Transition de séchage dans des nanopores et la tension de ligne de l eau
|
|
|
- Ashlynn Boone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Transition de séchage dans des nanopores et la tension de ligne de l eau L. Guillemot, T. Biben, A. Gallarneau, G. Vigier, E. Charlaix Laboratoire LiPhy Université Joseph Fourier Laboratoire MATEIS INSA-Lyon Institut Gerhardt, Montpellier
2 Wetting & dewetting of hydrophobic surfaces at a nanoscale Biological matter, hydrophobic interactions Energy applications
3 Micelle-templated silicas (MTS) : model nanopores CTAB + TMB Kresge & al Nature 1992 Hydrophobic MTS : C8-silane grafting n-octyl-dimethylchlorosilane Martin & di Renzo, Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal 2001 Ø 2nm Ø 6.4nm Ø 4nm Ø 10nm
4 MTS: an ideal experimental model to study wetting at a nanoscale ü Well-defined geometry ü Well-controlled physico-chemistry (very low contamination)
5 Intrusion-extrusion experiments mesoporous powder Eroshenko & Fadeev, Colloid J 1995 Water Ø ~ 1-10 nm Hydrophobic grafting Pressure (MPa) R pore < 1 nm 1nm < R pore < 3nm intrusion R pore > 3 nm extrusion intrusion Volume No energy dissipation à Actuator, energy storage Volume Partial energy dissipation à Damper No extrusion Total energy dissipation à Anti-crash device
6 Experimental set-up water+porous material (no air) Temp sensor sample Pressure transmitting liquid Pressure cell Pressure sensor Traction/compression machine for P V cycles
7 MTS: Influence of the pore radius on the intrusion pressure Lefevre et al, J. Chem. Phys. 120, 2004 MCM 41 R p : 1.3 to 5.6 nm Intrusion pressure liquid R p cos θ a = Classical capillarity: P cap advancing angle describes very well intrusion down to R p =1.3nm
8 Influence of the pore radius on extrusion pressure Lefevre et al, Coll Surf. A. 241, 265, Intrusion - 4 extrusion capillary pressure does not control extrusion
9 Dynamics of intrusion-extrusion cycles Guillemot et al, RSI, 83, (2012) Pressure = 1 50 MPa Température = T amb 80 C Frequency f = Hz
10 Déplacement piston
11 Extrusion has a logarithmic kinetics P ext (MPa) C 50 C 40 C 30 C t ext (sec) Guillemot et al, PNAS 109, 19557, (2012)
12 Dewetting : surface-induced 1st order transition P < P int Slow dynamics Fast dynamics requires the nucleation of a 2-meniscii bubble
13 Nucleation model nucleation rate in each pore n = 1 b exp k B T P ext (MPa) C 50 C 40 C 30 C b 1Å s 12 k B T/V nuc Observed nucleation time nlt ext = t ext (sec) pore length Energy barrier = k B T ln(t ext )+Cte P = k BT V nuc ln(t ext )+Cte = PV nuc +surf.terms critical nucleus volume
14 The nucleus volume SBA-15 R p =1.62nm HMS R p =2.27nm MCM-41 R p =1.32nm 10nm
15 Comparison with classical nucleation theory Saugey et al J Chem Phys bubble energy Grand canonical free energy
16 Classical nucleation theory in a cylinder Saugey et al J Chem Phys 2004 /4 LV R 2 p P L R p /2 LV = P L R p /2 LV = =P L V bub + A LV LV + A SV LV cos V bub /R 3 p Grand canonical free energy Energy barrier tabulated functions ' P L K 1 ( )R 3 p + LV K 2 ( )R 2 p
17 Experiments vs classical nucleation theory Guillemot et al, PNAS 109, 19557, (2012) R p =2.27 ±0.5nm R p =1.32 ±0.2nm R p =1.62 ±0.2nm : nitrogen sorption : intrusion pressure Excellent agreement no adjustable parameter
18 1st Conclusion ü Drying of hydrophobic nano-cavities exhibits logarithmic dynamics ü Dynamics is controlled by vapor nucleation. ü Classical capillarity predicts: P ext = k BT V nuc ln t ext t o + P o ext(t ) u Nucleus volume is very well predicted u?
19 Classical theory: Pext(T o )= k BT to L ln V nuc b K2 ( ) K 1 ( ) LV (T ) R p Experiments Classical theory for MCM-41 Classical theory gives much too low cavitation pressure Overestimates energy barrier at least by 200 k B T
20 Can defects favor vapor nucleation? Local non-wetting defect Topographic defect Energy is too small is not filled at maximum pressure reached in experiment Extended non-wetting defect OK for energy, but is not wetted at maximum pressure reached in experiment
21 2nd Conclusion Classical capillarity with homogeneous pore walls overestimates utterly the energy barrier and predicts too low cavitation pressure Wall defects cannot account for the low energy barrier self-consistantly within classical capillarity
22 Effect of long range interactions? Van der Waals disjonction pressure for solid/liquid/vapor interactions: (e) = A SLV 6 e 3 Silica-water Hamaker constant q At the scale of the pore e = R p 0.5 MPa A SLV J negligible q Close to contact line: line tension
23 Line tension effect From Drelich CSA 1996 J.W. Gibbs, 1876 On the equilibrium of heterogeneous surfaces 3-phase line tension: Can be positive or negative a ( ~ 20 pn for water) Numerical simulations: <0 for LJ fluids Andreotti et al POF 2011 No reliable measurements below some 100 pn Checco et al PRL 2006 Mugele et al 2010
24 Line tension effect T. Biben ILM Lyon 3-phase line tension
25 3rd conclusion Line tension changes dramatically the energy barrier for nucleation Some tens of pn account for cavitation pressure Cavitation pressure gives very sensitive determination of line tension (± 0.5 pn)
26 3rd conclusion Line tension lowers dramatically the energy of nanobubbles of water vapor on hydrophobic surfaces Classical capillarity can describe quantitatively the drying of hydrophobic nano-cavities, provided the line tension is taken into account. Values of line tension between -25 pn to -35 pn are found for water on C8-silanized surfaces of various curvature. Good agreement with available theoretical and numerical estimations.
27 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Ludivine GUILLEMOT PhD student Anne GALARNEAU Institut Gerhardt, School of Chemistry, Montpellier Thierry BIBEN Institut Lumière Matière, Lyon Gérard VIGIER National Institute of Applied Sciences, Lyon Thierry ABENSUR EADS - Astrium
28 THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Xiao Cheng Zeng Publications Published Research - Department of Chemistry 10-1-2006 Homogeneous nucleation at high supersaturation
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Xiao Cheng Zeng Publications Published Research - Department of Chemistry 10-1-2006 Homogeneous nucleation at high supersaturation
Theory of Nucleation- Thermodynamics
 Colloid Science 02.11.2006 Nanochemistry UIO 1 Theory of Nucleation- Thermodynamics Theory of Nucleation ΔG = free energy of particle with radius r, ΔG s = surface tension of particle with radius r, Δ
Colloid Science 02.11.2006 Nanochemistry UIO 1 Theory of Nucleation- Thermodynamics Theory of Nucleation ΔG = free energy of particle with radius r, ΔG s = surface tension of particle with radius r, Δ
MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript
 MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript Max Planck Institute of of Colloids and Interfaces Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Stocco, A., & Möhwald, H. (2015). The influence of long-range
MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript Max Planck Institute of of Colloids and Interfaces Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Stocco, A., & Möhwald, H. (2015). The influence of long-range
Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS
 Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS dynamics dynamics freezing dynamics freezing microscopics of capillarity Menu 1. surface tension: thermodynamics & microscopics 2. wetting (statics): thermodynamics & microscopics
Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS dynamics dynamics freezing dynamics freezing microscopics of capillarity Menu 1. surface tension: thermodynamics & microscopics 2. wetting (statics): thermodynamics & microscopics
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF HETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION OF LIQUID DROPLET ON SOLID SURFACE
 MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF HETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION OF LIQUID DROPLET ON SOLID SURFACE Tatsuto Kimura* and Shigeo Maruyama** *Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tokyo 7-- Hongo,
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF HETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION OF LIQUID DROPLET ON SOLID SURFACE Tatsuto Kimura* and Shigeo Maruyama** *Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tokyo 7-- Hongo,
Generalized Cassie-Baxter equation for wetting of a spherical droplet within a smooth and heterogeneous conical cavity
 Science Front Publishers Journal for Foundations and pplications of Physics, vol. 4, No. (017) (sciencefront.org) ISSN 394-3688 Generalized Cassie-axter equation for wetting of a spherical droplet within
Science Front Publishers Journal for Foundations and pplications of Physics, vol. 4, No. (017) (sciencefront.org) ISSN 394-3688 Generalized Cassie-axter equation for wetting of a spherical droplet within
Foundations of. Colloid Science SECOND EDITION. Robert J. Hunter. School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
Foundations of Colloid Science SECOND EDITION Robert J. Hunter School of Chemistry University of Sydney OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS 1 NATURE OF COLLOIDAL DISPERSIONS 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Technological
A coherent picture for water at extreme negative pressure
 A coherent picture for water at extreme negative pressure Mouna El Mekki Azouzi 1, Claire Ramboz 2, Jean-François Lenain 3 and Frédéric Caupin 1 1 Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée et Nanostructures,
A coherent picture for water at extreme negative pressure Mouna El Mekki Azouzi 1, Claire Ramboz 2, Jean-François Lenain 3 and Frédéric Caupin 1 1 Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée et Nanostructures,
Endcapping Treatment of Inner Surfaces of a Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica
 Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 26 (2012) 2135 2141 brill.nl/jast Endcapping Treatment of Inner Surfaces of a Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica Weiyi Lu a, Aijie Han b, Taewan Kim c, Brian J. Chow
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 26 (2012) 2135 2141 brill.nl/jast Endcapping Treatment of Inner Surfaces of a Hexagonal Mesoporous Silica Weiyi Lu a, Aijie Han b, Taewan Kim c, Brian J. Chow
Interfaces and interfacial energy
 Interfaces and interfacial energy 1/14 kinds: l/g }{{ l/l } mobile s/g s/l s/s Example. Estimate the percetage of water molecules on the surface of a fog droplet of diameter (i) 0.1 mm (naked eye visibility
Interfaces and interfacial energy 1/14 kinds: l/g }{{ l/l } mobile s/g s/l s/s Example. Estimate the percetage of water molecules on the surface of a fog droplet of diameter (i) 0.1 mm (naked eye visibility
Molecular dynamics study of the lifetime of nanobubbles on the substrate
 Molecular dynamics study of the lifetime of nanobubbles on the substrate - Links of Hierarchies KOHNO Shunsuke Division of Physics and Astronomy, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University Outline Introduction
Molecular dynamics study of the lifetime of nanobubbles on the substrate - Links of Hierarchies KOHNO Shunsuke Division of Physics and Astronomy, Graduate School of Science, Kyoto University Outline Introduction
Liquid-vapour oscillations of water in hydrophobic nanopores
 Alicante 2003 4th European Biophysics Congress Liquid-vapour oscillations of water in hydrophobic nanopores 7 th July 2003 Oliver Beckstein and Mark S. P. Sansom Department of Biochemistry, Laboratory
Alicante 2003 4th European Biophysics Congress Liquid-vapour oscillations of water in hydrophobic nanopores 7 th July 2003 Oliver Beckstein and Mark S. P. Sansom Department of Biochemistry, Laboratory
Interpretation of Full Sorption-Desorption Isotherms as a Tool for Understanding Concrete Pore Structure
 Interpretation of Full Sorption-Desorption Isotherms as a Tool for Understanding Concrete Pore Structure The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Interpretation of Full Sorption-Desorption Isotherms as a Tool for Understanding Concrete Pore Structure The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
Nucleation rate (m -3 s -1 ) Radius of water nano droplet (Å) 1e+00 1e-64 1e-128 1e-192 1e-256
 Supplementary Figures Nucleation rate (m -3 s -1 ) 1e+00 1e-64 1e-128 1e-192 1e-256 Calculated R in bulk water Calculated R in droplet Modified CNT 20 30 40 50 60 70 Radius of water nano droplet (Å) Supplementary
Supplementary Figures Nucleation rate (m -3 s -1 ) 1e+00 1e-64 1e-128 1e-192 1e-256 Calculated R in bulk water Calculated R in droplet Modified CNT 20 30 40 50 60 70 Radius of water nano droplet (Å) Supplementary
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 30 Aug 2016
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 30 Aug 2016 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.soft] 30 Aug 2016](/thumbs/85/91746129.jpg) Free-energy barrier of filling a spherical cavity in arxiv:1608.08286v1 [cond-mat.soft] 30 Aug 2016 the presence of line tension: Implication to the energy barrier between the Cassie and Wenzel state on
Free-energy barrier of filling a spherical cavity in arxiv:1608.08286v1 [cond-mat.soft] 30 Aug 2016 the presence of line tension: Implication to the energy barrier between the Cassie and Wenzel state on
Effects of post-processing treatment on sorption isotherm of an effectively hydrophilic zeolite b
 Philosophical Magazine Letters, Vol. 88, No. 1, January 2008, 37 42 Effects of post-processing treatment on sorption isotherm of an effectively hydrophilic zeolite b A. HAN, V. K. PUNYAMURTULA and Y. QIAO*
Philosophical Magazine Letters, Vol. 88, No. 1, January 2008, 37 42 Effects of post-processing treatment on sorption isotherm of an effectively hydrophilic zeolite b A. HAN, V. K. PUNYAMURTULA and Y. QIAO*
Supplementary Information on Thermally Enhanced Self-Propelled Droplet Motion on Gradient Surfaces
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information on Thermally Enhanced Self-Propelled Droplet Motion on Gradient Surfaces
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information on Thermally Enhanced Self-Propelled Droplet Motion on Gradient Surfaces
U nderstanding on the line tension becomes particularly important because of its relevance to a number of
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: WETTING SURFACE CHEMISTRY NANOSCALE MATERIALS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Received 15 March 2013 Accepted 30 May 2013 Published 18 June 2013 Correspondence and requests for materials should
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: WETTING SURFACE CHEMISTRY NANOSCALE MATERIALS STATISTICAL PHYSICS Received 15 March 2013 Accepted 30 May 2013 Published 18 June 2013 Correspondence and requests for materials should
Chemical Potential. Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties)
 Chemical Potential Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties) du = TdS pdv Hence For an open system, that is, one that can gain or lose mass, U will also
Chemical Potential Combining the First and Second Laws for a closed system, Considering (extensive properties) du = TdS pdv Hence For an open system, that is, one that can gain or lose mass, U will also
Heterogeneous nucleation on mesoscopic wettable particles: A hybrid thermodynamic/densityfunctional
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Xiao Cheng Zeng Publications Published esearch - Department of Chemistry 7--00 Heterogeneous nucleation on mesoscopic wettable
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Xiao Cheng Zeng Publications Published esearch - Department of Chemistry 7--00 Heterogeneous nucleation on mesoscopic wettable
Bioinspired surfaces for robust submerged superhydrophobicity: insights from molecular dynamics
 Bioinspired surfaces for robust submerged superhydrophobicity: insights from molecular dynamics PRACE project SLIP - Salvinia-like surfaces in action: slip, cavitation, drag reduction Alberto Giacomello
Bioinspired surfaces for robust submerged superhydrophobicity: insights from molecular dynamics PRACE project SLIP - Salvinia-like surfaces in action: slip, cavitation, drag reduction Alberto Giacomello
Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants
 Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants Fuquan Tu, Bum Jun Park and Daeyeon Lee*. Description of the term notionally swollen droplets When particles are adsorbed
Thermodynamically Stable Emulsions Using Janus Dumbbells as Colloid Surfactants Fuquan Tu, Bum Jun Park and Daeyeon Lee*. Description of the term notionally swollen droplets When particles are adsorbed
DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY FOR STUDIES OF MULTIPLE STATES OF INHOMOGENEOUS FLUIDS AT SOLID SURFACES AND IN PORES.
 J. Smith, D. Stroud, MRS Symposium Proceedings Series, v.49, p.7-33, 998. DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY FOR STUDIES OF MULTIPLE STATES OF INHOMOGENEOUS FLUIDS AT SOLID SURFACES AND IN PORES. A.. NEIMARK, and
J. Smith, D. Stroud, MRS Symposium Proceedings Series, v.49, p.7-33, 998. DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY FOR STUDIES OF MULTIPLE STATES OF INHOMOGENEOUS FLUIDS AT SOLID SURFACES AND IN PORES. A.. NEIMARK, and
APPLICATION OF DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY TO CORE ANALYSIS
 SCA2013-055 1/7 APPLICATION OF DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY TO CORE ANALYSIS Evgeny Dyshlyuk, Schlumberger This paper was prepared for presentation at the International Symposium of the Society of
SCA2013-055 1/7 APPLICATION OF DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY TO CORE ANALYSIS Evgeny Dyshlyuk, Schlumberger This paper was prepared for presentation at the International Symposium of the Society of
hydrate systems Gránásy Research Institute for Solid State Physics & Optics H-1525 Budapest, POB 49, Hungary László
 Phase field theory of crystal nucleation: Application to the hard-sphere and CO 2 Bjørn Kvamme Department of Physics, University of Bergen Allégaten 55, N-5007 N Bergen, Norway László Gránásy Research
Phase field theory of crystal nucleation: Application to the hard-sphere and CO 2 Bjørn Kvamme Department of Physics, University of Bergen Allégaten 55, N-5007 N Bergen, Norway László Gránásy Research
Surface analysis algorithms in the mardyn program and the ls1 project
 Surface analysis algorithms in the mardyn program and the ls1 project Stuttgart, 15 th December 1 M. T. Horsch Surface tension The virial route Bakker-Buff equation: γ R 2 out in dz z Normal pressure decays
Surface analysis algorithms in the mardyn program and the ls1 project Stuttgart, 15 th December 1 M. T. Horsch Surface tension The virial route Bakker-Buff equation: γ R 2 out in dz z Normal pressure decays
APPLICATION OF A NOVEL DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY TO THE PORE SIZE ANALYSIS OF MICRO/MESOPOROUS CARBONS. Abstract. Introduction
 APPLICATION OF A NOVEL DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY TO THE PORE SIZE ANALYSIS OF MICRO/MESOPOROUS CARBONS Peter I. Ravikovitch, Princeton, NJ 854 Matthias Thommes, Quantachrome Instr., Boynton Beach, FL 33426,
APPLICATION OF A NOVEL DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY TO THE PORE SIZE ANALYSIS OF MICRO/MESOPOROUS CARBONS Peter I. Ravikovitch, Princeton, NJ 854 Matthias Thommes, Quantachrome Instr., Boynton Beach, FL 33426,
A MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF A BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON SOLID SURFACE
 A MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF A BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON SOLID SURFACE Shigeo Maruyama and Tatsuto Kimura Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Tokyo 7-- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo -866,
A MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF A BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON SOLID SURFACE Shigeo Maruyama and Tatsuto Kimura Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Tokyo 7-- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo -866,
CHARACTERIZATION OF FLUID-ROCK INTERACTION BY ADSORPTION CALORIMETRY
 SCA2018_053 1/8 CHARACTERIZATION OF FLUID-ROCK INTERACTION BY ADSORPTION CALORIMETRY D. Korobkov 1, V. Pletneva 1, E. Dyshlyuk 2 1 Schlumberger, Moscow Research Center and 2 Dahran Carbonate Research Center
SCA2018_053 1/8 CHARACTERIZATION OF FLUID-ROCK INTERACTION BY ADSORPTION CALORIMETRY D. Korobkov 1, V. Pletneva 1, E. Dyshlyuk 2 1 Schlumberger, Moscow Research Center and 2 Dahran Carbonate Research Center
Supporting Information: On Localized Vapor Pressure Gradients Governing Condensation and Frost Phenomena
 Supporting Information: On Localized Vapor Pressure Gradients Governing Condensation and Frost Phenomena Saurabh Nath and Jonathan B. Boreyko Department of Biomedical Engineering and Mechanics, Virginia
Supporting Information: On Localized Vapor Pressure Gradients Governing Condensation and Frost Phenomena Saurabh Nath and Jonathan B. Boreyko Department of Biomedical Engineering and Mechanics, Virginia
Thermodynamics I. Properties of Pure Substances
 Thermodynamics I Properties of Pure Substances Dr.-Eng. Zayed Al-Hamamre 1 Content Pure substance Phases of a pure substance Phase-change processes of pure substances o Compressed liquid, Saturated liquid,
Thermodynamics I Properties of Pure Substances Dr.-Eng. Zayed Al-Hamamre 1 Content Pure substance Phases of a pure substance Phase-change processes of pure substances o Compressed liquid, Saturated liquid,
Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation
 Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation 7.1 Mixing and Segregation (Chapter 9) Mixing vs. segregation (1) Types of Mixture * Perfect mixing Random mixing Segregating mixing Figure 9.1 (2) Segregation 1) Causes
Chapter 7 Mixing and Granulation 7.1 Mixing and Segregation (Chapter 9) Mixing vs. segregation (1) Types of Mixture * Perfect mixing Random mixing Segregating mixing Figure 9.1 (2) Segregation 1) Causes
dewetting driving forces dewetting mechanism? dewetting dynamics? final equilibrium state: drops with θ = θ Y
 dewetting initial state: continuous film of partially wetting liquid final equilibrium state: drops wit θ = θ Y driving forces dewetting mecanism? dewetting dynamics? 1 free energy vs. film tickness water
dewetting initial state: continuous film of partially wetting liquid final equilibrium state: drops wit θ = θ Y driving forces dewetting mecanism? dewetting dynamics? 1 free energy vs. film tickness water
Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces
 Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
STATE-OF-THE-ART ZEOLITE CHARACTERIZATION: ARGON ADSORPTION AT 87.3 K AND NONLOCAL DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY (NLDFT)
 STATE-OF-THE-ART ZEOLITE CHARACTERIZATION: ARGON ADSORPTION AT 87.3 K AND NONLOCAL DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY (NLDFT) Physical adsorption in materials consisting of micropores, as for instance in zeolites
STATE-OF-THE-ART ZEOLITE CHARACTERIZATION: ARGON ADSORPTION AT 87.3 K AND NONLOCAL DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY (NLDFT) Physical adsorption in materials consisting of micropores, as for instance in zeolites
Surface and Interfacial Tensions. Lecture 1
 Surface and Interfacial Tensions Lecture 1 Surface tension is a pull Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Thermodynamics for Interfacial Systems Work must be done to increase surface area just as work must be done
Surface and Interfacial Tensions Lecture 1 Surface tension is a pull Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Thermodynamics for Interfacial Systems Work must be done to increase surface area just as work must be done
MEGASONIC CLEANING OF WAFERS IN ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS: POSSIBLE ROLE OF ELECTRO-ACOUSTIC AND CAVITATION EFFECTS. The University of Arizona, Tucson
 MEGASONIC CLEANING OF WAFERS IN ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS: POSSIBLE ROLE OF ELECTRO-ACOUSTIC AND CAVITATION EFFECTS Manish Keswani 1, Srini Raghavan 1, Pierre Deymier 1 and Steven Verhaverbeke 2 1 The University
MEGASONIC CLEANING OF WAFERS IN ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS: POSSIBLE ROLE OF ELECTRO-ACOUSTIC AND CAVITATION EFFECTS Manish Keswani 1, Srini Raghavan 1, Pierre Deymier 1 and Steven Verhaverbeke 2 1 The University
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces.
 Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák & István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://kolloid.unideb.hu/~kolloid/
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák & István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://kolloid.unideb.hu/~kolloid/
(Crystal) Nucleation: The language
 Why crystallization requires supercooling (Crystal) Nucleation: The language 2r 1. Transferring N particles from liquid to crystal yields energy. Crystal nucleus Δµ: thermodynamic driving force N is proportional
Why crystallization requires supercooling (Crystal) Nucleation: The language 2r 1. Transferring N particles from liquid to crystal yields energy. Crystal nucleus Δµ: thermodynamic driving force N is proportional
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique
 Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Synthesis of ordered microporous carbons via template technique Zhou Ying, Yao Qimei, Qiu Jieshan *, Guo Hongchen, Sun Zongwei Carbon Research Laboratory, Center for Nano Materials and Science, School
Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line.
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 28 (6), pp. 415-420 (1994) 20 November 1994 Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line. J. CRASSOUS
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 28 (6), pp. 415-420 (1994) 20 November 1994 Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line. J. CRASSOUS
Hill s nano-thermodynamics is equivalent with Gibbs thermodynamics for curved surfaces
 Hill s nano-thermodynamics is equivalent with Gibbs thermodynamics for curved surfaces arxiv:1806.03444v1 [physics.chem-ph] 9 Jun 2018 Dick Bedeaux and Signe Kjelstrup Porelab, Department of Chemistry,
Hill s nano-thermodynamics is equivalent with Gibbs thermodynamics for curved surfaces arxiv:1806.03444v1 [physics.chem-ph] 9 Jun 2018 Dick Bedeaux and Signe Kjelstrup Porelab, Department of Chemistry,
PHYSICS OF FLUID SPREADING ON ROUGH SURFACES
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 5, Supp, Pages 85 92 c 2008 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information PHYSICS OF FLUID SPREADING ON ROUGH SURFACES K. M. HAY AND
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF NUMERICAL ANALYSIS AND MODELING Volume 5, Supp, Pages 85 92 c 2008 Institute for Scientific Computing and Information PHYSICS OF FLUID SPREADING ON ROUGH SURFACES K. M. HAY AND
Sorption and Phase Transitions in Nanopores
 7 th International Conference on Fundamental of Adsorption, May 2-25, 21, Nagasaki, Japan Sorption and Phase Transitions in Nanopores Alexander V. Neimark, Peter I. Ravikovitch, Aleksey Vishnyakov Center
7 th International Conference on Fundamental of Adsorption, May 2-25, 21, Nagasaki, Japan Sorption and Phase Transitions in Nanopores Alexander V. Neimark, Peter I. Ravikovitch, Aleksey Vishnyakov Center
DLVO interaction between the spheres
 DLVO interaction between the spheres DL-interaction energy for two spheres: D w ( x) 64c π ktrϕ e λ DL 2 x λ 2 0 0 D DLVO interaction w ( x) 64πkTRϕ e λ DLVO AR /12x 2 x λd 2 0 D Lecture 11 Contact angle
DLVO interaction between the spheres DL-interaction energy for two spheres: D w ( x) 64c π ktrϕ e λ DL 2 x λ 2 0 0 D DLVO interaction w ( x) 64πkTRϕ e λ DLVO AR /12x 2 x λd 2 0 D Lecture 11 Contact angle
Supplemental Material for Curvature-dependence of the liquid-vapor surface tension beyond the Tolman approximation
 Supplemental Material for Curvature-dependence of the liquid-vapor surface tension beyond the Tolman approximation Nicolas Bruot and Frédéric Caupin Institut Lumière Matière, UMR536 Université Claude Bernard
Supplemental Material for Curvature-dependence of the liquid-vapor surface tension beyond the Tolman approximation Nicolas Bruot and Frédéric Caupin Institut Lumière Matière, UMR536 Université Claude Bernard
Energetic Performances of the Metal-Organic Framework ZIF-8 by. High Pressure Water Intrusion-Extrusion Experiments
 Energetic Performances of the Metal-Organic Framework ZIF-8 by High Pressure Water Intrusion-Extrusion Experiments Guillaume Ortiz, Habiba Nouali, Claire Marichal, Gérald Chaplais, Joël Patarin Equipe
Energetic Performances of the Metal-Organic Framework ZIF-8 by High Pressure Water Intrusion-Extrusion Experiments Guillaume Ortiz, Habiba Nouali, Claire Marichal, Gérald Chaplais, Joël Patarin Equipe
Neutrons on a surface of liquid helium.
 Neutrons on a surface of liquid helium. P. Grigoriev*, O. Zimmer**, A. Grigoriev +, and T. Ziman** * L. D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Chernogolovka, Russia; **Institute Laue-Laungevin, Grenoble,
Neutrons on a surface of liquid helium. P. Grigoriev*, O. Zimmer**, A. Grigoriev +, and T. Ziman** * L. D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Chernogolovka, Russia; **Institute Laue-Laungevin, Grenoble,
SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS. Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France
 SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France Outline IV - FORMATION OF SOLIDS FROM SOLUTIONS 1) Glass
SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France Outline IV - FORMATION OF SOLIDS FROM SOLUTIONS 1) Glass
KOROSH TORABI. Ph.D. Chemical Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN Dec. 2011
 KOROSH TORABI 2 7 2 5 C E N T R A L S T. A P T 2 S E V A N S T O N, I L 6 0 2 0 1 P H O N E ( 3 1 2 ) 3 3 9-0 6 6 5 E - M A I L : K O R O S H. T O R A B I @ N O R T H W E S T E R N. E D U W E B P A G E
KOROSH TORABI 2 7 2 5 C E N T R A L S T. A P T 2 S E V A N S T O N, I L 6 0 2 0 1 P H O N E ( 3 1 2 ) 3 3 9-0 6 6 5 E - M A I L : K O R O S H. T O R A B I @ N O R T H W E S T E R N. E D U W E B P A G E
On the Landau-Levich Transition
 10116 Langmuir 2007, 23, 10116-10122 On the Landau-Levich Transition Maniya Maleki Institute for AdVanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS), Zanjan 45195, P.O. Box 45195-1159, Iran Etienne Reyssat and
10116 Langmuir 2007, 23, 10116-10122 On the Landau-Levich Transition Maniya Maleki Institute for AdVanced Studies in Basic Sciences (IASBS), Zanjan 45195, P.O. Box 45195-1159, Iran Etienne Reyssat and
A drop forms when liquid is forced out of a small tube. The shape of the drop is determined by a balance of pressure, gravity, and surface tension
 A drop forms when liquid is forced out of a small tube. The shape of the drop is determined by a balance of pressure, gravity, and surface tension forces. 2 Objectives 3 i i 2 1 INTRODUCTION Property:
A drop forms when liquid is forced out of a small tube. The shape of the drop is determined by a balance of pressure, gravity, and surface tension forces. 2 Objectives 3 i i 2 1 INTRODUCTION Property:
Wetting & Adhesion on Soft Surfaces Young s Law is dead long live Young s Law. Eric Dufresne
 Wetting & Adhesion on Soft Surfaces Young s Law is dead long live Young s Law Eric Dufresne KITP 2014 Wetting Adhesion 3mm 30 um Young s Law relates contact line geometry and material properties in equilibrium
Wetting & Adhesion on Soft Surfaces Young s Law is dead long live Young s Law Eric Dufresne KITP 2014 Wetting Adhesion 3mm 30 um Young s Law relates contact line geometry and material properties in equilibrium
Finite size scaling of the dynamical free-energy in the interfacial regime of a kinetically constrained model
 Finite size scaling of the dynamical free-energy in the interfacial regime of a kinetically constrained model Thierry Bodineau 1, Vivien Lecomte 2, Cristina Toninelli 2 1 DMA, ENS, Paris, France 2 LPMA,
Finite size scaling of the dynamical free-energy in the interfacial regime of a kinetically constrained model Thierry Bodineau 1, Vivien Lecomte 2, Cristina Toninelli 2 1 DMA, ENS, Paris, France 2 LPMA,
Rare Event Simulations
 Rare Event Simulations Homogeneous nucleation is a rare event (e.g. Liquid Solid) Crystallization requires supercooling (µ solid < µ liquid ) Crystal nucleus 2r Free - energy gain r 3 4! 3! GBulk = ñr!
Rare Event Simulations Homogeneous nucleation is a rare event (e.g. Liquid Solid) Crystallization requires supercooling (µ solid < µ liquid ) Crystal nucleus 2r Free - energy gain r 3 4! 3! GBulk = ñr!
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context
 Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
Acoustic nucleation of solid helium 4 on a clean glass plate
 Acoustic nucleation of solid helium 4 on a clean glass plate X. Chavanne, S. Balibar, and F. Caupin Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure, associé aux Universités Paris 6 et
Acoustic nucleation of solid helium 4 on a clean glass plate X. Chavanne, S. Balibar, and F. Caupin Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure, associé aux Universités Paris 6 et
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF VAPOR BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON A SOLID SURFACE. Tatsuto Kimura and Shigeo Maruyama
 MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF VAPOR BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON A SOLID SURFACE Tatsuto Kimura and Shigeo Maruyama * Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tokyo, 7-- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF VAPOR BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON A SOLID SURFACE Tatsuto Kimura and Shigeo Maruyama * Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tokyo, 7-- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo
Thermodynamic expansion of nucleation free-energy barrier and size of critical nucleus near the vapor-liquid coexistence
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1999 hermodynamic expansion of nucleation free-energy barrier and size of critical nucleus near the vapor-liquid coexistence Kenichiro Koga
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 110, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1999 hermodynamic expansion of nucleation free-energy barrier and size of critical nucleus near the vapor-liquid coexistence Kenichiro Koga
Peter A. Monson. Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 01003, USA. Acknowledgements: John Edison (Utrecht)
 Understanding Adsorption/Desorption Hysteresis for Fluids in Mesoporous Materials using Simple Molecular Models and Classical Density Functional Theory Peter A. Monson Department of Chemical Engineering,
Understanding Adsorption/Desorption Hysteresis for Fluids in Mesoporous Materials using Simple Molecular Models and Classical Density Functional Theory Peter A. Monson Department of Chemical Engineering,
contact line dynamics
 contact line dynamics Jacco Snoeijer Physics of Fluids - University of Twente sliding drops flow near contact line static contact line Ingbrigtsen & Toxvaerd (2007) γ γ sv θ e γ sl molecular scales macroscopic
contact line dynamics Jacco Snoeijer Physics of Fluids - University of Twente sliding drops flow near contact line static contact line Ingbrigtsen & Toxvaerd (2007) γ γ sv θ e γ sl molecular scales macroscopic
2D surface confined nanoporous molecular networks at the liquid-solid interface: a scanning tunneling microscopy study
 2D surface confined nanoporous molecular networks at the liquid-solid interface: a scanning tunneling microscopy study Shengbin Lei Laboratory of Photochemistry and Spectroscopy and INPAC KULeuven Content
2D surface confined nanoporous molecular networks at the liquid-solid interface: a scanning tunneling microscopy study Shengbin Lei Laboratory of Photochemistry and Spectroscopy and INPAC KULeuven Content
Thermodynamics of Fluid Phase Equilibria Dr. Jayant K. Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Thermodynamics of Fluid Phase Equilibria Dr. Jayant K. Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 01 Review of basic concepts of thermodynamics Welcome to
Thermodynamics of Fluid Phase Equilibria Dr. Jayant K. Singh Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 01 Review of basic concepts of thermodynamics Welcome to
Surface property corrected modification of the classical nucleation theory
 CCP5 Annual Meeting Surface property corrected modification of the classical nucleation theory Sheffield Hallam University, September 15, 2010 Martin Horsch, Hans Hasse, and Jadran Vrabec The critical
CCP5 Annual Meeting Surface property corrected modification of the classical nucleation theory Sheffield Hallam University, September 15, 2010 Martin Horsch, Hans Hasse, and Jadran Vrabec The critical
Frieder Mugele. Physics of Complex Fluids. University of Twente. Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT
 coorganizers: Frieder Mugele Physics of Comple Fluids Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT University of Twente Anton Darhuber Mesoscopic Transport Phenomena / Tu/e speakers: José Bico (ESPCI Paris) Daniel
coorganizers: Frieder Mugele Physics of Comple Fluids Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT University of Twente Anton Darhuber Mesoscopic Transport Phenomena / Tu/e speakers: José Bico (ESPCI Paris) Daniel
The expansion coefficient of liquid helium 3 and the shape of its stability limit
 The expansion coefficient of liquid helium 3 and the shape of its stability limit Frédéric Caupin, Sébastien Balibar and Humphrey J. Maris Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure
The expansion coefficient of liquid helium 3 and the shape of its stability limit Frédéric Caupin, Sébastien Balibar and Humphrey J. Maris Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure
DYNAMIC CONDENSATION OF WATER AT CRACK TIPS IN FUSED SILICA GLASS
 DYNAMIC CONDENSATION OF WATER AT CRACK TIPS IN FUSED SILICA GLASS M. Ciccotti 1,*, M. George 1, V. Ranieri 1, L. Wondraczek 2 and C. Marlière 3 1 Laboratoire des Colloïdes, Verres et Nanomatériaux, Université
DYNAMIC CONDENSATION OF WATER AT CRACK TIPS IN FUSED SILICA GLASS M. Ciccotti 1,*, M. George 1, V. Ranieri 1, L. Wondraczek 2 and C. Marlière 3 1 Laboratoire des Colloïdes, Verres et Nanomatériaux, Université
Hard-sphere fluids in contact with curved substrates
 Hard-sphere fluids in contact with curved substrates P. Bryk, 1,2,3 R. Roth, 2,3 K. R. Mecke, 2,3 and S. Dietrich 2,3 1 Department for the Modeling of Physico-Chemical Processes, Maria Curie-Skłodowska
Hard-sphere fluids in contact with curved substrates P. Bryk, 1,2,3 R. Roth, 2,3 K. R. Mecke, 2,3 and S. Dietrich 2,3 1 Department for the Modeling of Physico-Chemical Processes, Maria Curie-Skłodowska
Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany
 Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany Preliminaries Learning Goals Phase Equilibria Phase diagrams and classical thermodynamics
Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany Preliminaries Learning Goals Phase Equilibria Phase diagrams and classical thermodynamics
ESS 5855 Surface Engineering for. MicroElectroMechanicalechanical Systems. Fall 2010
 ESS 5855 Surface Engineering for Microelectromechanical Systems Fall 2010 MicroElectroMechanicalechanical Systems Miniaturized systems with integrated electrical and mechanical components for actuation
ESS 5855 Surface Engineering for Microelectromechanical Systems Fall 2010 MicroElectroMechanicalechanical Systems Miniaturized systems with integrated electrical and mechanical components for actuation
EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES. By Ertanto Vetra
 EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines - TV, PV, PT, PVT Diagram - Property Tables - Introduction to Enthalpy - Reference State & Reference Values - Ideal Gas Equation
EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines - TV, PV, PT, PVT Diagram - Property Tables - Introduction to Enthalpy - Reference State & Reference Values - Ideal Gas Equation
Pollution des sols et interaction avec la biosphère
 Pollution des sols et interaction avec la biosphère Mazen SAAD Ecole Centrale de Nantes Laboratoire de Mathématiques Jean Leray FRANCE Mathématiques Pour La Planète La Rochelle 17 octobre 2013 Plan 1 Transport
Pollution des sols et interaction avec la biosphère Mazen SAAD Ecole Centrale de Nantes Laboratoire de Mathématiques Jean Leray FRANCE Mathématiques Pour La Planète La Rochelle 17 octobre 2013 Plan 1 Transport
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Relationship between wetting and nucleation. (a) Relative decrease in the energy barrier (free energy change of heterogeneous nucleation,
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Relationship between wetting and nucleation. (a) Relative decrease in the energy barrier (free energy change of heterogeneous nucleation,
Molecular Modeling and Simulation of Phase Equilibria for Chemical Engineering
 InPROMT 2012, Berlin, 16. November 2012 DFG Transregio CRC 63 Molecular Modeling and Simulation of Phase Equilibria for Chemical Engineering Hans Hasse 1, Martin Horsch 1, Jadran Vrabec 2 1 Laboratory
InPROMT 2012, Berlin, 16. November 2012 DFG Transregio CRC 63 Molecular Modeling and Simulation of Phase Equilibria for Chemical Engineering Hans Hasse 1, Martin Horsch 1, Jadran Vrabec 2 1 Laboratory
Gauge cell method for simulation studies of phase transitions in confined systems
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 4 OCTOBER 2000 Gauge cell method for simulation studies of phase transitions in confined systems Alexander V. Neimark* and Aleksey Vishnyakov TRI/Princeton, 601 Prospect
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 4 OCTOBER 2000 Gauge cell method for simulation studies of phase transitions in confined systems Alexander V. Neimark* and Aleksey Vishnyakov TRI/Princeton, 601 Prospect
PROBLEM 6.3. Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property. In each case, locate the state on sketches of the T-v and T-s diagrams.
 PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
Chapter 2 Experimental sources of intermolecular potentials
 Chapter 2 Experimental sources of intermolecular potentials 2.1 Overview thermodynamical properties: heat of vaporization (Trouton s rule) crystal structures ionic crystals rare gas solids physico-chemical
Chapter 2 Experimental sources of intermolecular potentials 2.1 Overview thermodynamical properties: heat of vaporization (Trouton s rule) crystal structures ionic crystals rare gas solids physico-chemical
Thin Film Behavior after Ink Transfer in Printing Processes N. Bornemann, H. M. Sauer, E. Dörsam
 Thin Film Behavior after Ink Transfer in Printing Processes N. Bornemann, H. M. Sauer, E. Dörsam 15.04.2010 Institute of Printing Science and Technology Thin Film Behavior N. Bornemann Overview Thin Film
Thin Film Behavior after Ink Transfer in Printing Processes N. Bornemann, H. M. Sauer, E. Dörsam 15.04.2010 Institute of Printing Science and Technology Thin Film Behavior N. Bornemann Overview Thin Film
Coarsening: transient and self-similar dynamics in 1-D
 Coarsening: transient and self-similar dynamics in 1-D ½ 1 5 1 4 h ln(t) Ú ¼º N 1 3 N t 2/5 1 2 1 5 1 15 x ¼ 1 ¼ ¼º ½ 1 1 4 1 8 1 12 1 16 Ü t Michael Gratton (Northwestern) and Thomas Witelsi (Due) Cahn-Hilliard
Coarsening: transient and self-similar dynamics in 1-D ½ 1 5 1 4 h ln(t) Ú ¼º N 1 3 N t 2/5 1 2 1 5 1 15 x ¼ 1 ¼ ¼º ½ 1 1 4 1 8 1 12 1 16 Ü t Michael Gratton (Northwestern) and Thomas Witelsi (Due) Cahn-Hilliard
Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and wetting
 Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and Contact angle phenomena and wetting Young s equation Drop on the surface complete spreading Establishing finite contact angle γ cosθ = γ γ L S SL γ S γ > 0 partial
Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and Contact angle phenomena and wetting Young s equation Drop on the surface complete spreading Establishing finite contact angle γ cosθ = γ γ L S SL γ S γ > 0 partial
SELF-ASSEMBLY AND NANOTECHNOLOGY A Force Balance Approach
 SELF-ASSEMBLY AND NANOTECHNOLOGY A Force Balance Approach Yoon S. Lee Scientific Information Analyst Chemical Abstracts Service A Division of the American Chemical Society Columbus, Ohio WILEY A JOHN WILEY
SELF-ASSEMBLY AND NANOTECHNOLOGY A Force Balance Approach Yoon S. Lee Scientific Information Analyst Chemical Abstracts Service A Division of the American Chemical Society Columbus, Ohio WILEY A JOHN WILEY
Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department. Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials
 Before starting Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials PhD 2011-2014: Self-assembly mechanism of mesoporous
Before starting Julien Schmitt, postdoc in the Physical Chemistry department Internship 2010: Study of the SAXS scattering pattern of mesoporous materials PhD 2011-2014: Self-assembly mechanism of mesoporous
Powder Surface Area and Porosity
 Powder Surface Area and Porosity Powder Technology Series Edited by B. Scarlett Department of Chemical Engineering University of Technology Loughborough Powder Surface Area and Porosity S. Lowell PhD Quantachrome
Powder Surface Area and Porosity Powder Technology Series Edited by B. Scarlett Department of Chemical Engineering University of Technology Loughborough Powder Surface Area and Porosity S. Lowell PhD Quantachrome
Colloids as nucleons
 Colloids as nucleons Willem Kegel & Jan Groenewold Van t Hoff Laboratory Utrecht University The Netherlands Finite-size equilibrium structures macroscopic phase separation Equilibrium clusters & periodic
Colloids as nucleons Willem Kegel & Jan Groenewold Van t Hoff Laboratory Utrecht University The Netherlands Finite-size equilibrium structures macroscopic phase separation Equilibrium clusters & periodic
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Experimental details 1. Preparation of KIT-6 mesoporous silica: Conc. HCl solution (37 wt%) and Pluronic P123 were dissolved in water. After the dissolution,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Experimental details 1. Preparation of KIT-6 mesoporous silica: Conc. HCl solution (37 wt%) and Pluronic P123 were dissolved in water. After the dissolution,
Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow
 MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
Field Method of Simulation of Phase Transformations in Materials. Alex Umantsev Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville, NC
 Field Method of Simulation of Phase Transformations in Materials Alex Umantsev Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville, NC What do we need to account for? Multi-phase states: thermodynamic systems
Field Method of Simulation of Phase Transformations in Materials Alex Umantsev Fayetteville State University, Fayetteville, NC What do we need to account for? Multi-phase states: thermodynamic systems
Nanoparticle Synthesis and Assembly from Atomistic Simulation Studies
 Nanoparticle Synthesis and Assembly from Atomistic Simulation Studies By Takumi Hawa School of Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Oklahoma Supercomputing Symposium 2008 October 7 Supported by NSF, ARL,
Nanoparticle Synthesis and Assembly from Atomistic Simulation Studies By Takumi Hawa School of Aerospace & Mechanical Engineering Oklahoma Supercomputing Symposium 2008 October 7 Supported by NSF, ARL,
3.10. Capillary Condensation and Adsorption Hysteresis
 3.10. Capillary Condensation and Adsorption Hysteresis We shall restrict our attention to the adsorption behavior of porous solids. Hysteresis: two quantities of adsorbed material for each equilibrium
3.10. Capillary Condensation and Adsorption Hysteresis We shall restrict our attention to the adsorption behavior of porous solids. Hysteresis: two quantities of adsorbed material for each equilibrium
Peter Buhler. NanothermodynamicS
 Peter Buhler NanothermodynamicS Introduction 7 Symbols and definitions 9 1. On the basic concepts of classical thermodynamics 1 5 1.1. Internal energy, heat, and work 1 7 1.1.1. Internal energy is a property
Peter Buhler NanothermodynamicS Introduction 7 Symbols and definitions 9 1. On the basic concepts of classical thermodynamics 1 5 1.1. Internal energy, heat, and work 1 7 1.1.1. Internal energy is a property
Statistical geometry of cavities in a metastable confined fluid
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 1 JULY 2000 Statistical geometry of cavities in a metastable confined fluid Aleksey Vishnyakov, 1 Pablo G. Debenedetti, 2 and Alexander V. Neimark 1, * 1 TRI/Princeton,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 62, NUMBER 1 JULY 2000 Statistical geometry of cavities in a metastable confined fluid Aleksey Vishnyakov, 1 Pablo G. Debenedetti, 2 and Alexander V. Neimark 1, * 1 TRI/Princeton,
On the Green-Kubo relationship for the liquid-solid friction coefficient
 On the Green-Kubo relationship for the liquid-solid friction coefficient Lydéric Bocquet and Jean-Louis Barrat Citation: J. Chem. Phys. 39, 044704 (203); doi: 0.063/.486006 View online: http://dx.doi.org/0.063/.486006
On the Green-Kubo relationship for the liquid-solid friction coefficient Lydéric Bocquet and Jean-Louis Barrat Citation: J. Chem. Phys. 39, 044704 (203); doi: 0.063/.486006 View online: http://dx.doi.org/0.063/.486006
Capillary rise between closely spaced plates : effect of Van der Waals forces
 Capillary rise between closely spaced plates : effect of Van der Waals forces B. Legait, P.G. De Gennes To cite this version: B. Legait, P.G. De Gennes. Capillary rise between closely spaced plates : effect
Capillary rise between closely spaced plates : effect of Van der Waals forces B. Legait, P.G. De Gennes To cite this version: B. Legait, P.G. De Gennes. Capillary rise between closely spaced plates : effect
Line Tension Effect upon Static Wetting
 Line Tension Effect upon Static Wetting Pierre SEPPECHER Université de Toulon et du Var, BP 132 La Garde Cedex seppecher@univ tln.fr Abstract. Adding simply, in the classical capillary model, a constant
Line Tension Effect upon Static Wetting Pierre SEPPECHER Université de Toulon et du Var, BP 132 La Garde Cedex seppecher@univ tln.fr Abstract. Adding simply, in the classical capillary model, a constant
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
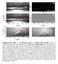 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Microporous Carbon adsorbents with high CO 2 capacities for industrial applications
 Microporous Carbon adsorbents with high CO 2 capacities for industrial applications Santiago Builes, a,b Thomas Roussel,* b Camelia Matei Ghimbeu, c Julien Parmentier, c Roger Gadiou, c Cathie Vix-Guterl
Microporous Carbon adsorbents with high CO 2 capacities for industrial applications Santiago Builes, a,b Thomas Roussel,* b Camelia Matei Ghimbeu, c Julien Parmentier, c Roger Gadiou, c Cathie Vix-Guterl
Köhler Curve. Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics
 Köhler Curve Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Review of Kelvin Effect Gibbs Energy for formation of a drop G = G &'()*+, G ).'+
Köhler Curve Covers Reading Material in Chapter 10.3 Atmospheric Sciences 5200 Physical Meteorology III: Cloud Physics Review of Kelvin Effect Gibbs Energy for formation of a drop G = G &'()*+, G ).'+
Biomaterial Scaffolds
 Biomaterial Scaffolds Biomaterial Properties Surface properties Bulk properties Biological properties Types of Biomaterials Biological materials Synthetic materials Surface Properties The body reads the
Biomaterial Scaffolds Biomaterial Properties Surface properties Bulk properties Biological properties Types of Biomaterials Biological materials Synthetic materials Surface Properties The body reads the
Thermodynamics of histories: application to systems with glassy dynamics
 Thermodynamics of histories: application to systems with glassy dynamics Vivien Lecomte 1,2, Cécile Appert-Rolland 1, Estelle Pitard 3, Kristina van Duijvendijk 1,2, Frédéric van Wijland 1,2 Juan P. Garrahan
Thermodynamics of histories: application to systems with glassy dynamics Vivien Lecomte 1,2, Cécile Appert-Rolland 1, Estelle Pitard 3, Kristina van Duijvendijk 1,2, Frédéric van Wijland 1,2 Juan P. Garrahan
Chapter 7 Solid Surface
 Chapter 7 Solid Surface Definition of solid : A matter that is rigid and resists stress. Difference between solid and liquid surface : Liquid : always in equilibrium and equipotential. (Fig 7.1a,b) Solid
Chapter 7 Solid Surface Definition of solid : A matter that is rigid and resists stress. Difference between solid and liquid surface : Liquid : always in equilibrium and equipotential. (Fig 7.1a,b) Solid
