Investigation of a Ball Screw Feed Drive System Based on Dynamic Modeling for Motion Control
|
|
|
- Cecily Glenn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Investigation of a Ball Screw Feed Drive System Based on Dynamic Modeling for Motion Control Yi-Cheng Huang *, Xiang-Yuan Chen Department of Mechatronics Engineering, National Changhua University of Education, Changhua, Taiwan. Received 1 Feruary 216; received in revised form 28 April 216; accepted 2 May 216 Astract This paper examines the frequency response relationship etween the all screw nut preload, all screw torsional stiffness variations and tale mass effect for a single-axis feed drive system. Identification for the frequency response of an industrial all screw drive system is very important for the precision motion when the viration modes of the system are critical for controller design. In this study, there is translation and rotation modes of a all screw feed drive system when positioning tale is actuated y a servo motor. A lumped dynamic model to study the all nut preload variation and torsional stiffness of the all screw drive system is derived first. The mathematical modeling and numerical simulation provide the information of peak frequency response as the different levels of all nut preload, all screw torsional stiffness and tale mass. The trend of increasing preload will indicate the arupt peak change in frequency response spectrum analysis in some mode shapes. This study provides an approach to investigate the dynamic frequency response of a all screw drive system, which provides significant information fo r etter control performance when precise motion control is concerned. Keywords: Ball nut preload, all screw drive system, dynamic modeling 1. Introduction Precision computer numerical control (CNC) machines are widely used in modern industry for mass production. The all screws are widely applied in the linear actuators of machinery and equipment ecause of the high efficiency, less acklash, easy lurication, and easy maintenance. Since all screw play a significant role in converting rotary motion into linear mot ion Preloading is effective to eliminate acklash and increase the stiffness of all screw for precision motion concerns. The dynamic frequency responses of the feed drive system depends on the stiffness cominations of the all screw, all nut, fixed support earings, the flexile coupler and the stiffness etween the all screw and the working tale. Such frequency response results from the axial mode shapes and torsional mode shape of the all screw drive system when it is actuated y servo motor. Each mode shape affects and determines the motion control frequency response andwidth when the control speed is limited and ecomes a critical issue. The working tale mass and the olt stiffness etween the machine ed ase and attached ground floor also plays an important role for the frequency response when the viration mode of the CNC machine is concerned with precision accuracy. As in intelligent control field, the control signals that fed into the controlled plant are ased on the feedack control error that should e learnale. Therefore, some control efforts [1-2] are focused the design of the andwidth of the filter that can filter out the un-learnale errors contents and can e get ack to control system for ettering control history. Since the andwidth of controlled system determines the motion speed response and its performance. The lumped dynamic model derivation is significant in determining the andwidth for motion control law that can e used for controller design. Since such frequency contents of compensated error are suggested to e within the andwidth when control signals are actuating. This paper will derive the dynamic model of the all screw feed drive system first and examine the relationship etween the all screw preload variation, all screw torsional stiffness and effect of tale mass. * Corresponding author, ychuang@cc.ncue.edu.tw 29
2 Simulation results will unveil the frequency response of the translational and torsional peak modes. Numerical simulation shows stale convergence y using hyrid particle swarm optimization of iterative learning control [2] on this developed all screw drive system. 2. Mathematical Model and Numerical Simulation 2.1. Dynamic Model of the Ball Screw Drive System To model the feed drive system, this paper set differnt stiffness of the all nut stiffness for different preload etween the all screw shaft and the all nut. The presetting preload value can e deployed y inserting different all size for single all nut design or using disk spring that applied to the all screw when doule all nut is the preference. Fig. 1 shows the picture of the in-la single-axis feed drive platform. To analyze the dynamic characteristic of the all screw system under different preload and varying tale mass, the feed drive system is modeled y a lumped parameter system shown in Fig. 2. Fig. 2 is the schematic illustration for the single-axis all screw feed drive system. In general, mechanical systems have three passive linear components. The spring and the mass are energy-storage elements, while the viscous damper is the dissipated energy. Both of the rotational and translation mechanical system modeled elow are actuated y the servo motor torque, indicated as T. As the same derivation in [3], the overall stiffness of a all screw feed drive system can e determined y the stiffness of the all screw itself, which is comprised of the all screw shaft, the all nut, supporting earings of the all screw, and the stiffness etween the all screw and the working tale. M t X t B t ( X t ) K n ( R X X t ) Rearranging Eqs (1)-(4), we have M t X t M [ X ] + J θ J m [ θ m] B t X t B [ X ] + Q θ Q m [ θ m] K n K n K n R K n K e + K n K n R K n R K n R K g + K n R 2 K g [ K g K g ] X t X [ θ ] = [ ] θ m T where the stiffness matrix is different from [3]. Fig. 1 The in-house single axis platform (4) (5) J m m Q m m K g ( m ) T J θ m + Q m θ + R [K n (R θ + X X t )] = K g (θ m θ ) M X + B (X ) + K e (X ) + K n (R θ + X X t ) = (1) (2) (3) Fig. 2 Illustration for the schematic diagram of the single-axis lumped parameters all screw drive system Copyright TAETI 3
3 2.2. Numerical Simulation Tale 1 list the simulated parameters and associated values used in Eqs (1)-(4). The dynamic equation of the single-axis feed drive system model with varied preload and tale mass can e expressed in a compact form: [M]{u } + [C]{u } + [K]{u} = f (6) where [M], [C], and [K] are the 4x4 square matrices, referred as the mass (or the moment of inertia), the viscous damping, and the stiffness matrices, respectively. {u} represents a four degree of freedom model. It consists with the X t, X, θ, and θ m for the displacement of the working tale, axial displacement of the all screw, rotation angle of the all screw, and the rotation angle of the motor, respectively. Tale 1 Important parameters of all screw drive system Parameters value working tale mass (Mt) 47.9Kg all screw mass (M) 9Kg inertia moment of the motor (Jm) kgm 2 inertia moment of the all screw (J) kgm 2 equivalent axial stiffness of all screw shaft (Ke) N/m stiffness of the all nut (Kn) N/m torsional stiffness of the all screw (Kg) N/m viscous damping coefficient of the guide way of the working 1N s/m tale (Bt) viscous damping coefficient of the supporting earing of the all 1N s/m screw (B) rotational viscous damping coefficient of the motor (Qm) N ms rotational viscous damping coefficient of the support earing of N ms all screw (Q) angle conversion axial displacement of the constant (R).25 motor torque (T) Nm/s 2 displacement of the working tale (Xt) State Variale (m) axial displacement of the all screw (X) State Variale (m) rotation angle of the motor (θm) State Variale (rad) rotation angle of the all screw (θ) State Variale (rad) The homogeneous solution of Eqs (5) represents the transient response of the lumped system whereas the forcing function of applied motor torque renders the tale positioning. Homogeneous solution of the Equation (2.1.5) results in four eigenvectors V1, V2, V3, and V4 associated with each eigenvalue ( λ = ω 2 ) of , , , (rad 2 /s 2 ) V1={ }V2={ } V3 ={ }V4={ } (7) The four eigenvectors corresponding to the Eigen frequencies of Hz, Hz, 5259 Hz, 93.9 Hz w is calculated y 2% of the rated dynamic load. These eigenvectors represent the mode shapes of the all screw feed drive system. The first three significant Eigen frequencies are related to the three resonant frequencies. The first and second modes are from the axial viration. The third mode is from the torsional viration. In Eqs (7), the first mode of the working tale and the all screw is moving in phase while the second mode is moving out of phase. Fig. 3 shows the ode plot of the dynamic system ased on different K n values. The preload variation is simulated from 2%, 4%, 6%, 8% to 1% of the rated dynamic loading of the all screw. Fig. 3 Bode plot of the all screw drive system ased on the preload value of 2%(lue), 4%(green), 6%(red), 8%(cyan) and 1%(purple) of the rated dynamic loading 31 Copyright TAETI
4 Enlargement of the first, second and third modes of the ode plot, the three frequencies are ranging from 3.5 Hz to 3.8 Hz, 294 Hz to 38 Hz and 52 Hz to 55 Hz respectively. It is ovious that the second translational mode will e affected more than the first mode when the all nut preload is varying. The solution of the fourth mode is aout 93 Hz, the contriution of this mode is not significant even though the preload is varied. the all screw is investigated y calculating K g y πd r 4 G/32L. Fig. 7 shows the variations of Kg in the range of ± 1%. As shown, the third mode demonstrates large frequency shift with increasing the torsional stiffness of the all screw. Fig. 8 indicates the frequency shift is range from 57 Hz to 58 Hz, while the first and second modes are not changed noticealy. Fig. 4 The enlargement of the first mode of the ode plot in Fig. 3 ased on different all nut stiffness Fig. 7 Bode plot of the all screw torsional stiffness 1%( lue), 15%(green), 11%(red), 95%(cyan), 9%( purple) Fig. 5 The enlargement of the second mode of the ode plot in Fig. 3 ased on different all ut stiffness Fig. 6 The enlargement of the third mode of ode plot in Fig. 3 ased on different all nut stiffness As stated, the third eigenvector indicates the torsional viration. Since the servo motor drives the all screw through a coupler providing damping and stiffness. The torsional stiffness of Fig. 8 The enlargement of the torsional mode of the ode plot in Fig. 7 ased on different all screw torsional stiffness Figs detail the effect of the tale mass. The characteristic frequency shifts from the 24Hz to 3.5Hz when the tale mass increases from 47.9 kg to kg. As predicted, the tale mass preserves the effect on the first andwidth in the translational mode and some effect on the second mode. Increasing tale mass does not affect the andwidth of the third torsional mode. Fig. 12 shows the numerical simulation plot of the convergence error when the all screw drive system is controlled y hyrid particle swarm optimization for the dynamic andwidth tuning of an iterative learning control. Copyright TAETI 32
5 3. Conclusions Fig. 9 Bode plot of the working tale mass 47.9Kg(lue), 7.63Kg(green), 94.18Kg(red) Fig. 1 The enlargement of the first mode of the ode plot in Fig. 9 ased on different working tale mass A lumped dynamic model for descriing different all nut preload level, all screw torsional stiffnesss and the tale mass effects of the all screw feed drive system is derived and numerically simulated. Based on the different percent of the preload and tale mass, the frequency spectrum analysis of the nu merical simulation provides the limits and constraints of andwidth tuning for motion control applications. The preload variation can e diagnosed y the peak frequency change and the magnitude of the peak frequency in a specific frequency range when the axial mode or the torsional mode is excited. The derivation and numerical simulation results of the lumped dynamic model provides significant information in determining the zero phase andwidth tuning. Application of a hyrid particle swarm optimization iterative learning control law deploys successfully when the frequency contents of the compensated error was constrained in every control actuation. Acknowledgement This work was supported y MOST Grant E for which the authors are very much grateful. References Fig. 11 The enlargement of the second mode of the ode plot in Fig. 9 ased on different working tale mass Fig. 12 Plot of a convergence error of the numerical s imulation y using HPSO-ILC [2] for all screw drive system [1] M. S. Tsai, C. L. Yen, and H. T. Yau, Integration of an empirical mode decomposition algorith m with iterative learn ing control for high-precision machining, IEEE/ASME Transaction on Mechatronic, vol. 18, no. 3, pp , 213. [2] Y. C. Huang, Y. W. Su, and P. C. Chuo, Iterative learning control andwidth tuning using the particle s warm optimization technique for high precis ion motion, Microsystem Technologies. DOI: 1.17/ s , 215. [3] G. H. Feng and Y. L. Pan, Investigation of all screw preload variation ased on dynamic modeling of a preload adjustale feed-drive system and spectrum analysis of all-nuts sensed viration s ignals, International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, vol. 52, no. 1, pp , Copyright TAETI
a) Find the equation of motion of the system and write it in matrix form.
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION
 1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
Design Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of High-Speed Motorized Spindle Systems Considering High-Speed Effects
 Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation August 5-8, 2007, Harin, China Design Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of High-Speed Motorized Spindle Systems Considering
Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation August 5-8, 2007, Harin, China Design Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of High-Speed Motorized Spindle Systems Considering
ASEISMIC DESIGN OF TALL STRUCTURES USING VARIABLE FREQUENCY PENDULUM OSCILLATOR
 ASEISMIC DESIGN OF TALL STRUCTURES USING VARIABLE FREQUENCY PENDULUM OSCILLATOR M PRANESH And Ravi SINHA SUMMARY Tuned Mass Dampers (TMD) provide an effective technique for viration control of flexile
ASEISMIC DESIGN OF TALL STRUCTURES USING VARIABLE FREQUENCY PENDULUM OSCILLATOR M PRANESH And Ravi SINHA SUMMARY Tuned Mass Dampers (TMD) provide an effective technique for viration control of flexile
Dynamic analysis of the Empact CVT Ratio and slip dependent, non-minimum phase dynamics
 Dynamic analysis of the Empact CVT Ratio and slip dependent, non-minimum phase dynamics T.W.G.L. Klaassen, B.G. Vroemen and M. Steinbuch Eindhoven University of Technology, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Dynamic analysis of the Empact CVT Ratio and slip dependent, non-minimum phase dynamics T.W.G.L. Klaassen, B.G. Vroemen and M. Steinbuch Eindhoven University of Technology, Department of Mechanical Engineering
PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION, MODELING, AND SIMULATION OF A CART AND PENDULUM
 PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION, MODELING, AND SIMULATION OF A CART AND PENDULUM Erin Bender Mechanical Engineering Erin.N.Bender@Rose-Hulman.edu ABSTRACT In this paper a freely rotating pendulum suspended from
PARAMETER IDENTIFICATION, MODELING, AND SIMULATION OF A CART AND PENDULUM Erin Bender Mechanical Engineering Erin.N.Bender@Rose-Hulman.edu ABSTRACT In this paper a freely rotating pendulum suspended from
System Parameter Identification for Uncertain Two Degree of Freedom Vibration System
 System Parameter Identification for Uncertain Two Degree of Freedom Vibration System Hojong Lee and Yong Suk Kang Department of Mechanical Engineering, Virginia Tech 318 Randolph Hall, Blacksburg, VA,
System Parameter Identification for Uncertain Two Degree of Freedom Vibration System Hojong Lee and Yong Suk Kang Department of Mechanical Engineering, Virginia Tech 318 Randolph Hall, Blacksburg, VA,
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Chapter a. Spring constant, k : The change in the force per unit length change of the spring. b. Coefficient of subgrade reaction, k:
 Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Precision Ball Screw/Spline
 58-2E Models BNS-A, BNS, NS-A and NS Seal Outer ring Shim plate Seal Spline nut Seal Collar Shim plate Seal End cap Ball Outer ring Ball screw nut Outer ring Ball Retainer Retainer Outer ring Point of
58-2E Models BNS-A, BNS, NS-A and NS Seal Outer ring Shim plate Seal Spline nut Seal Collar Shim plate Seal End cap Ball Outer ring Ball screw nut Outer ring Ball Retainer Retainer Outer ring Point of
Comments on A Time Delay Controller for Systems with Uncertain Dynamics
 Comments on A Time Delay Controller for Systems with Uncertain Dynamics Qing-Chang Zhong Dept. of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College of Science, Technology, and Medicine Exhiition Rd.,
Comments on A Time Delay Controller for Systems with Uncertain Dynamics Qing-Chang Zhong Dept. of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College of Science, Technology, and Medicine Exhiition Rd.,
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping
 A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
Expedient Modeling of Ball Screw Feed Drives
 S. Frey a A. Dadalau a A. Verl a Expedient Modeling of Ball Screw Feed Drives Stuttgart, February 2011 a Institute for Control Engineering of Machine Tools and Manufacturing Units (ISW), University of
S. Frey a A. Dadalau a A. Verl a Expedient Modeling of Ball Screw Feed Drives Stuttgart, February 2011 a Institute for Control Engineering of Machine Tools and Manufacturing Units (ISW), University of
THE subject of the analysis is system composed by
 MECHANICAL VIBRATION ASSIGNEMENT 1 On 3 DOF system identification Diego Zenari, 182160, M.Sc Mechatronics engineering Abstract The present investigation carries out several analyses on a 3-DOF system.
MECHANICAL VIBRATION ASSIGNEMENT 1 On 3 DOF system identification Diego Zenari, 182160, M.Sc Mechatronics engineering Abstract The present investigation carries out several analyses on a 3-DOF system.
Dynamic Analysis on Vibration Isolation of Hypersonic Vehicle Internal Systems
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 55-60 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Dynamic Analysis on Vibration
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 55-60 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Dynamic Analysis on Vibration
In the presence of viscous damping, a more generalized form of the Lagrange s equation of motion can be written as
 2 MODELING Once the control target is identified, which includes the state variable to be controlled (ex. speed, position, temperature, flow rate, etc), and once the system drives are identified (ex. force,
2 MODELING Once the control target is identified, which includes the state variable to be controlled (ex. speed, position, temperature, flow rate, etc), and once the system drives are identified (ex. force,
506. Modeling and diagnostics of gyroscopic rotor
 506. Modeling and diagnostics of gyroscopic rotor V. Barzdaitis 1,a, M. Bogdevičius 2,, R. Didžiokas 3,c, M. Vasylius 3,d 1 Kaunas University of Technology, Department of Engineering Mechanics, Donelaičio
506. Modeling and diagnostics of gyroscopic rotor V. Barzdaitis 1,a, M. Bogdevičius 2,, R. Didžiokas 3,c, M. Vasylius 3,d 1 Kaunas University of Technology, Department of Engineering Mechanics, Donelaičio
Final Exam April 30, 2013
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
MOOC QP Set 2 Principles of Vibration Control
 Section I Section II Section III MOOC QP Set 2 Principles of Vibration Control (TOTAL = 100 marks) : 20 questions x 1 mark/question = 20 marks : 20 questions x 2 marks/question = 40 marks : 8 questions
Section I Section II Section III MOOC QP Set 2 Principles of Vibration Control (TOTAL = 100 marks) : 20 questions x 1 mark/question = 20 marks : 20 questions x 2 marks/question = 40 marks : 8 questions
DESIGN SUPPORT FOR MOTION CONTROL SYSTEMS Application to the Philips Fast Component Mounter
 DESIGN SUPPORT FOR MOTION CONTROL SYSTEMS Application to the Philips Fast Component Mounter Hendri J. Coelingh, Theo J.A. de Vries and Jo van Amerongen Dreel Institute for Systems Engineering, EL-RT, University
DESIGN SUPPORT FOR MOTION CONTROL SYSTEMS Application to the Philips Fast Component Mounter Hendri J. Coelingh, Theo J.A. de Vries and Jo van Amerongen Dreel Institute for Systems Engineering, EL-RT, University
Manufacturing Equipment Control
 QUESTION 1 An electric drive spindle has the following parameters: J m = 2 1 3 kg m 2, R a = 8 Ω, K t =.5 N m/a, K v =.5 V/(rad/s), K a = 2, J s = 4 1 2 kg m 2, and K s =.3. Ignore electrical dynamics
QUESTION 1 An electric drive spindle has the following parameters: J m = 2 1 3 kg m 2, R a = 8 Ω, K t =.5 N m/a, K v =.5 V/(rad/s), K a = 2, J s = 4 1 2 kg m 2, and K s =.3. Ignore electrical dynamics
Hybrid modelling and simulation of a computer numerical control machine tool feed drive
 1 Hybrid modelling and simulation of a computer numerical control machine tool feed drive C Pislaru*,DGFordand G Holroyd Ultra Precision Engineering Centre, University of Huddersfield, UK Abstract: The
1 Hybrid modelling and simulation of a computer numerical control machine tool feed drive C Pislaru*,DGFordand G Holroyd Ultra Precision Engineering Centre, University of Huddersfield, UK Abstract: The
Speed Control of Torsional Drive Systems with Backlash
 Speed Control of Torsional Drive Systems with Backlash S.Thomsen, F.W. Fuchs Institute of Power Electronics and Electrical Drives Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel, D-2443 Kiel, Germany Phone: +49
Speed Control of Torsional Drive Systems with Backlash S.Thomsen, F.W. Fuchs Institute of Power Electronics and Electrical Drives Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel, D-2443 Kiel, Germany Phone: +49
Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #02: DC Motor Position Control. DC Motor Control Trainer (DCMCT) Student Manual
 Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #02: DC Motor Position Control DC Motor Control Trainer (DCMCT) Student Manual Table of Contents 1 Laboratory Objectives1 2 References1 3 DCMCT Plant
Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #02: DC Motor Position Control DC Motor Control Trainer (DCMCT) Student Manual Table of Contents 1 Laboratory Objectives1 2 References1 3 DCMCT Plant
3D Finite Element Modeling and Vibration Analysis of Gas Turbine Structural Elements
 3D Finite Element Modeling and Vibration Analysis of Gas Turbine Structural Elements Alexey I. Borovkov Igor A. Artamonov Computational Mechanics Laboratory, St.Petersburg State Polytechnical University,
3D Finite Element Modeling and Vibration Analysis of Gas Turbine Structural Elements Alexey I. Borovkov Igor A. Artamonov Computational Mechanics Laboratory, St.Petersburg State Polytechnical University,
Backlash Estimation of a Seeker Gimbal with Two-Stage Gear Reducers
 Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2003) 21:604 611 Ownership and Copyright 2003 Springer-Verlag London Limited Backlash Estimation of a Seeker Gimbal with Two-Stage Gear Reducers J. H. Baek, Y. K. Kwak and S. H.
Int J Adv Manuf Technol (2003) 21:604 611 Ownership and Copyright 2003 Springer-Verlag London Limited Backlash Estimation of a Seeker Gimbal with Two-Stage Gear Reducers J. H. Baek, Y. K. Kwak and S. H.
WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2011 Mechanical Vibrations, Singiresu S. Rao, 2010 Mechanical Vibrations: Theory and
WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2011 Mechanical Vibrations, Singiresu S. Rao, 2010 Mechanical Vibrations: Theory and
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump
 An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum
 STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum Overview of Structural Dynamics Structure Members, joints, strength, stiffness, ductility Structure
STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum Overview of Structural Dynamics Structure Members, joints, strength, stiffness, ductility Structure
ROLLER BEARING FAILURES IN REDUCTION GEAR CAUSED BY INADEQUATE DAMPING BY ELASTIC COUPLINGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIONS
 ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
Introduction to structural dynamics
 Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Design and Analysis of Silicon Resonant Accelerometer
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(3): 970-974, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; E-ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Sumitted: June 22, 2012 Accepted: July 23,
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 5(3): 970-974, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; E-ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Sumitted: June 22, 2012 Accepted: July 23,
1820. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation
 8. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation Tomasz Matyja, Bogusław Łazarz Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Gliwice, Poland Corresponding author
8. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation Tomasz Matyja, Bogusław Łazarz Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Gliwice, Poland Corresponding author
Engineering Science OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Mechatronics Engineering. Li Wen
 Mechatronics Engineering Li Wen Bio-inspired robot-dc motor drive Unstable system Mirko Kovac,EPFL Modeling and simulation of the control system Problems 1. Why we establish mathematical model of the control
Mechatronics Engineering Li Wen Bio-inspired robot-dc motor drive Unstable system Mirko Kovac,EPFL Modeling and simulation of the control system Problems 1. Why we establish mathematical model of the control
Fatigue Failure Analysis of a Cooling Fan Blade: A Case Study
 Fatigue Failure Analysis of a Cooling Fan Blade: A Case Study Triloki Nath Kushwaha * NTPC Limited,Farakka,742236,india Email:-tnkushwaha@ntpc.co.in Astract Cooling tower (CT) fan lade are long in size
Fatigue Failure Analysis of a Cooling Fan Blade: A Case Study Triloki Nath Kushwaha * NTPC Limited,Farakka,742236,india Email:-tnkushwaha@ntpc.co.in Astract Cooling tower (CT) fan lade are long in size
557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer
 557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer M. Sivčák 1, J. Škoda, Technical University in Liberec, Studentská, Liberec, Czech Republic e-mail: 1 michal.sivcak@tul.cz; jan.skoda@pevnosti.cz
557. Radial correction controllers of gyroscopic stabilizer M. Sivčák 1, J. Škoda, Technical University in Liberec, Studentská, Liberec, Czech Republic e-mail: 1 michal.sivcak@tul.cz; jan.skoda@pevnosti.cz
Precision tracking control of a horizontal arm coordinate measuring machine in the presence of dynamic flexibilities
 Int J Adv Manuf Technol 2006) 27: 960 968 DOI 10.1007/s00170-004-2292-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tugrul Özel Precision tracking control of a horizontal arm coordinate measuring machine in the presence of dynamic
Int J Adv Manuf Technol 2006) 27: 960 968 DOI 10.1007/s00170-004-2292-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tugrul Özel Precision tracking control of a horizontal arm coordinate measuring machine in the presence of dynamic
! 2 = k a ! = 125, Problems and Solutions Section 5.3 (5.27 through 5.36)
 5 3 Problems and Solutions Section 53 57 through 536) 57 A motor is mounted on a platform that is observed to vibrate excessively at an operating speed of 6000 rpm producing a 50N force Design a vibration
5 3 Problems and Solutions Section 53 57 through 536) 57 A motor is mounted on a platform that is observed to vibrate excessively at an operating speed of 6000 rpm producing a 50N force Design a vibration
Energy balance in self-powered MR damper-based vibration reduction system
 BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES, Vol. 59, No. 1, 2011 DOI: 10.2478/v10175-011-0011-4 Varia Energy balance in self-powered MR damper-based vibration reduction system J. SNAMINA
BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES, Vol. 59, No. 1, 2011 DOI: 10.2478/v10175-011-0011-4 Varia Energy balance in self-powered MR damper-based vibration reduction system J. SNAMINA
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser
 Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
Modal Analysis: What it is and is not Gerrit Visser What is a Modal Analysis? What answers do we get out of it? How is it useful? What does it not tell us? In this article, we ll discuss where a modal
INVESTIGATION OF BALL SCREWS FOR FEED DRIVE 1. INTRODUCTION
 Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 3, No. 4, 203 ball screws, machine tools, rigidity, impact forces Jerzy Z. SOBOLEWSKI INVESTIGATION OF BALL SCEWS FO FEED DIVE The paper presents a method which enables
Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 3, No. 4, 203 ball screws, machine tools, rigidity, impact forces Jerzy Z. SOBOLEWSKI INVESTIGATION OF BALL SCEWS FO FEED DIVE The paper presents a method which enables
ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010
 ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010 PROBLEM 1: You are given the lumped parameter dynamic differential equations of motion for a two degree-offreedom model of an automobile suspension system for small
ME 563 HOMEWORK # 5 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010 PROBLEM 1: You are given the lumped parameter dynamic differential equations of motion for a two degree-offreedom model of an automobile suspension system for small
Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Applied and Computational Mechanics 3 (2009) 331 338 Mathematical Modeling and Dynamic Simulation of a Class of Drive Systems with Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors M. Mikhov a, a Faculty of Automatics,
Laboratory 11 Control Systems Laboratory ECE3557. State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Joint
 Laboratory 11 State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Joint 11.1 Objective The objective of this laboratory is to design a full state feedback controller for endpoint position control
Laboratory 11 State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Joint 11.1 Objective The objective of this laboratory is to design a full state feedback controller for endpoint position control
Application of a novel method to identify multi-axis joint properties
 Application of a novel method to identify multi-axis joint properties Scott Noll, Jason Dreyer, and Rajendra Singh The Ohio State University, 219 W. 19 th Avenue, Columbus, Ohio 4321 USA ABSTRACT This
Application of a novel method to identify multi-axis joint properties Scott Noll, Jason Dreyer, and Rajendra Singh The Ohio State University, 219 W. 19 th Avenue, Columbus, Ohio 4321 USA ABSTRACT This
Analysis of a High-Precision Grinding Machine
 ISSN 47-98 International Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering Research (IJETER), Vol. No.1, Pages : 1 16 (015) Analysis of a High-Precision Grinding Machine Seon-Yeol Oh 1, Joon Jang, Woo Chun Choi
ISSN 47-98 International Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering Research (IJETER), Vol. No.1, Pages : 1 16 (015) Analysis of a High-Precision Grinding Machine Seon-Yeol Oh 1, Joon Jang, Woo Chun Choi
Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3
 - 1 - Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3 In version 4.3 nonlinear rolling element bearings can be considered for transient analyses. The nonlinear forces are calculated with a
- 1 - Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3 In version 4.3 nonlinear rolling element bearings can be considered for transient analyses. The nonlinear forces are calculated with a
Dynamics of Structures
 Dynamics of Structures Elements of structural dynamics Roberto Tomasi 11.05.2017 Roberto Tomasi Dynamics of Structures 11.05.2017 1 / 22 Overview 1 SDOF system SDOF system Equation of motion Response spectrum
Dynamics of Structures Elements of structural dynamics Roberto Tomasi 11.05.2017 Roberto Tomasi Dynamics of Structures 11.05.2017 1 / 22 Overview 1 SDOF system SDOF system Equation of motion Response spectrum
Section 8.5. z(t) = be ix(t). (8.5.1) Figure A pendulum. ż = ibẋe ix (8.5.2) (8.5.3) = ( bẋ 2 cos(x) bẍ sin(x)) + i( bẋ 2 sin(x) + bẍ cos(x)).
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 8.5 Applications: Pendulums Mass-Spring Systems In this section we will investigate two applications of our work in Section 8.4. First, we will consider
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 8.5 Applications: Pendulums Mass-Spring Systems In this section we will investigate two applications of our work in Section 8.4. First, we will consider
Mechatronics Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Case-Study Exercise
 Mechatronics Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Case-Study Exercise Goal: This exercise is designed to take a real-world problem and apply the modeling and analysis concepts discussed in class. As
Mechatronics Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Case-Study Exercise Goal: This exercise is designed to take a real-world problem and apply the modeling and analysis concepts discussed in class. As
Dynamic stiffness compensation with active aerostatic thrust bearings
 Dynamic stiffness compensation with active aerostatic thrust bearings G. Aguirre, F. Al-Bender, H. Van Brussel K.U.Leuven, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Celestijnenlaan 300 B, B-3001, Heverlee,
Dynamic stiffness compensation with active aerostatic thrust bearings G. Aguirre, F. Al-Bender, H. Van Brussel K.U.Leuven, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Celestijnenlaan 300 B, B-3001, Heverlee,
SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 1. Position Control. Student Handout
 SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 1 Position Control Student Handout SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 1 Position Control Student Handout 1. Objectives The objective in this experiment is to introduce the
SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 1 Position Control Student Handout SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 1 Position Control Student Handout 1. Objectives The objective in this experiment is to introduce the
Numerical simulation of the coil spring and investigation the impact of tension and compression to the spring natural frequencies
 Numerical simulation of the coil spring and investigation the impact of tension and compression to the spring natural frequencies F. D. Sorokin 1, Zhou Su 2 Bauman Moscow State Technical University, Moscow,
Numerical simulation of the coil spring and investigation the impact of tension and compression to the spring natural frequencies F. D. Sorokin 1, Zhou Su 2 Bauman Moscow State Technical University, Moscow,
DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 41514
 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 454 PROJECT : Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Holistic Overview of the Project Steps & Their Conceptual Links
DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY 454 PROJECT : Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Holistic Overview of the Project Steps & Their Conceptual Links
Francisco Paulo Lépore Neto. Marcelo Braga dos Santos. Introduction 1. Nomenclature. Experimental Apparatus and Formulation
 A Procedure for the Parametric Identification of Viscoelastic Dampers Accounting for Preload Francisco Paulo Lépore Neto fplepore@mecanica.ufu.br Federal University of Uberlândia School of Mechanical Engineering
A Procedure for the Parametric Identification of Viscoelastic Dampers Accounting for Preload Francisco Paulo Lépore Neto fplepore@mecanica.ufu.br Federal University of Uberlândia School of Mechanical Engineering
Joint Torque Control for Backlash Compensation in Two-Inertia System
 Joint Torque Control for Backlash Compensation in Two-Inertia System Shota Yamada*, Hiroshi Fujimoto** The University of Tokyo 5--5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba, 227-856 Japan Phone: +8-4-736-3873*, +8-4-736-43**
Joint Torque Control for Backlash Compensation in Two-Inertia System Shota Yamada*, Hiroshi Fujimoto** The University of Tokyo 5--5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa, Chiba, 227-856 Japan Phone: +8-4-736-3873*, +8-4-736-43**
T1 T e c h n i c a l S e c t i o n
 1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
The student will experimentally determine the parameters to represent the behavior of a damped oscillatory system of one degree of freedom.
 Practice 3 NAME STUDENT ID LAB GROUP PROFESSOR INSTRUCTOR Vibrations of systems of one degree of freedom with damping QUIZ 10% PARTICIPATION & PRESENTATION 5% INVESTIGATION 10% DESIGN PROBLEM 15% CALCULATIONS
Practice 3 NAME STUDENT ID LAB GROUP PROFESSOR INSTRUCTOR Vibrations of systems of one degree of freedom with damping QUIZ 10% PARTICIPATION & PRESENTATION 5% INVESTIGATION 10% DESIGN PROBLEM 15% CALCULATIONS
Research on Optimization of Bearing Span of Main Reducer Gear System Based on the Transfer Matrix
 MATEC Web of Conferences 3, () DOI:.5/ matecconf/3 MMME Research on Optimization of Bearing Span of Main Reducer Gear System Based on the Transfer Matrix Feng Yun HUANG, Li TIAN a, Ding WEI and Huan Huan
MATEC Web of Conferences 3, () DOI:.5/ matecconf/3 MMME Research on Optimization of Bearing Span of Main Reducer Gear System Based on the Transfer Matrix Feng Yun HUANG, Li TIAN a, Ding WEI and Huan Huan
Kaunadis [5] analyzed the vibration analysis of cantilever beam in free and forced condition. The cantilever beam was loaded at different locations.
![Kaunadis [5] analyzed the vibration analysis of cantilever beam in free and forced condition. The cantilever beam was loaded at different locations. Kaunadis [5] analyzed the vibration analysis of cantilever beam in free and forced condition. The cantilever beam was loaded at different locations.](/thumbs/90/101585362.jpg) Vibration Analysis of Cantilever Beam: An Experimental Study Mr. P.Kumar 1, Dr. S.Bhaduri 2, Dr. A. Kumar 3 1-3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology Mesra, Jharkhand, India
Vibration Analysis of Cantilever Beam: An Experimental Study Mr. P.Kumar 1, Dr. S.Bhaduri 2, Dr. A. Kumar 3 1-3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology Mesra, Jharkhand, India
Dr Ian R. Manchester Dr Ian R. Manchester AMME 3500 : Review
 Week Date Content Notes 1 6 Mar Introduction 2 13 Mar Frequency Domain Modelling 3 20 Mar Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 27 Mar Block Diagrams Assign 1 Due 5 3 Apr Feedback System Characteristics
Week Date Content Notes 1 6 Mar Introduction 2 13 Mar Frequency Domain Modelling 3 20 Mar Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 27 Mar Block Diagrams Assign 1 Due 5 3 Apr Feedback System Characteristics
Modeling and simulation of multi-disk auto-balancing rotor
 IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Volume, Issue 6, November 6 ISSN (Print): 69-8 ISSN (Online): 69-78 www.ijcsi.org https://doi.org/.9/66.8897 88 Modeling and simulation of multi-disk
IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Volume, Issue 6, November 6 ISSN (Print): 69-8 ISSN (Online): 69-78 www.ijcsi.org https://doi.org/.9/66.8897 88 Modeling and simulation of multi-disk
DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF EARTHQUAKE EXCITED INELASTIC PRIMARY- SECONDARY SYSTEMS
 DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF EARTHQUAKE EXCITED INELASTIC PRIMARY- SECONDARY SYSTEMS Christoph ADAM 1 And Peter A FOTIU 2 SUMMARY The objective of the paper is to investigate numerically the effect of ductile material
DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF EARTHQUAKE EXCITED INELASTIC PRIMARY- SECONDARY SYSTEMS Christoph ADAM 1 And Peter A FOTIU 2 SUMMARY The objective of the paper is to investigate numerically the effect of ductile material
INFLUENCE OF FRICTION PENDULUM SYSTEM ON THE RESPONSE OF BASE ISOLATED STRUCTURES
 Octoer 12-17, 28, Beijing, China INFLUENCE OF FRICTION PENDULUM SYSTEM ON THE RESPONSE OF BASE ISOLATED STRUCTURES M. Garevski 1 and M. Jovanovic 2 1 Director, Professor, Institute of Earthquake Engineering
Octoer 12-17, 28, Beijing, China INFLUENCE OF FRICTION PENDULUM SYSTEM ON THE RESPONSE OF BASE ISOLATED STRUCTURES M. Garevski 1 and M. Jovanovic 2 1 Director, Professor, Institute of Earthquake Engineering
Parameter Design of High Speed Coupling for 6 MW Wind Turbine Considering Torsional Vibration
 Parameter Design of High Speed Coupling for 6 MW Wind Turbine Considering Torsional Vibration JongHun Kang 1, Junwoo Bae 2, Seungkeun Jeong 3, SooKeun Park 4 and Hyoung Woo Lee 1 # 1 Department of Mechatronics
Parameter Design of High Speed Coupling for 6 MW Wind Turbine Considering Torsional Vibration JongHun Kang 1, Junwoo Bae 2, Seungkeun Jeong 3, SooKeun Park 4 and Hyoung Woo Lee 1 # 1 Department of Mechatronics
Analysis of Non-Linear Machine Tool Dynamic Behaviour
 Proceedings of the 5 th Manufacturing Engineering Society International Conference Zaragoza June 13 Analysis of Non-Linear Machine Tool Dynamic Behaviour A. S. Delgado (1), E. Ozturk (), N. Sims (3) (1)
Proceedings of the 5 th Manufacturing Engineering Society International Conference Zaragoza June 13 Analysis of Non-Linear Machine Tool Dynamic Behaviour A. S. Delgado (1), E. Ozturk (), N. Sims (3) (1)
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM J. E. Jam, F. Meisami Composite Materials and Technology Center Tehran, IRAN jejaam@gmail.com N. G. Nia Iran Polymer & Petrochemical Institute, Tehran,
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF TIE-ROD/TIE-BOLT ROTORS USING FEM J. E. Jam, F. Meisami Composite Materials and Technology Center Tehran, IRAN jejaam@gmail.com N. G. Nia Iran Polymer & Petrochemical Institute, Tehran,
Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations
 Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations Bogumil Chiliński 1, Maciej Zawisza 2 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Machine Design Fundamentals,
Modelling of lateral-torsional vibrations of the crank system with a damper of vibrations Bogumil Chiliński 1, Maciej Zawisza 2 Warsaw University of Technology, Institute of Machine Design Fundamentals,
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber
 Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
PROJECT 1 DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 41514
 PROJECT DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 454 Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Ilmar Ferreira Santos, Professor Dr.-Ing., Dr.Techn., Livre-Docente
PROJECT DYNAMICS OF MACHINES 454 Theoretical and Experimental Modal Analysis and Validation of Mathematical Models in Multibody Dynamics Ilmar Ferreira Santos, Professor Dr.-Ing., Dr.Techn., Livre-Docente
Cork Institute of Technology. Summer 2007 Mechanics of Machines (Time: 3 Hours)
 Cork Institute of Technology Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) in Mechanical Engineering- Award Instructions Answer FOUR questions. All questions carry equal marks. (NFQ Level 8) Summer 2007 Mechanics
Cork Institute of Technology Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) in Mechanical Engineering- Award Instructions Answer FOUR questions. All questions carry equal marks. (NFQ Level 8) Summer 2007 Mechanics
Influence of the gap and the friction on trajectory reproduction accuracy in a multiaxis machine with CNC
 Influence of the gap and the friction on trajectory reproduction accuracy in a multiaxis machine with CNC O. V. Pas 1, N. A. Serkov 2 Blagonravov Institute of Engineering Science, Russian Academy of Sciences,
Influence of the gap and the friction on trajectory reproduction accuracy in a multiaxis machine with CNC O. V. Pas 1, N. A. Serkov 2 Blagonravov Institute of Engineering Science, Russian Academy of Sciences,
10 Measurement of Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Transducers
 Chapter 10: Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Measurement Dr. Lufti Al-Sharif (Revision 1.0, 25/5/2008) 1. Introduction This chapter examines the measurement of acceleration, vibration and shock. It starts
Chapter 10: Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Measurement Dr. Lufti Al-Sharif (Revision 1.0, 25/5/2008) 1. Introduction This chapter examines the measurement of acceleration, vibration and shock. It starts
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(7): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 4, 6(7): 44-4 Research Article ISSN : 975-784 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Analysis on static characteristics of linear rolling guide
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 4, 6(7): 44-4 Research Article ISSN : 975-784 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Analysis on static characteristics of linear rolling guide
Random Eigenvalue Problems in Structural Dynamics: An Experimental Investigation
 Random Eigenvalue Problems in Structural Dynamics: An Experimental Investigation S. Adhikari, A. Srikantha Phani and D. A. Pape School of Engineering, Swansea University, Swansea, UK Email: S.Adhikari@swansea.ac.uk
Random Eigenvalue Problems in Structural Dynamics: An Experimental Investigation S. Adhikari, A. Srikantha Phani and D. A. Pape School of Engineering, Swansea University, Swansea, UK Email: S.Adhikari@swansea.ac.uk
2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer
 2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer Chuan Chen 1, Yuhu Yang 2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, P. R. China 1 Corresponding author E-mail: 1 chenchuan1985728@126.com,
2108. Free vibration properties of rotate vector reducer Chuan Chen 1, Yuhu Yang 2 School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, P. R. China 1 Corresponding author E-mail: 1 chenchuan1985728@126.com,
Francisco Paulo Lépore Neto. Marcelo Braga dos Santos. Introduction 1. Nomenclature. Experimental Apparatus and Formulation
 Francisco Paulo Lépore Neto and Marcelo Braga dos Santos Francisco Paulo Lépore Neto fplepore@mecanica.ufu.br Federal University of Uberlandia School of Mechanical Engineering 38408-902 Uberlandia, MG,
Francisco Paulo Lépore Neto and Marcelo Braga dos Santos Francisco Paulo Lépore Neto fplepore@mecanica.ufu.br Federal University of Uberlandia School of Mechanical Engineering 38408-902 Uberlandia, MG,
DESIGN AND VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF SCREW COMPRESSOR
 DESIGN AND VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF SCREW COMPRESSOR Ankita Mozar *1,Komal Mahanavar *2,Snehal Kedar *3 Aboli Barge *4,Asst. Prof. R. S.Lahane *5 1 Dept. Of Mechanical Engineering, D.Y.Patil College Of Engineering,Akurdi,
DESIGN AND VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF SCREW COMPRESSOR Ankita Mozar *1,Komal Mahanavar *2,Snehal Kedar *3 Aboli Barge *4,Asst. Prof. R. S.Lahane *5 1 Dept. Of Mechanical Engineering, D.Y.Patil College Of Engineering,Akurdi,
6) Motors and Encoders
 6) Motors and Encoders Electric motors are by far the most common component to supply mechanical input to a linear motion system. Stepper motors and servo motors are the popular choices in linear motion
6) Motors and Encoders Electric motors are by far the most common component to supply mechanical input to a linear motion system. Stepper motors and servo motors are the popular choices in linear motion
Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams.
 Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
On the Stability Analysis and Modelling of a Multirate Control Direct-Drive Machine Tool Axis Subject to Large Changes in Load Dynamics
 21 American Control Conference Marriott Waterfront, Baltimore, MD, USA June 3-July 2, 21 WeB21.6 On the Stability Analysis and Modelling of a Multirate Control Direct-Drive Machine Tool Axis Subject to
21 American Control Conference Marriott Waterfront, Baltimore, MD, USA June 3-July 2, 21 WeB21.6 On the Stability Analysis and Modelling of a Multirate Control Direct-Drive Machine Tool Axis Subject to
Vibration Analysis of a Horizontal Washing Machine, Part IV: Optimal Damped Vibration Absorber
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Vibration Analysis of a Horizontal Washing Machine, Part IV: Optimal Damped Vibration Absorber Galal Ali Hassaan Department of Mechanical Design & Production, Faculty of Engineering, Cairo
RESEARCH ARTICLE Vibration Analysis of a Horizontal Washing Machine, Part IV: Optimal Damped Vibration Absorber Galal Ali Hassaan Department of Mechanical Design & Production, Faculty of Engineering, Cairo
Exact Free Vibration of Webs Moving Axially at High Speed
 Eact Free Viration of Wes Moving Aially at High Speed S. HATAMI *, M. AZHARI, MM. SAADATPOUR, P. MEMARZADEH *Department of Engineering, Yasouj University, Yasouj Department of Civil Engineering, Isfahan
Eact Free Viration of Wes Moving Aially at High Speed S. HATAMI *, M. AZHARI, MM. SAADATPOUR, P. MEMARZADEH *Department of Engineering, Yasouj University, Yasouj Department of Civil Engineering, Isfahan
Simple Modeling and Modal Analysis of Reciprocating Compressor Crankshaft System
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2010 Simple Modeling and Modal Analysis of Reciprocating Compressor Crankshaft System Binyan
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2010 Simple Modeling and Modal Analysis of Reciprocating Compressor Crankshaft System Binyan
VIBRATION PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING
 VIBRATION PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING FIFTH EDITION W. WEAVER, JR. Professor Emeritus of Structural Engineering The Late S. P. TIMOSHENKO Professor Emeritus of Engineering Mechanics The Late D. H. YOUNG Professor
VIBRATION PROBLEMS IN ENGINEERING FIFTH EDITION W. WEAVER, JR. Professor Emeritus of Structural Engineering The Late S. P. TIMOSHENKO Professor Emeritus of Engineering Mechanics The Late D. H. YOUNG Professor
Vibration Suppression of a 2-Mass Drive System with Multiple Feedbacks
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 11, November 2015 168 Vibration Suppression of a 2-Mass Drive System with Multiple Feedbacks L. Vidyaratan Meetei, Benjamin
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 11, November 2015 168 Vibration Suppression of a 2-Mass Drive System with Multiple Feedbacks L. Vidyaratan Meetei, Benjamin
Experimental analysis and modeling of transmission torsional vibrations
 Experimental analysis and modeling of transmission torsional vibrations ENRICO GALVAGNO *, GUIDO RICARDO GUERCIONI, MAURO VELARDOCCHIA Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (DIMEAS) Politecnico
Experimental analysis and modeling of transmission torsional vibrations ENRICO GALVAGNO *, GUIDO RICARDO GUERCIONI, MAURO VELARDOCCHIA Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (DIMEAS) Politecnico
(Refer Slide Time: 00:01:30 min)
 Control Engineering Prof. M. Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 3 Introduction to Control Problem (Contd.) Well friends, I have been giving you various
Control Engineering Prof. M. Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 3 Introduction to Control Problem (Contd.) Well friends, I have been giving you various
LECTURE 12. STEADY-STATE RESPONSE DUE TO ROTATING IMBALANCE
 LECTURE 12. STEADY-STATE RESPONSE DUE TO ROTATING IMBALANCE Figure 3.18 (a) Imbalanced motor with mass supported by a housing mass m, (b) Freebody diagram for, The product is called the imbalance vector.
LECTURE 12. STEADY-STATE RESPONSE DUE TO ROTATING IMBALANCE Figure 3.18 (a) Imbalanced motor with mass supported by a housing mass m, (b) Freebody diagram for, The product is called the imbalance vector.
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
 2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
SLIDE GUIDE SGL TYPE SLIDE GUIDE BLOCK TYPES ACCURACY
 SGL YPE he N slide is a linear motion earing utilizing the rotational motion of all elements along four rows of raceway grooves. It can e used in various applications due to its compactness and high load
SGL YPE he N slide is a linear motion earing utilizing the rotational motion of all elements along four rows of raceway grooves. It can e used in various applications due to its compactness and high load
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES
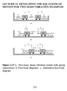 LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Product description. Compact Modules. Characteristic features. Further highlights
 4 Compact Modules Product description Characteristic features Five fine-tuned sizes based on a compact precision aluminum profile with two integrated pre-tensioned ball rail systems Identical external
4 Compact Modules Product description Characteristic features Five fine-tuned sizes based on a compact precision aluminum profile with two integrated pre-tensioned ball rail systems Identical external
ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS. Lecture 6 Mathematical Representation of Physical Systems II 1/67
 1/67 ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Lecture 6 Mathematical Representation of Physical Systems II State Variable Models for Dynamic Systems u 1 u 2 u ṙ. Internal Variables x 1, x 2 x n y 1 y 2. y m Figure
1/67 ECEN 420 LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEMS Lecture 6 Mathematical Representation of Physical Systems II State Variable Models for Dynamic Systems u 1 u 2 u ṙ. Internal Variables x 1, x 2 x n y 1 y 2. y m Figure
Experimental testing and modelling of a passive mechanical steering compensator for high-performance motorcycles
 Proceedings of the European Control Conference 27 Kos, Greece, July 2-5, 27 WeC12.5 Experimental testing and modelling of a passive mechanical steering compensator for high-performance motorcycles Christakis
Proceedings of the European Control Conference 27 Kos, Greece, July 2-5, 27 WeC12.5 Experimental testing and modelling of a passive mechanical steering compensator for high-performance motorcycles Christakis
Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral. mechanism under the vibration environment
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 3-9364 ISSN (Print): 3-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ December. 5 ǁ PP.-6 Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 3-9364 ISSN (Print): 3-9356 Volume 3 Issue ǁ December. 5 ǁ PP.-6 Research on the synchronous vibration of the non-integral
Misalignment Fault Detection in Dual-rotor System Based on Time Frequency Techniques
 Misalignment Fault Detection in Dual-rotor System Based on Time Frequency Techniques Nan-fei Wang, Dong-xiang Jiang *, Te Han State Key Laboratory of Control and Simulation of Power System and Generation
Misalignment Fault Detection in Dual-rotor System Based on Time Frequency Techniques Nan-fei Wang, Dong-xiang Jiang *, Te Han State Key Laboratory of Control and Simulation of Power System and Generation
