Machine Learning. Linear Models. Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017
|
|
|
- Ginger Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10,
2 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w i x i + b i=1 Note: each member of L d is a function x w, x + b b: bias 2
3 Linear Models Hypothesis class H: φ L d, where φ : R Y h H is h : R d Y φ depends on the learning problem Example binary classification, Y = { 1, 1} φ(z) = sign(z) regression, Y = R φ(z) = z 3
4 Equivalent Notation Given x X, w R d, b R, define: w = (b, w 1, w 2,..., w d ) R d+1 x = (1, x 1, x 2,..., x d ) R d+1 Then: h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w, x (1) we will consider bias term as part of w and assume x = (1, x 1, x 2,..., x d ) when needed, with h w (x) = w, x 4
5 Linear Classification X = R d, Y = { 1, 1}, 0-1 loss Hypothesis class = halfspaces HS d = sign L d = {x sign(h x,b (x)) : h w,b L d } (2) Example: X = R 2 5
6 Finding a Good Hypothesis Linear classification with hypothesis set H = halfspaces. How do we find a good hypothesis? Good = ERM rule Perceptron Algorithm (Rosenblatt, 1958) Note: if y i w, x i > 0 for all i = 1,..., m all points are classified correctly by model w 6
7 Perceptron Input: training set (x 1, y 1 ),..., (x m, y m ) initialize w (1) = (0,..., 0); for t = 1, 2,... do if i s.t. y i w (t), x i 0 then w (t+1) w (t) + y i x i ; else return w (t) ; Interpretation of update: Note that: y i w (t+1), x i = y i w (t) + y i x i, x i = y i w (t), x i + x i 2 update guides w to be more correct on (x i, y i ). Termination? Depends on the realizability assumption! 7
8 Perceptron with Linearly Separable Data Realizability assumption for halfspace = linearly separable data Proposition Assume that (x 1, y 1 ),..., (x m, y m ) is linearly separable, let: B = min{ w : y i w, x i 1 i, i = 1,..., m, }, and R = max i x i. Then the Perceptron algorithm stops after at most (RB) 2 iterations and when it stops it holds that i, i {1,..., m} : y i w (t), x i > 0. 8
9 Perceptron: Notes simple to implement for separable data convergence is guaranteed converge depends on B, which can be exponential in d... an ILP approach may be better to find ERM solution in such cases potentially multiple solutions, which one is picked depends on starting values non separable data? run for some time and keep best solution found up to that point (pocket algorithm) 9
10 10 X = R d, Y = R Linear Regression Hypothesis class: H reg = L d = {x w, x + b : w R d, b R} Note: h H reg : R d R Commonly used loss function: squared-loss l(h, (x, y)) def = (h(x) y) 2 empirical risk function (training error): Mean Squared Error L S (h) = 1 m (h(x i ) y i ) 2 m i=1
11 Linear Regression - Example 11 d = 1
12 Least Squares 12 How to find a ERM hypothesis? Least Squares algorithm Best hypothesis: arg min L 1 S(h w ) = arg min w w m m ( w, x i y i ) 2 Equivalent formulation: w minimizing Residual Sum of Squares (RSS), i.e. m arg min ( w, x i y i ) 2 w i=1 i=1
13 13 Let RSS: Matrix Form x 1 x 2 X =. x m X: design matrix y 1 y 2 y =. y m we have that RSS is m ( w, x i y i ) 2 = (y Xw) T (y Xw) i=1
14 14 Want to find w that minimizes RSS (=objective function): RSS(w) = arg min (y w Xw)T (y Xw) How? Compute gradient RSS(w) w compare it to 0. of objective function w.r.t w and RSS(w) w = 2X T (y Xw) Then we need to find w such that 2X T (y Xw) = 0
15 15 2X T (y Xw) = 0 is equivalent to X T Xw = X T y If X T X is invertible solution to ERM problem is: w = (X T X) 1 X T y
16 Complexity Considerations 16 We need to compute (X T X) 1 X T y Algorithm: 1 compute X T X: product of (d + 1) m matrix and m (d + 1) matrix 2 compute (X T X) 1 inversion of (d + 1) (d + 1) matrix 3 compute (X T X) 1 X T : product of (d + 1) (d + 1) matrix and (d + 1) m matrix 4 compute (X T X) 1 X T : product of (d + 1) m matrix and m 1 matrix Most expensive operation? Inversion! done for (d + 1) (d + 1) matrix
17 X T X not invertible? How do we get w such that X T Xw = X T y if X T X is not invertible? Let A = X T X Let A + be the generalized inverse of A, i.e.: AA + A = A Proposition If A = X T X is not invertible, then ŵ = A + X T y is a solution to X T Xw = X T y. Proof: [UML]
18 Generalized Inverse of A 18 Note A = X T X is symmetric eigenvalue decomposition of A: A = VDV T with D: diagonal matrix (entries = eigenvalues of A) V: orthonormal matrix (V T V = I d d ) Define D + diagonal matrix such that: { 0 if D + Di,i = 0 i,i = otherwise 1 D i,i
19 19 Let A + = VD + V T Then AA + A = VDV T VD + V T VDV T = VDD + DV T = VDV T = A A + is the generalized inverse of A.
20 Logistic Regression 20 Learn a function h from R d to [0, 1]. What can this be used for? Classification! Example: binary classification (Y = { 1, 1}) - h(x) = probability that label of x is 1. For simplicity of presentation, we consider binary classification with Y = { 1, 1}, but similar considerations apply for multiclass classification.
Machine Learning. Linear Models. Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017
 Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017 1 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w
Machine Learning Linear Models Fabio Vandin October 10, 2017 1 Linear Predictors and Affine Functions Consider X = R d Affine functions: L d = {h w,b : w R d, b R} where ( d ) h w,b (x) = w, x + b = w
Machine Learning. Regularization and Feature Selection. Fabio Vandin November 13, 2017
 Machine Learning Regularization and Feature Selection Fabio Vandin November 13, 2017 1 Learning Model A: learning algorithm for a machine learning task S: m i.i.d. pairs z i = (x i, y i ), i = 1,..., m,
Machine Learning Regularization and Feature Selection Fabio Vandin November 13, 2017 1 Learning Model A: learning algorithm for a machine learning task S: m i.i.d. pairs z i = (x i, y i ), i = 1,..., m,
The Perceptron algorithm
 The Perceptron algorithm Tirgul 3 November 2016 Agnostic PAC Learnability A hypothesis class H is agnostic PAC learnable if there exists a function m H : 0,1 2 N and a learning algorithm with the following
The Perceptron algorithm Tirgul 3 November 2016 Agnostic PAC Learnability A hypothesis class H is agnostic PAC learnable if there exists a function m H : 0,1 2 N and a learning algorithm with the following
Machine Learning. Support Vector Machines. Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017
 Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017 1 Classification and Margin Consider a classification problem with two classes: instance set X = R d label set Y = { 1, 1}. Training
Machine Learning Support Vector Machines Fabio Vandin November 20, 2017 1 Classification and Margin Consider a classification problem with two classes: instance set X = R d label set Y = { 1, 1}. Training
Lecture 4: Linear predictors and the Perceptron
 Lecture 4: Linear predictors and the Perceptron Introduction to Learning and Analysis of Big Data Kontorovich and Sabato (BGU) Lecture 4 1 / 34 Inductive Bias Inductive bias is critical to prevent overfitting.
Lecture 4: Linear predictors and the Perceptron Introduction to Learning and Analysis of Big Data Kontorovich and Sabato (BGU) Lecture 4 1 / 34 Inductive Bias Inductive bias is critical to prevent overfitting.
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Lecture 11: Review. Henry Chai 10/02/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 11: Review Henry Chai 10/02/18 Unknown Target Function!: # % Training data Formal Setup & = ( ), + ),, ( -, + - Learning Algorithm 2 Hypothesis Set H
Machine Learning. Model Selection and Validation. Fabio Vandin November 7, 2017
 Machine Learning Model Selection and Validation Fabio Vandin November 7, 2017 1 Model Selection When we have to solve a machine learning task: there are different algorithms/classes algorithms have parameters
Machine Learning Model Selection and Validation Fabio Vandin November 7, 2017 1 Model Selection When we have to solve a machine learning task: there are different algorithms/classes algorithms have parameters
Machine Learning. Regularization and Feature Selection. Fabio Vandin November 14, 2017
 Machine Learning Regularization and Feature Selection Fabio Vandin November 14, 2017 1 Regularized Loss Minimization Assume h is defined by a vector w = (w 1,..., w d ) T R d (e.g., linear models) Regularization
Machine Learning Regularization and Feature Selection Fabio Vandin November 14, 2017 1 Regularized Loss Minimization Assume h is defined by a vector w = (w 1,..., w d ) T R d (e.g., linear models) Regularization
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression
 Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
Lecture 5: Linear models for classification. Logistic regression. Gradient Descent. Second-order methods.
 Lecture 5: Linear models for classification. Logistic regression. Gradient Descent. Second-order methods. Linear models for classification Logistic regression Gradient descent and second-order methods
Lecture 5: Linear models for classification. Logistic regression. Gradient Descent. Second-order methods. Linear models for classification Logistic regression Gradient descent and second-order methods
Discriminative Models
 No.5 Discriminative Models Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering York University, Toronto, Canada Outline Generative vs. Discriminative models
No.5 Discriminative Models Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering York University, Toronto, Canada Outline Generative vs. Discriminative models
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F10 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers
 Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Engineering Part IIB: Module 4F0 Statistical Pattern Processing Lecture 5: Single Layer Perceptrons & Estimating Linear Classifiers Phil Woodland: pcw@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 202 Engineering Part IIB:
Introduction to Machine Learning (67577) Lecture 3
 Introduction to Machine Learning (67577) Lecture 3 Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem General Learning Model and Bias-Complexity tradeoff Shai Shalev-Shwartz
Introduction to Machine Learning (67577) Lecture 3 Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem General Learning Model and Bias-Complexity tradeoff Shai Shalev-Shwartz
Discriminative Models
 No.5 Discriminative Models Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering York University, Toronto, Canada Outline Generative vs. Discriminative models
No.5 Discriminative Models Hui Jiang Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Lassonde School of Engineering York University, Toronto, Canada Outline Generative vs. Discriminative models
Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks
 Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks Logistic regression Comparison with generative models Feed-forward neural networks Backpropagation Tricks for training neural networks COMP-652, Lecture
Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks Logistic regression Comparison with generative models Feed-forward neural networks Backpropagation Tricks for training neural networks COMP-652, Lecture
Linear Classifiers. Michael Collins. January 18, 2012
 Linear Classifiers Michael Collins January 18, 2012 Today s Lecture Binary classification problems Linear classifiers The perceptron algorithm Classification Problems: An Example Goal: build a system that
Linear Classifiers Michael Collins January 18, 2012 Today s Lecture Binary classification problems Linear classifiers The perceptron algorithm Classification Problems: An Example Goal: build a system that
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771
 Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Logistic regression and linear classifiers COMS 4771 1. Prediction functions (again) Learning prediction functions IID model for supervised learning: (X 1, Y 1),..., (X n, Y n), (X, Y ) are iid random
Regression and Classification" with Linear Models" CMPSCI 383 Nov 15, 2011!
 Regression and Classification" with Linear Models" CMPSCI 383 Nov 15, 2011! 1 Todayʼs topics" Learning from Examples: brief review! Univariate Linear Regression! Batch gradient descent! Stochastic gradient
Regression and Classification" with Linear Models" CMPSCI 383 Nov 15, 2011! 1 Todayʼs topics" Learning from Examples: brief review! Univariate Linear Regression! Batch gradient descent! Stochastic gradient
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
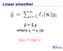 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Binary Classification / Perceptron
 Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Binary Classification / Perceptron Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from David Sontag and Vibhav Gogate Supervised Learning Input: x 1, y 1,, (x n, y n ) x i is the i th data
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Linear Regression (continued)
 Linear Regression (continued) Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 6, 2017 1 / 39 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Linear regression
Linear Regression (continued) Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 6, 2017 1 / 39 Outline 1 Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Linear regression
CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes
 CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes John Duchi Binary classification In binary classification problems, the target y can take on at only two values. In this set of notes, we show how to model this problem
CS229 Supplemental Lecture notes John Duchi Binary classification In binary classification problems, the target y can take on at only two values. In this set of notes, we show how to model this problem
Machine Learning and Data Mining. Linear classification. Kalev Kask
 Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear classification Kalev Kask Supervised learning Notation Features x Targets y Predictions ŷ = f(x ; q) Parameters q Program ( Learner ) Learning algorithm Change q
Machine Learning and Data Mining Linear classification Kalev Kask Supervised learning Notation Features x Targets y Predictions ŷ = f(x ; q) Parameters q Program ( Learner ) Learning algorithm Change q
6.867 Machine learning: lecture 2. Tommi S. Jaakkola MIT CSAIL
 6.867 Machine learning: lecture 2 Tommi S. Jaakkola MIT CSAIL tommi@csail.mit.edu Topics The learning problem hypothesis class, estimation algorithm loss and estimation criterion sampling, empirical and
6.867 Machine learning: lecture 2 Tommi S. Jaakkola MIT CSAIL tommi@csail.mit.edu Topics The learning problem hypothesis class, estimation algorithm loss and estimation criterion sampling, empirical and
Machine Learning Linear Models
 Machine Learning Linear Models Outline II - Linear Models 1. Linear Regression (a) Linear regression: History (b) Linear regression with Least Squares (c) Matrix representation and Normal Equation Method
Machine Learning Linear Models Outline II - Linear Models 1. Linear Regression (a) Linear regression: History (b) Linear regression with Least Squares (c) Matrix representation and Normal Equation Method
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Part of the slides are adapted from Ziko Kolter
 Part of the slides are adapted from Ziko Kolter OUTLINE 1 Supervised learning: classification........................................................ 2 2 Non-linear regression/classification, overfitting,
Part of the slides are adapted from Ziko Kolter OUTLINE 1 Supervised learning: classification........................................................ 2 2 Non-linear regression/classification, overfitting,
Classification Logistic Regression
 Announcements: Classification Logistic Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Sham Kakade University of Washington HW due on Friday. Today: Review: sub-gradients,lasso Logistic Regression October 3, 26 Sham
Announcements: Classification Logistic Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Sham Kakade University of Washington HW due on Friday. Today: Review: sub-gradients,lasso Logistic Regression October 3, 26 Sham
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
FA Homework 2 Recitation 2
 FA17 10-701 Homework 2 Recitation 2 Logan Brooks,Matthew Oresky,Guoquan Zhao October 2, 2017 Logan Brooks,Matthew Oresky,Guoquan Zhao FA17 10-701 Homework 2 Recitation 2 October 2, 2017 1 / 15 Outline
FA17 10-701 Homework 2 Recitation 2 Logan Brooks,Matthew Oresky,Guoquan Zhao October 2, 2017 Logan Brooks,Matthew Oresky,Guoquan Zhao FA17 10-701 Homework 2 Recitation 2 October 2, 2017 1 / 15 Outline
SPSS, University of Texas at Arlington. Topics in Machine Learning-EE 5359 Neural Networks
 Topics in Machine Learning-EE 5359 Neural Networks 1 The Perceptron Output: A perceptron is a function that maps D-dimensional vectors to real numbers. For notational convenience, we add a zero-th dimension
Topics in Machine Learning-EE 5359 Neural Networks 1 The Perceptron Output: A perceptron is a function that maps D-dimensional vectors to real numbers. For notational convenience, we add a zero-th dimension
Computational and Statistical Learning Theory
 Computational and Statistical Learning Theory TTIC 31120 Prof. Nati Srebro Lecture 17: Stochastic Optimization Part II: Realizable vs Agnostic Rates Part III: Nearest Neighbor Classification Stochastic
Computational and Statistical Learning Theory TTIC 31120 Prof. Nati Srebro Lecture 17: Stochastic Optimization Part II: Realizable vs Agnostic Rates Part III: Nearest Neighbor Classification Stochastic
Mark your answers ON THE EXAM ITSELF. If you are not sure of your answer you may wish to provide a brief explanation.
 CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
Notes on the framework of Ando and Zhang (2005) 1 Beyond learning good functions: learning good spaces
 Notes on the framework of Ando and Zhang (2005 Karl Stratos 1 Beyond learning good functions: learning good spaces 1.1 A single binary classification problem Let X denote the problem domain. Suppose we
Notes on the framework of Ando and Zhang (2005 Karl Stratos 1 Beyond learning good functions: learning good spaces 1.1 A single binary classification problem Let X denote the problem domain. Suppose we
An Introduction to Statistical and Probabilistic Linear Models
 An Introduction to Statistical and Probabilistic Linear Models Maximilian Mozes Proseminar Data Mining Fakultät für Informatik Technische Universität München June 07, 2017 Introduction In statistical learning
An Introduction to Statistical and Probabilistic Linear Models Maximilian Mozes Proseminar Data Mining Fakultät für Informatik Technische Universität München June 07, 2017 Introduction In statistical learning
GRADIENT DESCENT AND LOCAL MINIMA
 GRADIENT DESCENT AND LOCAL MINIMA 25 20 5 15 10 3 2 1 1 2 5 2 2 4 5 5 10 Suppose for both functions above, gradient descent is started at the point marked red. It will walk downhill as far as possible,
GRADIENT DESCENT AND LOCAL MINIMA 25 20 5 15 10 3 2 1 1 2 5 2 2 4 5 5 10 Suppose for both functions above, gradient descent is started at the point marked red. It will walk downhill as far as possible,
Machine Learning (CSE 446): Probabilistic Machine Learning
 Machine Learning (CSE 446): Probabilistic Machine Learning oah Smith c 2017 University of Washington nasmith@cs.washington.edu ovember 1, 2017 1 / 24 Understanding MLE y 1 MLE π^ You can think of MLE as
Machine Learning (CSE 446): Probabilistic Machine Learning oah Smith c 2017 University of Washington nasmith@cs.washington.edu ovember 1, 2017 1 / 24 Understanding MLE y 1 MLE π^ You can think of MLE as
Single layer NN. Neuron Model
 Single layer NN We consider the simple architecture consisting of just one neuron. Generalization to a single layer with more neurons as illustrated below is easy because: M M The output units are independent
Single layer NN We consider the simple architecture consisting of just one neuron. Generalization to a single layer with more neurons as illustrated below is easy because: M M The output units are independent
ECS171: Machine Learning
 ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 3: Linear Models I (LFD 3.2, 3.3) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 17, 2018 Linear Regression (LFD 3.2) Regression Classification: Customer record Yes/No Regression: predicting
ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 3: Linear Models I (LFD 3.2, 3.3) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 17, 2018 Linear Regression (LFD 3.2) Regression Classification: Customer record Yes/No Regression: predicting
Lecture 4: Types of errors. Bayesian regression models. Logistic regression
 Lecture 4: Types of errors. Bayesian regression models. Logistic regression A Bayesian interpretation of regularization Bayesian vs maximum likelihood fitting more generally COMP-652 and ECSE-68, Lecture
Lecture 4: Types of errors. Bayesian regression models. Logistic regression A Bayesian interpretation of regularization Bayesian vs maximum likelihood fitting more generally COMP-652 and ECSE-68, Lecture
Machine Learning Foundations
 Machine Learning Foundations ( 機器學習基石 ) Lecture 11: Linear Models for Classification Hsuan-Tien Lin ( 林軒田 ) htlin@csie.ntu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan
Machine Learning Foundations ( 機器學習基石 ) Lecture 11: Linear Models for Classification Hsuan-Tien Lin ( 林軒田 ) htlin@csie.ntu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science & Information Engineering National Taiwan
AdaBoost. Lecturer: Authors: Center for Machine Perception Czech Technical University, Prague
 AdaBoost Lecturer: Jan Šochman Authors: Jan Šochman, Jiří Matas Center for Machine Perception Czech Technical University, Prague http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz Motivation Presentation 2/17 AdaBoost with trees
AdaBoost Lecturer: Jan Šochman Authors: Jan Šochman, Jiří Matas Center for Machine Perception Czech Technical University, Prague http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz Motivation Presentation 2/17 AdaBoost with trees
ECS171: Machine Learning
 ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
ECS171: Machine Learning Lecture 4: Optimization (LFD 3.3, SGD) Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis Jan 22, 2018 Gradient descent Optimization Goal: find the minimizer of a function min f (w) w For now we assume f
Recap from previous lecture
 Recap from previous lecture Learning is using past experience to improve future performance. Different types of learning: supervised unsupervised reinforcement active online... For a machine, experience
Recap from previous lecture Learning is using past experience to improve future performance. Different types of learning: supervised unsupervised reinforcement active online... For a machine, experience
MLCC 2017 Regularization Networks I: Linear Models
 MLCC 2017 Regularization Networks I: Linear Models Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT June 27, 2017 About this class We introduce a class of learning algorithms based on Tikhonov regularization We study computational
MLCC 2017 Regularization Networks I: Linear Models Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT June 27, 2017 About this class We introduce a class of learning algorithms based on Tikhonov regularization We study computational
Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification
 Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, C. M. Bishop, 2006. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and echnology 77 Cheongam-ro,
Ch 4. Linear Models for Classification Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, C. M. Bishop, 2006. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and echnology 77 Cheongam-ro,
More about the Perceptron
 More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive
More about the Perceptron CMSC 422 MARINE CARPUAT marine@cs.umd.edu Credit: figures by Piyush Rai and Hal Daume III Recap: Perceptron for binary classification Classifier = hyperplane that separates positive
Perceptron (Theory) + Linear Regression
 10601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Perceptron (Theory) Linear Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 6 Feb. 5, 2018 1 Q&A
10601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Perceptron (Theory) Linear Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 6 Feb. 5, 2018 1 Q&A
SCMA292 Mathematical Modeling : Machine Learning. Krikamol Muandet. Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science, Mahidol University.
 SCMA292 Mathematical Modeling : Machine Learning Krikamol Muandet Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science, Mahidol University February 9, 2016 Outline Quick Recap of Least Square Ridge Regression
SCMA292 Mathematical Modeling : Machine Learning Krikamol Muandet Department of Mathematics Faculty of Science, Mahidol University February 9, 2016 Outline Quick Recap of Least Square Ridge Regression
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop , Fall 2018 Lecture 4
 Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron
 CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
Lecture Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers
 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Amir Globerson Lecture 6 Fall Semester Scribe: Yishay Mansour 6.1 Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers Classification is one of the most important tasks in
Introduction to Machine Learning Lecturer: Amir Globerson Lecture 6 Fall Semester Scribe: Yishay Mansour 6.1 Support Vector Machine (SVM) Classifiers Classification is one of the most important tasks in
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Final Review. Henry Chai 12/4/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
Machine Learning 2017
 Machine Learning 2017 Volker Roth Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Basel 21st March 2017 Volker Roth (University of Basel) Machine Learning 2017 21st March 2017 1 / 41 Section
Machine Learning 2017 Volker Roth Department of Mathematics & Computer Science University of Basel 21st March 2017 Volker Roth (University of Basel) Machine Learning 2017 21st March 2017 1 / 41 Section
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides borrowed from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(50) Introduction Linear Classifiers Classifiers
Machine Learning for NLP Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides borrowed from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(50) Introduction Linear Classifiers Classifiers
Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis
 Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 8, 207 / 40 Outline Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Basic
Overfitting, Bias / Variance Analysis Professor Ameet Talwalkar Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms February 8, 207 / 40 Outline Administration 2 Review of last lecture 3 Basic
IFT Lecture 7 Elements of statistical learning theory
 IFT 6085 - Lecture 7 Elements of statistical learning theory This version of the notes has not yet been thoroughly checked. Please report any bugs to the scribes or instructor. Scribe(s): Brady Neal and
IFT 6085 - Lecture 7 Elements of statistical learning theory This version of the notes has not yet been thoroughly checked. Please report any bugs to the scribes or instructor. Scribe(s): Brady Neal and
Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms. D = {(x i,y i )} n i=1. x i 2 R d 9/3/13. Preliminaries. Chapter 1, 7.
 Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
Preliminaries Linear models: the perceptron and closest centroid algorithms Chapter 1, 7 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression d T x = i x i The dot product is also
CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm
 CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava January 17, 2017 Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm January 17, 2017 1 / 1 Recap:
CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava January 17, 2017 Roger Grosse and Nitish Srivastava CSC321 Lecture 4 The Perceptron Algorithm January 17, 2017 1 / 1 Recap:
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
From Binary to Multiclass Classification. CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018
 From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
CSE 151 Machine Learning. Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri
 CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Linear Classification Given labeled data: (xi, feature vector yi) label i=1,..,n where y is 1 or 1, find a hyperplane to separate from Linear Classification
CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Linear Classification Given labeled data: (xi, feature vector yi) label i=1,..,n where y is 1 or 1, find a hyperplane to separate from Linear Classification
Evaluation. Andrea Passerini Machine Learning. Evaluation
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Basic concepts requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Basic concepts requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain
Preliminaries. Definition: The Euclidean dot product between two vectors is the expression. i=1
 90 8 80 7 70 6 60 0 8/7/ Preliminaries Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, T x + b < 0 T x + b > 0 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression
90 8 80 7 70 6 60 0 8/7/ Preliminaries Preliminaries Linear models and the perceptron algorithm Chapters, T x + b < 0 T x + b > 0 Definition: The Euclidean dot product beteen to vectors is the expression
MIDTERM: CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE October,
 MIDTERM: CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE October, 23 2013 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run
MIDTERM: CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE October, 23 2013 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Statistical Machine Learning Hilary Term 2018
 Statistical Machine Learning Hilary Term 2018 Pier Francesco Palamara Department of Statistics University of Oxford Slide credits and other course material can be found at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~palamara/sml18.html
Statistical Machine Learning Hilary Term 2018 Pier Francesco Palamara Department of Statistics University of Oxford Slide credits and other course material can be found at: http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~palamara/sml18.html
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Linear Regression. Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington. Oct 5, Kevin Jamieson 1
 Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington Oct 5, 2017 1 The regression problem Given past sales data on zillow.com, predict: y = House sale price from x = {# sq.
Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington Oct 5, 2017 1 The regression problem Given past sales data on zillow.com, predict: y = House sale price from x = {# sq.
Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized
 Evaluation Basic concepts Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain (generalization error) approximation
Evaluation Basic concepts Evaluation requires to define performance measures to be optimized Performance of learning algorithms cannot be evaluated on entire domain (generalization error) approximation
Midterm exam CS 189/289, Fall 2015
 Midterm exam CS 189/289, Fall 2015 You have 80 minutes for the exam. Total 100 points: 1. True/False: 36 points (18 questions, 2 points each). 2. Multiple-choice questions: 24 points (8 questions, 3 points
Midterm exam CS 189/289, Fall 2015 You have 80 minutes for the exam. Total 100 points: 1. True/False: 36 points (18 questions, 2 points each). 2. Multiple-choice questions: 24 points (8 questions, 3 points
Day 3: Classification, logistic regression
 Day 3: Classification, logistic regression Introduction to Machine Learning Summer School June 18, 2018 - June 29, 2018, Chicago Instructor: Suriya Gunasekar, TTI Chicago 20 June 2018 Topics so far Supervised
Day 3: Classification, logistic regression Introduction to Machine Learning Summer School June 18, 2018 - June 29, 2018, Chicago Instructor: Suriya Gunasekar, TTI Chicago 20 June 2018 Topics so far Supervised
Neural Network Training
 Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM
 Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM Corso di AA, anno 2018/19, Padova Fabio Aiolli 19/26 Novembre 2018 Fabio Aiolli Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM 19/26 Novembre 2018 1 / 36 Outline Linear methods
Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM Corso di AA, anno 2018/19, Padova Fabio Aiolli 19/26 Novembre 2018 Fabio Aiolli Modelli Lineari (Generalizzati) e SVM 19/26 Novembre 2018 1 / 36 Outline Linear methods
Empirical Risk Minimization Algorithms
 Empirical Risk Minimization Algorithms Tirgul 2 Part I November 2016 Reminder Domain set, X : the set of objects that we wish to label. Label set, Y : the set of possible labels. A prediction rule, h:
Empirical Risk Minimization Algorithms Tirgul 2 Part I November 2016 Reminder Domain set, X : the set of objects that we wish to label. Label set, Y : the set of possible labels. A prediction rule, h:
1 Machine Learning Concepts (16 points)
 CSCI 567 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Max 16 10 16 42 24 12 120 Points Please read the following instructions
CSCI 567 Fall 2018 Midterm Exam DO NOT OPEN EXAM UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO PLEASE TURN OFF ALL CELL PHONES Problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Max 16 10 16 42 24 12 120 Points Please read the following instructions
Warm up. Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not instructors.
 Warm up Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not email instructors. 1 float in NumPy = 8 bytes 10 6 2 20 bytes = 1 MB 10 9 2 30 bytes = 1 GB For each block compute the memory required
Warm up Regrade requests submitted directly in Gradescope, do not email instructors. 1 float in NumPy = 8 bytes 10 6 2 20 bytes = 1 MB 10 9 2 30 bytes = 1 GB For each block compute the memory required
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Perceptrons and Support Vector machines
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Semester 2016 Lessons 6 10 Jan 2017 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector machines Notation... 2 Perceptrons... 3 History...3
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning James L. Crowley ENSIMAG 3 - MMIS Fall Semester 2016 Lessons 6 10 Jan 2017 Outline Perceptrons and Support Vector machines Notation... 2 Perceptrons... 3 History...3
Machine Learning. Lecture 3: Logistic Regression. Feng Li.
 Machine Learning Lecture 3: Logistic Regression Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 2016 Logistic Regression Classification
Machine Learning Lecture 3: Logistic Regression Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 2016 Logistic Regression Classification
Linear Regression. Aarti Singh. Machine Learning / Sept 27, 2010
 Linear Regression Aarti Singh Machine Learning 10-701/15-781 Sept 27, 2010 Discrete to Continuous Labels Classification Sports Science News Anemic cell Healthy cell Regression X = Document Y = Topic X
Linear Regression Aarti Singh Machine Learning 10-701/15-781 Sept 27, 2010 Discrete to Continuous Labels Classification Sports Science News Anemic cell Healthy cell Regression X = Document Y = Topic X
CSC242: Intro to AI. Lecture 21
 CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 21 Administrivia Project 4 (homeworks 18 & 19) due Mon Apr 16 11:59PM Posters Apr 24 and 26 You need an idea! You need to present it nicely on 2-wide by 4-high landscape pages
CSC242: Intro to AI Lecture 21 Administrivia Project 4 (homeworks 18 & 19) due Mon Apr 16 11:59PM Posters Apr 24 and 26 You need an idea! You need to present it nicely on 2-wide by 4-high landscape pages
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression
 COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression Instructor: (jpineau@cs.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/comp551 Unless otherwise noted, all material posted for this
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 2: Linear regression Instructor: (jpineau@cs.mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/comp551 Unless otherwise noted, all material posted for this
Machine Learning: A Statistics and Optimization Perspective
 Machine Learning: A Statistics and Optimization Perspective Nan Ye Mathematical Sciences School Queensland University of Technology 1 / 109 What is Machine Learning? 2 / 109 Machine Learning Machine learning
Machine Learning: A Statistics and Optimization Perspective Nan Ye Mathematical Sciences School Queensland University of Technology 1 / 109 What is Machine Learning? 2 / 109 Machine Learning Machine learning
Logistic Regression. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier
 CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier 1 / 28 Overview Last time: binary classification, perceptron algorithm Limitations of the perceptron
CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 4: Learning a Classifier 1 / 28 Overview Last time: binary classification, perceptron algorithm Limitations of the perceptron
Optimization in the Big Data Regime 2: SVRG & Tradeoffs in Large Scale Learning. Sham M. Kakade
 Optimization in the Big Data Regime 2: SVRG & Tradeoffs in Large Scale Learning. Sham M. Kakade Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548 University of Washington S. M. Kakade (UW) Optimization for
Optimization in the Big Data Regime 2: SVRG & Tradeoffs in Large Scale Learning. Sham M. Kakade Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548 University of Washington S. M. Kakade (UW) Optimization for
Linear classifiers: Logistic regression
 Linear classifiers: Logistic regression STAT/CSE 416: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington April 19, 2018 How confident is your prediction? The sushi & everything else were awesome! The
Linear classifiers: Logistic regression STAT/CSE 416: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington April 19, 2018 How confident is your prediction? The sushi & everything else were awesome! The
Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression. 1 Linearly Separable Data: Hard Margin SVMs
 E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
E0 270 Machine Learning Lecture 5 (Jan 22, 203) Support Vector Machines for Classification and Regression Lecturer: Shivani Agarwal Disclaimer: These notes are a brief summary of the topics covered in
Chapter ML:VI. VI. Neural Networks. Perceptron Learning Gradient Descent Multilayer Perceptron Radial Basis Functions
 Chapter ML:VI VI. Neural Networks Perceptron Learning Gradient Descent Multilayer Perceptron Radial asis Functions ML:VI-1 Neural Networks STEIN 2005-2018 The iological Model Simplified model of a neuron:
Chapter ML:VI VI. Neural Networks Perceptron Learning Gradient Descent Multilayer Perceptron Radial asis Functions ML:VI-1 Neural Networks STEIN 2005-2018 The iological Model Simplified model of a neuron:
Logistic Regression Logistic
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. October 7, Efficiency: If size(w) = 100B, each prediction is expensive:
 Simple Variable Selection LASSO: Sparse Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 7, 2013 1 Sparsity Vector w is sparse, if many entries are zero: Very useful
Simple Variable Selection LASSO: Sparse Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 7, 2013 1 Sparsity Vector w is sparse, if many entries are zero: Very useful
ESS2222. Lecture 4 Linear model
 ESS2222 Lecture 4 Linear model Hosein Shahnas University of Toronto, Department of Earth Sciences, 1 Outline Logistic Regression Predicting Continuous Target Variables Support Vector Machine (Some Details)
ESS2222 Lecture 4 Linear model Hosein Shahnas University of Toronto, Department of Earth Sciences, 1 Outline Logistic Regression Predicting Continuous Target Variables Support Vector Machine (Some Details)
On the tradeoff between computational complexity and sample complexity in learning
 On the tradeoff between computational complexity and sample complexity in learning Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Joint work with Sham
On the tradeoff between computational complexity and sample complexity in learning Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Joint work with Sham
Neural Networks, Computation Graphs. CMSC 470 Marine Carpuat
 Neural Networks, Computation Graphs CMSC 470 Marine Carpuat Binary Classification with a Multi-layer Perceptron φ A = 1 φ site = 1 φ located = 1 φ Maizuru = 1 φ, = 2 φ in = 1 φ Kyoto = 1 φ priest = 0 φ
Neural Networks, Computation Graphs CMSC 470 Marine Carpuat Binary Classification with a Multi-layer Perceptron φ A = 1 φ site = 1 φ located = 1 φ Maizuru = 1 φ, = 2 φ in = 1 φ Kyoto = 1 φ priest = 0 φ
Regression with Numerical Optimization. Logistic
 CSG220 Machine Learning Fall 2008 Regression with Numerical Optimization. Logistic regression Regression with Numerical Optimization. Logistic regression based on a document by Andrew Ng October 3, 204
CSG220 Machine Learning Fall 2008 Regression with Numerical Optimization. Logistic regression Regression with Numerical Optimization. Logistic regression based on a document by Andrew Ng October 3, 204
Classification. The goal: map from input X to a label Y. Y has a discrete set of possible values. We focused on binary Y (values 0 or 1).
 Regression and PCA Classification The goal: map from input X to a label Y. Y has a discrete set of possible values We focused on binary Y (values 0 or 1). But we also discussed larger number of classes
Regression and PCA Classification The goal: map from input X to a label Y. Y has a discrete set of possible values We focused on binary Y (values 0 or 1). But we also discussed larger number of classes
Lecture 2 Machine Learning Review
 Lecture 2 Machine Learning Review CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago March 29, 2017 Things we will look at today Formal Setup for Supervised Learning Things
Lecture 2 Machine Learning Review CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago March 29, 2017 Things we will look at today Formal Setup for Supervised Learning Things
