4.6: Mean Value Theorem
|
|
|
- Malcolm Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4.6: Mean Value Theorem Problem 1 Given the four functions on the interval [1, 5], answer the questions below. (a) List the function that satisfies (or functions that satisfy) the conditions of the Mean Value Theorem on [1, 5]. Solution: Only the graph (D) satisfies the conditions of the Mean Value Theorem on [1, 5]. (b) List the function (or functions) for which there exists a point c in (1, 5) such that 5 1 Solution: Only the graphs (A) and (D). (A): = 1 5 = 1 and for any c in (1, 5), (D): = 4 4 = 0 and f () = 0, since the x-axis is the tangent line to the curve y = f(x) at x =. 1
2 Problem A curve is given in the figure below, where f(x) = 8/x. (a) In the figure above, draw a secant line joining the points A = (1, f(1)) and B = (8, f(8)). (b) Find the slope, m sec, of this secant line. Solution: m sec = f(8) f(1) 8 1 = = 7 7 = 1 (c) Show that the function f satisfies the conditions of the Mean Value Theorem on the interval [1, 8] and find a point (or points) guaranteed to exist by the Mean Value Theorem. Solution: f is continuous on the interval [1, 8], f is differentiable on the interval (1, 8). By the Mean Value Theorem there exists a(t least one) point c in (1, 8) such that Now f (x) = 8/x hence f(8) f(1) c c = 8 = 1 = 1 c = ± Since c must be in (1, 8) we have that c = is the only point in (1, 8) with 1.
3 Problem Heidi drives from her house in Columbus, OH to Indianapolis, IN for vacation. Google maps says her driving distance is 170 miles. The drive takes her.5 hours. The police send her a speeding ticket in the mail, saying she must have sped to arrive so quickly. She is fighting the ticket, saying she just never stopped through the whole drive. Can you prove she broke the 65 mph speed limit at some point during her drive? Solution: Let us define s(t) to be the position function of Heidi after t hours. s(t) will be continuous and differentiable because the location of a car is continuous and differentiable. Heidi s average speed for the whole trip is mph. By the Mean Value Theorem, Heidis instantaneous speed was 68 mph at some.5 point of her trip: hence, she broke the 65 mph speed limit. Problem 4 Does the function given in the graph below satisfy the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem in the interval [ 1, 6]? If so, estimate the values of all numbers c that satisfy the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem. Solution: The function is continuous on [ 1, 6] and differentiable on ( 1, 6): hence it satisfies the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem. Problem 5 Verify that the given function satisfies the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem in the given interval. Then algebraically find all numbers c that satisfy the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem. Using
4 the graph provided, label the point(s) c and sketch the secant line and the tangent line at c. f(x) = x x + on [1, 4] Solution: The function f(x) = x is continuous on [1, 4] and differentiable on (1, 4) since it is a rational x + function, and is therefore continuous and differentiable on its domain. Therefore, f satisfies the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem. We have that f (x) = (x + )(1) x(1) (x + ) = (x + ) f(4) f(1) 4 1 = 1 So we are looking to find all points c (1, 4) which satisfy that 1. So we solve: 9 (c + ) = 1 9 (c + ) = 18 = 1 9 c = 18 = Note that we omitted 18 above because it is not in the interval (1, 4). Therefore, c =. Problem 6 Let f(x) = (x ). Show that there is no value c in (1, 4) such that f(4) f(1) = f (c)(4 1). Why does this not contradict the Mean Value Theorem? 4
5 Solution: First notice that and so we are looking for a value c such that f(4) f(1) = 1 ( ) = = 4 4 = 1 4 Then since f (x) =, we can compute: (x ) (c ) := 1 4 (c ) = 8 c = = 1 But 1 is not in the interval (1, 4). This does not contradict the Mean Value Theorem since f is not continuous at x =. Problem 7 Two runners start a race at the same time and finish in a tie. Prove that at some time during the race they have the same speed. (Hint: Consider the function h(t) = f(t) g(t), where f(t) and g(t) are the position of the first and second runner at time t, respectively.) Solution: Let f(t) be the position of the first runner at time t, and let g(t) be the position of the second runner at time t. Let T denote the time that the two runners finish the race (which is the same, since they finish in a tie). Also, let h(t) = f(t) g(t). Since h(0) = 0 and h(t ) = 0, by Rolle s Theorem there exists some c with 0 < c < T such that h (c) = 0. But since h (t) = f (t) g (t), we have that g (c). Therefore, the runners have the same speed at time c. 5
=. Consider the following properties
 Name Date Period Worksheet 3.2 Rolle s Theorem and the MVT Show all work. No calculator unless otherwise stated. Multiple Choice 1. Determine if the function f ( x) = x 6 x satisfies the hypothesis of
Name Date Period Worksheet 3.2 Rolle s Theorem and the MVT Show all work. No calculator unless otherwise stated. Multiple Choice 1. Determine if the function f ( x) = x 6 x satisfies the hypothesis of
[ 0,6 ], and if it does, find all numbers c satisfying the conclusion of that theorem.
![[ 0,6 ], and if it does, find all numbers c satisfying the conclusion of that theorem. [ 0,6 ], and if it does, find all numbers c satisfying the conclusion of that theorem.](/thumbs/84/91195235.jpg) Rolle s Theorem and the MVT 1. Determine if the function f ( x) = x 6 x satisfies the hypothesis of Rolle s Theorem on the interval [ 0,6 ], and if it does, find all numbers c satisfying the conclusion
Rolle s Theorem and the MVT 1. Determine if the function f ( x) = x 6 x satisfies the hypothesis of Rolle s Theorem on the interval [ 0,6 ], and if it does, find all numbers c satisfying the conclusion
Limits, Rates of Change, and Tangent Lines
 Limits, Rates of Change, and Tangent Lines jensenrj July 2, 2018 Contents 1 What is Calculus? 1 2 Velocity 2 2.1 Average Velocity......................... 3 2.2 Instantaneous Velocity......................
Limits, Rates of Change, and Tangent Lines jensenrj July 2, 2018 Contents 1 What is Calculus? 1 2 Velocity 2 2.1 Average Velocity......................... 3 2.2 Instantaneous Velocity......................
The Mean Value Theorem Rolle s Theorem
 The Mean Value Theorem In this section, we will look at two more theorems that tell us about the way that derivatives affect the shapes of graphs: Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. Rolle s Theorem
The Mean Value Theorem In this section, we will look at two more theorems that tell us about the way that derivatives affect the shapes of graphs: Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. Rolle s Theorem
12 Rates of Change Average Rates of Change. Concepts: Average Rates of Change
 12 Rates of Change Concepts: Average Rates of Change Calculating the Average Rate of Change of a Function on an Interval Secant Lines Difference Quotients Approximating Instantaneous Rates of Change (Section
12 Rates of Change Concepts: Average Rates of Change Calculating the Average Rate of Change of a Function on an Interval Secant Lines Difference Quotients Approximating Instantaneous Rates of Change (Section
1 y = Recitation Worksheet 1A. 1. Simplify the following: b. ( ) a. ( x ) Solve for y : 3. Plot these points in the xy plane:
 Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Simplify the following: a ( ) 7 b ( ) 3 4 9 3 5 3 c 15 3 d 3 15 Solve for y : 8 y y 5= 6 3 3 Plot these points in the y plane: A ( 0,0 ) B ( 5,0 ) C ( 0, 4) D ( 3,5) 4
Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Simplify the following: a ( ) 7 b ( ) 3 4 9 3 5 3 c 15 3 d 3 15 Solve for y : 8 y y 5= 6 3 3 Plot these points in the y plane: A ( 0,0 ) B ( 5,0 ) C ( 0, 4) D ( 3,5) 4
2.4 Rates of Change and Tangent Lines Pages 87-93
 2.4 Rates of Change and Tangent Lines Pages 87-93 Average rate of change the amount of change divided by the time it takes. EXAMPLE 1 Finding Average Rate of Change Page 87 Find the average rate of change
2.4 Rates of Change and Tangent Lines Pages 87-93 Average rate of change the amount of change divided by the time it takes. EXAMPLE 1 Finding Average Rate of Change Page 87 Find the average rate of change
Derivatives and Shapes of Curves
 MATH 1170 Section 43 Worksheet NAME Derivatives and Shapes of Curves In Section 42 we discussed how to find the extreme values of a function using the derivative These results say, In Chapter 2, we discussed
MATH 1170 Section 43 Worksheet NAME Derivatives and Shapes of Curves In Section 42 we discussed how to find the extreme values of a function using the derivative These results say, In Chapter 2, we discussed
INTERMEDIATE VALUE THEOREM
 THE BIG 7 S INTERMEDIATE VALUE If f is a continuous function on a closed interval [a, b], and if k is any number between f(a) and f(b), where f(a) f(b), then there exists a number c in (a, b) such that
THE BIG 7 S INTERMEDIATE VALUE If f is a continuous function on a closed interval [a, b], and if k is any number between f(a) and f(b), where f(a) f(b), then there exists a number c in (a, b) such that
Quarter 1 Calculus Test. The attached problems do not comprise a comprehensive test review. Test topics
 Quarter 1 Calculus Test The attached problems do not comprise a comprehensive test review. As review, use: this packet your 3 quizzes and first test your 3 quiz review packets and first test review packet
Quarter 1 Calculus Test The attached problems do not comprise a comprehensive test review. As review, use: this packet your 3 quizzes and first test your 3 quiz review packets and first test review packet
Math 1A UCB, Fall 2010 A. Ogus Solutions 1 for Problem Set 4
 Math 1A UCB, Fall 010 A. Ogus Solutions 1 for Problem Set 4.5 #. Explain, using Theorems 4, 5, 7, and 9, why the function 3 x(1 + x 3 ) is continuous at every member of its domain. State its domain. By
Math 1A UCB, Fall 010 A. Ogus Solutions 1 for Problem Set 4.5 #. Explain, using Theorems 4, 5, 7, and 9, why the function 3 x(1 + x 3 ) is continuous at every member of its domain. State its domain. By
AP Calculus AB Class Starter October 30, Given find. 2. Find for. 3. Evaluate at the point (1,2) for
 October 30, 2017 1. Given find 2. Find for 3. Evaluate at the point (1,2) for 4. Find all points on the circle x 2 + y 2 = 169 where the slope is 5/12. Oct 31 6:58 AM 1 October 31, 2017 Find the critical
October 30, 2017 1. Given find 2. Find for 3. Evaluate at the point (1,2) for 4. Find all points on the circle x 2 + y 2 = 169 where the slope is 5/12. Oct 31 6:58 AM 1 October 31, 2017 Find the critical
Full file at
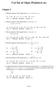 . Find the equation of the tangent line to y 6 at. y 9 y y 9 y Ans: A Difficulty: Moderate Section:.. Find an equation of the tangent line to y = f() at =. f y = 6 + 8 y = y = 6 + 8 y = + Ans: D Difficulty:
. Find the equation of the tangent line to y 6 at. y 9 y y 9 y Ans: A Difficulty: Moderate Section:.. Find an equation of the tangent line to y = f() at =. f y = 6 + 8 y = y = 6 + 8 y = + Ans: D Difficulty:
2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed
 2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed Part I: Using a table of values for a position function The table below represents the position of an object as a function of time. Use the table to answer
2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed Part I: Using a table of values for a position function The table below represents the position of an object as a function of time. Use the table to answer
MIDTERM 2 REVIEW: ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS. 1 2 x + 1. y = + 1 = x 1/ = 1. y = 1 2 x 3/2 = 1. into this equation would have then given. y 1.
 MIDTERM 2 REVIEW: ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS ) If x + y =, find y. IMPLICIT DIFFERENTIATION Solution. Taking the derivative (with respect to x) of both sides of the given equation, we find that 2 x + 2 y y =
MIDTERM 2 REVIEW: ADDITIONAL PROBLEMS ) If x + y =, find y. IMPLICIT DIFFERENTIATION Solution. Taking the derivative (with respect to x) of both sides of the given equation, we find that 2 x + 2 y y =
For a function f(x) and a number a in its domain, the derivative of f at a, denoted f (a), is: D(h) = lim
 Name: Section: Names of collaborators: Main Points: 1. Definition of derivative as limit of difference quotients 2. Interpretation of derivative as slope of graph 3. Interpretation of derivative as instantaneous
Name: Section: Names of collaborators: Main Points: 1. Definition of derivative as limit of difference quotients 2. Interpretation of derivative as slope of graph 3. Interpretation of derivative as instantaneous
CHAPTER 2. Motion Notes
 CHAPTER 2 Motion Notes DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT Distance and displacement are two quantities which may seem to mean the same thing, yet have distinctly different definitions and meanings. DISTANCE Distance
CHAPTER 2 Motion Notes DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT Distance and displacement are two quantities which may seem to mean the same thing, yet have distinctly different definitions and meanings. DISTANCE Distance
AB.Q103.NOTES: Chapter 2.4, 3.1, 3.2 LESSON 1. Discovering the derivative at x = a: Slopes of secants and tangents to a curve
 AB.Q103.NOTES: Chapter 2.4, 3.1, 3.2 LESSON 1 Discovering the derivative at x = a: Slopes of secants and tangents to a curve 1 1. Instantaneous rate of change versus average rate of change Equation of
AB.Q103.NOTES: Chapter 2.4, 3.1, 3.2 LESSON 1 Discovering the derivative at x = a: Slopes of secants and tangents to a curve 1 1. Instantaneous rate of change versus average rate of change Equation of
Slopes and Rates of Change
 Slopes and Rates of Change If a particle is moving in a straight line at a constant velocity, then the graph of the function of distance versus time is as follows s s = f(t) t s s t t = average velocity
Slopes and Rates of Change If a particle is moving in a straight line at a constant velocity, then the graph of the function of distance versus time is as follows s s = f(t) t s s t t = average velocity
Acceleration. 3. Changing Direction occurs when the velocity and acceleration are neither parallel nor anti-parallel
 Acceleration When the velocity of an object changes, we say that the object is accelerating. This acceleration can take one of three forms: 1. Speeding Up occurs when the object s velocity and acceleration
Acceleration When the velocity of an object changes, we say that the object is accelerating. This acceleration can take one of three forms: 1. Speeding Up occurs when the object s velocity and acceleration
2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed. Time (sec) Position (m)
 2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed Part I: Using a table of values for a position function The table below represents the position of an object as a function of time. Use the table to answer
2.1 How Do We Measure Speed? Student Notes HH6ed Part I: Using a table of values for a position function The table below represents the position of an object as a function of time. Use the table to answer
Section 3.7. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem
 Section.7 Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem The two theorems which are at the heart of this section draw connections between the instantaneous rate of change and the average rate of change of
Section.7 Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem The two theorems which are at the heart of this section draw connections between the instantaneous rate of change and the average rate of change of
The Mean Value Theorem and its Applications
 The Mean Value Theorem and its Applications Professor Richard Blecksmith richard@math.niu.edu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences Northern Illinois University http://math.niu.edu/ richard/math229 1. Extreme
The Mean Value Theorem and its Applications Professor Richard Blecksmith richard@math.niu.edu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences Northern Illinois University http://math.niu.edu/ richard/math229 1. Extreme
Final Review Topics, Terms, Labs, and Relationships Definitions Independent Variable:
 Final Review Topics, Terms, Labs, and Relationships Definitions Independent Variable: Dependent Variable: Controlled Variable: Sample Data Table: Sample Graph: Graph shapes and Variable Relationships (written
Final Review Topics, Terms, Labs, and Relationships Definitions Independent Variable: Dependent Variable: Controlled Variable: Sample Data Table: Sample Graph: Graph shapes and Variable Relationships (written
Math 1241, Spring 2014 Section 3.3. Rates of Change Average vs. Instantaneous Rates
 Math 1241, Spring 2014 Section 3.3 Rates of Change Average vs. Instantaneous Rates Average Speed The concept of speed (distance traveled divided by time traveled) is a familiar instance of a rate of change.
Math 1241, Spring 2014 Section 3.3 Rates of Change Average vs. Instantaneous Rates Average Speed The concept of speed (distance traveled divided by time traveled) is a familiar instance of a rate of change.
average rate of change
 average rate of change Module 2 : Investigation 5 MAT 170 Precalculus August 31, 2016 question 1 A car is driving away from a crosswalk. The distance d (in feet) of the car from the crosswalk t seconds
average rate of change Module 2 : Investigation 5 MAT 170 Precalculus August 31, 2016 question 1 A car is driving away from a crosswalk. The distance d (in feet) of the car from the crosswalk t seconds
Today Applications of MVT Find where functions are increasing/decreasing Derivative tests for extrema
 Today Applications of MVT Find where functions are increasing/decreasing Derivative tests for extrema Mean Value Theorem (proved by Cauchy in 1823) If f is continuous on [a, b] f(b) differentiable on (a,
Today Applications of MVT Find where functions are increasing/decreasing Derivative tests for extrema Mean Value Theorem (proved by Cauchy in 1823) If f is continuous on [a, b] f(b) differentiable on (a,
Section 1.6 Inverse Functions
 0 Chapter 1 Section 1.6 Inverse Functions A fashion designer is travelling to Milan for a fashion show. He asks his assistant, Betty, what 7 degrees Fahrenheit is in Celsius, and after a quick search on
0 Chapter 1 Section 1.6 Inverse Functions A fashion designer is travelling to Milan for a fashion show. He asks his assistant, Betty, what 7 degrees Fahrenheit is in Celsius, and after a quick search on
( ) for t 0. Rectilinear motion CW. ( ) = t sin t ( Calculator)
 Rectilinear motion CW 1997 ( Calculator) 1) A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity at any time t is given by v(t) = 3t 2 2t 1. The position x(t) is 5 for t = 2. a) Write a polynomial expression
Rectilinear motion CW 1997 ( Calculator) 1) A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity at any time t is given by v(t) = 3t 2 2t 1. The position x(t) is 5 for t = 2. a) Write a polynomial expression
Fall 2008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and 2 Please write your CID Colton
 Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Fall 008 RED Barcode Here Physics 105, sections 1 and Exam 1 Please write your CID Colton -3669 3 hour time limit. One 3 5 handwritten note card permitted (both sides). Calculators permitted. No books.
Test # 1 Review Math MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Test # 1 Review Math 13 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the slope of the curve at the given point P and an equation of the
Test # 1 Review Math 13 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the slope of the curve at the given point P and an equation of the
0,0 B 5,0 C 0, 4 3,5. y x. Recitation Worksheet 1A. 1. Plot these points in the xy plane: A
 Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Plot these points in the y plane: A 0,0 B 5,0 C 0, 4 D 3,5 Without using a calculator, sketch a graph o each o these in the y plane: A y B 3 Consider the unction a Evaluate
Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Plot these points in the y plane: A 0,0 B 5,0 C 0, 4 D 3,5 Without using a calculator, sketch a graph o each o these in the y plane: A y B 3 Consider the unction a Evaluate
A secant line is a line drawn through two points on a curve. The Mean Value Theorem relates the slope of a secant line to the slope of a tangent line.
 The Mean Value Theorem 10-1-005 A secant line is a line drawn through two points on a curve. The Mean Value Theorem relates the slope of a secant line to the slope of a tangent line. The Mean Value Theorem.
The Mean Value Theorem 10-1-005 A secant line is a line drawn through two points on a curve. The Mean Value Theorem relates the slope of a secant line to the slope of a tangent line. The Mean Value Theorem.
VIDEO LINKS: a) b)
 CALCULUS 30: OUTCOME 4A DAY 1 SLOPE AND RATE OF CHANGE To review the concepts of slope and rate of change. VIDEO LINKS: a) https://goo.gl/r9fhx3 b) SLOPE OF A LINE: Is a measure of the steepness of a line
CALCULUS 30: OUTCOME 4A DAY 1 SLOPE AND RATE OF CHANGE To review the concepts of slope and rate of change. VIDEO LINKS: a) https://goo.gl/r9fhx3 b) SLOPE OF A LINE: Is a measure of the steepness of a line
Study 3.4, p motion, population; # , 165 a, b,c. 3.4 Derivative as a Rate of Change. Derivative as a Rate of Change.
 GOALS: 1. Recognize the derivative as a rate of change of one variable with respect to another. change of position with respect to time: v(t) = s '(t) 3. Recognize acceleration as the instantaneous rate
GOALS: 1. Recognize the derivative as a rate of change of one variable with respect to another. change of position with respect to time: v(t) = s '(t) 3. Recognize acceleration as the instantaneous rate
Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs. Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute
 Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute 1 Grade 11 Physics Graphing Properties Property d-t Graph v-t Graph a-t Graph Not Moving Does Not Apply Constant Velocity Change
Physics 30S Unit 2 Motion Graphs Mrs. Kornelsen Teulon Collegiate Institute 1 Grade 11 Physics Graphing Properties Property d-t Graph v-t Graph a-t Graph Not Moving Does Not Apply Constant Velocity Change
Lesson 22: Solving Equations Using Algebra
 Student Outcomes Students use algebra to solve equations (of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers); using techniques of making zero (adding the additive
Student Outcomes Students use algebra to solve equations (of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers); using techniques of making zero (adding the additive
2/18/2019. Position-versus-Time Graphs. Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school.
 Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
I still have no voice, so Wendy (another calculus teacher) will be lecturing today. Yes, she always dresses up this extravagantly for Halloween.
 I still have no voice, so Wendy (another calculus teacher) will be lecturing today. Yes, she always dresses up this extravagantly for Halloween. I will be grading your tests over the weekend and I will
I still have no voice, so Wendy (another calculus teacher) will be lecturing today. Yes, she always dresses up this extravagantly for Halloween. I will be grading your tests over the weekend and I will
5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down?
 5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? Answer: 9.8 m/s 2 downward 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down? Answer: 9.8 m/ s 2 downward
5) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way up? Answer: 9.8 m/s 2 downward 6) A stone is thrown straight up. What is its acceleration on the way down? Answer: 9.8 m/ s 2 downward
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Average rates of change May be used to estimate the derivative at a point
 Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
Study Guide and Intervention. The Quadratic Formula and the Discriminant. Quadratic Formula. Replace a with 1, b with -5, and c with -14.
 4-6 Study Guide and Intervention Quadratic Formula The Quadratic Formula can be used to solve any quadratic equation once it is written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0. Quadratic Formula The solutions of
4-6 Study Guide and Intervention Quadratic Formula The Quadratic Formula can be used to solve any quadratic equation once it is written in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0. Quadratic Formula The solutions of
Name Date Class Unit 4 Test 1 Review: Linear Functions
 Name Date Class Unit 4 Test 1 Review: Linear Functions Select the best answer. 1. Does this graph represent a linear function? Explain your answer in the space provided. 2. A jogger runs 4 mi/h. The function
Name Date Class Unit 4 Test 1 Review: Linear Functions Select the best answer. 1. Does this graph represent a linear function? Explain your answer in the space provided. 2. A jogger runs 4 mi/h. The function
Integrated Math 3 Module 8 Honors Limits & Introduction to Derivatives Ready, Set Go Homework Solutions
 1 Integrated Math 3 Module 8 Honors Limits & Introduction to Derivatives Ready, Set Go Homework Solutions Adapted from The Mathematics Vision Project: Scott Hendrickson, Joleigh Honey, Barbara Kuehl, Travis
1 Integrated Math 3 Module 8 Honors Limits & Introduction to Derivatives Ready, Set Go Homework Solutions Adapted from The Mathematics Vision Project: Scott Hendrickson, Joleigh Honey, Barbara Kuehl, Travis
Density. Mass Volume. Density =
 Mass Mass is a property of an object that measures how much matter is there in the object. It doesn t depend on where the object is. It doesn t have a direction. Weight Weight is due to the gravitational
Mass Mass is a property of an object that measures how much matter is there in the object. It doesn t depend on where the object is. It doesn t have a direction. Weight Weight is due to the gravitational
Section 11.3 Rates of Change:
 Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Interpreting Function Graphs
 Interpreting Function Graphs Algebra Understanding and interpreting graphs can be difficult. Uderstanding the relationship between the and y-ais is very important. Eample: The following graph shows the
Interpreting Function Graphs Algebra Understanding and interpreting graphs can be difficult. Uderstanding the relationship between the and y-ais is very important. Eample: The following graph shows the
Position-versus-Time Graphs
 Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Position-versus-Time Graphs Below is a motion diagram, made at 1 frame per minute, of a student walking to school. A motion diagram is one way to represent the student s motion. Another way is to make
Introduction to Kinematics. Motion, Forces and Energy
 Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
Introduction to Kinematics Motion, Forces and Energy Mechanics: The study of motion Kinematics The description of how things move 1-D and 2-D motion Dynamics The study of the forces that cause motion Newton
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 7 FUNCTIONS ANSWERS FOR EXERCISES
 MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 7 FUNCTIONS FOR EXERCISES LESSON 2: WHAT A GRAPH CAN TELL YOU 1. A Increasing and nonlinear 2. D 4 to 3. a. x (input) 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 (output) 1 4 1 3 1 2 1 Not defined 1 1 2 1 3 1 4
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 7 FUNCTIONS FOR EXERCISES LESSON 2: WHAT A GRAPH CAN TELL YOU 1. A Increasing and nonlinear 2. D 4 to 3. a. x (input) 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 (output) 1 4 1 3 1 2 1 Not defined 1 1 2 1 3 1 4
Lecture 7 3.5: Derivatives - Graphically and Numerically MTH 124
 Procedural Skills Learning Objectives 1. Given a function and a point, sketch the corresponding tangent line. 2. Use the tangent line to estimate the value of the derivative at a point. 3. Recognize keywords
Procedural Skills Learning Objectives 1. Given a function and a point, sketch the corresponding tangent line. 2. Use the tangent line to estimate the value of the derivative at a point. 3. Recognize keywords
Algebra 1, Chapter 4 Post Test
 Class: Date: Algebra 1, Chapter 4 Post Test Review 4.1.1: I can represent mathematical relationships using graphs. 1. (2 points) Sketch a graph of the speed of a city bus on a daily route. Label each section.
Class: Date: Algebra 1, Chapter 4 Post Test Review 4.1.1: I can represent mathematical relationships using graphs. 1. (2 points) Sketch a graph of the speed of a city bus on a daily route. Label each section.
x 3x 1 if x 3 On problems 8 9, use the definition of continuity to find the values of k and/or m that will make the function continuous everywhere.
 CALCULUS AB WORKSHEET ON CONTINUITY AND INTERMEDIATE VALUE THEOREM Work the following on notebook paper. On problems 1 4, sketch the graph of a function f that satisfies the stated conditions. 1. f has
CALCULUS AB WORKSHEET ON CONTINUITY AND INTERMEDIATE VALUE THEOREM Work the following on notebook paper. On problems 1 4, sketch the graph of a function f that satisfies the stated conditions. 1. f has
Worksheet 1: One-Dimensional Kinematics
 Worksheet 1: One-Dimensional Kinematics Objectives Relate,, and in examples of motion along one dimension. Visualize motion using graphs of,, and vs.. Solve numeric problems involving constant and constant.
Worksheet 1: One-Dimensional Kinematics Objectives Relate,, and in examples of motion along one dimension. Visualize motion using graphs of,, and vs.. Solve numeric problems involving constant and constant.
Important Vocabulary Speed vs Velocity Acceleration Graphs of Motion Momentum
 Important Vocabulary Speed vs Velocity Acceleration Graphs of Motion Momentum Important Vocabulary Position-location of an object Distance-how far an object has traveled, regardless of direction Displacement-change
Important Vocabulary Speed vs Velocity Acceleration Graphs of Motion Momentum Important Vocabulary Position-location of an object Distance-how far an object has traveled, regardless of direction Displacement-change
Velocity. UF PHY2053, Lecture 3: Motion in One Dimension
 Velocity 1 Average Velocity vs Average Speed Average Velocity is the change in position during a time interval vav,x Δx Δt x f - xi tf - ti Average Speed is the distance traveled during a time interval
Velocity 1 Average Velocity vs Average Speed Average Velocity is the change in position during a time interval vav,x Δx Δt x f - xi tf - ti Average Speed is the distance traveled during a time interval
Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem
 Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem Before we continue with the problem of describing graphs using calculus we shall briefly pause to examine some interesting applications of the derivative. In previous
Section 4.2: The Mean Value Theorem Before we continue with the problem of describing graphs using calculus we shall briefly pause to examine some interesting applications of the derivative. In previous
Rolle s Theorem. The theorem states that if f (a) = f (b), then there is at least one number c between a and b at which f ' (c) = 0.
 Rolle s Theorem Rolle's Theorem guarantees that there will be at least one extreme value in the interior of a closed interval, given that certain conditions are satisfied. As with most of the theorems
Rolle s Theorem Rolle's Theorem guarantees that there will be at least one extreme value in the interior of a closed interval, given that certain conditions are satisfied. As with most of the theorems
4.1 Areas and Distances. The Area Problem: GOAL: Find the area of the region S that lies under the curve y = f(x) from a to b.
 4.1 Areas and Distances The Area Problem: GOAL: Find the area of the region S that lies under the curve y = f(x) from a to b. Easier Problems: Find the area of a rectangle with length l and width w. Find
4.1 Areas and Distances The Area Problem: GOAL: Find the area of the region S that lies under the curve y = f(x) from a to b. Easier Problems: Find the area of a rectangle with length l and width w. Find
Formulas that must be memorized:
 Formulas that must be memorized: Position, Velocity, Acceleration Speed is increasing when v(t) and a(t) have the same signs. Speed is decreasing when v(t) and a(t) have different signs. Section I: Limits
Formulas that must be memorized: Position, Velocity, Acceleration Speed is increasing when v(t) and a(t) have the same signs. Speed is decreasing when v(t) and a(t) have different signs. Section I: Limits
AP Calculus AB. Chapter IV Lesson B. Curve Sketching
 AP Calculus AB Chapter IV Lesson B Curve Sketching local maxima Absolute maximum F I A B E G C J Absolute H K minimum D local minima Summary of trip along curve critical points occur where the derivative
AP Calculus AB Chapter IV Lesson B Curve Sketching local maxima Absolute maximum F I A B E G C J Absolute H K minimum D local minima Summary of trip along curve critical points occur where the derivative
Pre-Calculus Module 4
 Pre-Calculus Module 4 4 th Nine Weeks Table of Contents Precalculus Module 4 Unit 9 Rational Functions Rational Functions with Removable Discontinuities (1 5) End Behavior of Rational Functions (6) Rational
Pre-Calculus Module 4 4 th Nine Weeks Table of Contents Precalculus Module 4 Unit 9 Rational Functions Rational Functions with Removable Discontinuities (1 5) End Behavior of Rational Functions (6) Rational
Calculus I Sample Exam #01
 Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without
 MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
MOTION, DISTANCE, AND DISPLACEMENT Q: What is motion? A: Motion is any change in the position or place of an object. is the study of motion (without considering the cause of the motion). Distance vs. Displacement
1.1 Motion and Motion Graphs
 Figure 1 A highway is a good example of the physics of motion in action. kinematics the study of motion without considering the forces that produce the motion dynamics the study of the causes of motion
Figure 1 A highway is a good example of the physics of motion in action. kinematics the study of motion without considering the forces that produce the motion dynamics the study of the causes of motion
Name. 1. Given the solution (3, y), what is the value of y if x + y = 6? 7. The graph of y = x 2 is shown below. A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D.
 Name 1. Given the solution (, y), what is the value of y if x + y = 6? 7. The graph of y = x is shown below. 5 D. 6. What are the solutions to the equation x - x = 0? x = - or x = - x = - or x = 1 x =
Name 1. Given the solution (, y), what is the value of y if x + y = 6? 7. The graph of y = x is shown below. 5 D. 6. What are the solutions to the equation x - x = 0? x = - or x = - x = - or x = 1 x =
LHS Algebra Pre-Test
 Your Name Teacher Block Grade (please circle): 9 10 11 12 Course level (please circle): Honors Level 1 Instructions LHS Algebra Pre-Test The purpose of this test is to see whether you know Algebra 1 well
Your Name Teacher Block Grade (please circle): 9 10 11 12 Course level (please circle): Honors Level 1 Instructions LHS Algebra Pre-Test The purpose of this test is to see whether you know Algebra 1 well
One Dimensional Motion. Motion in x or y only
 One Dimensional Motion Motion in x or y only Scalar vs. Vector Scalar Defined as quantity with magnitude (size) only Example: 3 m, 62 seconds, 4.2 miles EASY Math!!! Vector Defined as quantity with magnitude
One Dimensional Motion Motion in x or y only Scalar vs. Vector Scalar Defined as quantity with magnitude (size) only Example: 3 m, 62 seconds, 4.2 miles EASY Math!!! Vector Defined as quantity with magnitude
Topic 1 Test: Linear Relations and Functions. Name: Date: 1. When Antonio first joined the swim team, he swam the race in 8 minutes.
 Name: Date: 1. When Antonio first joined the swim team, he swam the race in 8 minutes. But now he can swim the race in that time. Henry swims the course in 4 minutes. Let T be the difference between Henry
Name: Date: 1. When Antonio first joined the swim team, he swam the race in 8 minutes. But now he can swim the race in that time. Henry swims the course in 4 minutes. Let T be the difference between Henry
2.1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change
 .1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Demonstrate an understanding of the slope of the tangent line to the graph. Demonstrate an understanding of the instantaneous
.1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Demonstrate an understanding of the slope of the tangent line to the graph. Demonstrate an understanding of the instantaneous
Each dot represents an object moving, between constant intervals of time. Describe the motion that you see. equation symbol: units: Velocity
 What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
CHAPTER 2: Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension
 CHAPTER : Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A car speedometer measures only speed. It does not give any information about the direction, and so does not measure velocity..
CHAPTER : Describing Motion: Kinematics in One Dimension Answers to Questions 1. A car speedometer measures only speed. It does not give any information about the direction, and so does not measure velocity..
0817AI Common Core State Standards
 0817AI Common Core State Standards 1 A part of Jennifer's work to solve the equation 2(6x 2 3) = 11x 2 x is shown below. Given: 2(6x 2 3) = 11x 2 x Step 1: 12x 2 6 = 11x 2 x Which property justifies her
0817AI Common Core State Standards 1 A part of Jennifer's work to solve the equation 2(6x 2 3) = 11x 2 x is shown below. Given: 2(6x 2 3) = 11x 2 x Step 1: 12x 2 6 = 11x 2 x Which property justifies her
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions
 Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by both magnitude AND direction
 Unit I: Motion Subunit A: Constant Velocity Chapter 2 Section 1 Texas Physics p. 38-45 Equations Variables, Units NOTES: scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by
Unit I: Motion Subunit A: Constant Velocity Chapter 2 Section 1 Texas Physics p. 38-45 Equations Variables, Units NOTES: scalar: quantity described by magnitude (size) only vector: quantity described by
Replacing the a in the definition of the derivative of the function f at a with a variable x, gives the derivative function f (x).
 Definition of The Derivative Function Definition (The Derivative Function) Replacing the a in the definition of the derivative of the function f at a with a variable x, gives the derivative function f
Definition of The Derivative Function Definition (The Derivative Function) Replacing the a in the definition of the derivative of the function f at a with a variable x, gives the derivative function f
PRACTICE FINAL , FALL What will NOT be on the final
 PRACTICE FINAL - 1010-004, FALL 2013 If you are completing this practice final for bonus points, please use separate sheets of paper to do your work and circle your answers. Turn in all work you did to
PRACTICE FINAL - 1010-004, FALL 2013 If you are completing this practice final for bonus points, please use separate sheets of paper to do your work and circle your answers. Turn in all work you did to
4.2 Mean Value Theorem Calculus
 4. MEAN VALUE THEOREM The Mean Value Theorem is considered b some to be the most important theorem in all of calculus. It is used to prove man of the theorems in calculus that we use in this course as
4. MEAN VALUE THEOREM The Mean Value Theorem is considered b some to be the most important theorem in all of calculus. It is used to prove man of the theorems in calculus that we use in this course as
QUIZ ON CHAPTER 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES; MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS
 Math 150 Name: QUIZ ON CHAPTER 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES; MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS = 100% Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and use good form and procedure
Math 150 Name: QUIZ ON CHAPTER 4 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES; MATH 150 FALL 2016 KUNIYUKI 105 POINTS TOTAL, BUT 100 POINTS = 100% Show all work, simplify as appropriate, and use good form and procedure
Review for Final. The final will be about 20% from chapter 2, 30% from chapter 3, and 50% from chapter 4. Below are the topics to study:
 Review for Final The final will be about 20% from chapter 2, 30% from chapter 3, and 50% from chapter 4. Below are the topics to study: Chapter 2 Find the exact answer to a limit question by using the
Review for Final The final will be about 20% from chapter 2, 30% from chapter 3, and 50% from chapter 4. Below are the topics to study: Chapter 2 Find the exact answer to a limit question by using the
Algebra 1 Mod 1 Review Worksheet I. Graphs Consider the graph below. Please do this worksheet in your notebook, not on this paper.
 Algebra 1 Mod 1 Review Worksheet I. Graphs Consider the graph below Please do this worksheet in your notebook, not on this paper. A) For the solid line; calculate the average speed from: 1) 1:00 pm to
Algebra 1 Mod 1 Review Worksheet I. Graphs Consider the graph below Please do this worksheet in your notebook, not on this paper. A) For the solid line; calculate the average speed from: 1) 1:00 pm to
Solutions to Problem Sheet for Week 8
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Solutions to Problem Sheet for Wee 8 MATH1901: Differential Calculus (Advanced) Semester 1, 017 Web Page: sydney.edu.au/science/maths/u/ug/jm/math1901/
THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Solutions to Problem Sheet for Wee 8 MATH1901: Differential Calculus (Advanced) Semester 1, 017 Web Page: sydney.edu.au/science/maths/u/ug/jm/math1901/
Introduction. Math Calculus 1 section 2.1 and 2.2. Julian Chan. Department of Mathematics Weber State University
 Math 1210 Calculus 1 section 2.1 and 2.2 Julian Chan Department of Mathematics Weber State University 2013 Objectives Objectives: to tangent lines to limits What is velocity and how to obtain it from the
Math 1210 Calculus 1 section 2.1 and 2.2 Julian Chan Department of Mathematics Weber State University 2013 Objectives Objectives: to tangent lines to limits What is velocity and how to obtain it from the
2 nd 6 Weeks TEST Study Guide Algebra I. SPIs to be tested
 2 nd 6 Weeks TEST Study Guide Algebra I SPIs to be tested SPI 3102.1.3 Apply properties to evaluate expressions, simplify expressions, and justify solutions to problems. SPI 3102.3.2 Operate with polynomials
2 nd 6 Weeks TEST Study Guide Algebra I SPIs to be tested SPI 3102.1.3 Apply properties to evaluate expressions, simplify expressions, and justify solutions to problems. SPI 3102.3.2 Operate with polynomials
Answers to SNC 2DI Exam Review: Motion Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions:
 Answers to SNC 2DI Exam Review: Motion Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Physics Time Acceleration Kinetic energy Average speed Negative acceleration
Answers to SNC 2DI Exam Review: Motion Unit 1. Understand the meaning of the following terms. Be able to recognize their definitions: Physics Time Acceleration Kinetic energy Average speed Negative acceleration
Section 2.1 Intercepts and symmetry. #1 4: Find the x and y-intercepts
 Section 2.1 Intercepts and symmetry #1 4: Find the x and y-intercepts 1) 2) 3) Section 2.1 Intercepts and symmetry 4) #5-18: Find the x and y-intercepts. 5) 3x - 6y = 24 6) 2x + 4y = 12 7) y 2 = x + 9
Section 2.1 Intercepts and symmetry #1 4: Find the x and y-intercepts 1) 2) 3) Section 2.1 Intercepts and symmetry 4) #5-18: Find the x and y-intercepts. 5) 3x - 6y = 24 6) 2x + 4y = 12 7) y 2 = x + 9
ALGEBRA 1 MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SEMESTER 1 CHAPTERS 1-5
 Name: Class: Date: ALGEBRA 1 MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SEMESTER 1 CHAPTERS 1-5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Solve p 6 16. A. p = 22 C. p =
Name: Class: Date: ALGEBRA 1 MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW SEMESTER 1 CHAPTERS 1-5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 Solve p 6 16. A. p = 22 C. p =
Chapter 2: Limits & Continuity
 Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 2: Limits & Continuity Sections: v 2.1 Rates of Change of Limits v 2.2 Limits Involving Infinity v 2.3 Continuity v 2.4 Rates of Change and Tangent Lines
Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 2: Limits & Continuity Sections: v 2.1 Rates of Change of Limits v 2.2 Limits Involving Infinity v 2.3 Continuity v 2.4 Rates of Change and Tangent Lines
Calculus is Cool. Math 160 Calculus for Physical Scientists I Exam 1 September 18, 2014, 5:00-6:50 pm. NAME: Instructor: Time your class meets:
 NAME: Instructor: Time your class meets: Math 160 Calculus for Physical Scientists I Exam 1 September 18, 2014, 5:00-6:50 pm How can it be that mathematics, being after all a product of human thought independent
NAME: Instructor: Time your class meets: Math 160 Calculus for Physical Scientists I Exam 1 September 18, 2014, 5:00-6:50 pm How can it be that mathematics, being after all a product of human thought independent
TEST. Name: A. $600 B. $1,200 C. $2,400 D. $3,600
 TEST 1. The graph shows two savings plans. If the same savings rates are continued, what will be the difference in the amount saved at the end of two years? A. $600 B. $1,200 C. $2,400 D. $3,600 2. Which
TEST 1. The graph shows two savings plans. If the same savings rates are continued, what will be the difference in the amount saved at the end of two years? A. $600 B. $1,200 C. $2,400 D. $3,600 2. Which
For problems 1 4, evaluate each expression, if possible. Write answers as integers or simplified fractions
 / MATH 05 TEST REVIEW SHEET TO THE STUDENT: This Review Sheet gives you an outline of the topics covered on Test as well as practice problems. Answers are at the end of the Review Sheet. I. EXPRESSIONS
/ MATH 05 TEST REVIEW SHEET TO THE STUDENT: This Review Sheet gives you an outline of the topics covered on Test as well as practice problems. Answers are at the end of the Review Sheet. I. EXPRESSIONS
v t t t t a t v t d dt t t t t t 23.61
 SECTION 4. MAXIMUM AND MINIMUM VALUES 285 The values of f at the endpoints are f 0 0 and f 2 2 6.28 Comparing these four numbers and using the Closed Interval Method, we see that the absolute minimum value
SECTION 4. MAXIMUM AND MINIMUM VALUES 285 The values of f at the endpoints are f 0 0 and f 2 2 6.28 Comparing these four numbers and using the Closed Interval Method, we see that the absolute minimum value
Unit 2 - Motion. Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed. Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76
 Unit 2 - Motion Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76 Precision and Accuracy Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how
Unit 2 - Motion Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76 Precision and Accuracy Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how
p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change
 1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
1 2 3 4 p105 Section 2.2: Basic Differentiation Rules and Rates of Change Find the derivative of a function using the Constant Rule Find the derivative of a function using the Power Rule Find the derivative
AP Calculus Chapter 2 Practice Test
 AP Calculus Chapter 2 Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Assume that a watermelon dropped from
AP Calculus Chapter 2 Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Assume that a watermelon dropped from
Chapter 1 Functions and Limits
 Contents Chapter 1 Functions and Limits Motivation to Chapter 1 2 4 Tangent and Velocity Problems 3 4.1 VIDEO - Secant Lines, Average Rate of Change, and Applications......................... 3 4.2 VIDEO
Contents Chapter 1 Functions and Limits Motivation to Chapter 1 2 4 Tangent and Velocity Problems 3 4.1 VIDEO - Secant Lines, Average Rate of Change, and Applications......................... 3 4.2 VIDEO
Math Exam 1 Answers Fall Circle the LETTER of the correct answer for #1-3.
 Math 1800 Exam 1 Answers Fall 011 Circle the LETTER of the correct answer for #1-. (7 pts)1. An eight inch candle burns at a rate of 1 in/min; a twelve inch candle burns at a rate of 1 in/min. Which candle
Math 1800 Exam 1 Answers Fall 011 Circle the LETTER of the correct answer for #1-. (7 pts)1. An eight inch candle burns at a rate of 1 in/min; a twelve inch candle burns at a rate of 1 in/min. Which candle
Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions
 Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions 1. Neatly sketch the following dot motion diagrams: (a) A particle moving right
Questions: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Physics 1100: 1D Kinematics Solutions 1. Neatly sketch the following dot motion diagrams: (a) A particle moving right
Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity. What we asked about
 Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity Outline for this unit: Displacement, Velocity: numerically and graphically Mechanics Lecture 1, Slide 1 What we asked about Would like to see more practice problems
Unit 01 Motion with constant velocity Outline for this unit: Displacement, Velocity: numerically and graphically Mechanics Lecture 1, Slide 1 What we asked about Would like to see more practice problems
