Mechanical and Structural Vibration: Theory and Applications
|
|
|
- Archibald Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanical and Structural Vibration: Theory and Applications Jerry H. Ginsberg Errata to the First Printing: 17 August 2001 Pg. 15, second line:...and L 2 + x 2 x 1, respectively,... Pg. 15, 2nd eq. and eq. (1.4.6): darken overdots above for damping terms. Pg. 16, eq. (1.4.8): insert overdots in damping term: ½ ¾ (c1 + c... 2 ) c 2 úx c 2 c 2 úx 2 Pg. 41, 6th line following Þgure: 3 =... = y... Pg. 41, 2nd equation: V sp = k 2 3 (y) 2 Pg. 41, 3rd equation from bottom: V = 1(K 2 11x 2 + Pg. 45, 3 lines from bottom:... express P dis in terms... Pg. 51, 2nd and 3rd equations: delete all overdots in expressions for r D and r E Pg. 51, 3rd equation from bottom: Result should be P in =0.866LF 1θ ú Pg. 52, 2nd Þgure: the downward force on the small gear is k 2 + µ ú 2 Pg. 54, equation at top of page: insert overdots in damping term: ½ úψ... [C] úθ ¾ +... Pg. 61, Exercise 1.47, third line:...spring stiffness k 1.and... Pg. 61, Figure for Exercise 1.47: distance from pivot to force point is 2L/3. Pg. 67, eq. (2.1.45), 2nd equation: change + to, i.e.... sin (ωt) = 1 [exp ( iωt) exp ( iωt)] 2i Pg. 67, eq. (2.1.6), 2nd equation: insert parentheses around iωt in both exponentials Pg. 69, 3rd equation: A =... = i Pg. 69, 11 lines from bottom:...we write abs (z), while... Pg. 70, eq. (2.1.3): Change sign preceding φ 2 toaplus:... + A 2 cos (ωt + φ 2 )
2 Pg. 70, eq. (2.1.4): Insert a minus sign before iφ 1 in both lines, i.e. A 1 i exp ( iφ 1) Pg. 98, 3rd equation:...= n> x (10 5 )... 4 Pg. 109, eq. (2.3.20): g (t τ) =lim... T 0 Pg. 110, 4th line from bottom:...the force, F /k... Pg. 111, Figure 2.19: the heading for the left graph should be ζ =0.05 Pg. 112, Exercise 2.5, Part (b), 2nd line from bottom:... Write the complex amplitude in... Pg. 113, 2nd and 3rd lines of Exercise 2.14: Delete dots above Pg. 116, Exercise 2.31, 2nd line following Item 3:... frequency ω nat, the ratio... Pg. 117, Þgure for Exercise 2.35: delete subscript 1 from label for displacement arrow Pg. 119, 4th line in Exercise 2.63: time ω nat t over... Pg. 123, Figure 3.2, lower 0 label for vertical axis to the bottom left corner Pg. 126, 5th line in Example 3.2, insert: L =2m. It may be assumed that the wheel remainsincontactwiththeground.(seeexercise3.36) i Pg. 129, last equation:...h ˆF exp (iωt)+ ˆF exp ( iωt) Pg. 134, 2nd line following Þgure:...The two curves intersect the... Pg. 143, Þrst graph: right label should be 200 Pg. 144, Figure 3.11: labels for spring and dashpot should be capitalized Pg. 144, eq. (3.4.1):... mω 2 r G/O Pg. 145, eq. (3.4.2):... F j Kq C úq = M q Pg. 149, 5th equation: y =...e iωtª Pg. 151, 7th equation: V =... = 1 2 kθ2 = Pg. 151, 2nd line after equation for V : 2aθ, ú which (i.e. insert overdot) Pg. 156, 2nd equation:... ˆF n exp ( inω 1 t) Pg. 160, 4th line from bottom of page: and G ( N/2+1) to G N/2 are... Pg. 161, eq. (3.7.25), 1st line:...k = N 2 +1, N 2 +2,..., N 2 Pg. 178, 3rd paragraph, 2nd line:... is well below the accelerometer s natural... Pg. 178, eq. (3.7.57), 2nd line: U n = K + inω 1 C K + inω 1 C n 2 ω 2 1M Z n 1+2inr 1 ζ 1+2inr 1 ζ n 2 r 2 1 Pg. 180, 2nd set of Þgures, heading for the left graph should be ω nat T =40π 2 Z n
3 Pg. 183, eq. (3.8.9) and 4 lines before : subscript in τ d should be roman type. Pg. 202, last line: Figure 3.26, as... Pg. 214, Exercise 3.42: h (1 x 2 /w 2 ) if x w z(x) = 0 if w x <L/2 z(x ± L) if x >L/2 Pg. 215, 2 lines before Exercise 3.45:...90% of the highest critical Pg. 224, eq. (4.2.4): [K] ω 2 [M] =0 Pg. 225, eq. (4.2.7): lower left element of rectangular matrix should be K(N 1)1 ω 2 jm (N 1)1 Pg. 226, eq. (4.2.8), 1st line: last element of column matrix is φ Nj Pg. 230, 5th line after Þgure:...Because θ is the pitch... Pg. 235, 2nd equation: lower left element of matrix should be 1.8(10 5 ) Pg. 239, 2nd equation:... +3Nx N =0 Pg. 240, 1st line: j =1: N; phi_norm(:, j) =phi_sort(:, j)/sqrt(mu(j, j)); end. Pg. 248, eq. (4.2.49), 2nd line...+α 22 φ 0 T j+1ª [M] φj+1ª 0 =0 Pg. 248, eq. (4.2.50), second line: α 22 = ª φ 0 T j+1 [M] ª φ j+2 φ 0 T j+1ª [M] ª φ 0 j+1 Pg. 250, last equation: ³φ <k 1>T M φ <k> φ <k> := φ <k> 1,1 ³φ <k 1>T M φ <k 1> φ <k 1> Pg. 255, Þrst equation: v 2m = úq 1 õ,... Pg. 256, 5th line of equations: m (cos θ) ω 2 n +(k mω 2 n) φ 2n =... Pg.267,2ndtextline:..[M] is κ G = L/ 8 Pg. 272, 6th line of Exercise 4.10:... = úx 2 =0at t =0... Pg. 284, Exercise 4.5, 7th line: and (b) m 1 =5kg, m 2 =... (Then delete the following sentence) Pg. 286, Exercise 4.12, part (d) [K] =...N/m, ω 2 =... Pg. 286, Exercise 4.12, part (d), list line: Determine the normal mode {Φ 2 }. 3 1,1
4 Pg. 286, Exercise 4.13, 2nd line of 4th item: described above is... Pg. 287, Exercise 4.20, equation: w =... Pg. 287, Exercise 4.21, last line: and normal modes of this system. Pg. 291, Exercise 4.47, one line before end: q n =Re[Y n exp (i20t)] and... Pg. 298, eq. (5.2.2): [G (ω)] = [[K](1+iγ) ω 2 [M]] 1 Pg. 309, equation: V = 1 2 k 0y Pg. 314, 7 lines before eq. (5.4.9). Insert:, Q j (k ) =β j f (k ), k =0, 1,..., K 1. Simultaneously,... Pg. 314, eq. (5.4.9), 2nd line: m =0, 1,..., K/2 Pg. 319, Exercise 5.12, 9th line:...cases, γ =0.001 and γ = Pg. 322, Exercise 5.23, part(b), last line:...platform at a designated... Pg. 322, Exercise 5.23, part (c)7th line. Insert:...part(b) corresponding to 20 Hz. Use... Pg. 325, 2nd paragraph, 3rd line:.. work of the Swiss mathematician... Pg. 328, eq. (6.1.7), change superscript: P dis = Z L 0 γea µ 2 úu dx + X c úu (x c,t) 2 x Pg. 339, eq. (6.1.27): θ =... Pg. 340, 2nd line: [K] {q} = {Q}. (i.e. delete repeated terms) Pg. 344, eq. (6.1.37):... 0 Z L... = K nj = EI d2 ψ j d 2 ψ n dx dx 2 dx2 Z L... = C nj = γei d2 ψ j d 2 ψ n dx 2 dx + c vψ 2 j ψ n dx +... Pg. 349, 4 th line of Matlab commands:... psi(n) H, y, 0, 1) Pg. 409, Exercise 6.17, 7th, 8th, and 9th lines: where ω is 95% and 105% of the fundamental and second natural frequencies, plot the Pg. 409, Exercise 6.19, insert at end of last sentence:...at midspan as a function of ω. Pg. 410, Exercise 6.27, last line: k =2000EI/L 3. Pg. 413, Exercise 6.56, reword 1st sentence: When a cantilerbeam is modeled by a certain Ritz series, the inertia... Pg. 440, Þrst Þgure: change + to 4 in vertical axis. Pg. 444, 2nd equation: ψ j (x) =... Also,insertclosebraceatendofequation. asymptotic Pg. 445, 2nd line of text:... by letting 1/ cosh(α) =0. This... 4
5 Pg. 445, 4th line of equation for B 4 : = C 1 lim α j {2[sin (α j)...} Pg. 449, line following equation for ψ : where α 4 = ρal 4 ω 2 /EI Pg. 453, Figure 7.12: Spring force on the right mass should be kw x=l Pg. 455, 2 lines before eq. (7.6.26):... are not inertially coupled. Interestingly... Pg. 464, 4th equation, 2nd line: insert close brace at end of equation Pg. 481, 4th line of equations: exp( kl) =1/ε 1, exp( 0.8kL) =1/ε 2 Pg. 494, eq. (7.9.40), 2nd line: = 1 X X Z L (ρaψ wj Ψ wn + ρiψ wj Ψ wn ) dx úη 2 j úη n j n 0 Pg. 495, 10 lines before end of Example 7.14:... function of α, L_d, and σ Pg. 496, 1st line: cross-section rotation χ at this frequency... Pg. 501, Exercises 7.25 and 7.26, insert at beginning of second sentence: Use Appendix C to decompose... Pg. 501, Exercise 7.29, 2nd line: Example 7.5 and Exercise What... Pg. 501, Exercise 7.33, change second sentence to: A torque Γh (t) is applied at the midpoint. Pg. 503, Exercise 7.52, last line: range 0 < ω < 2000 rad/s Pg 513, equation for [K e ]: The denominators for K2,6, e K3,5, e K5,3, e and K6,2 e should be L 2. h h n o Pg. 520, 1st line: Once we have formed ˆMi, ˆKi, and ˆQ, we... Pg. 529, Exercise 8.6, 7th line:...derive linear interpolating functions... Also, delete parenthetical last sentence. Pg. 530, Exercise 5.16, 3rd line:...use a single Þnite element for bar BD, Pg. 539, 2nd line of equations: a 2(j+3N) =1, Pg. 541, 3rd line of equation for V 1 : index in Þrst summation sign should be j Pg. 544, eq. (9.1.31), 2nd line: =[B] T {Q} +[B] T [a] T {λ} Pg. 546: 3rd line of equations: M jn = 1ρALδ 2 jn Pg. 546: equation for V, 2nd line: delete exponent two for q j term Pg. 546: equation for V, 3rd line: delete exponent 2 and x from second factor Pg. 546: equation for V, 4th line: K jn = j 4 π4 EI 2L δ 3 jn
6 µ x Pg. 556, 2nd equation: ψ F` wj = C`jψ, α j L` Pg. 558, eq. (9.2.3): K` = " K` FF K` FC K` CF K` CC # Pg. 558, eq. (9.2.4), insert: K` CF h i K` FC T = Pg. 558, 1st sentence after eq. (9.2.4) should be: In the special case where the Þxedinterface modes are those of a bar that is immobilized at both ends, the off-diagonal partitions of K` are identically zero. Pg. 558, last sentence of paragraph following eq. (9.2.4) should be: If ψ F` j is deþned to have zero displacement and rotation at interfaces, each work term will be zero. Pg. 559, 4th line following eq. (9.2.6): eqs. (9.2.3). These matrices... Pg. 560, paragraph following equation for K` CC, insert after second sentence: All jn K` FC should evaluate to zero according to the note on page 558. jn Pg. 564, Exercise 9.23, change second sentence: Determine the constraint modes and Jacobian constraint matrix corresponding to using clamped-clamped ßexural modes as the Þxed interface modes for bar AB. Pg. 564, Exercise 9.26, change 1st sentence: Select clamped-clamped ßexural and Þxedfree torsional modes as the Þxed-interface... Pg. 572, 3rd line after 1st set of equations: eigenvalues to those derived from undamped modal analysis. Also, compare... Pg. 572, 3rd set of equations: Mathcad: zero = identity (3) 0 S := stack(augment( K, zero),augment(zero,m)) R := stack(augment(zero,k),augment(k, C)) Pg. 572, 4th set of equations, insert after MATLAB : lambda = diag(lambda); Pg. 572, 4th set of equations, 2nd line: (imag (lambda (j)) < 0) ; Pg. 592, Exercise 10.6, 2nd line, insert at end:...to 16, and let f j be a set of random numbers in the range 0.05 < f j < Pg. 598, 1st line after eq. ( ): When the quadratic coefficients of T actually... NX Pg. 598, eq. ( ), insert term: E jn q n + ún j J j Pg. 599, 1st line after eq. ( ):...use eqs ( ) and ( ) to form... n o Pg. 599, eq. ( ), insert term: = {Q} N ú + {J} {F 0 } n=1 6
7 n o Pg. 600, eq. ( ), 2nd line, insert term: = {Q} N ú + {J} {F 0 } Pg. 600, eq. ( ): [S] d dt {x} [R] {x} = ( n o{0} {Q} N ú + {J} {F 0 } ) Pg. 606, 1st line after eq. (11.2.1):... into eq. ( ) and... Pg. 607, 1st line after eq. ( ):... leads to {v} = λ {u}, which... Pg. 620, eq. ( ): n o n o ½ ¾ T úξ {0} [λ] {ξ} = Ψ n, n =1,..., 2N {Q} Pg. 621, eq. ( ): Numerators should be n Ψ n o T {F } and n Ψ n o T {F } Pg. 622, 3rd equation from bottom:... ω 2 y n 2ω úz n Pg. 622, 2nd equation from bottom:... ω 2 z n +2ω úy n Pg. 623, 3rd set of equations from the bottom: 1st row of [G 0 ] should be 0 ω 0 0 Pg. 626, upper left graph: Delete the small circle at the top of the larger ellipse Pg. 634, MATLAB program steps, 2nd and 3rd lines: eigval = eig (S (sig(j)),r(sig(j))) ; Re_lam(:,j)=sort(real(eigval)); Im_lam(:,j)=sort(imag(eigval)); end Pg. 634, Mathcad program steps, 1st line:...λ <j> := genvals (R (σ j ),S(σ j )) Pg. 635, 3rd paragraph, lines 4 and 5, and following equation: exp (λ n τ) Pg. 639, 4th equation: µ ψn f jn = x ψ j x=l Pg. 642, Exercise 11.4: T = 1 2 ml2 1 3 ú θ 2 + µ1+cos(θ) cos (θ)2 ω I T ω 2 Pg. 645, Exercise 11.23, 1st line:... a height of 2`/3 above.. Pg. 646, Exercise 11.27, insert after 2nd sentence: The rotation rate is ω =0.6(k/m) 1/2. Pg 6.57, eq. (12.3.1): right sides are εmω 2 cos (ωt) and εmω 2 sin (ωt) Pg. 665, last set of equations: M33 0 = M44 0 = κ 2 y, G 0 34 = G 0 43 =2κ 2 xω Pg. 670, eq. (12.5.6), 2nd line:... = εmω 2 cos (ωt) 7
8 Pg. 670, eq. (12.5.6), 4th line:... = εmω 2 sin (ωt) Pg. 672, 7th line:... has a parametric instability. Typical... Pg. 672, 3rd and 2nd lines from bottom:...condition Im(λ) =0also approximates... Pg. 675, Exercise 12.11, part (c), delete last sentence, which begins with Explain why... Pg. 676, Exercise 12.15, insert after last sentence: The damping ratios are ζ E = ζ I = Pg. 685, Appendix B, entry for Free vibration: Insert plus sign at the beginning of the second line Pg. 685, Appendix B, entry for Quadratic excitation, last line: insert close parentheses after ζ 3 Pg. 685, Appendix B, entry for Transient co-sinusoidal excitation, last line: fraction should be: ζω nat (ω 2 nat + ω 2 ) ω d µ 1/2 E Inside back cover, left page, Þrst line: ω n = α ρl 2 n Inside back cover, right page, entry for Clamped at x =0, Clamped at x = L, 1st line: cos (α)cosh(α) 1=0 8
Errata 1. p. 5 The third line from the end should read one of the four rows... not one of the three rows.
 Errata 1 Front inside cover: e 2 /4πɛ 0 should be 1.44 10 7 ev-cm. h/e 2 should be 25800 Ω. p. 5 The third line from the end should read one of the four rows... not one of the three rows. p. 8 The eigenstate
Errata 1 Front inside cover: e 2 /4πɛ 0 should be 1.44 10 7 ev-cm. h/e 2 should be 25800 Ω. p. 5 The third line from the end should read one of the four rows... not one of the three rows. p. 8 The eigenstate
Laboratory notes. Torsional Vibration Absorber
 Titurus, Marsico & Wagg Torsional Vibration Absorber UoB/1-11, v1. Laboratory notes Torsional Vibration Absorber Contents 1 Objectives... Apparatus... 3 Theory... 3 3.1 Background information... 3 3. Undamped
Titurus, Marsico & Wagg Torsional Vibration Absorber UoB/1-11, v1. Laboratory notes Torsional Vibration Absorber Contents 1 Objectives... Apparatus... 3 Theory... 3 3.1 Background information... 3 3. Undamped
Corrections and Minor Revisions of Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences, third edition, by Mary L. Boas (deceased)
 Corrections and Minor Revisions of Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences, third edition, by Mary L. Boas (deceased) Updated December 6, 2017 by Harold P. Boas This list includes all errors known
Corrections and Minor Revisions of Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences, third edition, by Mary L. Boas (deceased) Updated December 6, 2017 by Harold P. Boas This list includes all errors known
Reduction in number of dofs
 Reduction in number of dofs Reduction in the number of dof to represent a structure reduces the size of matrices and, hence, computational cost. Because a subset of the original dof represent the whole
Reduction in number of dofs Reduction in the number of dof to represent a structure reduces the size of matrices and, hence, computational cost. Because a subset of the original dof represent the whole
Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material
 Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material The candidate is expected to have a thorough understanding of engineering vibrations topics. These topics are listed below for clarification. Not all instructors
Vibrations Qualifying Exam Study Material The candidate is expected to have a thorough understanding of engineering vibrations topics. These topics are listed below for clarification. Not all instructors
Engineering Dynamics: A Comprehensive Introduction Errata. N. Jeremy Kasdin & Derek A. Paley
 Engineering Dynamics: A Comprehensive Introduction Errata N. Jeremy Kasdin & Derek A. Paley Last updated November 10, 2017 PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS PRINCETON AND OXFORD Chapter 2: i) [First printing
Engineering Dynamics: A Comprehensive Introduction Errata N. Jeremy Kasdin & Derek A. Paley Last updated November 10, 2017 PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS PRINCETON AND OXFORD Chapter 2: i) [First printing
Errata for Instructor s Solutions Manual for Gravity, An Introduction to Einstein s General Relativity 1st printing
 Errata for Instructor s Solutions Manual for Gravity, An Introduction to Einstein s General Relativity st printing Updated 7/7/003 (hanks to Scott Fraser who provided almost all of these.) Statement of
Errata for Instructor s Solutions Manual for Gravity, An Introduction to Einstein s General Relativity st printing Updated 7/7/003 (hanks to Scott Fraser who provided almost all of these.) Statement of
ERRATA AND ADDITIONS FOR "ENGINEERING NOISE CONTROL" 4th Edn. First printing April 23, 2018
 ERRATA AND ADDITIONS FOR "ENGINEERING NOISE CONTROL" 4th Edn. First printing April 3, 08 p4, Eq..3 should not have the ± symbol on the RHS p36, 3 lines from the bottom of the page, replace cos b with cos
ERRATA AND ADDITIONS FOR "ENGINEERING NOISE CONTROL" 4th Edn. First printing April 3, 08 p4, Eq..3 should not have the ± symbol on the RHS p36, 3 lines from the bottom of the page, replace cos b with cos
kx m x B N 1 C L, M Mg θ
 .004 MODELING DYNAMICS AND CONTROL II Spring 00 Solutions to Problem Set No. 7 Problem 1. Pendulum mounted on elastic support. This problem is an execise in the application of momentum principles. Two
.004 MODELING DYNAMICS AND CONTROL II Spring 00 Solutions to Problem Set No. 7 Problem 1. Pendulum mounted on elastic support. This problem is an execise in the application of momentum principles. Two
Errata for SOLIDIFICATION (First Edition, 2009)
 Errata for SOLIDIFICATION (First Edition, 29) J. A. Dantzig and M. Rappaz March 2, 217 Chapter 1: Overview Page 2, first line: the definition of r should have a square root. i.e., r = (ξ 2 + y 2 + z 2
Errata for SOLIDIFICATION (First Edition, 29) J. A. Dantzig and M. Rappaz March 2, 217 Chapter 1: Overview Page 2, first line: the definition of r should have a square root. i.e., r = (ξ 2 + y 2 + z 2
Quantum Mechanics: A Paradigms Approach David H. McIntyre. 27 July Corrections to the 1 st printing
 Quantum Mechanics: A Paradigms Approach David H. McIntyre 7 July 6 Corrections to the st printing page xxi, last paragraph before "The End", nd line: Change "become" to "became". page, first line after
Quantum Mechanics: A Paradigms Approach David H. McIntyre 7 July 6 Corrections to the st printing page xxi, last paragraph before "The End", nd line: Change "become" to "became". page, first line after
CHAPTER 12 OSCILLATORY MOTION
 CHAPTER 1 OSCILLATORY MOTION Before starting the discussion of the chapter s concepts it is worth to define some terms we will use frequently in this chapter: 1. The period of the motion, T, is the time
CHAPTER 1 OSCILLATORY MOTION Before starting the discussion of the chapter s concepts it is worth to define some terms we will use frequently in this chapter: 1. The period of the motion, T, is the time
Finite element analysis of rotating structures
 Finite element analysis of rotating structures Dr. Louis Komzsik Chief Numerical Analyst Siemens PLM Software Why do rotor dynamics with FEM? Very complex structures with millions of degrees of freedom
Finite element analysis of rotating structures Dr. Louis Komzsik Chief Numerical Analyst Siemens PLM Software Why do rotor dynamics with FEM? Very complex structures with millions of degrees of freedom
The distance of the object from the equilibrium position is m.
 Answers, Even-Numbered Problems, Chapter..4.6.8.0..4.6.8 (a) A = 0.0 m (b).60 s (c) 0.65 Hz Whenever the object is released from rest, its initial displacement equals the amplitude of its SHM. (a) so 0.065
Answers, Even-Numbered Problems, Chapter..4.6.8.0..4.6.8 (a) A = 0.0 m (b).60 s (c) 0.65 Hz Whenever the object is released from rest, its initial displacement equals the amplitude of its SHM. (a) so 0.065
DIGITAL FILTERS Analysis, Design, and Applications by A. Antoniou ERRATA. Page 10, Table 1.1: The upper limit of the summation should be K.
 DIGITAL FILTERS Analysis, Design, and Applications by A. Antoniou ERRATA Printing #1 Page vii, line 4 : Replace Geophysicists by Geoscientists. Page 1, Table 1.1: The upper limit of the summation should
DIGITAL FILTERS Analysis, Design, and Applications by A. Antoniou ERRATA Printing #1 Page vii, line 4 : Replace Geophysicists by Geoscientists. Page 1, Table 1.1: The upper limit of the summation should
Errata for Quantum Mechanics by Ernest Abers August 1, 2004
 Errata for Quantum Mechanics by Ernest Abers August, 004 Preface Page xv: Add a sentence at the end of the next-to-last paragraph: Rudaz (University of Minnesota, and several anonymous reviewers. My special
Errata for Quantum Mechanics by Ernest Abers August, 004 Preface Page xv: Add a sentence at the end of the next-to-last paragraph: Rudaz (University of Minnesota, and several anonymous reviewers. My special
Solution of Vibration and Transient Problems
 . 9 Solution of Vibration and Transient Problems 9 Chapter 9: SOLUTION OF VIBRATION AND TRANSIENT PROBLEMS 9 9. MODAL APPROACH TO TRANSIENT ANALYSIS Consider the following large-order finite element model
. 9 Solution of Vibration and Transient Problems 9 Chapter 9: SOLUTION OF VIBRATION AND TRANSIENT PROBLEMS 9 9. MODAL APPROACH TO TRANSIENT ANALYSIS Consider the following large-order finite element model
Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum
 STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum Overview of Structural Dynamics Structure Members, joints, strength, stiffness, ductility Structure
STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum Overview of Structural Dynamics Structure Members, joints, strength, stiffness, ductility Structure
2.010 Fall 2000 Solution of Homework Assignment 1
 2. Fall 2 Solution of Homework Assignment. Compact Disk Player. This is essentially a reprise of Problems and 2 from the Fall 999 2.3 Homework Assignment 7. t is included here to encourage you to review
2. Fall 2 Solution of Homework Assignment. Compact Disk Player. This is essentially a reprise of Problems and 2 from the Fall 999 2.3 Homework Assignment 7. t is included here to encourage you to review
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES
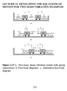 LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
Chapter 3 Mathematical Methods
 Chapter 3 Mathematical Methods Slides to accompany lectures in Vibro-Acoustic Design in Mechanical Systems 0 by D. W. Herrin Department of Mechanical Engineering Lexington, KY 40506-0503 Tel: 859-8-0609
Chapter 3 Mathematical Methods Slides to accompany lectures in Vibro-Acoustic Design in Mechanical Systems 0 by D. W. Herrin Department of Mechanical Engineering Lexington, KY 40506-0503 Tel: 859-8-0609
Dynamics of Structures: Theory and Analysis
 1. Free vibrations 2. Forced vibrations 3. Transient response 4. Damping mechanisms Dynamics of Structures: Theory and Analysis Steen Krenk Technical University of Denmark 5. Modal analysis I: Basic idea
1. Free vibrations 2. Forced vibrations 3. Transient response 4. Damping mechanisms Dynamics of Structures: Theory and Analysis Steen Krenk Technical University of Denmark 5. Modal analysis I: Basic idea
kg meter ii) Note the dimensions of ρ τ are kg 2 velocity 2 meter = 1 sec 2 We will interpret this velocity in upcoming slides.
 II. Generalizing the 1-dimensional wave equation First generalize the notation. i) "q" has meant transverse deflection of the string. Replace q Ψ, where Ψ may indicate other properties of the medium that
II. Generalizing the 1-dimensional wave equation First generalize the notation. i) "q" has meant transverse deflection of the string. Replace q Ψ, where Ψ may indicate other properties of the medium that
Date: 1 April (1) The only reference material you may use is one 8½x11 crib sheet and a calculator.
 PH1140: Oscillations and Waves Name: Solutions Conference: Date: 1 April 2005 EXAM #1: D2005 INSTRUCTIONS: (1) The only reference material you may use is one 8½x11 crib sheet and a calculator. (2) Show
PH1140: Oscillations and Waves Name: Solutions Conference: Date: 1 April 2005 EXAM #1: D2005 INSTRUCTIONS: (1) The only reference material you may use is one 8½x11 crib sheet and a calculator. (2) Show
Lecture 27: Structural Dynamics - Beams.
 Chapter #16: Structural Dynamics and Time Dependent Heat Transfer. Lectures #1-6 have discussed only steady systems. There has been no time dependence in any problems. We will investigate beam dynamics
Chapter #16: Structural Dynamics and Time Dependent Heat Transfer. Lectures #1-6 have discussed only steady systems. There has been no time dependence in any problems. We will investigate beam dynamics
Date: 31 March (1) The only reference material you may use is one 8½x11 crib sheet and a calculator.
 PH1140: Oscillations and Waves Name: SOLUTIONS AT END Conference: Date: 31 March 2005 EXAM #1: D2006 INSTRUCTIONS: (1) The only reference material you may use is one 8½x11 crib sheet and a calculator.
PH1140: Oscillations and Waves Name: SOLUTIONS AT END Conference: Date: 31 March 2005 EXAM #1: D2006 INSTRUCTIONS: (1) The only reference material you may use is one 8½x11 crib sheet and a calculator.
ME scope Application Note 28
 App Note 8 www.vibetech.com 3/7/17 ME scope Application Note 8 Mathematics of a Mass-Spring-Damper System INTRODUCTION In this note, the capabilities of ME scope will be used to build a model of the mass-spring-damper
App Note 8 www.vibetech.com 3/7/17 ME scope Application Note 8 Mathematics of a Mass-Spring-Damper System INTRODUCTION In this note, the capabilities of ME scope will be used to build a model of the mass-spring-damper
2C9 Design for seismic and climate changes. Jiří Máca
 2C9 Design for seismic and climate changes Jiří Máca List of lectures 1. Elements of seismology and seismicity I 2. Elements of seismology and seismicity II 3. Dynamic analysis of single-degree-of-freedom
2C9 Design for seismic and climate changes Jiří Máca List of lectures 1. Elements of seismology and seismicity I 2. Elements of seismology and seismicity II 3. Dynamic analysis of single-degree-of-freedom
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering Dynamics and Control II Fall 2007
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering.4 Dynamics and Control II Fall 7 Problem Set #9 Solution Posted: Sunday, Dec., 7. The.4 Tower system. The system parameters are
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mechanical Engineering.4 Dynamics and Control II Fall 7 Problem Set #9 Solution Posted: Sunday, Dec., 7. The.4 Tower system. The system parameters are
of the four-bar linkage shown in Figure 1 is T 12
 ME 5 - Machine Design I Fall Semester 0 Name of Student Lab Section Number FINL EM. OPEN BOOK ND CLOSED NOTES Wednesday, December th, 0 Use the blank paper provided for your solutions write on one side
ME 5 - Machine Design I Fall Semester 0 Name of Student Lab Section Number FINL EM. OPEN BOOK ND CLOSED NOTES Wednesday, December th, 0 Use the blank paper provided for your solutions write on one side
Transient Response Analysis of Structural Systems
 . 21 Transient Response Analysis of Structural Systems 21 1 Chapter 21: TRANSIENT RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS 21 2 21.1 MODAL APPROACH TO TRANSIENT ANALYSIS Consider the following large-order
. 21 Transient Response Analysis of Structural Systems 21 1 Chapter 21: TRANSIENT RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURAL SYSTEMS 21 2 21.1 MODAL APPROACH TO TRANSIENT ANALYSIS Consider the following large-order
Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints)
 Page Number Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints) Description of Correction Mechanics of Materials, 8e James M. Gere & Barry J. Goodno ISBN: 9781111577735 11 Figure
Page Number Errata (Includes critical corrections only for the 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd reprints) Description of Correction Mechanics of Materials, 8e James M. Gere & Barry J. Goodno ISBN: 9781111577735 11 Figure
SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine May 24, 2010
 SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 4, 010 Introduction The primary purpose of this tutorial is to present the Modal Transient method
SHOCK RESPONSE OF MULTI-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEMS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com May 4, 010 Introduction The primary purpose of this tutorial is to present the Modal Transient method
Errata for Bioelectricity: A Quantitative Approach, 3rd edition by Robert Plonsey and Roger C. Barr (Springer 2007)
 Errata for Bioelectricity: A Quantitative Approach, 3rd edition by Robert Plonsey and Roger C. Barr (Springer 2007) Frederick J. Vetter Department of Electrical, Computer and Biomedical Engineering University
Errata for Bioelectricity: A Quantitative Approach, 3rd edition by Robert Plonsey and Roger C. Barr (Springer 2007) Frederick J. Vetter Department of Electrical, Computer and Biomedical Engineering University
Chapter a. Spring constant, k : The change in the force per unit length change of the spring. b. Coefficient of subgrade reaction, k:
 Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Errata. The following errors are known to be present in The Mechanics of Inhaled Pharmaceutical Aerosols: An Introduction:
 Errata The following errors are known to be present in The Mechanics of Inhaled Pharmaceutical Aerosols: An Introduction: p. 4, line 2: x and dx should be x and x+dx p. 6: Both sides of eqn. (2.15) should
Errata The following errors are known to be present in The Mechanics of Inhaled Pharmaceutical Aerosols: An Introduction: p. 4, line 2: x and dx should be x and x+dx p. 6: Both sides of eqn. (2.15) should
Chapter 8: Frequency Domain Analysis
 Chapter 8: Frequency Domain Analysis Samantha Ramirez Preview Questions 1. What is the steady-state response of a linear system excited by a cyclic or oscillatory input? 2. How does one characterize the
Chapter 8: Frequency Domain Analysis Samantha Ramirez Preview Questions 1. What is the steady-state response of a linear system excited by a cyclic or oscillatory input? 2. How does one characterize the
Laboratory handout 5 Mode shapes and resonance
 laboratory handouts, me 34 82 Laboratory handout 5 Mode shapes and resonance In this handout, material and assignments marked as optional can be skipped when preparing for the lab, but may provide a useful
laboratory handouts, me 34 82 Laboratory handout 5 Mode shapes and resonance In this handout, material and assignments marked as optional can be skipped when preparing for the lab, but may provide a useful
Oscillations. Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass on a Spring The equation of motion for a mass m is attached to a spring of constant k is
 Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics I (PY 10) Oscillations Textbook Reference: Chapter 14 sections 1-8. Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass on a Spring The equation of motion for a mass m is attached to a spring
Dr. Alain Brizard College Physics I (PY 10) Oscillations Textbook Reference: Chapter 14 sections 1-8. Simple Harmonic Motion of a Mass on a Spring The equation of motion for a mass m is attached to a spring
Final Exam December 13, 2016
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-boo, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Do NOT unstaple your exam. Do NOT write
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-boo, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Do NOT unstaple your exam. Do NOT write
Outline of parts 1 and 2
 to Harmonic Loading http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano March, 6 Outline of parts and of an Oscillator
to Harmonic Loading http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano March, 6 Outline of parts and of an Oscillator
Final Exam December 11, 2017
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are NOT allowed to use a calculator with communication capabilities during the exam. Usage
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are NOT allowed to use a calculator with communication capabilities during the exam. Usage
Chapter 15 Periodic Motion
 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Slide 1-1 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Concepts Slide 1-2 Section 15.1: Periodic motion and energy Section Goals You will learn to Define the concepts of periodic motion, vibration,
Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Slide 1-1 Chapter 15 Periodic Motion Concepts Slide 1-2 Section 15.1: Periodic motion and energy Section Goals You will learn to Define the concepts of periodic motion, vibration,
MATH 23 Exam 2 Review Solutions
 MATH 23 Exam 2 Review Solutions Problem 1. Use the method of reduction of order to find a second solution of the given differential equation x 2 y (x 0.1875)y = 0, x > 0, y 1 (x) = x 1/4 e 2 x Solution
MATH 23 Exam 2 Review Solutions Problem 1. Use the method of reduction of order to find a second solution of the given differential equation x 2 y (x 0.1875)y = 0, x > 0, y 1 (x) = x 1/4 e 2 x Solution
Chapter 15 - Oscillations
 The pendulum of the mind oscillates between sense and nonsense, not between right and wrong. -Carl Gustav Jung David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 211 Oscillatory motion is motion that is periodic
The pendulum of the mind oscillates between sense and nonsense, not between right and wrong. -Carl Gustav Jung David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 211 Oscillatory motion is motion that is periodic
ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010
 ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010 PROBLEM 1: You are given the lumped parameter dynamic differential equations of motion for a two degree-offreedom model of an automobile suspension system for small
ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010 PROBLEM 1: You are given the lumped parameter dynamic differential equations of motion for a two degree-offreedom model of an automobile suspension system for small
a) Find the equation of motion of the system and write it in matrix form.
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion
 Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
. D CR Nomenclature D 1
 . D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
. D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
PROJECT 1 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 41514
 PROJECT DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 454 Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Ilmar Ferreira Santos, Professor Dr.-Ing., Dr.Techn., Livre-Docente
PROJECT DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 454 Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Ilmar Ferreira Santos, Professor Dr.-Ing., Dr.Techn., Livre-Docente
Forced Response - Particular Solution x p (t)
 Governing Equation 1.003J/1.053J Dynamics and Control I, Spring 007 Proessor Peacoc 5/7/007 Lecture 1 Vibrations: Second Order Systems - Forced Response Governing Equation Figure 1: Cart attached to spring
Governing Equation 1.003J/1.053J Dynamics and Control I, Spring 007 Proessor Peacoc 5/7/007 Lecture 1 Vibrations: Second Order Systems - Forced Response Governing Equation Figure 1: Cart attached to spring
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Oscillations. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER. Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 15 Oscillations Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums 1. The displacement of a particle oscillating along the x axis is given as a function
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 15 Oscillations Simple harmonic motion Mass-spring system Energy in SHM Pendulums 1. The displacement of a particle oscillating along the x axis is given as a function
AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 2016)
 AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 206) Solution of Homework #3 Control Tab Figure : Schematic for the control tab. Inadequacy of a static-test A static-test for measuring θ would ideally
AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 206) Solution of Homework #3 Control Tab Figure : Schematic for the control tab. Inadequacy of a static-test A static-test for measuring θ would ideally
1 x(k +1)=(Φ LH) x(k) = T 1 x 2 (k) x1 (0) 1 T x 2(0) T x 1 (0) x 2 (0) x(1) = x(2) = x(3) =
 567 This is often referred to as Þnite settling time or deadbeat design because the dynamics will settle in a Þnite number of sample periods. This estimator always drives the error to zero in time 2T or
567 This is often referred to as Þnite settling time or deadbeat design because the dynamics will settle in a Þnite number of sample periods. This estimator always drives the error to zero in time 2T or
Control of Electromechanical Systems
 Control of Electromechanical Systems November 3, 27 Exercise Consider the feedback control scheme of the motor speed ω in Fig., where the torque actuation includes a time constant τ A =. s and a disturbance
Control of Electromechanical Systems November 3, 27 Exercise Consider the feedback control scheme of the motor speed ω in Fig., where the torque actuation includes a time constant τ A =. s and a disturbance
Numerical Methods for Engineers, Second edition: Chapter 1 Errata
 Numerical Methods for Engineers, Second edition: Chapter 1 Errata 1. p.2 first line, remove the Free Software Foundation at 2. p.2 sixth line of the first proper paragraph, fe95.res should be replaced
Numerical Methods for Engineers, Second edition: Chapter 1 Errata 1. p.2 first line, remove the Free Software Foundation at 2. p.2 sixth line of the first proper paragraph, fe95.res should be replaced
Final Exam April 30, 2013
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
4. Complex Oscillations
 4. Complex Oscillations The most common use of complex numbers in physics is for analyzing oscillations and waves. We will illustrate this with a simple but crucially important model, the damped harmonic
4. Complex Oscillations The most common use of complex numbers in physics is for analyzing oscillations and waves. We will illustrate this with a simple but crucially important model, the damped harmonic
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Chapter 2 SDOF Vibration Control 2.1 Transfer Function
 Chapter SDOF Vibration Control.1 Transfer Function mx ɺɺ( t) + cxɺ ( t) + kx( t) = F( t) Defines the transfer function as output over input X ( s) 1 = G( s) = (1.39) F( s) ms + cs + k s is a complex number:
Chapter SDOF Vibration Control.1 Transfer Function mx ɺɺ( t) + cxɺ ( t) + kx( t) = F( t) Defines the transfer function as output over input X ( s) 1 = G( s) = (1.39) F( s) ms + cs + k s is a complex number:
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 1.2 Viscous damping Luc St-Pierre October 30, 2017 1 / 22 Summary so far We analysed the spring-mass system and found that its motion is governed by: mẍ(t) + kx(t) = 0 k y m x x
Dynamics of structures 1.2 Viscous damping Luc St-Pierre October 30, 2017 1 / 22 Summary so far We analysed the spring-mass system and found that its motion is governed by: mẍ(t) + kx(t) = 0 k y m x x
Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3.12 in Boas)
 Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3 in Boas) As suggested in Lecture 8 the formalism of eigenvalues/eigenvectors has many applications in physics, especially in
Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3 in Boas) As suggested in Lecture 8 the formalism of eigenvalues/eigenvectors has many applications in physics, especially in
Free vibration analysis of elastically connected multiple-beams with general boundary conditions using improved Fourier series method
 Free vibration analysis of elastically connected multiple-beams with general boundary conditions using improved Fourier series method Jingtao DU*; Deshui XU; Yufei ZHANG; Tiejun YANG; Zhigang LIU College
Free vibration analysis of elastically connected multiple-beams with general boundary conditions using improved Fourier series method Jingtao DU*; Deshui XU; Yufei ZHANG; Tiejun YANG; Zhigang LIU College
DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 41514
 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 454 PROJECT : Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Holistic Overview of the Project Steps & Their Conceptual Links
DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 454 PROJECT : Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Holistic Overview of the Project Steps & Their Conceptual Links
TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A. By Tom Irvine February 25, 2008
 TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com February 5, 008 Introduction Consider a base plate mass m and an avionics mass m modeled as two-degree-of-freedom.
TWO-STAGE ISOLATION FOR HARMONIC BASE EXCITATION Revision A By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com February 5, 008 Introduction Consider a base plate mass m and an avionics mass m modeled as two-degree-of-freedom.
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 10 Homework
 Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 0 Homework Chapter 0 Questions: 4, 6, 8 Exercises & Problems 6, 3, 6, 4, 45, 5, 5, 7, 8 Answers to Questions: Q 0-4 (a) positive (b) zero (c) negative (d) negative Q 0-6
Physics 4A Solutions to Chapter 0 Homework Chapter 0 Questions: 4, 6, 8 Exercises & Problems 6, 3, 6, 4, 45, 5, 5, 7, 8 Answers to Questions: Q 0-4 (a) positive (b) zero (c) negative (d) negative Q 0-6
Aalto University School of Engineering
 Aalto University School of Engineering Kul-24.4120 Ship Structural Design (P) Lecture 8 - Local and Global Vibratory Response Kul-24.4120 Ship Structures Response Lecture 5: Tertiary Response: Bending
Aalto University School of Engineering Kul-24.4120 Ship Structural Design (P) Lecture 8 - Local and Global Vibratory Response Kul-24.4120 Ship Structures Response Lecture 5: Tertiary Response: Bending
Discrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with Applications
 Discrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with Applications Errata Sheet March 6, 009 Please report any errors you find in the text to Patrick J. Van Fleet at pjvanfleet@stthomas.edu. The
Discrete Wavelet Transformations: An Elementary Approach with Applications Errata Sheet March 6, 009 Please report any errors you find in the text to Patrick J. Van Fleet at pjvanfleet@stthomas.edu. The
WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2011 Mechanical Vibrations, Singiresu S. Rao, 2010 Mechanical Vibrations: Theory and
WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2011 Mechanical Vibrations, Singiresu S. Rao, 2010 Mechanical Vibrations: Theory and
THE subject of the analysis is system composed by
 MECHANICAL VIBRATION ASSIGNEMENT 1 On 3 DOF system identification Diego Zenari, 182160, M.Sc Mechatronics engineering Abstract The present investigation carries out several analyses on a 3-DOF system.
MECHANICAL VIBRATION ASSIGNEMENT 1 On 3 DOF system identification Diego Zenari, 182160, M.Sc Mechatronics engineering Abstract The present investigation carries out several analyses on a 3-DOF system.
Chapter 15. Oscillations
 Chapter 15 Oscillations 15.1 Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillatory Motion: Motion which is periodic in time; motion that repeats itself in time. Examples: SHM: Power line oscillates when the wind blows past.
Chapter 15 Oscillations 15.1 Simple Harmonic Motion Oscillatory Motion: Motion which is periodic in time; motion that repeats itself in time. Examples: SHM: Power line oscillates when the wind blows past.
Oscillations. Oscillations and Simple Harmonic Motion
 Oscillations AP Physics C Oscillations and Simple Harmonic Motion 1 Equilibrium and Oscillations A marble that is free to roll inside a spherical bowl has an equilibrium position at the bottom of the bowl
Oscillations AP Physics C Oscillations and Simple Harmonic Motion 1 Equilibrium and Oscillations A marble that is free to roll inside a spherical bowl has an equilibrium position at the bottom of the bowl
Solutions for homework 5
 1 Section 4.3 Solutions for homework 5 17. The following equation has repeated, real, characteristic roots. Find the general solution. y 4y + 4y = 0. The characteristic equation is λ 4λ + 4 = 0 which has
1 Section 4.3 Solutions for homework 5 17. The following equation has repeated, real, characteristic roots. Find the general solution. y 4y + 4y = 0. The characteristic equation is λ 4λ + 4 = 0 which has
Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams.
 Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02. Rotary Experiment #11: 1-DOF Torsion. 1-DOF Torsion Position Control using QuaRC. Student Manual
 Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02 Rotary Experiment #11: 1-DOF Torsion 1-DOF Torsion Position Control using QuaRC Student Manual Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. PREREQUISITES...1 3. OVERVIEW OF
Rotary Motion Servo Plant: SRV02 Rotary Experiment #11: 1-DOF Torsion 1-DOF Torsion Position Control using QuaRC Student Manual Table of Contents 1. INTRODUCTION...1 2. PREREQUISITES...1 3. OVERVIEW OF
Medical Imaging Signals and Systems Jerry L. Prince and Jonathan M. Links Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006
 i Medical Imaging Signals and Systems Jerry L. Prince and Jonathan M. Links Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006 Errata, Version 1.02, August 8, 2006 This errata applies to the first printing
i Medical Imaging Signals and Systems Jerry L. Prince and Jonathan M. Links Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006 Errata, Version 1.02, August 8, 2006 This errata applies to the first printing
The Damped Pendulum. Physics 211 Lab 3 3/18/2016
 PHYS11 Lab 3 Physics 11 Lab 3 3/18/16 Objective The objective of this lab is to record the angular position of the pendulum vs. time with and without damping. The data is then analyzed and compared to
PHYS11 Lab 3 Physics 11 Lab 3 3/18/16 Objective The objective of this lab is to record the angular position of the pendulum vs. time with and without damping. The data is then analyzed and compared to
Corrections to Quantum Theory for Mathematicians
 Corrections to Quantum Theory for Mathematicians B C H January 2018 Thanks to ussell Davidson, Bruce Driver, John Eggers, Todd Kemp, Benjamin ewis, Jeff Margrave, Alexander Mukhin, Josh asmussen, Peter
Corrections to Quantum Theory for Mathematicians B C H January 2018 Thanks to ussell Davidson, Bruce Driver, John Eggers, Todd Kemp, Benjamin ewis, Jeff Margrave, Alexander Mukhin, Josh asmussen, Peter
2.3 Damping, phases and all that
 2.3. DAMPING, PHASES AND ALL THAT 107 2.3 Damping, phases and all that If we imagine taking our idealized mass on a spring and dunking it in water or, more dramatically, in molasses), then there will be
2.3. DAMPING, PHASES AND ALL THAT 107 2.3 Damping, phases and all that If we imagine taking our idealized mass on a spring and dunking it in water or, more dramatically, in molasses), then there will be
Department of Architecture & Civil Engineering
 MODE ANSWER age: 1 4. The students are given approximately 4 hours of lectures devoted to this topic. Thus the emphasis in the answer must be in demonstrating an understanding of the physical principals
MODE ANSWER age: 1 4. The students are given approximately 4 hours of lectures devoted to this topic. Thus the emphasis in the answer must be in demonstrating an understanding of the physical principals
Chapter 7: Time Domain Analysis
 Chapter 7: Time Domain Analysis Samantha Ramirez Preview Questions How do the system parameters affect the response? How are the parameters linked to the system poles or eigenvalues? How can Laplace transforms
Chapter 7: Time Domain Analysis Samantha Ramirez Preview Questions How do the system parameters affect the response? How are the parameters linked to the system poles or eigenvalues? How can Laplace transforms
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Somnath Bharadwaj and S. Pratik Khastgir Department of Physics and Meteorology IIT Kharagpur Module : Oscillations Lecture : Oscillations Oscillations are ubiquitous. It would be
Oscillations and Waves Somnath Bharadwaj and S. Pratik Khastgir Department of Physics and Meteorology IIT Kharagpur Module : Oscillations Lecture : Oscillations Oscillations are ubiquitous. It would be
2. page 13*, righthand column, last line of text, change 3 to 2,... negative slope of 2 for 1 < t 2: Now... REFLECTOR MITTER. (0, d t ) (d r, d t )
 SP First ERRATA. These are mostly typos, but there are a few crucial mistakes in formulas. Underline is not used in the book, so I ve used it to denote changes. JHMcClellan, February 3, 00. page 0*, Figure
SP First ERRATA. These are mostly typos, but there are a few crucial mistakes in formulas. Underline is not used in the book, so I ve used it to denote changes. JHMcClellan, February 3, 00. page 0*, Figure
JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE Jeppiaar Nagar, Rajiv Gandhi Salai 600 119 DEPARTMENT OFMECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER ME6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Regulation 013 SUBJECT YEAR /SEM: III
JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE Jeppiaar Nagar, Rajiv Gandhi Salai 600 119 DEPARTMENT OFMECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER ME6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Regulation 013 SUBJECT YEAR /SEM: III
Laboratory handouts, ME 340
 Laboratory handouts, ME 34 This document contains summary theory, solved exercises, prelab assignments, lab instructions, and report assignments for Lab 6. 214-216 Harry Dankowicz, unless otherwise noted
Laboratory handouts, ME 34 This document contains summary theory, solved exercises, prelab assignments, lab instructions, and report assignments for Lab 6. 214-216 Harry Dankowicz, unless otherwise noted
Part D: Frames and Plates
 Part D: Frames and Plates Plane Frames and Thin Plates A Beam with General Boundary Conditions The Stiffness Method Thin Plates Initial Imperfections The Ritz and Finite Element Approaches A Beam with
Part D: Frames and Plates Plane Frames and Thin Plates A Beam with General Boundary Conditions The Stiffness Method Thin Plates Initial Imperfections The Ritz and Finite Element Approaches A Beam with
Chapter 13: Oscillatory Motions
 Chapter 13: Oscillatory Motions Simple harmonic motion Spring and Hooe s law When a mass hanging from a spring and in equilibrium, the Newton s nd law says: Fy ma Fs Fg 0 Fs Fg This means the force due
Chapter 13: Oscillatory Motions Simple harmonic motion Spring and Hooe s law When a mass hanging from a spring and in equilibrium, the Newton s nd law says: Fy ma Fs Fg 0 Fs Fg This means the force due
NATURAL MODES OF VIBRATION OF BUILDING STRUCTURES CE 131 Matrix Structural Analysis Henri Gavin Fall, 2006
 NATURAL MODES OF VIBRATION OF BUILDING STRUCTURES CE 131 Matrix Structural Analysis Henri Gavin Fall, 006 1 Mass and Stiffness Matrices Consider a building frame modeled by a set of rigid, massive flos
NATURAL MODES OF VIBRATION OF BUILDING STRUCTURES CE 131 Matrix Structural Analysis Henri Gavin Fall, 006 1 Mass and Stiffness Matrices Consider a building frame modeled by a set of rigid, massive flos
FREE VIBRATIONS OF FRAMED STRUCTURES WITH INCLINED MEMBERS
 FREE VIBRATIONS OF FRAMED STRUCTURES WITH INCLINED MEMBERS A Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Technology in Civil Engineering By JYOTI PRAKASH SAMAL
FREE VIBRATIONS OF FRAMED STRUCTURES WITH INCLINED MEMBERS A Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Technology in Civil Engineering By JYOTI PRAKASH SAMAL
Errata and suggested changes for Understanding Advanced Statistical Methods, by Westfall and Henning
 Errata and suggested changes for Understanding Advanced Statistical Methods, by Westfall and Henning Special thanks to Robert Jordan and Arkapravo Sarkar for suggesting and/or catching many of these. p.
Errata and suggested changes for Understanding Advanced Statistical Methods, by Westfall and Henning Special thanks to Robert Jordan and Arkapravo Sarkar for suggesting and/or catching many of these. p.
Driven Harmonic Oscillator
 Driven Harmonic Oscillator Physics 6B Lab Experiment 1 APPARATUS Computer and interface Mechanical vibrator and spring holder Stands, etc. to hold vibrator Motion sensor C-209 spring Weight holder and
Driven Harmonic Oscillator Physics 6B Lab Experiment 1 APPARATUS Computer and interface Mechanical vibrator and spring holder Stands, etc. to hold vibrator Motion sensor C-209 spring Weight holder and
EFFECTIVE MODAL MASS & MODAL PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F
 EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com March 9, 1 Introduction The effective modal mass provides a method for judging the significance of a vibration
EFFECTIVE MODA MASS & MODA PARTICIPATION FACTORS Revision F By Tom Irvine Email: tomirvine@aol.com March 9, 1 Introduction The effective modal mass provides a method for judging the significance of a vibration
Math 4263 Homework Set 1
 Homework Set 1 1. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2u t + 3u x = 0 u (x, 0) = sin (x) u x + e x u y = 0 u (0, y) = y 2 3. (a) Find the curves γ : t (x (t), y (t)) such that that
Homework Set 1 1. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2. Solve the following PDE/BVP 2u t + 3u x = 0 u (x, 0) = sin (x) u x + e x u y = 0 u (0, y) = y 2 3. (a) Find the curves γ : t (x (t), y (t)) such that that
Oscillatory Motion SHM
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
Elementary Statistics for Geographers, 3 rd Edition
 Errata Elementary Statistics for Geographers, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1 p. 31: 1 st paragraph: 1 st line: 20 should be 22 Chapter 2 p. 41: Example 2-1: 1 st paragraph: last line: Chapters 2, 3, and 4 and
Errata Elementary Statistics for Geographers, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1 p. 31: 1 st paragraph: 1 st line: 20 should be 22 Chapter 2 p. 41: Example 2-1: 1 st paragraph: last line: Chapters 2, 3, and 4 and
Examiner: D. Burbulla. Aids permitted: Formula Sheet, and Casio FX-991 or Sharp EL-520 calculator.
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Solutions to Final Examination, June 017 Duration: and 1/ hrs First Year - CHE, CIV, CPE, ELE, ENG, IND, LME, MEC, MMS MAT187H1F - Calculus
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Solutions to Final Examination, June 017 Duration: and 1/ hrs First Year - CHE, CIV, CPE, ELE, ENG, IND, LME, MEC, MMS MAT187H1F - Calculus
Estimation of dynamic characteristics of a spring-mass-beam system
 Shock and Vibration 14 (2007) 271 282 271 IOS Press Estimation of dynamic characteristics of a spring-mass-beam system Ding Zhou a,b, and Tianjian Ji b a College of Civil Engineering, Nanjing University
Shock and Vibration 14 (2007) 271 282 271 IOS Press Estimation of dynamic characteristics of a spring-mass-beam system Ding Zhou a,b, and Tianjian Ji b a College of Civil Engineering, Nanjing University
PH.D. PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering FALL SEMESTER 2014 Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials NAME PH.D. PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Problem
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering FALL SEMESTER 2014 Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials NAME PH.D. PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS Problem
