SCIENTIFIC REPORT. Universität zu Köln, Germany. Institut für Geophysik und Meteorologie, Universität zu Köln, Germany
|
|
|
- Dulcie Kelley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCIENTIFIC REPORT 1 ACTION: ES1303 TOPROF STSM: COST-STSM-ES TOPIC: Boundary layer classification PERIOD: 9-13 November 2015 VENUE: Institut für Geophysik und Meteorologie, Universität zu Köln, Germany Host: Ulrich Löhnert Institut für Geophysik und Meteorologie, Universität zu Köln, Germany Applicant: Antti Manninen Department of Physics University of Helsinki, Finland Submission date: 4 December 2015 Contribution by: Tobias Marke Institut für Geophysik und Meteorologie, Universität zu Köln, Germany Ewan O Connor Finnish Meteorological Institute (Finland) University of Reading (UK)
2 Introduction I went for a Short-Term Scientific Mission (STSM), which took place from 9th to 13th November 2015 at the Institut für Geophysik und Meteorologie, Universität zu Köln. The STSM goal was to begin the generation of a boundary layer (BL) classification. The STSM allowed me to network with some of the researchers in the same field, and thus greatly benefit from the group work. 2 Motivation and objectives This work will eventually be incorporated into Cloudnet (Illingworth et al., 2007) and provide several products, with one being the BL classification. The classification is created in order to understand better the complex and continuously evolving BL. Its infinite number of states can be condensed into more perceptible finite number of states. The BL classification product requires several Doppler lidar quantities and can greatly benefit from additional quantities, e.g. sensible heat flux. In theory, the classification presented here can be carried out at any site where a scanning Doppler lidar is deployed and also where sensible heat flux measurement is available. However, the classification could also be carried out with only Doppler lidar measurements, but possibly with a reduced number of states that can be classified. Harvey et al. (2013) proposed a BL classification method, which covered a number of states where clouds where present within the BL, but only two where clouds were not present. Building upon their work, we can extend the classification scheme to improve the classification of the non-cloudy periods as well. Different weather forecast and climate models require different input parameters and schemes. For example, the scheme Harvey et al. (2013) discussed provides for the UK Met Office BL classification evaluation product. However, ECMWF, Meteo France, and Deutsche Wetterdienst would have different requirements. The goal of our work is to provide parameters that can be used in these different BL classification evaluation products.
3 Instrumentation Halo Photonics Streamline scanning Doppler lidar Halo Photonics Ltd manufactures the Doppler lidar used in this work (Fig. 1). The Halo Doppler lidar is commercially available and has been developed to perform continuous and autonomous long-term measurements (e.g. Pearson et al., 2009). The instrument emits laser pulses in the near infrared spectral region at 1.5 µm, and outputs a profile of back-scattered light intensity, in terms of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), together with a radial Doppler velocity determined from the Doppler shift of the back-scattered light. Horizontal wind speeds can be determined from combining orthogonal beams when scanning off-vertical. If the telescope function is known, the attenuated backscatter coefficients can be calculated (Hirsikko et al., 2014). It is important to acknowledge that any error in the SNR will transfer to the Doppler velocity measurement uncertainty (Manninen et al., 2015). Thus, with some Halo Doppler lidar units, correcting for the artifacts present in the background SNR is essential (Fig. 2). 3 Figure 1. Halo Photonics Streamline scanning Doppler lidar at Jülich, Germany
4 The background SNR artifacts can be corrected with the background correction method presented in Manninen et al. (2015) and Vakkari et al. (manuscript in preparation). After the correction the data availability in the lowest most range gates can be increased as much as 50%, especially in regions with low aerosol loading. In locations where the data availability is not an issue, such as in Juelich, the correction is still essential for calculating the turbulent properties. 4 From the Halo Doppler lidar measurement, several quantities (and their uncertainties) can be calculated (Fig. 3), such as the top of the aerosol layer (note: not the height of the BL), vertical velocity skewness, turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate (O Connor et al., 2010), and the vector wind shear. Figure 2. An example day of the Halo Doppler lidar SNR, which requires background correction: (top) uncorrected SNR; (middle) SNR after background ripple correction; (bottom) corrected SNR. 9 June 2014 at Hyytiälä, Finland.
5 5 Figure 3. The Halo Doppler lidar quantities used in the boundary layer classification: (top left) attenuated backscatter coefficients and top of aerosol layer; (top right) vertical velocity skewness; (bottom left) turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate; (bottom right) vector wind shear on 1 April 2013 at Jülich, Germany. Eddy Covariance stations The sonic anemometer measures the three components of the wind and the sonic temperature, which is equivalent to the virtual temperature, at a rate of 20 Hz. Standard eddy covariance methods can be used to calculate sensible and latent heat fluxes (e.g. Harvey et al., 2013). In the method discussed here, the sign of the sensible heat flux at 10 min temporal resolution is then used in estimating the stability of the surface layer.
6 6 Figure 4. Eddy covariance stations (blue) are located 5 and 8.5 km from the Halo Doppler lidar (red), at Jülich, Germany. 200 Sensible heat flux [W m -2 ] Time UTC Figure 5. Sensible heat flux calculated with standard eddy-correlation methods from three wind components and sonic temperature measured by the sonic anemometer on 1 April 2013 at Jülich, Germany.
7 Results The result can be seen as a proof-of-concept and is very preliminary. To classify the BL into small number of predefined states, we used specific thresholds for each of the quantities (Table 1). In the future we plan to move towards dynamic thresholds and assigning probabilities to the different states of the BL. With the thresholds, the quantities are reduced to two states, and together they comprise a bit field, which can then be used with a chosen logic to classify the BL. 7 Figure 6 illustrates the two states where the different Halo Doppler lidar quantities are reduced. The attenuated backscatter coefficients are used in detecting the top of the aerosol layer, but also whether or not there are clouds present within the aerosol layer. Turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate is used in detecting turbulent parts of the BL. The vertical velocity skewness can be used with the information on cloud presence and turbulence to assess whether the turbulence is cloud driven or surface driven. Since the example day used here is assumed to be mostly cloud free, vertical velocity skewness was not used in our logic. The vector wind shear information is used in detecting time periods when wind shear is high and, in combination with the dissipation rate, whether the shear is a result of convection or some other mechanism (typically friction-induced). Table 1. Overview of the thresholds chosen for the boundary layer classification.
8 8 Figure 6. The Halo Doppler lidar quantities used in the boundary layer classification are classified into two states after applying the initial thresholds: (top left) attenuated backscatter coefficients and top of aerosol layer; (top right) vertical velocity skewness; (bottom left) Turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate; (bottom right) vector wind shear on 1 April 2013 at Jülich, Germany. The sensible heat flux data is reduced into three states. If the sensible heat flux is between ± 10 W m -2 it is assigned to be neutral, if below -10, stable, and if above +10, unstable (Fig. 7). The Table 2 shows the logic used for the classification. For example, to be classified as a friction-induced (shear) surface layer, heat flux has to be negative but larger than -10 W m -2, dissipation rate has to be larger than 10-3 m 2 s -3, and the vector shear has to be larger than m s -1.
9 Sensible heat flux [W m -2 ] neutral stable unstable Time UTC Figure 7. Sensible heat flux classified into three states after applying the heat flux threshold, on 1 April 2013 at Jülich, Germany. Table 2. The decision logic which uses the bit field to unambiguously assign a combination of bits to every boundary layer class.
10 10 Figure 8. The initial results of the boundary layer based on 1 April 2013 at Jülich, Germany. Note that the neutral, stable and unstable states shown in the figure illustrate the BL states based on the surface sensible heat flux, and are not related to height but plotted into the background for illustration purposes. Figure 8 illustrates the preliminary results of the BL classification for 1 April 2013 at Jülich, Germany. Based on our method, we can separate the day into neutral, unstable, and stable states. Also, the BL can be classified as non-turbulent, shear or surface layer, convective, and decaying/intermittent types. By inclusion of the vertical velocity skewness and cloud detection, additional information on cloud driven turbulence could be obtained. Conclusions We have shown that BL classification can be carried out successfully with using Doppler lidar quantities in combination with sensible heat flux information. In order to estimate the uncertainty of our classification, uncertainties of the calculated quantities have to be incorporated together with assigning probabilities for the different BL types. This STSM has been successful in the sense that proof-of-concept was successful, and we have worked closely together outside of our usual research groups.
11 References Harvey, N.J., Hogan, R.J., and Dacre, H.F. (2013). A method to diagnose boundarylayer type using Doppler lidar: A Method to Diagnose Boundary-Layer Type. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 139, Hirsikko, A., O Connor, E.J., Komppula, M., Korhonen, K., Pfüller, A., Giannakaki, E., Wood, C.R., Bauer-Pfundstein, M., Poikonen, A., Karppinen, T., et al. (2014). Observing wind, aerosol particles, cloud and precipitation: Finland s new groundbased remote-sensing network. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 7, Illingworth, A.J., Hogan, R.J., O Connor, E.J., Bouniol, D., Delanoë, J., Pelon, J., Protat, A., Brooks, M.E., Gaussiat, N., Wilson, D.R., et al. (2007). Cloudnet: Continuous Evaluation of Cloud Profiles in Seven Operational Models Using Ground- Based Observations. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 88, Manninen, A.J., O Connor, E.J., Vakkari, V., and Petäjä, T. (2015). A generalised background correction algorithm for a Halo Doppler lidar and its application to data from Finland. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques Discussions, 8, O Connor, E.J., Illingworth, A.J., Brooks, I.M., Westbrook, C.D., Hogan, R.J., Davies, F., and Brooks, B.J. (2010). A Method for Estimating the Turbulent Kinetic Energy Dissipation Rate from a Vertically Pointing Doppler Lidar, and Independent Evaluation from Balloon-Borne In Situ Measurements. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 27, Pearson, G., Davies, F., and Collier, C. (2009). An Analysis of the Performance of the UFAM Pulsed Doppler Lidar for Observing the Boundary Layer. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 26, Vakkari, V., O Connor, E.J., et al. (manuscript in preparation). Improving Halo Doppler lidar background checks.
ACTION: STSM: TOPIC: VENUE: PERIOD:
 SCIENTIFIC REPORT ACTION: ES1303 TOPROF STSM: COST-STSM-ES1303-TOPROF TOPIC: Measurement of wind gusts using Doppler lidar VENUE: Technical University of Denmark, Risø, Roskilde, Denmark PERIOD: 7 11 December,
SCIENTIFIC REPORT ACTION: ES1303 TOPROF STSM: COST-STSM-ES1303-TOPROF TOPIC: Measurement of wind gusts using Doppler lidar VENUE: Technical University of Denmark, Risø, Roskilde, Denmark PERIOD: 7 11 December,
Oleg A. Krasnov 1 and Herman W. J. Russchenberg Introduction. 2. The results and discussion.
 6.12 An Application of the LWC Retrieval Radar-Lidar Technique to the Cloudnet and ARM Data: the Comparison with Microwave Radiometer and Numerical Weather Models Oleg A. Krasnov 1 and Herman W. J. Russchenberg
6.12 An Application of the LWC Retrieval Radar-Lidar Technique to the Cloudnet and ARM Data: the Comparison with Microwave Radiometer and Numerical Weather Models Oleg A. Krasnov 1 and Herman W. J. Russchenberg
CLOUD RADAR - INITIAL MEASUREMENTS FROM THE 94GHZ FMCW RADAR
 CLOUD RADAR - INITIAL MEASUREMENTS FROM THE 94GHZ FMCW RADAR Alec Bennett 1, Catherine Gaffard 1, Tim Oakley 1, Peter Huggard 2, Brian Moyna 2 and Matthew Oldfield 2 1 UK Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter,
CLOUD RADAR - INITIAL MEASUREMENTS FROM THE 94GHZ FMCW RADAR Alec Bennett 1, Catherine Gaffard 1, Tim Oakley 1, Peter Huggard 2, Brian Moyna 2 and Matthew Oldfield 2 1 UK Met Office, FitzRoy Road, Exeter,
WLS70: A NEW COMPACT DOPPLER WIND LIDAR FOR BOUNDARY LAYER DYNAMIC STUDIES.
 WLS70: A NEW COMPACT DOPPLER WIND LIDAR FOR BOUNDARY LAYER DYNAMIC STUDIES. VALIDATION RESULTS AND INTERCOMPARISON IN THE FRAME OF THE 8TH CIMO-WMO CAMPAIGN. S. Lolli 1, L.Sauvage 1, M. Boquet 1, 1 Leosphere,
WLS70: A NEW COMPACT DOPPLER WIND LIDAR FOR BOUNDARY LAYER DYNAMIC STUDIES. VALIDATION RESULTS AND INTERCOMPARISON IN THE FRAME OF THE 8TH CIMO-WMO CAMPAIGN. S. Lolli 1, L.Sauvage 1, M. Boquet 1, 1 Leosphere,
Submitted to J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 18 January 2010
 1 A method for estimating the turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate from a vertically-pointing Doppler lidar, and independent evaluation from balloon-borne in-situ measurements Ewan J. O Connor 1,2,
1 A method for estimating the turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate from a vertically-pointing Doppler lidar, and independent evaluation from balloon-borne in-situ measurements Ewan J. O Connor 1,2,
Meteorological Measurements made during RxCADRE
 Meteorological Measurements made during RxCADRE Craig B. Clements, Daisuke Seto, Jon Contezac, and Braniff Davis Fire Weather Research Laboratory Department of Meteorology and Climate Science San José
Meteorological Measurements made during RxCADRE Craig B. Clements, Daisuke Seto, Jon Contezac, and Braniff Davis Fire Weather Research Laboratory Department of Meteorology and Climate Science San José
SCIENTIFIC REPORT. Host: Sven-Erik Gryning (DTU Wind Energy, Denmark) Applicant: Lucie Rottner (Météo-France, CNRM, France)
 SCIENTIFIC REPORT ACTION: ES1303 TOPROF STSM: COST-STSM-ES1303-30536 TOPIC: Validation of real time turbulence estimation and measurement of wind gust using Doppler lidar. VENUE: Technical University of
SCIENTIFIC REPORT ACTION: ES1303 TOPROF STSM: COST-STSM-ES1303-30536 TOPIC: Validation of real time turbulence estimation and measurement of wind gust using Doppler lidar. VENUE: Technical University of
Windcube TM Pulsed lidar wind profiler Overview of more than 2 years of field experience J.P.Cariou, R. Parmentier, M. Boquet, L.
 Windcube TM Pulsed lidar wind profiler Overview of more than 2 years of field experience J.P.Cariou, R. Parmentier, M. Boquet, L.Sauvage 15 th Coherent Laser Radar Conference Toulouse, France 25/06/2009
Windcube TM Pulsed lidar wind profiler Overview of more than 2 years of field experience J.P.Cariou, R. Parmentier, M. Boquet, L.Sauvage 15 th Coherent Laser Radar Conference Toulouse, France 25/06/2009
2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET
 2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET Peter A. Cook * and Ian A. Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1
2.1 OBSERVATIONS AND THE PARAMETERISATION OF AIR-SEA FLUXES DURING DIAMET Peter A. Cook * and Ian A. Renfrew School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1
Large eddy simulation studies on convective atmospheric boundary layer
 Large eddy simulation studies on convective atmospheric boundary layer Antti Hellsten & Sergej Zilitinkevich Finnish Meteorological Institute Outline Short introduction to atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)
Large eddy simulation studies on convective atmospheric boundary layer Antti Hellsten & Sergej Zilitinkevich Finnish Meteorological Institute Outline Short introduction to atmospheric boundary layer (ABL)
Physics of the Convective Boundary Layer based on Radar/Lidar Profiler measurements and simulation
 Physics of the Convective Boundary Layer based on Radar/Lidar Profiler measurements and simulation D. Vanhoenacker Janvier (1), A. Graziani (1), D. Kovalev (1), C. Pereira (1), M. Duponcheel (2), R. Wilson
Physics of the Convective Boundary Layer based on Radar/Lidar Profiler measurements and simulation D. Vanhoenacker Janvier (1), A. Graziani (1), D. Kovalev (1), C. Pereira (1), M. Duponcheel (2), R. Wilson
Deutscher Wetterdienst
 Deutscher Wetterdienst Modelling the Volcanic Ash Episode: Experiences with COSMO-ART Detlev Majewski (FE1) Bernhard Vogel, Heike Vogel (KIT) Thomas Hanisch, Jochen Förstner (FE13), Ulrich Pflüger (FE15)
Deutscher Wetterdienst Modelling the Volcanic Ash Episode: Experiences with COSMO-ART Detlev Majewski (FE1) Bernhard Vogel, Heike Vogel (KIT) Thomas Hanisch, Jochen Förstner (FE13), Ulrich Pflüger (FE15)
Doppler Lidar Measurements of Turbulent Structure Function over an Urban Area
 MAY 004 DAVIES ET AL. 753 Doppler Lidar Measurements of Turbulent Structure Function over an Urban Area F. DAVIES AND C. G. COLLIER TIES Research Institute, University of Salford, Greater Manchester, United
MAY 004 DAVIES ET AL. 753 Doppler Lidar Measurements of Turbulent Structure Function over an Urban Area F. DAVIES AND C. G. COLLIER TIES Research Institute, University of Salford, Greater Manchester, United
Aerosols and clouds observations using active lidar remote sensing
 ÓPTICA PURA Y APLICADA Vol. 37, núm. 3-2004 Aerosols and clouds observations using active lidar remote sensing C. Pietras (1), Y. Morille (1), B. Romand (1), F. Lapouge (1), C. Boitel (1), M. Grall (1),
ÓPTICA PURA Y APLICADA Vol. 37, núm. 3-2004 Aerosols and clouds observations using active lidar remote sensing C. Pietras (1), Y. Morille (1), B. Romand (1), F. Lapouge (1), C. Boitel (1), M. Grall (1),
Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken during DYNAMO
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken
TOPROF Towards Operational Ground-based PROFiling with ceilometers, Doppler lidars and microwave radiometers for improving weather forecasts:
 TOPROF Towards Operational Ground-based PROFiling with ceilometers, Doppler lidars and microwave radiometers for improving weather forecasts: Anthony Illingworth, U of Reading, UK MC7 Dublin - 4 September
TOPROF Towards Operational Ground-based PROFiling with ceilometers, Doppler lidars and microwave radiometers for improving weather forecasts: Anthony Illingworth, U of Reading, UK MC7 Dublin - 4 September
Lecture 11: Doppler wind lidar
 Lecture 11: Doppler wind lidar Why do we study winds? v Winds are the most important variable studying dynamics and transport in the atmosphere. v Wind measurements are critical to improvement of numerical
Lecture 11: Doppler wind lidar Why do we study winds? v Winds are the most important variable studying dynamics and transport in the atmosphere. v Wind measurements are critical to improvement of numerical
A new lidar for water vapor and temperature measurements in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer
 A new lidar for water vapor and temperature measurements in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer M. Froidevaux 1, I. Serikov 2, S. Burgos 3, P. Ristori 1, V. Simeonov 1, H. Van den Bergh 1, and M.B. Parlange
A new lidar for water vapor and temperature measurements in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer M. Froidevaux 1, I. Serikov 2, S. Burgos 3, P. Ristori 1, V. Simeonov 1, H. Van den Bergh 1, and M.B. Parlange
Evaluating forecasts of the evolution of the cloudy boundary layer using diurnal composites of radar and lidar observations
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L17811, doi:10.1029/2009gl038919, 2009 Evaluating forecasts of the evolution of the cloudy boundary layer using diurnal composites of
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L17811, doi:10.1029/2009gl038919, 2009 Evaluating forecasts of the evolution of the cloudy boundary layer using diurnal composites of
Evidence that ice forms primarily in supercooled liquid clouds at temperatures > -27 C
 1 2 Evidence that ice forms primarily in supercooled liquid clouds at temperatures > -27 C 3 C. D. Westbrook and A. J. Illingworth 4 Abstract: 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Using 4 years of radar and lidar observations
1 2 Evidence that ice forms primarily in supercooled liquid clouds at temperatures > -27 C 3 C. D. Westbrook and A. J. Illingworth 4 Abstract: 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Using 4 years of radar and lidar observations
Estimating drizzle drop size and precipitation rate using two-colour lidar measurements
 Manuscript prepared for Atmos. Meas. Tech. with version 3. of the L A TEX class copernicus.cls. Date: 1 March 21 Estimating drizzle drop size and precipitation rate using two-colour lidar measurements
Manuscript prepared for Atmos. Meas. Tech. with version 3. of the L A TEX class copernicus.cls. Date: 1 March 21 Estimating drizzle drop size and precipitation rate using two-colour lidar measurements
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2)
 Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
Lecture 3. Turbulent fluxes and TKE budgets (Garratt, Ch 2) The ABL, though turbulent, is not homogeneous, and a critical role of turbulence is transport and mixing of air properties, especially in the
2.5 COMPARING WATER VAPOR VERTICAL PROFILES USING CNR-IMAA RAMAN LIDAR AND CLOUDNET DATA
 2.5 COMPARING WATER VAPOR VERTICAL PROFILES USING CNR-IMAA RAMAN LIDAR AND CLOUDNET DATA Lucia Mona*, 1, Aldo Amodeo 1, Carmela Cornacchia 1, Fabio Madonna 1, Gelsomina Pappalardo 1 and Ewan O Connor 2
2.5 COMPARING WATER VAPOR VERTICAL PROFILES USING CNR-IMAA RAMAN LIDAR AND CLOUDNET DATA Lucia Mona*, 1, Aldo Amodeo 1, Carmela Cornacchia 1, Fabio Madonna 1, Gelsomina Pappalardo 1 and Ewan O Connor 2
Mixing height over London: spatio-temporal characteristics observed by Ceilometer networks
 Department of Meteorology Mixing height over London: spatio-temporal characteristics observed by Ceilometer networks Simone Kotthaus 1, Charley Stockdale 2, Cristina Charlton-Perez 3, Ewan O'Connor 1,4,
Department of Meteorology Mixing height over London: spatio-temporal characteristics observed by Ceilometer networks Simone Kotthaus 1, Charley Stockdale 2, Cristina Charlton-Perez 3, Ewan O'Connor 1,4,
Observational Needs for Polar Atmospheric Science
 Observational Needs for Polar Atmospheric Science John J. Cassano University of Colorado with contributions from: Ed Eloranta, Matthew Lazzara, Julien Nicolas, Ola Persson, Matthew Shupe, and Von Walden
Observational Needs for Polar Atmospheric Science John J. Cassano University of Colorado with contributions from: Ed Eloranta, Matthew Lazzara, Julien Nicolas, Ola Persson, Matthew Shupe, and Von Walden
Wind and turbulence structure in the boundary layer around an isolated mountain: airborne measurements during the MATERHORN field study
 Wind and turbulence structure in the boundary layer around an isolated mountain: airborne measurements during the MATERHORN field study Stephan F.J. De Wekker 1, G.D. Emmitt 2, S. Greco 2, K. Godwin 2,
Wind and turbulence structure in the boundary layer around an isolated mountain: airborne measurements during the MATERHORN field study Stephan F.J. De Wekker 1, G.D. Emmitt 2, S. Greco 2, K. Godwin 2,
State of the art of wind forecasting and planned improvements for NWP Helmut Frank (DWD), Malte Mülller (met.no), Clive Wilson (UKMO)
 State of the art of wind forecasting and planned improvements for NWP Helmut Frank (DWD), Malte Mülller (met.no), Clive Wilson (UKMO) thanks to S. Bauernschubert, U. Blahak, S. Declair, A. Röpnack, C.
State of the art of wind forecasting and planned improvements for NWP Helmut Frank (DWD), Malte Mülller (met.no), Clive Wilson (UKMO) thanks to S. Bauernschubert, U. Blahak, S. Declair, A. Röpnack, C.
Turbulent structure and scaling of the inertial subrange in a stratocumulus-topped boundary layer observed by a Doppler lidar
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 15, 5873 5885, 2015 doi:1194/acp-15-5873-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Turbulent structure and scaling of the inertial subrange in a stratocumulus-topped boundary
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 15, 5873 5885, 2015 doi:1194/acp-15-5873-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Turbulent structure and scaling of the inertial subrange in a stratocumulus-topped boundary
Tr a n s r e g i o n a l C o l l a b o r a t i v e Re s e a r c h C e n t r e TR 172
 Tr a n s r e g i o n a l C o l l a b o r a t i v e Re s e a r c h C e n t r e TR 172 ArctiC Amplification: Climate Relevant Atmospheric and SurfaCe Processes, and Feedback Mechanisms (AC) 3 Towards a better
Tr a n s r e g i o n a l C o l l a b o r a t i v e Re s e a r c h C e n t r e TR 172 ArctiC Amplification: Climate Relevant Atmospheric and SurfaCe Processes, and Feedback Mechanisms (AC) 3 Towards a better
OceanFlux Sea Spray Aerosol (OSSA): a new formulation for production fluxes and implications for climate studies
 OceanFlux Sea Spray Aerosol (OSSA): a new formulation for production fluxes and implications for climate studies G. de Leeuw 1, 2, 3, J. Ovadnevaite 4, A. Manders- Groot 3, S. Norris 5, I.M. Brooks 5,
OceanFlux Sea Spray Aerosol (OSSA): a new formulation for production fluxes and implications for climate studies G. de Leeuw 1, 2, 3, J. Ovadnevaite 4, A. Manders- Groot 3, S. Norris 5, I.M. Brooks 5,
Use of reanalysis data in atmospheric electricity studies
 Use of reanalysis data in atmospheric electricity studies Report for COST Action CA15211 ElectroNet Short-Term Scientific Missions (STSM) 1. APPLICANT Last name: Mkrtchyan First name: Hripsime Present
Use of reanalysis data in atmospheric electricity studies Report for COST Action CA15211 ElectroNet Short-Term Scientific Missions (STSM) 1. APPLICANT Last name: Mkrtchyan First name: Hripsime Present
WP11 PHYSICAL ACCESS TO RIs
 WP11 PHYSICAL ACCESS TO RIs ENVRIplus multi-disciplinary test platforms SMEAR II-Hyytiälä, Univ of Helsinki, Finland Boreal landscape, rural site: mixed/conifer forest, peatlands and lakes Co-located activities
WP11 PHYSICAL ACCESS TO RIs ENVRIplus multi-disciplinary test platforms SMEAR II-Hyytiälä, Univ of Helsinki, Finland Boreal landscape, rural site: mixed/conifer forest, peatlands and lakes Co-located activities
Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction
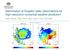 Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction Susan Rennie, Peter Steinle, Mark Curtis, Yi Xiao, Alan Seed Introduction Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
Assimilation of Doppler radar observations for high-resolution numerical weather prediction Susan Rennie, Peter Steinle, Mark Curtis, Yi Xiao, Alan Seed Introduction Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
Cloud Observations at UFS Schneefernerhaus Towards the Evaluation of Satellite Observations and Numerical Weather Prediction
 Cloud Observations at UFS Schneefernerhaus Towards the Evaluation of Satellite Observations and Numerical Weather Prediction Martin Hagen 1, Tobias Zinner 2, Bernhard Mayer 2, Axel Häring 1,2 1 Institut
Cloud Observations at UFS Schneefernerhaus Towards the Evaluation of Satellite Observations and Numerical Weather Prediction Martin Hagen 1, Tobias Zinner 2, Bernhard Mayer 2, Axel Häring 1,2 1 Institut
Evaluating cloud fraction and ice
 527 Evaluating cloud fraction and ice water content in the ECMWF Integrated Forecast System and three other operational models using long-term ground-based radar and lidar measurements D. Bouniol 1, A.
527 Evaluating cloud fraction and ice water content in the ECMWF Integrated Forecast System and three other operational models using long-term ground-based radar and lidar measurements D. Bouniol 1, A.
Atmospheric Lidar The Atmospheric Lidar (ATLID) is a high-spectral resolution lidar and will be the first of its type to be flown in space.
 www.esa.int EarthCARE mission instruments ESA s EarthCARE satellite payload comprises four instruments: the Atmospheric Lidar, the Cloud Profiling Radar, the Multi-Spectral Imager and the Broad-Band Radiometer.
www.esa.int EarthCARE mission instruments ESA s EarthCARE satellite payload comprises four instruments: the Atmospheric Lidar, the Cloud Profiling Radar, the Multi-Spectral Imager and the Broad-Band Radiometer.
FINNISH INSTITUTE OF MARINE RESEARCH CRUISE REPORT. R/V Aranda. Cruise 2 / February - 22 April 2002
 FINNISH INSTITUTE OF MARINE RESEARCH CRUISE REPORT R/V Aranda Cruise 2 / 2002 11 February - 22 April 2002 The report is based on preliminary data and is subject to changes. Finnish Institute of Marine
FINNISH INSTITUTE OF MARINE RESEARCH CRUISE REPORT R/V Aranda Cruise 2 / 2002 11 February - 22 April 2002 The report is based on preliminary data and is subject to changes. Finnish Institute of Marine
Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics
 Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics Richard Forbes (ECMWF) ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop, 15-17 June 2010 Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics A Complex System! Ice Nucleation
Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics Richard Forbes (ECMWF) ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop, 15-17 June 2010 Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics A Complex System! Ice Nucleation
AUTOMATIC MONITORING OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER ABSTRACT
 AUTOMATIC MONITORING OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER Christoph Münkel 1, Reijo Roininen 1 Vaisala GmbH, Schnackenburgallee 1d, 55 Hamburg, Germany Phone +9 89 1, Fax +9 89 11, E-mail christoph.muenkel@vaisala.com
AUTOMATIC MONITORING OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER Christoph Münkel 1, Reijo Roininen 1 Vaisala GmbH, Schnackenburgallee 1d, 55 Hamburg, Germany Phone +9 89 1, Fax +9 89 11, E-mail christoph.muenkel@vaisala.com
Remote sensing of meteorological conditions at airports for air quality issues
 Remote sensing of meteorological conditions at airports for air quality issues Stefan Emeis, Klaus Schäfer Institute for Meteorology and Climate Research Atmospheric Environmental Research (IMK-IFU) Forschungszentrum
Remote sensing of meteorological conditions at airports for air quality issues Stefan Emeis, Klaus Schäfer Institute for Meteorology and Climate Research Atmospheric Environmental Research (IMK-IFU) Forschungszentrum
Wind Assessment & Forecasting
 Wind Assessment & Forecasting GCEP Energy Workshop Stanford University April 26, 2004 Mark Ahlstrom CEO, WindLogics Inc. mark@windlogics.com WindLogics Background Founders from supercomputing industry
Wind Assessment & Forecasting GCEP Energy Workshop Stanford University April 26, 2004 Mark Ahlstrom CEO, WindLogics Inc. mark@windlogics.com WindLogics Background Founders from supercomputing industry
Deutscher Wetterdienst
 Deutscher Wetterdienst Comparison of wind profiler radar measurements with Doppler wind lidar profiles measurements at the Lindenberg GRUAN site Bernd Stiller, Ronny Leinweber, Volker Lehmann DWD - Deutscher
Deutscher Wetterdienst Comparison of wind profiler radar measurements with Doppler wind lidar profiles measurements at the Lindenberg GRUAN site Bernd Stiller, Ronny Leinweber, Volker Lehmann DWD - Deutscher
5.3 INVESTIGATION OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER USING A NOVEL ROBUST ALGORITHM. Christoph Münkel * Vaisala GmbH, Hamburg, Germany
 5. INVESTIGATION OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER USING A NOVEL ROBUST ALGORITHM Christoph Münkel * Vaisala GmbH, Hamburg, Germany Reijo Roininen Vaisala Oyj, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION
5. INVESTIGATION OF BOUNDARY LAYER STRUCTURES WITH CEILOMETER USING A NOVEL ROBUST ALGORITHM Christoph Münkel * Vaisala GmbH, Hamburg, Germany Reijo Roininen Vaisala Oyj, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION
Doppler radial wind spatially correlated observation error: operational implementation and initial results
 Doppler radial wind spatially correlated observation error: operational implementation and initial results D. Simonin, J. Waller, G. Kelly, S. Ballard,, S. Dance, N. Nichols (Met Office, University of
Doppler radial wind spatially correlated observation error: operational implementation and initial results D. Simonin, J. Waller, G. Kelly, S. Ballard,, S. Dance, N. Nichols (Met Office, University of
Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site
 Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site R. L. Coulter, B. M. Lesht, M. L. Wesely, D. R. Cook,
Performance of Radar Wind Profilers, Radiosondes, and Surface Flux Stations at the Southern Great Plains (SGP) Cloud and Radiation Testbed (CART) Site R. L. Coulter, B. M. Lesht, M. L. Wesely, D. R. Cook,
High resolution precipitation analysis and forecast validation over complex terrain using an inverse VERA approach
 4 th International Verification Methods Workshop Helsinki, Finland, 8-10 June 2009 High resolution precipitation analysis and forecast validation over complex terrain using an inverse VERA approach Benedikt
4 th International Verification Methods Workshop Helsinki, Finland, 8-10 June 2009 High resolution precipitation analysis and forecast validation over complex terrain using an inverse VERA approach Benedikt
Preliminary Results from the ATHENA-OAWL Venture Tech Airborne Mission
 Preliminary Results from the ATHENA-OAWL Venture Tech Airborne Mission Sunil Baidar (a, b), Sara Tucker (c), Mike Hardesty (a, b) (a) Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences, University
Preliminary Results from the ATHENA-OAWL Venture Tech Airborne Mission Sunil Baidar (a, b), Sara Tucker (c), Mike Hardesty (a, b) (a) Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences, University
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP
 Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
Evaluating Parametrizations using CEOP Paul Earnshaw and Sean Milton Met Office, UK Crown copyright 2005 Page 1 Overview Production and use of CEOP data Results SGP Seasonal & Diurnal cycles Other extratopical
Spaceborne Wind Lidar Observations by Aeolus Data Products and Pre-Launch Validation with an Airborne Instrument
 DRAGON 3 Project ID 10532 Cal/Val Spaceborne Wind Lidar Observations by Aeolus Data Products and Pre-Launch Validation with an Airborne Instrument Reitebuch Oliver, Lemmerz Christian, Marksteiner Uwe,
DRAGON 3 Project ID 10532 Cal/Val Spaceborne Wind Lidar Observations by Aeolus Data Products and Pre-Launch Validation with an Airborne Instrument Reitebuch Oliver, Lemmerz Christian, Marksteiner Uwe,
Cyclogenesis in the Western Mediterranean causing Heavy-Rain Events (NEPTUN)
 Cyclogenesis in the Western Mediterranean causing Heavy-Rain Events (NEPTUN) A Proposal for a coordinated mission of the HALO research aircraft in the field Transport processes and atmospheric dynamics
Cyclogenesis in the Western Mediterranean causing Heavy-Rain Events (NEPTUN) A Proposal for a coordinated mission of the HALO research aircraft in the field Transport processes and atmospheric dynamics
Working Group Initiation of Convection
 Working Group Initiation of Convection Ulrich Corsmeier Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung (IMK) Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe/Universität Karlsruhe 2 nd COPS Workshop June 27 June 28, 2005 University
Working Group Initiation of Convection Ulrich Corsmeier Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung (IMK) Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe/Universität Karlsruhe 2 nd COPS Workshop June 27 June 28, 2005 University
Analysis of Near-Surface Oceanic Measurements Obtained During CBLAST-Low
 Analysis of Near-Surface Oceanic Measurements Obtained During CBLAST-Low John H. Trowbridge Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, MS#12, Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2296 fax: (508) 457-2194 email:
Analysis of Near-Surface Oceanic Measurements Obtained During CBLAST-Low John H. Trowbridge Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, MS#12, Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2296 fax: (508) 457-2194 email:
Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO
 Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO Allen White and Jeff Hare, University of Colorado/CIRES Bruce Albrecht and Pavlos Kolias,
Ship-based measurements of cloud microphysics and PBL properties in precipitating trade cumulus clouds during RICO Allen White and Jeff Hare, University of Colorado/CIRES Bruce Albrecht and Pavlos Kolias,
Validation of ADM-Aeolus L2 aerosol and cloud product employing advanced ground-based lidar measurements (VADAM)
 Validation of ADM-Aeolus L2 aerosol and cloud product employing advanced ground-based lidar measurements (VADAM) V. Amiridis, National Observatory of Athens, Greece U. Wandinger, TROPOS-Leibniz Institute
Validation of ADM-Aeolus L2 aerosol and cloud product employing advanced ground-based lidar measurements (VADAM) V. Amiridis, National Observatory of Athens, Greece U. Wandinger, TROPOS-Leibniz Institute
PoS(ICRC2015)568. An Estimate of the Live Time of Optical Measurements of Air Showers at the South Pole
 An Estimate of the Live Time of Optical Measurements of Air Showers at the South Pole a and Stephen Drury a a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA Email: sybenzvi@pas.rochester.edu
An Estimate of the Live Time of Optical Measurements of Air Showers at the South Pole a and Stephen Drury a a Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA Email: sybenzvi@pas.rochester.edu
VALIDATION OF MIPAS TEMPERATURE DATA WITH THE U. BONN LIDAR AT THE ESRANGE DURING JULY AND AUGUST 2002
 VALIDATION OF MIPAS TEMPERATURE DATA WITH THE U. BONN LIDAR AT THE ESRANGE DURING JULY AND AUGUST 2002 U. Blum and K. H. Fricke Physikalisches Institut der Universität Bonn, D-53115 Bonn, Germany blum@physik.uni-bonn.de
VALIDATION OF MIPAS TEMPERATURE DATA WITH THE U. BONN LIDAR AT THE ESRANGE DURING JULY AND AUGUST 2002 U. Blum and K. H. Fricke Physikalisches Institut der Universität Bonn, D-53115 Bonn, Germany blum@physik.uni-bonn.de
Boundary Layer Science Challenges in the Context of Wind Energy
 Boundary Layer Science Challenges in the Context of Wind Energy WILLIAM J. SHAW 1 Pacific Northwest National Laboratory National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Workshop on the Future
Boundary Layer Science Challenges in the Context of Wind Energy WILLIAM J. SHAW 1 Pacific Northwest National Laboratory National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Workshop on the Future
Aeolus ESA s Wind Lidar Mission: Objectives, Design & Status
 Aeolus ESA s Wind Lidar Mission: Objectives, Design & Status Anne Grete Straume on behalf of Anders Elfving European Space Agency/ESTEC Working Group on Space-based Lidar Winds Boulder, 28/04/2015 Atmospheric
Aeolus ESA s Wind Lidar Mission: Objectives, Design & Status Anne Grete Straume on behalf of Anders Elfving European Space Agency/ESTEC Working Group on Space-based Lidar Winds Boulder, 28/04/2015 Atmospheric
Low level mixing height detection in coastal locations with a scanning Doppler lidar
 Low level mixing height detection in coastal locations with a scanning Doppler lidar Article Published Version Creative Commons: Attribution 3. (CC BY) Open Access Vakkari, V., O'Connor, E. J., Nisantzi,
Low level mixing height detection in coastal locations with a scanning Doppler lidar Article Published Version Creative Commons: Attribution 3. (CC BY) Open Access Vakkari, V., O'Connor, E. J., Nisantzi,
Doppler lidar observations of Russian forest fire plumes over Helsinki
 Doppler lidar observations of Russian forest fire plumes over Helsinki Bozier, KE, Pearson, GN and Collier, CG http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/wea.48 Title Authors Type URL Doppler lidar observations of Russian
Doppler lidar observations of Russian forest fire plumes over Helsinki Bozier, KE, Pearson, GN and Collier, CG http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/wea.48 Title Authors Type URL Doppler lidar observations of Russian
Measuring In-cloud Turbulence: The NEXRAD Turbulence Detection Algorithm
 Measuring In-cloud Turbulence: The NEXRAD Turbulence Detection Algorithm John K. Williams,, Greg Meymaris,, Jason Craig, Gary Blackburn, Wiebke Deierling,, and Frank McDonough AMS 15 th Conference on Aviation,
Measuring In-cloud Turbulence: The NEXRAD Turbulence Detection Algorithm John K. Williams,, Greg Meymaris,, Jason Craig, Gary Blackburn, Wiebke Deierling,, and Frank McDonough AMS 15 th Conference on Aviation,
Analysis of one- and two-dimensional mean gust shapes using a largeeddy simulation model
 Analysis of one- and two-dimensional mean gust shapes using a largeeddy simulation model Knigge, Christoph* 1), Raasch, Siegfried 1) 1) Institut für Meteorologie und Klimatologie, Leibniz Universität Hannover,
Analysis of one- and two-dimensional mean gust shapes using a largeeddy simulation model Knigge, Christoph* 1), Raasch, Siegfried 1) 1) Institut für Meteorologie und Klimatologie, Leibniz Universität Hannover,
La circulation atmosphérique dans le sud du Portugal et l'effet du réservoir d'alqueva. Cas d étude ALEX 2014
 8th Meso-NH user's meeting La circulation atmosphérique dans le sud du Portugal et l'effet du réservoir d'alqueva. Cas d étude ALEX 2014, Carlos Policarpo et Miguel Potes Instituto de Ciências da Terra
8th Meso-NH user's meeting La circulation atmosphérique dans le sud du Portugal et l'effet du réservoir d'alqueva. Cas d étude ALEX 2014, Carlos Policarpo et Miguel Potes Instituto de Ciências da Terra
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Opportunities provided by fine-scale meteorological sensor array
 Opportunities provided by fine-scale meteorological sensor array R.M. Randall, C.M Hocut, D.K. Knapp, B.T. MacCall, & J.A. Smith MSA Program Overview Army Challenge Research gaps exist which challenge
Opportunities provided by fine-scale meteorological sensor array R.M. Randall, C.M Hocut, D.K. Knapp, B.T. MacCall, & J.A. Smith MSA Program Overview Army Challenge Research gaps exist which challenge
Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken during DYNAMO
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT: Approved for public release, distribution is unlimited. Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT: Approved for public release, distribution is unlimited. Investigation of the Air-Wave-Sea Interaction Modes Using an Airborne Doppler Wind Lidar: Analyses of the HRDL data taken
PARAFOG: a new decision support system for the airports to monitor and to predict radiation fog based on automatic LIDARceilometer
 PARAFOG: a new decision support system for the airports to monitor and to predict radiation fog based on automatic LIDARceilometer measurements Quentin Laffineur Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium
PARAFOG: a new decision support system for the airports to monitor and to predict radiation fog based on automatic LIDARceilometer measurements Quentin Laffineur Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium
Orbit and Transmit Characteristics of the CloudSat Cloud Profiling Radar (CPR) JPL Document No. D-29695
 Orbit and Transmit Characteristics of the CloudSat Cloud Profiling Radar (CPR) JPL Document No. D-29695 Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109 26 July 2004 Revised
Orbit and Transmit Characteristics of the CloudSat Cloud Profiling Radar (CPR) JPL Document No. D-29695 Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109 26 July 2004 Revised
Climate & Earth System Science. Introduction to Meteorology & Climate. Chapter 05 SOME OBSERVING INSTRUMENTS. Instrument Enclosure.
 Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Climate & Earth System Science Introduction to Meteorology & Climate MAPH 10050 Peter Lynch Peter Lynch Meteorology & Climate Centre School of Mathematical Sciences University College Dublin Meteorology
Facilitating cloud radar and lidar algorithms: the Cloudnet Instrument Synergy/Target Categorization product
 Facilitating cloud radar and lidar algorithms: the Cloudnet Instrument Synergy/Target Categorization product Robin J. Hogan and Ewan J. O Connor August 17, 2004 1 Introduction There is a growing recognition
Facilitating cloud radar and lidar algorithms: the Cloudnet Instrument Synergy/Target Categorization product Robin J. Hogan and Ewan J. O Connor August 17, 2004 1 Introduction There is a growing recognition
Projeto Temático FAPESP 2013/ Climate Ecosystems Atmospheric Composition
 Projeto Temático FAPESP 2013/05014-0 Climate Ecosystems Atmospheric Composition GoAmazon2014/15 Experiment Manaus is a city of 2 million people surrounded by just forest in a radius of 1.500 Km. UNIQUE
Projeto Temático FAPESP 2013/05014-0 Climate Ecosystems Atmospheric Composition GoAmazon2014/15 Experiment Manaus is a city of 2 million people surrounded by just forest in a radius of 1.500 Km. UNIQUE
NARVAL. North Atlantic Rainfall Validation. Christian Klepp, Stephan Bakan, Gerhard Peters, Bjorn Stevens, Lutz Hirsch, Johannes Quaas
 NARVAL North Atlantic Rainfall Validation Christian Klepp, Stephan Bakan, Gerhard Peters, Bjorn Stevens, Lutz Hirsch, Johannes Quaas Klima Campus Meteorologisches Institut, Universität Hamburg Max-Planck-Institut
NARVAL North Atlantic Rainfall Validation Christian Klepp, Stephan Bakan, Gerhard Peters, Bjorn Stevens, Lutz Hirsch, Johannes Quaas Klima Campus Meteorologisches Institut, Universität Hamburg Max-Planck-Institut
European ceilometer and lidar networks for aerosol profiling and aviation safety the German contribution
 European ceilometer and lidar networks for aerosol profiling and aviation safety the German contribution Werner Thomas Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) Hohenpeissenberg Meteorological Observatory www.dwd.de/ceilomap
European ceilometer and lidar networks for aerosol profiling and aviation safety the German contribution Werner Thomas Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) Hohenpeissenberg Meteorological Observatory www.dwd.de/ceilomap
Variations in the power-law index with stability and height for wind profiles in the urban boundary layer
 Variations in the power-law index with stability and height for wind profiles in the urban boundary layer Hideki Kikumoto 1, Ryozo Ooka 2, Hirofumi Sugawara 3 Hideki Kikumoto 1 Institute of Industrial
Variations in the power-law index with stability and height for wind profiles in the urban boundary layer Hideki Kikumoto 1, Ryozo Ooka 2, Hirofumi Sugawara 3 Hideki Kikumoto 1 Institute of Industrial
Cloud analysis from METEOSAT data using image segmentation for climate model verification
 Cloud analysis from METEOSAT data using image segmentation for climate model verification R. Huckle 1, F. Olesen 2 Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung, 1 University of Karlsruhe, 2 Forschungszentrum
Cloud analysis from METEOSAT data using image segmentation for climate model verification R. Huckle 1, F. Olesen 2 Institut für Meteorologie und Klimaforschung, 1 University of Karlsruhe, 2 Forschungszentrum
DYNAMIC SUB-GRID MODELLING OF AN EVOLVING CBL AT GREY-ZONE RESOLUTIONS
 DYNAMIC SUB-GRID MODELLING OF AN EVOLVING CBL AT GREY-ZONE RESOLUTIONS George Efstathiou 1 R. S. Plant 2, M. M. Bopape 2,3 and R. J. Beare 1 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Exeter 2 Department
DYNAMIC SUB-GRID MODELLING OF AN EVOLVING CBL AT GREY-ZONE RESOLUTIONS George Efstathiou 1 R. S. Plant 2, M. M. Bopape 2,3 and R. J. Beare 1 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Exeter 2 Department
Status-quo of COPS Scientific Preparation, Candidate Instrumentation, Workshop Overview
 Status-quo of COPS Scientific Preparation, Candidate Instrumentation, Workshop Overview Andreas Behrendt, Volker Wulfmeyer Institut für Physik und Meteorologie (IPM), Universität Hohenheim, Stuttgart Christoph
Status-quo of COPS Scientific Preparation, Candidate Instrumentation, Workshop Overview Andreas Behrendt, Volker Wulfmeyer Institut für Physik und Meteorologie (IPM), Universität Hohenheim, Stuttgart Christoph
Satellite coherent Doppler wind lidar performance simulation based on CALIOP measurements
 Satellite coherent Doppler wind lidar performance simulation based on CALIOP measurements Dong Wu, Pei Zhang, Suzhen Yu College of Information Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China, 38 Songling
Satellite coherent Doppler wind lidar performance simulation based on CALIOP measurements Dong Wu, Pei Zhang, Suzhen Yu College of Information Science and Engineering, Ocean University of China, 38 Songling
Turbulence Measurements. Turbulence Measurements In Low Signal-to-Noise. Larry Cornman National Center For Atmospheric Research
 Turbulence Measurements In Low Signal-to-Noise Larry Cornman National Center For Atmospheric Research Turbulence Measurements Turbulence is a stochastic process, and hence must be studied via the statistics
Turbulence Measurements In Low Signal-to-Noise Larry Cornman National Center For Atmospheric Research Turbulence Measurements Turbulence is a stochastic process, and hence must be studied via the statistics
Introduction to climate modeling. ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008
 Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Introduction to climate modeling ECOLMAS Course 1-4 April 2008 Course description Goal: To equipe you with a comfortable basic knowledge in the trade of climate modeling Course web site: http://www.geo.unibremen.de/~apau/ecolmas_modeling2
Validation of 2-meters temperature forecast at cold observed conditions by different NWP models
 Validation of 2-meters temperature forecast at cold observed conditions by different NWP models Evgeny Atlaskin Finnish Meteorological Institute / Russian State Hydrometeorological University OUTLINE Background
Validation of 2-meters temperature forecast at cold observed conditions by different NWP models Evgeny Atlaskin Finnish Meteorological Institute / Russian State Hydrometeorological University OUTLINE Background
Turbulence in the Stable Boundary Layer
 Turbulence in the Stable Boundary Layer Chemical-Biological Information Systems Austin, TX 11 January 2006 Walter D. Bach, Jr. and Dennis M. Garvey AMSRD-ARL-RO-EV & -CI-EE JSTO Project: AO06MSB00x Outline
Turbulence in the Stable Boundary Layer Chemical-Biological Information Systems Austin, TX 11 January 2006 Walter D. Bach, Jr. and Dennis M. Garvey AMSRD-ARL-RO-EV & -CI-EE JSTO Project: AO06MSB00x Outline
A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model. Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton. Univ.
 A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton Univ. of Washington 16 June 1998 Introduction This report describes a preliminary
A Preliminary Assessment of the Simulation of Cloudiness at SHEBA by the ECMWF Model Tony Beesley and Chris Bretherton Univ. of Washington 16 June 1998 Introduction This report describes a preliminary
Years of the Maritime Continent (YMC) Science Plan Overview. Chidong Zhang, RSMAS, University of Miami
 Years of the Maritime Continent (YMC) Science Plan Overview Chidong Zhang, RSMAS, University of Miami YMC Motivations - Global Importance: Connections between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, between the
Years of the Maritime Continent (YMC) Science Plan Overview Chidong Zhang, RSMAS, University of Miami YMC Motivations - Global Importance: Connections between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, between the
The Concordiasi Project
 The Concordiasi Project WWRP, THORPEX, WCRP POLAR PREDICTION WORKSHOP Oslo, 6-8 October 2010 by Florence Rabier, Concordiasi project leader and Eric Brun CNRM/GAME : Météo-France and CNRS 1 Part of THORPEX-IPY
The Concordiasi Project WWRP, THORPEX, WCRP POLAR PREDICTION WORKSHOP Oslo, 6-8 October 2010 by Florence Rabier, Concordiasi project leader and Eric Brun CNRM/GAME : Météo-France and CNRS 1 Part of THORPEX-IPY
EXPERIMENTAL ASSIMILATION OF SPACE-BORNE CLOUD RADAR AND LIDAR OBSERVATIONS AT ECMWF
 EXPERIMENTAL ASSIMILATION OF SPACE-BORNE CLOUD RADAR AND LIDAR OBSERVATIONS AT ECMWF Marta Janisková, Sabatino Di Michele, Edouard Martins ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading, U.K. Abstract Space-borne active
EXPERIMENTAL ASSIMILATION OF SPACE-BORNE CLOUD RADAR AND LIDAR OBSERVATIONS AT ECMWF Marta Janisková, Sabatino Di Michele, Edouard Martins ECMWF, Shinfield Park, Reading, U.K. Abstract Space-borne active
Observations needed for verification of additional forecast products
 Observations needed for verification of additional forecast products Clive Wilson ( & Marion Mittermaier) 12th Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems, ECMWF, 2-6 November 2009 Additional forecast
Observations needed for verification of additional forecast products Clive Wilson ( & Marion Mittermaier) 12th Workshop on Meteorological Operational Systems, ECMWF, 2-6 November 2009 Additional forecast
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1
 APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
APPENDIX 2 OVERVIEW OF THE GLOBAL PRECIPITATION MEASUREMENT (GPM) AND THE TROPICAL RAINFALL MEASURING MISSION (TRMM) 2-1 1. Introduction Precipitation is one of most important environmental parameters.
Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations. Atmospheric Instrumentation
 Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations Outline Polar-Orbiting Observations: Review of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Systems Overview of Currently Active Satellites / Sensors Overview of Sensor
Interpretation of Polar-orbiting Satellite Observations Outline Polar-Orbiting Observations: Review of Polar-Orbiting Satellite Systems Overview of Currently Active Satellites / Sensors Overview of Sensor
Nicola Bodini et al. Correspondence to: Nicola Bodini
 Supplement of Atmos. Meas. Tech., 11, 4291 4308, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-11-4291-2018-supplement Author(s) 2018. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. Supplement
Supplement of Atmos. Meas. Tech., 11, 4291 4308, 2018 https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-11-4291-2018-supplement Author(s) 2018. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. Supplement
Development of new products by operational forecasters
 Development of new products by operational forecasters Probability of Thunder -algorithm Paavo Korpela Operational meteorologist & developer Safety Weather Centre Finnish Meteorological Institute Content
Development of new products by operational forecasters Probability of Thunder -algorithm Paavo Korpela Operational meteorologist & developer Safety Weather Centre Finnish Meteorological Institute Content
The European Wind Profiler Network CWINDE Problems and Prospects
 The European Wind Profiler Network CWINDE Problems and Prospects Volker Lehmann Deutscher Wetterdienst GB Forschung und Entwicklung Meteorologisches Observatorium Lindenberg Volker.Lehmann@dwd.de but first...
The European Wind Profiler Network CWINDE Problems and Prospects Volker Lehmann Deutscher Wetterdienst GB Forschung und Entwicklung Meteorologisches Observatorium Lindenberg Volker.Lehmann@dwd.de but first...
Course outline, objectives, workload, projects, expectations
 Course outline, objectives, workload, projects, expectations Introductions Remote Sensing Overview Elements of a remote sensing observing system 1. platform (satellite, surface, etc) 2. experimental design
Course outline, objectives, workload, projects, expectations Introductions Remote Sensing Overview Elements of a remote sensing observing system 1. platform (satellite, surface, etc) 2. experimental design
RPAS based observation on the Arctic Boundary Layer during the ISOBAR campaigns on Andøya and Hailuoto
 U N I V E R S I T Y O F B E R G E N RPAS based observation on the Arctic Boundary Layer during the ISOBAR campaigns on Andøya and Hailuoto S Kral 1, J Reuder 1, L Båserud 1, G Urbancic 1,M Jonassen 2;1,
U N I V E R S I T Y O F B E R G E N RPAS based observation on the Arctic Boundary Layer during the ISOBAR campaigns on Andøya and Hailuoto S Kral 1, J Reuder 1, L Båserud 1, G Urbancic 1,M Jonassen 2;1,
Atmospheric Processes
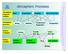 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model
 Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
Incorporation of 3D Shortwave Radiative Effects within the Weather Research and Forecasting Model W. O Hirok and P. Ricchiazzi Institute for Computational Earth System Science University of California
Short-Term Forecasting of Surface Solar Irradiance Based on Meteosat-SEVIRI Data Using a Nighttime Cloud lndex
 Short-Term Forecasting of Surface Solar Irradiance Based on Meteosat-SEVIRI Data Using a Nighttime Cloud lndex Annette Hammer Energy Meteorology Group Institute of Physics Carl von Ossietzky University
Short-Term Forecasting of Surface Solar Irradiance Based on Meteosat-SEVIRI Data Using a Nighttime Cloud lndex Annette Hammer Energy Meteorology Group Institute of Physics Carl von Ossietzky University
Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Large-Eddy Simulations of Tropical Convective Systems, the Boundary Layer, and Upper Ocean Coupling Eric D. Skyllingstad
Assimilation of Satellite Cloud and Precipitation Observations in NWP Models: Report of a Workshop
 Assimilation of Satellite Cloud and Precipitation Observations in NWP Models: Report of a Workshop George Ohring and Fuzhong Weng Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation Ron Errico NASA/GSFC Global
Assimilation of Satellite Cloud and Precipitation Observations in NWP Models: Report of a Workshop George Ohring and Fuzhong Weng Joint Center for Satellite Data Assimilation Ron Errico NASA/GSFC Global
WRF Land Surface Schemes and Paris Air Quality
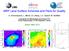 WRF Land Surface Schemes and Paris Air Quality D. Khvorostyanov, L. Menut, Ch. Zheng, J.-C. Dupont, M. Haeffelin Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique IPSL Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau, France
WRF Land Surface Schemes and Paris Air Quality D. Khvorostyanov, L. Menut, Ch. Zheng, J.-C. Dupont, M. Haeffelin Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique IPSL Ecole Polytechnique, 91128 Palaiseau, France
