IB Math SL Year 2 Name Date Lesson 10-4: Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Revisited
|
|
|
- Aubrie Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Date Lesson 10-4: Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Revisited Learning Goals: How do you apply integrals to real-world scenarios? Recall: Linear Motion When an object is moving, a ball in the air for example, we can use functions and calculus to analyze its displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Displacement- position (distance from original location) Velocity - speed in a given direction over time; change in positioning over time Acceleration - change in the rate of speed (or the change in velocity). *note, calculator should be in radians for application questions, unless otherwise specified! 1. The velocity, v, in meters per second of a particle moving in a straight line is given by:, where t is time in seconds. a) Find the acceleration of the particle at t = 1 b) Find the displacement of the particle traveled between 2 seconds and 8 seconds.
2 2. A particle moves in a straight line. Its velocity after t seconds is given by a. After p seconds, the particle is 2 m from its initial position. Find the possible values of p b. Determine the acceleration of the particle after 1 second
3 Group Practice Warm-Up 1. The velocity, v(t), of a ball in feet per second line is given by:, where t is time in seconds. a) Write an integral to express the displacement of the ball over the first four seconds. b) Hence, find the displacement of the ball over the first four seconds. 2. For the given velocity v = find the displacement between t = 0.2 and t = 0.9.
4 Practice Complete for HW 3. The acceleration a ms -2, of a particle at time t seconds is given by: Given that the particle is at rest (which means velocity is ) when t = 1. Determine the function for velocity. Hence, find the velocity of the particle when t = For the given velocity v = find the displacement traveled between t = and t =.
5 5. The following diagram shows the graph of the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of a moving particle as functions of time, x. a. Complete the following table by noting which graph I, II, or III corresponds to each function: Function Displacement Acceleration Graph b. Write down the value of t when the velocity is the greatest. 6. A rocket moving in a straight line has a velocity of v km/s and displacement s km at time t seconds. The velocity v is given by v(t) = 6e 2t + t. When t = 0, s = 10. Find an expression for the displacement, s, of the rocket in terms of t.
6 7. A particle moves in a straight line. Its velocity, v ms -1 at time t seconds is given by: a. Find the velocity of the particle when t = 1 b. Find the value of t for which the particle is at rest. c. Show that the acceleration of the particle is given by:
7 8. The velocity, v, in meters per second of a particle moving in a straight line is given by:, where t is time in seconds. a) Find the acceleration of the particle at t = 1 b) Find the displacement of the particle traveled between 2 seconds and 8 seconds. (calculator only for final answer, show all calculus)!
8 9. A particle moves in a straight line with velocity, for t, where v is in centimetres per second and t is in seconds. a. Find the acceleration of the particle after 2.7 seconds. b. Find the displacement of the particle after the first 1.3 seconds. 10. If f (x) = cos x, and f = 2, find f (x). 2
Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value
 AP Calculus Unit 6 Basic Integration & Applications Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value b (1) v( t) dt p( b) p( a), where v(t) represents the velocity and
AP Calculus Unit 6 Basic Integration & Applications Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value b (1) v( t) dt p( b) p( a), where v(t) represents the velocity and
Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: Kinematics of Linear Motion
 Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: William and Mary February 24, 2015 Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: Learning Objectives Today, we will be looking at applications of derivatives in the field of kinematics. Learning
Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: William and Mary February 24, 2015 Spring 2015, Math 111 Lab 4: Learning Objectives Today, we will be looking at applications of derivatives in the field of kinematics. Learning
The Definite Integral. Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area
 The Definite Integral Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area ARRIVAL---HW Questions Working in PODS Additional Practice Packet p. 13 and 14 Make good use of your time! Practice makes perfect!
The Definite Integral Day 6 Motion Problems Strategies for Finding Total Area ARRIVAL---HW Questions Working in PODS Additional Practice Packet p. 13 and 14 Make good use of your time! Practice makes perfect!
AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics ANSWERS 1982B1 2
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics ANSWERS 198B1 a. For the first seconds, while acceleration is constant, d = ½ at Substituting the given values d = 10 meters, t = seconds gives a = 5 m/s b.
AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics ANSWERS 198B1 a. For the first seconds, while acceleration is constant, d = ½ at Substituting the given values d = 10 meters, t = seconds gives a = 5 m/s b.
Particle Motion. Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x()
 Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
MATH CALCULUS I 4.1: Area and Distance
 MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 4.1: Area and Distance Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 / 8 The Area and Distance Problems
MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 4.1: Area and Distance Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 / 8 The Area and Distance Problems
From last time. Light and heavy objects fall identically. Objects maintain their state of motion unless acted on by an external force.
 From last time Light and heavy objects fall identically. Objects maintain their state of motion unless acted on by an external force. I.e. either at rest, or straight line motion at constant speed This
From last time Light and heavy objects fall identically. Objects maintain their state of motion unless acted on by an external force. I.e. either at rest, or straight line motion at constant speed This
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 1: Ch.12, Sec.1-3h
 1 / 30 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 1: Ch.12, Sec.1-3h Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, August 21, 2012 2 / 30 INTRODUCTION
1 / 30 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 1: Ch.12, Sec.1-3h Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, August 21, 2012 2 / 30 INTRODUCTION
MATH 1271 Monday, 21 November 2018
 MATH 1271 Monday, 21 November 218 Today: Section 5.4 - Indefinite Integrals and the Theorem Homework: 5-17 odd, 21-45 odd, 51-63 odd, 67, 71 1/13 Def Total displacement is the integral of the velocity
MATH 1271 Monday, 21 November 218 Today: Section 5.4 - Indefinite Integrals and the Theorem Homework: 5-17 odd, 21-45 odd, 51-63 odd, 67, 71 1/13 Def Total displacement is the integral of the velocity
Ms. Peralta s IM3 HW 5.4. HW 5.4 Solving Quadratic Equations. Solve the following exercises. Use factoring and/or the quadratic formula.
 HW 5.4 HW 5.4 Solving Quadratic Equations Name: Solve the following exercises. Use factoring and/or the quadratic formula. 1. 2. 3. 4. HW 5.4 5. 6. 4x 2 20x + 25 = 36 7. 8. HW 5.4 9. 10. 11. 75x 2 30x
HW 5.4 HW 5.4 Solving Quadratic Equations Name: Solve the following exercises. Use factoring and/or the quadratic formula. 1. 2. 3. 4. HW 5.4 5. 6. 4x 2 20x + 25 = 36 7. 8. HW 5.4 9. 10. 11. 75x 2 30x
Please read for extra test points: Thanks for reviewing the notes you are indeed a true scholar!
 Please read for extra test points: Thanks for reviewing the notes you are indeed a true scholar! See me any time B4 school tomorrow and mention to me that you have reviewed your integration notes and you
Please read for extra test points: Thanks for reviewing the notes you are indeed a true scholar! See me any time B4 school tomorrow and mention to me that you have reviewed your integration notes and you
Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals
 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals MATH 151 Calculus for Management J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives After completing this lesson we will be able to use the definition
Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals MATH 151 Calculus for Management J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives After completing this lesson we will be able to use the definition
CHAPTER 9 MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE FORM 5 PAPER 2
 PPER. particle moves in a straight line and passes through a fixed point O, with a velocity of m s. Its acceleration, a m s, t seconds after passing through O is given by a 8 4t. The particle stops after
PPER. particle moves in a straight line and passes through a fixed point O, with a velocity of m s. Its acceleration, a m s, t seconds after passing through O is given by a 8 4t. The particle stops after
Particle Motion Notes Position When an object moves, its position is a function of time. For its position function, we will denote the variable s(t).
 Particle Motion Notes Position When an object moves, its position is a function of time. For its position function, we will denote the variable s(t). Example 1: For s( t) t t 3, show its position on the
Particle Motion Notes Position When an object moves, its position is a function of time. For its position function, we will denote the variable s(t). Example 1: For s( t) t t 3, show its position on the
Particle Motion Problems
 Particle Motion Problems Particle motion problems deal with particles that are moving along the x or y axis. Thus, we are speaking of horizontal or vertical movement. The position, velocity, or acceleration
Particle Motion Problems Particle motion problems deal with particles that are moving along the x or y axis. Thus, we are speaking of horizontal or vertical movement. The position, velocity, or acceleration
Motion in One Dimension
 Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
Motion in One Dimension Much of the physics we ll learn this semester will deal with the motion of objects We start with the simple case of one-dimensional motion Or, motion in x: As always, we begin by
an expression, in terms of t, for the distance of the particle from O at time [3]
![an expression, in terms of t, for the distance of the particle from O at time [3] an expression, in terms of t, for the distance of the particle from O at time [3]](/thumbs/88/114967411.jpg) HORIZON EDUCATION SINGAPORE Additional Mathematics Practice Questions: Kinematics Set 1 1 A particle moves in a straight line so that t seconds after passing through O, its velocity v cm s -1, is given
HORIZON EDUCATION SINGAPORE Additional Mathematics Practice Questions: Kinematics Set 1 1 A particle moves in a straight line so that t seconds after passing through O, its velocity v cm s -1, is given
Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a
 Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer. C potential difference
Motion Unit Review 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer. C potential difference
Unit #6 Basic Integration and Applications Homework Packet
 Unit #6 Basic Integration and Applications Homework Packet For problems, find the indefinite integrals below.. x 3 3. x 3x 3. x x 3x 4. 3 / x x 5. x 6. 3x x3 x 3 x w w 7. y 3 y dy 8. dw Daily Lessons and
Unit #6 Basic Integration and Applications Homework Packet For problems, find the indefinite integrals below.. x 3 3. x 3x 3. x x 3x 4. 3 / x x 5. x 6. 3x x3 x 3 x w w 7. y 3 y dy 8. dw Daily Lessons and
STAAR Science Tutorial 21 TEK 6.8D: Graphing Motion
 Distance (meters) Name: _ Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 21 TEK 6.8D: Graphing Motion TEK 6.8D: Measure and graph changes in motion. Graphing Speed on a Distance Graph Speed is defined as the
Distance (meters) Name: _ Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 21 TEK 6.8D: Graphing Motion TEK 6.8D: Measure and graph changes in motion. Graphing Speed on a Distance Graph Speed is defined as the
Remember... Average rate of change slope of a secant (between two points)
 3.7 Rates of Change in the Natural and Social Sciences Remember... Average rate of change slope of a secant (between two points) Instantaneous rate of change slope of a tangent derivative We will assume
3.7 Rates of Change in the Natural and Social Sciences Remember... Average rate of change slope of a secant (between two points) Instantaneous rate of change slope of a tangent derivative We will assume
PARTICLE MOTION. Section 3.7A Calculus BC AP/Dual, Revised /30/2018 1:20 AM 3.7A: Particle Motion 1
 PARTICLE MOTION Section 3.7A Calculus BC AP/Dual, Revised 2017 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/2018 1:20 AM 3.7A: Particle Motion 1 WHEN YOU SEE THINK When you see Think Initially t = 0 At rest v t = 0 At
PARTICLE MOTION Section 3.7A Calculus BC AP/Dual, Revised 2017 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/2018 1:20 AM 3.7A: Particle Motion 1 WHEN YOU SEE THINK When you see Think Initially t = 0 At rest v t = 0 At
Remember... Average rate of change slope of a secant (between two points)
 3.7 Rates of Change in the Natural and Social Sciences Remember... Average rate of change slope of a secant (between two points) Instantaneous rate of change slope of a tangent derivative We will assume
3.7 Rates of Change in the Natural and Social Sciences Remember... Average rate of change slope of a secant (between two points) Instantaneous rate of change slope of a tangent derivative We will assume
( ) 4 and 20, find the value. v c is equal to this average CALCULUS WORKSHEET 1 ON PARTICLE MOTION
 CALCULUS WORKSHEET 1 ON PARTICLE MOTION Work these on notebook paper. Use your calculator only on part (f) of problems 1. Do not use your calculator on the other problems. Write your justifications in
CALCULUS WORKSHEET 1 ON PARTICLE MOTION Work these on notebook paper. Use your calculator only on part (f) of problems 1. Do not use your calculator on the other problems. Write your justifications in
Created by T. Madas CALCULUS KINEMATICS. Created by T. Madas
 CALCULUS KINEMATICS CALCULUS KINEMATICS IN SCALAR FORM Question (**) A particle P is moving on the x axis and its acceleration a ms, t seconds after a given instant, is given by a = 6t 8, t 0. The particle
CALCULUS KINEMATICS CALCULUS KINEMATICS IN SCALAR FORM Question (**) A particle P is moving on the x axis and its acceleration a ms, t seconds after a given instant, is given by a = 6t 8, t 0. The particle
MATH CALCULUS I 2.2: Differentiability, Graphs, and Higher Derivatives
 MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 2.2: Differentiability, Graphs, and Higher Derivatives Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 /
MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 2.2: Differentiability, Graphs, and Higher Derivatives Professor Donald L. White Department of Mathematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. White (Kent State University) 1 /
Calculus I Homework: The Tangent and Velocity Problems Page 1
 Calculus I Homework: The Tangent and Velocity Problems Page 1 Questions Example The point P (1, 1/2) lies on the curve y = x/(1 + x). a) If Q is the point (x, x/(1 + x)), use Mathematica to find the slope
Calculus I Homework: The Tangent and Velocity Problems Page 1 Questions Example The point P (1, 1/2) lies on the curve y = x/(1 + x). a) If Q is the point (x, x/(1 + x)), use Mathematica to find the slope
Worksheet 1. What You Need to Know About Motion Along the x-axis (Part 1)
 Curriculum Module: Calculus: Motion Worksheet 1. What You Need to Know About Motion Along the x-axis (Part 1) In discussing motion, there are three closely related concepts that you need to keep straight.
Curriculum Module: Calculus: Motion Worksheet 1. What You Need to Know About Motion Along the x-axis (Part 1) In discussing motion, there are three closely related concepts that you need to keep straight.
IB Math SL Year 2 Name: Date: 8-1 Rate of Change and Motion
 Name: Date: 8-1 Rate of Change and Motion Today s Goals: How can I calculate and interpret constant rate of change? How can I calculate and interpret instantaneous rate of change? How can we use derivatives
Name: Date: 8-1 Rate of Change and Motion Today s Goals: How can I calculate and interpret constant rate of change? How can I calculate and interpret instantaneous rate of change? How can we use derivatives
AP Calculus BC Class Starter January 22, 2018
 January 22, 2018 1. Given the function, find the following. (a) Evaluate f(4). (b) The definition of the derivative can be written two ways, as indicated below. Find both forms and evaluate the derivative
January 22, 2018 1. Given the function, find the following. (a) Evaluate f(4). (b) The definition of the derivative can be written two ways, as indicated below. Find both forms and evaluate the derivative
Particle Motion. Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x()
 Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Typically, if a particle is moving along the x-axis at any time, t, x() t represents the position of the particle; along the y-axis, yt () is often used; along another straight line, st () is often used.
Chapter 3: Derivatives
 Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 3: Derivatives Sections: v 2.4 Rates of Change & Tangent Lines v 3.1 Derivative of a Function v 3.2 Differentiability v 3.3 Rules for Differentiation
Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 3: Derivatives Sections: v 2.4 Rates of Change & Tangent Lines v 3.1 Derivative of a Function v 3.2 Differentiability v 3.3 Rules for Differentiation
Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time
 Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Recall the initial position and clock reading data from the previous lab. When considering
Lesson 12: Position of an Accelerating Object as a Function of Time 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Recall the initial position and clock reading data from the previous lab. When considering
LECTURE 27: Gravitational potential energy
 Lectures Page 1 LECTURE 27: Gravitational potential energy Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: i. ii. Construct an expression for the work due to gravity, defining this expression as gravitational potential energy
Lectures Page 1 LECTURE 27: Gravitational potential energy Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: i. ii. Construct an expression for the work due to gravity, defining this expression as gravitational potential energy
3.4 Solutions.notebook March 24, Horizontal Tangents
 Note Fix From 3.3 Horizontal Tangents Just for fun, sketch y = sin x and then sketch its derivative! What do you notice? More on this later 3.4 Velocity and Other Rates of Change A typical graph of the
Note Fix From 3.3 Horizontal Tangents Just for fun, sketch y = sin x and then sketch its derivative! What do you notice? More on this later 3.4 Velocity and Other Rates of Change A typical graph of the
Lesson 1: What is a Parabola?
 Lesson 1: What is a Parabola? Parabola Vocabulary Write the defintion of the given word. Label #3-6 on the graph. 1. Parabola: Name Class Date 2. Trajectory: 3. Zeros: 4. Axis of Symmetry: 5. Vertex: Online
Lesson 1: What is a Parabola? Parabola Vocabulary Write the defintion of the given word. Label #3-6 on the graph. 1. Parabola: Name Class Date 2. Trajectory: 3. Zeros: 4. Axis of Symmetry: 5. Vertex: Online
PARTICLE MOTION: DAY 2
 PARTICLE MOTION: DAY 2 Section 3.6A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2018 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/2018 1:24 AM 3.6A: Particle Motion Day 2 1 WHEN YOU SEE THINK When you see Think Initially t = 0 At rest
PARTICLE MOTION: DAY 2 Section 3.6A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2018 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/2018 1:24 AM 3.6A: Particle Motion Day 2 1 WHEN YOU SEE THINK When you see Think Initially t = 0 At rest
PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16
 PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement
PUM Physics II - Kinematics Lesson 12 Solutions Page 1 of 16 12.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement
Topics for the test and Sample Problems
 Topics for the test and Sample Problems Be able to Rearrange Every Motion Equation on the Equation Page x = v t x f = x i + vt v=a t v f = v i + at x f = x i + v i t + ½ at v f - v i = a (x f -x i ) Δx
Topics for the test and Sample Problems Be able to Rearrange Every Motion Equation on the Equation Page x = v t x f = x i + vt v=a t v f = v i + at x f = x i + v i t + ½ at v f - v i = a (x f -x i ) Δx
AP CALCULUS AB 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP CALCULUS AB 27 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity v at time 2 t is given by vt () = sin ( t ). The graph of v is shown above for t 5 π. The
AP CALCULUS AB 27 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity v at time 2 t is given by vt () = sin ( t ). The graph of v is shown above for t 5 π. The
APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION
 4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.9 Antiderivatives In this section, we will learn about: Antiderivatives and how they are useful in solving certain scientific problems.
4 APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION 4.9 Antiderivatives In this section, we will learn about: Antiderivatives and how they are useful in solving certain scientific problems.
Name: Total Points: Physics 201. Midterm 1
 Physics 201 Midterm 1 QUESTION 1 [25 points] An object moves in 1 dimension It starts at rest and uniformly accelerates at 5m/s 2 for 2s It then moves with constant velocity for 4s It then uniformly accelerates
Physics 201 Midterm 1 QUESTION 1 [25 points] An object moves in 1 dimension It starts at rest and uniformly accelerates at 5m/s 2 for 2s It then moves with constant velocity for 4s It then uniformly accelerates
AP Calculus Worksheet: Chapter 2 Review Part I
 AP Calculus Worksheet: Chapter 2 Review Part I 1. Given y = f(x), what is the average rate of change of f on the interval [a, b]? What is the graphical interpretation of your answer? 2. The derivative
AP Calculus Worksheet: Chapter 2 Review Part I 1. Given y = f(x), what is the average rate of change of f on the interval [a, b]? What is the graphical interpretation of your answer? 2. The derivative
1. Find the area bounded by the curve and the x axis between 5 and Find the area bounded by and the x axis between 3 and 3.
 AP Calculus November 15, 2017 1. Find the area bounded by the curve and the x axis between 5 and 0. 2. Find the area bounded by and the x axis between 3 and 3. 3. Find the area bounded by the curve graphed
AP Calculus November 15, 2017 1. Find the area bounded by the curve and the x axis between 5 and 0. 2. Find the area bounded by and the x axis between 3 and 3. 3. Find the area bounded by the curve graphed
CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS. Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (Chain Rule Version): f t dt
 CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS d d d d t dt 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: d f tdt d a d d 4 t dt d d a f t dt d d 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental
CALCULUS EXPLORATION OF THE SECOND FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS d d d d t dt 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: d f tdt d a d d 4 t dt d d a f t dt d d 6 cos t dt Second Fundamental
Speed how fast an object is moving (also, the magnitude of the velocity) scalar
 Mechanics Recall Mechanics Kinematics Dynamics Kinematics The description of motion without reference to forces. Terminology Distance total length of a journey scalar Time instant when an event occurs
Mechanics Recall Mechanics Kinematics Dynamics Kinematics The description of motion without reference to forces. Terminology Distance total length of a journey scalar Time instant when an event occurs
Calculus Review. v = x t
 Calculus Review Instructor : Kim 1. Average Rate of Change and Instantaneous Velocity To find the average velocity(v ) of a particle, we need to find the particle s displacement (=change in position) divided
Calculus Review Instructor : Kim 1. Average Rate of Change and Instantaneous Velocity To find the average velocity(v ) of a particle, we need to find the particle s displacement (=change in position) divided
Calculating Acceleration
 Calculating Acceleration Textbook pages 392 405 Before You Read Section 9. 2 Summary How do you think a velocity-time graph might differ from the position-time graph you learned about in the previous chapter?
Calculating Acceleration Textbook pages 392 405 Before You Read Section 9. 2 Summary How do you think a velocity-time graph might differ from the position-time graph you learned about in the previous chapter?
Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension)
 Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension) Learn the concepts of displacement, velocity, and acceleration in one-dimension. Describe motions at constant acceleration. Be able to graph
Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line (Motion in One-Dimension) Learn the concepts of displacement, velocity, and acceleration in one-dimension. Describe motions at constant acceleration. Be able to graph
AP Calculus. Particle Motion. Student Handout
 AP Calculus Particle Motion Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright 016
AP Calculus Particle Motion Student Handout 016-017 EDITION Use the following link or scan the QR code to complete the evaluation for the Study Session https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/s_sss Copyright 016
v t 2 2t 8. Fig. 7 (i) Write down the velocity of the insect when t 0. (ii) Show that the insect is instantaneously at rest when t 2and when t 4.
 1 Fig. 7 is a sketch of part of the velocity-time graph for the motion of an insect walking in a straight line. Its velocity, v ms 1, at time t seconds for the time interval 3 t 5 is given by v ms -1 v
1 Fig. 7 is a sketch of part of the velocity-time graph for the motion of an insect walking in a straight line. Its velocity, v ms 1, at time t seconds for the time interval 3 t 5 is given by v ms -1 v
Calculus with the Graphing Calculator
 Calculus with the Graphing Calculator Using a graphing calculator on the AP Calculus exam Students are expected to know how to use their graphing calculators on the AP Calculus exams proficiently to accomplish
Calculus with the Graphing Calculator Using a graphing calculator on the AP Calculus exam Students are expected to know how to use their graphing calculators on the AP Calculus exams proficiently to accomplish
AP Physics C: One Dimensional Kinematics
 Slide 1 / 33 P Physics : One imensional Kinematics Multiple hoice Questions Slide 2 / 33 1 In the absence of air resistance, a ball dropped near the surface of the arth experiences a constant acceleration
Slide 1 / 33 P Physics : One imensional Kinematics Multiple hoice Questions Slide 2 / 33 1 In the absence of air resistance, a ball dropped near the surface of the arth experiences a constant acceleration
Antiderivatives. Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if. F x f x for all x I.
 Antiderivatives Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if F x f x for all x I. Theorem If F is an antiderivative of f on I, then every function of
Antiderivatives Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if F x f x for all x I. Theorem If F is an antiderivative of f on I, then every function of
RECAP!! Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on a straight road. Time (s)
 RECAP!! What is uniform motion? > Motion in a straight line > Moving at a constant speed Yes or No? Yes or No? Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on
RECAP!! What is uniform motion? > Motion in a straight line > Moving at a constant speed Yes or No? Yes or No? Paul is a safe driver who always drives the speed limit. Here is a record of his driving on
Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics
 Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics Description of motion involves the relationship between position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. A fundamental goal of 1D kinematics is to determine x(t) if given initial
Chapter 2: 1D Kinematics Description of motion involves the relationship between position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. A fundamental goal of 1D kinematics is to determine x(t) if given initial
AP Calculus AB. Review for Test: Applications of Integration
 Name Review for Test: Applications of Integration AP Calculus AB Test Topics: Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (section 4.4) Average Value of a Function (manipulation of MVT for Integrals) (section 4.4)
Name Review for Test: Applications of Integration AP Calculus AB Test Topics: Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (section 4.4) Average Value of a Function (manipulation of MVT for Integrals) (section 4.4)
f x x, where f x (E) f, where ln
 AB Review 08 Calculator Permitted (unless stated otherwise) 1. h0 ln e h 1 lim is h (A) f e, where f ln (B) f e, where f (C) f 1, where ln (D) f 1, where f ln e ln 0 (E) f, where ln f f 1 1, where t is
AB Review 08 Calculator Permitted (unless stated otherwise) 1. h0 ln e h 1 lim is h (A) f e, where f ln (B) f e, where f (C) f 1, where ln (D) f 1, where f ln e ln 0 (E) f, where ln f f 1 1, where t is
Sierzega: Kinematics 10 Page 1 of 14
 Sierzega: Kinematics 10 Page 1 of 14 10.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement of an object. For
Sierzega: Kinematics 10 Page 1 of 14 10.1 Hypothesize (Derive a Mathematical Model) Graphically we know that the area beneath a velocity vs. time graph line represents the displacement of an object. For
Pre-Test Developed by Sean Moroney and James Petersen UNDERSTANDING THE VELOCITY CURVE. The Velocity Curve in Calculus
 in Calculus UNDERSTANDING THE VELOCITY CURVE Pre-Test Developed by Sean Moroney and James Petersen Introductory Calculus - in Calculus the Pre-Test Learning about the Velocity Curve During the course of
in Calculus UNDERSTANDING THE VELOCITY CURVE Pre-Test Developed by Sean Moroney and James Petersen Introductory Calculus - in Calculus the Pre-Test Learning about the Velocity Curve During the course of
AP Calculus Exam Format and Calculator Tips:
 AP Calculus Exam Format and Calculator Tips: Exam Format: The exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long and has two sections multiple choice and free response. A graphing calculator is required for parts of
AP Calculus Exam Format and Calculator Tips: Exam Format: The exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long and has two sections multiple choice and free response. A graphing calculator is required for parts of
As you already know by now, when you're finding derivatives, you're finding the slope.
 As you already know by now, when you're finding derivatives, you're finding the slope. Slope is a "rate of change" There are many other "rates of change" out there in the Real World. For example, a doctor
As you already know by now, when you're finding derivatives, you're finding the slope. Slope is a "rate of change" There are many other "rates of change" out there in the Real World. For example, a doctor
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
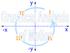 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
4.1 & 4.2 Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives. for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number f()
 4.1 & 4. Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives Definition A function f has an absolute maximum (or global maximum) at c if f ( c) f ( x) for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number
4.1 & 4. Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives Definition A function f has an absolute maximum (or global maximum) at c if f ( c) f ( x) for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number
Goal: Approximate the area under a curve using the Rectangular Approximation Method (RAM) RECTANGULAR APPROXIMATION METHODS
 AP Calculus 5. Areas and Distances Goal: Approximate the area under a curve using the Rectangular Approximation Method (RAM) Exercise : Calculate the area between the x-axis and the graph of y = 3 2x.
AP Calculus 5. Areas and Distances Goal: Approximate the area under a curve using the Rectangular Approximation Method (RAM) Exercise : Calculate the area between the x-axis and the graph of y = 3 2x.
We can regard an indefinite integral as representing an entire family of functions (one antiderivative for each value of the constant C).
 4.4 Indefinite Integrals and the Net Change Theorem Because of the relation given by the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus between antiderivatives and integrals, the notation f(x) dx is traditionally used
4.4 Indefinite Integrals and the Net Change Theorem Because of the relation given by the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus between antiderivatives and integrals, the notation f(x) dx is traditionally used
Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10
 1 / 37 Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10 Instructor: Prof. Noronha-Hostler Course Administrator: Prof. Roy Montalvo PHY-123 ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IA Phys- 123 Sep. 12 th, 2018 Contact Already read the syllabus
1 / 37 Lecture 2- Linear Motion Chapter 10 Instructor: Prof. Noronha-Hostler Course Administrator: Prof. Roy Montalvo PHY-123 ANALYTICAL PHYSICS IA Phys- 123 Sep. 12 th, 2018 Contact Already read the syllabus
Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only)
 Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only) Parametric Functions Parametric functions are another way of viewing functions. This time, the values of x and y are both dependent on another independent
Parametric Functions and Vector Functions (BC Only) Parametric Functions Parametric functions are another way of viewing functions. This time, the values of x and y are both dependent on another independent
Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration in one dimension
 Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration in one dimension In this document we consider the general relationship between displacement, velocity and acceleration. Displacement, velocity and acceleration are
Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration in one dimension In this document we consider the general relationship between displacement, velocity and acceleration. Displacement, velocity and acceleration are
Math 116 Practice for Exam 1
 Math 116 Practice for Exam 1 Generated September 3, 218 Name: SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section Number: 1. This exam has 4 questions. Note that the problems are not of equal difficulty, so you may want to
Math 116 Practice for Exam 1 Generated September 3, 218 Name: SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section Number: 1. This exam has 4 questions. Note that the problems are not of equal difficulty, so you may want to
Calculus AB a Solutions Thomas Handout Student Questions
 Give the positions s = f(t) of a body moving on a coordinate line, with s in meters and t in seconds. (a) Find the body's displacement and average velocity for the given time interval. (b) Fine the body's
Give the positions s = f(t) of a body moving on a coordinate line, with s in meters and t in seconds. (a) Find the body's displacement and average velocity for the given time interval. (b) Fine the body's
2.1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change
 .1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Demonstrate an understanding of the slope of the tangent line to the graph. Demonstrate an understanding of the instantaneous
.1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Demonstrate an understanding of the slope of the tangent line to the graph. Demonstrate an understanding of the instantaneous
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section. Name: Date: Period:
 AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The graph in the xy-plane represented
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The graph in the xy-plane represented
When does the function assume this value?
 Calculus Write your questions and thoughts here! 9.3 Average Value Name: Recall: Average Rate of Change: Mean Value Theorem (MVT) for Derivatives: Notes Average Value of a Function: 1 1. Find the average
Calculus Write your questions and thoughts here! 9.3 Average Value Name: Recall: Average Rate of Change: Mean Value Theorem (MVT) for Derivatives: Notes Average Value of a Function: 1 1. Find the average
Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics
 Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics Kari Eloranta 2018 Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio Pre Diploma Program Year October 11, 2017 1 / 17 3.1 Displacement Definition of Displacement Displacement is the change
Chapter 3: Introduction to Kinematics Kari Eloranta 2018 Jyväskylän Lyseon lukio Pre Diploma Program Year October 11, 2017 1 / 17 3.1 Displacement Definition of Displacement Displacement is the change
Lesson 11: Motion of a Falling Object
 Lesson 11: Motion of a Falling Object 11.1 Observe and find a pattern using your choice of one of the following: 1. The video at this web site: http://paer.rutgers.edu/pt3/experiment.php?topicid=2&exptid=38
Lesson 11: Motion of a Falling Object 11.1 Observe and find a pattern using your choice of one of the following: 1. The video at this web site: http://paer.rutgers.edu/pt3/experiment.php?topicid=2&exptid=38
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 Simplest case with non-zero acceleration Constant acceleration: a
Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 Simplest case with non-zero acceleration Constant acceleration: a
Logarithmic Differentiation (Sec. 3.6)
 Logarithmic Differentiation (Sec. 3.6) Logarithmic Differentiation Use logarithmic differentiation if you are taking the derivative of a function whose formula has a lot of MULTIPLICATION, DIVISION, and/or
Logarithmic Differentiation (Sec. 3.6) Logarithmic Differentiation Use logarithmic differentiation if you are taking the derivative of a function whose formula has a lot of MULTIPLICATION, DIVISION, and/or
Announcement. Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday
 Going over HW3.05 Announcement Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday As the red ball rolls off the edge, a green ball is dropped from rest from the same height at the same
Going over HW3.05 Announcement Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday As the red ball rolls off the edge, a green ball is dropped from rest from the same height at the same
Review for Chapter 8
 Review for Chapter 8 The function v(t) is the velocity of an object moving on the x-axis at any time t 0 where the velocity is measured in ft/sec. a) Determine when the object is moving right, left and
Review for Chapter 8 The function v(t) is the velocity of an object moving on the x-axis at any time t 0 where the velocity is measured in ft/sec. a) Determine when the object is moving right, left and
Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity
 Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity 7.1 Observe and Represent Another way of comparing trend lines is by calculating the slope of each line and comparing the numerical values of the slopes.
Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity 7.1 Observe and Represent Another way of comparing trend lines is by calculating the slope of each line and comparing the numerical values of the slopes.
V-t graphs and acceleration. Book page 5 8 Syllabus
 V-t graphs and acceleration Book page 5 8 Syllabus 1.5 1.8 What does the graph show? Multiple-choice quiz Does this show acceleration? Aim Interpret velocity / time graphs to: - compare acceleration between
V-t graphs and acceleration Book page 5 8 Syllabus 1.5 1.8 What does the graph show? Multiple-choice quiz Does this show acceleration? Aim Interpret velocity / time graphs to: - compare acceleration between
Graphical Analysis Part III. Motion Graphs. Basic Equations. Velocity is Constant. acceleration is zero. and. becomes
 Graphical Analysis Part III Motion Graphs Basic Equations d = vt+ 0 1 at v = v 0 + at Velocity is Constant acceleration is zero and becomes 1 d = v 0 t+ at d = vt 1 Velocity is Constant the slope of d
Graphical Analysis Part III Motion Graphs Basic Equations d = vt+ 0 1 at v = v 0 + at Velocity is Constant acceleration is zero and becomes 1 d = v 0 t+ at d = vt 1 Velocity is Constant the slope of d
Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. is continuous.
 Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. + +. Evaluate lim + (a (b (c (d 0 (e None of the above.. Evaluate lim (a (b (c (d 0 (e + + None of the above.. Find
Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. No work needed. No partial credit available. + +. Evaluate lim + (a (b (c (d 0 (e None of the above.. Evaluate lim (a (b (c (d 0 (e + + None of the above.. Find
Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration
 Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration Name 1) A truck on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 24 m/s. Then the truck travels for 20 s at constant
Formative Assessment: Uniform Acceleration Name 1) A truck on a straight road starts from rest and accelerates at 3.0 m/s 2 until it reaches a speed of 24 m/s. Then the truck travels for 20 s at constant
Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium
 Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter: Two Mechanical Equilibrium Big Idea / Key Concepts Student Outcomes 2.1: Force 2.2: Mechanical Equilibrium 2.3: Support Force 2.4: Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter: Two Mechanical Equilibrium Big Idea / Key Concepts Student Outcomes 2.1: Force 2.2: Mechanical Equilibrium 2.3: Support Force 2.4: Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Related Rates STEP 1 STEP 2:
 Related Rates You can use derivative analysis to determine how two related quantities also have rates of change which are related together. I ll lead off with this example. 3 Ex) A spherical ball is being
Related Rates You can use derivative analysis to determine how two related quantities also have rates of change which are related together. I ll lead off with this example. 3 Ex) A spherical ball is being
Math3A Exam #02 Solution Fall 2017
 Math3A Exam #02 Solution Fall 2017 1. Use the limit definition of the derivative to find f (x) given f ( x) x. 3 2. Use the local linear approximation for f x x at x0 8 to approximate 3 8.1 and write your
Math3A Exam #02 Solution Fall 2017 1. Use the limit definition of the derivative to find f (x) given f ( x) x. 3 2. Use the local linear approximation for f x x at x0 8 to approximate 3 8.1 and write your
Accl g Motion graph prac
 Accl g Motion graph prac 1. An object starts from rest and falls freely. What is the velocity of the object at the end of 3.00 seconds? A) 9.81 m/s B) 19.6 m/s C) 29.4 m/s D) 88.2 m/s 2. An object is dropped
Accl g Motion graph prac 1. An object starts from rest and falls freely. What is the velocity of the object at the end of 3.00 seconds? A) 9.81 m/s B) 19.6 m/s C) 29.4 m/s D) 88.2 m/s 2. An object is dropped
Motion Part 2: Uniform Linear Motion
 Motion Part 2: Uniform Linear Motion Last modified: 13/03/2018 Links Motion Quantities Uniform Velocity in One Dimension Uniform Acceleration in One Dimension Notation Extra Equations Uniform Acceleration
Motion Part 2: Uniform Linear Motion Last modified: 13/03/2018 Links Motion Quantities Uniform Velocity in One Dimension Uniform Acceleration in One Dimension Notation Extra Equations Uniform Acceleration
SM2H 1.6 HW-Average Rate of Change
 Distance (meters) SMH Name: Period: Core Alignment: F.IF.4, F.IF.6, F.IF.9 SMH.6 HW-Average Rate of Change The average rate of change between two points is essentially the slope of the line that connects
Distance (meters) SMH Name: Period: Core Alignment: F.IF.4, F.IF.6, F.IF.9 SMH.6 HW-Average Rate of Change The average rate of change between two points is essentially the slope of the line that connects
5.5 Worksheet - Linearization
 AP Calculus 4.5 Worksheet 5.5 Worksheet - Linearization All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers ma receive NO credit. 1. Consider the function = sin. a) Find the equation
AP Calculus 4.5 Worksheet 5.5 Worksheet - Linearization All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers ma receive NO credit. 1. Consider the function = sin. a) Find the equation
LECTURE 23: Momentum-Impulse
 Lectures Page 1 LECTURE 23: Momentum-Impulse Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. Introduce the concept that objects possess momentum. Introduce the concept of impulse. Be able
Lectures Page 1 LECTURE 23: Momentum-Impulse Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. Introduce the concept that objects possess momentum. Introduce the concept of impulse. Be able
1 (a) A bus travels at a constant speed. It stops for a short time and then travels at a higher constant speed.
 1 (a) A bus travels at a constant. It stops for a short time and then travels at a higher constant. Using the axes in Fig. 1.1, draw a distance-time graph for this bus journey. distance time Fig. 1.1 [3]
1 (a) A bus travels at a constant. It stops for a short time and then travels at a higher constant. Using the axes in Fig. 1.1, draw a distance-time graph for this bus journey. distance time Fig. 1.1 [3]
acceleration versus time. LO Determine a particle s change in position by graphical integration on a graph of velocity versus time.
 Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
Motion with Integrals Worksheet 4: What you need to know about Motion along the x-axis (Part 2)
 Motion with Integrals Worksheet 4: What you need to know about Motion along the x-axis (Part 2) 1. Speed is the absolute value of. 2. If the velocity and acceleration have the sign (either both positive
Motion with Integrals Worksheet 4: What you need to know about Motion along the x-axis (Part 2) 1. Speed is the absolute value of. 2. If the velocity and acceleration have the sign (either both positive
Lesson 3 Velocity Graphical Analysis
 Physics 2 Lesson 3 Velocity Graphical Analysis I. Pearson Textbook Reference Refer to pages 11 to 2. II. Position-time Graphs Position-time graphs indicate the position of an object relative to a reference
Physics 2 Lesson 3 Velocity Graphical Analysis I. Pearson Textbook Reference Refer to pages 11 to 2. II. Position-time Graphs Position-time graphs indicate the position of an object relative to a reference
STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST
 STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST Name: 1. The number of significant figures in the number 0.030 is a) b) 3 c) d) 5. The number 35.5 rounded to significant figures is a) 35.0 b) 35 c) 35.5 d) 0 3. Five different
STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST Name: 1. The number of significant figures in the number 0.030 is a) b) 3 c) d) 5. The number 35.5 rounded to significant figures is a) 35.0 b) 35 c) 35.5 d) 0 3. Five different
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs,
 Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
Distance vs. Displacement, Speed vs. Velocity, Acceleration, Free-fall, Average vs. Instantaneous quantities, Motion diagrams, Motion graphs, Kinematic formulas. A Distance Tells how far an object is from
