Whither WIMPs: Direct Detection of SUSY Cold Dark Matter
|
|
|
- Susan Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Whither WIMPs: Direct Detection of SUSY Cold Dark Matter One Tonne - Have we got what it takes? Report To NFAC Committee Jly 25,2002 Brown University, Department of Physics sefl information at Gaitskell
2 NaIAD UK DRIFT I CDMS II XENON Dark Matter Experiments (Worldwide) (Rnning/Active Collaboration) ZEPLIN I ZEPLIN III ZEPLIN II US CRESST II Edelweiss II France Canada IGEX Majorana(DM) Germany Orphes Switzerland ANAIS DAMA LIBRA Italy Japan Rosebd CsI Xenon Simple HDMS/Genino LiF XMASS(DM) Picasso Rssia Elegant V&VI Spain Coricino Taiwan US
3 Dark Matter Experiments - By Site Site Experiment Techniqe Target Stats Baksan (Rssia) IGEX Ionisation 3kg Ge Bern (Switzerland) ORPHEUS SSD 0.5kg Sn Bolby (UK) NaI NaIAD ZEPLIN I ZEPLIN II/III ZEPLIN-MAX DRIFT-I DRIFT-10 Scintillator Scintillator Scintillator Scintillator/Ionisation Scintillator/Ionisation TPC TPC 5kg NaI 50kg NaI 5kg Lxe 30kg/7kg Xe 1000kg Xe 0.2kg CS 2 2kg CS 2 Completed Constrction Planned Planned Canfranc (Spain) COSME IGEX ANAIS ROSEBUD Ionisation Ionisation Scintillator Thermal 0.2kg Ge 2.1kg Ge 107kg NaI Al 2 O 3,Ge,CaWO 4 Completed Constrction Frejs (France) Saclay-NaI EDELWEISS I EDELWEISS II Scintillation Thermal/Ionisation Thermal/Ionisation 10kg NaI 0.07kg Ge 1.3 kg Ge Completed Completed Gran Sasso (Italy) Hdlberg/Mscw HDMS Genis DAMA LIBRA Xenon CRESST-I CRESST-II CUORICINO CUORE Ionisation Ionisation Ionisation Scintillation Scintillation Scintillation Thermal Thermal/Scintillation Thermal Thermal 2.7kg Ge 0.2kg Ge 100kg Ge 100kg NaI 250kg NaI 6kg Xe 1kg Al 2 O 3 10kg CaWO 4 40kg TeO 2 760kg TeO 2 Completed Planned Constrction Constrction Constrction Planned Kamioke (Japan) XMAS Scintillator/Ionisation 3 kg Xe 1000 kg Xe Planned Otto-Cosmo (Japan) Elegants V Elegants VI LiF Scintillation Scintillation Thermal NaI CaF 2 LiF Rstrel (France) SIMPLE SDD Freon Stanford (USA) CDMS-1 Thermal/Ionisation 0.1kg Si, 1kg Ge Completed Sodan (USA) CDMS-II CryoArray Phonons/Ionisation 0.3ks Si, 0.75kg Ge 2 kg Si, 7 kg Ge kg Ge Constrction Constrction Planned??? (USA) XENON Scintillator/Ionisation 1000 kg Xe Planned Sdbry (Canada) PICASSO SDD 1g Freon
4 Talk Overview Cosmology & WIMPs in the Early Universe WIMPs in or own galaxy SUSY Framework DM Detection: History & Ftre Projections Highlight Selection of Crrent Detectors & Their Evoltion Site Reqirements & Backgronds Smmary
5 Netralino Coplings Annihilation (many channels) Spin Independent - Scalar q Scattering from Nclei (A ncleons) Spin Independent - Scalar q q Spin Dependent - Axial Vector Coherent s~a 2 -->dominates Spin Dependent - Axial Vector a.d.t. time
6 SUSY Calclations of s Broad Spectrm of Theorists Making WIMP Rate Predictions Using SUSY inspired frameworks, broad consistemcy in reslts Ellis, Ferstl, Olive; Baltz, Gondolo; Corsetti, Nath; Arnowitt, Nath; Mandic, Pierce, Gondolo, Mayama; Baer, Brhlik; Bednyakov, Klapdor- Kleingrothas, Kovalenko; Bottino Codes based on DarkSUSY and NetDriver See Ellis, Ferstl, Olive PLB 532 (2002) 318 and refs therein Predicted Range of Cross-Sections Large range of SUSY space still allowed, SUSY mass scale ncertainty feeds directly into s ncertainty UPPER LIMIT Unable to make models consistent with DAMA signal, nless constraints on Ω m >0.2 (<0.6) are relaxed. Lower abndance, raises allowed annihilation s LOWER LIMIT? Plots on dmtools web site Important experimentally! Sets maximm scale of discovery detector
7 SUSY Calclations/Experimental Inpt (2) Important Inpts from Existing Accelerator Constraints SUSY m WIMP >50 GeV & m h (Lightest Higgs) >114 GeV Higgs constraints UPPER limit (now doing K) / LEP(final) Mon BNL (Anomalos Magnetic Moment) data a µ =(g-2)/2, a µ (exp)-a µ (SM)=4.3 ±1.6 x 10-10, where a µ measred ±1.3 ppm, theory ± 0.6ppm Represents 1.6s away from Standard Model prediction (revised down from 2.6s when SM theoretical calclation fond to contain nmerical sign error) Provides strong LOWER LIMIT ON WIMP s for models with µ>0 (see next slide)
8 SUSY Calclations/Experimental Inpt (3) Possible Ftre Inflential Accelerator Data BNL - New annoncement coming Tesday data 2000 data (4 times existing set): expect an exp. error of ppm If new reslt for a µ (exp is same as previos will give 2.6s deviation from SM If new reslt is consistent (@1s) with 1999 reslt then deviation cold be in range 0-4s) (Novosebirsk e+e-) Providing experimental rather than theoretical SM inpts to theoretical calc Crent claim takes crrent 1.6s -> 2s effect Ftre analysis data Expect finish analysis ~end redced systematics vs 2000 since better freqency choices Experiement is becoming systematics dominated (little statistical improvement possible) Tevatron (starting to rn ) SUSY discovery less likely However, strong SUSY loop inflence in b->bµµ decay channel G~(tanb) 6 Signal possible if tanb>30 BBar/Belle (rnning) Not likely, CP focs
9 SUSY Calclations/Experimental Inpt (4) LHC (Rnning by 2008) Consider LHC as backstop for SUSY Sensitive to sqarks&glinos <2.5 TeV, m1/2~1 TeV, m0~1.5 TeV For discovery at LHC, chosen framework wold have to imply m WIMP <500 GeVs Wide Range of Models Possible with crrent constraints If µ>0 (if g-2 reslts holds p, favors lower m 1/2, m 0 and µ>0) then If µ<0 Spin-independent s SI has range 6x x10-10 pb Spin-dependent s SD has range x10-7 pb Possible cancellation in SI interaction s SI ~ 0 Rely on SD interaction >10-8 pb
10 Crrent Experiments & SUSY Theory Range Edelweiss (Jne 2002) ~0.25 event/kg/d ~1 event/kg/yr ~ 1 event/100 kg/yr
11 Homestake (87) Direct Detection: History & Ftre 90% CL Limit on Cross section for 60 GeV WIMP (scalar copling) Gaitskell (astroph ) Oroville (88) [m=20 GeV] ~1 event kg -1 day -1 H-M (94) Edelweiss (98) UKDMC (96) H berg-moscow (98), IGEX (00) [m=100 GeV] DAMA (98) DAMA (00) CDMS SUF (99) DAMA (96) Edelweiss (01) ZEPLIN I Xe (02) CDMS SUF (02) Edelweiss (02) NOW ZEPLIN I 6 kg Xe (T) Different Colors Indicate Different Technologies Ge NaI Cryodet Liq Xe (T) Target Signal Majorana Phase 1 (T) GENINO (T) 100 kg Ge Diode ~1 event 100 kg -1 yr -1 ~1 event kg -1 yr -1 CDMS Sodan (T) 7 kg Ge+Si Cryodet ZEPLIN II+III 10 kg Xe (T) GENIUS (T) 100 kg Ge Diode CryoArray (T) LHC XENON / ZEPLIN 1t Xe tonne Cryodet [m =?? GeV - if significantly better limit obtained at different mass] Not meant to be a complete list - see rjg
12 Resolving Interpretation of DAMA Signal Positive Annal Modlation Signal No other experiment <2004 able to check annal mod Except for DAMA pgrade 250 kg Improved light yield (NaI / PMT) Lower backgrond (factor ~ few) Wold like to see revised acqisition strategy Retain mltiple events as control grop Direct Calibration of signal bin stability (g sorces & LEDs) Assming Scalar WIMP s ~ A 2 Cryogenic Ge CDMS I - netron backgrond limiting, bt inconsistent with mod amp. Reqire ~factor 3 lower limit to exclde all of 99% CL region at 90% Edelweiss already looking inconsistent ann mod. In 2002 look for ~10 kg-day exposre and zero events to rle ot CDMS II - First Dark start end 2002 Assming? particle (Not SUSY) Reqire NaI target to remove ncertainties Anias(Spain) & NaAID(UK) programs aim to se plse shape discrimination to srpass necessary sensitivity (DAMA do not plan to se PSD)
13 Key Points: Detectors, their environment & location Probable that we are witnessing the peak of worldwide diversity in DM Crrent WIMP detection limit ~0.25 events/kg/day (no WIMP-like events seen in ~10 kg-days exposre) Expect Rapid Progress in (based on assessment of crrent programs that are rnning, or in constrction) Will be achieving large exposres with Zero Backgrond Eqivalent for ~100 kg-days Reqired scale may prohibit some new technology entering arena, nless spported by large engineering effort Challenges for next stage
14 Key Points: Detectors, their environment & location (2) Greatest Challenges Constrction & Operation of Detector Arrays Undergrond Many of experiments experiencing delays All Grops wold benefit greatly from infrastrctre/spport of Undergrond Lab Knowledgeable Technical/Engineering Assistance Achieving Detector Discrimination Performance (free systematics) (Demanding Backgrond Discrimination >>99%) Improvements needed in Screening Facilities Redce Internal Radioactivity Crrent scale of typical collaboration has difficlty meeting all screening reqirements Experiments >2005 clearly demand access to systems beyond simple HPGe screening Srface/low energy radioactivity screening (Providing Inpt to NUSL -> Screen Fac Initiative) Fabrication of some (internal) constrction materials ndergrond Still being stdied by grops
15 Key Points: Detectors, their environment & location (3) Backgronds External Radioactivity Shielding Most dedicated (discriminating) WIMP experiments will se traditional shield This is not seen as a difficlty in larger experiments Pb for g s Poly (H) to moderate external (a,n) netrons (<10 MeV) from rock High Energy Netrons from mons in rock are a concern (see next slide)
16 Key Points: Detectors, their environment & location (3) Site Depth Reqirement Shallow ~1700 mwe (1 mons/m 2 /minte) will be satisfactory for compact (non-gas) targets Satisfactory for cosmogenic activation Mons passing throgh detector array can be vetoed by simple mon veto (>99% being achieved) Mons otside mon veto will generate high energy netrons ( MeV) that cannot be moderated directly sing poly A nmber of shielding strategies being developed, bt they all involve traditional technology Additional cost of thick active shield will not dominate total cost - consenss Withot thick shield, HE netrons events occr jst below CDMS II level (1 event/100 kg/day) Collaborations wold like to develop Monte Carlos of fll experiments to ensre that goal of backgrond <1 event/100 kg/year can be met Intermediate ~3800 mwe (Factor ~50x redction in mons/he netrons) Redced thick shielding cost Additional comfort factor, general consenss that 1 tonne experiments can fnction comfortably wrt to HE netrons from mons Depth may be necessary for gas target given mch large srface area to shield Deep ~6000 mwe (Frther factor ~50x redction in mon/he netrons) Not crrently on the road map - consenss overkill
17 High Energy (E>10 MeV) Netrons from Mons Netron prodction ~ Mon Flx With slight modification for hardening of mon spectrm mean(e m )~ Depth 0.47 Sodan Site * Not excavated (Mltiple levels given in ft) Relative Mon Flx Relative Netron Flx >10 MeV WIPP (2130 ft) x 65 x 45 Sodan x 30 x 25 Kamioke x 12 x 11 Bolby x 4 x 4 Gran Sasso Frejs, Homestake (4860 ft) x 1 x 1 Mont Blanc x 6-1 x 6-1 Sdbry x 25-1 x 25-1 Homestake (8200 ft) x 50-1 x 50-1 Aglietta et.al. Nove Cimento 12, N4, page 467
18 Key Points: Detectors, their environment & location (4) Technologies have/are crossing over Detectors: DBD decay Solar Netrino Netrino Magnetic Moment Searches Low backgrond techniqes/screening facilities: Pt in place strctre for mlti-ser
19 Inter-Collaboration / Synergies: Dark Matter Dark Matter has new concerns, beyond those of Crrent Low Backgrond Experiments kev Srface Contamination This will reqire New Screening Strategies Stdies/proposals nderway in US (-> NUSL) Los Alamos / Princeton List Created at Aspen Jne 2002 DM Workshop New Sorces of Backgrond Not jst U / Th / K What are the phenomenologies?.. plate-ot rates, materials preferences etc Low Backgrond Materials Selection Database from previos and live experiments e.g. Jst starting a database at Los Alamos (Tom Bowles), attached to NUSL Monte Carlos Low Backgrond Modeling NUSLib / BolbyLib / GranSassoLib? GEANT4 - able to track down to 250 ev
20 Collaboration / Synergies: Dark Matter (2) Ftre Alignment with Demands of/soltions from other experiments e.g. pp solar netrino, DBD experiments Read-ot Technologies Gas Readot Schemes MWPC / GEMs / MicroMegas Photo Detectors Cryogenic Detectors Field spported a diverse range of technologies Will it create difficlties when the necessary reintegration occrs for larger experiments? Proto-collaborations of collaborations forming. Individal DM Experiments Benefit from Progress of Other DM Experiments c.f. John Nash
21 Collaboration / Synergies: Dark Matter (3) Spport from International Laboratories Intermediate Scale Experiments Not capable of bringing fll resorce reqirements to hole in grond Probable that those labs providing best spport will benefit as will the experiments drawn to best labs
22 WIMP SUSY Dark Matter Conclsion (1) Cosmology: Need for Non-Baryonic Dark Matter (Ω~ ) Crrent Direct Detection Experiments Testing some SUSY models As sensitivity improves - will contine to test more models Recent/crrent accelerator constraints shrinking bonds Mainly constrained UPPER bond of cross-section g-2 can provide constraint on LOWER bond (for µ>0) if it remains statistically significant DAMA 4s positive signal, is being/will be tested (need to rle ot systematics) in 2002 by CDMS and Edelweiss (both look incompatible at present for s~a 2 ) Anais(Spain) ~50 kg NaI (Plse Shape Discrimination) in 2003/4 DAMA 250 kg pgrade (Ann Mod / Low backgronds / Higher Light Yield) Axial Vector (Spin Dependent) Qark-WIMP Coplings?.
23 WIMP SUSY Dark Matter Conclsion (2) Experimental Stats Cryogenic experiments (reporting reslts) Systematics increasingly well nderstood and dealt with (matring technology) able to zero signal contamination - Edelweiss 2002 (+ CDMS II detectors when moved to Sodan 2003 based on shallow site tests 80 kg-days) + Others Scale p to ~10 kg targets in 2003/4 Liqid Xe ZEP I 3 kg fid. single phase crrently rnning ndergrond (Bolby) ZEP II & III ~7 kg 2-phase (gas & liqid) being constrcted - deploy 2003 Performance data of prototypes sed to assess ZEPLIN MAX~100 kg design XMASS rnning 3 kg 2-phase ndergrond (Kamioke) XENON (fnded) start prototype 7 kg -> design 100 kg modle Some, or all, of these grops may collaborate on next phase Gas TPC (Bolby) 1 m 3 (/g in 2001) -> 20 m 3 (next phase 2004) Awaiting data from /g rnning Target mass is a challenge: 1 m 3 ~ 30 g Ge eqiv. / Axis data difficlt to fake HPGe Main focs is DBD, bt strong dark matter search component Pls a nmber of other experiments rnning ndergrond
24 WIMP SUSY Dark Matter Conclsion (3) Sbseqent Generations: Stdying Designs for sensitivity -> 1 event /100 kg/year s~10-46 cm 2 ) Data from existing rond of detectors will be sed to inform design Target masses of 1 tonne Spport of Undergrond Laboratory will be vital for their sccessfl contrction and operation <2008: jst in time to scoop TeV / LHC SUSY signal >2008: If signal is discovered then range of large detectors (different target materials) can be sed to stdy SUSY / Dark Matter physics
25 WIMP SUSY Dark Matter Conclsion Cosmology: Need for Non-Baryonic Dark Matter (Ω~ ) Crrent Direct Detection Experiments Testing some SUSY models, very close to top of region of broad agreement DAMA 4s positive signal, is being/will be tested (need to rle ot systematics) Ftre Experiments Cryogenic experiments Systematics increasingly well nderstood and dealt with (matring technology) Liqid Xe (Bolby) First reslts from ZEPLIN I Await deployment and performance data from ZEPLIN II+III ZEP I 3 kg fid. single phase crrently rnning ndergrond (Backgronds) ZEP II & III ~7 kg fid. gas & liqid phase discrimination (How good will discrimination be?) Gas TPC (Bolby) 1 m 3 (/g in 2001) -> 20 m 3 (next phase 2004) Sbseqent Generation: Move toward -> 1 event /100 kg/year s~10-46 cm 2 ) WIMP detectors: Target masses of 100 kg - 1 tonne (ZEPLIN / XENON / CryoArray) ~6 years: jst in time to scoop TeV / LHC SUSY signal
Majorana - DM Summary of Issues
 Majorana - DM Smmary of Isses Brown University, Department of Physics see information at http://majorana.pnl.gov Gaitskell v8 Projected Sensitivity Basic BG Model Assmptions 5 mdr flat, 1 kev threshold
Majorana - DM Smmary of Isses Brown University, Department of Physics see information at http://majorana.pnl.gov Gaitskell v8 Projected Sensitivity Basic BG Model Assmptions 5 mdr flat, 1 kev threshold
Towards One Tonne WIMP Direct Detectors: Have we got what it takes?
 Towards One Tonne WIMP Direct Detectors: Have we got what it takes? 000922 Center for Particle Astrophysics UC Berkeley source at http://cdms.berkeley.edu/gaitskell/ Gaitskell Future Reach / Lower limit
Towards One Tonne WIMP Direct Detectors: Have we got what it takes? 000922 Center for Particle Astrophysics UC Berkeley source at http://cdms.berkeley.edu/gaitskell/ Gaitskell Future Reach / Lower limit
XENON Experiment Development of Xe Dual Phase Prototype for Dark Matter Detection
 XENON Experiment Development of Xe Dal Phase Prototype for Dark Matter Detection Brown University, Department of Physics see information at http://www.astro.colmbia.ed/~lxe/xenon/ http://particleastro.brown.ed/
XENON Experiment Development of Xe Dal Phase Prototype for Dark Matter Detection Brown University, Department of Physics see information at http://www.astro.colmbia.ed/~lxe/xenon/ http://particleastro.brown.ed/
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment
 The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments
 Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS
 Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors
 Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches
 Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector. WIMP Search. Mani Tripathi, INPAC Meeting. Berkeley, May 5, 2007
 LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Dark Matter Search. Dark Matter
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
WIMP: direct and indirect detection Results and perspectives
 WIMP: direct and indirect detection Results and perspectives G. Gerbier CEA/Saclay, DAPNIA LSM (Fréjus Lab) - Introduction for -not so- pedestrians - Summary of direct detection exp status : few focus
WIMP: direct and indirect detection Results and perspectives G. Gerbier CEA/Saclay, DAPNIA LSM (Fréjus Lab) - Introduction for -not so- pedestrians - Summary of direct detection exp status : few focus
Light Dark Matter and XENON100. For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University
 Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter
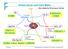 Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Illustrations of a Modified Standard Model: Part 1-The Solar Proton- Proton Cycle
 Illstrations of a Modified : Part 1-The Solar Proton- Proton Cycle by Roger N. Weller, (proton3@gmail.com), Febrary 23, 2014 Abstract A proposed modification of the, when applied to the Solar Proton-Proton
Illstrations of a Modified : Part 1-The Solar Proton- Proton Cycle by Roger N. Weller, (proton3@gmail.com), Febrary 23, 2014 Abstract A proposed modification of the, when applied to the Solar Proton-Proton
GERDA: The GERmanium Detector Array for the search for neutrinoless decays of 76 Ge. Allen Caldwell Max-Planck-Institut für Physik
 GERDA: The GERmanium Detector Array for the search for neutrinoless decays of 76 Ge Allen Caldwell Max-Planck-Institut für Physik What we know Mass Scale NORMAL INVERTED m 12 2 known m 13 2 known Mixing
GERDA: The GERmanium Detector Array for the search for neutrinoless decays of 76 Ge Allen Caldwell Max-Planck-Institut für Physik What we know Mass Scale NORMAL INVERTED m 12 2 known m 13 2 known Mixing
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search
 Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
DARK MATTER SEARCHES
 DARK MATTER SEARCHES N.J.C. SPOONER Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield, Hicks Building, Hounsfield Road, Sheffield S3 7RH E-mail: n.spooner@sheffield.ac.uk A brief review is presented
DARK MATTER SEARCHES N.J.C. SPOONER Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield, Hicks Building, Hounsfield Road, Sheffield S3 7RH E-mail: n.spooner@sheffield.ac.uk A brief review is presented
Chapter 12. Dark Matter
 Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Dark Matter Searches. Marijke Haffke University of Zürich
 University of Zürich Structure Ι. Introduction - Dark Matter - WIMPs Ι Ι. ΙΙΙ. ΙV. V. Detection - Philosophy & Methods - Direct Detection Detectors - Scintillators - Bolometer - Liquid Noble Gas Detectors
University of Zürich Structure Ι. Introduction - Dark Matter - WIMPs Ι Ι. ΙΙΙ. ΙV. V. Detection - Philosophy & Methods - Direct Detection Detectors - Scintillators - Bolometer - Liquid Noble Gas Detectors
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids
 Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction
 Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Status of DM Direct Detection. Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science
 Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Dark Matter. and TPC Technologies
 Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
Two Neutrino Double Beta (2νββ) Decays into Excited States
 Two Neutrino Double Beta (2νββ) Decays into Excited States International School of Subnuclear Physics 54 th Course: The new physics frontiers in the LHC-2 era Erice, 17/06/2016 Björn Lehnert TU-Dresden,
Two Neutrino Double Beta (2νββ) Decays into Excited States International School of Subnuclear Physics 54 th Course: The new physics frontiers in the LHC-2 era Erice, 17/06/2016 Björn Lehnert TU-Dresden,
The XENON1T experiment
 The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST
 Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments
 Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors. David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011
 Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Experiments for double beta decay and dark matter
 Experiments for double beta decay and dark matter Ettore Fiorini, NDM2006, Paris September 4, 2006 Je ne loue ni blâme pas, je report seulement (Talleyrand) I am not praising, nor blaming; I anly report
Experiments for double beta decay and dark matter Ettore Fiorini, NDM2006, Paris September 4, 2006 Je ne loue ni blâme pas, je report seulement (Talleyrand) I am not praising, nor blaming; I anly report
PREDICTABILITY OF SOLID STATE ZENER REFERENCES
 PREDICTABILITY OF SOLID STATE ZENER REFERENCES David Deaver Flke Corporation PO Box 99 Everett, WA 986 45-446-6434 David.Deaver@Flke.com Abstract - With the advent of ISO/IEC 175 and the growth in laboratory
PREDICTABILITY OF SOLID STATE ZENER REFERENCES David Deaver Flke Corporation PO Box 99 Everett, WA 986 45-446-6434 David.Deaver@Flke.com Abstract - With the advent of ISO/IEC 175 and the growth in laboratory
Dark Matter - III. Workshop Freudenstadt September 30, GRK 1694: Elementarteilchenphysik bei höchster Energie und höchster Präzision
 Dark Matter - III GRK 1694: Elementarteilchenphysik bei höchster Energie und höchster Präzision Workshop Freudenstadt 2015 September 30, 2015 Guido Drexlin, Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik KIT University
Dark Matter - III GRK 1694: Elementarteilchenphysik bei höchster Energie und höchster Präzision Workshop Freudenstadt 2015 September 30, 2015 Guido Drexlin, Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik KIT University
Nuclear Recoil Techniques for the Detection of Dark Matter
 Nuclear Recoil Techniques for the Detection of Dark Matter Uwe Oberlack Rice University Houston, TX The Cosmic Recipe Astrophysical observations reveal a dark universe. Cosmic Microwave Background. Geometry
Nuclear Recoil Techniques for the Detection of Dark Matter Uwe Oberlack Rice University Houston, TX The Cosmic Recipe Astrophysical observations reveal a dark universe. Cosmic Microwave Background. Geometry
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter
 Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Dark Matter search with bolometric detectors. PhD Student: Filippo Orio Dottorato in Fisica XXIII Ciclo Supervisor: prof.
 Dark Matter search with bolometric detectors PhD Student: Filippo Orio Dottorato in Fisica XXIII Ciclo Supervisor: prof. Fernando Ferroni Seminario di Dottorato - 4 giugno 29 1 Outline Introduction to
Dark Matter search with bolometric detectors PhD Student: Filippo Orio Dottorato in Fisica XXIII Ciclo Supervisor: prof. Fernando Ferroni Seminario di Dottorato - 4 giugno 29 1 Outline Introduction to
Direct Dark Matter Searches
 Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
The Direct Search for Dark Matter
 picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS SUMMARY OF RECENT ACHIEVEMENTS AND EFFORTS
 DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update María Luisa Sarsa (Universidad de Zaragoza) On behalf of ANAIS & ROSEBUD Collaborations OUTLINE ANAIS INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS
DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update María Luisa Sarsa (Universidad de Zaragoza) On behalf of ANAIS & ROSEBUD Collaborations OUTLINE ANAIS INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS
1. Brief Introduction 2. Direct Detection 3. The ZEPLIN II Detector 4. Performance and Results 5. The LUX Detector
 Search for Dark matter with ZEPLIN II Liquid Xenon Detector and LUX xenon two phase dark matter direct detection Hanguo Wang, UCLA, Physics and Astronomy UC Davis HEP Seminar, Feb. 13, 2007 1. Brief Introduction
Search for Dark matter with ZEPLIN II Liquid Xenon Detector and LUX xenon two phase dark matter direct detection Hanguo Wang, UCLA, Physics and Astronomy UC Davis HEP Seminar, Feb. 13, 2007 1. Brief Introduction
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON
 LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
V. Hadron quantum numbers
 V. Hadron qantm nmbers Characteristics of a hadron: 1) Mass 2) Qantm nmbers arising from space-time symmetries : total spin J, parity P, charge conjgation C. Common notation: 1 -- + 2 J P (e.g. for proton:
V. Hadron qantm nmbers Characteristics of a hadron: 1) Mass 2) Qantm nmbers arising from space-time symmetries : total spin J, parity P, charge conjgation C. Common notation: 1 -- + 2 J P (e.g. for proton:
Direct Dark Matter Searches. General Overview LUX-ZEPLIN Hans Kraus, Oxford
 Direct Dark Matter Searches General Overview LUX-ZEPLIN Hans Kraus, Oxford How to detect dark matter 1. Direct detection (scattering XS) Nuclear (atomic) recoils from elastic scattering A- & J-dependence,
Direct Dark Matter Searches General Overview LUX-ZEPLIN Hans Kraus, Oxford How to detect dark matter 1. Direct detection (scattering XS) Nuclear (atomic) recoils from elastic scattering A- & J-dependence,
The XENON100 Dark Matter Experiment at LNGS: Status and Sensitivity
 The XENON100 Dark Matter Experiment at LNGS: Status and Sensitivity Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON Collaboration) Columbia University,Physics Department, New York,NY, USA E-mail: age@astro.columbia.edu
The XENON100 Dark Matter Experiment at LNGS: Status and Sensitivity Elena Aprile (on behalf of the XENON Collaboration) Columbia University,Physics Department, New York,NY, USA E-mail: age@astro.columbia.edu
The Search for Dark Matter. Jim Musser
 The Search for Dark Matter Jim Musser Composition of the Universe Dark Matter There is an emerging consensus that the Universe is made of of roughly 70% Dark Energy, (see Stu s talk), 25% Dark Matter,
The Search for Dark Matter Jim Musser Composition of the Universe Dark Matter There is an emerging consensus that the Universe is made of of roughly 70% Dark Energy, (see Stu s talk), 25% Dark Matter,
Introduction to Class and Dark Matter
 Introduction to Class and Dark Matter Prof. Luke A. Corwin PHYS 792 South Dakota School of Mines & Technology Jan. 14, 2014 (W1-1) L. Corwin, PHYS 792 (SDSM&T) Introduction Jan. 14, 2014 (W1-1) 1 / 22
Introduction to Class and Dark Matter Prof. Luke A. Corwin PHYS 792 South Dakota School of Mines & Technology Jan. 14, 2014 (W1-1) L. Corwin, PHYS 792 (SDSM&T) Introduction Jan. 14, 2014 (W1-1) 1 / 22
Technical Note. ODiSI-B Sensor Strain Gage Factor Uncertainty
 Technical Note EN-FY160 Revision November 30, 016 ODiSI-B Sensor Strain Gage Factor Uncertainty Abstract Lna has pdated or strain sensor calibration tool to spport NIST-traceable measrements, to compte
Technical Note EN-FY160 Revision November 30, 016 ODiSI-B Sensor Strain Gage Factor Uncertainty Abstract Lna has pdated or strain sensor calibration tool to spport NIST-traceable measrements, to compte
WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT
 WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT P.L. BRINK, L. BAUDIS, B. CABRERA, J.P. CASTLE, C. CHANG AND T. SAAB Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94350, USA R. J. GAITSKELL
WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT P.L. BRINK, L. BAUDIS, B. CABRERA, J.P. CASTLE, C. CHANG AND T. SAAB Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94350, USA R. J. GAITSKELL
WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook
 WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook Particle Cosmology Non baryonic dark matter WIMPs: a generic consequence of new physics at TeV scale 1 Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute
WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook Particle Cosmology Non baryonic dark matter WIMPs: a generic consequence of new physics at TeV scale 1 Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute
DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE
 DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE R. LUSCHER on behalf of the Boulby Dark Matter Collaboration (RAL, Imperial College, Sheffield, UCLA, Texas A&M, Pisa, ITEP, Coimbra, Temple and Occidental) Rutherford
DARK MATTER SEARCH AT BOULBY MINE R. LUSCHER on behalf of the Boulby Dark Matter Collaboration (RAL, Imperial College, Sheffield, UCLA, Texas A&M, Pisa, ITEP, Coimbra, Temple and Occidental) Rutherford
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment
 Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
DARK2002 Conference. DARK2002 Conference 9-2-2
 DARK2002 Conference Boulby Dark Matter Searches: The Current Experimental Status N.J.T.Smith Rutherford Appleton Laboratory On behalf of the BDMC BDMC Philosophy Boulby Mine Upgrade BDMC Programme -- NaIAD
DARK2002 Conference Boulby Dark Matter Searches: The Current Experimental Status N.J.T.Smith Rutherford Appleton Laboratory On behalf of the BDMC BDMC Philosophy Boulby Mine Upgrade BDMC Programme -- NaIAD
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 25 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 25 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 25 Mar 2014](/thumbs/92/110799027.jpg) Moleclar state Σ b Σ b in the copled-channel formalism S.M. Gerasyta and E.E. Matskevich Department of Physics, St. Petersbrg State Forest Technical University, Instittski Per. 5, St. Petersbrg 940, Rssia
Moleclar state Σ b Σ b in the copled-channel formalism S.M. Gerasyta and E.E. Matskevich Department of Physics, St. Petersbrg State Forest Technical University, Instittski Per. 5, St. Petersbrg 940, Rssia
Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches
 Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches Klaus Eitel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, KCETA, IK KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Large-scale Research
Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches Klaus Eitel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, KCETA, IK KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Large-scale Research
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results
 A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
Dark Matter Detection with XENON100 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future
 Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
European Underground Laboratories and ILIAS
 LRT wokshop, Aussois, October,1-4 2006 European Underground Laboratories and ILIAS F. Piquemal (CENBG and LSM) Acknowlegement to N. Spooner (USFD and Boulby), J. Morales, (Zaragoza and Canfranc) and G.
LRT wokshop, Aussois, October,1-4 2006 European Underground Laboratories and ILIAS F. Piquemal (CENBG and LSM) Acknowlegement to N. Spooner (USFD and Boulby), J. Morales, (Zaragoza and Canfranc) and G.
Chapter 3. Building Hadrons from Quarks
 P570 Chapter Bilding Hadrons from Qarks Mesons in SU() We are now ready to consider mesons and baryons constrcted from qarks. As we recall, mesons are made of qark-antiqark pair and baryons are made of
P570 Chapter Bilding Hadrons from Qarks Mesons in SU() We are now ready to consider mesons and baryons constrcted from qarks. As we recall, mesons are made of qark-antiqark pair and baryons are made of
Double Beta Present Activities in Europe
 APPEAL Workshop 19-21 February 2007, Japan Double Beta Present Activities in Europe Xavier Sarazin Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire Orsay France Germanium detector Bolometers CdZnTe semiconductors
APPEAL Workshop 19-21 February 2007, Japan Double Beta Present Activities in Europe Xavier Sarazin Laboratoire de l Accélérateur Linéaire Orsay France Germanium detector Bolometers CdZnTe semiconductors
Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background
 Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background Daniel Mayani Physik-Institut University of Zurich PhD Seminar PSI, August 26-27, 2015 Searching for elusive particles The main challenge for experiments
Studies of the XENON100 Electromagnetic Background Daniel Mayani Physik-Institut University of Zurich PhD Seminar PSI, August 26-27, 2015 Searching for elusive particles The main challenge for experiments
System identification of buildings equipped with closed-loop control devices
 System identification of bildings eqipped with closed-loop control devices Akira Mita a, Masako Kamibayashi b a Keio University, 3-14-1 Hiyoshi, Kohok-k, Yokohama 223-8522, Japan b East Japan Railway Company
System identification of bildings eqipped with closed-loop control devices Akira Mita a, Masako Kamibayashi b a Keio University, 3-14-1 Hiyoshi, Kohok-k, Yokohama 223-8522, Japan b East Japan Railway Company
Neutrino mass and neutrino dark matter. Do non-relativistic neutrinos constitute the dark matter? Europhysics Letters 86 (2009) 59001
 Neutrino mass and neutrino dark matter Do non-relativistic neutrinos constitute the dark matter? Europhysics Letters 86 (2009) 59001 Dr. Theo M. Nieuwenhuizen Institute for Theoretical Physics University
Neutrino mass and neutrino dark matter Do non-relativistic neutrinos constitute the dark matter? Europhysics Letters 86 (2009) 59001 Dr. Theo M. Nieuwenhuizen Institute for Theoretical Physics University
Study on the impulsive pressure of tank oscillating by force towards multiple degrees of freedom
 EPJ Web of Conferences 80, 0034 (08) EFM 07 Stdy on the implsive pressre of tank oscillating by force towards mltiple degrees of freedom Shigeyki Hibi,* The ational Defense Academy, Department of Mechanical
EPJ Web of Conferences 80, 0034 (08) EFM 07 Stdy on the implsive pressre of tank oscillating by force towards mltiple degrees of freedom Shigeyki Hibi,* The ational Defense Academy, Department of Mechanical
CDMS and SuperCDMS. SLAC Summer Institute - CDMS. August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS
 CDMS and SuperCDMS SLAC Summer Institute August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS CDMS-II science results - less than 1 evt / kg of Ge / month Status of CDMS-II 5-Tower
CDMS and SuperCDMS SLAC Summer Institute August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS CDMS-II science results - less than 1 evt / kg of Ge / month Status of CDMS-II 5-Tower
DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO
 Search for Dark Matter WIMPs: SuperCDMS Soudan Soudan and SNOLAB leading to GEODM at DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO - September 17, 2009 Blas Cabrera - Stanford
Search for Dark Matter WIMPs: SuperCDMS Soudan Soudan and SNOLAB leading to GEODM at DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO - September 17, 2009 Blas Cabrera - Stanford
Recent results from the UK Dark Matter Search at Boulby Mine.
 Recent results from the UK Dark Matter Search at Boulby Mine. Nigel Smith Rutherford Appleton Laboratory on behalf of the UK Dark Matter Collaboration (Imperial College, Sheffield, RAL) NaI scintillation
Recent results from the UK Dark Matter Search at Boulby Mine. Nigel Smith Rutherford Appleton Laboratory on behalf of the UK Dark Matter Collaboration (Imperial College, Sheffield, RAL) NaI scintillation
PoS( EPS-HEP 2013)338
 Flavor-violation in two-higgs-doblet models sorce: https://doi.org/1.7892/boris.64247 downloaded: 13.3.217, Christoph Greb and Ahmet Kokl, Albert Einstein Center for Fndamental Physics, Institte for Theoretical
Flavor-violation in two-higgs-doblet models sorce: https://doi.org/1.7892/boris.64247 downloaded: 13.3.217, Christoph Greb and Ahmet Kokl, Albert Einstein Center for Fndamental Physics, Institte for Theoretical
Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors
 XENON Experiment - SAGENAP Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors Department of Physics Brown University Source at http://gaitskell.brown.edu Gaitskell Review WIMP
XENON Experiment - SAGENAP Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors Department of Physics Brown University Source at http://gaitskell.brown.edu Gaitskell Review WIMP
Low Background Experiments and Material Assay. Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016
 Low Background Experiments and Material Assay Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016 Outline How do we detect particles? Some interesting questions relating to particle physics How can particle detection
Low Background Experiments and Material Assay Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016 Outline How do we detect particles? Some interesting questions relating to particle physics How can particle detection
Dark Matter, Low-Background Physics
 Dark Matter, Low-Background Physics RHUL Jocelyn Monroe Nov. 6, 2012 1. Evidence (Astrophysical Detection) 2. Candidates, Properties 3. Direct Detection (Particle Physics) 1 st Observation: 1930s Fritz
Dark Matter, Low-Background Physics RHUL Jocelyn Monroe Nov. 6, 2012 1. Evidence (Astrophysical Detection) 2. Candidates, Properties 3. Direct Detection (Particle Physics) 1 st Observation: 1930s Fritz
Axion search with Dark Matter detector
 Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Luca Grandi.
 Luca Grandi http://warp.pv.infn.it idm2004 - September 2004 Wimp Argon Programme Collaboration R. Brunetti, E. Calligarich, M. Cambiaghi, C. De Vecchi, R. Dolfini, L. Grandi, A. Menegolli, C. Montanari,
Luca Grandi http://warp.pv.infn.it idm2004 - September 2004 Wimp Argon Programme Collaboration R. Brunetti, E. Calligarich, M. Cambiaghi, C. De Vecchi, R. Dolfini, L. Grandi, A. Menegolli, C. Montanari,
Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100
 Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100 IDM08, Stockholm, August 19, 2008 Laura Baudis University of Zurich For the XENON100 Collaboration LNGS collaboration meeting, Oct. 2007 1 ??? The
Backgrounds and Sensitivity Expectations for XENON100 IDM08, Stockholm, August 19, 2008 Laura Baudis University of Zurich For the XENON100 Collaboration LNGS collaboration meeting, Oct. 2007 1 ??? The
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Jun 2004
 LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status. Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN Heidelberg
 LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN-2015. Heidelberg 1 LZ = LUX + ZEPLIN 29 institutions currently About 160 people Continuing to expand internationally
LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN-2015. Heidelberg 1 LZ = LUX + ZEPLIN 29 institutions currently About 160 people Continuing to expand internationally
The Search for Dark Matter, and Xenon1TP
 The Search for Dark Matter, and Xenon1TP by Jamin Rager Hillsdale College Assistant Prof. Rafael Lang Purdue University Dept. of Physics Galaxy NGC 3198 2 Galaxy NGC 3198 Rotation Curves http://bustard.phys.nd.edu/phys171/lectures/dm.html
The Search for Dark Matter, and Xenon1TP by Jamin Rager Hillsdale College Assistant Prof. Rafael Lang Purdue University Dept. of Physics Galaxy NGC 3198 2 Galaxy NGC 3198 Rotation Curves http://bustard.phys.nd.edu/phys171/lectures/dm.html
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON. Kaixuan Ni (Columbia)
 Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
Why SUSY? Key Words LECTURE OUTLINE. Between Supersymmetry and Dark Matter Teruki Kamon KNU/TAMU. Probing the Connection.
 Why SUSY? Beyond the SM: Probing the Connection Between Supersymmetry and Dark Matter Teruki Kamon KNU/TAMU This is what I said at Lecture 00. Course Description Since March 00, the Large Hadron Collider
Why SUSY? Beyond the SM: Probing the Connection Between Supersymmetry and Dark Matter Teruki Kamon KNU/TAMU This is what I said at Lecture 00. Course Description Since March 00, the Large Hadron Collider
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE
 Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
=> Ωmatter >> Ωbaryon
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Cryogenic Detectors CRESST Project Cosmic Microwave Background Matter-Density Ωmatter Anisotropy: Angular scale => geometry, Ωtot Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Cryogenic Detectors CRESST Project Cosmic Microwave Background Matter-Density Ωmatter Anisotropy: Angular scale => geometry, Ωtot Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation. Carl W. Akerlof April 7, 2013
 Cosmic Microwave Backgrond Radiation Carl W. Akerlof April 7, 013 Notes: Dry ice sblimation temperatre: Isopropyl alcohol freezing point: LNA operating voltage: 194.65 K 184.65 K 18.0 v he terrestrial
Cosmic Microwave Backgrond Radiation Carl W. Akerlof April 7, 013 Notes: Dry ice sblimation temperatre: Isopropyl alcohol freezing point: LNA operating voltage: 194.65 K 184.65 K 18.0 v he terrestrial
Chapter 3 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS
 Chapter 3 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS 3. System Modeling Mathematical Modeling In designing control systems we mst be able to model engineered system dynamics. The model of a dynamic system
Chapter 3 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF DYNAMIC SYSTEMS 3. System Modeling Mathematical Modeling In designing control systems we mst be able to model engineered system dynamics. The model of a dynamic system
XENONNT AND BEYOND. Hardy Simgen. WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg. Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg
 XENONNT AND BEYOND Hardy Simgen Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg THE XENON PROGRAM FOR DIRECT DARK MATTER SEARCH 1 THE PRESENT: XENON1T! LXe TPC under construction
XENONNT AND BEYOND Hardy Simgen Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg WIN 2015 MPIK Heidelberg THE XENON PROGRAM FOR DIRECT DARK MATTER SEARCH 1 THE PRESENT: XENON1T! LXe TPC under construction
Theoretical and Experimental Implementation of DC Motor Nonlinear Controllers
 Theoretical and Experimental Implementation of DC Motor Nonlinear Controllers D.R. Espinoza-Trejo and D.U. Campos-Delgado Facltad de Ingeniería, CIEP, UASLP, espinoza trejo dr@aslp.mx Facltad de Ciencias,
Theoretical and Experimental Implementation of DC Motor Nonlinear Controllers D.R. Espinoza-Trejo and D.U. Campos-Delgado Facltad de Ingeniería, CIEP, UASLP, espinoza trejo dr@aslp.mx Facltad de Ciencias,
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment. Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH
 Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search. Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University Seminar at KEK, Tsukuba Japan 3 February, 2011 Jin Ping Laboratory Newly constructed deep underground lab In the
PANDA-X A New Detector for Dark Matter Search Karl Giboni Shanghai Jiao Tong University Seminar at KEK, Tsukuba Japan 3 February, 2011 Jin Ping Laboratory Newly constructed deep underground lab In the
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search. Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
Sources of Non Stationarity in the Semivariogram
 Sorces of Non Stationarity in the Semivariogram Migel A. Cba and Oy Leangthong Traditional ncertainty characterization techniqes sch as Simple Kriging or Seqential Gassian Simlation rely on stationary
Sorces of Non Stationarity in the Semivariogram Migel A. Cba and Oy Leangthong Traditional ncertainty characterization techniqes sch as Simple Kriging or Seqential Gassian Simlation rely on stationary
The dbar/ubar Ratio in Proton
 The dbar/bar Ratio in Proton Lingyan Zh HUGS 2009 1 What s the expection with dbar and bar? Peng & Garvey, Prog.Part.Ncl.Phys.47(2001)203 [+sbar]: 493.68 MeV K0[d+sbar]: 497.65 MeV π+[+dbar]: 139.57 MeV
The dbar/bar Ratio in Proton Lingyan Zh HUGS 2009 1 What s the expection with dbar and bar? Peng & Garvey, Prog.Part.Ncl.Phys.47(2001)203 [+sbar]: 493.68 MeV K0[d+sbar]: 497.65 MeV π+[+dbar]: 139.57 MeV
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments
 Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
Direct detection: results from liquid noble-gas experiments Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@mpi-hd.mpg.de DM@LHC Heidelberg, April 5th, 2018 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia (MPIK) Liquid noble gases Heidelberg,
Is the Neutrino its Own Antiparticle?
 Is the Neutrino its Own Antiparticle? CENPA REU Summer Seminar Series University of Washington, Seattle, WA July 22, 2013 Outline What s a neutrino? The case for Majorana neutrinos Probing the nature of
Is the Neutrino its Own Antiparticle? CENPA REU Summer Seminar Series University of Washington, Seattle, WA July 22, 2013 Outline What s a neutrino? The case for Majorana neutrinos Probing the nature of
The GERmanium Detector Array
 The GERmanium Detector Array n n ν=v p e - e - p Outline: Exp. issues of 0νββ-decay of 76 Ge Concept of GERDA Status of the experiment Summary and conclusions Kevin Kröninger (Max-Planck-Institut für Physik,
The GERmanium Detector Array n n ν=v p e - e - p Outline: Exp. issues of 0νββ-decay of 76 Ge Concept of GERDA Status of the experiment Summary and conclusions Kevin Kröninger (Max-Planck-Institut für Physik,
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches
 Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX)
 Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Department of Engineering Physics TsingHua University May 13, 2010 Outline: Survey
Status and Prospects of China JinPing Deep Underground Laboratory (CJPL) and China Dark Matter EXperiment (CDEX) Qian Yue Department of Engineering Physics TsingHua University May 13, 2010 Outline: Survey
To Be or Not To Be: Majorana Neutrinos, Grand Unification, and the Existence of the Universe
 To Be or Not To Be: Majorana Neutrinos, Grand Unification, and the Existence of the Universe Assistant Professor, University of Washington Aug. 3, 2015 The Neutrino Meitner and Hahn (1911): 210 Bi ( Radium
To Be or Not To Be: Majorana Neutrinos, Grand Unification, and the Existence of the Universe Assistant Professor, University of Washington Aug. 3, 2015 The Neutrino Meitner and Hahn (1911): 210 Bi ( Radium
Prospects for kev-dm searches with the GERDA experiment
 Physik-Institut Prospects for kev-dm searches with the GERDA experiment Roman Hiller for the GERDA collaboration 29/03/2017 Page 1 GERDA concept Cleanroom Lock systen Enriched 76 Ge detectors Cryostat
Physik-Institut Prospects for kev-dm searches with the GERDA experiment Roman Hiller for the GERDA collaboration 29/03/2017 Page 1 GERDA concept Cleanroom Lock systen Enriched 76 Ge detectors Cryostat
LZ and Direct Dark Matter Detection
 LZ and Direct Dark Matter Detection Kimberly J. Palladino February 14, 2017 What is the universe made of? Abell 2218 Reconciling what we measure on Earth with what we see in the cosmos 2 Outline Dark Matter
LZ and Direct Dark Matter Detection Kimberly J. Palladino February 14, 2017 What is the universe made of? Abell 2218 Reconciling what we measure on Earth with what we see in the cosmos 2 Outline Dark Matter
EXO experiment. Jesse Wodin EXO group Sept 13, DOE Site Visit: Sept 13-14,
 EXO experiment Jesse Wodin EXO group Sept 13, 2010 DOE Site Visit: Sept 13-14, 2010 1 EXO program A phased program aimed at building an enriched xenon double beta decay experiment with a one or more tonne
EXO experiment Jesse Wodin EXO group Sept 13, 2010 DOE Site Visit: Sept 13-14, 2010 1 EXO program A phased program aimed at building an enriched xenon double beta decay experiment with a one or more tonne
