SM2H 1.6 HW-Average Rate of Change
|
|
|
- Emil Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Distance (meters) SMH Name: Period: Core Alignment: F.IF.4, F.IF.6, F.IF.9 SMH.6 HW-Average Rate of Change The average rate of change between two points is essentially the slope of the line that connects the two points. For example, if the function f(t) represents the distance in miles a car travels at any time t 0 (hours), then finding the slope between t = and t = 4 will give the average speed (mph) the car was y y y traveling during those three hours. Recall that slope is. In this example y is the distance x x x traveled and x is the time interval that elapses. The slope or rate of change shows the change in distance divided by the change in time which results in the average speed. Below is the graph of two runners as they run a 400 meter hurdles race. Runner A is the dashed line and Runner B is the solid line. Time Runner A s Distance Runner B s Distance Time (seconds) A. Which runner has a faster average speed for the first 9 seconds? Explain how you know. B. Which runner has a faster average speed for 9 to 0 seconds? Explain how you know. C. Which runner has a faster average speed for 0 to 3 seconds? Explain how you know. D. Which runner has a faster average speed for 9 to 3 seconds? Explain how you know. E. Which runner wins the race? Use mathematical evidence to support your answer.
2 For each of the following, draw the line that connects the two points. Write the coordinates of the two points then calculate the average rate of change on the specified interval.. f ( x) x 6x 9 on [, 6]. f ( x) x on [-3, 3] 3 3. f ( x) 3 x on [0, ] x 4. f ( x) 5 on [0, 3] 5. f ( x) x 4 on [-3, -] 6. f ( x) 3x x on [-3, 0] 7. f ( x) 3x 4 on [0, 3] 8. f ( x) 4 x 3 on [0, ] 9. f ( x) x 3 on [, 5]
3 0. Population Growth: Suppose 5 flour beetles are left undisturbed in a warehouse bin. The x beetle population doubles in size every week. The equation P( x) 5 can be used to determine the number of beetles after x weeks. Complete the table below. Week Population a. Calculate the average growth rate between weeks and 3. b. Calculate the average growth rate for the first five weeks [0, 5]. c. Which average growth rate is higher? Why do you think it is higher?. Gravity and the Moon: The gravitational constant on the moon is very different from the gravitational constant on the earth. If a rocket were launched from the moon s surface with an initial velocity of meters per second, then the equation h t 0.8t t would model the rocket s height, in meters, at any time t, in seconds. Complete the table below. Time Height a. Calculate the average velocity of the rocket for the first 3 seconds of flight. b. Calculate the average velocity of the rocket for 6 to 9 seconds of flight. c. Calculate the average velocity of the rocket for 9 to 5 seconds. d. Which interval had the greatest average rate of the change? Why do you think this interval had the greatest average rate of change?
4 Write the coordinates of the endpoints of the interval then find the average rate of change over the specified interval.. f x x ( ) on [-3, ] 3. f ( x) x 6x 4 on [-,3] x 4. f( x) 3 7 on [0, ] 5. f ( x) x 5x on [-6, - ] 6. f x x ( ) 5 on [-4, 0] 4 7. f( x) 0.5 x on [-3, 0]
5 Height (meters) 8. A rocket is launched with an initial velocity of 7 meters per second from a platform that is meter above the earth s surface. The height of the rocket was recorded at 0.5 second intervals. Scientists wondered how this launch would compare to a similar launch on the planet of Saturn. Based on the gravitational constants of each planet the scientists came up with the following models for Earth and Saturn. Time (Seconds) Earth Height (Meters) Saturn Time (seconds) a. What is the domain for Earth? What is the domain for Saturn? b. What is the range for Earth? What is the range for Saturn? c. Would the rocket reach the greatest height on Earth or Saturn? Explain. d. On which planet would the rocket reach its maximum height the fastest? e. On which planet would the rocket have the greatest average rate of change for the first three seconds? f. On which planet would the rocket have the greatest average rate of change between and 3 seconds? g. On which planet would the rocket be in the air the longest? Explain. h. On which planet would the rocket hit the ground in the shortest amount of time? Explain.
6 Review is the precalculus analyzing functions with graphs assignment.
SM2H Average Rate of Change
 Name Period Core Alignment: F.IF., F.IF., F.IF.9 SMH 5. - Average Rate of Change The average rate of change between two points is essentiall the slope of the line that connects the two points. For eample,
Name Period Core Alignment: F.IF., F.IF., F.IF.9 SMH 5. - Average Rate of Change The average rate of change between two points is essentiall the slope of the line that connects the two points. For eample,
Topics for the test and Sample Problems
 Topics for the test and Sample Problems Be able to Rearrange Every Motion Equation on the Equation Page x = v t x f = x i + vt v=a t v f = v i + at x f = x i + v i t + ½ at v f - v i = a (x f -x i ) Δx
Topics for the test and Sample Problems Be able to Rearrange Every Motion Equation on the Equation Page x = v t x f = x i + vt v=a t v f = v i + at x f = x i + v i t + ½ at v f - v i = a (x f -x i ) Δx
Physics #1 - Motion Notebook
 Name Hour Group # Test Date Physics #1 - Motion Notebook Physics #1 - LEARNING Targets Physics #1 Vocabulary: You re The Scientist #1 Getting to Know a Physicist! You will research a physicist and create
Name Hour Group # Test Date Physics #1 - Motion Notebook Physics #1 - LEARNING Targets Physics #1 Vocabulary: You re The Scientist #1 Getting to Know a Physicist! You will research a physicist and create
Kinematics 2. What equation relates the known quantities to what is being asked?
 Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: List
Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: List
Forces and Motion Study Guide
 Forces and Motion Study Guide Name 8 th Grade PSI 1. A snail travels 10 m in 3000 seconds. What is the snail s average speed? a. 60000 m/s b. 0.02 m/s c. 600 m/s d. 0.003 m/s 2. A blimp travels at 3 m/s
Forces and Motion Study Guide Name 8 th Grade PSI 1. A snail travels 10 m in 3000 seconds. What is the snail s average speed? a. 60000 m/s b. 0.02 m/s c. 600 m/s d. 0.003 m/s 2. A blimp travels at 3 m/s
1.5 Look Out Below! A Solidify Understanding Task
 22 1.5 Look Out Below A Solidify Understanding Task What happens when you drop a ball? It falls to the ground. That question sounds as silly as Why did the chicken cross the road? (To get to the other
22 1.5 Look Out Below A Solidify Understanding Task What happens when you drop a ball? It falls to the ground. That question sounds as silly as Why did the chicken cross the road? (To get to the other
1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False Answer: B Var: 1
 University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
IB Math SL Year 2 Name Date Lesson 10-4: Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Revisited
 Name Date Lesson 10-4: Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Revisited Learning Goals: How do you apply integrals to real-world scenarios? Recall: Linear Motion When an object is moving, a ball in the air
Name Date Lesson 10-4: Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration Revisited Learning Goals: How do you apply integrals to real-world scenarios? Recall: Linear Motion When an object is moving, a ball in the air
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
P2a Acceleration and Motion Graphs Foundation
 P2a Acceleration and Motion Graphs Foundation 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 12 Q1. (a) The diagram shows two forces acting on an object. What is the resultant force acting on the object? Tick ( ) one box.
P2a Acceleration and Motion Graphs Foundation 46 minutes 46 marks Page 1 of 12 Q1. (a) The diagram shows two forces acting on an object. What is the resultant force acting on the object? Tick ( ) one box.
Mass and Weight. Aren t they the same? 19/05/2016. cgrahamphysics.com 2016
 Mass and Weight Aren t they the same? Starter One of Four Which of these are the units of speed? meters 0 C miles m/s Which of these are the units of speed? meters 0 C miles m/s Which of these has the
Mass and Weight Aren t they the same? Starter One of Four Which of these are the units of speed? meters 0 C miles m/s Which of these are the units of speed? meters 0 C miles m/s Which of these has the
AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics 1982B1. The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining
AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics 1982B1. The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining
Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers
 Position (m) Mass (g) Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers A physics student was interested in finding the mass of a penny. To do so she grabbed a bunch of pennies and placed them on a scale. She gathered
Position (m) Mass (g) Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers A physics student was interested in finding the mass of a penny. To do so she grabbed a bunch of pennies and placed them on a scale. She gathered
Final Exam Review Answers
 Weight (Pounds) Final Exam Review Answers Questions 1-8 are based on the following information: A student sets out to lose some weight. He made a graph of his weight loss over a ten week period. 180 Weight
Weight (Pounds) Final Exam Review Answers Questions 1-8 are based on the following information: A student sets out to lose some weight. He made a graph of his weight loss over a ten week period. 180 Weight
For a function f(x) and a number a in its domain, the derivative of f at a, denoted f (a), is: D(h) = lim
 Name: Section: Names of collaborators: Main Points: 1. Definition of derivative as limit of difference quotients 2. Interpretation of derivative as slope of graph 3. Interpretation of derivative as instantaneous
Name: Section: Names of collaborators: Main Points: 1. Definition of derivative as limit of difference quotients 2. Interpretation of derivative as slope of graph 3. Interpretation of derivative as instantaneous
The force of gravity holds us on Earth and helps objects in space stay
 96 R E A D I N G The force of gravity holds us on Earth and helps objects in space stay in orbit. The planets in the Solar System could not continue to orbit the Sun without the force of gravity. Astronauts
96 R E A D I N G The force of gravity holds us on Earth and helps objects in space stay in orbit. The planets in the Solar System could not continue to orbit the Sun without the force of gravity. Astronauts
1. is the force that opposes motion between two objects in contact.
 Name: Vocabulary: Write the correct word in each space. Word Bank: force acceleration friction velocity gravity speed net force motion 1. is the force that opposes motion between two objects in contact.
Name: Vocabulary: Write the correct word in each space. Word Bank: force acceleration friction velocity gravity speed net force motion 1. is the force that opposes motion between two objects in contact.
Vectors v Scalars. Physics 1 st Six Weeks
 Vectors v Scalars Physics 1 st Six Weeks An Appetizer to Start... Vectors vs. Scalars In Physics all quantities are in two categories: scalars & vectors. Scalar quantities are described by magnitude (i.e.
Vectors v Scalars Physics 1 st Six Weeks An Appetizer to Start... Vectors vs. Scalars In Physics all quantities are in two categories: scalars & vectors. Scalar quantities are described by magnitude (i.e.
What You Will Learn In This Chapter. Displacement Vector Distance Velocity Vectors Acceleration Vectors Motion with constant Acceleration
 Chapter 2 What You Will Learn In This Chapter Displacement Vector Distance Velocity Vectors Acceleration Vectors Motion with constant Acceleration 2.1 Introduction to kinematics Kinematics is the study
Chapter 2 What You Will Learn In This Chapter Displacement Vector Distance Velocity Vectors Acceleration Vectors Motion with constant Acceleration 2.1 Introduction to kinematics Kinematics is the study
Density. Mass Volume. Density =
 Mass Mass is a property of an object that measures how much matter is there in the object. It doesn t depend on where the object is. It doesn t have a direction. Weight Weight is due to the gravitational
Mass Mass is a property of an object that measures how much matter is there in the object. It doesn t depend on where the object is. It doesn t have a direction. Weight Weight is due to the gravitational
1 (a) A bus travels at a constant speed. It stops for a short time and then travels at a higher constant speed.
 1 (a) A bus travels at a constant. It stops for a short time and then travels at a higher constant. Using the axes in Fig. 1.1, draw a distance-time graph for this bus journey. distance time Fig. 1.1 [3]
1 (a) A bus travels at a constant. It stops for a short time and then travels at a higher constant. Using the axes in Fig. 1.1, draw a distance-time graph for this bus journey. distance time Fig. 1.1 [3]
1 Antiderivatives graphically and numerically
 Math B - Calculus by Hughes-Hallett, et al. Chapter 6 - Constructing antiderivatives Prepared by Jason Gaddis Antiderivatives graphically and numerically Definition.. The antiderivative of a function f
Math B - Calculus by Hughes-Hallett, et al. Chapter 6 - Constructing antiderivatives Prepared by Jason Gaddis Antiderivatives graphically and numerically Definition.. The antiderivative of a function f
1 y = Recitation Worksheet 1A. 1. Simplify the following: b. ( ) a. ( x ) Solve for y : 3. Plot these points in the xy plane:
 Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Simplify the following: a ( ) 7 b ( ) 3 4 9 3 5 3 c 15 3 d 3 15 Solve for y : 8 y y 5= 6 3 3 Plot these points in the y plane: A ( 0,0 ) B ( 5,0 ) C ( 0, 4) D ( 3,5) 4
Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Simplify the following: a ( ) 7 b ( ) 3 4 9 3 5 3 c 15 3 d 3 15 Solve for y : 8 y y 5= 6 3 3 Plot these points in the y plane: A ( 0,0 ) B ( 5,0 ) C ( 0, 4) D ( 3,5) 4
Practice Test 1 1. A steel cylinder is 39 mm in height and 39 mm in diameter.
 Practice Test 1 1. A steel cylinder is 39 mm in height and 39 mm in diameter. (a) How much does it weigh? (density of steel: ρ = 7560 kg/m3) 2. An automobile moving along a straight track changes its velocity
Practice Test 1 1. A steel cylinder is 39 mm in height and 39 mm in diameter. (a) How much does it weigh? (density of steel: ρ = 7560 kg/m3) 2. An automobile moving along a straight track changes its velocity
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0.
 Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Goal: Describe Motion Kinematics 'How' Dynamics 'Why' (Forces): Chapter 4. Position, Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration
 Chapter 2 - Kinematics Goal: Describe Motion Kinematics 'How' Dynamics 'Why' (Forces): Chapter 4 Position, Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration All vector quantities 3-d Displacement: a vector that points
Chapter 2 - Kinematics Goal: Describe Motion Kinematics 'How' Dynamics 'Why' (Forces): Chapter 4 Position, Displacement, Velocity, Acceleration All vector quantities 3-d Displacement: a vector that points
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016
 Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around us.
Name: Earth 110 Exploration of the Solar System Assignment 1: Celestial Motions and Forces Due on Tuesday, Jan. 19, 2016 Why are celestial motions and forces important? They explain the world around us.
AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D
 AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D 1 Algebra Based Physics Kinematics in One Dimension 2015 08 25 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents: Kinematics Motion in One Dimension Position and Reference Frame Displacement
AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D 1 Algebra Based Physics Kinematics in One Dimension 2015 08 25 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents: Kinematics Motion in One Dimension Position and Reference Frame Displacement
Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers
 Position (m) Mass (g) Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers A physics student was interested in finding the mass of a penny. To do so she grabbed a bunch of pennies and placed them on a scale. She gathered
Position (m) Mass (g) Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers A physics student was interested in finding the mass of a penny. To do so she grabbed a bunch of pennies and placed them on a scale. She gathered
5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down?
 5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? Answer: 9.8 m/s 2 downward 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down? Answer: 9.8 m/ s 2 downward
5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? Answer: 9.8 m/s 2 downward 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down? Answer: 9.8 m/ s 2 downward
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction
 What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
Chapter 2. Forces & Newton s Laws
 Chapter 2 Forces & Newton s Laws 1st thing you need to know Everything from chapter 1 Speed formula Acceleration formula All their units There is only 1 main formula, but some equations will utilize previous
Chapter 2 Forces & Newton s Laws 1st thing you need to know Everything from chapter 1 Speed formula Acceleration formula All their units There is only 1 main formula, but some equations will utilize previous
Describing Mo tion. Speed and Velocity. What is speed?
 CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
College Physics: A Strategic Approach, 3e (Knight) Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension. 2.1 Conceptual Questions
 College Physics: A Strategic Approach, 3e (Knight) Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) Consider a deer that runs from point A to point B. The distance the deer runs can be greater
College Physics: A Strategic Approach, 3e (Knight) Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) Consider a deer that runs from point A to point B. The distance the deer runs can be greater
Physics Essentials Homework Packet
 Name Date Hour Physics Essentials Homework Packet Unit 3: Motion 1 P age Speed Practice Problems Answer the questions below using the formulas for speed and velocity as discussed in class. Be sure to show
Name Date Hour Physics Essentials Homework Packet Unit 3: Motion 1 P age Speed Practice Problems Answer the questions below using the formulas for speed and velocity as discussed in class. Be sure to show
a. Determine the sprinter's constant acceleration during the first 2 seconds.
 AP Physics 1 FR Practice Kinematics 1d 1 The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90
AP Physics 1 FR Practice Kinematics 1d 1 The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
Worksheet 3. Sketch velocity vs time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object.
 Worksheet 3 Sketch velocity vs time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. 1. The object is moving away from the origin at a constant (steady) speed. 2. The object
Worksheet 3 Sketch velocity vs time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. 1. The object is moving away from the origin at a constant (steady) speed. 2. The object
1.6 The Tortoise and the Hare A Solidify Understanding Task
 29 1.6 The Tortoise and the Hare A Solidify Understanding Task In the children s story of the tortoise and the hare, the hare mocks the tortoise for being slow. The tortoise replies, Slow and steady wins
29 1.6 The Tortoise and the Hare A Solidify Understanding Task In the children s story of the tortoise and the hare, the hare mocks the tortoise for being slow. The tortoise replies, Slow and steady wins
A scalar quantity has just magnitude A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction
 Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
RATES AND UNIT RATES
 RATES AND UNIT RATES 7.. 7.. Rate of change is a ratio that describes how one quantity is changing with respect to another. Unit rate is a rate that compares the change in one quantity to a one-unit change
RATES AND UNIT RATES 7.. 7.. Rate of change is a ratio that describes how one quantity is changing with respect to another. Unit rate is a rate that compares the change in one quantity to a one-unit change
One Dimensional Motion. Motion in x or y only
 One Dimensional Motion Motion in x or y only Scalar vs. Vector Scalar Defined as quantity with magnitude (size) only Example: 3 m, 62 seconds, 4.2 miles EASY Math!!! Vector Defined as quantity with magnitude
One Dimensional Motion Motion in x or y only Scalar vs. Vector Scalar Defined as quantity with magnitude (size) only Example: 3 m, 62 seconds, 4.2 miles EASY Math!!! Vector Defined as quantity with magnitude
Centripetal Force Review. 1. The graph given shows the weight of three objects on planet X as a function of their mass.
 Name: ate: 1. The graph given shows the weight of three objects on planet X as a function of their mass. 3. If the circular track were to suddenly become frictionless at the instant shown in the diagram,
Name: ate: 1. The graph given shows the weight of three objects on planet X as a function of their mass. 3. If the circular track were to suddenly become frictionless at the instant shown in the diagram,
A car travels at a constant speed of 110 Km/hour between Montreal and Toronto. Determine the independent variable for this functional situation.
 Question 1 A car travels at a constant speed of 110 Km/hour between Montreal and Toronto. Determine the independent variable for this functional situation. Answer: Question 2 A function is described by
Question 1 A car travels at a constant speed of 110 Km/hour between Montreal and Toronto. Determine the independent variable for this functional situation. Answer: Question 2 A function is described by
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
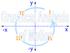 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Gravitation
 NAME: Gravitation 1. The gravitational force of attraction between the Sun and an asteroid travelling in an orbit of radius 4.14x10 11 m is 4.62 x 10 17 N. What is the mass of the asteroid? 2. A certain
NAME: Gravitation 1. The gravitational force of attraction between the Sun and an asteroid travelling in an orbit of radius 4.14x10 11 m is 4.62 x 10 17 N. What is the mass of the asteroid? 2. A certain
4.6: Mean Value Theorem
 4.6: Mean Value Theorem Problem 1 Given the four functions on the interval [1, 5], answer the questions below. (a) List the function that satisfies (or functions that satisfy) the conditions of the Mean
4.6: Mean Value Theorem Problem 1 Given the four functions on the interval [1, 5], answer the questions below. (a) List the function that satisfies (or functions that satisfy) the conditions of the Mean
Chapter 2 Describing Motion
 Chapter 2 Describing Motion Chapter 2 Overview In chapter 2, we will try to accomplish two primary goals. 1. Understand and describe the motion of objects. Define concepts like speed, velocity, acceleration,
Chapter 2 Describing Motion Chapter 2 Overview In chapter 2, we will try to accomplish two primary goals. 1. Understand and describe the motion of objects. Define concepts like speed, velocity, acceleration,
1. Find the area bounded by the curve and the x axis between 5 and Find the area bounded by and the x axis between 3 and 3.
 AP Calculus November 15, 2017 1. Find the area bounded by the curve and the x axis between 5 and 0. 2. Find the area bounded by and the x axis between 3 and 3. 3. Find the area bounded by the curve graphed
AP Calculus November 15, 2017 1. Find the area bounded by the curve and the x axis between 5 and 0. 2. Find the area bounded by and the x axis between 3 and 3. 3. Find the area bounded by the curve graphed
1. Complete the following table: Term Definition Unit Examples Speed Velocity Scalar Vector Displacement Distance
 Motion Review Name: Answer ALL questions on separate paper. Draw diagrams to help you visualize each scenario. Show all steps, as we have in class, to solve math questions. 1. Complete the following table:
Motion Review Name: Answer ALL questions on separate paper. Draw diagrams to help you visualize each scenario. Show all steps, as we have in class, to solve math questions. 1. Complete the following table:
CHAPTER 2: Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension
 CHAPTER : Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A car speedometer measures only speed. It does not give any information about the direction, and so does not measure velocity..
CHAPTER : Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A car speedometer measures only speed. It does not give any information about the direction, and so does not measure velocity..
Algebra 2 Honors. Unit 4, Day 1 Period: Date: Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form. (Three more problems on the back )
 Algebra Honors Name: Unit 4, Day 1 Period: Date: Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form 1. y = 3x. y = 5x + 1 3. y = x 5 4. y = 1 5 x 6. y = x + x + 1 7. f(x) = 6x 4x 5 (Three more problems on the
Algebra Honors Name: Unit 4, Day 1 Period: Date: Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form 1. y = 3x. y = 5x + 1 3. y = x 5 4. y = 1 5 x 6. y = x + x + 1 7. f(x) = 6x 4x 5 (Three more problems on the
KINEMATICS WHERE ARE YOU? HOW FAST? VELOCITY OR SPEED WHEN YOU MOVE. Typical Cartesian Coordinate System. usually only the X and Y axis.
 KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Web Resources for Physics 1 Physics Classroom http://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/physics/ Quantities in Motion Any motion involves three
Chapter 2 Motion in One Dimension Web Resources for Physics 1 Physics Classroom http://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/physics/ Quantities in Motion Any motion involves three
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #39 ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #39 ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS INTRODUCTION Our sun is not exactly in the center of the orbits of the planets, and therefore the planetary orbits are not circular.
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: LAB PARTNERS: LAB #39 ECCENTRICITY OF PLANETARY ORBITS INTRODUCTION Our sun is not exactly in the center of the orbits of the planets, and therefore the planetary orbits are not circular.
Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) v = 0 a = 0
 Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) Object at rest (not moving) Position is constant v (m/s) a (m/s 2 ) v = 0 a = 0 Constant velocity Position increases at constant
Summary of motion graphs Object is moving to the right (in positive direction) Object at rest (not moving) Position is constant v (m/s) a (m/s 2 ) v = 0 a = 0 Constant velocity Position increases at constant
(L-4) Free fall, review
 (L-4) Free fall, review If we neglect air resistance, all objects, regardless of their mass, fall to earth with the same acceleration g 10 m/s 2 This means that if they start at the same height, they will
(L-4) Free fall, review If we neglect air resistance, all objects, regardless of their mass, fall to earth with the same acceleration g 10 m/s 2 This means that if they start at the same height, they will
Kinematics 2. Kinematics Equations. How to solve a Physics problem:
 Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: What is the question asking for? List the given quantities with units Equation Substitution with units Solution with units Does the answer
Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: What is the question asking for? List the given quantities with units Equation Substitution with units Solution with units Does the answer
As you already know by now, when you're finding derivatives, you're finding the slope.
 As you already know by now, when you're finding derivatives, you're finding the slope. Slope is a "rate of change" There are many other "rates of change" out there in the Real World. For example, a doctor
As you already know by now, when you're finding derivatives, you're finding the slope. Slope is a "rate of change" There are many other "rates of change" out there in the Real World. For example, a doctor
ASTROMATH 101: BEGINNING MATHEMATICS IN ASTRONOMY
 Name Partner(s) Section Date ASTROMATH 101: BEGINNING MATHEMATICS IN ASTRONOMY Astronomers deal with very, very large distances, some incredible temperatures, and even really, really small wavelengths.
Name Partner(s) Section Date ASTROMATH 101: BEGINNING MATHEMATICS IN ASTRONOMY Astronomers deal with very, very large distances, some incredible temperatures, and even really, really small wavelengths.
5. Use the graph below to determine the displacement of the object at the end of the first seven seconds.
 Name: Hour: 1. The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the: Sem 1 Exam Review Advanced Physics 2015-2016 2. The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: 3. The graph below
Name: Hour: 1. The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the: Sem 1 Exam Review Advanced Physics 2015-2016 2. The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: 3. The graph below
AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics ANSWERS 1982B1 2
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics ANSWERS 198B1 a. For the first seconds, while acceleration is constant, d = ½ at Substituting the given values d = 10 meters, t = seconds gives a = 5 m/s b.
AP Physics Free Response Practice Kinematics ANSWERS 198B1 a. For the first seconds, while acceleration is constant, d = ½ at Substituting the given values d = 10 meters, t = seconds gives a = 5 m/s b.
Unit 5 Gravitation. Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion
 Unit 5 Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Into to Gravity Phet Simulation Today: Make sure to collect all data. Finished lab due tomorrow!! Universal Law
Unit 5 Gravitation Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Kepler s Laws of Planetary Motion Into to Gravity Phet Simulation Today: Make sure to collect all data. Finished lab due tomorrow!! Universal Law
MLK Day!!! Solving Equations with Radicals Day 1. Practice. Solving Equations with Radicals Day 2. Practice. Applications of Radicals.
 Name Algebra 2 Agenda Period Week.3 Objective Stamp Grade Monday January 8, 206 MLK Day!!! Tuesday January 9, 206 Solving Equations with Radicals Day Practice Wednesday January 20, 206 Solving Equations
Name Algebra 2 Agenda Period Week.3 Objective Stamp Grade Monday January 8, 206 MLK Day!!! Tuesday January 9, 206 Solving Equations with Radicals Day Practice Wednesday January 20, 206 Solving Equations
Gravity and Orbits. Objectives. Clarify a number of basic concepts. Gravity
 Gravity and Orbits Objectives Clarify a number of basic concepts Speed vs. velocity Acceleration, and its relation to force Momentum and angular momentum Gravity Understand its basic workings Understand
Gravity and Orbits Objectives Clarify a number of basic concepts Speed vs. velocity Acceleration, and its relation to force Momentum and angular momentum Gravity Understand its basic workings Understand
Kinematics A train accelerates from rest at a rate of 2 m/(s*s), for a time of 20 seconds. How much distance does the train cover?
 Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: 1.
Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: 1.
Announcement. Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday
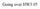 Going over HW3.05 Announcement Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday As the red ball rolls off the edge, a green ball is dropped from rest from the same height at the same
Going over HW3.05 Announcement Quiz on Friday (Graphing and Projectile Motion) No HW due Wednesday As the red ball rolls off the edge, a green ball is dropped from rest from the same height at the same
KINEMATICS. File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation. Monday, June 17, 13
 KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
KINEMATICS File:The Horse in Motion.jpg - Wikimedia Foundation 1 WHERE ARE YOU? Typical Cartesian Coordinate System usually only the X and Y axis meters File:3D coordinate system.svg - Wikimedia Foundation
Recitation Questions 1D Motion (part 2)
 Recitation Questions 1D Motion (part 2) 23 January Question 1: a braking car A car is traveling at 30 m/s and applies its brakes to slow down to 10 m/s. If it is able to decelerate at 5 m/s 2, how far
Recitation Questions 1D Motion (part 2) 23 January Question 1: a braking car A car is traveling at 30 m/s and applies its brakes to slow down to 10 m/s. If it is able to decelerate at 5 m/s 2, how far
To conduct the experiment, each person in your group should be given a role:
 Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
12.2 Acceleration. You will need a calculator today!
 12.2 Acceleration You will need a calculator today! Acceleration Acceleration A vector that changes speed or direction or both. When a object changes velocity Measured in m/s 2 Acceleration may be positive,
12.2 Acceleration You will need a calculator today! Acceleration Acceleration A vector that changes speed or direction or both. When a object changes velocity Measured in m/s 2 Acceleration may be positive,
Assignment - Kinematics. Reading: Chapter 2. Objectives/HW
 Assignment - Kinematics Reading: Chapter 2 Objectives/HW The student will be able to: HW: 1 Define and distinguish the concepts scalar and vector. Make the connection between the visual representation
Assignment - Kinematics Reading: Chapter 2 Objectives/HW The student will be able to: HW: 1 Define and distinguish the concepts scalar and vector. Make the connection between the visual representation
Topics for the test and Sample Problems
 Topics for the test and Sample Problems 1. Be able to Rearrange Every Motion Equation on the Equation Page and Be able to use GUESS to choose correct equation. See the notes from 9/13 and 9/1 x = v t x
Topics for the test and Sample Problems 1. Be able to Rearrange Every Motion Equation on the Equation Page and Be able to use GUESS to choose correct equation. See the notes from 9/13 and 9/1 x = v t x
The University of Texas at Austin. Air Resistance
 UTeach Outreach The University of Texas at Austin Air Resistance Time of Lesson: 50-60 minutes Content Standards Addressed in Lesson: 8.6A demonstrate and calculate how unbalanced forces change the speed
UTeach Outreach The University of Texas at Austin Air Resistance Time of Lesson: 50-60 minutes Content Standards Addressed in Lesson: 8.6A demonstrate and calculate how unbalanced forces change the speed
Motion, Forces, and Energy
 Motion, Forces, and Energy What is motion? Motion - when an object changes position Types of Motion There are 2 ways of describing motion: Distance Displacement Distance Distance is the total path traveled.
Motion, Forces, and Energy What is motion? Motion - when an object changes position Types of Motion There are 2 ways of describing motion: Distance Displacement Distance Distance is the total path traveled.
AP Physics I Summer Work
 AP Physics I Summer Work 2018 (20 points) Please complete the following set of questions and word problems. Answers will be reviewed in depth during the first week of class followed by an assessment based
AP Physics I Summer Work 2018 (20 points) Please complete the following set of questions and word problems. Answers will be reviewed in depth during the first week of class followed by an assessment based
Physics is about finding the simplest and least complicated explanation for things.
 WHAT IS PHYSICS Physics is about finding the simplest and least complicated explanation for things. It is about observing how things work and finding the connections between cause and effect that explain
WHAT IS PHYSICS Physics is about finding the simplest and least complicated explanation for things. It is about observing how things work and finding the connections between cause and effect that explain
CHAPTER 7 GRAVITATION
 Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 7 GRAVITATION Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 7.1 Planetary Motion & Gravitation Assignment
Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 7 GRAVITATION Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 7.1 Planetary Motion & Gravitation Assignment
PLC Papers Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Year 11 Topic Practice Paper: Solving Quadratics (Graphically) Quadratic equations (graphical methods) 1 Grade 6 Objective: Find approximate solutions to quadratic equations using
PLC Papers Created For: Year 11 Topic Practice Paper: Solving Quadratics (Graphically) Quadratic equations (graphical methods) 1 Grade 6 Objective: Find approximate solutions to quadratic equations using
Have you ever launched a model rocket? Can you describe the motion of the rocket? Where does the rocket get its energy to launch?
 Have you ever launched a model rocket? Can you describe the motion of the rocket? Where does the rocket get its energy to launch? The Energy of Motion Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. Only matter
Have you ever launched a model rocket? Can you describe the motion of the rocket? Where does the rocket get its energy to launch? The Energy of Motion Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. Only matter
Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
 Name Physics Honors Pd Date Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs Sketch velocity vs. time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an
Name Physics Honors Pd Date Unit 2 Kinematics Worksheet 1: Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs Sketch velocity vs. time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an
Each dot represents an object moving, between constant intervals of time. Describe the motion that you see. equation symbol: units: Velocity
 What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed
 2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed Part I: Using a table of values for a position function The table below represents the position of an object as a function of time. Use the table to answer
2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed Part I: Using a table of values for a position function The table below represents the position of an object as a function of time. Use the table to answer
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Chapter 2 Linear Motion
 Chapter 2 Linear Motion Conceptual Questions 2.1 An object will slow down when its acceleration vector points in the opposite direction to its velocity vector. Recall that acceleration is the change in
Chapter 2 Linear Motion Conceptual Questions 2.1 An object will slow down when its acceleration vector points in the opposite direction to its velocity vector. Recall that acceleration is the change in
Section 2: Friction, Gravity, and Elastic Forces
 Chapter 10, Section 2 Friction, Gravity, & Elastic Forces Section 2: Friction, Gravity, and Elastic Forces What factors determine the strength of the friction force between two surfaces? What factors affect
Chapter 10, Section 2 Friction, Gravity, & Elastic Forces Section 2: Friction, Gravity, and Elastic Forces What factors determine the strength of the friction force between two surfaces? What factors affect
Kinematics Multiple-Choice Questions
 Kinematics Multiple-Choice Questions 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle. Which of the following
Kinematics Multiple-Choice Questions 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle. Which of the following
Worksheet At t = 0 a car has a speed of 30 m/s. At t = 6 s, its speed is 14 m/s. What is its average acceleration during this time interval?
 Worksheet 9 1. A poorly tuned Geo Metro (really old cheap, slow, car) can accelerate from rest to a speed of 28 m/s in 20 s. a) What is the average acceleration of the car? b) What distance does it travel
Worksheet 9 1. A poorly tuned Geo Metro (really old cheap, slow, car) can accelerate from rest to a speed of 28 m/s in 20 s. a) What is the average acceleration of the car? b) What distance does it travel
(f) none of the above
 Honors Physics TEST: Kinematics in 1D 10/30/12 Part 1. Multiple Choice: Answer the following multiple choice questions by picking the selection that best answers the question. Write your answers on a separate
Honors Physics TEST: Kinematics in 1D 10/30/12 Part 1. Multiple Choice: Answer the following multiple choice questions by picking the selection that best answers the question. Write your answers on a separate
4.1 Areas and Distances. The Area Problem: GOAL: Find the area of the region S that lies under the curve y = f(x) from a to b.
 4.1 Areas and Distances The Area Problem: GOAL: Find the area of the region S that lies under the curve y = f(x) from a to b. Easier Problems: Find the area of a rectangle with length l and width w. Find
4.1 Areas and Distances The Area Problem: GOAL: Find the area of the region S that lies under the curve y = f(x) from a to b. Easier Problems: Find the area of a rectangle with length l and width w. Find
Kinetic energy. Objectives. Equations. Energy of motion 6/3/14. Kinetic energy is energy due to motion. kinetic energy kinetic en
 Objectives Investigate examples of kinetic energy. Calculate the kinetic energy, mass, or velocity of an object using the kinetic energy equation. Employ proportional reasoning to predict the effect of
Objectives Investigate examples of kinetic energy. Calculate the kinetic energy, mass, or velocity of an object using the kinetic energy equation. Employ proportional reasoning to predict the effect of
Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity
 3 Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object is to describe how far it has moved, which is distance. The SI unit
3 Motion Chapter 3, Section 1: Distance, Displacement, Speed, Velocity Distance An important part of describing the motion of an object is to describe how far it has moved, which is distance. The SI unit
Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions
 Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions 1. Neatly sketch the following dot motion diagrams: (a) A particle moving right
Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions 1. Neatly sketch the following dot motion diagrams: (a) A particle moving right
A B C D. Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment
 Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
Unit 6 (1-Dimensional Motion) Practice Assessment Choose the best answer to the following questions. Indicate the confidence in your answer by writing C (Confident), S (So-so), or G (Guessed) next to the
1. What is the distance formula? Use it to find the distance between the points (5, 19) and ( 3, 7).
 Precalculus Worksheet P. 1. What is the distance formula? Use it to find the distance between the points (5, 19) and ( 3, 7).. What is the midpoint formula? Use it to find the midpoint between the points
Precalculus Worksheet P. 1. What is the distance formula? Use it to find the distance between the points (5, 19) and ( 3, 7).. What is the midpoint formula? Use it to find the midpoint between the points
Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces
 Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
Chapter 2 Test Item File
 Chapter 2 Test Item File Chapter 2: Describing Motion: Kinetics in One Dimension 1. What must be your average speed in order to travel 350 km in 5.15 h? a) 66.0 km/h b) 67.0 km/h c) 68.0 km/h d) 69.0 km/h
Chapter 2 Test Item File Chapter 2: Describing Motion: Kinetics in One Dimension 1. What must be your average speed in order to travel 350 km in 5.15 h? a) 66.0 km/h b) 67.0 km/h c) 68.0 km/h d) 69.0 km/h
9/27/12. Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces. Motion and Position. Motion. Distance. Relative Motion
 9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
To summarize the car s velocity information, let the horizontal axis represent time, and the vertical axis represent velocity.
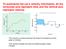 To summarize the car s velocity information, let the horizontal axis represent time, and the vertical axis represent velocity. The velocity is constant wherever the slope of the distance-vs-time graph
To summarize the car s velocity information, let the horizontal axis represent time, and the vertical axis represent velocity. The velocity is constant wherever the slope of the distance-vs-time graph
Position, Velocity, Acceleration
 191 CHAPTER 7 Position, Velocity, Acceleration When we talk of acceleration we think of how quickly the velocity is changing. For example, when a stone is dropped its acceleration (due to gravity) is approximately
191 CHAPTER 7 Position, Velocity, Acceleration When we talk of acceleration we think of how quickly the velocity is changing. For example, when a stone is dropped its acceleration (due to gravity) is approximately
