Introduction to cardiac electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András 2018
|
|
|
- Daisy Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to cardiac electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth ndrás 2018
2 Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential
3 1 Transmembran transport
4 Major types of transmembran transport
5 J: net rate (flux) of diffusion : area dc/dx: concentration gradient D: diffusion coefficient (D: cm 2 /s) J J D dc D dx c D x J dc dx Fick s first law of diffusion
6 Time required for diffusion as a square function of distance
7 J J K Fick s law for membrane D D D x c x c x : partition coefficient K: permeability coefficient Diffusion kinetics across a semipermeable membrane
8 Osmotic diffusion across a semipermeable membrane
9 Mechanism of facilitated diffusion
10 Principle of transport (facilitated diffusion!!!) of ions across ion channels
11 The principle of active transzport via the Na /K TPase
12 Secondary active transport processes
13 Michaelis-Menten equation V max : maximal rate of transport K m : concentration of substrate at a transport rate equal to V max /2 Protein-mediated transport shows saturation kinetics
14 Q: What are the principal differences between the following iontransporters? 1. Sodium-calcium exchanger 2. Sodium-hidrogen exchanger 3. Calcium pump of the sarcolemma
15 2 Ionic equilibrium
16 o RT ln C zf RT ln X X B zf B lectrochemical potential (difference)
17 quilibriu m 0 RT ln X X B zf B zf X B RT ln X RT X B ln zf X B B For monovalent cations Z = 1 X 60mV lg X X B Deduction of the Nernst equation
18 Q: What does equilibrium potential mean for a given ion?
19 Let s see, how the Nernst equation can be utilized to analyze ion movements in case of diffusible ions:
20 B B 0.1 M 0.01 M 1 M 0.1 M K K HCO 3 - HCO 3 - B = -60 mv B = 100 mv Is there equilibrium in any of the two cases? xamples of use of the Nernst equation 1.
21 B B 0.1 M K 0.01 M K 1 M HCO M HCO 3 - B = 60 mv t 60 mv the K is in electrochemical equilibrium across the membran No electric force!!! xamples of use of the Nernst equation 2.
22 B B 0.1 M K 0.01 M K 1 M HCO M HCO 3 - B = 60 mv t -60 mv the K is in electrochemical equilibrium across the membran No electric force B = 100 mv t the given membran potential the HCO 3- ion is not in electrochemical equilibrium lectric force: 40 mv xamples of uses of the Nernst equation 3.
23 Let s see, what happens, if the cell membrane is NOT permeable for at least one ion:
24 B B [K ] = 0.1 M [P - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = 0.1 M [Cl - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = [Cl - ] = [P - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = [Cl - ] = Initial state quilibrium? 1. The principle of electroneutrality should be preserved!!! 2. The electrochemical potential should be zero for each diffusible ion!!! (But not for the undiffusible ion!!!) Before Gibbs-Donnan equilibrium is established 1
25 B B [K ] = 0.1 M [P - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = 0.1 M [Cl - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = M* [Cl - ] = M* [P - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = M* [Cl - ] = M* Initial state quilibrium state* (!?) 1. The principle of elektroneutrality is, indeed, valid!!! 2. The electrochemical potential is zero for both K and Cl -!!! 3. * So, is there any problem??? Gibbs-Donnan equilibrium has been attained
26 P Hydro = 2.99 atm!!! B B [K ] = 0.1 M [P - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = 0.1 M [Cl - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = M [Cl - ] = M [P - ] = 0.1 M [K ] = M [Cl - ] = M Starting state quilibrium state (There is no equilibrium between pressures!!!) In Gibbs-Donnan equilibrium a huge transmembrane hydrostatic pressure gradient is present
27 Q: When is Gibbs-Donnan equilibrium present across a living cell membrane?
28 3 Resting potential
29 B 0.1 M NaCl 0.01 M NaCl If the membrane is permeable for cations, but not for anions, a cation current is needed to reach equilibrium!!! The principle of the concentration battery 1
30 Na B 0.1 M NaCl 0.01 M NaCl In case of electrochemical equilibrium: B = - 60 mv The principle of the concentration battery 2
31 Q: How many Na ions should pass the membrane to reach equilibrium?. Very-very little? Very little? Rather little? Medium? Rather much? Very much? Very-very much?
32 Let s see, how living cells can be modelled as multi-ion concentration batteries
33 Intra- and extracellular ionconcentrations and corresponding resting membrane potential determined experimentally
34 Cl - Na 1) Na IC (mm) 12 C (mm) 145 eq 65 mv cc cc K 160 3,5-100 mv Cl - 3, mv -90 mv Prot ) P K 100 P Na cc K 3) Prot 0 4) m 90 mv simplified model of the resting membrane potential in the human skeletal muscle
35 K K m K Na Na m Na Cl Cl m Cl g I g I g I R g R U I ) ( ) ( 0 ) ( 1 quilibrium conditions for the chord conductance equation Theoretical estimation for the resting potential 1.
36 Na m K I Na ( m m I g K K Na g 0 ) g K g Na Na ( K m g K g K Na ) g In case of: g Na = 1 & g K = 100 g Na K Na m K Na The chord conductance equation
37 Theoretical estimation for the resting potential 2. m RT F ln k k pk pk [ K [ K ] ] o i k k pna pna [ Na [ Na ] ] o i k k pcl pcl [ Cl [ Cl ] ] i o The constant field (Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz) equation
38 Major factors affecting resting potential C
39 Q: Which are the primary conditions for establishing and maintaining steady resting potential?
40 : 1. Separated ion compartments 2. Selective permeability of the membrane 3. Ionic concentration gradients 4. nergy supply and ion transporters
41 Cardiac cells
42 lso in cardiac cells the resting potential should show strong [K ] dependency
43 In cardiac cells the resting potential is, indeed, primarely [K ] dependent (measured: Vm, and calculated: k curves)
44 Q: What may be the reason why in a given cell type (e.g. RBC) the resting potential is 30 mv, while in another (e.g. cardiac) cell type it is 90 mv?
45 Q: What are the major factors determining the actual value of membrane potential?
46 : 1. Concentration gradients of the monovalent cations 2. Selective permeability of the membrane for cations 3. Concentration of non-permeable intracellular anions
47 To be continued!
Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András
 Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András Today topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Level of significance Entry level (even under 6) Student level (for most of
Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András Today topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Level of significance Entry level (even under 6) Student level (for most of
Introduction to electrophysiology. Dr. Tóth András
 Introduction to electrophysiology Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of the
Introduction to electrophysiology Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of the
Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András
 Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of
Introduction to electrophysiology 1. Dr. Tóth András Topics Transmembran transport Donnan equilibrium Resting potential Ion channels Local and action potentials Intra- and extracellular propagation of
Cell membrane resistance and capacitance
 Cell membrane resistance and capacitance 1 Two properties of a cell membrane gives rise to two passive electrical properties: Resistance: Leakage pathways allow inorganic ions to cross the membrane. Capacitance:
Cell membrane resistance and capacitance 1 Two properties of a cell membrane gives rise to two passive electrical properties: Resistance: Leakage pathways allow inorganic ions to cross the membrane. Capacitance:
Lojayn Salah. Zaid R Al Najdawi. Mohammad-Khatatbeh
 7 Lojayn Salah Zaid R Al Najdawi Mohammad-Khatatbeh Salam everyone, I made my best to make this sheet clear enough to be easily understood let the party begin :P Quick Revision about the previous lectures:
7 Lojayn Salah Zaid R Al Najdawi Mohammad-Khatatbeh Salam everyone, I made my best to make this sheet clear enough to be easily understood let the party begin :P Quick Revision about the previous lectures:
Resting membrane potential,
 Resting membrane potential Inside of each cell is negative as compared with outer surface: negative resting membrane potential (between -30 and -90 mv) Examination with microelectrode (Filled with KCl
Resting membrane potential Inside of each cell is negative as compared with outer surface: negative resting membrane potential (between -30 and -90 mv) Examination with microelectrode (Filled with KCl
BIOELECTRIC PHENOMENA
 Chapter 11 BIOELECTRIC PHENOMENA 11.3 NEURONS 11.3.1 Membrane Potentials Resting Potential by separation of charge due to the selective permeability of the membrane to ions From C v= Q, where v=60mv and
Chapter 11 BIOELECTRIC PHENOMENA 11.3 NEURONS 11.3.1 Membrane Potentials Resting Potential by separation of charge due to the selective permeability of the membrane to ions From C v= Q, where v=60mv and
Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential
 Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Math Physiology p.1/23 Basic Problem The cell is full of stuff: Proteins, ions, fats, etc.
Introduction to Physiology II: Control of Cell Volume and Membrane Potential J. P. Keener Mathematics Department Math Physiology p.1/23 Basic Problem The cell is full of stuff: Proteins, ions, fats, etc.
Electrical Properties of the Membrane
 BIOE 2520 Electrical Properties of the Membrane Reading: Chapter 11 of Alberts et al. Stephen Smith, Ph.D. 433 Biotech Center shs46@pitt.edu Permeability of Lipid membrane Lipid bilayer is virtually impermeable
BIOE 2520 Electrical Properties of the Membrane Reading: Chapter 11 of Alberts et al. Stephen Smith, Ph.D. 433 Biotech Center shs46@pitt.edu Permeability of Lipid membrane Lipid bilayer is virtually impermeable
2.6 The Membrane Potential
 2.6: The Membrane Potential 51 tracellular potassium, so that the energy stored in the electrochemical gradients can be extracted. Indeed, when this is the case experimentally, ATP is synthesized from
2.6: The Membrane Potential 51 tracellular potassium, so that the energy stored in the electrochemical gradients can be extracted. Indeed, when this is the case experimentally, ATP is synthesized from
Cells have an unequal distribution of charge across their membrane: more postiive charges on the outside; more negative charges on the inside.
 Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the cell with a voltmeter. neurons, muscle cells, heart cells, endocrine cells...
Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the cell with a voltmeter. neurons, muscle cells, heart cells, endocrine cells...
Neurons and the membrane potential. N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016
 Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Neurons and the membrane potential N500 John Beggs 23 Aug, 2016 My background, briefly Neurons Structural elements of a typical neuron Figure 1.2 Some nerve cell morphologies found in the human
Action Potential Propagation
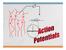 Action Potential Propagation 2 Action Potential is a transient alteration of transmembrane voltage (or membrane potential) across an excitable membrane generated by the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
Action Potential Propagation 2 Action Potential is a transient alteration of transmembrane voltage (or membrane potential) across an excitable membrane generated by the activity of voltage-gated ion channels.
Quantitative Electrophysiology
 ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Tuesday, September 18, 2012 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Tuesday, September 18, 2012 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
Nernst Equilibrium Potential. p. 1
 Nernst Equilibrium Potential p. 1 Diffusion The conservation law for a compound with concentration c: rate change of c = local production + accumulation due to transport. Model: d c dv = p dv J n da dt
Nernst Equilibrium Potential p. 1 Diffusion The conservation law for a compound with concentration c: rate change of c = local production + accumulation due to transport. Model: d c dv = p dv J n da dt
Quantitative Electrophysiology
 ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Wednesday, September 13, 2006 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in
ECE 795: Quantitative Electrophysiology Notes for Lecture #1 Wednesday, September 13, 2006 1. INTRODUCTION TO EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in
Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the
Vert Phys PCB3743 Membrane Potential Fox Chapter 6 pt 2 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Resting Membrane potential (V m ) or RMP Many cells have a membrane potential (Vm) that can be measured from an electrode in the
There should be nothing new for you in this lecture. If there is, stay for office hours and / or ask for help from the TAs.
 Membranes 02 The goal of this lecture is to review pre-requisite material related to the structure and function of biological membranes and to provide students a further overview of material to be covered
Membranes 02 The goal of this lecture is to review pre-requisite material related to the structure and function of biological membranes and to provide students a further overview of material to be covered
Computational Neuroscience. Session 2-1
 Computational Neuroscience. Session 2-1 Dr. Marco A Roque Sol 06/04/2018 All living cells exhibit an electrical potential difference between the inner and outer surface of the cytoplasmic membrane. This
Computational Neuroscience. Session 2-1 Dr. Marco A Roque Sol 06/04/2018 All living cells exhibit an electrical potential difference between the inner and outer surface of the cytoplasmic membrane. This
Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission. Membrane Potential
 Cl Cl - - + K + K+ K + K Cl - 2/2/15 Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission Core Curriculum II Spring 2015 Membrane Potential Example 1: K +, Cl - equally permeant no charge
Cl Cl - - + K + K+ K + K Cl - 2/2/15 Membrane Potentials, Action Potentials, and Synaptic Transmission Core Curriculum II Spring 2015 Membrane Potential Example 1: K +, Cl - equally permeant no charge
2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary
 2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary Griffith University, Nathan Campus Semester 1, 2014 Topics include: - Diffusion, Membranes & Action Potentials - Fundamentals of the Nervous System - Neuroanatomy
2002NSC Human Physiology Semester Summary Griffith University, Nathan Campus Semester 1, 2014 Topics include: - Diffusion, Membranes & Action Potentials - Fundamentals of the Nervous System - Neuroanatomy
Cellular Electrophysiology. Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Part 1: Resting and Action Potentials Cardiac Electrophysiology Theory Simulation Experiment Scale The membrane: structure, channels and gates The cell: resting potential, whole cell currents, cardiac
Part 1: Resting and Action Potentials Cardiac Electrophysiology Theory Simulation Experiment Scale The membrane: structure, channels and gates The cell: resting potential, whole cell currents, cardiac
Properties of the living organism. Interaction between living organism and the environment. Processing informations. Definitions
 thermodynamics material energy Interaction between living organism and the environment Open system: free material and energy exchange. Processing informations information processing answer Properties of
thermodynamics material energy Interaction between living organism and the environment Open system: free material and energy exchange. Processing informations information processing answer Properties of
Channels can be activated by ligand-binding (chemical), voltage change, or mechanical changes such as stretch.
 1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
1. Describe the basic structure of an ion channel. Name 3 ways a channel can be "activated," and describe what occurs upon activation. What are some ways a channel can decide what is allowed to pass through?
Biological membranes and bioelectric phenomena
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Dept. Biophysics, Medical faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biological membranes and bioelectric phenomena A part of this lecture was prepared on the basis of a presentation
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Dept. Biophysics, Medical faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Biological membranes and bioelectric phenomena A part of this lecture was prepared on the basis of a presentation
Chapter 2 Cellular Homeostasis and Membrane Potential
 Chapter 2 Cellular Homeostasis and Membrane Potential 2.1 Membrane Structure and Composition The human cell can be considered to consist of a bag of fluid with a wall that separates the internal, or intracellular,
Chapter 2 Cellular Homeostasis and Membrane Potential 2.1 Membrane Structure and Composition The human cell can be considered to consist of a bag of fluid with a wall that separates the internal, or intracellular,
CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT. Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines GENERIC SIGNALLING PATHWAY CELL RESPONSE TO SIGNALS CELL RESPONSE
CELL SIGNALLING and MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Mark Louie D. Lopez Department of Biology College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines GENERIC SIGNALLING PATHWAY CELL RESPONSE TO SIGNALS CELL RESPONSE
لجنة الطب البشري رؤية تنير دروب تميزكم
 1) Hyperpolarization phase of the action potential: a. is due to the opening of voltage-gated Cl channels. b. is due to prolonged opening of voltage-gated K + channels. c. is due to closure of the Na +
1) Hyperpolarization phase of the action potential: a. is due to the opening of voltage-gated Cl channels. b. is due to prolonged opening of voltage-gated K + channels. c. is due to closure of the Na +
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Electrophysiology: Electrotonic Properties 2 Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. The Model Neuron Lab Your PC/CSB115 http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~pineda/cogs107a/index.html Labs - Electrophysiology
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Electrophysiology: Electrotonic Properties 2 Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. The Model Neuron Lab Your PC/CSB115 http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/~pineda/cogs107a/index.html Labs - Electrophysiology
Mathematical Models. Chapter Modelling the Body as a Volume Conductor
 Chapter 2 Mathematical Models 2.1 Modelling the Body as a Volume Conductor As described in the previous chapter, the human body consists of billions of cells, which may be connected by various coupling
Chapter 2 Mathematical Models 2.1 Modelling the Body as a Volume Conductor As described in the previous chapter, the human body consists of billions of cells, which may be connected by various coupling
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 9 - TRANSPORT ACROSS MEMBRANES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
!! www.clutchprep.com K + K + K + K + CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: PRINCIPLES OF TRANSMEMBRANE TRANSPORT Membranes and Gradients Cells must be able to communicate across their membrane barriers to materials
Ionic basis of the resting membrane potential. Foundations in Neuroscience I, Oct
 Ionic basis of the resting membrane potential Foundations in Neuroscience I, Oct 3 2017 The next 4 lectures... - The resting membrane potential (today) - The action potential - The neural mechanisms behind
Ionic basis of the resting membrane potential Foundations in Neuroscience I, Oct 3 2017 The next 4 lectures... - The resting membrane potential (today) - The action potential - The neural mechanisms behind
Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain
 Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain Chapter 3: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Slide 2 Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 3 Not at rest
Slide 1 Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain Chapter 3: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Slide 2 Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 3 Not at rest
ELEMENTARY ASPECTS OF IONIC EQUILIBRIA
 ELEMENTRY SPETS OF IONI EQUILIRI ( self-instructional package) Howard Kutchai Department of Physiology University of Virginia harlottesville, Va. 22908 opyright 2003 by Howard Kutchai 2 INTRODUTION Ions
ELEMENTRY SPETS OF IONI EQUILIRI ( self-instructional package) Howard Kutchai Department of Physiology University of Virginia harlottesville, Va. 22908 opyright 2003 by Howard Kutchai 2 INTRODUTION Ions
PNS Chapter 7. Membrane Potential / Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu
 PNS Chapter 7 Membrane Potential 18-698 / 42-632 Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu Roadmap Introduction to neuroscience Chapter 1 The brain and behavior Chapter 2 Nerve cells and behavior
PNS Chapter 7 Membrane Potential 18-698 / 42-632 Neural Signal Processing Spring 2017 Prof. Byron Yu Roadmap Introduction to neuroscience Chapter 1 The brain and behavior Chapter 2 Nerve cells and behavior
General Physics. Nerve Conduction. Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power. Fluids. Direct Current (DC)
 Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power Fluids Direct Current (DC) Nerve Conduction Wave properties of light Ionizing Radiation General Physics Prepared by: Sujood Alazzam 2017/2018 CHAPTER OUTLINE
Newton s laws of Motion Work, Energy and Power Fluids Direct Current (DC) Nerve Conduction Wave properties of light Ionizing Radiation General Physics Prepared by: Sujood Alazzam 2017/2018 CHAPTER OUTLINE
Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007
 BtuB OM vitamin B12 transporter F O F 1 ATP synthase Human multiple drug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007 Transport and membrane motors Concentrations
BtuB OM vitamin B12 transporter F O F 1 ATP synthase Human multiple drug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein Transporters and Membrane Motors Nov 15, 2007 Transport and membrane motors Concentrations
Passive Membrane Properties
 Passive Membrane Properties Communicating through a leaky garden hose... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics
Passive Membrane Properties Communicating through a leaky garden hose... Topics I Introduction & Electrochemical Gradients Passive Membrane Properties Action Potentials Voltage-Gated Ion Channels Topics
Chapter 3 Part 1! 10 th ed.: pp ! 11 th ed.: pp !! Cellular Transport Mechanisms! The Cell Cycle!
 Chapter 3 Part 1! 10 th ed.: pp. 87 105! 11 th ed.: pp. 90 107!! Cellular Transport Mechanisms! The Cell Cycle! Transport Processes: Passive and Active (1 of 2)! 1. Passive transport! Does not use ATP!
Chapter 3 Part 1! 10 th ed.: pp. 87 105! 11 th ed.: pp. 90 107!! Cellular Transport Mechanisms! The Cell Cycle! Transport Processes: Passive and Active (1 of 2)! 1. Passive transport! Does not use ATP!
Chapter 3 Part 1! 10 th ed.: pp ! 11 th ed.: pp !! Cellular Transport Mechanisms! The Cell Cycle!
 Chapter 3 Part 1! 10 th ed.: pp. 87 105! 11 th ed.: pp. 90 107!! Cellular Transport Mechanisms! The Cell Cycle! Transport Processes: Passive and Active (1 of 2)! 1. Passive transport! Does not use ATP!
Chapter 3 Part 1! 10 th ed.: pp. 87 105! 11 th ed.: pp. 90 107!! Cellular Transport Mechanisms! The Cell Cycle! Transport Processes: Passive and Active (1 of 2)! 1. Passive transport! Does not use ATP!
Biomedical Instrumentation
 ELEC ENG 4BD4: Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 5 Bioelectricity 1. INTRODUCTION TO BIOELECTRICITY AND EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
ELEC ENG 4BD4: Biomedical Instrumentation Lecture 5 Bioelectricity 1. INTRODUCTION TO BIOELECTRICITY AND EXCITABLE CELLS Historical perspective: Bioelectricity first discovered by Luigi Galvani in 1780s
Problem Set No. 4 Due: Monday, 11/18/10 at the start of class
 Department of Chemical Engineering ChE 170 University of California, Santa Barbara Fall 2010 Problem Set No. 4 Due: Monday, 11/18/10 at the start of class Objective: To understand the thermodynamic and
Department of Chemical Engineering ChE 170 University of California, Santa Barbara Fall 2010 Problem Set No. 4 Due: Monday, 11/18/10 at the start of class Objective: To understand the thermodynamic and
Physics of biological membranes, diffusion, osmosis Dr. László Nagy
 Physics of biological membranes, diffusion, osmosis Dr. László Nagy -Metabolic processes and transport processes. - Macrotransport : transport of large amount of material : through vessel systems : in
Physics of biological membranes, diffusion, osmosis Dr. László Nagy -Metabolic processes and transport processes. - Macrotransport : transport of large amount of material : through vessel systems : in
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Lecture Notes 8C120 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren. Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation. Nico Kuijpers
 Lecture Notes 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation Nico Kuijpers nico.kuijpers@bf.unimaas.nl February 9, 2 2 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Extracellular
Lecture Notes 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation Nico Kuijpers nico.kuijpers@bf.unimaas.nl February 9, 2 2 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Extracellular
Housekeeping, 26 January 2009
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
Neurons. 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan Finish Solutes + Water. 2. Neurons. Chapter 11
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Neurons Chapter 11 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes + Water 2. Neurons
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics. Eileen Nugent
 Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
The Membrane Potential
 The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion
The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.aw.com/bc) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion
NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials. The Electrochemical Gradient
 NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials Communication by neurons is based on changes in the membrane s permeability to ions This depends on the presence of specific membrane ion channels and the presence
NeuroPhysiology and Membrane Potentials Communication by neurons is based on changes in the membrane s permeability to ions This depends on the presence of specific membrane ion channels and the presence
What are neurons for?
 5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes Water 2. Neurons Neurons Chapter 11
5 th & 6 th Lectures Mon 26 & Wed 28 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Solutes Water 2. Neurons Neurons Chapter 11
Physiology Coloring Book: Panels 29, 32, 33,
 ELEC4623/ELEC9734: Semester 2, 2009 Dr Stephen Redmond School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications Email: s.redmond@unsw.edu.au Ph: 9385 6101 Rm: 458, ELECENG (G17) Physiology Coloring Book:
ELEC4623/ELEC9734: Semester 2, 2009 Dr Stephen Redmond School of Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications Email: s.redmond@unsw.edu.au Ph: 9385 6101 Rm: 458, ELECENG (G17) Physiology Coloring Book:
Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.
 Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Membranes (CH4) 2. Nervous System
Lecture 04, 04 Sept 2003 Chapters 4 and 5 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 University of Arizona Fall 2003 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Bret Pasch Vertebrate Physiology 437 1. Membranes (CH4) 2. Nervous System
Membrane transport 1. Summary
 Membrane transport 1. Summary A. Simple diffusion 1) Diffusion by electrochemical gradient no energy required 2) No channel or carrier (or transporter protein) is needed B. Passive transport (= Facilitated
Membrane transport 1. Summary A. Simple diffusion 1) Diffusion by electrochemical gradient no energy required 2) No channel or carrier (or transporter protein) is needed B. Passive transport (= Facilitated
The Membrane Potential
 The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion channel
The Membrane Potential Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) ** It is suggested that you carefully label each ion channel
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. The Nervous System and Muscle
 The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
Rahaf Nasser mohammad khatatbeh
 7 7... Hiba Abu Hayyeh... Rahaf Nasser mohammad khatatbeh Mohammad khatatbeh Brief introduction about membrane potential The term membrane potential refers to a separation of opposite charges across the
7 7... Hiba Abu Hayyeh... Rahaf Nasser mohammad khatatbeh Mohammad khatatbeh Brief introduction about membrane potential The term membrane potential refers to a separation of opposite charges across the
Supplementary Material. Model Details
 Supplementary Material Model Details The core of the model is the astrocyte lane, as depicted in Fig. 1A of the paper. For the numerical solution, each astrocyte is represented by a rectangular cartesian
Supplementary Material Model Details The core of the model is the astrocyte lane, as depicted in Fig. 1A of the paper. For the numerical solution, each astrocyte is represented by a rectangular cartesian
- the flow of electrical charge from one point to the other is current.
 Biology 325, Fall 2004 Resting membrane potential I. Introduction A. The body and electricity, basic principles - the body is electrically neutral (total), however there are areas where opposite charges
Biology 325, Fall 2004 Resting membrane potential I. Introduction A. The body and electricity, basic principles - the body is electrically neutral (total), however there are areas where opposite charges
BIOELECTRIC POTENTIALS
 3 BIOELECTRIC POTENTIALS In this book we will be examining the behavior of excitable cells, notably nerve and muscle, both descriptively and quantitatively. The behavior is described mostly in terms of
3 BIOELECTRIC POTENTIALS In this book we will be examining the behavior of excitable cells, notably nerve and muscle, both descriptively and quantitatively. The behavior is described mostly in terms of
Neuroscience 201A (2016) Peter Sargent, PhD Voice (cell)
 Neuroscience 201A (2016) Peter Sargent, PhD peter.sargent@ucsf.edu Voice (cell) 415.728.8139 Outline for Today Course organization and logistics Electricity 101 The Electrical Properties of Neurons The
Neuroscience 201A (2016) Peter Sargent, PhD peter.sargent@ucsf.edu Voice (cell) 415.728.8139 Outline for Today Course organization and logistics Electricity 101 The Electrical Properties of Neurons The
Phys498BIO; Prof. Paul Selvin Hw #9 Assigned Wed. 4/18/12: Due 4/25/08
 1. Ionic Movements Across a Permeable Membrane: The Nernst Potential. In class we showed that if a non-permeable membrane separates a solution with high [KCl] from a solution with low [KCl], the net charge
1. Ionic Movements Across a Permeable Membrane: The Nernst Potential. In class we showed that if a non-permeable membrane separates a solution with high [KCl] from a solution with low [KCl], the net charge
Chapt. 12, Movement Across Membranes. Chapt. 12, Movement through lipid bilayer. Chapt. 12, Movement through lipid bilayer
 Chapt. 12, Movement Across Membranes Two ways substances can cross membranes Passing through the lipid bilayer Passing through the membrane as a result of specialized proteins 1 Chapt. 12, Movement through
Chapt. 12, Movement Across Membranes Two ways substances can cross membranes Passing through the lipid bilayer Passing through the membrane as a result of specialized proteins 1 Chapt. 12, Movement through
The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump
 The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump 1. Define the following terms: Ion: A Student Activity on Membrane Potentials Cation: Anion: Concentration gradient: Simple diffusion: Sodium-Potassium
The Nervous System and the Sodium-Potassium Pump 1. Define the following terms: Ion: A Student Activity on Membrane Potentials Cation: Anion: Concentration gradient: Simple diffusion: Sodium-Potassium
2. At quasi-steady state or equilibrium, the net in-flux of the carrier-substrate complex CS is balanced by the net out-flux of the free carrier C.
 Facilitated Transport Instructor: Nam un Wang facilitmcd Process escription In facilitated transport, a carrier molecule C binds to the substrate to form a carrier-substrate complex C at the outer side
Facilitated Transport Instructor: Nam un Wang facilitmcd Process escription In facilitated transport, a carrier molecule C binds to the substrate to form a carrier-substrate complex C at the outer side
Membrane Physiology. Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Oct-18 1
 Membrane Physiology Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 22-10-2018 29-Oct-18 1 Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular fluids. 29-Oct-18 2 Transport through the cell membrane occurs by one of two basic processes:
Membrane Physiology Dr. Hiwa Shafiq 22-10-2018 29-Oct-18 1 Chemical compositions of extracellular and intracellular fluids. 29-Oct-18 2 Transport through the cell membrane occurs by one of two basic processes:
Transport of ions across plasma membranes
 Transport of ions across plasma membranes Plasma Membranes of Excitable tissues Ref: Guyton, 13 th ed: pp: 61-71. 12 th ed: pp: 57-69. 11th ed: p57-71, Electrical properties of plasma membranes Part A:
Transport of ions across plasma membranes Plasma Membranes of Excitable tissues Ref: Guyton, 13 th ed: pp: 61-71. 12 th ed: pp: 57-69. 11th ed: p57-71, Electrical properties of plasma membranes Part A:
Chapter 1 subtitles Ion gradients
 CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 1 subtitles Ion gradients Introduction In this first chapter, I'll explain the basic knowledge required to understand the electrical signals generated
CELLULAR NEUROPHYSIOLOGY CONSTANCE HAMMOND Chapter 1 subtitles Ion gradients Introduction In this first chapter, I'll explain the basic knowledge required to understand the electrical signals generated
Electrophysiology of the neuron
 School of Mathematical Sciences G4TNS Theoretical Neuroscience Electrophysiology of the neuron Electrophysiology is the study of ionic currents and electrical activity in cells and tissues. The work of
School of Mathematical Sciences G4TNS Theoretical Neuroscience Electrophysiology of the neuron Electrophysiology is the study of ionic currents and electrical activity in cells and tissues. The work of
Physiology Unit 2. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES
 Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES In Physiology Today Ohm s Law I = V/R Ohm s law: the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the
Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES In Physiology Today Ohm s Law I = V/R Ohm s law: the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the
Main idea of this lecture:
 Ac#ve Transport Main idea of this lecture: How do molecules, big and small, get in OR out of a cell? 2 Main ways: Passive Transport (Does not require energy) Lecture 1 Ac=ve Transport (Requires energy)
Ac#ve Transport Main idea of this lecture: How do molecules, big and small, get in OR out of a cell? 2 Main ways: Passive Transport (Does not require energy) Lecture 1 Ac=ve Transport (Requires energy)
Chapter 2 Basic Cardiac Electrophysiology: Excitable Membranes
 Chapter Basic Cardiac Electrophysiology: Excitable Membranes Deborah A. Jaye, Yong-Fu Xiao, and Daniel C. Sigg Abstract Cardiomyocytes are excitable cells that have the ability to contract after excitation;
Chapter Basic Cardiac Electrophysiology: Excitable Membranes Deborah A. Jaye, Yong-Fu Xiao, and Daniel C. Sigg Abstract Cardiomyocytes are excitable cells that have the ability to contract after excitation;
Supplementary information Fig. S1.
 Supplementary information Kinetic equivalence of transmembrane ph and electrical potential differences in ATP synthesis Naoki Soga, Kazuhiko Kinosita, Jr., Masasuke Yoshida and Toshiharu Suzuki Fig. S1.
Supplementary information Kinetic equivalence of transmembrane ph and electrical potential differences in ATP synthesis Naoki Soga, Kazuhiko Kinosita, Jr., Masasuke Yoshida and Toshiharu Suzuki Fig. S1.
Equivalent Circuit Model of the Neuron
 Generator Potentials, Synaptic Potentials and Action Potentials All Can Be Described by the Equivalent Circuit Model of the Membrane Equivalent Circuit Model of the Neuron PNS, Fig 211 The Nerve (or Muscle)
Generator Potentials, Synaptic Potentials and Action Potentials All Can Be Described by the Equivalent Circuit Model of the Membrane Equivalent Circuit Model of the Neuron PNS, Fig 211 The Nerve (or Muscle)
OT Exam 1, August 9, 2002 Page 1 of 8. Occupational Therapy Physiology, Summer Examination 1. August 9, 2002
 Page 1 of 8 Occupational Therapy Physiology, Summer 2002 Examination 1 August 9, 2002 Dr. Heckman's section is questions 1-6 and each question is worth 5 points for a total of 30 points. Dr. Driska's section
Page 1 of 8 Occupational Therapy Physiology, Summer 2002 Examination 1 August 9, 2002 Dr. Heckman's section is questions 1-6 and each question is worth 5 points for a total of 30 points. Dr. Driska's section
Lecture 04, 01 Sept 2005 Chapters 2, 3, and 10. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005
 Lecture 04, 01 Sept 2005 Chapters 2, 3, and 10 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter 1 Vertebrate Physiology
Lecture 04, 01 Sept 2005 Chapters 2, 3, and 10 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter 1 Vertebrate Physiology
Lecture 04, 01 Sept 2005 Chapters 2, 3, and 10. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005
 Lecture 04, 01 Sept 2005 Chapters 2, 3, and 10 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter Vertebrate Physiology 437
Lecture 04, 01 Sept 2005 Chapters 2, 3, and 10 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter Vertebrate Physiology 437
6 Mechanotransduction. rotation
 rotation inflow outflow Figure 6.3: Circumferential and uniaxial flow devices applying shear stress to the cell culture. They are stimulated through a circumferential fluid flow generating by a rotating
rotation inflow outflow Figure 6.3: Circumferential and uniaxial flow devices applying shear stress to the cell culture. They are stimulated through a circumferential fluid flow generating by a rotating
Chapter 2 Models of Ion Transport in Mammalian Cells
 Chapter 2 Models of Ion Transport in Mammalian Cells Cardiomyocytes, neurons, hepatocytes and erythrocytes are considered based on the algorithm one ion one transport system models of some mammalian cells.
Chapter 2 Models of Ion Transport in Mammalian Cells Cardiomyocytes, neurons, hepatocytes and erythrocytes are considered based on the algorithm one ion one transport system models of some mammalian cells.
The nerve impulse. INTRODUCTION
 The nerve impulse. INTRODUCTION Axons are responsible for the transmission of information between different points of the nervous system and their function is analogous to the wires that connect different
The nerve impulse. INTRODUCTION Axons are responsible for the transmission of information between different points of the nervous system and their function is analogous to the wires that connect different
FRTF01 L8 Electrophysiology
 FRTF01 L8 Electrophysiology Lecture Electrophysiology in general Recap: Linear Time Invariant systems (LTI) Examples of 1 and 2-dimensional systems Stability analysis The need for non-linear descriptions
FRTF01 L8 Electrophysiology Lecture Electrophysiology in general Recap: Linear Time Invariant systems (LTI) Examples of 1 and 2-dimensional systems Stability analysis The need for non-linear descriptions
Alaa' Alajrami. Hussam Twaissi. Mohammad khatatbeh
 6 Alaa' Alajrami Hussam Twaissi Mohammad khatatbeh Keep smiling stay beautiful,,, We will continue talking about cell membrane and what cause the potential across it. * Proton depended carrier: (secondary
6 Alaa' Alajrami Hussam Twaissi Mohammad khatatbeh Keep smiling stay beautiful,,, We will continue talking about cell membrane and what cause the potential across it. * Proton depended carrier: (secondary
Biochemistry. Biochemistry 9/20/ Bio-Energetics. 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes
 9/20/15 Biochemistry Biochemistry 4. Bio-Energetics 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes Aquaporin, the water channel, consists of four identical transmembrane polypeptides
9/20/15 Biochemistry Biochemistry 4. Bio-Energetics 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes Aquaporin, the water channel, consists of four identical transmembrane polypeptides
Nernst Equation and Equilibrium Potentials
 CELLULAR AND AUTONOMIC PHYSIOLOGY 13 Case 3 Nernst Equation and Equilibrium Potentials This case will guide you through the principles underlying diffusion potentials and electrochemical equilibrium. veil
CELLULAR AND AUTONOMIC PHYSIOLOGY 13 Case 3 Nernst Equation and Equilibrium Potentials This case will guide you through the principles underlying diffusion potentials and electrochemical equilibrium. veil
Lecture 3 13/11/2018
 Lecture 3 13/11/2018 1 Plasma membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids. protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump Lipid bilayer allows water, carbon
Lecture 3 13/11/2018 1 Plasma membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids. protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump Lipid bilayer allows water, carbon
[Part II] Chemistry and Physiology
![[Part II] Chemistry and Physiology [Part II] Chemistry and Physiology](/thumbs/74/70281995.jpg) [Part II] Quantitative Acid-Base Chemistry and Physiology [Chapter 10] Normal [SID] Peter Wilkes 10.1 Introduction This chapter will discuss issues surrounding the measurement and conceptualization of
[Part II] Quantitative Acid-Base Chemistry and Physiology [Chapter 10] Normal [SID] Peter Wilkes 10.1 Introduction This chapter will discuss issues surrounding the measurement and conceptualization of
Biochemistry. Biochemistry 7/11/ Bio-Energetics. 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes
 Biochemistry Biochemistry 4. Bio-Energetics 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes Aquaporin, the water channel, consists of four identical transmembrane polypeptides Key Energy
Biochemistry Biochemistry 4. Bio-Energetics 4.2) Transport of ions and small molecules across cell membranes Aquaporin, the water channel, consists of four identical transmembrane polypeptides Key Energy
Chapter 8 Calcium-Induced Calcium Release
 Chapter 8 Calcium-Induced Calcium Release We started in Chap. 2 by assuming that the concentrations of the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum (JSR) and the network sarcoplasmic reticulum (NSR) are identical
Chapter 8 Calcium-Induced Calcium Release We started in Chap. 2 by assuming that the concentrations of the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum (JSR) and the network sarcoplasmic reticulum (NSR) are identical
768 Lecture #11 of 18
 Lecture #11 of 18 768 769 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 2 main concepts: Section 2.1 : Section 2.3: Salt; Activity; Underpotential deposition Transference numbers; Liquid junction potentials
Lecture #11 of 18 768 769 Q: What s in this set of lectures? A: B&F Chapter 2 main concepts: Section 2.1 : Section 2.3: Salt; Activity; Underpotential deposition Transference numbers; Liquid junction potentials
Ionic gradients, membrane potential and ionic currents Constance Hammond
 C H A P T E R 3 c0015 Ionic gradients, membrane potential and ionic currents Constance Hammond O U T L I N E u0010 u0015 u0020 3.1 There is an unequal distribution of ions across neuronal plasma membrane.
C H A P T E R 3 c0015 Ionic gradients, membrane potential and ionic currents Constance Hammond O U T L I N E u0010 u0015 u0020 3.1 There is an unequal distribution of ions across neuronal plasma membrane.
ACTION POTENTIAL. Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil
 ACTION POTENTIAL Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil DEFINITIONS: Stimulus: A stimulus is an external force or event which when applied to an excitable tissue produces a characteristic response. Subthreshold
ACTION POTENTIAL Dr. Ayisha Qureshi Professor MBBS, MPhil DEFINITIONS: Stimulus: A stimulus is an external force or event which when applied to an excitable tissue produces a characteristic response. Subthreshold
1 Hodgkin-Huxley Theory of Nerve Membranes: The FitzHugh-Nagumo model
 1 Hodgkin-Huxley Theory of Nerve Membranes: The FitzHugh-Nagumo model Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley developed the first quantitative model of the propagation of an electrical signal (the action potential)
1 Hodgkin-Huxley Theory of Nerve Membranes: The FitzHugh-Nagumo model Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley developed the first quantitative model of the propagation of an electrical signal (the action potential)
Solutes & Water Chapter 4
 4 th Lecture, 23 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Solutes & Water Chapter 4 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Molecules, Membranes, etc. 2. Solutes
4 th Lecture, 23 Jan 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Solutes & Water Chapter 4 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh 1. Finish Molecules, Membranes, etc. 2. Solutes
STUDIES OF CHANGING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL * : 1. BASIC ELECTRICAL THEORY, 2. GRADED AND ACTION POTENTIALS 3. THE VOLTAGE CLAMP AND MEMBRANE POTENTIALS
 STUDIES OF CHANGING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL * : 1. BASIC ELECTRICAL THEORY, 2. GRADED AND ACTION POTENTIALS 3. THE VOLTAGE CLAMP AND MEMBRANE POTENTIALS I. INTRODUCTION A. So far we have only considered the
STUDIES OF CHANGING MEMBRANE POTENTIAL * : 1. BASIC ELECTRICAL THEORY, 2. GRADED AND ACTION POTENTIALS 3. THE VOLTAGE CLAMP AND MEMBRANE POTENTIALS I. INTRODUCTION A. So far we have only considered the
Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease
 Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease Lecture 4: Membrane Transport Proteins Kiaran Kirk Research School of Biology Learning objectives To understand: The need for membrane transport proteins in
Biol2174 Cell Physiology in Health & Disease Lecture 4: Membrane Transport Proteins Kiaran Kirk Research School of Biology Learning objectives To understand: The need for membrane transport proteins in
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 5 Μοντέλο Hodgkin-Huxley (Hodgkin-Huxley Model) Response to Current Injection 2 Hodgin & Huxley Sir Alan Lloyd
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 5 Μοντέλο Hodgkin-Huxley (Hodgkin-Huxley Model) Response to Current Injection 2 Hodgin & Huxley Sir Alan Lloyd
Oxidation & Reduction II. Suggested reading: Chapter 5
 Lecture 1 Oxidation & Reduction II Suggested reading: Chapter 5 Recall from Last time: Redox Potentials The Nernst equation: E cell E 0 RT F ln Q Cell Potential and ph For the H + /H couple at 1 bar and
Lecture 1 Oxidation & Reduction II Suggested reading: Chapter 5 Recall from Last time: Redox Potentials The Nernst equation: E cell E 0 RT F ln Q Cell Potential and ph For the H + /H couple at 1 bar and
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS
 2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Monday, 27 June, 9.30 am 12.30 pm Answer
2757 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C7: BIOLOGICAL PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Monday, 27 June, 9.30 am 12.30 pm Answer
Physiology Unit 2. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES
 Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES Neuron Communication Neurons are stimulated by receptors on dendrites and cell bodies (soma) Ligand gated ion channels GPCR s Neurons stimulate cells
Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES Neuron Communication Neurons are stimulated by receptors on dendrites and cell bodies (soma) Ligand gated ion channels GPCR s Neurons stimulate cells
