6]: X = np.hstack([np.ones([c.shape[0],]), x[c], x[c]]) X = np.hstack([np.ones([c.shape[0],]), x[c], x[c]]) X = np.vstack([x, X]) y = np.vstack([np.ones([c.shape[0],]), -np.ones([c.shape[0],])]) X = np.asmatrix(x) y = np.asmatrix(y) where (x, y) is a misclassified training point ω = ω ω ω 3 ω ω + yx In [7]: w = np.ones([3,]) w = np.asmatrix(w) n_iter = y.shape[0] for k in range(n_iter): for i in range(n_iter): if y[i,0]!= np.sign(x[i,:]*w)[0,0]: w += y[i,0]*x[i,:]. print(w) [[-9. ] [.97353] [ ]] g(x) = ω x + ω 0 = ω x + ω x + ω 0 = 0 x = ω ω 0 x ω ω
11 In [8]: xp = np.linspace(0,8,00).reshape(-,) xp = - w[,0]/w[,0]*xp - w[0,0]/w[,0] plt.figure(figsize=(0, 6)) plt.scatter(x[c], x[c], c='r', s=50, label='c') plt.scatter(x[c], x[c], c='b', s=50, label='c') plt.plot(xp, xp, c='k', label='perceptron') plt.xlim([0,8]) plt.xlabel('$x_$', fontsize = 0) plt.ylabel('$x_$', fontsize = 0) plt.legend(loc = 4, fontsize = 5) plt.show()
12 In [9]: # animation import matplotlib.animation as animation % matplotlib qt5 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(0, 6)) ax = fig.add_subplot(,, ) plot_c, = ax.plot(x[c], x[c], 'go', label='c') plot_c, = ax.plot(x[c], x[c], 'bo', label='c') plot_perceptron, = ax.plot([], [], 'k', label='perceptron') ax.set_xlim(0, 8) ax.set_ylim(-3.5, 4.5) ax.set_xlabel(r'$x_$', fontsize=0) ax.set_ylabel(r'$x_$', fontsize=0) ax.legend(fontsize=5, loc='upper left') n_iter = y.shape[0] def init(): plot_perceptron.set_data(xp, xp) return plot_perceptron, def animate(i): global w idx = i%n_iter if y[idx,0]!= np.sign(x[idx,:]*w)[0,0]: w += y[idx,0]*x[idx,:]. xp = - w[,0]/w[,0]*xp - w[0,0]/w[,0] plot_perceptron.set_data(xp, xp) return plot_perceptron, w = np.ones([3,]) xp = np.linspace(0,8,00).reshape(-,) xp = - w[,0]/w[,0]*xp - w[0,0]/w[,0] ani = animation.funcanimation(fig, animate, np.arange(0, n_iter**), init_func=init, interval=0, repeat=false) plt.show() In [0]: %%javascript $.getscript(' js')
Perceptron. by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab POSTECH. Table of Contents
 Perceptron by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I.. Supervised Learning II.. Classification III. 3. Perceptron I. 3.. Linear Classifier II. 3..
Perceptron by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I.. Supervised Learning II.. Classification III. 3. Perceptron I. 3.. Linear Classifier II. 3..
Supervised Learning. 1. Optimization. without Scikit Learn. by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab
 Supervised Learning without Scikit Learn by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSECH able of Contents I.. Optimization II.. Linear Regression III. 3. Classification (Linear)
Supervised Learning without Scikit Learn by Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSECH able of Contents I.. Optimization II.. Linear Regression III. 3. Classification (Linear)
Support Vector Machine
 Support Vector Machine by Prof. Seungchul Lee isystems Design Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ UNIS able of Contents I.. Classification (Linear) II.. Distance from a Line III. 3. Illustrative Example I.
Support Vector Machine by Prof. Seungchul Lee isystems Design Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ UNIS able of Contents I.. Classification (Linear) II.. Distance from a Line III. 3. Illustrative Example I.
Logistic Regression. by Prof. Seungchul Lee isystems Design Lab UNIST. Table of Contents
 Logistic Regression by Prof. Seungchul Lee isystes Design Lab http://isystes.unist.ac.kr/ UNIST Table of Contents I.. Linear Classification: Logistic Regression I... Using all Distances II..2. Probabilistic
Logistic Regression by Prof. Seungchul Lee isystes Design Lab http://isystes.unist.ac.kr/ UNIST Table of Contents I.. Linear Classification: Logistic Regression I... Using all Distances II..2. Probabilistic
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories /
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Prof. Seungchul Lee Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories /
Support Vector Machine. Industrial AI Lab.
 Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
Support Vector Machine Industrial AI Lab. Classification (Linear) Autonomously figure out which category (or class) an unknown item should be categorized into Number of categories / classes Binary: 2 different
(Artificial) Neural Networks in TensorFlow
 (Artificial) Neural Networks in TensorFlow By Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I. 1. Recall Supervised Learning Setup II. 2. Artificial Neural
(Artificial) Neural Networks in TensorFlow By Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I. 1. Recall Supervised Learning Setup II. 2. Artificial Neural
Learning From Data Lecture 2 The Perceptron
 Learning From Data Lecture 2 The Perceptron The Learning Setup A Simple Learning Algorithm: PLA Other Views of Learning Is Learning Feasible: A Puzzle M. Magdon-Ismail CSCI 4100/6100 recap: The Plan 1.
Learning From Data Lecture 2 The Perceptron The Learning Setup A Simple Learning Algorithm: PLA Other Views of Learning Is Learning Feasible: A Puzzle M. Magdon-Ismail CSCI 4100/6100 recap: The Plan 1.
(Artificial) Neural Networks in TensorFlow
 (Artificial) Neural Networks in TensorFlow By Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I. 1. Recall Supervised Learning Setup II. 2. Artificial Neural
(Artificial) Neural Networks in TensorFlow By Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I. 1. Recall Supervised Learning Setup II. 2. Artificial Neural
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Lecture 11: Review. Henry Chai 10/02/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
Recurrent Neural Network
 Recurrent Neural Network By Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I. 1. Time Series Data I. 1.1. Deterministic II. 1.2. Stochastic III. 1.3. Dealing
Recurrent Neural Network By Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I. 1. Time Series Data I. 1.1. Deterministic II. 1.2. Stochastic III. 1.3. Dealing
More about the Perceptron
 More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive
More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive
Regression and Classification" with Linear Models" CMPSCI 383 Nov 15, 2011!
 Regression and Classification" with Linear Models" CMPSCI 383 Nov 15, 2011! 1 Todayʼs topics" Learning from Examples: brief review! Univariate Linear Regression! Batch gradient descent! Stochastic gradient
Regression and Classification" with Linear Models" CMPSCI 383 Nov 15, 2011! 1 Todayʼs topics" Learning from Examples: brief review! Univariate Linear Regression! Batch gradient descent! Stochastic gradient
DM534 - Introduction to Computer Science
 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark, Odense October 21, 2016 Marco Chiarandini DM534 - Introduction to Computer Science Training Session, Week 41-43, Autumn 2016
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark, Odense October 21, 2016 Marco Chiarandini DM534 - Introduction to Computer Science Training Session, Week 41-43, Autumn 2016
COMP 652: Machine Learning. Lecture 12. COMP Lecture 12 1 / 37
 COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
Recurrent Neural Network
 Recurrent Neural Network By Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I. 1. Time Series Data I. 1.1. Deterministic II. 1.2. Stochastic III. 1.3. Dealing
Recurrent Neural Network By Prof. Seungchul Lee Industrial AI Lab http://isystems.unist.ac.kr/ POSTECH Table of Contents I. 1. Time Series Data I. 1.1. Deterministic II. 1.2. Stochastic III. 1.3. Dealing
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 11. Linear Soft Margin Support Vector Machines
 CS142: Machine Learning Spring 2017 Lecture 11 Instructor: Pedro Felzenszwalb Scribes: Dan Xiang, Tyler Dae Devlin Linear Soft Margin Support Vector Machines We continue our discussion of linear soft margin
CS142: Machine Learning Spring 2017 Lecture 11 Instructor: Pedro Felzenszwalb Scribes: Dan Xiang, Tyler Dae Devlin Linear Soft Margin Support Vector Machines We continue our discussion of linear soft margin
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification
 Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, C. M. Bishop, 2006. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and echnology 77 Cheongam-ro,
Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, C. M. Bishop, 2006. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and echnology 77 Cheongam-ro,
Machine Learning. Linear Models. Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017
 Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017 1 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w
Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017 1 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w
Linear Classifiers. Michael Collins. January 18, 2012
 Linear Classifiers Michael Collins January 18, 2012 Today s Lecture Binary classification problems Linear classifiers The perceptron algorithm Classification Problems: An Example Goal: build a system that
Linear Classifiers Michael Collins January 18, 2012 Today s Lecture Binary classification problems Linear classifiers The perceptron algorithm Classification Problems: An Example Goal: build a system that
Binary Classification / Perceptron
 Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Learning: Binary Perceptron. Examples: Perceptron. Separable Case. In the space of feature vectors
 Linear Classifiers CS 88 Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons and Logistic Regression Pieter Abbeel & Dan Klein University of California, Berkeley Feature Vectors Some (Simplified) Biology Very loose inspiration
Linear Classifiers CS 88 Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons and Logistic Regression Pieter Abbeel & Dan Klein University of California, Berkeley Feature Vectors Some (Simplified) Biology Very loose inspiration
CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm
 CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava January 17, 2017 Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm January 17, 2017 1 / 1 Recap:
CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava January 17, 2017 Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm January 17, 2017 1 / 1 Recap:
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
CSC242: Intro to AI. Lecture 21
 CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 21 Administrivia Project 4 (homeworks 18 & 19) due Mon Apr 16 11:59PM Posters Apr 24 and 26 You need an idea! You need to present it nicely on 2-wide by 4-high landscape pages
CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 21 Administrivia Project 4 (homeworks 18 & 19) due Mon Apr 16 11:59PM Posters Apr 24 and 26 You need an idea! You need to present it nicely on 2-wide by 4-high landscape pages
Exercise_set7_programming_exercises
 Exercise_set7_programming_exercises May 13, 2018 1 Part 1(d) We start by defining some function that will be useful: The functions defining the system, and the Hamiltonian and angular momentum. In [1]:
Exercise_set7_programming_exercises May 13, 2018 1 Part 1(d) We start by defining some function that will be useful: The functions defining the system, and the Hamiltonian and angular momentum. In [1]:
MIRA, SVM, k-nn. Lirong Xia
 MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Linear classification. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear classification Kalev Kask Supervised learning Notation Features x Targets y Predictions ŷ = f(x ; q) Parameters q Program ( Learner ) Learning algorithm Change q
Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear classification Kalev Kask Supervised learning Notation Features x Targets y Predictions ŷ = f(x ; q) Parameters q Program ( Learner ) Learning algorithm Change q
Linear Classification. CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Linear Classification CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Example of Linear Classification Red points: patterns belonging
Linear Classification CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Example of Linear Classification Red points: patterns belonging
Unsupervised Learning: Dimension Reduction
 Unsupervised Learning: Diension Reduction by Prof. Seungchul Lee isystes Design Lab http://isystes.unist.ac.kr/ UNIST Table of Contents I.. Principal Coponent Analysis (PCA) II. 2. PCA Algorith I. 2..
Unsupervised Learning: Diension Reduction by Prof. Seungchul Lee isystes Design Lab http://isystes.unist.ac.kr/ UNIST Table of Contents I.. Principal Coponent Analysis (PCA) II. 2. PCA Algorith I. 2..
CSE 151 Machine Learning. Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri
 CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Linear Classification Given labeled data: (xi, feature vector yi) label i=1,..,n where y is 1 or 1, find a hyperplane to separate from Linear Classification
CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Linear Classification Given labeled data: (xi, feature vector yi) label i=1,..,n where y is 1 or 1, find a hyperplane to separate from Linear Classification
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
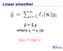 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 2, part 1: Basic linear algebra; linear algebra in NumPy and SciPy. Richard Johansson
 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 2, part 1: Basic linear algebra; linear algebra in NumPy and SciPy Richard Johansson linear algebra linear algebra is the branch of mathematics that deals with relationships
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 2, part 1: Basic linear algebra; linear algebra in NumPy and SciPy Richard Johansson linear algebra linear algebra is the branch of mathematics that deals with relationships
Chapter 14 Combining Models
 Chapter 14 Combining Models T-61.62 Special Course II: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Spring 27 Laboratory of Computer and Information Science TKK April 3th 27 Outline Independent Mixing Coefficients
Chapter 14 Combining Models T-61.62 Special Course II: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Spring 27 Laboratory of Computer and Information Science TKK April 3th 27 Outline Independent Mixing Coefficients
MAS212 Scientific Computing and Simulation
 MAS212 Scientific Computing and Simulation Dr. Sam Dolan School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Sheffield Autumn 2017 http://sam-dolan.staff.shef.ac.uk/mas212/ G18 Hicks Building s.dolan@sheffield.ac.uk
MAS212 Scientific Computing and Simulation Dr. Sam Dolan School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Sheffield Autumn 2017 http://sam-dolan.staff.shef.ac.uk/mas212/ G18 Hicks Building s.dolan@sheffield.ac.uk
The Perceptron Algorithm
 The Perceptron Algorithm Greg Grudic Greg Grudic Machine Learning Questions? Greg Grudic Machine Learning 2 Binary Classification A binary classifier is a mapping from a set of d inputs to a single output
The Perceptron Algorithm Greg Grudic Greg Grudic Machine Learning Questions? Greg Grudic Machine Learning 2 Binary Classification A binary classifier is a mapping from a set of d inputs to a single output
Conjugate-Gradient. Learn about the Conjugate-Gradient Algorithm and its Uses. Descent Algorithms and the Conjugate-Gradient Method. Qx = b.
 Lab 1 Conjugate-Gradient Lab Objective: Learn about the Conjugate-Gradient Algorithm and its Uses Descent Algorithms and the Conjugate-Gradient Method There are many possibilities for solving a linear
Lab 1 Conjugate-Gradient Lab Objective: Learn about the Conjugate-Gradient Algorithm and its Uses Descent Algorithms and the Conjugate-Gradient Method There are many possibilities for solving a linear
Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron
 Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Andrey Kan Copyright: University of Melbourne This lecture Notes on linear algebra Vectors
Lecture 6. Notes on Linear Algebra. Perceptron COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Andrey Kan Copyright: University of Melbourne This lecture Notes on linear algebra Vectors
Neural Networks. CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington
 Neural Networks CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Perceptrons x 0 = 1 x 1 x 2 z = h w T x Output: z x D A perceptron
Neural Networks CSE 6363 Machine Learning Vassilis Athitsos Computer Science and Engineering Department University of Texas at Arlington 1 Perceptrons x 0 = 1 x 1 x 2 z = h w T x Output: z x D A perceptron
From Binary to Multiclass Classification. CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018
 From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 4: Curse of Dimensionality, High Dimensional Feature Spaces, Linear Classifiers, Linear Regression, Python, and Jupyter Notebooks Peter Belhumeur Computer Science
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 4: Curse of Dimensionality, High Dimensional Feature Spaces, Linear Classifiers, Linear Regression, Python, and Jupyter Notebooks Peter Belhumeur Computer Science
10/05/2016. Computational Methods for Data Analysis. Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES. Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers
 Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Security Analytics. Topic 6: Perceptron and Support Vector Machine
 Security Analytics Topic 6: Perceptron and Support Vector Machine Purdue University Prof. Ninghui Li Based on slides by Prof. Jenifer Neville and Chris Clifton Readings Principle of Data Mining Chapter
Security Analytics Topic 6: Perceptron and Support Vector Machine Purdue University Prof. Ninghui Li Based on slides by Prof. Jenifer Neville and Chris Clifton Readings Principle of Data Mining Chapter
Preliminaries. Definition: The Euclidean dot product between two vectors is the expression. i=1
 90 8 80 7 70 6 60 0 8/7/ Preliminaries Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, T x + b < 0 T x + b > 0 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression
90 8 80 7 70 6 60 0 8/7/ Preliminaries Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, T x + b < 0 T x + b > 0 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression
CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II
 CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II Perceptrons Instructor: Alan Ritter Ohio State University [These slides were adapted from CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All materials available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.]
CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II Perceptrons Instructor: Alan Ritter Ohio State University [These slides were adapted from CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All materials available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.]
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771
 Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Logistic Regression. Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor
 Logistic Regression Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor Naïve Bayes Recap Bag of words (order independent) Features are assumed independent given class P (x 1,...,x n c) =P (x 1
Logistic Regression Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor Naïve Bayes Recap Bag of words (order independent) Features are assumed independent given class P (x 1,...,x n c) =P (x 1
Linear Transformations
 Lab 4 Linear Transformations Lab Objective: Linear transformations are the most basic and essential operators in vector space theory. In this lab we visually explore how linear transformations alter points
Lab 4 Linear Transformations Lab Objective: Linear transformations are the most basic and essential operators in vector space theory. In this lab we visually explore how linear transformations alter points
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F10 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers
 Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Data Mining Prof. Pabitra Mitra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Data Mining Prof. Pabitra Mitra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 21 K - Nearest Neighbor V In this lecture we discuss; how do we evaluate the
Data Mining Prof. Pabitra Mitra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 21 K - Nearest Neighbor V In this lecture we discuss; how do we evaluate the
Lorenz Equations. Lab 1. The Lorenz System
 Lab 1 Lorenz Equations Chaos: When the present determines the future, but the approximate present does not approximately determine the future. Edward Lorenz Lab Objective: Investigate the behavior of a
Lab 1 Lorenz Equations Chaos: When the present determines the future, but the approximate present does not approximately determine the future. Edward Lorenz Lab Objective: Investigate the behavior of a
Machine Learning 2017
 Machine Learning 2017 Volker Roth Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Basel 21st March 2017 Volker Roth (University of Basel) Machine Learning 2017 21st March 2017 1 / 41 Section
Machine Learning 2017 Volker Roth Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Basel 21st March 2017 Volker Roth (University of Basel) Machine Learning 2017 21st March 2017 1 / 41 Section
Linear models and the perceptron algorithm
 8/5/6 Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, 3 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression dx T x = i x i The dot product is also referred to as
8/5/6 Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, 3 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression dx T x = i x i The dot product is also referred to as
Single layer NN. Neuron Model
 Single layer NN We consider the simple architecture consisting of just one neuron. Generalization to a single layer with more neurons as illustrated below is easy because: M M The output units are independent
Single layer NN We consider the simple architecture consisting of just one neuron. Generalization to a single layer with more neurons as illustrated below is easy because: M M The output units are independent
CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING
 CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING 5: Vector Data: Support Vector Machine Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu October 18, 2017 Homework 1 Announcements Due end of the day of this Thursday (11:59pm)
CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING 5: Vector Data: Support Vector Machine Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu October 18, 2017 Homework 1 Announcements Due end of the day of this Thursday (11:59pm)
Machine Learning. Linear Models. Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017
 Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017 1 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w
Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017 1 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w
SPSS, University of Texas at Arlington. Topics in Machine Learning-EE 5359 Neural Networks
 Topics in Machine Learning-EE 5359 Neural Networks 1 The Perceptron Output: A perceptron is a function that maps D-dimensional vectors to real numbers. For notational convenience, we add a zero-th dimension
Topics in Machine Learning-EE 5359 Neural Networks 1 The Perceptron Output: A perceptron is a function that maps D-dimensional vectors to real numbers. For notational convenience, we add a zero-th dimension
LINEAR CLASSIFICATION, PERCEPTRON, LOGISTIC REGRESSION, SVC, NAÏVE BAYES. Supervised Learning
 LINEAR CLASSIFICATION, PERCEPTRON, LOGISTIC REGRESSION, SVC, NAÏVE BAYES Supervised Learning Linear vs non linear classifiers In K-NN we saw an example of a non-linear classifier: the decision boundary
LINEAR CLASSIFICATION, PERCEPTRON, LOGISTIC REGRESSION, SVC, NAÏVE BAYES Supervised Learning Linear vs non linear classifiers In K-NN we saw an example of a non-linear classifier: the decision boundary
Training the linear classifier
 215, Training the linear classifier A natural way to train the classifier is to minimize the number of classification errors on the training data, i.e. choosing w so that the training error is minimized.
215, Training the linear classifier A natural way to train the classifier is to minimize the number of classification errors on the training data, i.e. choosing w so that the training error is minimized.
Lecture 8. Instructor: Haipeng Luo
 Lecture 8 Instructor: Haipeng Luo Boosting and AdaBoost In this lecture we discuss the connection between boosting and online learning. Boosting is not only one of the most fundamental theories in machine
Lecture 8 Instructor: Haipeng Luo Boosting and AdaBoost In this lecture we discuss the connection between boosting and online learning. Boosting is not only one of the most fundamental theories in machine
6.036 midterm review. Wednesday, March 18, 15
 6.036 midterm review 1 Topics covered supervised learning labels available unsupervised learning no labels available semi-supervised learning some labels available - what algorithms have you learned that
6.036 midterm review 1 Topics covered supervised learning labels available unsupervised learning no labels available semi-supervised learning some labels available - what algorithms have you learned that
Learning Linear Detectors
 Learning Linear Detectors Instructor - Simon Lucey 16-423 - Designing Computer Vision Apps Today Detection versus Classification Bayes Classifiers Linear Classifiers Examples of Detection 3 Learning: Detection
Learning Linear Detectors Instructor - Simon Lucey 16-423 - Designing Computer Vision Apps Today Detection versus Classification Bayes Classifiers Linear Classifiers Examples of Detection 3 Learning: Detection
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188
Mistake Bound Model, Halving Algorithm, Linear Classifiers, & Perceptron
 Stat 928: Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 18 Mistake Bound Model, Halving Algorithm, Linear Classifiers, & Perceptron Instructor: Sham Kakade 1 Introduction This course will be divided into 2 parts.
Stat 928: Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 18 Mistake Bound Model, Halving Algorithm, Linear Classifiers, & Perceptron Instructor: Sham Kakade 1 Introduction This course will be divided into 2 parts.
The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt.
 1 The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt. The algorithm applies only to single layer models
1 The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt. The algorithm applies only to single layer models
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions
 Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an
Gradient Descent Methods
 Lab 18 Gradient Descent Methods Lab Objective: Many optimization methods fall under the umbrella of descent algorithms. The idea is to choose an initial guess, identify a direction from this point along
Lab 18 Gradient Descent Methods Lab Objective: Many optimization methods fall under the umbrella of descent algorithms. The idea is to choose an initial guess, identify a direction from this point along
Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms. D = {(x i,y i )} n i=1. x i 2 R d 9/3/13. Preliminaries. Chapter 1, 7.
 Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Logistic Regression. COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala
 Logistic Regression COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala Binary Classification Given an instance x we must classify it to either positive (1) or negative (0) class We can use {1,-1} instead of {1,0} but we will
Logistic Regression COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala Binary Classification Given an instance x we must classify it to either positive (1) or negative (0) class We can use {1,-1} instead of {1,0} but we will
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
Linear Discrimination Functions
 Laurea Magistrale in Informatica Nicola Fanizzi Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Bari November 4, 2009 Outline Linear models Gradient descent Perceptron Minimum square error approach
Laurea Magistrale in Informatica Nicola Fanizzi Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Bari November 4, 2009 Outline Linear models Gradient descent Perceptron Minimum square error approach
SGN (4 cr) Chapter 5
 SGN-41006 (4 cr) Chapter 5 Linear Discriminant Analysis Jussi Tohka & Jari Niemi Department of Signal Processing Tampere University of Technology January 21, 2014 J. Tohka & J. Niemi (TUT-SGN) SGN-41006
SGN-41006 (4 cr) Chapter 5 Linear Discriminant Analysis Jussi Tohka & Jari Niemi Department of Signal Processing Tampere University of Technology January 21, 2014 J. Tohka & J. Niemi (TUT-SGN) SGN-41006
NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION Nonlinear Classification and Regression: Outline 2 Multi-Layer Perceptrons The Back-Propagation Learning Algorithm Generalized Linear Models Radial Basis Function
NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION Nonlinear Classification and Regression: Outline 2 Multi-Layer Perceptrons The Back-Propagation Learning Algorithm Generalized Linear Models Radial Basis Function
Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP
 CS546: Machine Learning in NLP (Spring 2018) http://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs546/ Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP Julia Hockenmaier juliahmr@illinois.edu 3324 Siebel Center Office hours: Tue/Thu 2pm-3pm
CS546: Machine Learning in NLP (Spring 2018) http://courses.engr.illinois.edu/cs546/ Lecture 5 Neural models for NLP Julia Hockenmaier juliahmr@illinois.edu 3324 Siebel Center Office hours: Tue/Thu 2pm-3pm
Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification
 Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification Professor Ameet Talwalkar Slide Credit: Professor Fei Sha Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms October 13, 2015
Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification Professor Ameet Talwalkar Slide Credit: Professor Fei Sha Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms October 13, 2015
Errors, and What to Do. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall What to Do About Errors. Later On. Some (Simplified) Biology
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
Data Analysis and Machine Learning: Logistic Regression
 Data Analysis and Machine Learning: Logistic Regression Morten Hjorth-Jensen 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of Oslo 2 Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron
Data Analysis and Machine Learning: Logistic Regression Morten Hjorth-Jensen 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of Oslo 2 Department of Physics and Astronomy and National Superconducting Cyclotron
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
Introduction to Support Vector Machines
 Introduction to Support Vector Machines Hsuan-Tien Lin Learning Systems Group, California Institute of Technology Talk in NTU EE/CS Speech Lab, November 16, 2005 H.-T. Lin (Learning Systems Group) Introduction
Introduction to Support Vector Machines Hsuan-Tien Lin Learning Systems Group, California Institute of Technology Talk in NTU EE/CS Speech Lab, November 16, 2005 H.-T. Lin (Learning Systems Group) Introduction
Neural networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 MARINE CARPUAT. Slides credit: Graham Neubig
 Neural networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Slides credit: Graham Neubig Outline Perceptron: recap and limitations Neural networks Multi-layer perceptron Forward propagation
Neural networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Slides credit: Graham Neubig Outline Perceptron: recap and limitations Neural networks Multi-layer perceptron Forward propagation
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
The Perceptron algorithm
 The Perceptron algorithm Tirgul 3 November 2016 Agnostic PAC Learnability A hypothesis class H is agnostic PAC learnable if there exists a function m H : 0,1 2 N and a learning algorithm with the following
The Perceptron algorithm Tirgul 3 November 2016 Agnostic PAC Learnability A hypothesis class H is agnostic PAC learnable if there exists a function m H : 0,1 2 N and a learning algorithm with the following
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued. Richard Johansson
 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Kernel Logistic Regression and the Import Vector Machine
 Kernel Logistic Regression and the Import Vector Machine Ji Zhu and Trevor Hastie Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2005 Presented by Mingtao Ding Duke University December 8, 2011 Mingtao
Kernel Logistic Regression and the Import Vector Machine Ji Zhu and Trevor Hastie Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2005 Presented by Mingtao Ding Duke University December 8, 2011 Mingtao
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Outline
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 21: Perceptrons Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides adapted from Dan Klein. Outline Generative vs. Discriminative Binary Linear Classifiers Perceptron Multi-class
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 21: Perceptrons Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides adapted from Dan Klein. Outline Generative vs. Discriminative Binary Linear Classifiers Perceptron Multi-class
Ensembles. Léon Bottou COS 424 4/8/2010
 Ensembles Léon Bottou COS 424 4/8/2010 Readings T. G. Dietterich (2000) Ensemble Methods in Machine Learning. R. E. Schapire (2003): The Boosting Approach to Machine Learning. Sections 1,2,3,4,6. Léon
Ensembles Léon Bottou COS 424 4/8/2010 Readings T. G. Dietterich (2000) Ensemble Methods in Machine Learning. R. E. Schapire (2003): The Boosting Approach to Machine Learning. Sections 1,2,3,4,6. Léon
The Perceptron Algorithm
 The Perceptron Algorithm Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Outline The Perceptron Algorithm Perceptron Mistake Bound Variants of Perceptron 2 Where are we? The Perceptron
The Perceptron Algorithm Machine Learning Spring 2018 The slides are mainly from Vivek Srikumar 1 Outline The Perceptron Algorithm Perceptron Mistake Bound Variants of Perceptron 2 Where are we? The Perceptron
Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron
 CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes
 CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes John Duchi Binary classification In binary classification problems, the target y can take on at only two values. In this set of notes, we show how to model this problem
CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes John Duchi Binary classification In binary classification problems, the target y can take on at only two values. In this set of notes, we show how to model this problem
EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron
 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi, Mari Ostendorf, Pedro Domingos, Carlos Guestrin, and Luke Zettelmoyer, Kevin Jamison EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron Instructor: Hanna Hajishirzi hannaneh@washington.edu
Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi, Mari Ostendorf, Pedro Domingos, Carlos Guestrin, and Luke Zettelmoyer, Kevin Jamison EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron Instructor: Hanna Hajishirzi hannaneh@washington.edu
Machine Learning Linear Models
 Machine Learning Linear Models Outline II - Linear Models 1. Linear Regression (a) Linear regression: History (b) Linear regression with Least Squares (c) Matrix representation and Normal Equation Method
Machine Learning Linear Models Outline II - Linear Models 1. Linear Regression (a) Linear regression: History (b) Linear regression with Least Squares (c) Matrix representation and Normal Equation Method
AN INTRODUCTION TO NEURAL NETWORKS. Scott Kuindersma November 12, 2009
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NEURAL NETWORKS Scott Kuindersma November 12, 2009 SUPERVISED LEARNING We are given some training data: We must learn a function If y is discrete, we call it classification If it is
AN INTRODUCTION TO NEURAL NETWORKS Scott Kuindersma November 12, 2009 SUPERVISED LEARNING We are given some training data: We must learn a function If y is discrete, we call it classification If it is
5615 Chapter 3. April 8, Set #3 RP Simulation 3 Working with rp1 in the Notebook Proper Numerical Integration 5
 5615 Chapter 3 April 8, 2015 Contents Mixed RV and Moments 2 Simulation............................................... 2 Set #3 RP Simulation 3 Working with rp1 in the Notebook Proper.............................
5615 Chapter 3 April 8, 2015 Contents Mixed RV and Moments 2 Simulation............................................... 2 Set #3 RP Simulation 3 Working with rp1 in the Notebook Proper.............................
Linear Discriminant Functions
 Linear Discriminant Functions Linear discriminant functions and decision surfaces Definition It is a function that is a linear combination of the components of g() = t + 0 () here is the eight vector and
Linear Discriminant Functions Linear discriminant functions and decision surfaces Definition It is a function that is a linear combination of the components of g() = t + 0 () here is the eight vector and
Machine learning for pervasive systems Classification in high-dimensional spaces
 Machine learning for pervasive systems Classification in high-dimensional spaces Department of Communications and Networking Aalto University, School of Electrical Engineering stephan.sigg@aalto.fi Version
Machine learning for pervasive systems Classification in high-dimensional spaces Department of Communications and Networking Aalto University, School of Electrical Engineering stephan.sigg@aalto.fi Version
ESS2222. Lecture 4 Linear model
 ESS2222 Lecture 4 Linear model Hosein Shahnas University of Toronto, Department of Earth Sciences, 1 Outline Logistic Regression Predicting Continuous Target Variables Support Vector Machine (Some Details)
ESS2222 Lecture 4 Linear model Hosein Shahnas University of Toronto, Department of Earth Sciences, 1 Outline Logistic Regression Predicting Continuous Target Variables Support Vector Machine (Some Details)
Support Vector Machine
 Support Vector Machine Kernel: Kernel is defined as a function returning the inner product between the images of the two arguments k(x 1, x 2 ) = ϕ(x 1 ), ϕ(x 2 ) k(x 1, x 2 ) = k(x 2, x 1 ) modularity-
Support Vector Machine Kernel: Kernel is defined as a function returning the inner product between the images of the two arguments k(x 1, x 2 ) = ϕ(x 1 ), ϕ(x 2 ) k(x 1, x 2 ) = k(x 2, x 1 ) modularity-
