Deep Learning for Computer Vision
|
|
|
- Shavonne Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 4: Curse of Dimensionality, High Dimensional Feature Spaces, Linear Classifiers, Linear Regression, Python, and Jupyter Notebooks Peter Belhumeur Computer Science Columbia University
2 If we want to build a minimum-error rate classifier then we need a very good estimate of P (! i x).
3 Let s say our feature space is just 1 dimensional and our feature x 2 [0, 1]. And let s say we have 10,000 training samples from which to estimate our a posteriori probabilities. We could estimate these probabilities using a histogram in which we divided the interval into 100 evenly spaced bins.
4 ! 1! On average each bin would have 100 samples. We could estimate (x! i ) as the number of samples from class i that fall in the same bin that falls into divided by the total number of samples in that bin. x
5 But this plan does not scale as we increase the dimensionality of the feature space!
6 The Curse of Dimensionality!
7 Let s say our feature space is just 3 dimensional and our feature. x 2 [0, 1] 3 Let s say we still have 10,000 training samples from which to estimate our a posteriori probabilities. If we estimate these probabilities using a histogram in which we divided the volume into the same width bins as before
8 On average each bin would only have 0.01 samples! Ugh.
9 So we never have enough training samples to densely sample high-dimensional feature spaces!
10 And to make matters worse, intuition about how things behave in high-dimensional spaces is mostly incorrect.
11 4
12 What fraction of the volume of the unit hypercube is occupied by the biggest hypersphere that fits within it in n-dimensions? Say if n=20?
13 Volume of n-d hypersphere = V n R n V n = n 2 ( n 2 + 1) 10 So if n = 20, the volume = (10 + 1) = ! =
14 Another way to think of this is if we uniformly sampled 100 million points in the unit hypercube, then we should expect less than 3 of them would lie within its contained hypersphere.
15 back to building classifiers
16 What if we gave up on finding the probabilities and instead found discriminant functions that defined surfaces that separated our classes.
17
18 So let s find a separating surface by seeing if we can produce a function such that is always positive for the features of one class and negative for the features of another.
19
20 Linear Regression
21 y x
22 Find the line that minimizes the sum of the squared vertical distances of the line to the sample points. Let the line be parameterized by y = x = T x = h (x) where = apple 0 and x = 1 apple 1 x
23 Now given sample points (x (i),y (i) ), we can write our loss function to minimize as J( ) = 1 2m mx i=1 h (x (i) ) y (i) 2 and its gradient as r J( ) = 1 m mx h (x (i) ) y (i) x (i) i=1
24 This is a convex optimization problem so we can easily find the solution using gradient descent: (t + 1) = (t) r J( (t))
25 Course Programming Language: Python
26 Course Coding Environment: Jupyter Notebooks
27
28
29 Binary Classifier Let s say we have set of training samples (xi, yi) with i = 1,, N and xi and. 2 R d y i 2 { 1, 1} The goal is to learn a classifier f(xi) such that f(x i )= 0 y i =+1 < 0 y i = 1
30 f(x) 0 f(x) =0 f(x) < 0
31 But let s find a simple parametric separating surface by fitting to the training data using some pre-chosen criterion of optimality. If we restrict the decision surface to a line, plane, or hyperplane, then we call this a linear classifier.
32 Linear Classifier Let s say we have set of training samples (xi, yi) with i = 1,, N and xi and. 2 R d y i 2 { 1, 1} The goal is to learn a classifier f(xi) such that f(x i )= 0 y i =+1 < 0 y i = 1 and where f(x) =w T x + b
33 Linear Classifier Note: The classifier is a line, plane, or hyperplane depending of the dimension d w is normal to the line b is known as the bias. f(x) =w T x + b
34 f(x) 0 f(x) =0 f(x) < 0
35 w T x + b 0 w w w T x + b =0 w T x + b<0
36 Linearly Separable Data w T x + b =0
37 NOT Linearly Separable Data w T x + b =0
38 NOT Linearly Separable Data
39 Linear Classifier How do we find the weights given by w and b? f(x) =w T x + b
40 Perceptron Classifier Stack b onto end of weight vector w and stack a 1 onto end of feature vector x then we can write f(x) =w T x The perceptron algorithm cycles through the data points until all points are correctly classified updating the weights for each misclassification as w w + sign (f(x i )) x i
41 We can do better. We need to choose our weights according to some notion of optimality. So what is the best w?
42 Support Vector Machine Choose weights w and b to maximize the margin between classes. f(x) =w T x + b
43 Linearly Separable Data w T x + b 0 margin w w T x + b =0 w T x + b<0
44 We can choose the normalization of w however we please since this is a free parameter. Let s choose it so for the positive and negative support vectors so we have w T x + + b =+1 w T x + b = 1 This makes the margin width 2 w
45 Linearly Separable Data w T x + b 0 2 w w w T x + b =1 w T x + b =0 w T x + b<0 w T x + b = 1
46 We can now set this choice of w up as an optimization: max w 2 w subject to wt x i + b +1 if y i =+1 w T x i + b apple 1ify i = 1 Or equivalently, min w w 2 subject to y i (w T x i + b) 1 This is a quadratic optimation with linear constraints and a unique minimum.
47 What if the data is not linearly separable or has some bad apples?
48 Soft Margin and Slack Variables We soften the optimization with slack variables: NX min w w 2 + C i i subject to y i (w T x i + b) 1 i and i 0
49 If we make our slack variables large enough we can satisfy all of the constraints C is the regularization parameter Large C makes constraints hard to ignore = small margin Small C makes constraints easy to ignore = large margin Still a unique minimum
50 NOT Linearly Separable Data i > 2 2 w b w 0 < i < 1 w w T x + b =1 w T x + b =0 w T x + b = 1
51 Soft Margin and Slack Variables And with a little manipulation we get NX min w w 2 + C i max(0, 1 y i f(x i )) regularization + loss function
52 If a point is on its side of the support vector(s), there is no contribution to the loss as y i f(x i )) 1 If the point is within the margin or on other side of the opposite support vector(s), then there IS contribution to the loss as y i f(x i )) < 1
53 Loss Hinge Loss y i f(x i ))
54 NOT Linearly Separable Data i > 2 2 w b w 0 < i < 1 w w T x + b =1 w T x + b =0 w T x + b = 1
55 Optimization There is a closed form solution to optimal w NX min w w 2 + C i max(0, 1 y i f(x i )) regularization + loss function Alternatively, you use gradient descent!
56 Optimization Convex Non-Convex
57 Optimization X Convex Non-Convex
58 Gradient Descent for SVM Our cost function for optimizing can be re-written: min w C(w) = 2 w N NX max(0, 1 y i f(x i )) i with = 2 NC and f(x) =wt x + b
59 Gradient Descent for SVM So gradient descent might look like: w t+1 w t t r w C(w t ) with the learning rate t and but this gradient is not differentiable r w C(w)
60 (Sub-)Gradient of Hinge Loss Loss L(x,y; w) = max(0, 1 yf(x)) r w L = yx 1 r w L = yf(x))
61 So now the whole gradient becomes: r w C(w) = w + 1 N NX 1[y i w T x i < 1] y i x i i where 1[t] is and indicator function = 1 if argument is true and 0 if false.
62 Pegasos Algorithm
63 Pegasos is a stochastic gradient descent algorithm with a mini batch size = 1!
64
Machine Learning Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13
 Machine Learning 10-701 Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13 1. True or False Please give an explanation for your answer, this is worth 1 pt/question. (a) (2 points) No classifier can do better than a naive Bayes
Machine Learning 10-701 Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13 1. True or False Please give an explanation for your answer, this is worth 1 pt/question. (a) (2 points) No classifier can do better than a naive Bayes
Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron
 CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines
 Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Kernelized Perceptron Support Vector Machines Emily Fox University of Washington February 13, 2017 What is the perceptron optimizing? 1 The perceptron algorithm [Rosenblatt 58, 62] Classification setting:
Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms. D = {(x i,y i )} n i=1. x i 2 R d 9/3/13. Preliminaries. Chapter 1, 7.
 Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Max Margin-Classifier
 Max Margin-Classifier Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 7 Outline Maximum Margin Criterion Math Maximizing the Margin Non-Separable Data Kernels and Non-linear Mappings Where does the maximization
Max Margin-Classifier Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 7 Outline Maximum Margin Criterion Math Maximizing the Margin Non-Separable Data Kernels and Non-linear Mappings Where does the maximization
Lecture Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers
 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Amir Globerson Lecture 6 Fall Semester Scribe: Yishay Mansour 6.1 Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers Classification is one of the most important tasks in
Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Amir Globerson Lecture 6 Fall Semester Scribe: Yishay Mansour 6.1 Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers Classification is one of the most important tasks in
(Kernels +) Support Vector Machines
 (Kernels +) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Torsten Möller Reading Chapter 5 of Machine Learning An Algorithmic Perspective by Marsland Chapter 6+7 of Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
(Kernels +) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Torsten Möller Reading Chapter 5 of Machine Learning An Algorithmic Perspective by Marsland Chapter 6+7 of Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
Multi-class SVMs. Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University
 Multi-class SVMs Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University Administrative We will have a make-up lecture on Saturday April 23, 2016. Project progress reports are due April 21, 2016 2 days
Multi-class SVMs Lecture 17: Aykut Erdem April 2016 Hacettepe University Administrative We will have a make-up lecture on Saturday April 23, 2016. Project progress reports are due April 21, 2016 2 days
Machine Learning A Geometric Approach
 Machine Learning A Geometric Approach CIML book Chap 7.7 Linear Classification: Support Vector Machines (SVM) Professor Liang Huang some slides from Alex Smola (CMU) Linear Separator Ham Spam From Perceptron
Machine Learning A Geometric Approach CIML book Chap 7.7 Linear Classification: Support Vector Machines (SVM) Professor Liang Huang some slides from Alex Smola (CMU) Linear Separator Ham Spam From Perceptron
Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions
 CS281B/Stat241B (Spring 2008) Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 3 Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Hao Zhang 1 Review We assume that there is a probability
CS281B/Stat241B (Spring 2008) Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 3 Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Hao Zhang 1 Review We assume that there is a probability
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I. Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang
 Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Review: machine learning basics Math formulation Given training data x i, y i : 1 i n i.i.d. from distribution
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 4: SVM I Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Review: machine learning basics Math formulation Given training data x i, y i : 1 i n i.i.d. from distribution
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Prof. Matteo Matteucci Discriminative vs. Generative Approaches 2 o Generative approach: we derived the classifier from some generative hypothesis about the way
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine
 CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression
 Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION Nonlinear Classification and Regression: Outline 2 Multi-Layer Perceptrons The Back-Propagation Learning Algorithm Generalized Linear Models Radial Basis Function
NONLINEAR CLASSIFICATION AND REGRESSION Nonlinear Classification and Regression: Outline 2 Multi-Layer Perceptrons The Back-Propagation Learning Algorithm Generalized Linear Models Radial Basis Function
Support Vector Machines. Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar
 Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Data Mining Support Vector Machines Introduction to Data Mining, 2 nd Edition by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 02/03/2018 Introduction to Data Mining 1 Support Vector Machines Find a linear hyperplane
Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function.
 Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Statistical Methods for Data Mining
 Statistical Methods for Data Mining Kuangnan Fang Xiamen University Email: xmufkn@xmu.edu.cn Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find
Statistical Methods for Data Mining Kuangnan Fang Xiamen University Email: xmufkn@xmu.edu.cn Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find
Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers)
 Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Binary Classification / Perceptron
 Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Support Vector Machines and Bayes Regression
 Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F11) Lecture #14 (Monday ctober 31th) Support Vector Machines and Bayes Regression Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Carl Doersch 1 1 Linear SVMs We begin by considering
Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F11) Lecture #14 (Monday ctober 31th) Support Vector Machines and Bayes Regression Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Carl Doersch 1 1 Linear SVMs We begin by considering
Linear classifiers Lecture 3
 Linear classifiers Lecture 3 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin ML Methodology Data: labeled instances, e.g. emails marked spam/ham
Linear classifiers Lecture 3 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin ML Methodology Data: labeled instances, e.g. emails marked spam/ham
Support Vector Machines. Machine Learning Fall 2017
 Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost 2 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost Produce
Support Vector Machines Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost 2 Where are we? Learning algorithms Decision Trees Perceptron AdaBoost Produce
Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression. 1 Linearly Separable Data: Hard Margin SVMs
 E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Linear classification. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear classification Kalev Kask Supervised learning Notation Features x Targets y Predictions ŷ = f(x ; q) Parameters q Program ( Learner ) Learning algorithm Change q
Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear classification Kalev Kask Supervised learning Notation Features x Targets y Predictions ŷ = f(x ; q) Parameters q Program ( Learner ) Learning algorithm Change q
CS6375: Machine Learning Gautam Kunapuli. Support Vector Machines
 Gautam Kunapuli Example: Text Categorization Example: Develop a model to classify news stories into various categories based on their content. sports politics Use the bag-of-words representation for this
Gautam Kunapuli Example: Text Categorization Example: Develop a model to classify news stories into various categories based on their content. sports politics Use the bag-of-words representation for this
Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression
 CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 04, 207 Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may
CIS 520: Machine Learning Oct 04, 207 Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are designed to be a supplement to the lecture. They may
Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter
 Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods
 2018 CS420 Machine Learning, Lecture 3 Hangout from Prof. Andrew Ng. http://cs229.stanford.edu/notes/cs229-notes3.pdf Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University
2018 CS420 Machine Learning, Lecture 3 Hangout from Prof. Andrew Ng. http://cs229.stanford.edu/notes/cs229-notes3.pdf Support Vector Machines and Kernel Methods Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University
HOMEWORK 4: SVMS AND KERNELS
 HOMEWORK 4: SVMS AND KERNELS CMU 060: MACHINE LEARNING (FALL 206) OUT: Sep. 26, 206 DUE: 5:30 pm, Oct. 05, 206 TAs: Simon Shaolei Du, Tianshu Ren, Hsiao-Yu Fish Tung Instructions Homework Submission: Submit
HOMEWORK 4: SVMS AND KERNELS CMU 060: MACHINE LEARNING (FALL 206) OUT: Sep. 26, 206 DUE: 5:30 pm, Oct. 05, 206 TAs: Simon Shaolei Du, Tianshu Ren, Hsiao-Yu Fish Tung Instructions Homework Submission: Submit
Statistical Pattern Recognition
 Statistical Pattern Recognition Support Vector Machine (SVM) Hamid R. Rabiee Hadi Asheri, Jafar Muhammadi, Nima Pourdamghani Spring 2013 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/91-92/2/ce725-1/ Agenda Introduction
Statistical Pattern Recognition Support Vector Machine (SVM) Hamid R. Rabiee Hadi Asheri, Jafar Muhammadi, Nima Pourdamghani Spring 2013 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/91-92/2/ce725-1/ Agenda Introduction
COMP 652: Machine Learning. Lecture 12. COMP Lecture 12 1 / 37
 COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
COMP 652: Machine Learning Lecture 12 COMP 652 Lecture 12 1 / 37 Today Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence (Linear) support vector machines Margin & max margin classifier Formulation
Foundation of Intelligent Systems, Part I. SVM s & Kernel Methods
 Foundation of Intelligent Systems, Part I SVM s & Kernel Methods mcuturi@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp FIS - 2013 1 Support Vector Machines The linearly-separable case FIS - 2013 2 A criterion to select a linear classifier:
Foundation of Intelligent Systems, Part I SVM s & Kernel Methods mcuturi@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp FIS - 2013 1 Support Vector Machines The linearly-separable case FIS - 2013 2 A criterion to select a linear classifier:
Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers)
 Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers) Solution only depends on a small subset of training
CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm
 CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava January 17, 2017 Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm January 17, 2017 1 / 1 Recap:
CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava January 17, 2017 Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm January 17, 2017 1 / 1 Recap:
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions
 Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2015 Solutions The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Perceptrons and Support Vector machines
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Semester 2016 Lessons 6 10 Jan 2017 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector machines Notation... 2 Perceptrons... 3 History...3
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Semester 2016 Lessons 6 10 Jan 2017 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector machines Notation... 2 Perceptrons... 3 History...3
L5 Support Vector Classification
 L5 Support Vector Classification Support Vector Machine Problem definition Geometrical picture Optimization problem Optimization Problem Hard margin Convexity Dual problem Soft margin problem Alexander
L5 Support Vector Classification Support Vector Machine Problem definition Geometrical picture Optimization problem Optimization Problem Hard margin Convexity Dual problem Soft margin problem Alexander
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F10 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers
 Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Lecture 16: Modern Classification (I) - Separating Hyperplanes
 Lecture 16: Modern Classification (I) - Separating Hyperplanes Outline 1 2 Separating Hyperplane Binary SVM for Separable Case Bayes Rule for Binary Problems Consider the simplest case: two classes are
Lecture 16: Modern Classification (I) - Separating Hyperplanes Outline 1 2 Separating Hyperplane Binary SVM for Separable Case Bayes Rule for Binary Problems Consider the simplest case: two classes are
Support Vector Machine (continued)
 Support Vector Machine continued) Overlapping class distribution: In practice the class-conditional distributions may overlap, so that the training data points are no longer linearly separable. We need
Support Vector Machine continued) Overlapping class distribution: In practice the class-conditional distributions may overlap, so that the training data points are no longer linearly separable. We need
The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt.
 1 The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt. The algorithm applies only to single layer models
1 The perceptron learning algorithm is one of the first procedures proposed for learning in neural network models and is mostly credited to Rosenblatt. The algorithm applies only to single layer models
Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators. Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators Binary classification can be viewed as the task of separating classes in feature space: w T x + b > 0 w T x + b = 0 w T x + b < 0 Department
Support Vector Machines Perceptron Revisited: Linear Separators Binary classification can be viewed as the task of separating classes in feature space: w T x + b > 0 w T x + b = 0 w T x + b < 0 Department
10/05/2016. Computational Methods for Data Analysis. Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES. Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers
 Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Computational Methods for Data Analysis Massimo Poesio SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Support Vector Machines Linear classifiers 1 Linear Classifiers denotes +1 denotes -1 w x + b>0 f(x,w,b) = sign(w x + b) How
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Natural Language Processing. Classification. Features. Some Definitions. Classification. Feature Vectors. Classification I. Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Learning by constraints and SVMs (2)
 Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F12) Lecture#14 (Wednesday ctober 17) Learning by constraints and SVMs (2) Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Albert Wu 1 1 Support Vector Ranking Machine pening
Statistical Techniques in Robotics (16-831, F12) Lecture#14 (Wednesday ctober 17) Learning by constraints and SVMs (2) Lecturer: Drew Bagnell Scribe: Albert Wu 1 1 Support Vector Ranking Machine pening
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
LECTURE NOTE #8 PROF. ALAN YUILLE. Can we find a linear classifier that separates the position and negative examples?
 LECTURE NOTE #8 PROF. ALAN YUILLE 1. Linear Classifiers and Perceptrons A dataset contains N samples: { (x µ, y µ ) : µ = 1 to N }, y µ {±1} Can we find a linear classifier that separates the position
LECTURE NOTE #8 PROF. ALAN YUILLE 1. Linear Classifiers and Perceptrons A dataset contains N samples: { (x µ, y µ ) : µ = 1 to N }, y µ {±1} Can we find a linear classifier that separates the position
Linear Classification and SVM. Dr. Xin Zhang
 Linear Classification and SVM Dr. Xin Zhang Email: eexinzhang@scut.edu.cn What is linear classification? Classification is intrinsically non-linear It puts non-identical things in the same class, so a
Linear Classification and SVM Dr. Xin Zhang Email: eexinzhang@scut.edu.cn What is linear classification? Classification is intrinsically non-linear It puts non-identical things in the same class, so a
Machine Learning. Support Vector Machines. Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017 1 Classification and Margin Consider a classification problem with two classes: instance set X = R d label set Y = { 1, 1}. Training
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017 1 Classification and Margin Consider a classification problem with two classes: instance set X = R d label set Y = { 1, 1}. Training
Non-Bayesian Classifiers Part II: Linear Discriminants and Support Vector Machines
 Non-Bayesian Classifiers Part II: Linear Discriminants and Support Vector Machines Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Fall 2018 CS 551, Fall
Non-Bayesian Classifiers Part II: Linear Discriminants and Support Vector Machines Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Fall 2018 CS 551, Fall
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued. Richard Johansson
 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1396 1 / 44 Table
Kernels. Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. October 28, Carlos Guestrin
 Kernels Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 28, 2013 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2013 1 Linear Separability: More formally, Using Margin Data linearly separable, if there
Kernels Machine Learning CSE446 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 28, 2013 Carlos Guestrin 2005-2013 1 Linear Separability: More formally, Using Margin Data linearly separable, if there
Learning Linear Detectors
 Learning Linear Detectors Instructor - Simon Lucey 16-423 - Designing Computer Vision Apps Today Detection versus Classification Bayes Classifiers Linear Classifiers Examples of Detection 3 Learning: Detection
Learning Linear Detectors Instructor - Simon Lucey 16-423 - Designing Computer Vision Apps Today Detection versus Classification Bayes Classifiers Linear Classifiers Examples of Detection 3 Learning: Detection
Energy Based Learning. Energy Based Learning
 Energy Based Learning Energy Based Learning The Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences The Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University New York University http://yann.lecun.com http://www.cs.nyu.edu/~yann
Energy Based Learning Energy Based Learning The Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences The Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences New York University New York University http://yann.lecun.com http://www.cs.nyu.edu/~yann
Linear Discrimination Functions
 Laurea Magistrale in Informatica Nicola Fanizzi Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Bari November 4, 2009 Outline Linear models Gradient descent Perceptron Minimum square error approach
Laurea Magistrale in Informatica Nicola Fanizzi Dipartimento di Informatica Università degli Studi di Bari November 4, 2009 Outline Linear models Gradient descent Perceptron Minimum square error approach
Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine
 Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine guest lecturer: Ming-Wei Chang CS 446 Fall, 2009 () / 25 Fall, 2009 / 25 Before we start () 2 / 25 Fall, 2009 2 / 25 Before we start Feel
Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine guest lecturer: Ming-Wei Chang CS 446 Fall, 2009 () / 25 Fall, 2009 / 25 Before we start () 2 / 25 Fall, 2009 2 / 25 Before we start Feel
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear Classifiers: predictions Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due Friday of next
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear Classifiers: predictions Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due Friday of next
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
LECTURE NOTE #3 PROF. ALAN YUILLE
 LECTURE NOTE #3 PROF. ALAN YUILLE 1. Three Topics (1) Precision and Recall Curves. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves (ROC). What to do if we do not fix the loss function? (2) The Curse of Dimensionality.
LECTURE NOTE #3 PROF. ALAN YUILLE 1. Three Topics (1) Precision and Recall Curves. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves (ROC). What to do if we do not fix the loss function? (2) The Curse of Dimensionality.
Statistical Methods for SVM
 Statistical Methods for SVM Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find a plane that separates the classes in feature space. If we cannot,
Statistical Methods for SVM Support Vector Machines Here we approach the two-class classification problem in a direct way: We try and find a plane that separates the classes in feature space. If we cannot,
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 3: Perceptron. Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang
 Machine Learning Basics Lecture 3: Perceptron Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Perceptron Overview Previous lectures: (Principle for loss function) MLE to derive loss Example: linear
Machine Learning Basics Lecture 3: Perceptron Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Perceptron Overview Previous lectures: (Principle for loss function) MLE to derive loss Example: linear
Announcements - Homework
 Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Support Vector Machine
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers)
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Support vector machines In a nutshell Linear classifiers selecting hyperplane maximizing separation margin between classes (large margin classifiers)
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes
 CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes John Duchi Binary classification In binary classification problems, the target y can take on at only two values. In this set of notes, we show how to model this problem
CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes John Duchi Binary classification In binary classification problems, the target y can take on at only two values. In this set of notes, we show how to model this problem
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities. Kakade Announcements: Project Proposals: due this Friday!
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Support Vector Machines
 Wien, June, 2010 Paul Hofmarcher, Stefan Theussl, WU Wien Hofmarcher/Theussl SVM 1/21 Linear Separable Separating Hyperplanes Non-Linear Separable Soft-Margin Hyperplanes Hofmarcher/Theussl SVM 2/21 (SVM)
Wien, June, 2010 Paul Hofmarcher, Stefan Theussl, WU Wien Hofmarcher/Theussl SVM 1/21 Linear Separable Separating Hyperplanes Non-Linear Separable Soft-Margin Hyperplanes Hofmarcher/Theussl SVM 2/21 (SVM)
Lecture 4: Training a Classifier
 Lecture 4: Training a Classifier Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Now that we ve defined what binary classification is, let s actually train a classifier. We ll approach this problem in much the same way as
Lecture 4: Training a Classifier Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Now that we ve defined what binary classification is, let s actually train a classifier. We ll approach this problem in much the same way as
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
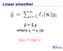 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Preliminaries. Definition: The Euclidean dot product between two vectors is the expression. i=1
 90 8 80 7 70 6 60 0 8/7/ Preliminaries Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, T x + b < 0 T x + b > 0 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression
90 8 80 7 70 6 60 0 8/7/ Preliminaries Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, T x + b < 0 T x + b > 0 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression
Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Linear classifier Which classifier? x 2 x 1 2 Linear classifier Margin concept x 2
Support Vector Machine (SVM) & Kernel CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Linear classifier Which classifier? x 2 x 1 2 Linear classifier Margin concept x 2
MIRA, SVM, k-nn. Lirong Xia
 MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning
 SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia, May 2016 www.cs.ubc.ca/~schmidtm/svan16 Some images from this lecture are
SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia, May 2016 www.cs.ubc.ca/~schmidtm/svan16 Some images from this lecture are
From Binary to Multiclass Classification. CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018
 From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING
 EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING DATE AND TIME: August 30, 2018, 14.00 19.00 RESPONSIBLE TEACHER: Niklas Wahlström NUMBER OF PROBLEMS: 5 AIDING MATERIAL: Calculator, mathematical
EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING DATE AND TIME: August 30, 2018, 14.00 19.00 RESPONSIBLE TEACHER: Niklas Wahlström NUMBER OF PROBLEMS: 5 AIDING MATERIAL: Calculator, mathematical
A vector from the origin to H, V could be expressed using:
 Linear Discriminant Function: the linear discriminant function: g(x) = w t x + ω 0 x is the point, w is the weight vector, and ω 0 is the bias (t is the transpose). Two Category Case: In the two category
Linear Discriminant Function: the linear discriminant function: g(x) = w t x + ω 0 x is the point, w is the weight vector, and ω 0 is the bias (t is the transpose). Two Category Case: In the two category
Dan Roth 461C, 3401 Walnut
 CIS 519/419 Applied Machine Learning www.seas.upenn.edu/~cis519 Dan Roth danroth@seas.upenn.edu http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~danroth/ 461C, 3401 Walnut Slides were created by Dan Roth (for CIS519/419 at Penn
CIS 519/419 Applied Machine Learning www.seas.upenn.edu/~cis519 Dan Roth danroth@seas.upenn.edu http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~danroth/ 461C, 3401 Walnut Slides were created by Dan Roth (for CIS519/419 at Penn
LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Classification: Problem Statement 2 In regression, we are modeling the relationship between a continuous input variable x and a continuous target variable t. In classification, the input
LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Classification: Problem Statement 2 In regression, we are modeling the relationship between a continuous input variable x and a continuous target variable t. In classification, the input
Midterm. Introduction to Machine Learning. CS 189 Spring You have 1 hour 20 minutes for the exam.
 CS 189 Spring 2013 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 1 hour 20 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. Please use non-programmable calculators
CS 189 Spring 2013 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 1 hour 20 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. Please use non-programmable calculators
EE613 Machine Learning for Engineers. Kernel methods Support Vector Machines. jean-marc odobez 2015
 EE613 Machine Learning for Engineers Kernel methods Support Vector Machines jean-marc odobez 2015 overview Kernel methods introductions and main elements defining kernels Kernelization of k-nn, K-Means,
EE613 Machine Learning for Engineers Kernel methods Support Vector Machines jean-marc odobez 2015 overview Kernel methods introductions and main elements defining kernels Kernelization of k-nn, K-Means,
Topics we covered. Machine Learning. Statistics. Optimization. Systems! Basics of probability Tail bounds Density Estimation Exponential Families
 Midterm Review Topics we covered Machine Learning Optimization Basics of optimization Convexity Unconstrained: GD, SGD Constrained: Lagrange, KKT Duality Linear Methods Perceptrons Support Vector Machines
Midterm Review Topics we covered Machine Learning Optimization Basics of optimization Convexity Unconstrained: GD, SGD Constrained: Lagrange, KKT Duality Linear Methods Perceptrons Support Vector Machines
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Final Review. Henry Chai 12/4/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recognition 1 / 48 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht
Pattern Recognition 2018 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recognition 1 / 48 Support Vector Machines Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht
Machine Learning Lecture 7
 Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Lecture 11: Review. Henry Chai 10/02/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
18.9 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides borrowed from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(50) Introduction Linear Classifiers Classifiers
Machine Learning for NLP Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides borrowed from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(50) Introduction Linear Classifiers Classifiers
Support Vector Machines
 EE 17/7AT: Optimization Models in Engineering Section 11/1 - April 014 Support Vector Machines Lecturer: Arturo Fernandez Scribe: Arturo Fernandez 1 Support Vector Machines Revisited 1.1 Strictly) Separable
EE 17/7AT: Optimization Models in Engineering Section 11/1 - April 014 Support Vector Machines Lecturer: Arturo Fernandez Scribe: Arturo Fernandez 1 Support Vector Machines Revisited 1.1 Strictly) Separable
Machine Learning Lecture 5
 Machine Learning Lecture 5 Linear Discriminant Functions 26.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory
Machine Learning Lecture 5 Linear Discriminant Functions 26.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory
Machine Learning (CS 567) Lecture 3
 Machine Learning (CS 567) Lecture 3 Time: T-Th 5:00pm - 6:20pm Location: GFS 118 Instructor: Sofus A. Macskassy (macskass@usc.edu) Office: SAL 216 Office hours: by appointment Teaching assistant: Cheol
Machine Learning (CS 567) Lecture 3 Time: T-Th 5:00pm - 6:20pm Location: GFS 118 Instructor: Sofus A. Macskassy (macskass@usc.edu) Office: SAL 216 Office hours: by appointment Teaching assistant: Cheol
Linear Regression (continued)
 Linear Regression (continued) Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 6, 2017 1 / 39 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Linear regression
Linear Regression (continued) Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 6, 2017 1 / 39 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Linear regression
Optimization and Gradient Descent
 Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers
 Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers COMPSCI 37D Machine Learning COMPSCI 37D Machine Learning Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers / 6 Outline What Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers Do 2 Margin I 3 Loss and Regularized
Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers COMPSCI 37D Machine Learning COMPSCI 37D Machine Learning Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers / 6 Outline What Linear, Binary SVM Classifiers Do 2 Margin I 3 Loss and Regularized
