LECTURE 12. STEADY-STATE RESPONSE DUE TO ROTATING IMBALANCE
|
|
|
- Geraldine Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LECTURE 12. STEADY-STATE RESPONSE DUE TO ROTATING IMBALANCE Figure 3.18 (a) Imbalanced motor with mass supported by a housing mass m, (b) Freebody diagram for, The product is called the imbalance vector. Y defines m s vertical position with respect to ground. From figure 3.17A, s vertical position with respect to ground is (3.46) The free-body diagram of figure 3.17B for the support mass 202
2 applies for upwards motion of the support housing that causes tension in the support springs and the support damper. The internal reaction force (acting at the motor s bearings) between the motor and the support mass is defined by the components. Applying to the individual masses of figure 3.17B gives: where Eq.(3.46) has been used to eliminate. Adding these equations eliminates the vertical reaction force and gives the single equation of motion, (3.47) This equation resembles Eq.(3.32), (3.32) except and have replaced m and, respectively. Dividing Eq.(3.47) by gives (3.48a) 203
3 where, (3.48b) We want the steady-state solution to Eq.(3.48a) due to the rotating-imbalance excitation term and are not interested in either the homogeneous solution due to initial conditions or the particular solution due to weight. Eq.(3.48a) (3.37) has the same form as Eq.(3.32) except. Hence, by comparison to Eq.(3.37), has replaced the steady-state response amplitude due to rotating imbalance is and the amplification factor due to the rotating imbalance is 204
4 (3.49) Amplitude Response for Rotating Imbalance Amplitude factor J(r) frequency ratio (r) Fi gure versus frequency ratio from Eq.(3.49) for a range of damping ratio values. 205
5 Figure XP3.4 Industrial blower supported by a welded-frame structure. The support structure is much stiffer in the vertical direction than in the horizontal; hence, the model of Eq.(3.48a), without the weight, holds for horizontal motion. This unit runs at 500 rpm, and has been running at high vibration levels. A rap test has been performed by mounting an accelerometer to the fan base, hitting the support structure below the fan with a large hammer, and recording the output of the accelerometer. This test shows a natural frequency of 10.4 Hz = 625 rpm with very little damping ( ). The rotating mass of the fan is 114 kg. The total weight of the fan (including the rotor) and its base plate was stated to weigh 1784 N according to the manufacturer. Answer 206
6 the following questions: a. Assuming that the vibration level on the fan is to be less than, how well should the fan be balanced; i.e., to what value should a be reduced? b. Assuming that the support structure could be stiffened laterally by approximately 50%, how well should the fan be balanced? Solution. In terms of the steady-state amplitude of the housing, the housing acceleration magnitude is, where. Hence, at the housing-amplitude specification is: Applying the notation of Eq.(3.49) gives and. Applying Eq.(3.49) gives 207
7 Hence, the imbalance vector magnitude a should be no more than which concludes Task a. Balancing and maintaining the rotor such that for a 114 kg fan rotor is not easy. Moving to Task b, and assuming that the structural stiffening does not appreciably increase the mass of the fan assembly, increasing the lateral stiffness by 50% would change the natural frequency to With a stiffened housing,,. Since, Hence, 208
8 Further, and Hence, by elevating the system natural frequency, the imbalancevector magnitude can be times greater without exceeding the vibration limit. Stated differently, the fan can tolerate a much higher imbalance when its operating speed ω is further away from resonance. Typically, appreciable damping is very difficult to introduce into this type of system; moreover, increasing the damping factor to in Task a reduces only slightly the required value for a to meet the housing-acceleration level specification. Damping would be more effective for. Of course, the vibration amplitudes would also be much higher.. 209
9 Table 3.2 Forced-excitation results where. Applicatio n Transfer Function Amplitude Ratio r for maximum response Forced Response Base Excitation Relative Deflection with Base Excitation Rotating Imbalance 210
MV Module 5 Solution. Module 5
 Module 5 Q68. With a neat diagram explain working principle of a vibrometer. D-14-Q5 (a)-10m Ans: A vibrometer or a seismometer is an instrument that measures the displacement of a vibrating body. It can
Module 5 Q68. With a neat diagram explain working principle of a vibrometer. D-14-Q5 (a)-10m Ans: A vibrometer or a seismometer is an instrument that measures the displacement of a vibrating body. It can
! 2 = k a ! = 125, Problems and Solutions Section 5.3 (5.27 through 5.36)
 5 3 Problems and Solutions Section 53 57 through 536) 57 A motor is mounted on a platform that is observed to vibrate excessively at an operating speed of 6000 rpm producing a 50N force Design a vibration
5 3 Problems and Solutions Section 53 57 through 536) 57 A motor is mounted on a platform that is observed to vibrate excessively at an operating speed of 6000 rpm producing a 50N force Design a vibration
Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body diagram
 Lecture 30. MORE GENERAL-MOTION/ROLLING- WITHOUT-SLIPPING EXAMPLES A Cylinder, Restrained by a Spring and Rolling on a Plane Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body
Lecture 30. MORE GENERAL-MOTION/ROLLING- WITHOUT-SLIPPING EXAMPLES A Cylinder, Restrained by a Spring and Rolling on a Plane Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body
Dynamics Qualifying Exam Sample
 Dynamics Qualifying Exam Sample Instructions: Complete the following five problems worth 20 points each. No material other than a calculator and pen/pencil can be used in the exam. A passing grade is approximately
Dynamics Qualifying Exam Sample Instructions: Complete the following five problems worth 20 points each. No material other than a calculator and pen/pencil can be used in the exam. A passing grade is approximately
e jωt = cos(ωt) + jsin(ωt),
 This chapter introduces you to the most useful mechanical oscillator model, a mass-spring system with a single degree of freedom. Basic understanding of this system is the gateway to the understanding
This chapter introduces you to the most useful mechanical oscillator model, a mass-spring system with a single degree of freedom. Basic understanding of this system is the gateway to the understanding
BEL Frahm Damper System
 BEL Frahm Damper System 1 Introduction The area of vibration control usual considers two system types: vibration dampers and vibration absorbers. Vibration dampers are systems that convert vibrational
BEL Frahm Damper System 1 Introduction The area of vibration control usual considers two system types: vibration dampers and vibration absorbers. Vibration dampers are systems that convert vibrational
SAMCEF For ROTORS. Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics. This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF A, Page 1
 SAMCEF For ROTORS Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF 101-01-A, Page 1 Table of Contents rotor dynamics Introduction Rotating parts Gyroscopic
SAMCEF For ROTORS Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF 101-01-A, Page 1 Table of Contents rotor dynamics Introduction Rotating parts Gyroscopic
CHAPTER 4 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF BEARINGS DUE TO SHAFT RUB
 53 CHAPTER 4 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF BEARINGS DUE TO SHAFT RUB 4.1 PHENOMENON OF SHAFT RUB Unwanted contact between the rotating and stationary parts of a rotating machine is more commonly referred to as rub.
53 CHAPTER 4 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF BEARINGS DUE TO SHAFT RUB 4.1 PHENOMENON OF SHAFT RUB Unwanted contact between the rotating and stationary parts of a rotating machine is more commonly referred to as rub.
Dynamic Analysis on Vibration Isolation of Hypersonic Vehicle Internal Systems
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 55-60 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Dynamic Analysis on Vibration
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 55-60 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Dynamic Analysis on Vibration
a) Find the equation of motion of the system and write it in matrix form.
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3
 - 1 - Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3 In version 4.3 nonlinear rolling element bearings can be considered for transient analyses. The nonlinear forces are calculated with a
- 1 - Nonlinear Rolling Element Bearings in MADYN 2000 Version 4.3 In version 4.3 nonlinear rolling element bearings can be considered for transient analyses. The nonlinear forces are calculated with a
18.12 FORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS
 8. ORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS Vibrations A mass m is attached to a helical spring and is suspended from a fixed support as before. Damping is also provided in the system ith a dashpot (ig. 8.). Before the
8. ORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS Vibrations A mass m is attached to a helical spring and is suspended from a fixed support as before. Damping is also provided in the system ith a dashpot (ig. 8.). Before the
Why You Can t Ignore Those Vibration Fixture Resonances Peter Avitabile, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts
 Why You Can t Ignore Those Vibration Fixture Resonances Peter Avitabile, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts SOUND AND VIBRATION March 1999 Vibration fixtures, at times, have resonant
Why You Can t Ignore Those Vibration Fixture Resonances Peter Avitabile, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts SOUND AND VIBRATION March 1999 Vibration fixtures, at times, have resonant
Lecture 9: Harmonic Loads (Con t)
 Lecture 9: Harmonic Loads (Con t) Reading materials: Sections 3.4, 3.5, 3.6 and 3.7 1. Resonance The dynamic load magnification factor (DLF) The peak dynamic magnification occurs near r=1 for small damping
Lecture 9: Harmonic Loads (Con t) Reading materials: Sections 3.4, 3.5, 3.6 and 3.7 1. Resonance The dynamic load magnification factor (DLF) The peak dynamic magnification occurs near r=1 for small damping
10 Measurement of Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Transducers
 Chapter 10: Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Measurement Dr. Lufti Al-Sharif (Revision 1.0, 25/5/2008) 1. Introduction This chapter examines the measurement of acceleration, vibration and shock. It starts
Chapter 10: Acceleration, Vibration and Shock Measurement Dr. Lufti Al-Sharif (Revision 1.0, 25/5/2008) 1. Introduction This chapter examines the measurement of acceleration, vibration and shock. It starts
Chapter 5 Design. D. J. Inman 1/51 Mechanical Engineering at Virginia Tech
 Chapter 5 Design Acceptable vibration levels (ISO) Vibration isolation Vibration absorbers Effects of damping in absorbers Optimization Viscoelastic damping treatments Critical Speeds Design for vibration
Chapter 5 Design Acceptable vibration levels (ISO) Vibration isolation Vibration absorbers Effects of damping in absorbers Optimization Viscoelastic damping treatments Critical Speeds Design for vibration
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
Vibration modelling of machine tool structures
 Vibration modelling of machine tool structures F. Haase, S. Lockwood & D.G. Ford The Precision Engineering Centre, University of Huddersfield (UK) Abstract Productivity in modem machine tools is acheved
Vibration modelling of machine tool structures F. Haase, S. Lockwood & D.G. Ford The Precision Engineering Centre, University of Huddersfield (UK) Abstract Productivity in modem machine tools is acheved
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements
 A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
A nonlinear dynamic vibration model of defective bearings: The importance of modelling the finite size of rolling elements Alireza Moazenahmadi, Dick Petersen and Carl Howard School of Mechanical Engineering,
Using Operating Deflection Shapes to Detect Misalignment in Rotating Equipment
 Using Operating Deflection Shapes to Detect Misalignment in Rotating Equipment Surendra N. Ganeriwala (Suri) & Zhuang Li Mark H. Richardson Spectra Quest, Inc Vibrant Technology, Inc 8205 Hermitage Road
Using Operating Deflection Shapes to Detect Misalignment in Rotating Equipment Surendra N. Ganeriwala (Suri) & Zhuang Li Mark H. Richardson Spectra Quest, Inc Vibrant Technology, Inc 8205 Hermitage Road
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES
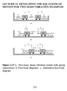 LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
Chapter a. Spring constant, k : The change in the force per unit length change of the spring. b. Coefficient of subgrade reaction, k:
 Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
ME 563 Mechanical Vibrations Lecture #1. Derivation of equations of motion (Newton-Euler Laws)
 ME 563 Mechanical Vibrations Lecture #1 Derivation of equations of motion (Newton-Euler Laws) Derivation of Equation of Motion 1 Define the vibrations of interest - Degrees of freedom (translational, rotational,
ME 563 Mechanical Vibrations Lecture #1 Derivation of equations of motion (Newton-Euler Laws) Derivation of Equation of Motion 1 Define the vibrations of interest - Degrees of freedom (translational, rotational,
Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody
 Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody diagram The term compound is used to distinguish the present
Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody diagram The term compound is used to distinguish the present
Name: Fall 2014 CLOSED BOOK
 Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump
 An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
An Analysis Technique for Vibration Reduction of Motor Pump Young Kuen Cho, Seong Guk Kim, Dae Won Lee, Paul Han and Han Sung Kim Abstract The purpose of this study was to examine the efficiency of the
Final Examination Thursday May Please initial the statement below to show that you have read it
 EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations Final Examination Thursday May 0 010 Division of Engineering rown University NME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is permitted on this examination. You may
EN40: Dynamics and Vibrations Final Examination Thursday May 0 010 Division of Engineering rown University NME: General Instructions No collaboration of any kind is permitted on this examination. You may
Module 4: Dynamic Vibration Absorbers and Vibration Isolator Lecture 19: Active DVA. The Lecture Contains: Development of an Active DVA
 The Lecture Contains: Development of an Active DVA Proof Mass Actutor Application of Active DVA file:///d /chitra/vibration_upload/lecture19/19_1.htm[6/25/2012 12:35:51 PM] In this section, we will consider
The Lecture Contains: Development of an Active DVA Proof Mass Actutor Application of Active DVA file:///d /chitra/vibration_upload/lecture19/19_1.htm[6/25/2012 12:35:51 PM] In this section, we will consider
Hammer crusher - influences of design and execution of vibroprotection and machine properties on vibration intensity
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) 149-154 Hammer crusher - influences of design and execution of vibroprotection and machine properties on vibration intensity D. Makovička a,*, J. Šmejkal b
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (2007) 149-154 Hammer crusher - influences of design and execution of vibroprotection and machine properties on vibration intensity D. Makovička a,*, J. Šmejkal b
2.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 10 with answer to the concept questions
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 10 with answer to the concept questions Problem 1 Figure 1. Cart with a slender rod A slender rod of length l (m) and mass m (0.5kg)is attached by a frictionless pivot
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 10 with answer to the concept questions Problem 1 Figure 1. Cart with a slender rod A slender rod of length l (m) and mass m (0.5kg)is attached by a frictionless pivot
The Design of a Multiple Degree of Freedom Flexure Stage with Tunable Dynamics for Milling Experimentation
 The Design of a Multiple Degree of Freedom Flexure Stage with Tunable Dynamics for Milling Experimentation Mark A. Rubeo *, Kadir Kiran *, and Tony L. Schmitz The University of North Carolina at Charlotte,
The Design of a Multiple Degree of Freedom Flexure Stage with Tunable Dynamics for Milling Experimentation Mark A. Rubeo *, Kadir Kiran *, and Tony L. Schmitz The University of North Carolina at Charlotte,
Structural System, Machines and Load Cases
 Machine-Induced Vibrations Machine-Induced Vibrations In the following example the dynamic excitation of two rotating machines is analyzed. A time history analysis in the add-on module RF-DYNAM Pro - Forced
Machine-Induced Vibrations Machine-Induced Vibrations In the following example the dynamic excitation of two rotating machines is analyzed. A time history analysis in the add-on module RF-DYNAM Pro - Forced
In this lecture you will learn the following
 Module 9 : Forced Vibration with Harmonic Excitation; Undamped Systems and resonance; Viscously Damped Systems; Frequency Response Characteristics and Phase Lag; Systems with Base Excitation; Transmissibility
Module 9 : Forced Vibration with Harmonic Excitation; Undamped Systems and resonance; Viscously Damped Systems; Frequency Response Characteristics and Phase Lag; Systems with Base Excitation; Transmissibility
MODELLING OF VIBRATION WITH ABSORBER
 Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 10, No.4, 2010 mumerical modelling, Simulink, vibration, machine, absorber Jiří VONDŘICH 1 Evžen THÖNDE 1 Slavomír JIRKŮ 1 MODEING OF VIBRATION WITH ABSORBER Machine
Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 10, No.4, 2010 mumerical modelling, Simulink, vibration, machine, absorber Jiří VONDŘICH 1 Evžen THÖNDE 1 Slavomír JIRKŮ 1 MODEING OF VIBRATION WITH ABSORBER Machine
Figure XP3.1 (a) Mass in equilibrium, (b) Freebody diagram, (c) Kinematic constraint relation Example Problem 3.1 Figure XP3.1 illustrates a mass m
 LECTURE 7. MORE VIBRATIONS ` Figure XP3.1 (a) Mass in equilibrium, (b) Freebody diagram, (c) Kinematic constraint relation Example Problem 3.1 Figure XP3.1 illustrates a mass m that is in equilibrium and
LECTURE 7. MORE VIBRATIONS ` Figure XP3.1 (a) Mass in equilibrium, (b) Freebody diagram, (c) Kinematic constraint relation Example Problem 3.1 Figure XP3.1 illustrates a mass m that is in equilibrium and
Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations
 Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations Second order linear equations with constant coefficients serve as mathematical models for mechanical and electrical oscillations. For example, the motion
Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations Second order linear equations with constant coefficients serve as mathematical models for mechanical and electrical oscillations. For example, the motion
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Improving the Accuracy of Dynamic Vibration Fatigue Simulation
 Improving the Accuracy of Dynamic Vibration Fatigue Simulation Kurt Munson HBM Prenscia Agenda 2 1. Introduction 2. Dynamics and the frequency response function (FRF) 3. Using finite element analysis (FEA)
Improving the Accuracy of Dynamic Vibration Fatigue Simulation Kurt Munson HBM Prenscia Agenda 2 1. Introduction 2. Dynamics and the frequency response function (FRF) 3. Using finite element analysis (FEA)
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Special edition paper
 Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
Development of New Aseismatic Structure Using Escalators Kazunori Sasaki* Atsushi Hayashi* Hajime Yoshida** Toru Masuda* Aseismatic reinforcement work is often carried out in parallel with improvement
EFFECT OF HYDRODYNAMIC THRUST BEARINGS ON ROTORDYNAMICS
 The 12th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery Honolulu, Hawaii, February 17-22, 2008 ISROMAC12-2008-20076 EFFECT OF HYDRODYNAMIC THRUST BEARINGS ON ROTORDYNAMICS
The 12th International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery Honolulu, Hawaii, February 17-22, 2008 ISROMAC12-2008-20076 EFFECT OF HYDRODYNAMIC THRUST BEARINGS ON ROTORDYNAMICS
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
COMPOUND PENDULUM. AIM: 01. To determine the radius of gyration k of given compo pendulum. 02. To verify the relation
 COMPOUND PENDULUM AIM: 01. To determine the radius of gyration k of given compo pendulum. 02. To verify the relation T= 2 π 2 2 K + (OG) g (OG) Where, T = Periodic time sec. K = Radius of gyration about
COMPOUND PENDULUM AIM: 01. To determine the radius of gyration k of given compo pendulum. 02. To verify the relation T= 2 π 2 2 K + (OG) g (OG) Where, T = Periodic time sec. K = Radius of gyration about
MEG6007: Advanced Dynamics -Principles and Computational Methods (Fall, 2017) Lecture DOF Modeling of Shock Absorbers. This lecture covers:
 MEG6007: Advanced Dynamics -Principles and Computational Methods (Fall, 207) Lecture 4. 2-DOF Modeling of Shock Absorbers This lecture covers: Revisit 2-DOF Spring-Mass System Understand the den Hartog
MEG6007: Advanced Dynamics -Principles and Computational Methods (Fall, 207) Lecture 4. 2-DOF Modeling of Shock Absorbers This lecture covers: Revisit 2-DOF Spring-Mass System Understand the den Hartog
PROPELLER INDUCED STRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUST BEARING
 PROPELLER INDUCED TRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUT BEARING Jie Pan, Nabil Farag, Terry Lin and Ross Juniper* DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL AND MATERIAL ENGINEERING THE UNIVERITY OF WETERN AUTRALIA 35 TIRLING
PROPELLER INDUCED TRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUT BEARING Jie Pan, Nabil Farag, Terry Lin and Ross Juniper* DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL AND MATERIAL ENGINEERING THE UNIVERITY OF WETERN AUTRALIA 35 TIRLING
Mathematical Modeling and response analysis of mechanical systems are the subjects of this chapter.
 Chapter 3 Mechanical Systems A. Bazoune 3.1 INRODUCION Mathematical Modeling and response analysis of mechanical systems are the subjects of this chapter. 3. MECHANICAL ELEMENS Any mechanical system consists
Chapter 3 Mechanical Systems A. Bazoune 3.1 INRODUCION Mathematical Modeling and response analysis of mechanical systems are the subjects of this chapter. 3. MECHANICAL ELEMENS Any mechanical system consists
Dynamics of Machinery
 Lab Manual Dynamics of Machinery (2161901) Name: Enrollment No.: Roll No.: Batch: Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology, Rajkot DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Certificate This is to certify
Lab Manual Dynamics of Machinery (2161901) Name: Enrollment No.: Roll No.: Batch: Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology, Rajkot DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Certificate This is to certify
Orbit Analysis. Jaafar Alsalaet College of Engineering-University of Basrah
 Orbit Analysis Jaafar Alsalaet College of Engineering-University of Basrah 1. Introduction Orbits are Lissajous patterns of time domain signals that are simultaneously plotted in the X Y coordinate plane
Orbit Analysis Jaafar Alsalaet College of Engineering-University of Basrah 1. Introduction Orbits are Lissajous patterns of time domain signals that are simultaneously plotted in the X Y coordinate plane
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Theory & Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 8 Balancing Lecture - 1 Introduce To Rigid Rotor Balancing Till
Chapter 7 Vibration Measurement and Applications
 Chapter 7 Vibration Measurement and Applications Dr. Tan Wei Hong School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) Pauh Putra Campus ENT 346 Vibration Mechanics Chapter Outline 7.1
Chapter 7 Vibration Measurement and Applications Dr. Tan Wei Hong School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) Pauh Putra Campus ENT 346 Vibration Mechanics Chapter Outline 7.1
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
IOMAC'15 6 th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference
 IOMAC'15 6 th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference 2015 May12-14 Gijón - Spain COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT TECHNIQUES TO SCALE MODE SHAPES IN OPERATIONAL MODAL ANALYSIS. Luis Borja Peral Mtnez
IOMAC'15 6 th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference 2015 May12-14 Gijón - Spain COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT TECHNIQUES TO SCALE MODE SHAPES IN OPERATIONAL MODAL ANALYSIS. Luis Borja Peral Mtnez
Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking
 Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking What is the maximum relative displacement and the amplitude of the total displacement of a SDOF structure subjected to ground shaking? magnitude of ground
Prob. 1 SDOF Structure subjected to Ground Shaking What is the maximum relative displacement and the amplitude of the total displacement of a SDOF structure subjected to ground shaking? magnitude of ground
Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction
 Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng. Professor Graduate School of Engineering Hiroshima University Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Chapter 1 : Introduction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng.
Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng. Professor Graduate School of Engineering Hiroshima University Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Chapter 1 : Introduction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng.
Modal analysis of rotor assembly of vertical turbine pump
 ISSN 2395-1621 Modal analysis of rotor assembly of vertical turbine pump #1 Mr. R. R. Kumatkar, #2 Mr. A.A. Panchwadkar 1 rrkumatkar@gmail.com 2 amit.panchwadkar@pccoepune.org #1 PG Student, Pimpri Chinchwad
ISSN 2395-1621 Modal analysis of rotor assembly of vertical turbine pump #1 Mr. R. R. Kumatkar, #2 Mr. A.A. Panchwadkar 1 rrkumatkar@gmail.com 2 amit.panchwadkar@pccoepune.org #1 PG Student, Pimpri Chinchwad
Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics
 Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin July 20, 2014 Overview 1 This lab is meant to
Modeling and Experimentation: Mass-Spring-Damper System Dynamics Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin July 20, 2014 Overview 1 This lab is meant to
T1 T e c h n i c a l S e c t i o n
 1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
Vibration Analysis of Shaft Misalignment and Diagnosis Method of Structure Faults for Rotating Machinery
 Available online at www.ijpe-online.com Vol. 3, No. 4, July 07, pp. 337-347 DOI: 0.3940/ijpe.7.04.p.337347 Vibration Analysis of Shaft Misalignment and Diagnosis Method of Structure Faults for Rotating
Available online at www.ijpe-online.com Vol. 3, No. 4, July 07, pp. 337-347 DOI: 0.3940/ijpe.7.04.p.337347 Vibration Analysis of Shaft Misalignment and Diagnosis Method of Structure Faults for Rotating
VTU-NPTEL-NMEICT Project
 VTU-NPTEL-NMEICT Project Progress Report The Project on Development of Remaining Three Quadrants to NPTEL Phase-I under grant in aid NMEICT, MHRD, New Delhi SME Name : Course Name: Type of the Course Module
VTU-NPTEL-NMEICT Project Progress Report The Project on Development of Remaining Three Quadrants to NPTEL Phase-I under grant in aid NMEICT, MHRD, New Delhi SME Name : Course Name: Type of the Course Module
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber
 Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF ROTARY DRIER
 Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 14, 2007, No. 4, p. 259 268 259 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF ROTARY DRIER František Palčák*, Martin Vančo* In this paper the transfer of vibration from motor to the bottom group of
Engineering MECHANICS, Vol. 14, 2007, No. 4, p. 259 268 259 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF ROTARY DRIER František Palčák*, Martin Vančo* In this paper the transfer of vibration from motor to the bottom group of
KNIFE EDGE FLAT ROLLER
 EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
EXPERIMENT N0. 1 To Determine jumping speed of cam Equipment: Cam Analysis Machine Aim: To determine jumping speed of Cam Formulae used: Upward inertial force = Wvω 2 /g Downward force = W + Ks For good
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 One degree of freedom systems in real life 2 1 Reduction of a system to a one dof system Example
Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 One degree of freedom systems in real life 2 1 Reduction of a system to a one dof system Example
A modal approach for vibration analysis and condition monitoring of a centrifugal pump
 A modal approach for vibration analysis and condition monitoring of a centrifugal pump Abstract Ramana Podugu Research scholar, Mechanical Engineering Department. JNTU, Hyderabad,Andhra Pradesh,India.
A modal approach for vibration analysis and condition monitoring of a centrifugal pump Abstract Ramana Podugu Research scholar, Mechanical Engineering Department. JNTU, Hyderabad,Andhra Pradesh,India.
USING ROTOR KIT BENTLY NEVADA FOR EXPERIMENTS WITH AEROSTATIC BEARINGS
 USING ROTOR KIT BENTLY NEVADA FOR EXPERIMENTS WITH AEROSTATIC BEARINGS ŠIMEK, J. 1, KOZÁNEK, J., STEINBAUER, P., NEUSSER, Z. 3 1 TECHLAB Ltd., Prague, Institute of Thermomechanics AS CR 3 CTU in Prague,
USING ROTOR KIT BENTLY NEVADA FOR EXPERIMENTS WITH AEROSTATIC BEARINGS ŠIMEK, J. 1, KOZÁNEK, J., STEINBAUER, P., NEUSSER, Z. 3 1 TECHLAB Ltd., Prague, Institute of Thermomechanics AS CR 3 CTU in Prague,
DYNAMIC BALANCING OF ROTATING MACHINERY EXPERIMENT
 DYNMIC LNCING OF OTTING MCHINEY EXPEIMENT Technical dvisor: Dr. K. Nisbett January 996 6. GENEL OJECTIVES ) To gain insight into the causes of undesirable vibration of rotors and to understand static and
DYNMIC LNCING OF OTTING MCHINEY EXPEIMENT Technical dvisor: Dr. K. Nisbett January 996 6. GENEL OJECTIVES ) To gain insight into the causes of undesirable vibration of rotors and to understand static and
PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 208(1), 1 14 PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1997) 208(1), 1 14 PARAMETER ESTIMATION IN IMBALANCED NON-LINEAR ROTOR-BEARING SYSTEMS FROM RANDOM RESPONSE Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology,
A-level Physics (7407/7408)
 A-level Physics (7407/7408) Further Mechanics Test Name: Class: Date: September 2016 Time: 55 Marks: 47 Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a strobe photograph of a mark on a trolley X, moving from right to left,
A-level Physics (7407/7408) Further Mechanics Test Name: Class: Date: September 2016 Time: 55 Marks: 47 Page 1 Q1.The diagram shows a strobe photograph of a mark on a trolley X, moving from right to left,
CHAPTER 6 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF UNBALANCED CNC MACHINE SPINDLE USING VIBRATION SIGNATURES-A CASE STUDY
 81 CHAPTER 6 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF UNBALANCED CNC MACHINE SPINDLE USING VIBRATION SIGNATURES-A CASE STUDY 6.1 INTRODUCTION For obtaining products of good quality in the manufacturing industry, it is absolutely
81 CHAPTER 6 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF UNBALANCED CNC MACHINE SPINDLE USING VIBRATION SIGNATURES-A CASE STUDY 6.1 INTRODUCTION For obtaining products of good quality in the manufacturing industry, it is absolutely
Experimental analysis of influence of initially stressed springs and parameters of excitation on vibration absorber effectiveness
 Experimental analysis of influence of initially stressed springs and parameters of excitation on vibration absorber effectiveness MSc, Eng. Piotr Jan Sulich Supervisor: PhD, Eng. Michael Pracik Abstract
Experimental analysis of influence of initially stressed springs and parameters of excitation on vibration absorber effectiveness MSc, Eng. Piotr Jan Sulich Supervisor: PhD, Eng. Michael Pracik Abstract
On Non-Ideal Simple Portal Frame Structural Model: Experimental Results Under A Non-Ideal Excitation
 On Non-Ideal Simple Portal Frame Structural Model: Experimental Results Under A Non-Ideal Excitation J M Balthazar 1,a, RMLRF Brasil,b and FJ Garzeri 3, c 1 State University of São Paulo at Rio Claro,
On Non-Ideal Simple Portal Frame Structural Model: Experimental Results Under A Non-Ideal Excitation J M Balthazar 1,a, RMLRF Brasil,b and FJ Garzeri 3, c 1 State University of São Paulo at Rio Claro,
1. Replace the given system of forces acting on a body as shown in figure 1 by a single force and couple acting at the point A.
 Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Mitigation of Diesel Generator Vibrations in Nuclear Applications Antti Kangasperko. FSD3020xxx-x_01-00
 Mitigation of Diesel Generator Vibrations in Nuclear Applications Antti Kangasperko FSD3020xxx-x_01-00 1 Content Introduction Vibration problems in EDGs Sources of excitation 2 Introduction Goal of this
Mitigation of Diesel Generator Vibrations in Nuclear Applications Antti Kangasperko FSD3020xxx-x_01-00 1 Content Introduction Vibration problems in EDGs Sources of excitation 2 Introduction Goal of this
Lecture 20. Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature MECH 373. Instrumentation and Measurements
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 20 Measuring Pressure and Temperature (Chapter 9) Measuring Pressure Measuring Temperature 1 Measuring Acceleration and Vibration Accelerometers using
:= 0.75 Ns m K N m. := 0.05 kg. K N m. (a.1) FBD and forces. (a.2) derive EOM From the FBD diagram, Newton's 2nd law states:
 P FA - Derive EO for simple mechanical system L San Andres (c) For the system shown in the figure, Z (t) Z o cos( t) is a periodic displacement input (known). Perform the following tasks: a) Set X(t) as
P FA - Derive EO for simple mechanical system L San Andres (c) For the system shown in the figure, Z (t) Z o cos( t) is a periodic displacement input (known). Perform the following tasks: a) Set X(t) as
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL ACTIVE ISOLATION CONCEPT 1
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL ACTIVE ISOLATION CONCEPT 1 Michiel J. Vervoordeldonk, Theo A.M. Ruijl, Rob M.G. Rijs Philips Centre for Industrial Technology, PO Box 518, 5600 MD Eindhoven, The Netherlands 2 1
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL ACTIVE ISOLATION CONCEPT 1 Michiel J. Vervoordeldonk, Theo A.M. Ruijl, Rob M.G. Rijs Philips Centre for Industrial Technology, PO Box 518, 5600 MD Eindhoven, The Netherlands 2 1
(Refer Slide Time: 1: 19)
 Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 46 Force Measurement So this will be lecture
Mechanical Measurements and Metrology Prof. S. P. Venkateshan Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 4 Lecture - 46 Force Measurement So this will be lecture
Mechanical Vibrations Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Mechanical Vibrations Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 12 Signature analysis and preventive maintenance Lecture - 3 Field balancing
Mechanical Vibrations Prof. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module - 12 Signature analysis and preventive maintenance Lecture - 3 Field balancing
Lecture 19. Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity
 MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
MECH 373 Instrumentation and Measurements Lecture 19 Measurement of Solid-Mechanical Quantities (Chapter 8) Measuring Strain Measuring Displacement Measuring Linear Velocity Measuring Accepleration and
The Importance of Feet on Machine Applications. Compliance in the Wrong area can be worse than no compliance
 The Importance of Feet on Machine Applications Compliance in the Wrong area can be worse than no compliance Various Feet Differences Depending on different applications, the selection of the feet of a
The Importance of Feet on Machine Applications Compliance in the Wrong area can be worse than no compliance Various Feet Differences Depending on different applications, the selection of the feet of a
Application Note #3413
 Application Note #3413 Manual Tuning Methods Tuning the controller seems to be a difficult task to some users; however, after getting familiar with the theories and tricks behind it, one might find the
Application Note #3413 Manual Tuning Methods Tuning the controller seems to be a difficult task to some users; however, after getting familiar with the theories and tricks behind it, one might find the
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Lecture 6 mechanical system modeling equivalent mass gears
 M2794.25 Mechanical System Analysis 기계시스템해석 lecture 6,7,8 Dongjun Lee ( 이동준 ) Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Seoul National University Dongjun Lee Lecture 6 mechanical system modeling
M2794.25 Mechanical System Analysis 기계시스템해석 lecture 6,7,8 Dongjun Lee ( 이동준 ) Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Seoul National University Dongjun Lee Lecture 6 mechanical system modeling
Analysis of the NOT Primary Mirror Dynamics
 Analysis of the NOT Primary Mirror Dynamics Graham C. Cox October 24, 2000 Introduction On the nights of 12th and 13th May 2000 observations were made using the JOSE camera system, borrowed from the ING,
Analysis of the NOT Primary Mirror Dynamics Graham C. Cox October 24, 2000 Introduction On the nights of 12th and 13th May 2000 observations were made using the JOSE camera system, borrowed from the ING,
First Name: Last Name: Section: 22 December, :25 2:25 PM Physics 207 FINAL EXAM
 1 First Name: Last Name: Section: 22 December, 2009 12:25 2:25 PM Physics 207 FINAL EXAM Please print your name and section number (or TA s name) clearly on the first page. Show all your work in the space
1 First Name: Last Name: Section: 22 December, 2009 12:25 2:25 PM Physics 207 FINAL EXAM Please print your name and section number (or TA s name) clearly on the first page. Show all your work in the space
Resonant Column and Torsional Cyclic Shear System
 Resonant Column and Torsional Cyclic Shear System Combined Resonant Column (RC) & Torsional Cyclic Shear (TCS) Test apparatus to determinate with saturated soil : Shear Modulus Damping Modulus versus Shear
Resonant Column and Torsional Cyclic Shear System Combined Resonant Column (RC) & Torsional Cyclic Shear (TCS) Test apparatus to determinate with saturated soil : Shear Modulus Damping Modulus versus Shear
Address for Correspondence
 Research Article EXPERIMENT STUDY OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF SOFT STOREY BUILDING MODEL C. S. Sanghvi 1, H S Patil 2 and B J Shah 3 Address for Correspondence 1 Associate Professor, Applied Mechanics Department,
Research Article EXPERIMENT STUDY OF DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF SOFT STOREY BUILDING MODEL C. S. Sanghvi 1, H S Patil 2 and B J Shah 3 Address for Correspondence 1 Associate Professor, Applied Mechanics Department,
2.72 Elements of Mechanical Design
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.72 Elements of Mechanical Design Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 2.72 Elements of
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.72 Elements of Mechanical Design Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 2.72 Elements of
Program System for Machine Dynamics. Abstract. Version 5.0 November 2017
 Program System for Machine Dynamics Abstract Version 5.0 November 2017 Ingenieur-Büro Klement Lerchenweg 2 D 65428 Rüsselsheim Phone +49/6142/55951 hd.klement@t-online.de What is MADYN? The program system
Program System for Machine Dynamics Abstract Version 5.0 November 2017 Ingenieur-Büro Klement Lerchenweg 2 D 65428 Rüsselsheim Phone +49/6142/55951 hd.klement@t-online.de What is MADYN? The program system
Structural Dynamic Behavior of a High-Speed Milling Machine
 Structural Dynamic Behavior of a High-Speed Milling Machine FEA Vs. EMA Assessment * J. Rotberg, ** B. Bork * "Technion" I.I.T ** Technische Universitat Darmstadt Faculty of Mechanical Eng. PTW Institut
Structural Dynamic Behavior of a High-Speed Milling Machine FEA Vs. EMA Assessment * J. Rotberg, ** B. Bork * "Technion" I.I.T ** Technische Universitat Darmstadt Faculty of Mechanical Eng. PTW Institut
1820. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation
 8. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation Tomasz Matyja, Bogusław Łazarz Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Gliwice, Poland Corresponding author
8. Selection of torsional vibration damper based on the results of simulation Tomasz Matyja, Bogusław Łazarz Silesian University of Technology, Faculty of Transport, Gliwice, Poland Corresponding author
Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect. Synopsis. Introduction
 Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect Synopsis A simplified analysis method for a reinforced concrete shear wall structure considering strain rate effects is presented.
Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect Synopsis A simplified analysis method for a reinforced concrete shear wall structure considering strain rate effects is presented.
TWISTING (TORSIONAL) STIFFNESS. Barry T. Cease Cease Industrial Consulting
 TWISTING (TORSIONAL) STIFFNESS Barry T. Cease Cease Industrial Consulting ceasevibration@icloud.com 843-200-9705 USUAL STIFFENING PRACTICES Most vibration analysts are familiar with methods of how to increase
TWISTING (TORSIONAL) STIFFNESS Barry T. Cease Cease Industrial Consulting ceasevibration@icloud.com 843-200-9705 USUAL STIFFENING PRACTICES Most vibration analysts are familiar with methods of how to increase
The student will experimentally determine the parameters to represent the behavior of a damped oscillatory system of one degree of freedom.
 Practice 3 NAME STUDENT ID LAB GROUP PROFESSOR INSTRUCTOR Vibrations of systems of one degree of freedom with damping QUIZ 10% PARTICIPATION & PRESENTATION 5% INVESTIGATION 10% DESIGN PROBLEM 15% CALCULATIONS
Practice 3 NAME STUDENT ID LAB GROUP PROFESSOR INSTRUCTOR Vibrations of systems of one degree of freedom with damping QUIZ 10% PARTICIPATION & PRESENTATION 5% INVESTIGATION 10% DESIGN PROBLEM 15% CALCULATIONS
Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session. Dr. David Herrin March 27, 2012
 Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session Dr. David Herrin March 7, 0 Example A 0 g ball is released vertically from a height of 0 m. The ball strikes a horizontal surface and bounces back.
Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session Dr. David Herrin March 7, 0 Example A 0 g ball is released vertically from a height of 0 m. The ball strikes a horizontal surface and bounces back.
Experimental Modal Analysis (EMA) on a vibration cube fixture M. Sc. Emanuel Malek Eindhoven November 2017
 Experimental Modal Analysis (EMA) on a vibration cube fixture M. Sc. Emanuel Malek Eindhoven November 207 Test and Measurement Solutions Content Introduction Basics Why EMA? Preparation and execution Testing
Experimental Modal Analysis (EMA) on a vibration cube fixture M. Sc. Emanuel Malek Eindhoven November 207 Test and Measurement Solutions Content Introduction Basics Why EMA? Preparation and execution Testing
Final Exam December 11, 2017
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are NOT allowed to use a calculator with communication capabilities during the exam. Usage
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are NOT allowed to use a calculator with communication capabilities during the exam. Usage
NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PILE-SOIL SYSTEM UNDER VERTICAL VIBRATION
 IGC 2009, Guntur, INDIA NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PILE-SOIL SYSTEM UNDER VERTICAL VIBRATION B. Manna Lecturer, Civil Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela 769008, India.
IGC 2009, Guntur, INDIA NONLINEAR CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PILE-SOIL SYSTEM UNDER VERTICAL VIBRATION B. Manna Lecturer, Civil Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela 769008, India.
ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS
 Transactions, SMiRT-24 ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS 1 Principal Engineer, MTR & Associates, USA INTRODUCTION Mansour Tabatabaie 1 Dynamic response
Transactions, SMiRT-24 ON THE PREDICTION OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FROM TWO PILE TESTS UNDER FORCED VIBRATIONS 1 Principal Engineer, MTR & Associates, USA INTRODUCTION Mansour Tabatabaie 1 Dynamic response
